Proteins of the Ciliated Protozoan Parasite Ichthyophthirius multifiliis Identified in Common Carp Skin Mucus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. The 26S Proteosome
2.2. Elongation Factor Alpha
2.3. Tubulins
2.4. Heat Shock Protein 90
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Ethics Statement
3.2. Common Carp and Collection of Skin Mucus
3.3. Protein Extraction, Separation, and In-Gel Digestion
3.4. Mass Spectrometry
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Esteban, M.A. An overview of the immunological defenses in fish skin. ISRN Immunol. 2012, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ewing, M.S.; Black, M.C.; Blazer, K.M.; Kocan, K.M. Plasma chloride and gill epithelial response of channel catfish to infection with Ichrhyophrhirius mulrifiliis. J. Aqua. Anim. Health. 1994, 6, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozel, T.R. Scanning electron microscopy of theronts of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis: Their penetration into host tissues. Trans. Am. Microsc. Soc. 1986, 105, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchmann, K.; Lindenstrøm, T.; Sigh, J. Partial cross-protection against Ichthyophthirius multifiliis in Gyrodactylus derjavini immunized rainbow trout. J. Helminthol. 1999, 73, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchmann, K.; Nielsen, M.E. Chemoattraction of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis (Ciliophora) to host molecules. Int. J. Parasitol. 1999, 29, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchmann, K.; Sigh, J.; Nielsen, C.V.; Dalgaard, M. Host responses against the fish parasitizing ciliate Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Vet. Parasitol. 2001, 100, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.; Kumar, G.; Abdel-Baki, A.A.; Dkhil, M.A.; El-Matbouli, M.; Al-Quraishy, S. Quantitative proteomic profiling of immune responses to Ichthyophthirius multifiliis in common carp skin mucus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, R.S.; Spira, D.T. Ichthyophthiriasis in the mirror carp Cyprinus carpio (L.) V. Acquired immunity. J. Fish Biol. 1974, 6, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.-Y.; Xu, Y.; Yuan, X.-M.; Yin, W.-L.; Yang, G.-L.; Lin, L.-Y.; Pan, X.-Y.; Wang, C.-F.; Shen, J.-Y. Proteomic analysis of differentially expressed proteins in the two developmental stages of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.M.; Kumar, G.; Soliman, F.M.; Adly, M.A.; Soliman, H.A.M.; El-Matbouli, M.; Saleh, M. Proteomics for understanding pathogenesis, immune modulation and host pathogen interactions in aquaculture. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2019, 32, 100625. [Google Scholar]
- Easy, R.H.; Ross, N.W. Changes in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) epidermal mucus protein composition profiles following infection with sea lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2009, 4, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.; Kumar, G.; Abdel-Baki, A.A.; Dkhil, M.A.; El-Matbouli, M.; Al-Quraishy, S. Quantitative shotgun proteomics distinguishes wound-healing biomarker signatures in common carp skin mucus in response to Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Vet Res. 2018, 49, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiménez, C.R.; Huang, L.; Qiu, Y.; Burlingame, A.L. In-gel digestion of proteins for MALDI-MS fingerprint mapping. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2001, 16, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevchenko, A.; Wilm, M.; Vorm, O.; Mann, M. Mass spectrometric sequencing of proteins from silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, H.J.; Babbitt, P.C.; Sajid, M. The global cysteine peptidase landscape in parasites. Trends Parasitol. 