Use of Recombinant Escherichia coli Strains in Immunofluorescence Assays for Melioidosis Diagnosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
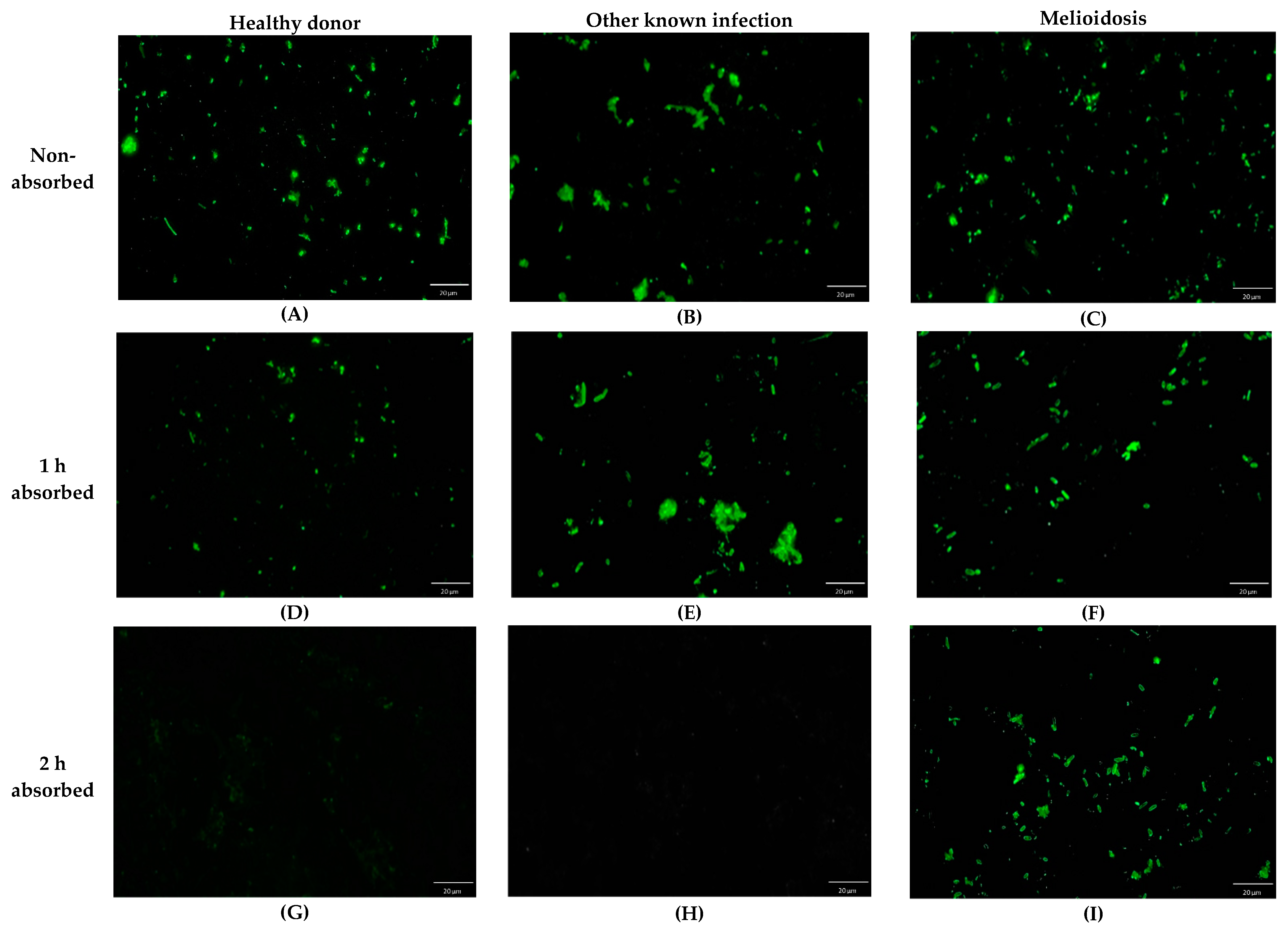
2.1. Effect of Serum Preabsorbed Step
2.2. Cutoff Value of Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay
2.3. Method Performances
2.4. The Method Agreement
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids, and Culture Conditions
4.2. Human Serum Samples and Preparation
4.3. Preparation of the Whole-Cell Antigens from the Recombinant E. coli for IFA
4.4. Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA)
4.5. Indirect Hemagglutination Assay (IHA)
4.6. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leelarasamee, A.; Bovornkitti, S. Melioidosis: Review and update. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1989, 11, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, B.J.; Fisher, D.A.; Howard, D.M.; Burrow, J.N.C.; Lo, D.; Selva-Nayagam, S.; Anstey, N.M.; Huffam, S.E.; Snelling, P.L.; Marks, P.J.; et al. Endemic Melioidosis in Tropical Northern Australia: A 10-Year Prospective Study and Review of the Literature. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 31, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currie, B.J.; Fisher, D.A.; Howard, D.M.; Burrow, J.N.; Selvanayagam, S.; Snelling, P.L.; Anstey, N.M.; Mayo, M.J. The epidemiology of melioidosis in Australia and Papua New Guinea. Acta Trop. 2000, 74, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.N.; Bryant, J.E.; Madsen, E.L.; Ghiorse, W.C. Evaluation and Optimization of DNA Extraction and Purification Procedures for Soil and Sediment Samples. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 4715–4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.C.; Currie, B.J. Melioidosis: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management. Clin. Microbiol Rev. 2005, 18, 383–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limmathurotsakul, D.; Wongratanacheewin, S.; Day, N.P.; Teerawattanasook, N.; Chaowagul, W.; Chaisuksant, S.; Chetchotisakd, P.; Peacock, S.J.; Wongsuvan, G. Increasing Incidence of Human Melioidosis in Northeast Thailand. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 82, 1113–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schully, K.L.; Young, C.C.; Mayo, M.; Connolly, A.L.; Rigas, V.; Spall, A.; Chan, A.; Salvador, M.G.; Lawler, J.V.; Opdyke, J.A.; et al. Next-generation Diagnostics for Melioidosis: Evaluation of a Prototype i-STAT Cartridge to Detect Burkholderia pseudomallei Biomarkers. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, M.C.; Rattanavong, S.; Bouthasavong, L.; Seubsanith, A.; Vongsouvath, M.; Davong, V.; De Silvestri, A.; Manciulli, T.; Newton, P.N.; Dance, D.A.B. Evaluation of the Active Melioidosis Detect™ test as a point-of-care tool for the early diagnosis of melioidosis: A comparison with culture in Laos. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 113, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, G.E.; Föderl-Höbenreich, E.; Assig, K.; Lipp, M.; Berner, A.; Kohler, C.; Lichtenegger, S.; Stiehler, J.; Karoonboonyanan, W.; Thanapattarapairoj, N.; et al. Melioidosis DS rapid test: A standardized serological dipstick assay with increased sensitivity and reliability due to multiplex detection. