Abstract
Toxoplasma gondii belongs to the Apicomplexan protozoa—an obligate intracellular parasite—causing toxoplasmosis that has a worldwide distribution and is very harmful to both human health and the livestock industry. However, the information on toxoplasmosis in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau Area (QTPA) and the seroprevalence of T. gondii in the food-borne animals in that area has been limited. Therefore, this study focused to T. gondii and toxoplasmosis to perform an indirect ELISA test based on recombinant TgSAG2 protein to establish a comprehensive record of the seroprevalence of T. gondii infections in a wide range of animals, including Tibetan sheep (Ovis aries), yaks (Bos grunniens), cows, chicken, pigs, and horses, in the QTPA. Overall, the seropositive rates of the specific-T. gondii IgG and IgM antibodies in all investigated animals were 44.1% (1179/2673) and 18.0% (469/2612), respectively. The 14.9% (389/2612) sera were determined to be both IgG and IgM positive samples, 30.2% (789/2673) were single-IgG seropositive, and a total of 80 in 2612 animals (3.0%) were single-IgM seropositive. Moreover, for the animal species, the pig was the most prevalent animal (90.2%, 304/337) for IgG positivity, followed by Tibetan sheep (50.7%, 460/907), chickens (45.8%, 229/500), yaks (21.1%, 140/663), cows (18.5%, 38/205) and horses (13.1%, 8/61), respectively. For the IgM antibody positivity, the pig was also the most prevalent animal (41.8%, 141/337), followed by Tibetan sheep (21.2%, 191/907), cows (15.1%, 31/205), chickens (12.4%, 62/500) and yaks (6.6%, 44/663), respectively. The significant differences in the prevalent distribution of T. gondii were found in the different altitudes. In conclusion, this study found the high seroprevalence for T. gondii infections among these animal species in the QTPA, and provides new data to facilitate further research for development of control measures against T. gondii infections in the surveyed locations.
1. Introduction
The Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau Area (QTPA), the largest plateau with the highest average altitude on the planet, is located in northwestern China [1]. The Qinghai province, located on the northeastern side of QTPA, has a unique and vigorous natural ecosystem due to the high altitude (an average elevation of more than 2000 m above sea level) and cold climate (an average annual temperature below 10 °C) [2,3]. Therefore, a variety of unique livestock has been domesticated in the province, including Tibetan sheep (Ovis aries), yaks (Bos grunniens), cows, chicken, pigs, and horses [4], which are the important economic livestock animals and food animals in this special area [5]. These animals share water and food in the plateau area [6,7].
Toxoplasma gondii is a very important food-borne zoonotic pathogen that can infect almost all warm-blooded animals, including humans, livestock and birds [8,9,10,11,12,13,14] and also causes economic losses in the livestock industry [15,16,17]. Tibetan sheep and yaks are indigenous species raised under extensive animal systems, while cows, chickens, pigs, and horses are important economic livestock animals in the QTPA. The animals could be the intermediate hosts of T. gondii in this plateau area. Humans or these animals might be infected by ingesting water and foods which contain infecting oocysts from cats to develop toxoplasmosis [8,14,16,17]. Therefore, this study focused on T. gondii and toxoplasmosis to investigate the seroprevalence of T. gondii IgG and IgM antibodies in a wide range of animals in the QTPA.
The serological tests play a crucial role in the diagnosis of toxoplasmosis and were widely used [18]. In China, some studies have been reported that humans and animals were infected by T. gondii with different prevalence, of which the prevalence in food animals (such as cattle, sheep, goat, chickens, and swine) was higher than that in humans [19,20]. Although there are several reports on the seroprevalence and epidemiology of T. gondii in animals from the different regions in the QTPA, most attempts of testing toxoplasmosis have been done in yaks which are the important economic animals and food-borne animals in the QTPA [21,22,23,24,25,26]. To date, information on toxoplasmosis in the QTPA and the seroprevalence of T. gondii in other food animals in that area has been limited.
