Oropharyngeal Carriage of hpl-Containing Haemophilus haemolyticus Predicts Lower Prevalence and Density of NTHi Colonisation in Healthy Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Carriage Profile of NTHi and Hh Varied between Participant Age Groups
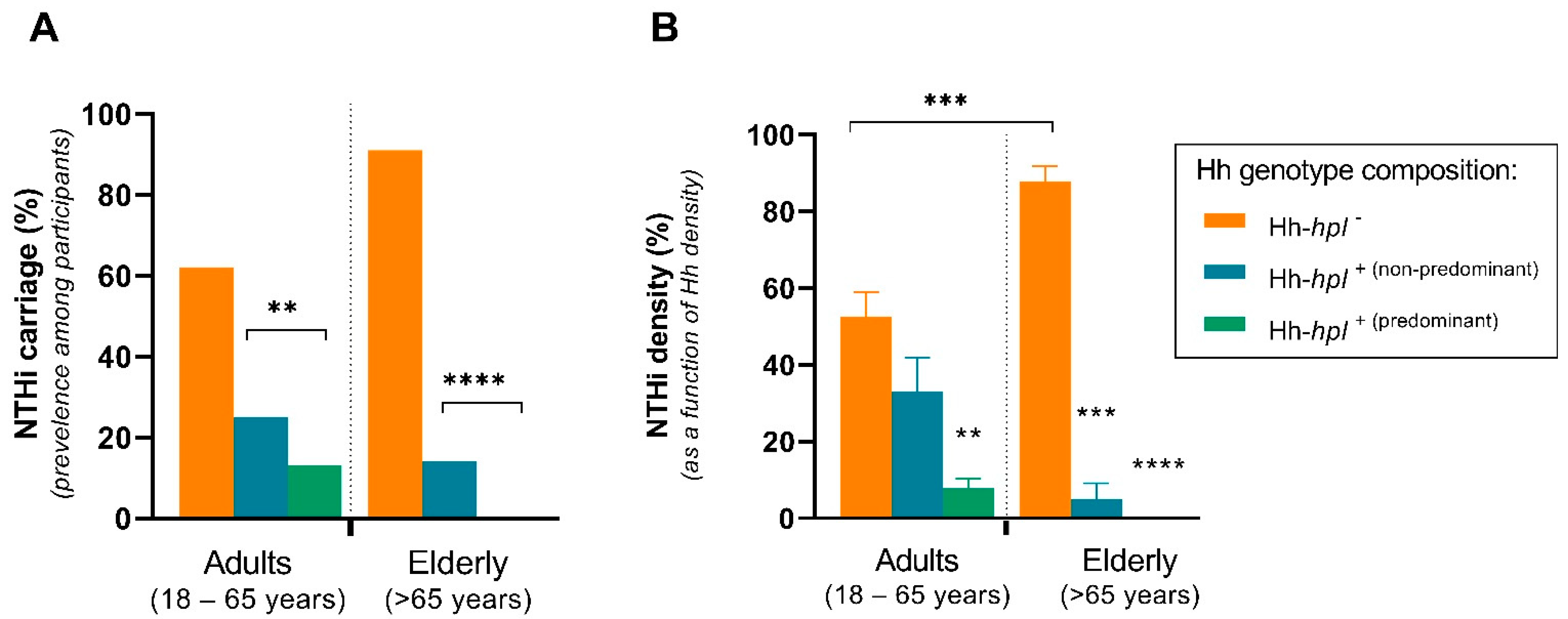
2.2. Carriage of hpl-Positive Hh Is Correlated with Reduced Prevalence and Density of NTHi Cocolonisation
2.3. Carriage of hpl-Positive Hh Prevents Persistent Colonisation or Acquisition of NTHi Carriage Status
2.4. Potential Therapeutic Utility of hpl-Positive Strains of Hh
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Oropharyngeal Swab Collection
3.3. Real-Time PCR Quantification of NTHi, Hh, and Hh-hpl+
3.4. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zanella, R.C.; Brandileone, M.C.d.C.; Almeida, S.C.G.; de Lemos, A.P.S.; Sacchi, C.T.; Gonçalves, C.R.; Gonçalves, M.G.; Fukasawa, L.O.; Saraiva, M.D.; Rangel, L.F. Nasopharyngeal carriage of Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Staphylococcus aureus in a Brazilian elderly cohort. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slack, M.P. A review of the role of Haemophilus influenzae in community-acquired pneumonia. Pneumonia 2015, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerquetti, M.; Giufrè, M. Why we need a vaccine for non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2016, 12, 2357–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Eldere, J.; Slack, M.P.; Ladhani, S.; Cripps, A.W. Non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae, an under-recognised pathogen. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 1281–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, G.A.; Leach, A.J.; Carapetis, J.R.; Fisher, J.; Morris, P.S. Epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carriage of respiratory bacterial pathogens in children and adults: Cross-sectional surveys in a population with high rates of pneumococcal disease. BMC Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukundan, D.; Ecevit, Z.; Patel, M.; Marrs, C.F.; Gilsdorf, J.R. Pharyngeal colonization dynamics of Haemophilus influenzae and haemophilus haemolyticus in healthy adult carriers. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, C.; Marti, S.; Fleites, A.; Trabazo, R.; Calatayud, L.; Linares, J.; Ardanuy, C. Oropharyngeal colonization by nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae among healthy children attending day care centers. Microb. Drug Resist. 2014, 20, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kempen, M.; Dhooge, I.; Vaneechoutte, M.; Claeys, G. Turnover of Haemophilus influenzae isolates in otitis-prone children. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Belg. 2001, 55, 83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaur, R.; Chang, A.; Xu, Q.; Casey, J.R.; Pichichero, M.E. Phylogenetic relatedness and diversity of non-typable Haemophilus influenzae in the nasopharynx and middle ear fluid of children with acute otitis media. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Harabuchi, Y.; Faden, H.; Yamanaka, N.; Duffy, L.; Wolf, J.; Krystofik, D.; Pediatrics, T.W. Nasopharyngeal colonization with nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae and recurrent otitis media. J. Infect. Dis. 1994, 170, 862–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kirkham, L.-A.S.; Wiertsema, S.P.; Mowe, E.N.; Bowman, J.M.; Riley, T.V.; Richmond, P.C. Nasopharyngeal carriage of Haemophilus haemolyticus in otitis-prone and healthy children. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 2557–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sethi, S.; Evans, N.; Grant, B.J.; Murphy, T.F. New strains of bacteria and exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith-Vaughan, H.; Byun, R.; Nadkarni, M.; Jacques, N.A.; Hunter, N.; Halpin, S.; Morris, P.S.; Leach, A.J. Measuring nasal bacterial load and its association with otitis media. BMC Ear Nose Throat Disord. 