Abstract
Salmonella enterica serovar Schwarzengrund is one of the most frequently isolated Salmonella serotypes responsible for human and poultry infections in Taiwan, and it has raised public health concerns. To better facilitate the understanding of transmission patterns and the dynamics of epidemics, sharing molecular data on pathogen profiles is urgently needed. The objectives of the current study were to determine and establish baseline data of S. enterica serovar Schwarzengrund isolates from 23 epidemiologically unrelated sources from year 2000 to 2018 and examine their phenotypic and genotypic characteristics. Genomic DNA of the Salmonella isolates was extracted and subjected to whole-genome sequencing using an Illumina platform. Results showed that all selected isolates exhibited multidrug resistance, and six of those were resistant to ciprofloxacin phenotypically. Genotypically, these isolates carried genes resistant to aminoglycoside (100%), phenicol (91.3%), β-lactams (69.5%), folate pathway antagonist (100%), tetracycline (82.6%), and fluoroquinolone (4.3%). Moreover, these isolates harbor integrons with five different gene cassettes identified for the first time, which are associated with resistance to trimethoprim, streptomycin, tetracycline, sulfonamide, chloramphenicol, and gentamicin. Furthermore, prevalence of IncFIB plasmid was found among studied isolates, which may increase its ability to colonize the chicken cecum and cause extra-intestinal disease. Salmonella pathogenicity islands SPI-1 to SPI-5, SPI-13, and SPI-14, as well as C63PI locus, were also detected in all isolates. This study demonstrated that a considerable high antimicrobial resistance with high virulence levels of Salmonella were found from animal sources. Sharing data on these pathogen profiles can not only help increase the reproducibility and accessibility of genomic analysis but can also support surveillance and epidemiological investigations for salmonellosis in the region.
1. Introduction
Throughout history, the emergence and reemergence of infectious diseases remain major causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide [1]. In 2016, infectious diseases killed approximately 10 million people, accounting for one-fifth of all deaths worldwide [2]. Even today, the world continues to confront old diseases such as salmonellosis and tuberculosis, as well as new diseases such as Ebola and COVID-19. Since infectious diseases are unavoidable in life, preventive strategies should be developed to control and mitigate the transmission of infections.
Insights into the genomes of infective organisms are paramount in disease prevention, management, and treatment. From the 1990s, public health authorities and food regulators started applying pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) molecular subtyping for surveillance and outbreak investigations [3]. Before the nationwide routine use of PFGE, only five outbreaks (a mean of 54 cases per outbreak) of listeriosis with an identified source were solved over 14 years [4]. However, after five years of routine PFGE usage, eleven outbreaks with a median of five cases per outbreak were identified [4]. Although PFGE has proven remarkably useful in detecting listeriosis clusters and other pathogens such as Salmonella [5] and E. coli [6], it has some limitations. Genomic insertions, deletions, rearrangement, and point mutation at the restriction enzyme sites can cause misinterpretation of the PFGE results, which may hamper or delay the discovery of an outbreak. Moreover, the PFGE database is a closed system, as only network participating laboratories can have access to it.
On the other hand, when compared to PFGE, the emergence of affordable whole-genome sequencing (WGS) technologies, along with the development of sophisticated bioinformatics analytical tools, offers a much finer resolution, as it captures DNA sequence changes across the entire genome of single microbial isolates [7]. WGS data are inherently digital, standardized, and can be accessed at any time by the general public, while PFGE data require standardized protocols to make inter-laboratory comparisons of DNA patterns [8]. Statistics also showed that, after 2 years of transition from PFGE to WGS for outbreak investigation, improvements in the number of clusters detected and outbreaks solved, with a marked reduction in median cluster size, were observed [9]. Due to these advantages, a 100 K Pathogen Genome Project launched in 2012 to sequence 100,000 pathogen genomes for use in host–microbe interactions, public health, and genome ecology [10]. To date, public health agencies have used pathogen genomics in almost every infectious disease program for surveillance and epidemiological investigations [11].
