Serology- and Blood-PCR-Based Screening for Schistosomiasis in Pregnant Women in Madagascar—A Cross-Sectional Study and Test Comparison Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
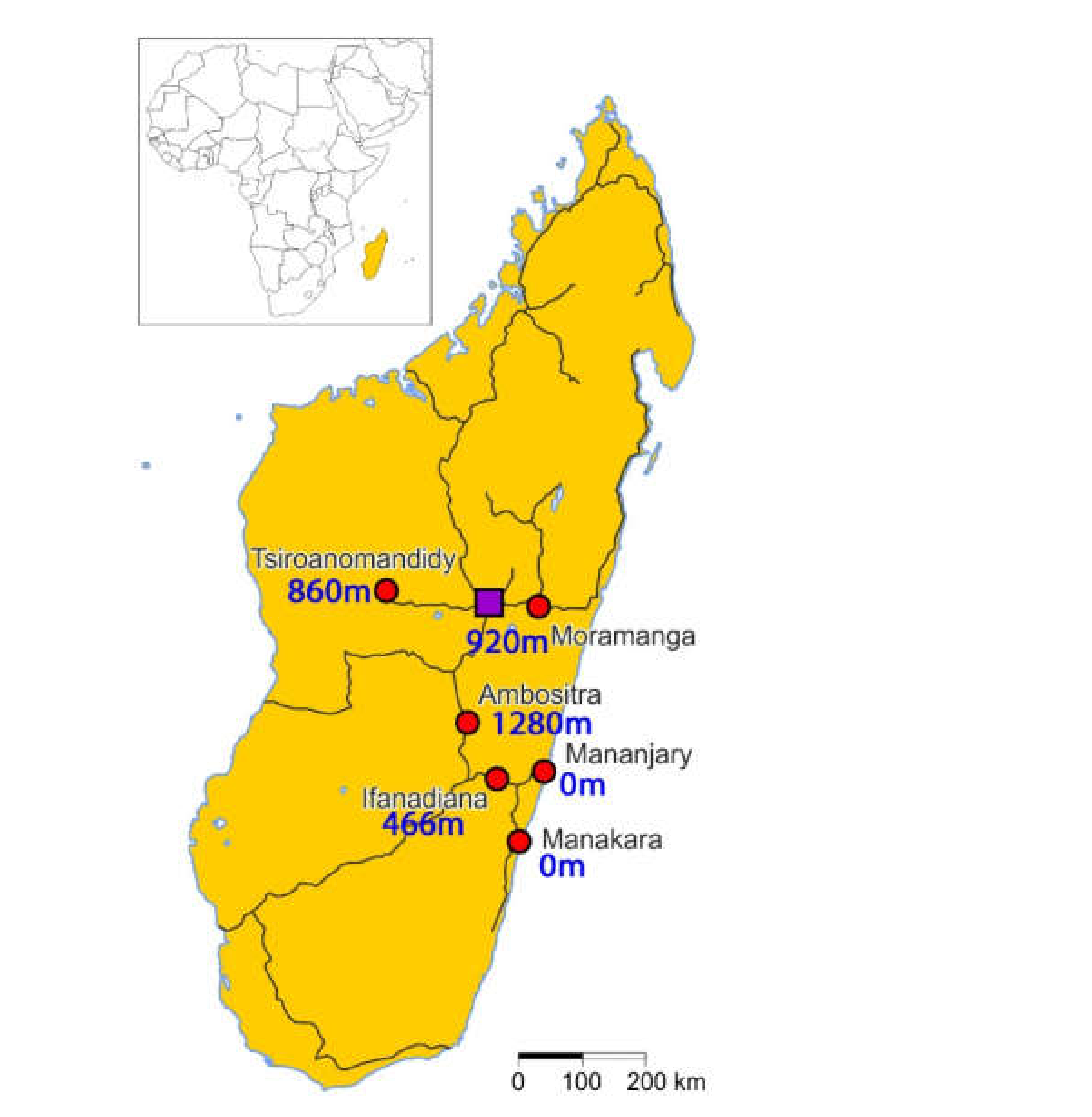
2.1. Local Epidemiology
2.2. Descriptive Comparison of the Test Results Applying Different Assays
2.3. Latent Class Assessment Based Calculation of the Test Characteristics and the Resulting Diagnostic-Accuracy Adjusted Overall Prevalence
2.4. Estimation of Potential Influence of Cross-Reacting Anti-Malarial Antibodies
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Sample Materials
4.2. PCR Protocols
4.3. Serology
4.4. Inclusion Or Exclusion Criteria
4.5. Statistical Assessment
4.6. Ethical Clearance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Distribution of the Excluded Samples due to Insufficient Sample Volumes on the Different Study Sides by Altitude
| Altitude | Total Number of Collected Samples (%) | Excluded Samples due to Insufficient Sample Volumes (%) |
| Littoral | 195 (100.0) | 8 (4.1) |
| Littoral | 251 (100.0) | 20 (8.0) |
| 466 m | 197 (100.0) | 23 (11.7) |
| 860 m | 203 (100.0) | 1 (0.5) |
| 920 m | 198 (100.0) | 32 (16.2) |
| 1280 m | 200 (100.0) | 6 (3.0) |
References
- Rasoamanamihaja, C.F.; Rahetilahy, A.M.; Ranjatoarivony, B.; Dhanani, N.; Andriamaro, L.; Andrianarisoa, S.H.; Jourdan, P.M. Baseline prevalence and intensity of schistosomiasis at sentinel sites in Madagascar: Informing a national control strategy. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, H.J.; Penney, J.M.S.; Linder, C.; Joekes, E.C.; Bustinduy, A.L.; Stothard, J.R.; Rakotomampianina, D.A.L.; Andriamasy, E.H.; Mahary, L.R.; Ranjanoro, E.P.; et al. A cross-sectional study of periportal fibrosis and Schistosoma mansoni infection among school-aged children in a hard-to-reach area of Madagascar. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 114, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boisier, P.; Serieye, J.; Ravaoalimalala, V.E.; Roux, J.; Esterre, P. Ultrasonographical assessment of morbidity in schistosomiasis mansoni in Madagascar: A community-based study in a rural population. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1995, 89, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, N.G.; Rakotozandrindrainy, R.; Heriniaina, J.N.; Randriamampionona, N.; Hahn, A.; Hogan, B.; Frickmann, H.; Dekker, D.; Poppert, S.; Razafindrabe, T.; et al. Schistosoma mansoni in schoolchildren in a Madagascan highland school assessed by PCR and sedimentation microscopy and Bayesian estimation of sensitivities and specificities. Acta Trop. 2014, 134, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, S.A.; Penney, J.M.S.J.; Russell, H.J.; Howe, A.P.; Linder, C.; Rakotomampianina, A.L.D.; Nandimbiniaina, A.M.; Squire, S.B.; Stothard, J.R.; Bustinduy, A.L.; et al. High burden of Schistosoma mansoni infection in school-aged children in Marolambo District, Madagascar. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfluger, W. Ecological studies in Madagascar of Biomphalaria pfeifferi, intermediate host of Schistosoma mansoni. 2. Biology and dynamics in the non-endemic area of Antananarivo. Arch. Inst. Pasteur Madagascar. 