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pumpuang, A.; Phunpang, R.; Ekchariyawat, P.; Dulsuk, A.; Loupha, S.; Kwawong, K.; Charoensawat, Y.; Thiansukhon, E.; Day, N.P.J.; Burtnick, M.N.; et al. Distinct classes and subclasses of antibodies to hemolysin co-regulated protein 1 and O-polysaccharide and correlation with clinical characteristics of melioidosis patients. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phokrai, P.; Karoonboonyanan, W.; Thanapattarapairoj, N.; Promkong, C.; Dulsuk, A.; Koosakulnirand, S.; Canovali, S.; Indrawattana, N.; Jutrakul, Y.; Wuthiekanun, V.; et al. A rapid immunochromatography test based on Hcp1 is a potential Point-of-Care test for serological diagnosis of melioidosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00346-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashdown, L.R.; Johnson, R.W.; Koehler, J.M.; Cooney, C.A. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the diagnosis of clinical and subclinical melioidosis. J. Infect. Dis. 1989, 160, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttisunhakul, V.; Wuthiekanun, V.; Brett, P.J.; Khusmith, S.; Day, N.P.J.; Burtnick, M.N.; Limmathurotsakul, D.; Chantratita, N. Development of rapid Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays for detection of antibodies to Burkholderia pseudomallei. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumpuang, A.; Dunachie, S.J.; Phokrai, P.; Jenjaroen, K.; Sintiprungrat, K.; Boonsilp, S.; Brett, P.J.; Burtnick, M.N.; Chantratita, N. Comparison of O-polysaccharide and hemolysin co-regulated protein as target antigens for serodiagnosis of melioidosis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.N.A.; Williams, N.L.; Morris, J.L.; Ketheesan, N.; Norton, R.E. Evidence of Burkholderia pseudomallei-specific immunity in patient sera persistently nonreactive by the indirect hemagglutination assay. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 1288–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.N.A.; Ketheesan, N.; Owens, L.; Norton, R.E. Clinical features that affect indirect-hemagglutination-assay responses to Burkholderia pseudomallei. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2009, 16, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadivelu, J.; Puthucheary, S.D. Diagnostic and prognostic value of an immunofluorescent assay for melioidosis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2000, 62, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kohler, C.; Dunachie, S.J.; Müller, E.; Kohler, A.; Jenjaroen, K.; Teparrukkul, P.; Baier, V.; Ehricht, R.; Steinmetz, I. Rapid and Sensitive Multiplex Detection of Burkholderia pseudomallei-Specific Antibodies in Melioidosis Patients Based on a Protein Microarray Approach. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarovich, D.S.; Price, E.P.; Webb, J.R.; Ward, L.M.; Voutsinos, M.Y.; Tuanyok, A.; Mayo, M.; Kaestli, M.; Currie, B.J. Variable virulence factors in Burkholderia pseudomallei (melioidosis) associated with human disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Thavaselvam, D.; Kumar, A.; Prakash, A.; Barua, A.; Sathyaseelan, K. Cloning, expression and purification of outer membrane protein (OmpA) of Burkholderia pseudomallei and evaluation of its potential for serodiagnosis of melioidosis. Diagn Microbiol Infect. Dis. 2015, 81, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, Y.; Mohamed, R.; Nathan, S. Immunogenic Burkholderia pseudomallei outer membrane proteins as potential candidate Vaccine targets. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.S.; Chen, Y.; Lim, Y.-C.; Tan, G.-Y.G.; Liu, Y.; Lim, Y.-T.; Macary, P.; Gan, Y.-H. Suppression of host innate immune response by Burkholderia pseudomallei through the virulence factor TssM. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 5160–5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wong, J.; Sun, G.W.; Liu, Y.; Tan, G.-Y.G.; Gan, Y.-H. Regulation of type VI secretion system during Burkholderia pseudomallei infection. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 3064–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kylilis, N.; Riangrungroj, P.; Lai, H.-E.; Salema, V.; Fernández, L.Á.; Stan, G.-B.V.; Freemont, P.S.; Polizzi, K.M. Whole-cell biosensor with tunable limit of detection enables low-cost agglutination assays for medical diagnostic applications. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaichana, P.; Jenjaroen, K.; Amornchai, P.; Chumseng, S.; Langla, S.; Rongkard, P.; Sumonwiriya, M.; Jeeyapant, A.; Chantratita, N.; Teparrukkul, P.; et al. Antibodies in Melioidosis: The Role of the Indirect Hemagglutination Assay in Evaluating Patients and Exposed Populations. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 99, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, Y.; Chin, C.-Y.; Mohamed, R.; Puthucheary, S.D.; Nathan, S. Multiple-antigen ELISA for melioidosis-a novel approach to the improved serodiagnosis of melioidosis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongprompitak, P.; Thepthai, C.; Songsivilai, S.; Dharakul, T. Burkholderia pseudomallei-specific recombinant protein and its potential in the diagnosis of melioidosis. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2001, 19, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mathai, E.; Jesudason, M.V.; Anbarasu, A. Indirect immunofluorescent antibody test for the rapid diagnosis of melioidosis. Indian J. Med. Res. 2003, 118, 68–70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khupulsup, K.; Petchclai, B. Application of indirect hemagglutination test and indirect fluorescent antibody test for IgM antibody for diagnosis of melioidosis in Thailand. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1986, 35, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puthucheary, S. Melioidosis in Malaysia. Med. J. Malaysia. 2009, 64, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sangwichian, O.; Whistler, T.; Nithichanon, A.; Kewcharoenwong, C.; Sein, M.M.; Arayanuphum, C.; Chantratita, N.; Lertmemongkolchai, G. Adapting microarray gene expression signatures for early melioidosis diagnosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e01906-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testamenti, V.A.; Noviana, R.; Iskandriati, D.; Norris, M.H.; Jiranantasak, T.; Tuanyok, A.; Wahyudi, A.T.; Sajuthi, D.; Pamungkas, J. Humoral immune responses to Burkholderia pseudomallei antigens in captive and wild macaques in the western part of Java, Indonesia. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuthiekanun, V.; Desakorn, V.; Wongsuvan, G.; Amornchai, P.; Cheng, A.C.; Maharjan, B.; Limmathurotsakul, D.; Chierakul, W.; White, N.J.; Day, N.P.J.; et al. Rapid immunofluorescence microscopy for diagnosis of melioidosis. Clin. Diagn Lab. Immunol. 2005, 12, 555–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadivelu, J.; Puthucheary, S.D.; Gendeh, G.S.; Parasakthi, N. Serodiagnosis of melioidosis in Malaysia. Singap. Med. J. 1995, 36, 299–302. [Google Scholar]