Raw sequence data can be stored in the sequence read archive (SRA) at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) of the US National Institutes of Health (NIH) [12]. From this aspect, this approach laid a foundation for the globalization of pathogen surveillance. Hence, to better facilitate the understanding of transmission patterns and the dynamics of epidemics, sharing molecular data on pathogen profiles is urgently needed. Among many Salmonella enterica serovars, serovar Schwarzengrund is one of the most frequently isolated Salmonella serotypes responsible for human and poultry infections [13]. In Taiwan, S. enterica serovar Schwarzengrund with high resistance to ampicillin, gentamicin, kanamycin, streptomycin, tetracycline, nalidixic acid, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and chloramphenicol was found to be the most prevalent serotype (30.5%) in raw chicken meat [14]. In Japan, the percentage of S. enterica serovar Schwarzengrund highly resistant to streptomycin, sulfamethoxazole, and oxytetracycline was found to steadily increase from 2.1 in 2009–2012 to 21.3 in 2013–2016 in broiler chickens [15]. This increase in the incidence of S. enterica serovar Schwarzengrund in food is considered a threat, as previous studies have shown that multi-drug-resistant S. enterica serovar Schwarzengrund could spread internationally from imported contaminated food products to persons in Denmark and the United States [16]. In addition, resistance genes may also spread from animals to humans via mobile genetic elements such as plasmids and integrons [17]. However, there is scarce information on the role of resistance plasmids in the spread of multi-drug-resistant Salmonella, particularly S. enterica serovar Schwarzengrund. Hence, the objectives of the current study were to determine and establish baseline data of S. enterica serovar Schwarzengrund isolates from 23 epidemiologically unrelated sources from year 2000 to 2018 and examine their phenotypic and genotypic characteristics.
2. Results
2.1. Genome Size and Characteristics
The total length of the final assemblies of 23 S. enterica serovar Schwarzengrund strains ranged from 4.64 to 5.02 Mb (Table 1). These assemblies produced between 12 and 201 contigs, with a GC content found between 51.8 and 52.2%. Genome annotation using RAST identified 4668 to 5176 coding sequences and 84 to 104 RNAs genes, distributed in 363 to 371 subsystems (Table 1), indicating about 3% variation among the S. enterica serovar Schwarzengrund genomes.

Table 1.
Genome annotation of twenty-three Salmonella enterica serovar Schwarzengrund strains.
Genes assigned to different subsystems are summarized in Table 2. Among 27 subsystems, 9 subsystems (“photosynthesis”, “miscellaneous”, “nucleosides and nucleotides”, “cell division and cell cycle”, “motility and chemotaxis”, “secondary metabolism”, “fatty acids, lipids, and isoprenoids”, “nitrogen metabolism”, “sulfur metabolism”) were identified with a similar number of genes within the 23 S. enterica serovar Schwarzengrund isolates (data not shown). The most abundant subsystems were amino acids and derivatives metabolism (ranging from 339 to 343 genes), followed by carbohydrate metabolism (ranging from 334 to 339 genes), and protein metabolism (ranging from 216 to 231 genes). Regarding virulence factors, 9 to 26 genes and 51 to 64 genes were annotated as belonging to the “phages, prophages, transposable elements, plasmids” and “virulence, disease and defense” categories, respectively.

Table 2.
RAST subsystem annotations of twenty-three Salmonella enterica serovar Schwarzengrund strains.
2.2. Phenotypic and Genotypic Antimicrobial Resistance
Phenotypically, all isolates examined in this study exhibited multidrug resistance (resistant to three or more classes of antimicrobial), and six of those were resistant to ciprofloxacin, the first-line drug for treating Salmonella infections (Table 3). Resistance genes were observed for aminoglycoside (aac(6’)-Iaa, aac(3)-IV; 100%), phenicol (cmlA1, catA2, floR; 91.3%), β-lactams (blaTEM-1B; 69.5%), folate pathway antagonist (sul1, sul2, sul3, dfrA12; 100%), tetracycline (tet(A), tet(M); 82.6%), and fluoroquinolone (aac(6’)-Ib-cr; 4.3%). The most common resistance gene identified was an aminoglycoside acetyltransferase gene aac(6′)-I-aa, which was present in all isolates. The second most prevalent genes were cmlA and dfrA, which confer resistance to chloramphenicol and trimethoprim, respectively. The phenotypic resistance correlated with the presence of antimicrobial resistance genes identified in 69.5% of the cases. It is worth noting that two isolates showed no resistance to chloramphenicol but carried cmlA1 resistance genes. Moreover, 2 and 5 of the 23 S. enterica serovar Schwarzengrund isolates, predicted to be ampicillin- and ciprofloxacin-susceptible, respectively, were resistant.

Table 3.
Phenotypic and genotypic antibiotic resistance, including resistance genes harbored by 23 Salmonella enterica serovar Schwarzengrund.