Among several serodetection tests used for diagnosis of toxoplasmosis, the latex agglutination test (LAT) and indirect haemagglutination (IHA) were shown to be insensitive in their present form, the indirect fluorescent antibody test (IFAT) and modified agglutination test (MAT) are considered time-consuming and expensive though specific; hence, the indirect ELISA test has been accepted as the most practical test especially for a large number of samples [9,11]. The surface antigen 2 (SAG2) of T. gondii has an added diagnostic relevance, as it is exposed to the immune system of the hosts [18], and has been identified and tested as an important candidate for the serological diagnosis for toxoplasmosis in many studies [27]. Furthermore, the ELISA based on recombinant SAG2 fusion protein has been used as an effective field serodiagnostic test for the detection of T. gondii infection in different animal species, such as cat, cattle, sheep, goat and pig [18]. Thus, the aim of this study was to perform an indirect ELISA test based on recombinant TgSAG2 protein (rTgSAG2) to establish a detailed record of the seroprevalence of T. gondii-specific IgG and IgM antibodies in Tibetan sheep, yaks, cows, chicken, pigs, and horses in the QTPA.
2. Results
In this study, the seroprevalence of T. gondii in the animals from the QTPA (Figure 1, Table 1), including Tibetan sheep, yaks, cows, chickens, pigs, and horses, was investigated by the indirect ELISA.
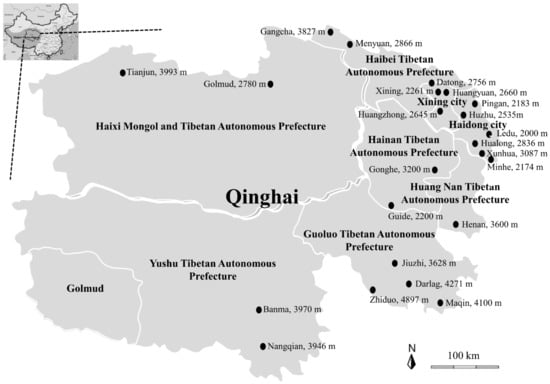
Figure 1.
The map of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau Area and Qinghai province, showing the name of sampling sites and the height above sea level of sampling site per sampling site included. The Tibetan sheep, yak, cow, chicken, pig, and horse serum samples were collected at two cities and six prefectures of the Qinghai province indicated by the black circle. The figure was generated and modified using GIMP 2.8.10 (gimp-2.8.22-setup, https://www.gimp.org/, accessed on 20 February 2021).

Table 1.
The sampling sites of the different animal species in Qinghai province in this study.
To confirm the rTgSAG2-based indirect ELISA in this study, the positive and negative serum samples of mice for T. gondii or the positive serum samples of mice for N. caninum were used to develop the ELISA assay. The results showed that rTgSAG2 protein could determine T. gondii positive sera but no any reaction with T. gondii negative or N. caninum sera (Figure 2A), suggesting current recombinant protein could be studied with animal sera for detecting the T. gondii specific-antibody. Moreover, the cut-off value for judging positive samples was determined by using negative controls. The cut off values were determined as 0.120, 0.114, 0.246, 0.482, 0.423 and 0.110 for IgG antibodies based on rTgSAG2-ELISA in Tibetan sheep, yaks, cows, chicken, pigs, and horses; and 0.411, 0.234, 0.306, 0.468 and 0.065 for IgM antibodies based on rTgSAG2-ELISA in Tibetan sheep, yaks, cows, chickens and pigs, respectively (Figure 2B,C).
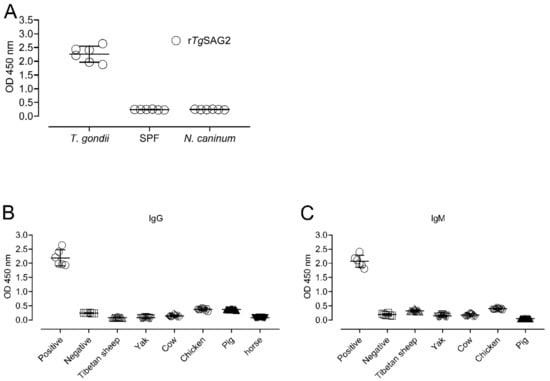
Figure 2.