2006, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Vaughan, H.C.; Binks, M.J.; Marsh, R.L.; Kaestli, M.; Ward, L.; Hare, K.M.; Pizzutto, S.J.; Thornton, R.B.; Morris, P.S.; Leach, A.J. Dominance of Haemophilus influenzae in ear discharge from Indigenous Australian children with acute otitis media with tympanic membrane perforation. BMC Ear Nose Throat Disord. 2013, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettigrew, M.M.; Laufer, A.S.; Gent, J.F.; Kong, Y.; Fennie, K.P.; Metlay, J.P. Upper respiratory tract microbial communities, acute otitis media pathogens, and antibiotic use in healthy and sick children. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 6262–6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witherden, E.A.; Tristram, S.G. Prevalence and mechanisms of β-lactam resistance in Haemophilus haemolyticus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1049–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Hotomi, M.; Maruyama, Y.; Hatano, M.; Sugimoto, H.; Yoshizaki, T.; Yamanaka, N. Clonal spread of β-lactamase-producing amoxicillin–clavulanate-resistant (BLPACR) strains of non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae among young children attending a day care in Japan. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2010, 74, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabernat, H.; Delmas, C. Epidemiology and evolution of antibiotic resistance of Haemophilus influenzae in children 5 years of age or less in France, 2001–2008: A retrospective database analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 31, 2745–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hare, K.M.; Leach, A.J.; Morris, P.S.; Smith-Vaughan, H.; Torzillo, P.; Bauert, P.; Cheng, A.C.; McDonald, M.; Brown, N.; Chang, A.B. Impact of recent antibiotics on nasopharyngeal carriage and lower airway infection in Indigenous Australian children with non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2012, 40, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, C.; Tristram, S. Antimicrobial resistance in cystic fibrosis isolates of Haemophilus influenzae. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 73, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, S.E. Commensal bacteria in the upper respiratory tract regulate susceptibility to infection. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2020, 66, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latham, R.D.; Gell, D.A.; Fairbairn, R.L.; Lyons, A.B.; Shukla, S.D.; Cho, K.Y.; Jones, D.A.; Harkness, N.M.; Tristram, S.G. An isolate of Haemophilus haemolyticus produces a bacteriocin-like substance that inhibits the growth of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 49, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atto, B.; Latham, R.; Kunde, D.; Gell, D.A.; Tristram, S. In vitro anti-NTHi activity of haemophilin-producing strains of Haemophilus haemolyticus. Pathogens 2020, 9, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atto, B.; Kunde, D.; Gell, D.A.; Tristram, S. Haemophilin-Producing Strains of Haemophilus haemolyticus Protect Respiratory Epithelia from NTHi Colonisation and Internalisation. Pathogens 2021, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xie, J.; Patel, M.; Bakhtyar, A.; Ehrlich, G.D.; Ahmed, A.; Earl, J.; Marrs, C.F.; Clemans, D.; Murphy, T.F. Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae genetic islands associated with chronic pulmonary infection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shak, J.R.; Cremers, A.J.; Gritzfeld, J.F.; de Jonge, M.I.; Hermans, P.W.; Vidal, J.E.; Klugman, K.P.; Gordon, S.B. Impact of experimental human pneumococcal carriage on nasopharyngeal bacterial densities in healthy adults. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, D.; Broides, A.; Blancovich, I.; Peled, N.; Givon-Lavi, N.; Dagan, R. Relative importance of nasopharyngeal versus oropharyngeal sampling for isolation of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae from healthy and sick individuals varies with age. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 4604–4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rawlings, B.A.; Higgins, T.S.; Han, J.K. Bacterial pathogens in the nasopharynx, nasal cavity, and osteomeatal complex during wellness and viral infection. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2013, 27, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, D.H.; Hendley, J.O.; French, P.; Arango, P.; Hayden, F.G.; Winther, B. Nasopharyngeal reservoir of bacterial otitis media and sinusitis pathogens in adults during wellness and viral respiratory illness. Am. J. Rhinol. 2003, 17, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullahi, O.; Nyiro, J.; Lewa, P.; Slack, M.; Scott, J.A.G. The descriptive epidemiology of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae nasopharyngeal carriage in children and adults in Kilifi district, Kenya. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2008, 27, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanya, S.H.; Thapa, S.; Dwedi, S.K.; Gokhale, S.; Sathian, B.; Nayak, N.; Bairy, I. Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus species colonization in health care workers: The launch of invasive infections? BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegbola, R.A.; DeAntonio, R.; Hill, P.C.; Roca, A.; Usuf, E.; Hoet, B.; Greenwood, B.M. Carriage of Streptococcus pneumoniae and other respiratory bacterial pathogens in low and lower-middle income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blain, A.; MacNeil, J.; Wang, X.; Bennett, N.; Farley, M.M.; Harrison, L.H.; Lexau, C.; Miller, L.; Nichols, M.; Petit, S. Invasive Haemophilus influenzae disease in adults ≥65 years, United States, 2011. OFID 2014, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drayß, M.; Claus, H.; Hubert, K.; Thiel, K.; Berger, A.; Sing, A.; van der Linden, M.; Vogel, U.; Lâm, T.-T. Asymptomatic carriage of Neisseria meningitidis, Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Group A Streptococcus and Staphylococcus aureus among adults aged 65 years and older. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, E.P.; Harris, T.M.; Spargo, J.; Nosworthy, E.; Beissbarth, J.; Chang, A.B.; Smith-Vaughan, H.C.; Sarovich, D.S. Simultaneous identification of Haemophilus influenzae and Haemophilus haemolyticus using real-time PCR. Future Microbiol. 2017, 12, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Zhang, J.; Peng, A. The pharyngeal carriage of Haemophilus influenzae among healthy population in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabernat, H.; Plisson-Sauné, M.-A.; Delmas, C.; Séguy, M.; Faucon, G.; Pélissier, R.; Carsenti, H.; Pradier, C.; Roussel-Delvallez, M.; Leroy, J. Haemophilus influenzae carriage in children attending French day care centers: A molecular epidemiological study. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 1664–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hare, K.M.; Binks, M.J.; Grimwood, K.; Chang, A.B.; Leach, A.J.; Smith-Vaughan, H. Culture and PCR detection of Haemophilus influenzae and Haemophilus haemolyticus in Australian Indigenous children with bronchiectasis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2444–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, J.; Richmond, P.C.; Kirkham, L.-A.S. Molecular tools for differentiation of non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae from Haemophilus haemolyticus. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, D.; Shleyfer, E.; Castel, H.; Terry, A.; Harman-Boehm, I.; Delgado, J.; Peled, N.; Lieberman, D. Nasopharyngeal versus oropharyngeal sampling for isolation of potential respiratory pathogens in adults. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zuo, X.; Pan, H.; Gu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, S.; Zheng, R.; Liu, Z. The role of NTHi colonization and infection in the pathogenesis of neutrophilic asthma. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, J.; Smith-Vaughan, H.; Beissbarth, J.; Bowman, J.; Wiertsema, S.; Riley, T.; Leach, A.J.; Richmond, P.; Lehmann, D.; Kirkham, L.-A. Diversity of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae strains colonizing Australian Aboriginal and non-Aboriginal children. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1352–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voss, M.; Wonnenberg, B.; Honecker, A.; Kamyschnikow, A.; Herr, C.; Bischoff, M.; Tschernig, T.; Bals, R.; Beisswenger, C. Cigarette smoke-promoted acquisition of bacterial pathogens in the upper respiratory tract leads to enhanced inflammation in mice. Respir. Res. 2015, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atto, B.; Eapen, M.S.; Sharma, P.; Frey, U.; Ammit, A.J.; Markos, J.; Chia, C.; Larby, J.; Haug, G.; Weber, H.C. New therapeutic targets for the prevention of infectious acute exacerbations of COPD: Role of epithelial adhesion molecules and inflammatory pathways. Clin. Sci. 2019, 133, 1663–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, S.; Wrona, C.; Grant, B.J.; Murphy, T.F. Strain-specific immune response to Haemophilus influenzae in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 169, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granland, C.M.; Scott, N.M.; Lauzon-Joset, J.-F.; Langereis, J.D.; De Gier, C.; Sutherland, K.M.; Clark, S.L.; Pickering, J.L.; Thornton, R.B.; Richmond, P.C. Nasal delivery of a commensal Pasteurellaceae species inhibits nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae colonization and delays onset of otitis media in mice. Infect. Immun. 2020, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Boeck, I.; van den Broek, M.F.; Allonsius, C.N.; Spacova, I.; Wittouck, S.; Martens, K.; Wuyts, S.; Cauwenberghs, E.; Jokicevic, K.; Vandenheuvel, D. Lactobacilli have a niche in the human nose. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hols, P.; Ledesma-García, L.; Gabant, P.; Mignolet, J. Mobilization of microbiota commensals and their bacteriocins for therapeutics. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaijalainen, T.; Ruokokoski, E.; Ukkonen, P.; Herva, E. Survival of Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis frozen in skim milk-tryptone-glucose-glycerol medium. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 412–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hare, K.M.; Smith-Vaughan, H.C.; Beissbarth, J.; Leach, A.J. Haemophilus influenzae isolates survive for up to 20 years at −70 °C in skim milk tryptone glucose glycerol broth (STGGB) if thawing is avoided during re-culture. J. Microbiol. Methods 2015, 119, 132–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| NTHi Colonisation at Visit 1 -> Visit 2 Frequency (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hh Genotype | NTHi+ | NTHi− (Colonisation Loss) | NTHi− | NTHi− (Never Colonised) | NTHi+ | NTHi+ (Consistently Colonised) | NTHi− | NTHi+ (Colonisation Gain) |
| Total | 8/50 (16) | 26/50 (52) | 4/50 (8) | 12/50 (24) |
| hpl+ | 7/8 (88) | 23/26 (88) | 2/4 (50) | 2/12 (17) |
| hpl− | 1/8 (12) | 3/26 (12) | 2/4 (50) | 10/12 (83) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Atto, B.; Kunde, D.; Gell, D.A.; Tristram, S. Oropharyngeal Carriage of hpl-Containing Haemophilus haemolyticus Predicts Lower Prevalence and Density of NTHi Colonisation in Healthy Adults. Pathogens 2021, 10, 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050577
Atto B, Kunde D, Gell DA, Tristram S. Oropharyngeal Carriage of hpl-Containing Haemophilus haemolyticus Predicts Lower Prevalence and Density of NTHi Colonisation in Healthy Adults. Pathogens. 2021; 10(5):577. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050577
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtto, Brianna, Dale Kunde, David A. Gell, and Stephen Tristram. 2021. "Oropharyngeal Carriage of hpl-Containing Haemophilus haemolyticus Predicts Lower Prevalence and Density of NTHi Colonisation in Healthy Adults" Pathogens 10, no. 5: 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050577
APA StyleAtto, B., Kunde, D., Gell, D. A., & Tristram, S. (2021). Oropharyngeal Carriage of hpl-Containing Haemophilus haemolyticus Predicts Lower Prevalence and Density of NTHi Colonisation in Healthy Adults. Pathogens, 10(5), 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050577