2.3. Plasmids, Integrons, and Salmonella Pathogenicity Islands Analysis
A total of 7 plasmid types were observed in 21 of the 23 S. enterica serovar Schwarzengrund isolate strains, including IncF, IncH, IncX, IncL, IncI, IncQ, and Col (Table 4). According to Plasmid Finder, 43.4% (10/23) of isolates carried at least one plasmid, while 47.8% (11/23) of isolates carried two or more plasmid types. The dominant incompatibility group was IncFIB, followed by IncQ, Col440I, and Col440II. Additionally, IncHI2, IncHI2A, Col(pHAD28), Col156, Col(BS512), IncX1, IncL, IncI2, IncFII(pCTU2), and IncI1-I(Alpha) were detected at lower levels.

Table 4.
Plasmids, integron, and Salmonella pathogenicity island of Salmonella enterica serovar Schwarzengrund from animal sources.
Using an Integron Finder followed by BLASTp analysis, a total of 22 complete integrons belonging to class I were found in 23 isolates (Table 4). At least two (n = 1), three (n = 5), four (n = 13), and up to five attC (n = 3) sites were found in a single isolate (data not shown). Among these integrons, six different gene cassette arrays, including dfrA12-aadA-cmlA-sul3, dfrA12-aadA-cmlA, dfrA12-aadA, aadA-cmlA-sul3, dfrA12-aadA-cmlA-tetR-tet(A), and dfrA12-aadA-aac(6’)-Ib-cr-cmlA-sul3, were identified in the isolates (Table 4).
Regarding the virulence capability of these isolates, eight SPIs (SPI-1, SPI-2, SPI-3, SPI-4, SPI-5, SPI-9, SPI-13, SPI-14), as well as centisome 63 pathogenicity island (C63PI), were detected in all genomes.
3. Discussion
As whole-genomic sequencing technologies have become affordable in recent years, these technologies are rapidly gaining acceptance as routine methods, and are transforming laboratory procedures [18]. As such, collection and sharing of genetic data is urgently needed, as it can provide more accurate bacterial identification, more robust phylogenetic relationships, and more definitive answer for epidemiological investigations. Hence, for the first time, 23 S. enterica serovar Schwarzengrund isolates were completely sequenced in this study to examine their phenotypic and genotypic characteristics and to provide a baseline for future medical, functional, and comparative studies. These isolates were selected to present a high genetic diversity; therefore, they cannot be used to imply their overall incidence of notified cases of salmonellosis. Yet, many conclusions still can be made with this fact in mind.
Consistent with a previous study that examined 27 S. enterica serovar Schwarzengrund isolates from clinical sources [19], genome features, including genomic sizes, GC content, number of contigs, and number of coding sequences, were comparable with the results observed here, suggesting a consistency of WGS performance across laboratories. After whole-genome annotation, RAST server showed that nine subsystems (“photosynthesis”, “miscellaneous”, “nucleosides and nucleotides”, “cell division and cell cycle”, “motility and chemotaxis”, “secondary metabolism”, “fatty acids, lipids, and isoprenoids”, “nitrogen metabolism”, “sulfur metabolism”) were conserved and shared among all genomes, pinpointing that these may be core genome genes dedicated to metabolic functions and are needed to sustain bacterial life [20].
On the other hand, genes that varied from strain to strain were also observed in this study, indicating that these genes are accessory genomes and are important drivers to persist in a particular environment [21]. Nevertheless, minimal variations were observed among the S. enterica serovar Schwarzengrund genomes (<5%) in other subsystems, except for “Virulence, Disease and Defense”, “Phages, Prophages, Transposable elements, Plasmids”, and “Membrane Transport” subsystems. These >5% variations in these subsystems were found among the strains, suggesting that each strain had acquired different mobile elements to increase their resistance and virulence, which can confer itself a selective advantage under a selection process [22]. As numerous studies have shown that Salmonella could transfer virulence determinants to the cytoplasm of the infected host cell via bacterial outer membrane vesicles [23], identification of these accessory genomic elements, such as resistance and virulence, can help prepare responses more quickly to outbreaks of multiple antibiotic-resistant strains in healthcare settings.