1978, 46, 241–269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stothard, J.R.; Brémond, P.; Andriamaro, L.; Sellin, B.; Sellin, E.; Rollinson, D. Bulinus species on Madagascar: Molecular evolution, genetic markers and compatibility with Schistosoma haematobium. Parasitology 2001, 123, S261–S275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charbonnel, N.; Angers, B.; Rasatavonjizay, R.; Bremond, P.; Debain, C.; Jarne, P. The influence of mating system, demography, parasites and colonization on the population structure of Biomphalaria pfeifferi in Madagascar. Mol. Ecol. 2002, 11, 2213–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.O.; Rafalimanantsoa, A.; Ramarokoto, C.; Rahetilahy, A.M.; Ravoniarimbinina, P.; Kawai, S.; Minamoto, T.; Sato, M.; Kirinoki, M.; Rasolofo, V.; et al. Usefulness of environmental DNA for detecting Schistosoma mansoni occurrence sites in Madagascar. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 76, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serieye, J.; Boisier, P.; Ravaoalimalala, V.E.; Ramarokoto, C.E.; Leutscher, P.; Esterre, P.; Roux, J. Schistosoma haematobium infection in western Madagascar: Morbidity determined by ultrasonography. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1996, 90, 398–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leutscher, P.; Raharisolo, C.; Pecarrere, J.L.; Ravaoalimalala, V.E.; Serieye, J.; Rasendramino, M.; Vennervald, B.; Feldmeier, H.; Esterre, P. Schistosoma haematobium induced lesions in the female genital tract in a village in Madagascar. Acta Trop. 1997, 66, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leutscher, P.; Ramarokoto, C.E.; Reimert, C.; Feldmeier, H.; Esterre, P.; Vennervald, B.J. Community-based study of genital schistosomiasis in men from Madagascar. Lancet 2000, 355, 117–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leutscher, P.D.; Høst, E.; Reimert, C.M. Semen quality in Schistosoma haematobium infected men in Madagascar. Acta Trop. 2009, 109, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramarakoto, C.E.; Leutscher, P.D.; Van Dam, G.; Christensen, N.O. Ultrasonographical findings in the urogenital organs in women and men infected with Schistosoma haematobium in northern Madagascar. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 102, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randrianasolo, B.S.; Jourdan, P.M.; Ravoniarimbinina, P.; Ramarokoto, C.E.; Rakotomanana, F.; Ravaoalimalala, V.E.; Gundersen, S.G.; Feldmeier, H.; Vennervald, B.J.; Van Lieshout, L.; et al. Gynecological manifestations, histopathological findings, and schistosoma-specific polymerase chain reaction results among women with Schistosoma haematobium infection: A cross-sectional study in Madagascar. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laxman, V.V.; Adamson, B.; Mahmood, T. Recurrent ectopic pregnancy due to Schistosoma hematobium. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2008, 28, 461–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegrist, D.; Siegrist-Obimpeh, P. Schistosoma haematobium infection in pregnancy. Acta Trop. 1992, 50, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.F.; Mital, P.; Kanzaria, H.K.; Olds, G.R.; Kurtis, J.D. Schistosomiasis and pregnancy. Trends Parasitol. 