Leptospiral Infection, Pathogenesis and Its Diagnosis—A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Risk Factors
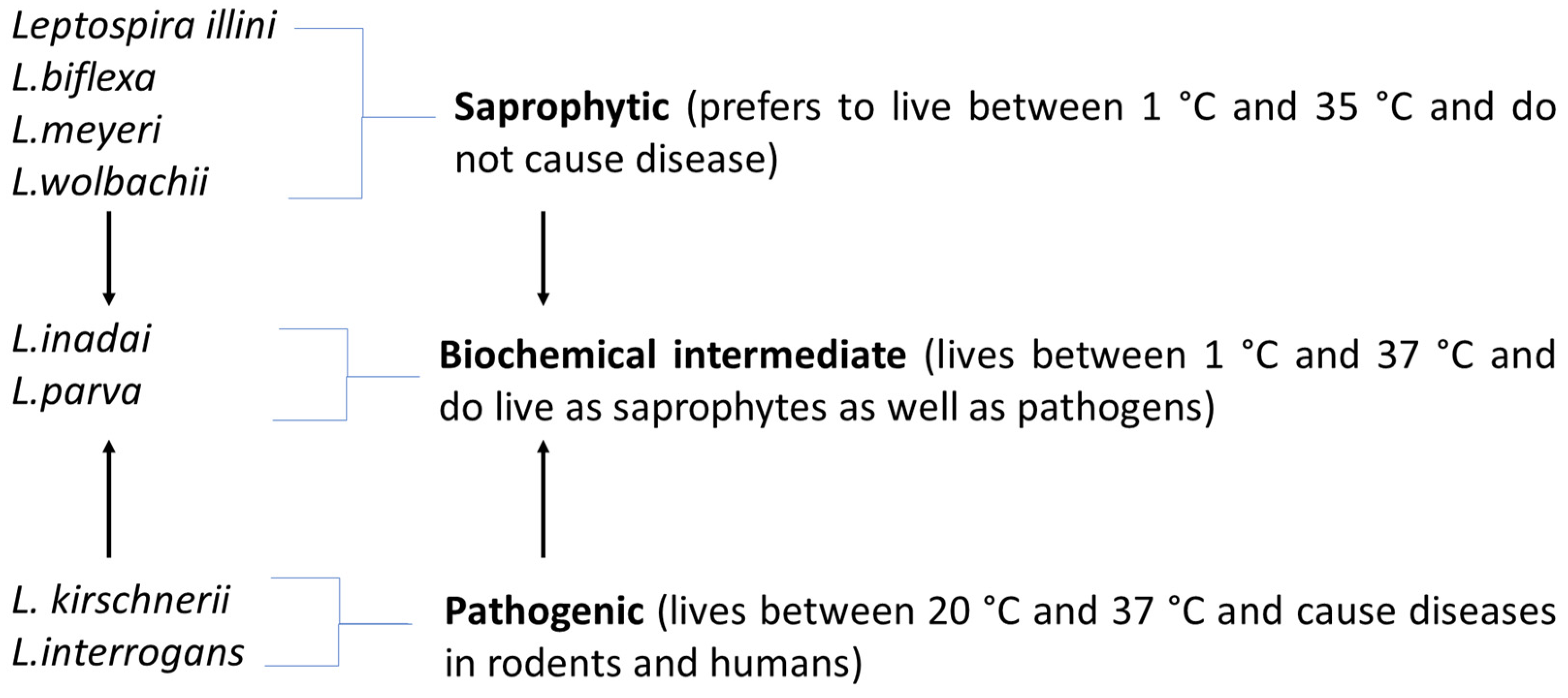
3. Classification of Leptospira
4. Morphology
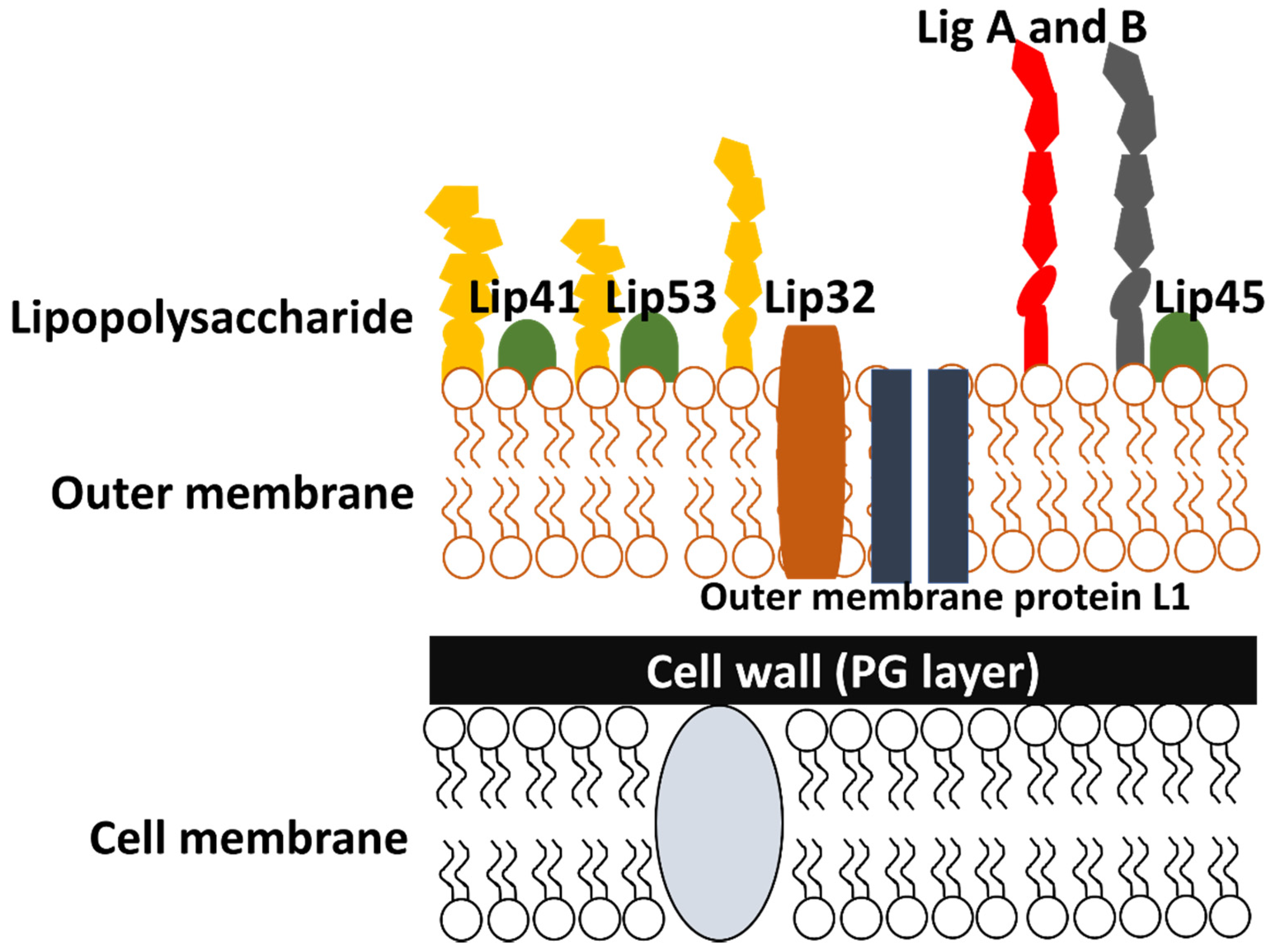
4.1. Cell Outer Membrane Structure and Its Proteins
4.1.1. Outer Membrane Proteins
4.1.2. LipL32
4.1.3. OmpL1
4.1.4. Loa22
4.1.5. LigB
4.1.6. LenA
4.2. Periplasmic Flagella
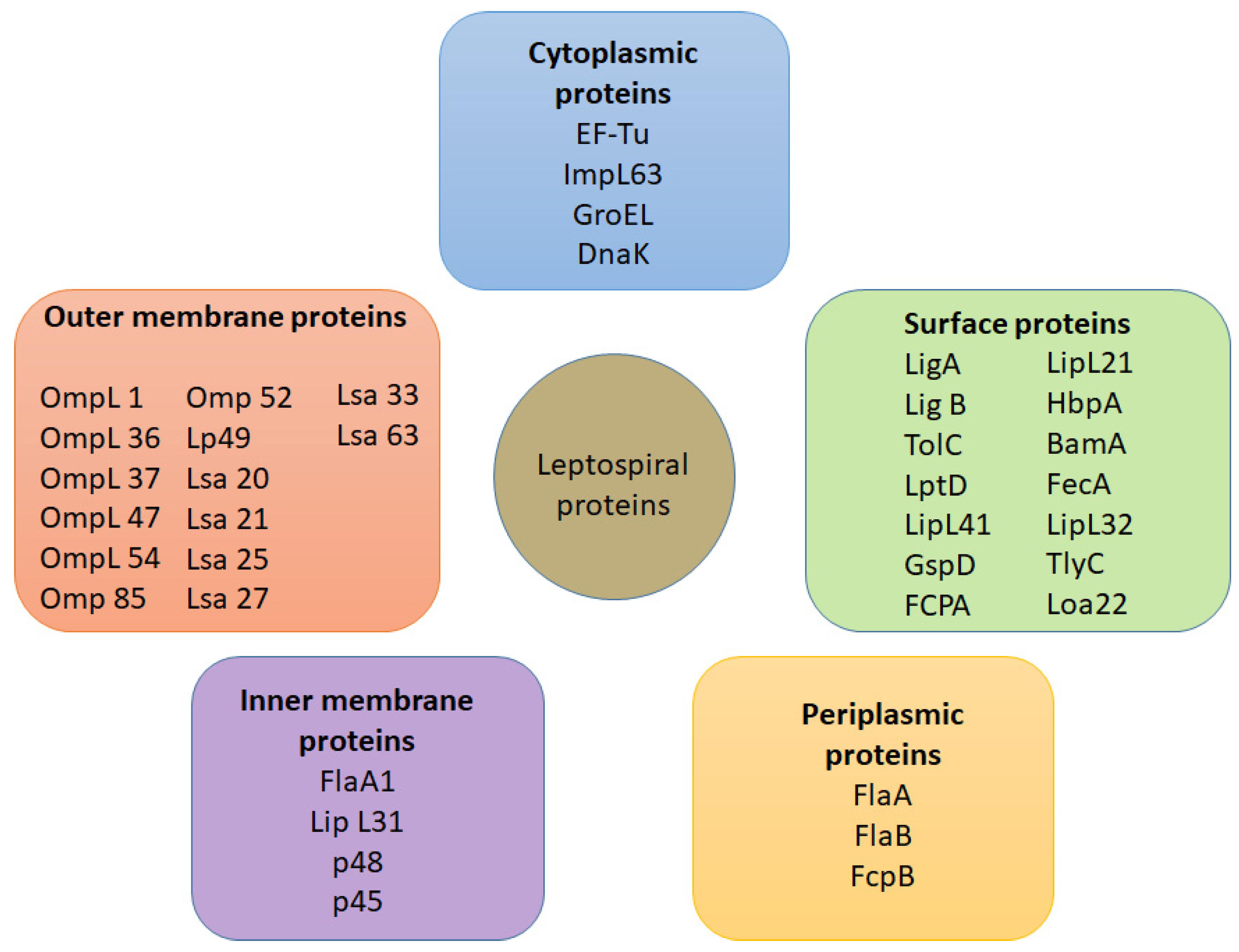
5. Antigens Involved in Leptospiral Infection
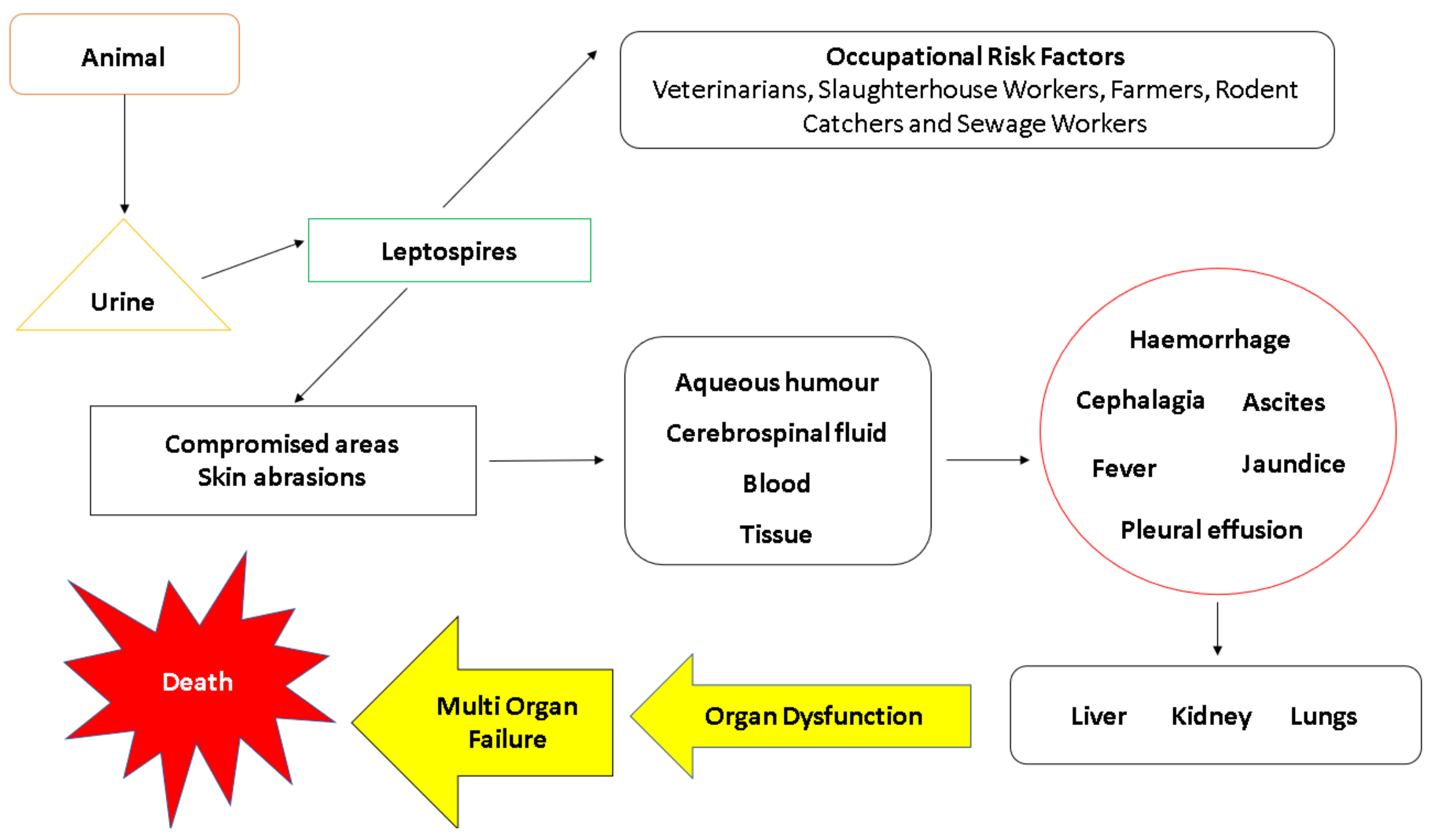
6. Transmission and Pathogenesis
6.1. Transmission
6.2. Leptospiraemic Phase
6.3. Adhesion and Cell Entry
6.4. Weil’s Disease
6.5. Evasion of Host Immune System and Virulence Factors
7. Co-Infections
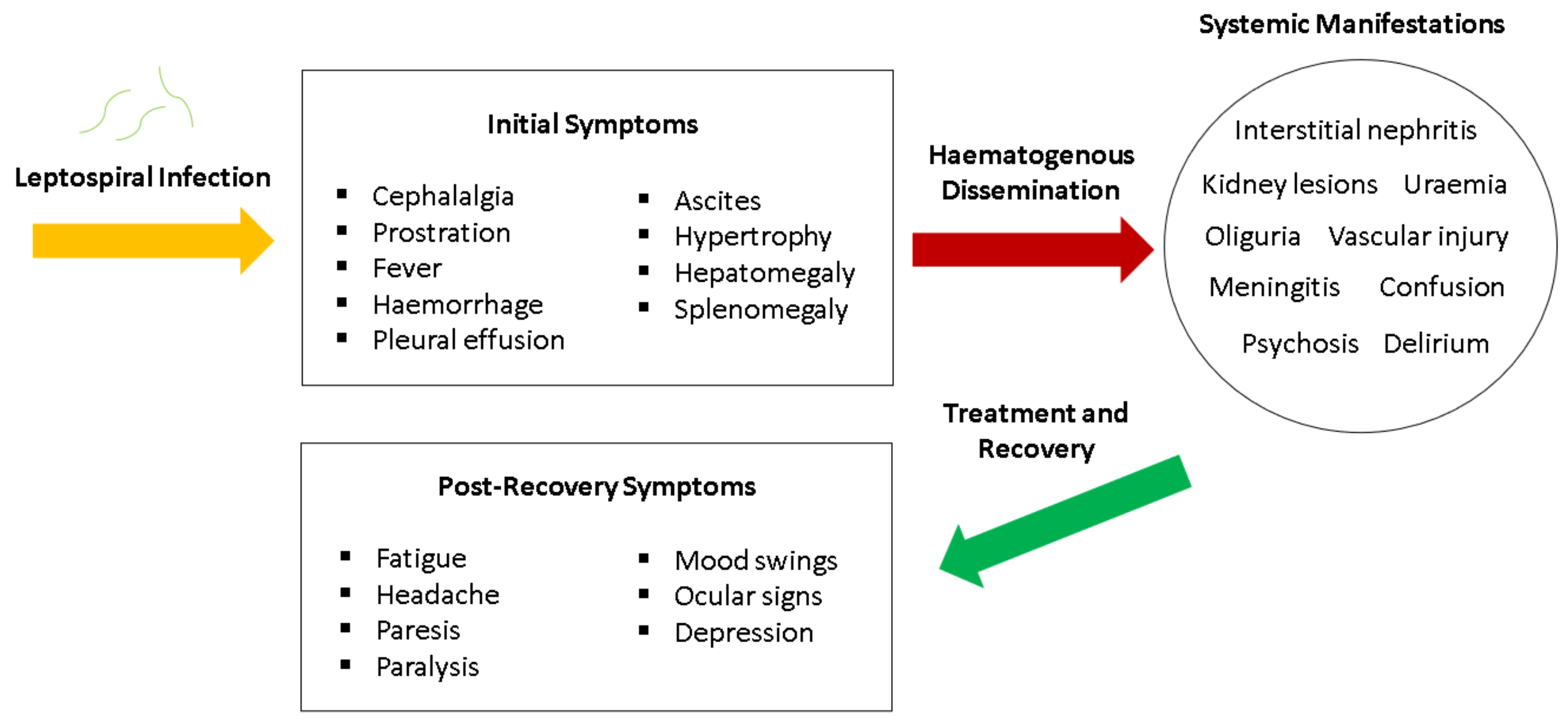
8. Clinical Manifestations
9. Diagnosis of Leptospirosis
9.1. Clinical Findings
9.2. Serological and Indirect Diagnostic Methods
9.2.1. Microscopic Agglutination Test (MAT)
9.2.2. Microsphere Immunoassay (MIA)
9.2.3. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
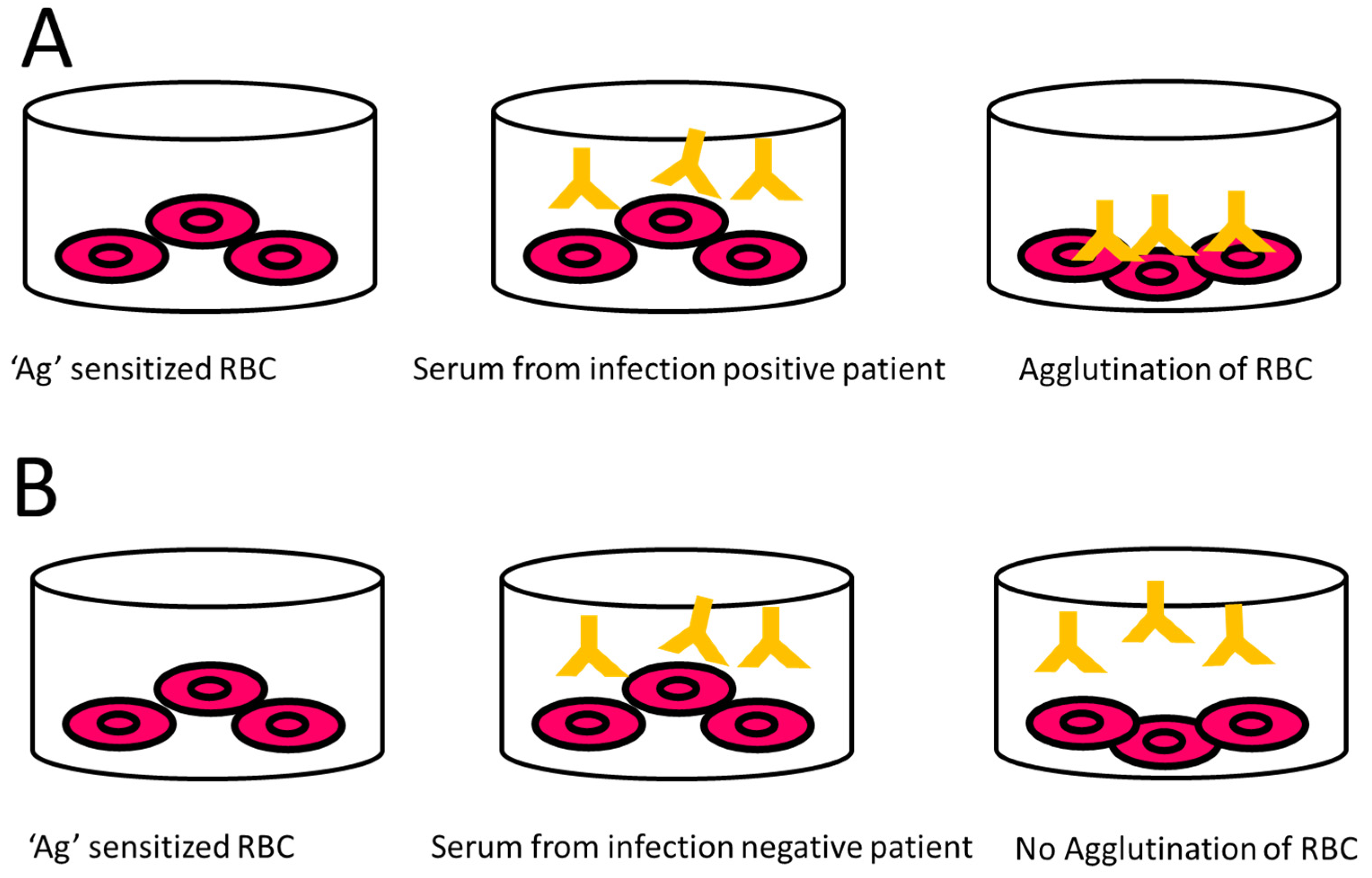
9.2.4. Indirect Haemagglutination Assay (IHA)
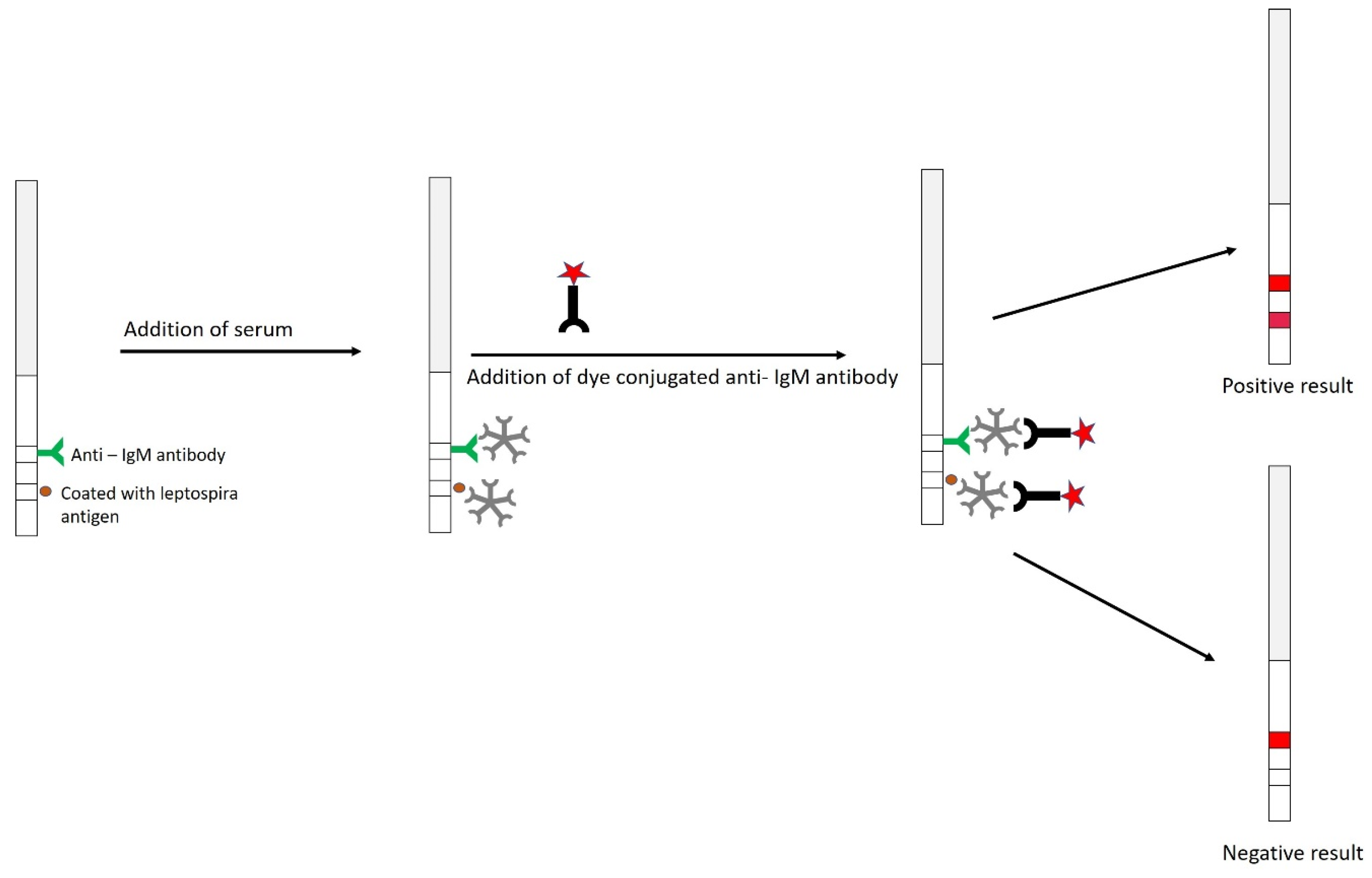
9.2.5. Dipstick Assay
9.2.6. Flow Cytometry (FCM)
9.3. Direct Diagnostic Methods
9.3.1. Microscopy Techniques
9.3.2. Staining Techniques
9.3.3. Culture Technique
9.3.4. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
10. Epidemiological and Transmission Patterns of Leptospirosis: Future Concerns
11. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Altizer, S.; Bartel, R.; Han, B.A. Animal migration and infectious disease risk. Science 2011, 331, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wu, J.; Ding, C.; Cui, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Deng, M.; Wang, C.; Xu, K.; Ren, J.; et al. Epidemiological features of and changes in incidence of infectious diseases in China in the first decade after the SARS outbreak: An observational trend study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostfeld, R.S.; Keesing, F. The function of biodiversity in the ecology of vector-borne zoonotic diseases. Can. J. Zool. 2000, 2061–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.E.; Patel, N.G.; Levy, M.A.; Storeygard, A.; Balk, D.; Gittleman, J.L.; Daszak, P. Global trends in emerging infectious diseases. Nature 2008, 451, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, P.; Bhaumik, S.; Chauhan, A.S.; Kakkar, M. Protocol for developing a Database of Zoonotic disease Research in India (DoZooRI). BMJ Open 2017, 7, e017825:1–e017825:4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, H. SpirochÆta icterohÆmorrhagiÆ in american wild rats and its relation to the japanese and european strains. First paper. J. Exp. Med. 1917, 25, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mayer, F.Q.; Dos Reis, E.M.; Bezerra, A.V.A.; Cerva, C.; Rosa, J.; Cibulski, S.P.; Lima, F.E.S.; Pacheco, S.M.; Rodrigues, R.O. Pathogenic Leptospira spp. in bats: Molecular investigation in Southern Brazil. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 52, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Leptospirosis Burden Epidemiology Reference Group (LERG). Available online: https://www.who.int/zoonoses/diseases/lerg/en/ (accessed on 3 October 2020).