Pathogens resistant to one or more clinically relevant antibiotics would necessitate new treatment strategies. Similar to previous studies [24], traditional first-line drugs such as ampicillin, chloramphenicol, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole are ineffective under this investigation, and ciprofloxacin remains the most effective treatment. Within these strains, two isolates (SS02 and SS06) showed no resistance to chloramphenicol but carried cmlA1-resistant genes. Moreover, 2 (SS16 and SS17) and 5 (SS04, SS14, SS15, SS16, and SS17) of the 23 S. enterica isolates predicted to be ampicillin- and ciprofloxacin-susceptible, respectively, were resistant. Hence, it is possible that these isolates contain an unknown gene or mutation that confers resistance. However, this assumption warrants further investigation.
Considering that all selected isolates exhibited multidrug resistance (resistant to three or more classes of antimicrobial) [25], and six of those were resistant to ciprofloxacin, this antibiotic resistance profile can be due to the prone usage of fluoroquinolone over traditional drugs and increased usage of fluoroquinolone in livestock for therapeutic and growth promotion purposes [26]. Previous research reported that the underlying mechanism for ciprofloxacin resistances may be caused by specific mutations in genes encoding DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV that decrease quinolone sensitivity by weakening the interactions between quinolones and bacterial enzymes [27]. With the availability of WGS data and ResFinder’ sister database, PointFinder, two mutations were detected in gyrA (S83F and D87G) in strain SS20, confirming their associations with ciprofloxacin resistance [28].
Other than antimicrobial resistance genes, mobile genetic elements such as plasmids and integrons are also pivotal in the dissemination and persistence of antimicrobial resistance [29]. Earlier investigation has shown that plasmids, especially those from incompatible groups IncHI, IncF, IncP, and IncB/O, are the most frequently observed in multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi [30]. In another study, 902 Salmonella isolates representing 59 different serovars showed that IncFIB plasmid (also commonly known as ColV plasmids) was found to occur predominantly in serovar Kentucky (72.9% of isolates tested), followed by Typhimurium (15%), and Heidelberg (1.7%) [31]. Moreover, the acquisition of the IncFIB plasmid by S. enterica serovar Kentucky was found to increase its ability to colonize chicken cecum and cause significant extra-intestinal disease [31]. Hence, for the first time in this study, results showed that IncFIB(K) plasmid was the most prevalent replicon type (69.5%), followed by IncQ, Col440I, and Col440II within S. enterica serovar Schwarzengrund strains. According to prior studies, IncF plasmids often carry a blaCTX-M gene [32] and IncQ plasmids often carry strAB, tetAR, and sul2 genes [33]. Despite the fact that Col plasmids encoded no known antimicrobial resistance genes, they seemed to be mobilized by co-resident conjugal plasmids, such as IncI1 and IncX [34]. As plasmids can be transferred between bacterial cells via horizontal gene transfer, determination of genetic determinant localized on plasmids may be required for further studies.
Integrons are also capable of mobilizing antimicrobial resistance genes among bacteria. The results of the present study demonstrated that 95.6% of the selected strains contained Class I integron, which was higher than the 11–66% class I integron found among human and animal sources from previous work [35]. Other than SS21, each strain harbors a complete integron, which includes a 5′ conserved segment, a 3′ conserved segment, and a gene cassette that encodes antimicrobial resistance determinants [36]. In this study, up to six different gene cassettes were found that were associated with resistance to trimethoprim, streptomycin, tetracycline, sulfonamide, chloramphenicol, and gentamicin. Only one gene cassette, dfrA12-aadA, was consistent with the previous observations of gene cassettes found in S. enterica serovar Schwarzengrund isolates [37]. Other gene cassettes, including dfrA12-aadA-cmlA, dfrA12-aadA-cmlA-sul3, aadA-cmlA-sul3, dfrA12-aadA-cmlA-tetR-tet(A), and dfrA12-aadA-aac(6’)-Ib-cr-cmlA-sul3, to our knowledge, were identified for the first time in S. enterica serovar Schwarzengrund isolates.