The confirmation of the rTgGRA7-based indirect ELISA. (A) The positive and negative serum samples of mice for T. gondii or the positive serum samples of mice for N. caninum were used to develop the ELISA assay. (B,C) The cut-off values for the positive samples of T. gondii IgG (B) and IgM (C) were determined by using negative controls of Tibetan sheep, yaks, cows, chickens and pigs, respectively.
In this study, a total of 2673 animal serum samples were tested in a detailed survey of specific anti-T. gondii IgG antibodies in different sampling sites among Tibetan sheep, yaks, cows, chickens, pigs, and horses, and the 2612 animal serum samples were investigated the specific anti-T. gondii IgM antibodies in different areas among Tibetan sheep, yaks, cows, chickens and pigs from Qinghai. The overall seropositive rates of IgG and IgM in all investigated animals were 44.1% (1179/2673) and 18.0% (469/2612), respectively (Table 2). Moreover, as shown in Table 3, the 47.1% (1258/2673) animals showed at least one T. gondii specific-IgG or IgM was positive. Analysis of the positive animals, showed that the 14.9% (389/2612) sera were determined to be both IgG and IgM positive samples, 30.2% (789/2673) were single-IgG seropositive, and a total of 80 in 2612 serum samples (3.0%) were single-IgM seropositive which contains 3.7% (34/907), 2.0% (14/663), 8.8% (18/205), 0.6% (3/500) and 3.3% (11/337) single-IgM positive animals for Tibetan sheep, yaks, cows, chickens and pigs, respectively (Table 3).

Table 2.
Seroprevalence of specific-T. gondii IgG and IgM among Tibetan sheep, yaks, cows, chickens, pigs, and horses in Qinghai.

Table 3.
The double and single IgG and IgM seropositive samples among Tibetan sheep, yaks, cows, chickens, pigs, and horses in Qinghai.
The seroprevalence among the different animal species was tested and analyzed. Of the animal samples, the pig was the most prevalent animal (90.2%, 304/337) for IgG positivity, followed by Tibetan sheep (50.7%, 460/907), chickens (45.8%, 229/500), yaks (21.1%, 140/663), cows (18.5%, 38/205) and horses (13.1%, 8/61) (Figure 3A,B). For the IgM antibody positivity, the pig was also the most prevalent animal (41.8%, 141/337), followed by Tibetan sheep (21.2%, 191/907), cows (15.1%, 31/205), chickens (12.4%, 62/500) and yaks (6.6%, 44/663) (Figure 3C,D), respectively.
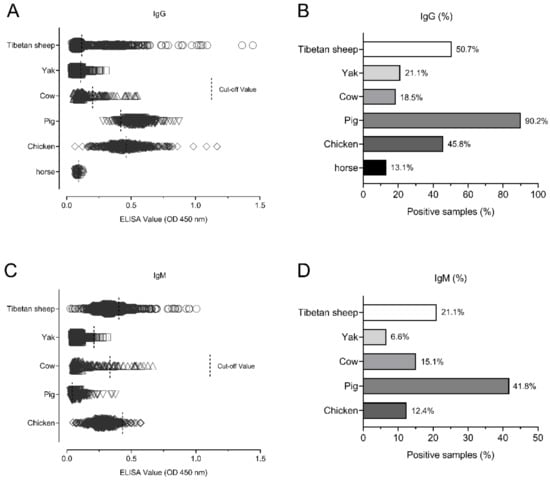
Figure 3.
The seroprevalence among different animals. (A,B) The seroprevalence for IgG positivity in the Tibetan sheep, yaks, cows, chickens, pigs, and horses. (C,D) The seroprevalence for IgM positivity in the Tibetan sheep, yaks, cows, chickens, pigs, and horses.
To analyze the effect of altitude in the seroprevalence, all serum samples were divided into three groups, 2000–3000, 3000–4000, and 4000–5000 m (Table 4). As shown in Table 4, the analyzed results showed that the T. gondii IgG and IgM seroprevalence among the altitude groups was significantly different (p < 0.05). Moreover, the seroprevalence of IgG and IgM significantly differed among animal species (p < 0.05).

Table 4.