2009, 25, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blackman, M.J. Malarial proteases and host cell egress: An ‘emerging’ cascade. Cell Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1925–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuang, R.; Gu, J.; Cai, H.; Wang, Y. Improved prediction of malaria degradomes by supervised learning with SVM and profile kernel. Genetica 2009, 136, 189–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. Data-mining approaches reveal hidden families of proteases in the genome of malaria parasite. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 601–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jousson, O.; Di Bello, D.; Donadio, E.; Felicioli, A.; Pretti, C. Differential expression of cysteine proteases in developmental stages of the parasitic ciliate Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 269, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemba, M.; Goldberg, D.E. Biological roles of proteases in parasitic protozoa. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2002, 71, 275–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; McKerrow, J.H. Cysteine proteases of parasitic organisms. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2002, 120, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parama, A.; Iglesias, R.; Alvarez, M.F.; Leiro, J.; Ubeira, F.M.; Sanmartin, M.L. Cysteine proteinase activities in the fish pathogen Philasterides dicentrarchi (Ciliophora: Scuticociliatida). Parasitology 2004, 128, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abernathy, J.; Xu, D.H.; Peatman, E.; Kucuktas, H.; Klesius, P.; Liu, Z.J. Gene expression profiling of a fish parasite Ichthyophthirius multifiliis: Insights into development and senescence-associated avirulence. Comp. Biochem. Phy. D 2011, 6, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyne, R.S.; Hannick, L.; Shanmugam, D.; Hostetler, J.B.; Brami, D.; Joardar, V.S.; Johnson, J.; Radune, D.; Singh, I.; Badger, J.H.; et al. Comparative genomics of the pathogenic ciliate Ichthyophthirius multifiliis, its free-living relatives and a host species provide insights into adoption of a parasitic lifestyle and prospects for disease control. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Chen, F.; Niu, T.; Qu, R.; Chen, J. Large-scale identification of encystment-related proteins and genes in Pseudourostyla cristata. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Timmerhaus, G.; Krasnov, A.; Nilsen, P.; Alarcon, M.; Afanasyev, S.; Rode, M.; Takle, H.; Jørgensen, S.M. Transcriptome profiling of immune responses to cardiomyopathy syndrome (CMS) in Atlantic salmon. BMC Genom. 2012, 12, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ono, R.; Kaisho, T.; Tanaka, T. PDLIM1 inhibits NF-κB-mediated inflammatory signaling by sequestering the p65 subunit of NF-κB in the cytoplasm. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shamovsky, I.; Ivannikov, M.; Kandel, E.S.; Gershon, D.; Nudler, E. RNA-mediated response to heat shock in mammalian cells. Nature 2006, 440, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiesgigl, M.; Clos, J. Heat shock protein 90 homeostasis controls stage differentiation in Leishmania donovani. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 3307–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vera, M.; Pani, B.; Griffiths, L.A.; Muchardt, C.; Abbott, C.M.; Singer, R.H.; Nudler, E. The translation elongation factor eEF1A1 couples transcription to translation during heat shock response. eLife 2014, 3, e03164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, J.M.; Clos, J.; De’Oliveira, C.C.; Shirvani, O.; Fang, Y.; Wang, C.; Foster, L.J.; Reiner, N.E. An exosome-based secretion pathway is responsible for protein export from Leishmania and communication with macrophages. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durso, N.A.; Cyr, R.J. Beyond translation: Elongation factor-1α and the cytoskeleton. Protoplasma 1994, 180, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurasawa, Y.; Hanyu, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Numata, O. F-actin bundling activity of Tetrahymena elongation factor 1α is regulated by Ca2+/calmodulin. J. Biochem. 1996, 119, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, M.; Moreira, D.; Laurent, J.; Le Guyader, H.; Fukami, Y.; Ito, K. Biochemical analysis of the interaction between elongation factor 1alpha and alpha/beta-tubulins from a ciliate, Tetrahymena pyriformis. FEBS Lett. 1999, 453, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, F.; Vij, N.; Roberts, L.; Lopez-Briones, S.; Joyce, S.; Chakravarti, S. A novel role of the lumican core protein in bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced innate immune response. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 26409–26417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raeder, I.L.; Paulsen, S.M.; Smalås, A.O.; Willassen, N.P. Effect of fish skin mucus on the soluble proteome of Vibrio salmonicida analysed by 2-D gel electrophoresis and tandem mass spectrometry. Microb. Pathog. 2007, 42, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennessey, T.M.; Kim, D.Y.; Oberski, D.J.; Hard, R.; Rankin, S.A.; Pennock, D.G. Inner arm dynein 1 is essential for Ca++-dependent ciliary reversals in Tetrahymena thermophila. Cell Motil. Cytoskel. 2002, 53, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, C.R.; Hard, R.; Hennessey, T.M. Targeted gene disruption of dynein heavy chain 7 of Tetrahymena thermophila results in altered ciliary waveform and reduced swim speed. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 3075–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cassidy-Hanley, D.M.; Pratt, C.M.; Pratt, L.H.; Devine, C.; Hossain, M.M.; Dickerson, H.W.; Clark, T.G. Transcriptional profiling of stage specific gene expression in the parasitic ciliate Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Mol. Biochem. Parasit. 2011, 178, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ensgraber, M.; Loos, M. A 66-kilodalton heat shock protein of Salmonella typhimuriumis responsible for binding of the bacterium to intestinal mucus. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 3072–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, K.; Charles, I.; Dougan, G.; Pickard, D.; Gaora, P.Ó.; Costa, G.; Ali, T.; Miller, I.; Hormaeche, C. The role of a stress–response protein in Salmonella typhimurium virulence. Mol. Microb. 1991, 5, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindquist, S.; Craig, E.A. The heat-shock proteins. Ann. Rev. Gen. 1988, 22, 631–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, N.E.; Nelsen, E.M. HSP70 and HSP90 homologs are associated with tubulin in hetero-oligomeric complexes, cilia and the cortex of Tetrahymena. J. Cell Sci. 1997, 110, 1665–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankel, J.; Williams, N.E.; Nelsen, E.M.; Keeling, P.J. An evaluation of Hsp90 as a mediator of cortical patterning in Tetrahymena. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2001, 48, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, B.M.H.; Bachi, A.; Wilm, M.; Gonzalez, C. Hsp90 is a core centrosomal component and is required at different stages of the centrosome cycle in Drosophila and vertebrates. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 1252–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freeman, B.C.; Morimoto, R.I. The human cytosolic molecular chaperones, hsp90, hsp70 (hsc-70) and hdj-l have distinct roles in recognition of a non-native protein and protein refolding. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 2969–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josepriya, T.A.; Chien, K.H.; Lin, H.Y.; Huang, H.N.; Wu, C.J.; Song, Y.L. Immobilization antigen vaccine adjuvanted by parasitic heat shock protein 70C confers high protection in fish against cryptocaryonosis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 45, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, T.G.; Gao, Y.; Gaertig, J.; Wang, X.; Cheng, G. The i-antigens of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis are GPI-anchored proteins. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2001, 48, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, S.F.; Chatziandreou, N.; Nielsen, M.E.; Li, W.; Rogers, J.; Taylor, R.; Santos, Y.; Cossins, A. Cutaneous immune responses in the common carp detected using transcript analysis. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 4, 1664–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, F.E.; Ismail, H.M.; Didangelos, A.; Peirce, M.; Vincent, T.L.; Wait, R.; Saklatvala, J. Src and fibroblast growth factor 2 independently regulate signaling and gene expression induced by experimental injury to intact articular cartilage. Arthritis Rheum 2013, 65, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halle, M.; Gomez, M.A.; Stuible, M.; Shimizu, H.; McMaster, W.R.; Olivier, M.; Tremblay, M.L. The Leishmania surface protease GP63 cleaves multiple intracellular proteins and actively participates in p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inactivation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 6893–6908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cordero, H.; Brinchmann, M.F.; Cuesta, A.; Meseguer, J.; Esteban, M.A. Skin mucus proteome map of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Proteomics 2015, 15, 4007–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
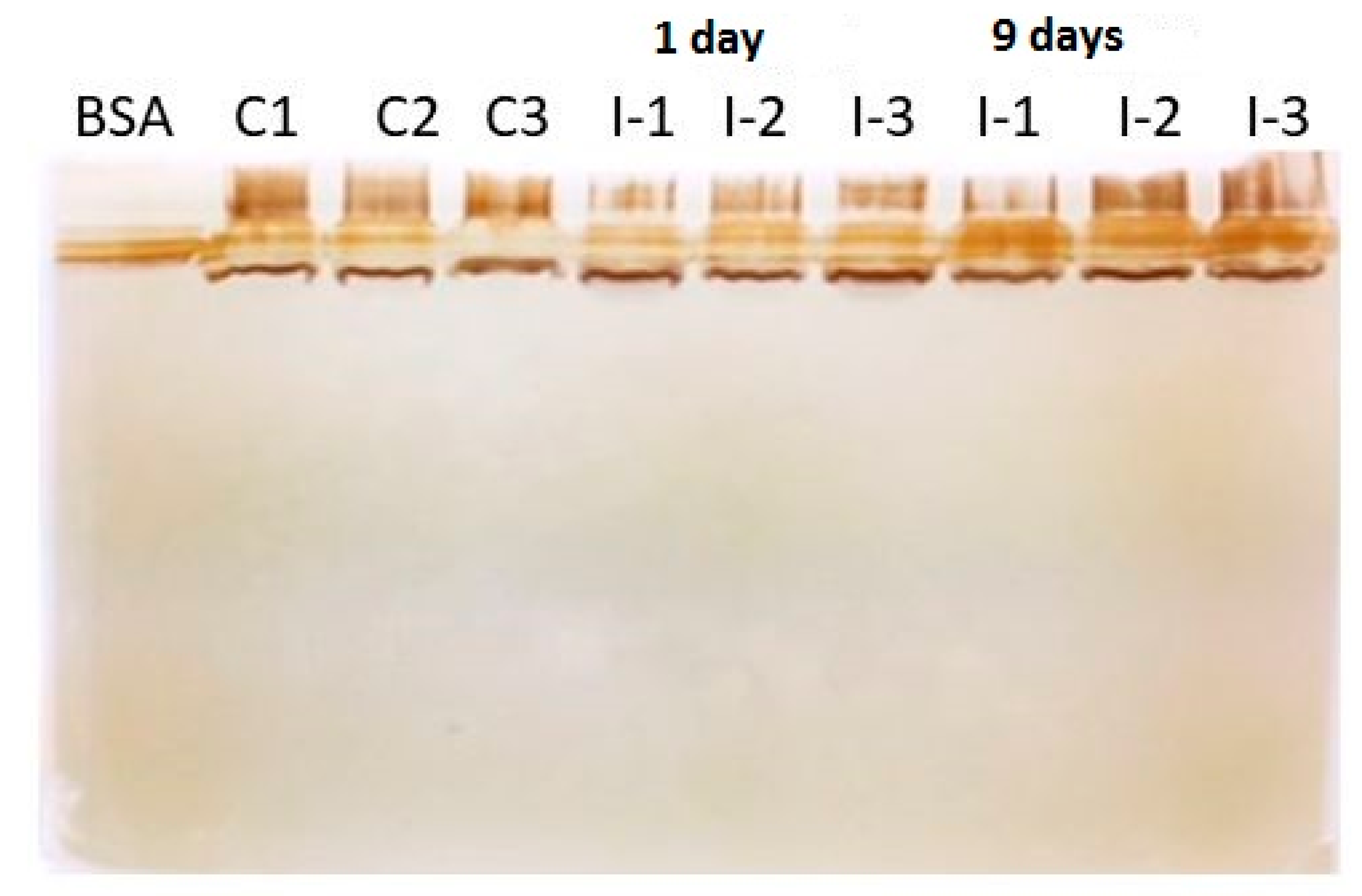
| UniProt Accession Number | Protein | Confident Peptides | Coverage (%) | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G0QTP1_ICHMG | Tubulin alpha chain | 12 | 25.4 | Microtubule-based process |
| G0QMB0_ICHMG | Tubulin beta chain | 9 | 33.0 | Microtubule-based process |
| G0QQR6_ICHMG | Elongation factor 1-alpha | 8 | 18.2 | Translation elongation factor activity |
| G0R170_ICHMG | 26S proteasome regulatory subunit | 3 | 5.3 | Protein catabolic process |
| G0QY27_ICHMG | 26S protease regulatory subunit 6B/AAA domain-containing protein | 3 | 10.1 | Protein catabolic process |
| G0QRA5_ICHMG | Heat shock protein 90/HATPase_c domain-containing protein | 3 | 5.8 | Protein folding |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saleh, M.; Abdel-Baki, A.-A.S.; Dkhil, M.A.; El-Matbouli, M.; Al-Quraishy, S. Proteins of the Ciliated Protozoan Parasite Ichthyophthirius multifiliis Identified in Common Carp Skin Mucus. Pathogens 2021, 10, 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10070790
Saleh M, Abdel-Baki A-AS, Dkhil MA, El-Matbouli M, Al-Quraishy S. Proteins of the Ciliated Protozoan Parasite Ichthyophthirius multifiliis Identified in Common Carp Skin Mucus. Pathogens. 2021; 10(7):790. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10070790
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaleh, Mona, Abdel-Azeem S. Abdel-Baki, Mohamed A. Dkhil, Mansour El-Matbouli, and Saleh Al-Quraishy. 2021. "Proteins of the Ciliated Protozoan Parasite Ichthyophthirius multifiliis Identified in Common Carp Skin Mucus" Pathogens 10, no. 7: 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10070790
APA StyleSaleh, M., Abdel-Baki, A.-A. S., Dkhil, M. A., El-Matbouli, M., & Al-Quraishy, S. (2021). Proteins of the Ciliated Protozoan Parasite Ichthyophthirius multifiliis Identified in Common Carp Skin Mucus. Pathogens, 10(7), 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10070790








