Microbial Contamination in Hospital Environment Has the Potential to Colonize Preterm Newborns’ Nasal Cavities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
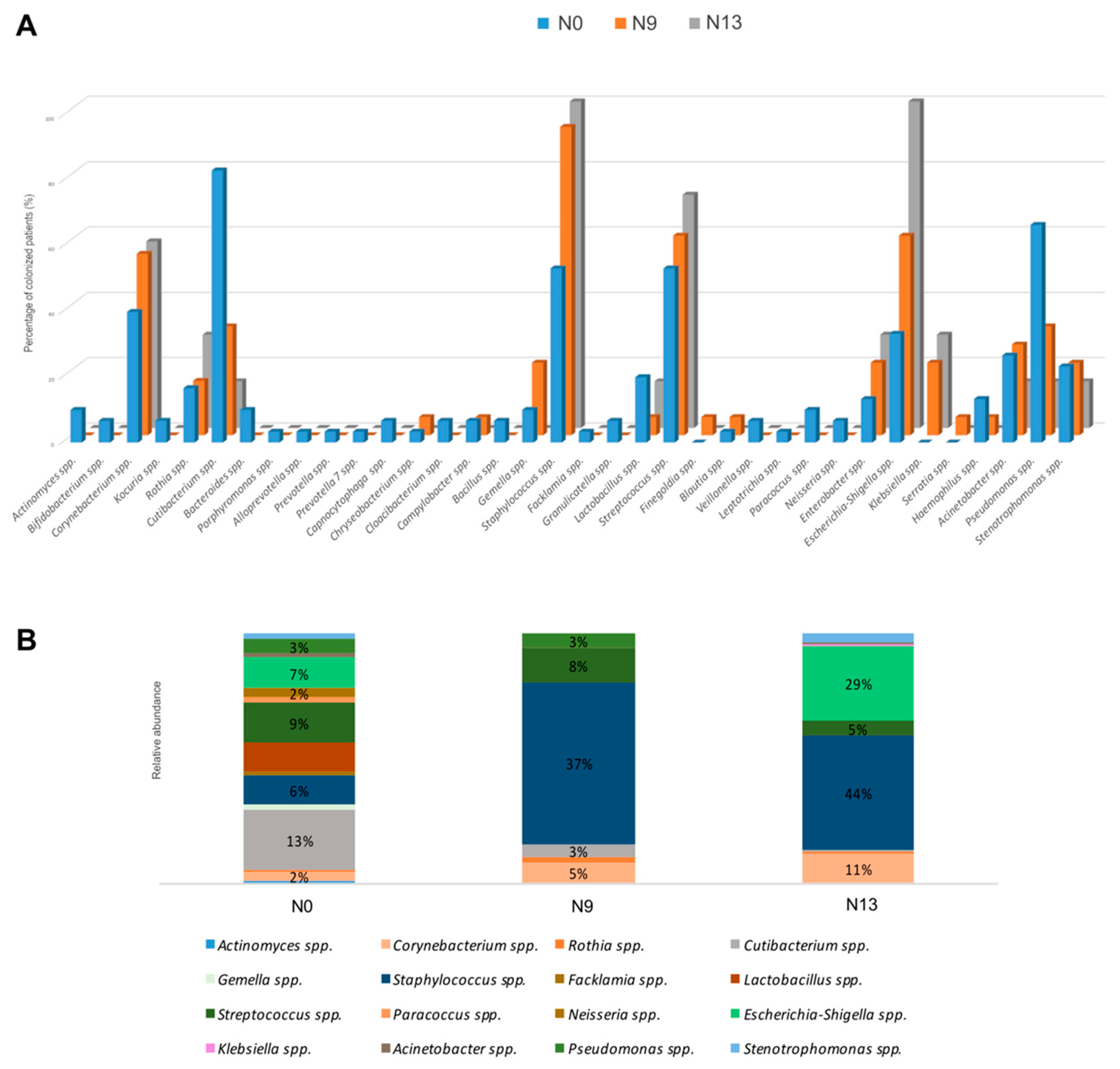
2.1. The Microbial Profile of Newborns Nasal Swabs
2.2. NGS Analysis
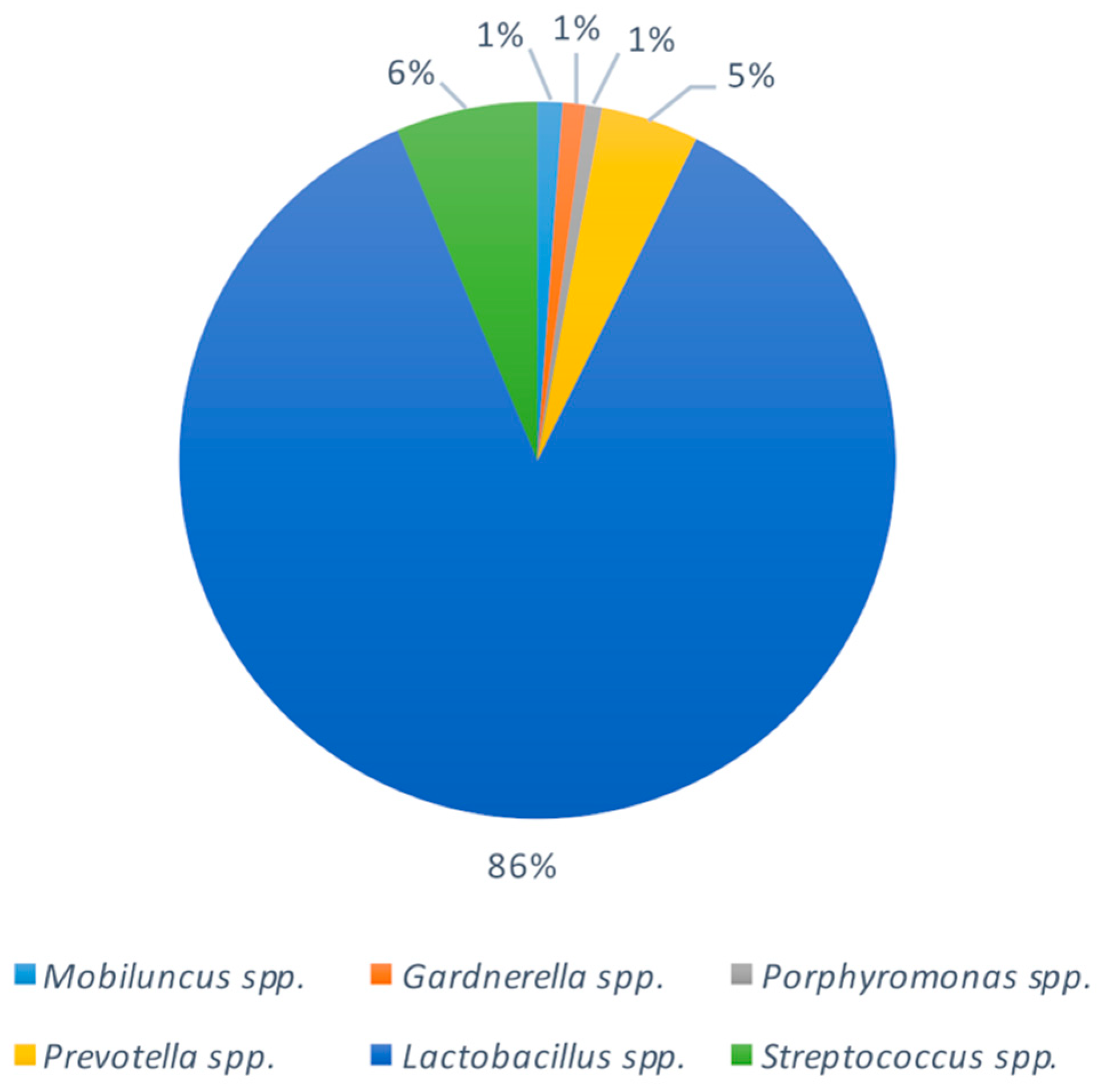
2.3. Bacterial Composition of Vaginal Swabs in Pregnant Women
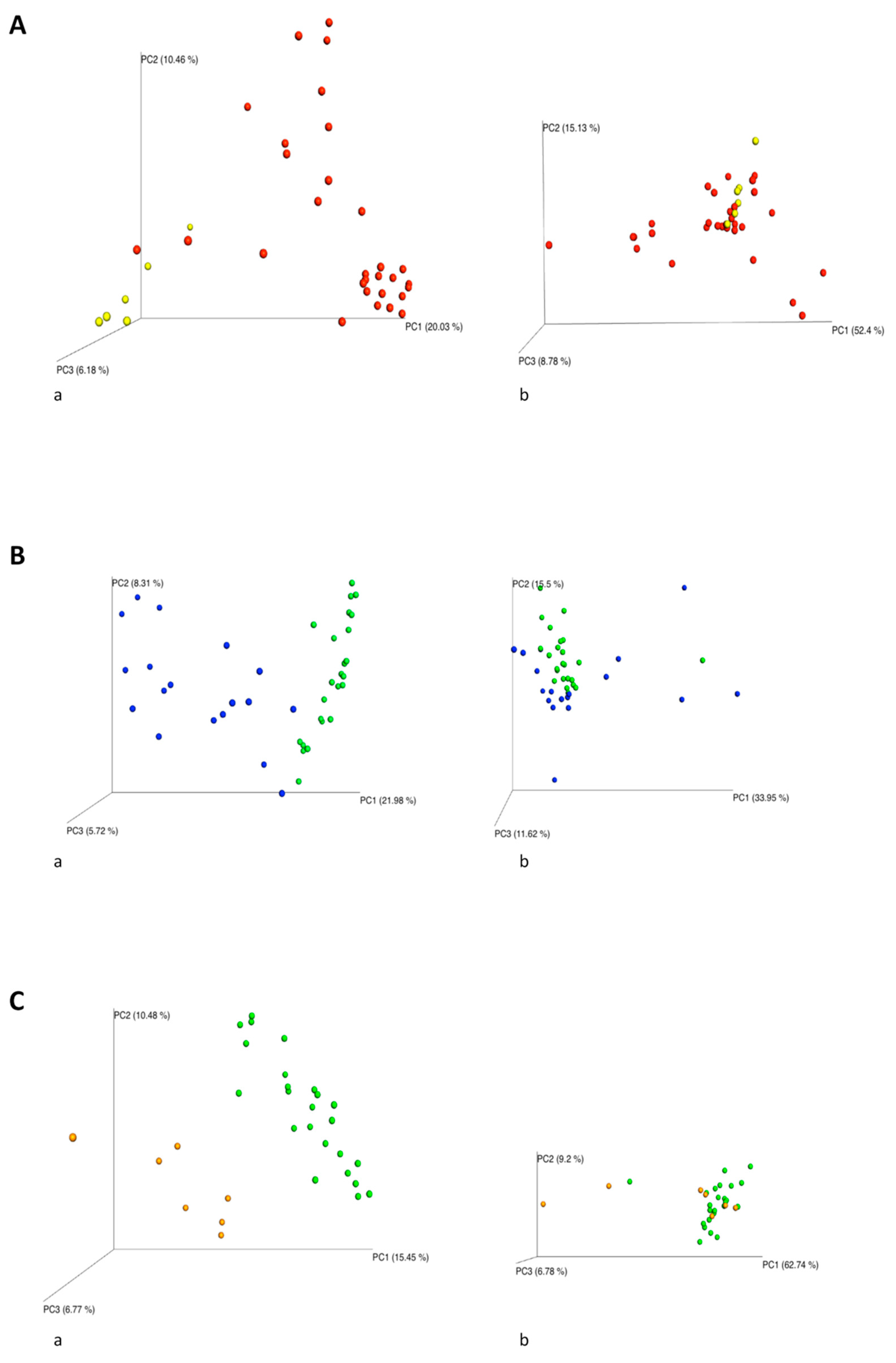
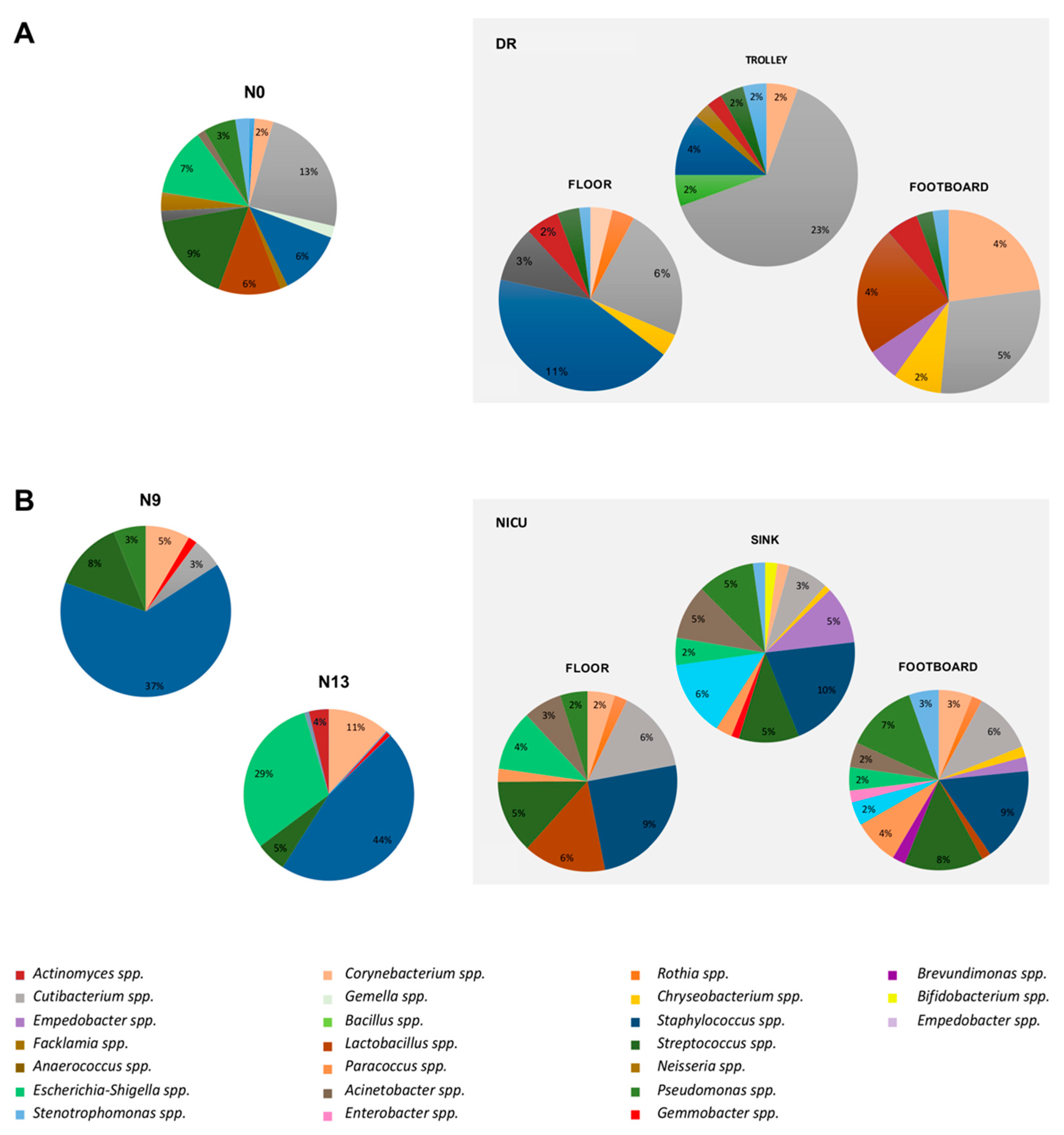
2.4. Impact of the Environmental Bacterial Microbiome on Nasal Colonization of Newborns
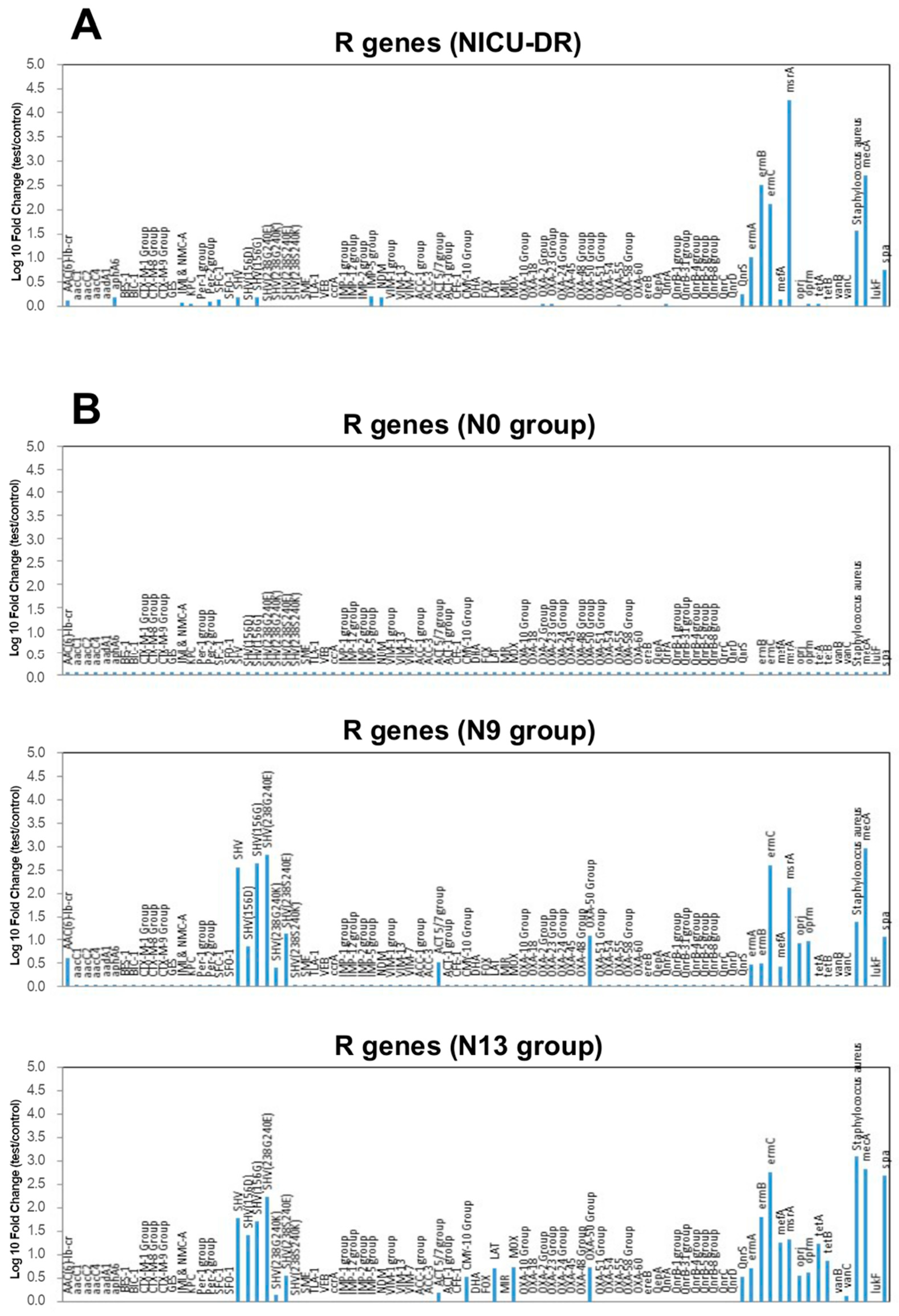
2.5. Microarray Analysis Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Samples
4.2. Nasal Swab Collection
4.3. Environmental Sampling
4.4. Vaginal Swabs Collection
4.5. Next Generation Sequencing Analysis
4.5.1. DNA Extraction
4.5.2. Library Preparation
4.5.3. Data Processing
4.6. qPCR Analyses
4.6.1. DNA Extraction
4.6.2. Microarray Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plano, L.R.W. The Changing Spectrum of Neonatal Infectious Disease. J. Perinatol. 2010, 30, S16–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, D.S.; Peppe, A.L.G.; dos Reis, H.; Abdallah, V.O.S.; Ribas, R.M.; Gontijo Filho, P.P. Late Onset Sepsis in Newborn Babies: Epidemiology and Effect of a Bundle to Prevent Central Line Associated Bloodstream Infections in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 19, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghesi, A.; Stronati, M. Strategies for the Prevention of Hospital-Acquired Infections in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. J. Hosp. Infect. 2008, 68, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolat, F.; Uslu, S.; Bolat, G.; Comert, S.; Can, E.; Bulbul, A.; Nuhoglu, A. Healthcare-Associated Infections in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit in Turkey. Indian Pediatr. 2012, 49, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawfik, D.S.; Sexton, J.B.; Kan, P.; Sharek, P.J.; Nisbet, C.C.; Rigdon, J.; Lee, H.C.; Profit, J. Burnout in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit and Its Relation to Healthcare-Associated Infections. J. Perinatol. 2017, 37, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawagoe, J.Y.; Segre, C.A.M.; Pereira, C.R.; Cardoso, M.F.S.; Silva, C.V.; Fukushima, J.T. Risk Factors for Nosocomial Infections in Critically Ill Newborns: A 5-Year Prospective Cohort Study. Am. J. Infect. Control 2001, 29, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, A.A.; Dinulos, J.G.H. Cutaneous Bacterial Infections in the Newborn. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2005, 17, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghesi, A.; Stronati, M.; Castagnoli, R.; Ioimo, I.; Achille, C.; Manzoni, P.; Tzialla, C. Novel Approaches to the Study of Neonatal Infections. Am. J. Perinatol. 2018, 35, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, A.K.; Huskins, W.C.; Thaver, D.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Abbas, Z.; Goldmann, D.A. Hospital-Acquired Neonatal Infections in Developing Countries. Lancet 2005, 365, 1175–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, P.L.; Morel, A.