Analysis of the influence of altitude on the seroprevalence of T. gondii IgG and IgM antibodies and the distribution of T. gondii in Qinghai.
3. Discussion
Tibetan sheep, yaks, cows, chickens, pigs, and horses play an important role in the agricultural economy in the QTPA, and are the main food-borne animals. Tibetan sheep, famous for their high-quality pelage and their nutritious delicious meat, are widely distributed in Qinghai. The majority of yaks in the world are living on the QTPA, while approximately 35.0% (~4.9/14 million of the yaks) of the yaks in a total of the QTPA are distributed in Qinghai province [22]. Toxoplasmosis has a wide distribution in this plateau area and is very harmful to both human health and the livestock industry. The current study provides a valuable note of the serological prevalence of T. gondii IgG antibodies and the first record of epidemiology of T. gondii IgM antibodies in all these surveyed animals on the whole Qinghai province, which contains two cities and six prefectures.
Since the indirect ELISA test has been accepted as the most practical test in the diagnosis of toxoplasmosis especially for a large number of samples, it has been used for seroprevalence and epidemiology of T. gondii in humans and animal species such as cat, cattle, sheep, goat and pig [18,27]. Therefore, in this study, we choose the indirect ELISA method to sero-detect the antibodies of T. gondii in sera samples from different animal species. The SAG2-based ELISA, presents its immunodominant nature, could determine T. gondii-specific antibodies with the high sensitivity from both acute and chronic T. gondii infection when used either alone or in combination with the other proteins. Importantly, the recombinant SAG2 protein has adequate diagnostic sensitivity and specificity for both T. gondii-specific IgG and IgM antibodies without cross reactivity [28]. Hence, all these special characteristics could make rTgSAG2 a promising candidate for the sero-diagnosis of T. gondii IgG and IgM antibodies in the different animal species in this study. Our study confirmed that current indirect ELISA based on rTgSAG2 not only detected the specific-T. gondii IgG and IgM antibodies but also distinguished them well.
In the current study the seroprevalence of T. gondii infection in Tibetan sheep was 50.7% (460/907). Previous studies showed a lower seroprevalence of T. gondii infection in Qinghai Tibetan sheep (29.8%), evaluated by indirect hemagglutination (IHA) test [23]. In the other two equally important provinces in QTPA, Gansu, and Tibet, adjacent to Qinghai, the seroprevalence results were also lower. In Gansu province was found a seroprevalence of 20.3%, evaluated by modified agglutination test (MAT) [29], and in Tibet province, a seroprevalence of 5.7% was found (26/455), using an IHA [26]. Although limited in current information, testing technologies, and the number of samples, our data indicate the epidemiological prevalence of T. gondii infection in Tibetan sheep with a high rate in Qinghai in the QTPA. T. gondii seroprevalence in sheep and goats varies with altitude and climate, and sheep and goats from the eastern coastal locations have a higher prevalence rate than that of sheep from the west plateau part in China [21]. However, the opposite is that for this plateau organism, we found the highest infection rate in the highest altitude in this study (Table 4). Therefore, the prevalence of pathogens will change with the changes in the living environment of animals, especially in the plateau environment. Moreover, the high prevalence of T. gondii infection in Tibetan sheep may be due to not only oocyst original infection but also transplacental transmission.
T. gondii could indirectly infect humans through ingesting the undercooked or raw meat or milk from yaks or cows. Although cattle are not considered to be an outstanding host for T. gondii [21], the positive rates of 21.1% or 18.5% for T. gondii IgG antibody and 6.6% or 15.1% for T. gondii IgM antibody in yaks or cows were found in this study, respectively. Yak is the main meat consumed by humans in Qinghai, while the cow is the source of milk for humans in the tested area [30]. The current seroprevalence of T. gondii in yaks or cows and the living habits (such as some ethnic groups that consume raw or undercooked meat or with milk) in the QTPA, not only cause economic losses, but also seriously threatens the local human health. Furthermore, the seroprevalence of T. gondii infection in the current study in yaks from Qinghai province was consistent with the average prevalence of T. gondii infection, which was 20.8% ranging from 8.3 to 26.4% in this area in 2008–2014 [30,31,32,33]. This suggests steady epidemiology of T. gondii in yaks in this plateau area. The higher seroprevalence of T. gondii in yaks may be due to geographical factors, such as rivers, foods, and wild animals that these animals share in the large ecological environment.