2007, 23, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mombo-Ngoma, G.; Honkpehedji, J.; Basra, A.; Mackanga, J.R.; Zoleko, R.M.; Zinsou, J.; Agobe, J.C.; Lell, B.; Matsiegui, P.B.; Gonzales, R.; et al. Urogenital schistosomiasis during pregnancy is associated with low birth weight delivery: Analysis of a prospective cohort of pregnant women and their offspring in Gabon. Int. J. Parasitol. 2017, 47, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajanga, A.; Lwambo, N.J.; Blair, L.; Nyandindi, U.; Fenwick, A.; Brooker, S. Schistosoma mansoni in pregnancy and associations with anaemia in northwest Tanzania. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 100, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tweyongyere, R.; Naniima, P.; Mawa, P.A.; Jones, F.M.; Webb, E.L.; Cose, S.; Dunne, D.W.; Elliott, A.M. Effect of maternal Schistosoma mansoni infection and praziquantel treatment during pregnancy on Schistosoma mansoni infection and immune responsiveness among offspring at age five years. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.d.A.; De Lorena, V.M.B.; Fernandes Éde, S.; Sales, I.R.; Nascimento, W.R.; De Miranda Gomes, Y.; Albuquerque, M.C.; Costa, V.M.; Souza, V.M. Gestation and breastfeeding in schistosomotic mothers differently modulate the immune response of adult offspring to postnatal Schistosoma mansoni infection. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2016, 111, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Da Paz, V.R.F.; Sequeira, D.; Pyrrho, A. Infection by Schistosoma mansoni during pregnancy: Effects on offspring immunity. Life Sci. 2017, 185, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacorcia, M.; Prazeres da Costa, C.U. Maternal Schistosomiasis: Immunomodulatory Effects with Lasting Impact on Allergy and Vaccine Responses. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, N.G.; Girmann, M.; Randriamampionona, N.; Bialonski, A.; Maus, D.; Krefis, A.C.; Njarasoa, C.; Rajanalison, J.F.; Ramandrisoa, H.D.; Randriarison, M.L.; et al. Seroprevalence of antibodies against Chikungunya, Dengue, and Rift Valley fever viruses after febrile illness outbreak, Madagascar. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1780–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, N.G.; Mertens, E.; Winter, D.; Maiga-Ascofaré, O.; Dekker, D.; Jansen, S.; Tappe, D.; Randriamampionona, N.; May, J.; Rakotozandrindrainy, R.; et al. No serological evidence for Zika virus infection and low specificity for anti-Zika virus ELISA in malaria positive individuals among pregnant women from Madagascar in 2010. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frickmann, H.; Schwarz, N.G.; Girmann, M.; Hagen, R.M.; Poppert, S.; Crusius, S.; Podbielski, A.; Heriniaina, J.N.; Razafindrabe, T.; Rakotondrainiarivelo, J.P.; et al. Serological survey of HIV and syphilis in pregnant women in Madagascar. Trop. Med. Int. Health. 2013, 18, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garigliany, M.M.; Hagen, R.M.; Frickmann, H.; May, J.; Schwarz, N.G.; Perse, A.; Jöst, H.; Börstler, J.; Shahhosseini, N.; Desmecht, D.; et al. Cyclovirus CyCV-VN species distribution is not limited to Vietnam and extends to Africa. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maïga-Ascofaré, O.; Rakotozandrindrainy, R.; Girmann, M.; Hahn, A.; Randriamampionona, N.; Poppert, S.; May, J.; Schwarz, N.G. Molecular epidemiology and seroprevalence in asymptomatic Plasmodium falciparum infections of Malagasy pregnant women in the highlands. Malar. J. 2015, 14, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Keller, C.; Krüger, A.; Schwarz, N.G.; Rakotozandrindrainy, R.; Rakotondrainiarivelo, J.P.; Razafindrabe, T.; Derschum, H.; Silaghi, C.; Pothmann, D.; Veit, A.; et al. High detection rate of Rickettsia africae in Amblyomma variegatum but low prevalence of anti-rickettsial antibodies in healthy pregnant women in Madagascar. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeng, B.B.; Aryeetey, Y.A.; De Dood, C.J.; Amoah, A.S.; Larbi, I.A.; Deelder, A.M.; Yazdanbakhsh, M.; Hartgers, F.C.; Boakye, D.A.; Verweij, J.J.; et al. Application of a circulating-cathodic-antigen (CCA) strip test and real-time PCR, in comparison with microscopy, for the detection of Schistosoma haematobium in urine samples from Ghana. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2008, 102, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochodo, E.A.; Gopalakrishna, G.; Spek, B.; Reitsma, J.B.; Van Lieshout, L.; Polman, K.; Lamberton, P.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Leeflang, M.M. Circulating antigen tests and urine reagent strips for diagnosis of active schistosomiasis in endemic areas. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 3, CD009579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wichmann, D.; Panning, M.; Quack, T.; Kramme, S.; Burchard, G.D.; Grevelding, C.; Drosten, C. Diagnosing schistosomiasis by detection of cell-free parasite DNA in human plasma. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, e422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cnops, L.; Soentjens, P.; Clerinx, J.; Van Esbroeck, M. A Schistosoma haematobium-specific real-time PCR for diagnosis of urogenital schistosomiasis in serum samples of international travelers and migrants. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guegan, H.; Fillaux, J.; Charpentier, E.; Robert-Gangneux, F.; Chauvin, P.; Guemas, E.; Boissier, J.; Valentin, A.; Cassaing, S.; Gangneux, J.P.; et al. Real-time PCR for diagnosis of imported schistosomiasis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinz, R.; Schwarz, N.G.; Hahn, A.; Frickmann, H. Serological approaches for the diagnosis of schistosomiasis—A review. Mol. Cell. Probes 2017, 31, 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuss, A.; Mazigo, H.D.; Mueller, A. Evaluation of serum-based real-time PCR to detect Schistosoma mansoni infection before and after treatment. Infect. Dis. Poverty. 2020, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairlie-Clarke, K.J.; Lamb, T.J.; Langhorne, J.; Graham, A.L.; Allen, J.E. Antibody isotype analysis of malaria-nematode co-infection: Problems and solutions associated with cross-reactivity. BMC Immunol. 