- Londe, L.D.; da Conceição, R.S.; Bernardes, T.; de Assis Dias, M.C. Flood-related leptospirosis outbreaks in Brazil: Perspectives for a joint monitoring by health services and disaster monitoring centers. Nat. Hazards 2008, 84, 1419–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Radi, M.F.; Hashim, J.H.; Jaafar, M.H.; Hod, R.; Ahmad, N.; Nawi, A.M.; Baloch, G.M.; Ismail, R.; Ayub, N.I.F. Leptospirosis outbreak after the 2014 major flooding event in Kelantan, Malaysia: A spatial-temporal analysis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 98, 1281–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, G.; Papadimitriou, P.; Siozopoulou, V.; Christou, L.; Akritidis, N. The globalization of leptospirosis: Worldwide incidence trends. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 12, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierks, J.; Servies, T.; Do, T. A Study on the Leptospirosis Outbreak Among US Marine Trainees in Okinawa, Japan. Mil. Med. 2018, 183, e208–e212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, S.; Schuch, R.A.; de Oliveira, N.R.; da Cunha, C.E.P.; Gomes, C.K.; Oliveira, T.L.; Rizzi, C.; Qadan, A.F.; Pacce, V.D.; Coelho Recuero, A.L.; et al. Human and animal leptospirosis in Southern Brazil: A five-year retrospective study. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2017, 18, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurilung, A.; Chanchaithong, P.; Lugsomya, K.; Niyomtham, W.; Wuthiekanun, V.; Prapasarakul, N. Molecular detection and isolation of pathogenic Leptospira from asymptomatic humans, domestic animals and water sources in Nan province, a rural area of Thailand. Res. Vet. Sci. 2017, 115, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilahun, Z.; Reta, D.; Simenew, K. Global Epidemiological Overview of Leptospirosis. Int. J. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 4, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, M.; Agnello, S.; Chetta, M.; Amato, B.; Vitale, G.; Bella, C.D.; Vicari, D.; Presti, V.D.M.L. Human leptospirosis cases in Palermo Italy. The role of rodents and climate. J. Infect. Public Health 2018, 11, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, M.; Abbas, S.N.; Farooqi, S.H.; Aqib, A.I.; Anwar, G.A.; Rehman, A.; Ali, M.M.; Mehmood, K.; Khan, A. Sero-epidemiology and hemato-biochemical study of bovine leptospirosis in flood affected zone of Pakistan. Acta Trop. 2018, 177, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomari, K.; Toyokawa, T.; Takahashi, T.; Kakita, T.; Okano, S.; Kyan, H.; Tonegawa, N.; Okawa, T.; Matsuoka, T.; Matsumora, T. Childhood leptospirosis in an industrialized country: Population-based study in Okinawa, Japan. Plos Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006294:1–e0006294:10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, L.F.; Guimarães, M.F.; de Souza, G.O.; da Silva, I.W.G.; Santos, J.R.; Azevedo, S.S.; Labruna, M.B.; Heinemann, M.B.; Horta, M.C. Seroepidemiological survey on Leptospira spp. infection in wild and domestic mammals in two distinct areas of the semi-arid region of northeastern Brazil. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2017, 49, 1715–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, A.; Kushwaha, A.; Chayanika, D.; Subhashree, N.; Varsha, P.; Marcia, A.; Lahari, L.; Shankar, S.; Patel, N. A Review on Bovine Leptospirosis with Special Reference to Seroprevalence in India. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 1813–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naotunna, C.; Agampodi, S.B.; Agampodi, T.C. Etiological agents causing leptospirosis in Sri Lanka: A review. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2016, 9, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartskeerl, R.A.; Collares-Pereira, M.; Ellis, W.A. Emergence, control and re-emerging leptospirosis: Dynamics of infection in the changing world. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, G. Spirochaetal Jaundice. BMJ 1927, 1, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.I. Leptospira spp. In Bacterial Pathogens and Their Virulence Factors; Johnson, D.I., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- Abela-Ridder, B.; Sikkema, R.; Hartskeerl, R.A. Estimating the burden of human leptospirosis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 36, S5–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Report of the Second Meeting of the Leptospirosis Burden Epidemiology Reference Group. 2011. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/44588/9789241501521_eng.pdf;jsessionid=B3BABBEB195C52A6FAA5DF9BEA06CA20?sequence=1 (accessed on 3 October 2020).