The current study was the first report for the seroprevalence and epidemiology of T. gondii in chickens, pigs and horses in the Qinghai, though these animals infected with T. gondii have been investigated in other province in China [25,34,35]. Of the investigated animal species in this study, the most prevalent animal for T. gondii infections was the pig, for which seroprevalence was significantly higher than other animals. Moreover, the current seroprevalence in pig showed significantly higher than that of previously reported in Shanxi, Jilin, Chongqing, and Tibet provinces in China [34,36,37,38]. These differences might be due to different climates and rearing systems. More important is that the contribution of cats and rodents could not be ignored in T. gondii infections [34]. Although the high levels of antibodies to T. gondii were not accompanied by severe clinical symptoms and high mortality in pigs in the current study, it could not be ignored that a serious toxoplasmosis outbreak in the neighboring province (Gansu province) led to pig deaths [39]. Therefore, the high seropositivity of IgG and IgM in pigs found in this study should attract more attention to prevent the outbreak of toxoplasmosis in the investigated area. In addition, the current seroprevalence of T. gondii in chickens was tested to be significantly higher than the average prevalence of T. gondii infection from 2000 to 2017 in China [21]. Generally, the chicken might be used as an indicator of environmental and soil contamination with the Toxoplasma oocysts because chickens could ingest the oocysts from soil or environmental food causing T. gondii infections [40]. Therefore, the local peoples should pay attention to the soil and environment polluted with Toxoplasma oocysts. Furthermore, the current ELISA test based on rTgSAG2 found a slightly lower seroprevalence of T. gondii in horses (13.1%, 8/61) than the average seroprevalence of T. gondii infection (18.0%, 615/3413) in China [35]. Although this study was limited to the number of the horse samples, the high prevalence suggests the horses should not ingest food and water that is probably contaminated by the oocysts of T. gondii that might reduce the seroprevalence.
In this study, our data demonstrated all tested animal species showed a positive for T. gondii infection with the high prevalence of IgG and IgM antibodies in two cities and six prefectures of Qinghai, suggesting that the distribution of toxoplasmosis is ubiquitous across Qinghai. Moreover, analysis of the seroprevalence of T. gondii IgG and IgM in the tested animals from the 44 sampling sites were conveniently chosen from 2174 m to 4897 m altitudes, suggesting the significant differences present in the infection rates at different altitudes. This may be due to the high-altitude areas in grazing areas where exist the possibility of sharing common water and food among animals, while in the low-altitude areas are a large number of activities for humans, and definitive-host cats leading to these food-borne animals are frequently exposed to the infecting source, causing T. gondii infections.
Here, we investigated the seroprevalence of the specific-T. gondii IgG and IgM antibodies. The diagnosis of acute T. gondii infection depends on the detection of Toxoplasma-specific IgG and IgM antibodies. The IgG avidity test and IgM analysis are considered to be suitable methods for determining acute infections [28]. The current results showed that all tested animal species present the single-IgG positive animals, both IgG and IgM positive animals, and single-IgM positive animals (Table 3). Considering that IgM is a T. gondii-specific antibody that appears in the early stage of acute Toxoplasma infection, and as the infection progresses, IgG and IgM antibodies will be observed together, while the IgM will reduce and IgG will keep the high level in the later stage of the infection, and the infection will turn into a chronic T. gondii infection. Therefore, our study attests that these animals from the different altitude sampling areas tested are suffering from acute or chronic Toxoplasma infection or have become carriers of T. gondii antibodies after the infections. To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first record of the epidemiology of T. gondii IgM antibodies and distinguishes T. gondii-specific IgG and IgM antibodies in these food-borne animals in the Qinghai province and in China.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection of Tibetan Sheep (Ovis aries), Yaks (Bos grunniens), Cows, Chickens, Pigs and Horses
In this study, a total of 2673 serum samples were collected from the different animals, and the 44 sampling sites were conveniently chosen from 2174 m above sea level to 4897 m in the two cities and six prefectures of the QTPA from June to November 2020 (Figure 1), including apparently healthy Tibetan sheep (n = 907), yaks (n = 663), cows (n = 205), chickens (n = 500), pigs (n = 337), and horses (n = 61) (Table 1). All procedures were carried out according to the ethical guidelines of Qinghai University.