2010, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naus, C.W.; Jones, F.M.; Satti, M.Z.; Joseph, S.; Riley, E.M.; Kimani, G.; Mwatha, J.K.; Kariuki, C.H.; Ouma, J.H.; Kabatereine, N.B.; et al. Serological responses among individuals in areas where both schistosomiasis and malaria are endemic: Cross-reactivity between Schistosoma mansoni and Plasmodium falciparum. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 187, 1272–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierrot, C.; Wilson, S.; Lallet, H.; Lafitte, S.; Jones, F.M.; Daher, W.; Capron, M.; Dunne, D.W.; Khalife, J. Identification of a novel antigen of Schistosoma mansoni shared with Plasmodium falciparum and evaluation of different cross-reactive antibody subclasses induced by human schistosomiasis and malaria. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 3347–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmby, H. Schistosomiasis and malaria: Another piece of the crossreactivity puzzle. Trends Parasitol. 2007, 23, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogan, W.J.; Gladen, B. Estimating prevalence from the results of a screening test. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1978, 107, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement of categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, A.; Podbielski, A.; Meyer, T.; Zautner, A.E.; Loderstädt, U.; Schwarz, N.G.; Krüger, A.; Cadar, D.; Frickmann, H. On detection thresholds-a review on diagnostic approaches in the infectious disease laboratory and the interpretation of their results. Acta Trop. 2020, 205, 105377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tweyongyere, R.; Mawa, P.A.; Emojong, N.O.; Mpairwe, H.; Jones, F.M.; Duong, T.; Dunne, D.W.; Vennervald, B.J.; Katunguka-Rwakishaya, E.; Elliott, A.M. Effect of praziquantel treatment of Schistosoma mansoni during pregnancy on intensity of infection and antibody responses to schistosome antigens: Results of a randomised, placebo-controlled trial. BMC Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.F.; Olveda, R.M.; Mirochnick, M.H.; Bustinduy, A.L.; Elliott, A.M. Praziquantel for the treatment of schistosomiasis during human pregnancy. Bull. World Health Organ. 2018, 96, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoekstra, P.T.; Schwarz, N.G.; Adegnika, A.A.; Andrianarivelo, M.R.; Corstjens, P.L.A.M.; Rakotoarivelo, R.A.; Rakotozandrindrainy, R.; Sicuri, E.; Kreidenweiss, A.; Van Dam, G.J. freeBILy consortium. Fast and reliable easy-to-use diagnostics for eliminating bilharzia in young children and mothers: An introduction to the freeBILy project. Acta Trop. 2020, 211, 105631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frickmann, H.; Lunardon, L.M.; Hahn, A.; Loderstädt, U.; Lindner, A.K.; Becker, S.L.; Mockenhaupt, F.P.; Weber, C.; Tannich, E. Evaluation of a duplex real-time PCR in human serum for simultaneous detection and differentiation of Schistosoma mansoni and Schistosoma haematobium infections—Cross-sectional study. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, A.; Meyer, C.G.; Frickmann, H. Impact of diagnostic methods on efficacy estimation—A proof-of-principle based on historical examples. Trop. Med. Int. Health. 