-S.; Zhou, J.; Wu, F.; Della-Latta, P.; Rubenstein, D.; Saiman, L. Epidemiology of Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus Aureus in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2002, 23, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimundo, O.; Heussler, H.; Bruhn, J.B.; Suntrarachun, S.; Kelly, N.; Deighton, M.A.; Garland, S.M. Molecular Epidemiology of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcal Bacteraemia in a Newborn Intensive Care Unit. J. Hosp. Infect. 2002, 51, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, D.R.; Harman, J.; Wald, E.R.; Kelleher, K.J. Antibiotic Prescribing by Primary Care Physicians for Children with Upper Respiratory Tract Infections. Arch Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2002, 156, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, R.H.; Bloom, B.T.; Spitzer, A.R.; Gerstmann, D.R. Empiric Use of Ampicillin and Cefotaxime, Compared with Ampicillin and Gentamicin, for Neonates at Risk for Sepsis is Associated with an Increased Risk of Neonatal Death. Pediatrics 2006, 117, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, E.M.; Hornik, C.P.; Clark, R.H.; Laughon, M.M.; Benjamin, D.K.; Smith, P.B.; Best Pharmaceuticals for Children Act—Pediatric Trials Network. Medication Use in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Am. J. Perinatol. 2014, 31, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaser, M.J. Antibiotic Use and Its Consequences for the Normal Microbiome. Science 2016, 352, 544–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskin-Parr, L.; Teyhan, A.; Blocker, A.; Henderson, A.J.W. Antibiotic Exposure in the First Two Years of Life and Development of Asthma and Other Allergic Diseases by 7.5 Yr: A Dose-Dependent Relationship. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 24, 762–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppala, V.S.; Meinzen-Derr, J.; Morrow, A.L.; Schibler, K.R. Prolonged Initial Empirical Antibiotic Treatment is Associated with Adverse Outcomes in Premature Infants. J. Pediatr. 2011, 159, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantey, J.B.; Wozniak, P.S.; Sánchez, P.J. Prospective Surveillance of Antibiotic Use in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: Results from the SCOUT Study. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2015, 34, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maragakis, L.L.; Perencevich, E.N.; Cosgrove, S.E. Clinical and Economic Burden of Antimicrobial Resistance. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2008, 6, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Man, P.; Verhoeven, B.A.; Verbrugh, H.A.; Vos, M.C.; van den Anker, J.N. An Antibiotic Policy to Prevent Emergence of Resistant Bacilli. Lancet 2000, 355, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotten, C.M.; McDonald, S.; Stoll, B.; Goldberg, R.N.; Poole, K.; Benjamin, D.K.; National Institute for Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. The Association of Third-Generation Cephalosporin Use and Invasive Candidiasis in Extremely Low Birth-Weight Infants. Pediatrics 2006, 118, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, V.N.; Northrup, V.; Bizzarro, M.J. Antibiotic Exposure in the Newborn Intensive Care Unit and the Risk of Necrotizing Enterocolitis. J. Pediatr. 2011, 159, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, L.C.; Forrest, C.B.; Zhang, P.; Richards, T.M.; Livshits, A.; DeRusso, P.A. Association of Antibiotics in Infancy with Early Childhood Obesity. JAMA Pediatr. 