4.2. Serum Harvest
These animal blood samples were kept in an icebox, then sent to the State Key Laboratory of Plateau Ecology and Agriculture, Qinghai University. The samples were centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 10 min, 4 °C to separate and harvest sera and stored at −20 °C until used.
4.3. Recombinant Protein Expression
The recombinant TgSAG2 was expressed with previously described methods [27], with slight modifications. The concentration of rTgSAG2 protein was measured with a bicinchoninic acid protein assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Rockford, IL, USA).
4.4. Indirect ELISA
The 96-well ELISA plates were coated with 1 μg/ml rTgSAG2 protein diluted in coating buffer (0.05 M Carbonate-Bicarbonate, pH 9.6) and incubated at 4 °C overnight. The ELISA plates were washed by PBS-T (0.05% Tween-20) three times, and then blocked with 3% skimmed milk, then washed once. Collected sera were diluted by 1:100 and incubated for 1 h at 37 °C. The plates were washed with PBS-T six times. Then, the HRP conjugated anti-IgG or IgM secondary antibodies of the corresponding species (Bethyl Laboratories, Montgomery, TX, USA), were diluted 1:4000 for the Tibetan sheep, yak, cow, chicken, pig and horse sera, and added and incubated for another 1 h at 37 °C. After washing six times, TMB, (3, 3′, 5, 5′-Tetramethylbenzidine) substrate containing 2.5% H2O2 was used to develop the reaction for 20 min, and 50 μL stop solution (2 M sulfuric acid) was added to each well to stop the action of horseradish peroxidase in the substrate. The results were measured at OD 450 nm. The cut-off point was calculated as the mean values of OD 450 nm for standard Toxoplasma-negative sera kept in our laboratory (ten samples of each animal) plus three times the standard deviations of OD450 values of these negative controls. The positive and negative serum samples of mice for T. gondii (kept at in our Lab) or the positive serum samples of mice for N. caninum (gift from Prof. Lijun Jia from Yanbian University, Jilin, China) were set as control to confirm the rTgSAG2-based indirect ELISA.
4.5. Statistical Analysis
To graph and analyze the data, GraphPad Prism 8 software (GraphPad Software Inc., USA) was used. The prevalence and 95% confidence intervals per pathogen species were calculated using the OpenEpi program (https://www.openepi.com/Proportion/Proportion.htm, accessed on 15 November 2020). The chi-squared test and the logistic regression analysis were used to compare proportions of detected sample positivity in different regions and among different animals. The differences were considered to be statistically significant when the resulting p-values were lower than 0.05.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrates the high seroprevalence for the specific-T. gondii IgG and IgM antibodies among Tibetan sheep, yaks, cows, chickens, pigs, and horses in the QTPA. These give the new valuable data on the epidemiology of T. gondii in the plateau area, and suggest that we should pay more attention to improve the animal’s survival environment, provide more water sources, avoid exposure to the cat, improve animal welfare, and strengthen future prevention and control of T. gondii infection in these food-borne animals in this region. However, the current study is limited to the range of sampling points, the number of samples, and the lack of records for the definitive host cat’s activity around the sampling point; thus, the serological prevalence of T. gondii infections should likewise be extensively investigated in animals of food-borne and economic importance, including cats and other meat-producing animals. Future studies should assess the epidemiology of T. gondii in these local animal species.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L.; formal analysis, J.L. and G.L.; investigation, G.L. and W.Z.; resources, G.L., J.Y. and T.Q.; data curation, G.L. and J.Y.; writing-original draft preparation, G.L. and J.L.; writing-review and editing, J.L. and Y.H. and W.C.; visualization, H.M. and W.Z.; supervision, G.L. and Y.S.; project administration, J.L. and M.K.; funding acquisition, M.K. and Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31660698), the Veterinary Bureau Scientific Research Foundation of Qinghai Province (Grant No. NMSY-2018-05, NMSY-2020-04) and the Regular Assistance Project of International Department of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant No. KY201904013).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all the people who were involved in making this project a success.