2020, 25, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wichmann, D.; Poppert, S.; Von Thien, H.; Clerinx, J.; Dieckmann, S.; Jensenius, M.; Parola, P.; Richter, J.; Schunk, M.; Stich, A.; et al. Prospective European-wide multicentre study on a blood based real-time PCR for the diagnosis of acute schistosomiasis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niesters, H.G.M. Quantitation of viral load using real-time amplification techniques. Methods 2001, 25, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Tan, M.; Kutner, M. Random effects models in latent class analysis for evaluating accuracy of diagnostic test. Biometrics 1996, 52, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köller, T.; Hahn, A.; Altangerel, E.; Verweij, J.J.; Landt, O.; Kann, S.; Dekker, D.; May, J.; Loderstädt, U.; Podbielski, A.; et al. Comparison of commercial and in-house real-time PCR platforms for 15 parasites and microsporidia in human stool samples without a gold standard. Acta Trop. 2020, 207, 105516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henny, J. Constitution d’un centre de ressources biologiques Aspects pratiques. Rev. Epidemiol. Sante Publique 2003, 51, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Paoli, P. Bio-banking in microbiology: From sample collection to epidemiology, diagnosis and research. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 897–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, J.R.; Simarro, P.P.; Diarra, A.; Ruiz-Postigo, J.A.; Jannin, J.G. The Human African trypanosomiasis specimen biobank: A necessary tool to support research of new diagnostics. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Immunofluorescence Assays, % Positives * | ELISA, % Positives * | PCRs, % Positives | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Altitude | N | IgM | IgG | IgM | IgG | Schisto-soma spp. 1 | S. haematobium2 | S. mansoni3 |
| Littoral | 187 | 37.4% | 48.7% | 29.4% | 37.4% | 7.5% | 0 | 32.6% |
| Littoral | 231 | 12.6% | 8.2% | 19.9% | 10.8% | 0 | 0 | 24.2% |
| 466 m | 174 | 29.9% | 30.5% | 42.5% | 37.4% | 5.2% | 0 | 41.4% |
| 920 m | 166 | 27.7% | 24.7% | 21.1% | 38.6% | 5.4% | 0 | 36.7% |
| 860 m | 202 | 37.1% | 51.0% | 32.2% | 54.0% | 1.5% | 0 | 50.0% |
| 1280 m | 194 | 29.4% | 63.4% | 29.4% | 71.1% | 14.4% | 0 | 69.1% |
| All sites | 1154 | 28.5% | 37.3% | 28.8% | 40.8% | 5.5% | - | 42.0% |
| Point biserial correlationcoefficient (p-value) | 1154 | 0.0672 (0.0224) | 0.2360 (0.0001) | 0.0270 (0.3595) | 0.3330 (0.0001) | 0.1183 (0.0001) | 0.2614 (0.0001) | |
| % Positive | % Concordant Positive | % Concordant Negative | % Discordant | Kappa (SE) | Kappa Interpretation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IF IgG | Positive | 37.3% | 31.2% | 53.1% | 15.7% | 67.1% (2.9%) | Substantial |
| ELISA IgG | 40.8% | ||||||
| IF IgG | Positive and borderline | 44.5% | 38.0% | 47.0% | 15.1% | 69.6% (2.9%) | Substantial |
| ELISA IgG | 46.5% | ||||||
| IF IgM | Positive | 28.5% | 19.8% | 62.5% | 17.8% | 56.5% (2.9%) | Moderate |
| ELISA IgM | 28.8% | ||||||
| IF IgM | Positive and borderline | 36.1% | 24.4% | 55.2% | 20.4% | 55.1% (2.9%) | Moderate |
| ELISA IgM | 33.2% |
| % Positive | % Concordantly Positive | % Concordantly Negative | % Discordant | Kappa (SE) | Kappa Interpretation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IF IgM * | 28.5% | 19.8% | 62.5% | 17.8% | 56.5% (2.9%) | Moderate |