Regarding virulence factors, 8 out of 23 known SPIs [38] were detected, including SPI-1, SPI-2, SPI-3, SPI-4, SPI-5, SPI-9, SPI-13, and SPI-14, as well as C63PI, and these were detected in all isolates. The Salmonella SPI-1 (located within C63PI) and the SPI-2 encode type III secretion systems (T3SS), which are required for intestinal invasion and the production of enteritis [39]. The SPI-5 genes co-regulated with either SPI-1 or SPI-2 genes and encoded the effector proteins for both the T3SS encoded by SPI-1 and SPI-2 [40]. Recently, SPI-14 was found to play a role in the activation of SPI-1 genes and mediate bacterial invasion [41]. In addition to bacterial invasion, genes encoded on SPI-3 are important for gut colonization and intracellular survival [42,43], genes encoded on SPI-4 and SPI-9 are necessary for epithelial cell adhesion [44,45], and genes encoded on SPI-13 are pivotal for intracellular viability [46]. Nevertheless, the vast majority of these findings has been obtained in a mouse model and not in poultry, the latter of which represents a major reservoir of Salmonella for the human population [47]. Hence, more infection models using pigs, cattle, or poultry should be conducted in future studies to broaden our understanding of how SPIs contribute to Salmonella infection biology.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Isolates
The S. enterica serovar Schwarzengrund strains analyzed in this study were collected between 2000 and 2018 (n = 23). These isolates were obtained from multiple sources, including duck (n = 2), pig (n = 7), dog (n = 1), broiler (n = 7), pet food (n = 1), crested goshawk (n = 1), moorhen (n = 1), and turkey (n = 3) (Figure 1). Recovered isolates were then subjected to serological tests, as previously described, for identification [48]. Prior to use, all strains were incubated overnight (14–16 h) on trypticase soy agar or in trypticase soy broth plated at 37 °C.
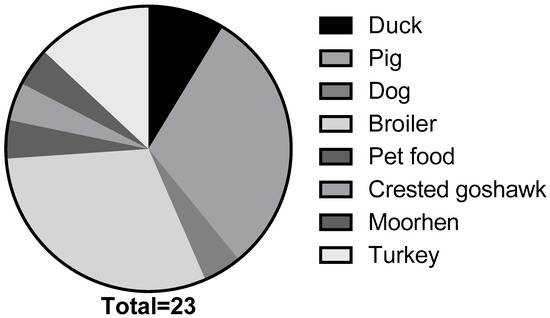
Figure 1.
Salmonella enterica serovar Schwarzengrund isolated from animal and environmental sources collected between 2000 and 2018 (n = 23).
4.2. Phenotypic Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
All antibiotics were acquired from Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC (Saint Louis, MO, USA). For the 23 isolates collected, phenotypic susceptibility to 9 different antibiotics belonging to 6 antimicrobial classes (aminoglycoside: amikacin, tobramycin, gentamicin; phenicol: chloramphenicol; beta-lactam: ampicillin; fluoroquinolone: ciprofloxacin; folate pathway antagonist: sulfisoxazole, trimethoprim; tetracycline: tetracycline) was determined by broth microdilution. Classification as resistance was determined using breakpoints set by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute [49].
4.3. Genome Library Preparation and Sequence Assembly
Genomic DNA was extracted using a DNeasy blood and tissue kit (Qiagen, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. DNA shearing was performed with a Misonix 3000 sonicator and checked by a DNA 1000 chip bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The DNA fragment length was between 180 and 200 base pairs (bp). Then, the sonicated DNA was end-repaired, A-tailed, and adaptor-ligated using the TruSeq DNA preparation kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) following the manufacturer’s guidelines. Libraries were sequenced using the NextSeq500 platform (Illumina, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) with 150PE protocol. The average sequencing depth of the libraries was 944.4 MegaBase (~190X). Afterwards, the raw reads were trimmed and filtered using Trimmomatic software (version 0.36) developed by Bolger et al. [50]. Only reads with quality scores >18 and read sizes >10 were used for subsequent analysis.
The trimmed reads of each sample were de novo assembled into contigs using SPAdes genome assembler (version 3.14.1) developed by Prjibelski et al. [51]. The assembled contigs of each sample were ordered, orientated, and joined into single scaffold using MeDuSa developed by Bosi et al. [52], based on the reference genome sequence (S. enterica subsp. enterica serovar Schwarzengrund strain CVM19633 of the EnsemblBacteria database (http://bacteria.ensembl.org/index.html), accessed on 12 August 2018). The WGS data used in this study were deposited to the NCBI database under BioProject accession number PRJNA635494.