Conflicts of Interest
We declare that we have no competing interests.
References
- Tang, L.; Duan, X.; Kong, F.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Mei, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, S. Influences of climate change on area variation of Qinghai Lake on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau since 1980s. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Yang, J.; Niu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Kan, W.; Hu, G.; Liu, G.; Luo, J.; Yin, H. Molecular prevalence of spotted fever group rickettsiae in ticks from Qinghai Province, northwestern China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 57, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubel, F.; Brugger, K.; Walter, M.; Vogelgesang, J.R.; Didyk, Y.M.; Fu, S.; Kahl, O. Geographical distribution, climate adaptation and vector competence of the Eurasian hard tick Haemaphysalis concinna. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 1080–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Ai, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Duan, Z. Cryptosporidium spp., Enterocytozoon bieneusi, and Giardia duodenalis from animal sources in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau Area (QTPA) in China. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 67, 101346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Fei, J.; Cai, J.; Wang, X.; Li, N.; Guo, Y.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Multilocus genotyping of Giardia duodenalis in Tibetan sheep and yaks in Qinghai, China. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 247, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Liu, L.; Zheng, F.; Chen, Q.; Li, Z.; Cao, X.; Yin, H.; Zhou, J.; Cai, X. Molecular investigation of bovine viral diarrhea virus infection in yaks (Bos gruniens) from Qinghai, China. Virol. J. 2014, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jian, Y.; Jia, L.; Galon, E.M.; Benedicto, B.; Wang, G.; Cai, Q.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Ji, S.; et al. Molecular characterization of tick-borne bacteria and protozoans in yaks (Bos grunniens), Tibetan sheep (Ovis aries) and Bactrian camels (Camelus bactrianus) in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau Area, China. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P. Advances in the life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 1998, 28, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis in pigs—The last 20 years. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 164, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. History of the discovery of the life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, S.A.; Jones, J.L.; Conrad, P.A.; Patton, S.; Lindsay, D.S.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasma gondii: Epidemiology, feline clinical aspects, and prevention. Trends. Parasitol. 2010, 26, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, J.G.; Liesenfeld, O. Toxoplasmosis. Lancet 2004, 363, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, L.M.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis: A history of clinical observations. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadatnia, G.; Golkar, M. A review on human toxoplasmosis. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 44, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirosh-Levy, S.; Steinman, A.; Minderigiu, A.; Arieli, O.; Savitski, I.; Fleiderovitz, L.; Edery, N.; Schvartz, G.; Mazuz, M.L. High exposure to Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora Spp. in donkeys in Israel: Serological survey and case reports. Animals 2020, 10, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Guo, H.; Galon, E.M.; Gao, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Ji, S.; Jia, H.; Xuan, X. Hydroxylamine and carboxymethoxylamine can inhibit Toxoplasma gondii growth through an aspartate aminotransferase-independent pathway. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e01889-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Humans, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 1–313. [Google Scholar]
- Sudan, V.; Tewari, A.K.; Singh, H. Detection of antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii in Indian cattle by recombinant SAG2 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Acta Parasitol. 2019, 64, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.J.; Zhao, Z.J.; He, Z.H.; Wang, T.; Yang, T.B.; Chen, X.G.; Shen, J.L.; Wang, Y.; Lv, F.L.; Hide, G.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii infection in pregnant women in China. Parasitology 2012, 139, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Lyu, C.; Zhao, J.; Shen, B. Sixty years (1957–2017) of research on toxoplasmosis in China-an overview. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Su, R.; Lu, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Jian, F.; Yang, Y. Prevalence, risk factors, and genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii in food animals and humans (2000–2017) from China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Shahzad, M.