2014, 168, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.C.B.; Anchieta, L.M.; Lopes, M.F.d.P.; Romanelli, R.M.d.C.; Silva, A.C.B.; Anchieta, L.M.; Lopes, M.F.d.P.; Romanelli, R.M.d.C. Inadequate Use of Antibiotics and Increase in Neonatal Sepsis Caused by Resistant Bacteria Related to Health Care Assistance: A Systematic Review. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 22, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciolà, A.; Pellicanò, G.F.; Visalli, G.; Paolucci, I.A.; Venanzi Rullo, E.; Ceccarelli, M.; D’Aleo, F.; Di Pietro, A.; Squeri, R.; Nunnari, G.; et al. The Role of the Hospital Environment in the Healthcare-Associated Infections: A General Review of the Literature. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 1266–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Xian-Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Peng-Zhou, X.; Wang, P.; Xue, J.; Ling-Huang, Y.; Li-Li, Y.; Fu-Qiu, J. Epidemiology of Pathogens and Drug Resistance of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia in Chinese Neonatal Intensive Care Units: A Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Infect. Control 2014, 42, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kung, Y.-H.; Hsieh, Y.-F.; Weng, Y.-H.; Lien, R.-I.; Luo, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-L.; Chen, C.-J. Risk Factors of Late-Onset Neonatal Sepsis in Taiwan: A Matched Case-Control Study. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2016, 49, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, R.G.; Kandefer, S.; Do, B.T.; Smith, P.B.; Stoll, B.J.; Bell, E.F.; Carlo, W.A.; Laptook, A.R.; Sánchez, P.J.; Shankaran, S.; et al. Late-Onset Sepsis in Extremely Premature Infants: 2000–2011. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2017, 36, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Manouni el Hassani, S.; Berkhout, D.J.C.; Niemarkt, H.J.; Mann, S.; de Boode, W.P.; Cossey, V.; Hulzebos, C.V.; van Kaam, A.H.; Kramer, B.W.; van Lingen, R.A.; et al. Risk Factors for Late-Onset Sepsis in Preterm Infants: A Multicenter Case-Control Study. NEO 2019, 116, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-H.; Hsu, J.-F.; Chu, S.-M.; Lien, R.; Huang, H.-R.; Chiang, M.-C.; Fu, R.-H.; Lee, C.-W.; Huang, Y.-C. Incidence, Clinical Characteristics and Risk Factors for Adverse Outcome in Neonates with Late-Onset Sepsis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2014, 33, e7–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantey, J.B.; Milstone, A.M. Bloodstream Infections: Epidemiology and Resistance. Clin. Perinatol. 2015, 42, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizzarro, M.J.; Raskind, C.; Baltimore, R.S.; Gallagher, P.G. Seventy-Five Years of Neonatal Sepsis at Yale: 1928–2003. Pediatrics 2005, 116, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.-L.; Lee, W.-T.; Chen, H.-L. Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia in Low Birth Weight Neonates at a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: A Retrospective Observational Study. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2017, 58, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGirt, M.J.; Zaas, A.; Fuchs, H.E.; George, T.M.; Kaye, K.; Sexton, D.J. Risk Factors for Pediatric Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Infection and Predictors of Infectious Pathogens. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 36, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanishi, F.; Yoshinaga, M.; Morita, M.; Shibata, Y.; Yamada, T.; Ooi, Y.; Ukimura, A. Risk Factors for Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Patients. J. Infect. Chemother. 2014, 20, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pople, I.K.; Bayston, R.; Hayward, R.D. Infection of Cerebrospinal Fluid Shunts in Infants: A Study of Etiological Factors. J. Neurosurg. 1992, 77, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, H.A.; Baig, F.K.; Mehboob, R. Nosocomial Infections: Epidemiology, Prevention, Control and Surveillance. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2017, 7, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talon, D.; Excoffon, L.; Tiv, M.; Pinçon, A.; Gbaguidi-Haoré, H.; Bertrand, X. Environmental Reservoirs of Meticillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus in Patients’ Rooms: Potential Impact on Care Practices. Br. J. Infect. Control 2008, 9, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, M.R.; Rathish, K.C.; Nagesha, C.N. Reservoirs of Nosocomial Pathogens in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. J. Indian Med. Assoc. 1997, 95, 72–74. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, M.J. Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: Reservoirs of Nosocomial Pathogens. West Afr. J. Med. 2002, 21, 310–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, A.; Schwebke, I.; Kampf, G. How Long Do Nosocomial Pathogens Persist on Inanimate Surfaces? A Systematic Review. BMC Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Mills, D.A.; Underwood, M.A. Surface Microbes in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: Changes with Routine Cleaning and over Time. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2617–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, B.; Firek, B.A.; Miller, C.S.; Sharon, I.; Thomas, B.C.; Baker, R.; Morowitz, M.J.; Banfield, J.F. Microbes in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Resemble Those Found in the Gut of Premature Infants. Microbiome 2014, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellington, M.J.; Ekelund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Canton, R.; Doumith, M.; Giske, C.; Grundman, H.; Hasman, H.; Holden, M.T.G.; Hopkins, K.L.; et al. The Role of Whole Genome Sequencing in Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Bacteria: Report from the EUCAST Subcommittee. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comar, M.; D’Accolti, M.; Cason, C.; Soffritti, I.; Campisciano, G.; Lanzoni, L.; Bisi, M.; Volta, A.; Mazzacane, S.; Caselli, E. Introduction of NGS in Environmental Surveillance for Healthcare-Associated Infection Control. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, W.H.; de Steenhuijsen Piters, W.A.A.; Bogaert, D. The Microbiota of the Respiratory Tract: Gatekeeper to Respiratory Health. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmu, A.A.; Ware, R.S.; Lambert, S.B.; Sarna, M.; Bialasiewicz, S.; Seib, K.L.; Atack, J.M.; Nissen, M.D.; Grimwood, K. Nasal Swab Bacteriology by PCR during the First 24-Months of Life: A Prospective Birth Cohort Study. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2019, 54, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, S.M.; Mok, D.; Pham, K.; Kusel, M.; Serralha, M.; Troy, N.; Holt, B.J.; Hales, B.J.; Walker, M.L.; Hollams, E.; et al. The Infant Nasopharyngeal Microbiome Impacts Severity of Lower Respiratory Infection and Risk of Asthma Development. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogaert, D.; de Groot, R.; Hermans, P. Streptococcus Pneumoniae Colonisation: The Key to Pneumococcal Disease. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2004, 4, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszak, T.; An, D.; Zeissig, S.; Vera, M.P.; Richter, J.; Franke, A.; Glickman, J.N.; Siebert, R.; Baron, R.M.; Kasper, D.L.; et al. Microbial Exposure during Early Life Has Persistent Effects on Natural Killer T Cell Function. Science 2012, 336, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuriel-Ohayon, M.; Neuman, H.; Koren, O. Microbial Changes during Pregnancy, Birth, and Infancy. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, M.A.; Sohn, K. The Microbiota of the Extremely Preterm Infant. Clin. Perinatol. 2017, 44, 407–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, P.; Pasolli, E.; Tett, A.; Asnicar, F.; Gorfer, V.; Fedi, S.; Armanini, F.; Truong, D.T.; Manara, S.; Zolfo, M.; et al. Mother-to-Infant Microbial Transmission from Different Body Sites Shapes the Developing Infant Gut Microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 24, 133–145.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grönlund, M.-M.; Grześkowiak, Ł.; Isolauri, E.; Salminen, S. Influence of Mother’s Intestinal Microbiota on Gut Colonization in the Infant. Gut Microbes 2011, 2, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooven, T.A.; Polin, R.A. Healthcare-Associated Infections in the Hospitalized Neonate: A Review. Early Hum. Dev. 2014, 90, S4–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasethu, J. Prevention and Treatment of Neonatal Nosocomial Infections. Matern. Health Neonatol. Perinatol. 2017, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingg, W.; Hopkins, S.; Gayet-Ageron, A.; Holmes, A.; Sharland, M.; Suetens, C.; Almeida, M.; Asembergiene, J.; Borg, M.A.; Budimir, A.; et al. Health-Care-Associated Infections in Neonates, Children, and Adolescents: An Analysis of Paediatric Data from the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control Point-Prevalence Survey. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericson, J.E.; Popoola, V.O.; Smith, P.B.; Benjamin, D.K.; Fowler, V.G.; Benjamin, D.K.; Clark, R.H.; Milstone, A.M. Burden of Invasive Staphylococcus Aureus Infections in Hospitalized Infants. JAMA Pediatr. 2015, 169, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuffrè, M.; Amodio, E.; Bonura, C.; Geraci, D.M.; Saporito, L.; Ortolano, R.; Corsello, G.; Mammina, C. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Nasal Colonization in a Level III Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: Incidence and Risk Factors. Am. J. Infect. Control 2015, 43, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Glaser, K.; Speer, C.P. New Threats from an Old Foe: Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Infections in Neonates. NEO 2018, 114, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, J.M.; Potter-Bynoe, G.; Chenevert, C.; King, T. Environmental Contamination Due to Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus: Possible Infection Control Implications. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 1997, 18, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagenvoort, J.H.T.; Sluijsmans, W.; Penders, R.J.R. Better Environmental Survival of Outbreak vs. Sporadic MRSA Isolates. J. Hosp. Infect. 2000, 45, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Speer, C.P. The Role of Staphylococcus Epidermidis in Neonatal Sepsis: Guarding Angel or Pathogenic Devil? Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridkin, S.K.; Kaufman, D.; Edwards, J.R.; Shetty, S.; Horan, T. Changing Incidence of Candida Bloodstream Infections Among NICU Patients in the United States: 1995–2004. Pediatrics 2006, 117, 1680–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibovitz, E.; Livshiz-Riven, I.; Borer, A.; Taraboulos-Klein, T.; Zamir, O.; Shany, E.; Melamed, R.; Rimon, O.-F.; Bradenstein, R.; Chodick, G.; et al. A Prospective Study of the Patterns and Dynamics of Colonization with Candida Spp. in Very Low Birth Weight Neonates. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 45, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliaga, S.; Clark, R.H.; Laughon, M.; Walsh, T.J.; Hope, W.W.; Benjamin, D.K.; Kaufman, D.; Arrieta, A.; Benjamin, D.K.; Smith, P.B. Changes in the Incidence of Candidiasis in Neonatal Intensive Care Units. Pediatrics 2014, 133, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoll, B.J.; Hansen, N.; Fanaroff, A.A.; Wright, L.L.; Carlo, W.A.; Ehrenkranz, R.A.; Lemons, J.A.; Donovan, E.F.; Stark, A.R.; Tyson, J.E.; et al. Late-Onset Sepsis in Very Low Birth Weight Neonates: The Experience of the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics 2002, 110, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senn, V.; Bassler, D.; Choudhury, R.; Scholkmann, F.; Righini-Grunder, F.; Vuille-dit-Bile, R.N.; Restin, T. Microbial Colonization from the Fetus to Early Childhood—A Comprehensive Review. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coscia, A.; Bardanzellu, F.; Caboni, E.; Fanos, V.; Peroni, D.G. When a Neonate is Born, So is a Microbiota. Life 2021, 11, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehgal, R.; Gaind, R.; Chellani, H.; Agarwal, P. Extended-Spectrum Beta Lactamase-Producing Gram-Negative Bacteria: Clinical Profile and Outcome in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Ann. Trop. Paediatr. 2007, 27, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folgori, L.; Bernaschi, P.; Piga, S.; Carletti, M.; Cunha, F.P.; Lara, P.H.; De, N.C.P.; Alves, B.G.; Sharland, M.; Araujo, A.d.S.; et al. Healthcare-Associated Infections in Pediatric and Neonatal Intensive Care Units: Impact of Underlying Risk Factors and Antimicrobial Resistance on 30-Day Case-Fatality in Italy and Brazil. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2016, 37, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, Y.; Gupta, A.; Todi, S.; Myatra, S.; Samaddar, D.P.; Patil, V.; Bhattacharya, P.K.; Ramasubban, S. Guidelines for Prevention of Hospital Acquired Infections. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 18, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shane, A.L.; Sánchez, P.J.; Stoll, B.J. Neonatal Sepsis. Lancet 2017, 390, 1770–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.H.; Bloom, B.T.; Spitzer, A.R.; Gerstmann, D.R. Reported Medication Use in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: Data from a Large National Data Set. Pediatrics 2006, 117, 1979–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dancer, S.J. The Role of Environmental Cleaning in the Control of Hospital-Acquired Infection. J. Hosp. Infect. 