- Tandhavanant, S.; Wongsuvan, G.; Wuthiekanun, V.; Teerawattanasook, N.; Day, N.P.J.; Limmathurotsakul, D.; Peacock, S.J.; Chantratita, N. Monoclonal antibody-based immunofluorescence microscopy for the rapid identification of Burkholderia pseudomallei in clinical specimens. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bundo, K.; Igarashi, A. Antibody-capture ELISA for detection of immunoglobulin M antibodies in sera from Japanese encephalitis and dengue hemorrhagic fever patients. J. Virol Methods 1985, 11, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Titer | Area Under Curve (AUC) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TssM | OmpH | AhpC | BimA | Hcp1 | |
| ≤1:8 | 0.958 | 0.918 | 0.908 | 0.895 | 0.804 |
| 1:16 | 0.963 | 0.942 | 0.929 | 0.910 | 0.811 |
| 1:32 | 0.963 | 0.942 | 0.929 | 0.910 | 0.811 |
| ≥1:64 | 0.963 | 0.942 | 0.929 | 0.910 | 0.811 |
| Serum Samples | Total No. | Number of Sample Positive with Antibody Titer | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TssM | OmpH | AhpC | BimA | Hcp1 | |||||||||||||||||
| 1:8 | 1:16 | 1:32 | 1:64 | 1:8 | 1:16 | 1:32 | 1:64 | 1:8 | 1:16 | 1:32 | 1:64 | 1:8 | 1:16 | 1:32 | 1:64 | 1:8 | 1:16 | 1:32 | 1:64 | ||
| Culture-confirmed melioidosis patients | 81 | 75 | 75 | 65 | 38 | 72 | 72 | 42 | 17 | 70 | 69 | 38 | 7 | 67 | 64 | 28 | 6 | 51 | 50 | 20 | 3 |
| Other known infections: | 70 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Pseudomonas spp. | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Staphylococcus spp. | 10 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Streptococcus spp. | 20 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Escherichia coli | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Bacillus spp. | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Klebsiella spp. | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Acinetobacter spp. | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Proteus spp. | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Salmonella spp. | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Hepatitis B virus (HBV) | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Human Immunodeficiency virus (HIV) | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Healthy donors | 120 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Serum Samples | Total No. | Antibody Titer by IHA Assay | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤1:10 | 1:20 | 1:40 | 1:80 | 1:160 | 1:320 | 1:640 | 1:1280 | 1:2560 | ≥1:5120 | ||