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Mehmood, K.; Zhao, X.; Li, J. Socio-economic burden of parasitic infections in yaks from 1984 to 2017 on Qinghai Tibetan Plateau of China-A review. Acta Trop. 2018, 183, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Ma, R.; Zhao, Q.; Shang, L.; Cai, J.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Hu, G.; Jin, H.; Gao, H. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in Tibetan sheep in northwestern China. J. Parasitol. 2010, 96, 1222–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.K.; Li, J.Y.; Pan, H. Seroprevalence and risk factors of Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum infections in small ruminants in China. Prev. Vet. Med. 2015, 118, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.Y.; Quan, M.X.; Tang, H.L.; Wu, X.T.; Liu, G.H.; Li, F.; Hu, S.F. Seroprevalence, risk factors, and genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii in free-range chickens intended for human consumption in China. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2020, 10, 1089. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.M.; Danba, C.; Huang, S.Y.; Zhang, D.L.; Chen, J.; Gong, G.; Xu, M.J.; Yuan, Z.G.; Zhu, X.Q. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in Tibetan sheep in Tibet, China. J. Parasitol. 2011, 97, 1188–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Cao, S.; Sevinc, F.; Sevinc, M.; Ceylan, O.; Liu, M.; Wang, G.; Moumouni, P.F.; Jirapattharasate, C.; Suzuki, H.; et al. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays using recombinant TgSAG2 and NcSAG1 to detect Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum-specific antibodies in domestic animals in Turkey. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 78, 1877–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanaliha, K.; Motazedian, M.H.; Kazemi, B.; Shahriari, B.; Bandehpour, M.; Sharifniya, Z. Evaluation of recombinant SAG1, SAG2, and SAG3 antigens for serodiagnosis of toxoplasmosis. Korean J. Parasitol. 2014, 52, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, M.Y.; Wang, J.L.; Huang, S.Y.; Qin, S.Y.; Zhou, D.H.; Liu, G.X.; Tan, Q.D.; Zhu, X.Q. Seroprevalence and risk factors of Toxoplasma gondii in Tibetan Sheep in Gansu province, Northwestern China. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Cai, J.; Zhao, Q.; Shang, L.; Ma, R.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Hu, G.; Jin, H.; Gao, H. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in yaks (Bos grunniens) in northwestern China. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2011, 43, 741–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cai, J.Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Q.; Chen, D.; Han, J.P.; Liu, Q.R. Seroepidemiology of Neospora caninum and Toxoplasma gondii infection in yaks (Bos grunniens) in Qinghai, China. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 152, 330–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Y.H.; Ye, Q.; Meng, P.; Yin, H.; Zhang, D.L. Serological survey of Toxoplasma gondii in Tibetan mastiffs (Canis lupus familiaris) and yaks (Bos grunniens) in Qinghai, China. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Gao, J.F.; Shahzad, M.; Han, Z.Q.; Nabi, F.; Liu, M.Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, J.K. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in yaks (Bos grunniens) on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau of China, 2014. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 205, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Wang, Y.L.; Yang, Z.; Li, X.L.; Li, Z.R.; Lin, Q. Seroprevalence and Risk Factors of Toxoplasma gondii in Slaughter Pigs in Shaanxi Province, Northwestern China. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2017, 17, 517–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ni, H.B.; Ren, W.X.; Jiang, J.; Gong, Q.L.; Zhang, X.X. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in horses: A global systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Trop. 2020, 201, 105222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Cai, Y.N.; Leng, X.; Wang, J.; Ma, W.; Mu, G.D.; Jiang, J.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, Z.D.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in pigs in Jilin Province, Northeastern China. Trop. Biomed. 2015, 32, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Lv, R.; Sun, X.; Shu, F.; Zhou, Z.; Nie, K.; Duan, G.; Zou, F. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies from slaughter pigs in Chongqing, China. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2012, 44, 685–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.M.; Ciren, D.; Huang, S.Y.; Xu, M.J.; Ga, G.; Yan, C.; Mahmoud, M.S.; Zou, F.C.; Zhu, X.Q. First report of Toxoplasma gondii prevalence in Tibetan pigs in Tibet, China. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012, 12, 654–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, F.; Li, T.; Zhang, D. An outbreak of lethal toxoplasmosis in pigs in the Gansu province of China. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2010, 22, 442–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.X.; Yang, Y.R. Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum in free-range chickens in Henan Province of China. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 8290536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).