2009, 73, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carling, P.C.; Parry, M.F.; Von, S.B. Identifying Opportunities to Enhance Environmental Cleaning in 23 Acute Care Hospitals. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2008, 29, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, E.R.; Platt, R.; Bass, R.; Onderdonk, A.B.; Yokoe, D.S.; Huang, S.S. Impact of an Environmental Cleaning Intervention on the Presence of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus and Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci on Surfaces in Intensive Care Unit Rooms. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2008, 29, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, L.J.; Wand, M.E.; Sutton, J.M. Varying Activity of Chlorhexidine-Based Disinfectants against Klebsiella Pneumoniae Clinical Isolates and Adapted Strains. J. Hosp. Infect. 2016, 93, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wand, M.E.; Bock, L.J.; Bonney, L.C.; Sutton, J.M. Mechanisms of Increased Resistance to Chlorhexidine and Cross-Resistance to Colistin Following Exposure of Klebsiella Pneumoniae Clinical Isolates to Chlorhexidine. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahimipour, A.K.; Ben Mamaar, S.; McFarland, A.G.; Blaustein, R.A.; Chen, J.; Glawe, A.J.; Kline, J.; Green, J.L.; Halden, R.U.; Van Den Wymelenberg, K.; et al. Antimicrobial Chemicals Associate with Microbial Function and Antibiotic Resistance Indoors. mSystems 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caselli, E.; D’Accolti, M.; Vandini, A.; Lanzoni, L.; Camerada, M.T.; Coccagna, M.; Branchini, A.; Antonioli, P.; Balboni, P.G.; Luca, D.D.; et al. Impact of a Probiotic-Based Cleaning Intervention on the Microbiota Ecosystem of the Hospital Surfaces: Focus on the Resistome Remodulation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caselli, E.; Brusaferro, S.; Coccagna, M.; Arnoldo, L.; Berloco, F.; Antonioli, P.; Tarricone, R.; Pelissero, G.; Nola, S.; La Fauci, V.; et al. Reducing Healthcare-Associated Infections Incidence by a Probiotic-Based Sanitation System: A Multicentre, Prospective, Intervention Study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundquist, A.; Bigdeli, S.; Jalili, R.; Druzin, M.L.; Waller, S.; Pullen, K.M.; El-Sayed, Y.Y.; Taslimi, M.M.; Batzoglou, S.; Ronaghi, M. Bacterial Flora-Typing with Targeted, Chip-Based Pyrosequencing. BMC Microbiol. 2007, 7, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, Interactive, Scalable and Extensible Microbiome Data Science Using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Accolti, M.; Soffritti, I.; Lanzoni, L.; Bisi, M.; Volta, A.; Mazzacane, S.; Caselli, E. Effective Elimination of Staphylococcal Contamination from Hospital Surfaces by a Bacteriophage-Probiotic Sanitation Strategy: A Monocentric Study. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandini, A.; Temmerman, R.; Frabetti, A.; Caselli, E.; Antonioli, P.; Balboni, P.G.; Platano, D.; Branchini, A.; Mazzacane, S. Hard Surface Biocontrol in Hospitals Using Microbial-Based Cleaning Products. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R. UniFrac—An Online Tool for Comparing Microbial Community Diversity in a Phylogenetic Context. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Main Bacterial Genera of DR | N0 Colonized Patients (%) | Main Bacterial Genera of NICU | N9 Colonized Patients (%) | N13 Colonized Patients (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus spp. | 53% | Staphylococcus spp. | 94% | 100% |