| ELISA IgM * | 28.8% | |||||
| S. mansoni PCR 2 | 42.3% | 4.9% | 57.5% | 37.6% | 12.3% (1.5%) | Slight |
| Schistosoma spp. PCR 1 | 5.5% | |||||
| IF IgM * | 28.5% | 15.9% | 45.3% | 38.8% | 16.6% (2.8%) | Slight |
| S. mansoni PCR 2 | 42.3% | |||||
| IF IgM * | 28.5% | 2.5% | 68.5% | 28.9% | 6.2% (2.0%) | Slight |
| Schistosoma spp. PCR 1 | 5.5% | |||||
| ELISA IgM * | 28.8% | 13.3% | 42.5% | 44.3% | 5.0% (2.8%) | Slight |
| S. mansoni PCR 2 | 42.3% | |||||
| ELISA IgM * | 28.8% | 0.9% | 66.6% | 32.5% | −4.5% (2.0%) | Poor |
| Schistosoma spp. PCR 1 | 5.5% |
| Immunofluorescence Assays | ELISA of | PCR | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 1154 | IgM | IgG | IgM | IgG | Schistosoma spp. | S. haematobium | S. mansoni |
| Sensitivity (0.95 CI) | 0.4913 (0.4438, 0.5391) | 0.8696 (0.8142, 0.9103) | 0.3829 (0.3377, 0.4302) | 0.8759 (0.8282, 0.9118) | 0.1349 (0.1061, 0.1702) | - | 0.7406 (0.6929, 0.7832) |
| Specificity (0.95 CI) | 0.8549 (0.8221, 0.8825) | 0.9647 (0.934, 0.9811) | 0.7769 (0.7418, 0.8085) | 0.9093 (0.8753, 0.9347) | 0.9999 (0, 1) | - | 0.7971 (0.7618, 0.8284) |
| Prevalence rate (0.95 CI) | 40.4% (36.8%, 44.1%) | ||||||
| Immunofluorescence Assays | ELISA | PCR | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 1154 | IgM | IgG | IgM | IgG | Schistosoma spp. | S. haematobium | S. mansoni |
| Phi coefficient * | 0.0372 | 0.1150 | 0.0297 | 0.1417 | 0.1231 | - | 0.1006 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoffmann, T.; Carsjens, I.; Rakotozandrindrainy, R.; Girmann, M.; Randriamampionona, N.; Maïga-Ascofaré, O.; Podbielski, A.; Hahn, A.; Frickmann, H.; Schwarz, N.G. Serology- and Blood-PCR-Based Screening for Schistosomiasis in Pregnant Women in Madagascar—A Cross-Sectional Study and Test Comparison Approach. Pathogens 2021, 10, 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10060722
Hoffmann T, Carsjens I, Rakotozandrindrainy R, Girmann M, Randriamampionona N, Maïga-Ascofaré O, Podbielski A, Hahn A, Frickmann H, Schwarz NG. Serology- and Blood-PCR-Based Screening for Schistosomiasis in Pregnant Women in Madagascar—A Cross-Sectional Study and Test Comparison Approach. Pathogens. 2021; 10(6):722. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10060722
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoffmann, Tanja, Imke Carsjens, Raphaël Rakotozandrindrainy, Mirko Girmann, Njary Randriamampionona, Oumou Maïga-Ascofaré, Andreas Podbielski, Andreas Hahn, Hagen Frickmann, and Norbert Georg Schwarz. 2021. "Serology- and Blood-PCR-Based Screening for Schistosomiasis in Pregnant Women in Madagascar—A Cross-Sectional Study and Test Comparison Approach" Pathogens 10, no. 6: 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10060722
APA StyleHoffmann, T., Carsjens, I., Rakotozandrindrainy, R., Girmann, M., Randriamampionona, N., Maïga-Ascofaré, O., Podbielski, A., Hahn, A., Frickmann, H., & Schwarz, N. G. (2021). Serology- and Blood-PCR-Based Screening for Schistosomiasis in Pregnant Women in Madagascar—A Cross-Sectional Study and Test Comparison Approach. Pathogens, 10(6), 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10060722