4.4. Genome Annotation
Genomes of twenty-three S. enterica serovar Schwarzengrund strains were annotated using Rapid Annotation using a Subsystem Technology (RAST) server (https://rast.nmpdr.org/, accessed on 10 January 2021). Moreover, the identification of plasmid, antibiotics resistance gene, and Salmonella Pathogenicity Island (SPI) was performed by submitting the complete nucleotide sequence to PlasmidFinder, ResFinder, and SPIFinder, respectively, available at the Center for Genomic Epidemiology web server (https://cge.cbs.dtu.dk/services/, accessed on 10 January 2021). Annotation of integrons was conducted using the IntegronFinder [36], followed by protein Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLASTP) analysis.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrated that a considerable high antimicrobial resistance with a high virulence level of Salmonella was found from animal and environmental sources. For the first time, IncFIB plasmid was found to occur predominantly in S. enterica serovar Schwarzengrund isolates, which may increase its ability to colonize chicken cecum and cause extra-intestinal disease. Moreover, five different gene cassettes associated with resistance to trimethoprim, streptomycin, tetracycline, sulfonamide, chloramphenicol, and gentamicin were identified for the first time in S. enterica serovar Schwarzengrund isolates. As virulence and fitness can be encoded by mobile genetic elements, such as plasmids and integrons via horizontal gene transfer between Salmonella, these virulent species of bacteria can be acquired by humans via contaminated foods, thereby increasing the threat to public health. Hence, the availability of pathogen genome sequences, especially on S. enterica serovar Schwarzengrund, can not only help increase the reproducibility and accessibility of genomic analysis but can also support future surveillance of and epidemiological investigations into salmonellosis. With these baseline data, microbiologists and veterinarians can identify virulence traits of new emerging pathogens efficiently, and they can assist in the control of salmonellosis at the farm level.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.-C.L.; Methodology, I.-C.L. and H.-H.W.; Formal Analysis, I.-C.L.; Resources, Z.-W.C. and C.-H.C.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, I.-C.L.; Writing—Review and Editing, Z.-W.C. and C.-H.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All experiments procedures performed on the animals were reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of National Taiwan University (Taipei, Taiwan, NTU105-EL-00166).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The WGS data used in this study were deposited to the NCBI database under BioProject accession number PRJNA635494.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Furuse, Y. Analysis of research intensity on infectious disease by disease burden reveals which infectious diseases are neglected by researchers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, S.I.; Abajobir, A.A.; Abate, K.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdulkader, R.S.; Abdulle, A.M.; Abebo, T.A.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 333 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1260–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslanka, S.E.; Kerr, J.G.; Williams, G.; Barbaree, J.M.; Carson, L.A.; Miller, J.M.; Swaminathan, B. Molecular subtyping of Clostridium perfringens by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis to facilitate food-borne-disease outbreak investigations. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 2209–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, E.J.; Jackson, K.A.; Johnson, S.D.; Graves, L.M.; Silk, B.J.; Mahon, B.E. Listeriosis outbreaks and associated food vehicles, United States, 1998–2008. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, S.J.; Green, A.; Hernandez, K.; Peralta, V.; Bottichio, L.; Defibaugh-Chavez, S.; Douris, A.; Gieraltowski, L.; Hise, K.; La-Pham, K.; et al. Utility of Combining Whole Genome Sequencing with Traditional Investigational Methods To Solve Foodborne Outbreaks of Salmonella Infections Associated with Chicken: A New Tool for Tackling This Challenging Food Vehicle. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chattaway, M.A.; Dallman, T.J.; Gentle, A.; Wright, M.J.; Long, S.E.; Ashton, P.M.; Perry, N.T.; Jenkins, C. Whole Genome Sequencing for Public Health Surveillance of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Other than Serogroup O157. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didelot, X.; Bowden, R.; Wilson, D.J.; Peto, T.E.A.; Crook, D.W. Transforming clinical microbiology with bacterial genome sequencing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsofor, C.A. Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis (PFGE): Principles and Applications in Molecular Epidemiology: A Review. Int. J. Curr. Res. 2016, 2, 38–51. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, B.R.; Tarr, C.; Strain, E.; Jackson, K.A.; Conrad, A.; Carleton, H.; Katz, L.S.; Stroika, S.; Gould, L.H.; Mody, R.K.; et al. Implementation of Nationwide Real-time Whole-genome Sequencing to Enhance Listeriosis Outbreak Detection and Investigation. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weimer, B.C. 100K Pathogen Genome Project. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e00594-00517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwinn, M.; MacCannell, D.; Armstrong, G.L. Next-Generation Sequencing of Infectious Pathogens. JAMA 2019, 321, 893–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinonen, R.; Sugawara, H.; Shumway, M.; International Nucleotide Sequence Database, C. The sequence read archive. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D19–D21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vugia, D.J.; Samuel, M.; Farley, M.M.; Marcus, R.; Shiferaw, B.; Shallow, S.; Smith, K.; Angulo, F.J.; for the Emerging Infections Program FoodNet Working Group. Invasive Salmonella infections in the United States, FoodNet, 1996–1999: Incidence, serotype distribution, and outcome. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 38, S149–S156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H.; Wang, S.W.; Hwang, W.Z.; Tsai, S.J.; Hsih, Y.C.; Chiou, C.S.; Tsen, H.Y. Contamination of Salmonella Schwarzengrund cells in chicken meat from traditional marketplaces in Taiwan and comparison of their antibiograms with those of the human isolates. Poult. Sci. 2010, 89, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duc, V.M.; Shin, J.; Nagamatsu, Y.; Fuhiwara, A.; Toyofuku, H.; Obi, T.; Chuma, T. Increased Salmonella Schwarzengrund prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Salmonella enterica isolated from broiler chickens in Kagoshima Prefecture in Japan between 2013 and 2016. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2020, 82, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarestrup, F.M.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Lockett, J.; Gay, K.; Teates, K.; McDermott, P.F.; White, D.G.; Hasman, H.; Sørensen, G.; Bangtrakulnonth, A.; et al. International spread of multidrug-resistant Salmonella Schwarzengrund in food products. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emond-Rheault, J.-G.; Hamel, J.; Jeukens, J.; Freschi, L.; Kukavica-Ibrulj, I.; Boyle, B.; Tamber, S.; Malo, D.; Franz, E.; Burnett, E.; et al. The Salmonella enterica Plasmidome as a Reservoir of Antibiotic Resistance. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriksen, R.S.; Bortolaia, V.; Tate, H.; Tyson, G.H.; Aarestrup, F.M.; McDermott, P.F. Using Genomics to Track Global Antimicrobial Resistance. Front. Public Health 2019, 7, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khajanchi, B.K.; Yoskowitz, N.C.; Han, J.; Wang, X.; Foley, S.L.; Dennehy, J.J. Draft Genome Sequences of 27 Salmonella enterica Serovar Schwarzengrund Isolates from Clinical Sources. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8, e01687-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, H.; Lan, R.; Wang, H.; Du, P.; Bai, X.; Ji, S.; Meng, Q.; Jin, D.; et al. Minimum Core Genome Sequence Typing of Bacterial Pathogens: A Unified Approach for Clinical and Public Health Microbiology. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2582–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, E.A.; Allen, J.P.; Hauser, A.R. Characterization of the core and accessory genomes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa using bioinformatic tools Spine and AGEnt. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beceiro, A.; Tomás, M.; Bou, G. Antimicrobial resistance and virulence: A successful or deleterious association in the bacterial world? Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 185–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Ansong, C.; Adkins, J.N.; Heffron, F. Discovery of Salmonella virulence factors translocated via outer membrane vesicles to murine macrophages. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 2182–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, B.; Ward, L.R.; Threlfall, E.J. Multidrug-resistant Salmonella typhi: A worldwide epidemic. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1997, 24, S106–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, J.; Kemper, N.; Hartung, J.; Janusch, F.; Mohring, S.A.I.; Hamscher, G. Analysis of fluoroquinolones in dusts from intensive livestock farming and the co-occurrence of fluoroquinolone-resistant Escherichia coli. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldred, K.J.; Kerns, R.J.; Osheroff, N. Mechanism of Quinolone Action and Resistance. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoi, S.T.; Thong, K.L. High Resolution Melting Analysis for Rapid Mutation Screening in Gyrase and Topoisomerase IV Genes in Quinolone-Resistant Salmonella enterica. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 718084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, S.; Baert, L.; Jagadeesan, B.; Ngom-Bru, C.; Griswold, T.; Katz, L.S.; Carleton, H.A.; Deng, X.; Dudley, E.G. Implications of Mobile Genetic Elements for Salmonella enterica Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism Subtyping and Source Tracking Investigations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01985-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutai, W.C.; Waiyaki, P.G.; Kariuki, S.; Muigai, A.W.T. Plasmid profiling and incompatibility grouping of multidrug resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi isolates in Nairobi, Kenya. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.J.; Thorsness, J.L.; Anderson, C.P.; Lynne, A.M.; Foley, S.L.; Han, J.; Fricke, W.F.; McDermott, P.F.; White, D.G.; Khatri, M.; et al. Horizontal gene transfer of a ColV plasmid has resulted in a dominant avian clonal type of Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A. Plasmids and the spread of resistance. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 303, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, M.; Monno, R.; D’Addabbo, P.; Pesole, G.; Dionisi, A.M.; Scrascia, M.; Chiara, M.; Horner, D.S.; Manzari, C.; Luzzi, I.; et al. A novel group of IncQ1 plasmids conferring multidrug resistance. Plasmid 2017, 89, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladeinde, A.; Cook, K.; Orlek, A.; Zock, G.; Herrington, K.; Cox, N.; Plumblee Lawrence, J.; Hall, C. Hotspot mutations and ColE1 plasmids contribute to the fitness of Salmonella Heidelberg in poultry litter. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, B.; Miko, A.; Pries, K.; Hildebrandt, G.; Kleer, J.; Schroeter, A.; Helmuth, R. Class 1 integrons and resistance gene cassettes among multidrug resistant Salmonella serovars isolated from slaughter animals and foods of animal origin in Ethiopia. Acta Trop. 2007, 103, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cury, J.; Jové, T.; Touchon, M.; Néron, B.; Rocha, E.P. Identification and analysis of integrons and cassette arrays in bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 4539–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krauland, M.G.; Marsh, J.W.; Paterson, D.L.; Harrison, L.H. Integron-mediated multidrug resistance in a global collection of nontyphoidal Salmonella enterica isolates. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayward, M.R.; AbuOun, M.; La Ragione, R.M.; Tchórzewska, M.A.; Cooley, W.A.; Everest, D.J.; Petrovska, L.; Jansen, V.A.; Woodward, M.J. SPI-23 of S. Derby: Role in adherence and invasion of porcine tissues. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, L.; Zhang, P.; Piao, R.; Wang, Y. Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 1 (SPI-1) and Its Complex Regulatory Network. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knodler, L.A.; Celli, J.; Hardt, W.D.; Vallance, B.A.; Yip, C.; Finlay, B.B. Salmonella effectors within a single pathogenicity island are differentially expressed and translocated by separate type III secretion systems. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 43, 1089–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Feng, L.; Yang, B.; Zhang, W.; Wang, P.; Jiang, X.; Wang, L. Signal transduction pathway mediated by the novel regulator LoiA for low oxygen tension induced Salmonella Typhimurium invasion. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.L.; Kaczmarek, M.T.; Kucharski, L.M.; Maguire, M.E. Magnesium transport in Salmonella typhimurium: Regulation of mgtA and mgtCB during invasion of epithelial and macrophage cells. Microbiology 1998, 144, 1835–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsey, C.W.; Laarakker, M.C.; Humphries, A.D.; Weening, E.H.; Bäumler, A.J. Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium MisL is an intestinal colonization factor that binds fibronectin. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 57, 196–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, E.; Campbell, J.D.; Rowe, S.C.; Bispham, J.; Stevens, M.P.; Bowen, A.J.; Barrow, P.A.; Maskell, D.J.; Wallis, T.S. Identification of host-specific colonization factors of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 994–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velásquez, J.C.; Hidalgo, A.A.; Villagra, N.; Santiviago, C.A.; Mora, G.C.; Fuentes, J.A. SPI-9 of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi is constituted by an operon positively regulated by RpoS and contributes to adherence to epithelial cells in culture. Microbiology 2016, 162, 1367–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Adkins, J.N.; Coleman, J.R.; Schepmoes, A.A.; Dohnkova, A.; Mottaz, H.M.; Norbeck, A.D.; Purvine, S.O.; Manes, N.P.; Smallwood, H.S.; et al. Proteomic Analysis of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Isolated from RAW 264.7 Macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 29131–29140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoelzer, K.; Moreno Switt, A.I.; Wiedmann, M. Animal contact as a source of human non-typhoidal salmonellosis. Vet. Res. 2011, 42, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimont, P.A.; Weill, F.X. Antigenic Formulae of the Salmonella serovars, 9th ed.; WHO Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Salmonella Institut Pasteur: Paris, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prjibelski, A.; Antipov, D.; Meleshko, D.; Lapidus, A.; Korobeynikov, A. Using SPAdes De Novo Assembler. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform 2020, 70, e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosi, E.; Donati, B.; Galardini, M.; Brunetti, S.; Sagot, M.F.; Lió, P.; Crescenzi, P.; Fani, R.; Fondi, M. MeDuSa: A multi-draft based scaffolder. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2443–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).