| Streptococcus spp. | 53% | Streptococcus spp. | 61% | 71% |
| Cutibacterium spp. | 83% | Cutibacterium spp. | 33% | 14% |
| Corynebacterium spp. | 40% | Corynebacterium spp. | 56% | 57% |
| Escherichia-Shigella spp. | 33% | Escherichia-Shigella spp. | 61% | 100% |
| Acinetobacter spp. | 67% | Acinetobacter spp. | 33% | 14% |
| Pseudomonas spp. | 67% | Pseudomonas spp. | 33% | 14% |
| Stenotrophomonas spp. | 23% | Stenotrophomonas spp. | 22% | 14% |
| Rothia spp. | 17% | Rothia spp. | 17% | 19% |
| Lactobacillus spp. | 20% | Lactobacillus spp. | 6% | 14% |
| Chryseobacterium spp. | 3% | Chryseobacterium spp. | 6% | / |
| Paracoccus spp. | 10% | Paracoccus spp. | / | / |
| Actinomyces spp. | 10% | Enterobacter spp. | 22% | 29% |
| Gemella spp. | 10% | Bifidobacterium spp. | / | / |
| Bacillus spp. | 7% | Alishewanella spp. | / | / |
| Neisseria spp. | 7% | Brevundimonas spp. | / | / |
| Facklamia spp. | 3% | Gemmobacter spp. | / | / |
| Empedobacter spp. | / | Empedobacter spp. | / | / |
| Anaerococcus spp. | / |
| R Genes | N0 Group | N9 Group | N13 Group |
|---|---|---|---|
| AAC(6)-lb-cr | − | + | − |
| SHV group | − | + | + |
| ACT 5/7 group | − | + | + |
| CMY-10 group | − | − | + |
| LAT | − | − | + |
| MOX | − | − | + |
| OXA-50 group | − | + | + |
| QnrS | − | − | + |
| ermB | − | − | + |
| ermC | − | + | + |
| mefA | − | − | + |
| msrA | − | + | + |
| oprj | − | + | + |
| oprm | − | + | + |
| tetA | − | − | + |
| vanC | − | − | + |
| mecA/spa | − | + | + |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cason, C.; D’Accolti, M.; Campisciano, G.; Soffritti, I.; Ponis, G.; Mazzacane, S.; Maggiore, A.; Risso, F.M.; Comar, M.; Caselli, E. Microbial Contamination in Hospital Environment Has the Potential to Colonize Preterm Newborns’ Nasal Cavities. Pathogens 2021, 10, 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050615
Cason C, D’Accolti M, Campisciano G, Soffritti I, Ponis G, Mazzacane S, Maggiore A, Risso FM, Comar M, Caselli E. Microbial Contamination in Hospital Environment Has the Potential to Colonize Preterm Newborns’ Nasal Cavities. Pathogens. 2021; 10(5):615. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050615
Chicago/Turabian StyleCason, Carolina, Maria D’Accolti, Giuseppina Campisciano, Irene Soffritti, Giuliano Ponis, Sante Mazzacane, Adele Maggiore, Francesco Maria Risso, Manola Comar, and Elisabetta Caselli. 2021. "Microbial Contamination in Hospital Environment Has the Potential to Colonize Preterm Newborns’ Nasal Cavities" Pathogens 10, no. 5: 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050615
APA StyleCason, C., D’Accolti, M., Campisciano, G., Soffritti, I., Ponis, G., Mazzacane, S., Maggiore, A., Risso, F. M., Comar, M., & Caselli, E. (2021). Microbial Contamination in Hospital Environment Has the Potential to Colonize Preterm Newborns’ Nasal Cavities. Pathogens, 10(5), 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050615