| Culture-confirmed melioidosis patients | 81 | 39 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 8 | 11 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Other known infections: | 70 | 67 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Pseudomonas spp. | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Staphylococcus spp. | 10 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Streptococcus spp. | 20 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Escherichia coli | 8 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Bacillus spp. | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Klebsiella spp. | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Acinetobacter spp. | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Proteus spp. | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Salmonella spp. | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Hepatitis B virus (HBV) | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Human Immunodeficiency virus (HIV) | 11 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Healthy donors | 120 | 117 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Performances | IFA (Cut-Off ≥ 1:16) | IHA (Cut-Off ≥ 1:160) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TssM | OmpH | AhpC | BimA | Hcp1 | ||
| Sensitivity (%) | 92.6 | 88.9 | 85.2 | 79.0 | 61.7 | 37.0 |
| Specificity (%) | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 99.5 |
| PPV (%) | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 69.77 |
| NPV (%) | 96.9 | 95.0 | 94.1 | 91.9 | 86.0 | 78.8 |
| Efficiency (%) | 97.8 | 96.7 | 95.5 | 93.7 | 88.6 | 80.8 |
| Accuracy (%) | 97.0 | 96.0 | 95.0 | 93.0 | 88.0 | 80.0 |
| Cross-reactivity (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.4 |
| Kappa coefficient (k) | 0.95 | 0.91 | 0.88 | 0.84 | 0.80 | 0.41 |
| Standard Culture Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | ||
| Alternative Method (IFA or IHA) | Positive | a (True positive) | b (False positive) |
| Negative | c (False negative) | d (True negative) | |
| Kappa Value (k) | Strange of Agreement |
|---|---|
| <0.00 | Poor |
| 0.00–0.20 | Slight |
| 0.21–0.40 | Fair |
| 0.41–0.60 | Moderate |
| 0.61–0.80 | Substantial |
| 0.81–1.00 | Almost Perfect |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lantong, K.; Songsri, J.; Wisessombat, S.; Mala, W.; Prommachote, W.; Senghoi, W.; Kotepui, M.; Kaewrakmuk, J.; Jiranantasak, T.; Tuanyok, A.; et al. Use of Recombinant Escherichia coli Strains in Immunofluorescence Assays for Melioidosis Diagnosis. Pathogens 2021, 10, 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050559
Lantong K, Songsri J, Wisessombat S, Mala W, Prommachote W, Senghoi W, Kotepui M, Kaewrakmuk J, Jiranantasak T, Tuanyok A, et al. Use of Recombinant Escherichia coli Strains in Immunofluorescence Assays for Melioidosis Diagnosis. Pathogens. 2021; 10(5):559. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050559
Chicago/Turabian StyleLantong, Kanoknart, Jirarat Songsri, Sueptrakool Wisessombat, Wanida Mala, Warinda Prommachote, Wilaiwan Senghoi, Manas Kotepui, Jedsada Kaewrakmuk, Treenate Jiranantasak, Apichai Tuanyok, and et al. 2021. "Use of Recombinant Escherichia coli Strains in Immunofluorescence Assays for Melioidosis Diagnosis" Pathogens 10, no. 5: 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050559
APA StyleLantong, K., Songsri, J., Wisessombat, S., Mala, W., Prommachote, W., Senghoi, W., Kotepui, M., Kaewrakmuk, J., Jiranantasak, T., Tuanyok, A., & Klangbud, W. K. (2021). Use of Recombinant Escherichia coli Strains in Immunofluorescence Assays for Melioidosis Diagnosis. Pathogens, 10(5), 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050559