- Mohammed, H.; Nozha, C.; Hakim, K.; Abdelaziz, F. Leptospira: Morphology, Classification and Pathogenesis. J. Bacteriol. Parasitol. 2011, 2, 1000120:1–1000120:4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulach, D.; Adler, B. Leptospiral genomics and pathogenesis. In Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology; Adler, B., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 189–214. [Google Scholar]
- Benacer, D.; Who, P.Y.; Zain, S.N.M.; Amran, F.; Thong, K.L. Pathogenic and saprophytic Leptospira species in water and soils from selected urban sites in peninsular Malaysia. Microbes Environ. 2013, 28, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovind-Hougen, K. Leptospiraceae, a new family to include Leptospira Noguchi 1917 and Leptonema gen. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1979, 29, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, K.M.; Schwartz, C.; Wachter, J.; Rosa, P.A.; Stewart, P.E. A widely conserved bacterial cytoskeletal component influences unique helical shape and motility of the spirochete Leptospira biflexa. Mol. Microbiol. 2018, 108, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovind-Hougen, K.; Ellis, W.A.; Birch-Andersen, A. Leptospira parva sp.nov.: Some morphological and biological characters. Zent. Für Bakteriol. Mikrobiol. Und Hyg. Abt. 1 Orig. A 1981, 250, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiwattanarungruengpaisan, S.; Suwanpakdee, S.; Sangkachai, N.; Chamsai, T.; Taruyanon, K.; Thongdee, M. Potentially Pathogenic Leptospira Species Isolated from a Waterfall in Thailand. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 71, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, P.H.; Steigerwalt, A.G.; Sulzer, K.R.; Kaufmann, A.F.; Rogers, F.; Brenner, D.J. Deoxyribonucleic Acid Relatedness between Serogroups and Serovars in the Family Leptospiraceae with Proposals for Seven New Leptospira Species. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1987, 37, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, C.E. Leptospiral Structure, Physiology, and Metabolism. In Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology; Adler, B., Ed.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 21–41. [Google Scholar]
- Asensio-Sánchez, V.M.; Haro-Álvarez, B.; Herreras, J.; Martín-Prieto, A. Unusual ocular clinical manifestation of leptospirosis. Arch. De La Soc. Española De Oftalmol. (Engl. Ed.) 2018, 93, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinam, S.R. Ocular leptospirosis. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2002, 13, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jutras, B.L.; Scott, M.; Parry, B.; Biboy, J.; Gray, J.; Vollmer, W.; Jacobs-Wagner, C. Lyme disease and relapsing fever Borrelia elongate through zones of peptidoglycan synthesis that mark division sites of daughter cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9162–9170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picardeau, M. Virulence of the zoonotic agent of leptospirosis: Still terra incognita? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, G.L.; Srikram, A.; Henry, R.; Hartskeerl, R.A.; Sermswan, R.W.; Adler, B. Mutations affecting Leptospira interrogans lipopolysaccharide attenuate virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 78, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, T.R.; Barbosa, A.S.; Isaac, L. Leptospirosis: Aspects of innate immunity, immunopathogenesis and immune evasion from the complement system. Scand. J. Immunol. 2011, 73, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, H.E.; Anderson, T.F. The Morphology of Leptospira icterohemorrhagiae and L. canicola as Revealed by the Electron Microscope. J. Bacteriol. 1943, 45, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.L.; Johnson, R.C. Electron Microscopy of Immune Disruption of Leptospires: Action of Complement and Lysozyme. J. Bacteriol. 1968, 95, 2293–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haake, D.A.; Matsunaga, J. Leptospira: A spirochaete with a hybrid outer membrane. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 77, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiRienzo, J.M.; Nakamura, K.; Inouye, M. The Outer Membrane Proteins of Gram-Negative Bacteria: Biosynthesis, Assembly, and Functions. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1978, 47, 481–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, P.A.; Haake, D.A.; Adler, B. Outer membrane proteins of pathogenic spirochetes. Fems Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 28, 291–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.W.; Wu, M.S.; Pan, M.J.; Hsieh, W.J.; Vandewalle, A.; Huang, C.C. The leptospira outer membrane protein LipL32 induces tubulointerstitial nephritis-mediated gene expression in mouse proximal tubule cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 2037–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werts, C.; Tapping, R.I.; Mathison, J.C.; Chuang, T.H.; Kravchenko, V.; Saint Girons, I.; Haake, D.A.; Godowski, P.J.; Hayashi, F.; Ozinsky, A.; et al. Leptospiral lipopolysaccharide activates cells through a TLR2-dependent mechanism. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.P.; Raman, R.; Sharma, Y.; Chang, Y.F. Calcium binds to leptospiral immunoglobulin-like protein, LigB, and modulates fibronectin binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 25140–25149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, B.; Choy, H.A.; Pinne, M.; Rotondi, M.L.; Miller, M.C.; DeMoll, E.; Kraiczy, P.; Cooley, A.E.; Creamer, T.P.; Suchard, M.A.; et al. Leptospira interrogans Endostatin-Like Outer Membrane Proteins Bind Host Fibronectin, Laminin and Regulators of Complement. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1188:1–e1188:11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, J.; Barocchi, M.A.; Croda, J.; Young, T.A.; Sanchez, Y.; Siqueira, I.; Bolin, C.A.; Reis, M.G.; Riley, L.W.; Haake, D.A.; et al. Pathogenic Leptospira species express surface-exposed proteins belonging to the bacterial immunoglobulin superfamily. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 49, 929–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristow, P.; Bourhy, P.; da Cruz McBride, F.W.; Figueira, C.P.; Huerre, M.; Ave, P.; Saint Girons, I.; Ko, A.I.; Picardeau, M. The OmpA-Like Protein Loa22 Is Essential for Leptospiral Virulence. PLos Pathog. 2007, 3, e97:1–e97:10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auran, N.E.; Johnson, R.C.; Ritzi, D.M. Isolation of the outer sheath of Leptospira and its immunogenic properties in hamsters. Infect. Immun. 1972, 5, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.A.; LeFebvre, R.B.; Pan, M.J. Protein and antigen profiles of prevalent serovars of Leptospira interrogans. Infect. Immun. 1991, 59, 1772–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kida, H.; Watanabe, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Yanagawa, R. Immunological and morphological analysis of sodium dodecyl sulfate extract of Leptospira. Zentralbl. Bakteriol. Orig. A 1976, 236, 328–335. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes-Edwards, P.L.; Thiermann, A.B.; Bassford, P.J.; Stamm, L.V. Identification and characterization of the protein antigens of Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo. Infect. Immun. 1985, 48, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haake, D.A.; Matsunaga, J. Characterization of the leptospiral outer membrane and description of three novel leptospiral membrane proteins. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 4936–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, D.G.; Castiblanco-Valencia, M.M.; Abe, C.M.; Monaris, D.; Morais, Z.M.; Souza, G.O.; Barbosa, A.S. Interaction of Leptospira elongation factor Tu with plasminogen and complement factor H: A metabolic leptospiral protein with moonlighting activities. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, H.; Croda, J.; Flannery, B.; Mazel, M.; Matsunaga, J.; Reis, M.G.; Haake, D.A. Leptospiral proteins recognized during the humoral immune response to leptospirosis in humans. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 4958–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, L.G.; Vieira, M.L.; Kirchgatter, K.; Alves, I.J.; de Morais, Z.M.; Vasconcellos, S.A.; Nascimento, A.L. OmpL1 is an extracellular matrix-and plasminogen-interacting protein of Leptospira spp. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 3679–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinne, M.; Choy, H.A.; Haake, D.A. The OmpL37 surface-exposed protein is expressed by pathogenic Leptospira during infection and binds skin and vascular elastin. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2010, 4, e815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinne, M.; Haake, D.A. A comprehensive approach to identification of surface-exposed, outer membrane-spanning proteins of Leptospira interrogans. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, W.J.; Chang, Y.F.; Chen, C.S.; Pan, M.J. Omp52 is a growth-phase-regulated outer membrane protein of Leptospira santarosai serovar Shermani. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 243, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuseppe, P.O.; Neves, F.O.; Nascimento, A.L.T.; Guimarães, B.G. The leptospiral antigen Lp49 is a two-domain protein with putative protein binding function. J. Struct. Biol. 2008, 163, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandachitra, M.; Jayakumar, V.; Manohar, B.M. Detection and Sequence analysis of Lig B and LSA 21 genes of leptospires fields isolates. Asian J. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 475–479. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, M.L.; de Morais, Z.M.; Gonçales, A.P.; Romero, E.C.; Vasconcellos, S.A.; Nascimento, A.L. Lsa63, a newly identified surface protein of Leptospira interrogans binds laminin and collagen IV. J. Infect. 2010, 60, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingos, R.F.; Vieira, M.L.; Romero, E.C.; Gonçales, A.P.; de Morais, Z.M.; Vasconcellos, S.A.; Nascimento, A.L. Features of two proteins of Leptospira interrogans with potential role in host-pathogen interactions. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshghi, A.; Pappalardo, E.; Hester, S.; Thomas, B.; Pretre, G.; Picardeau, M. Pathogenic Leptospira interrogans exoproteins are primarily involved in heterotrophic processes. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 3061–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassmann, A.A.; Kremer, F.S.; dos Santos, J.C.; Souza, J.D.; Pinto, L.D.S.; McBride, A.J.A. Discovery of novel leptospirosis vaccine candidates using reverse and structural vaccinology. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Hsiao, C.D.; Huang, S.H.; Wang, M.S.; Ko, Y.C.; Sun, Y.J. LipL41, a hemin binding protein from Leptospira santarosai serovar Shermani. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haake, D.A.; Zückert, W.R. The leptospiral outer membrane. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 387, 187–221. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, Y.; Kawamoto, A.; Tahara, H.; Kasuga, K.; Sato, R.; Ohnishi, M.; Nakamura, S.; Koizumi, N. Leptospiral flagellar sheath protein FcpA interacts with FlaA2 and FlaB1 in Leptospira biflexa. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asuthkar, S.; Velineni, S.; Stadlmann, J.; Altmann, F.; Sritharan, M. Expression and characterization of an iron-regulated hemin-binding protein, HbpA, from Leptospira interrogans serovar Lai. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 4582–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louvel, H.; Saint Girons, I.; Picardeau, M. Isolation and characterization of FecA-and FeoB-mediated iron acquisition systems of the spirochete Leptospira biflexa by random insertional mutagenesis. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 3249–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.Y.; Cheng, Y.C.; Hsu, S.H.; Ma, T.L.; Chou, L.F.; Hsu, H.H.; Pan, R.L. Leptospiral outer membrane protein LipL32 induces inflammation and kidney injury in zebrafish larvae. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, E.; Barbosa, A.S.; Gómez, R.M.; Cianciarullo, A.M.; Hauk, P.; Abreu, P.A.; Morais, Z.M. Leptospiral TlyC is an extracellular matrix-binding protein and does not present hemolysin activity. FEBS Lett. 2009, 2009 583, 1381–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunder Jr, E.A.; Slamti, L.; Suwondo, D.N.; Gibson, K.H.; Shang, Z.; Sindelar, C.V.; Picardeau, M. FcpB is a surface filament protein of the endoflagellum required for the motility of the spirochete Leptospira. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoduvayil, S.; Dhandapani, G.; Brahma, R.; Devasahayam Arokia Balaya, R.; Mangalaparthi, K.K.; Patel, K.; Pinto, S.M. Triton X-114 Fractionated Subcellular Proteome of Leptospira interrogans Shows Selective Enrichment of Pathogenic and Outer Membrane Proteins in the Detergent Fraction. Proteomics 2020, 20, 2000170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.W.; Wu, M.S.; Pan, M.J. Leptospirosis renal disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2001, 16, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuerner, R.L.; Knudtson, W.; Bolin, C.A.; Trueba, G. Characterization of outer membrane and secreted proteins of Leptospira interrogans serovar pomona. Microb. Pathog. 1991, 10, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, J.Y.; Yang, C.W.; Chou, S.W.; Lin, C.C.; Sun, Y.J. Calcium binds to LipL32, a lipoprotein from pathogenic Leptospira, and modulates fibronectin binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 3245–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoke, D.E.; Egan, S.; Cullen, P.A.; Adler, B. LipL32 is an extracellular matrix-interacting protein of Leptospira spp. and Pseudoalteromonas tunicata. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 2063–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauk, P.; Macedo, F.; Romero, E.C.; Vasconcellos, S.A.; De Morais, Z.M.; Barbosa, A.S.; Ho, P.L. In LipL32, the major leptospiral lipoprotein, the C terminus is the primary immunogenic domain and mediates interaction with collagen IV and plasma fibronectin. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 2642–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witchell, T.D.; Eshghi, A.; Nally, J.E.; Hof, R.; Boulanger, M.J.; Wunder, E.A.; Ko, A.I.; Haake, D.A.; Cameron, C.E. Post-translational Modification of LipL32 during Leptospira interrogans Infection. Plos Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3280:1–e3280:13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Ojcius, D.M.; Yang, X.F.; Zhang, C.; Ding, S.; Lin, X.; Yan, J. Leptospiral hemolysins induce proinflammatory cytokines through toll-like receptor 2-and 4-mediated JNK and NF-κB signaling pathways. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42266:1–e42266:15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.W.; Hung, C.C.; Wu, M.S.; Tian, Y.C.; Chang, C.T.; Pan, M.J.; Vandewalle, A. Toll-like receptor 2 mediates early inflammation by leptospiral outer membrane proteins in proximal tubule cells. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, Y.Y.; Hsu, S.H.; Ko, Y.C.; Hung, C.C.; Chang, M.Y.; Hsu, H.H.; Pan, M.J.; Chen, Y.W.; Lee, C.H.; Tseng, F.G.; et al. Essential calcium-binding cluster of Leptospira LipL32 protein for inflammatory responses through the Toll-like receptor 2 pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 12335–12344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.A.; Sandai, D.A.; Musa, S.; Hock, H.C.; Riadzi, M.; Leong, L.K.; Hock, T.T. Rapid Diagnosis of Leptospirosis by Multiplex PCR. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 19, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tarigan, S. Recombinant LipL32 Protein for Leptospirosis Detection in Indonesia. Procedia Chem. 2016, 18, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, E.S.; Exner, M.M.; Summers, T.A.; Martinich, C.; Champion, C.I.; Hancock, R.E.W.; Haake, D.A. The rare outer membrane protein, OmpL1, of pathogenic Leptospira species is a heat-modifiable porin. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 3174–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Hu, Y.; Xue, F.; Sun, D.; Ojcius, D.M.; Mao, Y.; Yan, J. Characterization of the ompL1 gene of pathogenic Leptospira species in China and cross-immunogenicity of the OmpL1 protein. BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8, 223:1–223:12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, J.K.; Barnett, D.; Bolin, C.A.; Summers, T.A.; Wagar, E.A.; Cheville, N.F.; Hartskeerl, R.A.; Haake, D.A. Expression and distribution of leptospiral outer membrane components during renal infection of hamsters. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Sun, A.; Ruan, P.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, J. Characterization of conserved combined T and B cell epitopes in Leptospira interrogans major outer membrane proteins OmpL1 and LipL41. Bmc Microbiol. 2011, 11, 21:1–21:9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haake, D.A.; Mazel, M.K.; McCoy, A.M.; Milward, F.; Chao, G.; Matsunaga, J.; Wagar, E.A. Leptospiral outer membrane proteins OmpL1 and LipL41 exhibit synergistic immunoprotection. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 6572–6582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, N.; Watanabe, H. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel leptospiral lipoprotein with OmpA domain. Fems Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 226, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaniappan, R.U.M.; Chang, Y.F.; Jusuf, S.S.D.; Artiushin, S.; Timoney, J.F.; McDonough, S.P.; Barr, S.C.; Divers, T.J.; Simpson, K.W.; McDonough, P.L.; et al. Cloning and molecular characterization of an immunogenic LigA protein of Leptospira interrogans. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 5924–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Palaniappan, R.U.M.; Chang, Y.F.; Hassan, F.; McDonough, S.P.; Pough, M.; Barr, S.C.; Simpson, K.W.; Mohammed, H.O.; Shin, S.; McDonough, P.; et al. Expression of leptospiral immunoglobulin-like protein by Leptospira interrogans and evaluation of its diagnostic potential in a kinetic ELISA. J. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cerqueira, G.M.; McBride, A.J.A.; Picardeau, M.; Ribeiro, S.G.; Moreira, Â.N.; Morel, V.; Reis, M.G.; Ko, A.I.; Dellagostin, O.A. Distribution of the leptospiral immunoglobulin-like (lig) genes in pathogenic Leptospira species and application of ligB to typing leptospiral isolates. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isberg, R.R.; Voorhis, D.L.; Falkow, S. Identification of invasin: A protein that allows enteric bacteria to penetrate cultured mammalian cells. Cell 1987, 50, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerse, A.E.; Yu, J.; Tall, B.D.; Kaper, J.B. A genetic locus of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli necessary for the production of attaching and effacing lesions on tissue culture cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 7839–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, J.; Lo, M.; Bulach, D.M.; Zuerner, R.L.; Adler, B.; Haake, D.A. Response of Leptospira interrogans to physiologic osmolarity: Relevance in signaling the environment-to-host transition. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 2864–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, J.; Sanchez, Y.; Xu, X.; Haake, D.A. Osmolarity, a key environmental signal controlling expression of leptospiral proteins LigA and LigB and the extracellular release of LigA. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.P.; Chang, Y.F. A domain of the Leptospira LigB contributes to high affinity binding of fibronectin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 362, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croda, J.; Ramos, J.G.R.; Matsunaga, J.; Queiroz, A.; Homma, A.; Riley, L.W.; Haake, D.A.; Reis, M.G.; Ko, A.I. Leptospira immunoglobulin-like proteins as a serodiagnostic marker for acute leptospirosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 1528–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, N.; Watanabe, H. Leptospiral immunoglobulin-like proteins elicit protective immunity. Vaccine 2004, 22, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.S.; Abreu, P.A.E.; Neves, F.O.; Atzingen, M.V.; Watanabe, M.M.; Vieira, M.L.; Morais, Z.M.; Vasconcellos, S.A.; Nascimento, A.L.T.O. A newly identified leptospiral adhesin mediates attachment to laminin. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 6356–6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Hellwage, J.; Artiushin, S.; Zipfel, P.F.; Kraiczy, P.; Timoney, J.F.; Stevenson, B. LfhA, a novel factor H-binding protein of Leptospira interrogans. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 2659–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zipfel, P.F.; Skerka, C.; Hellwage, J.; Jokiranta, S.T.; Meri, S.; Brade, V.; Kraiczy, P.; Noris, M.; Remuzzi, G. Factor H family proteins: On complement, microbes and human diseases. In Proceedings of the Biochemical Society Transactions. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2002, 30, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, M.L.; Vasconcellos, S.A.; Gonçales, A.P.; De Morais, Z.M.; Nascimento, A.L.T.O. Plasminogen acquisition and activation at the surface of Leptospira species lead to fibronectin degradation. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 4092–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, M.L.; Atzingen, M.V.; Oliveira, R.; Mendes, R.S.; Domingos, R.F.; Vasconcellos, S.A.; Nascimento, A.L.T.O. Plasminogen binding proteins and plasmin generation on the surface of Leptospira spp.: The contribution to the bacteria-host interactions. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 758513:1–758513:17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takabe, K.; Tahara, H.; Islam, M.S.; Affroze, S.; Kudo, S.; Nakamura, S. Viscosity-dependent variations in the cell shape and swimming manner of Leptospira. Microbiology 2017, 163, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Motaleb, M.A.; Sal, M.; Goldstein, S.F.; Charon, N.W. Spirochete periplasmic flagella and motility. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 2, 345–354. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie, A.E.; Ellinghausen, H.C. Electron Microscopy of Leptospires. I. Anatomical Features of Leptospira pomona. J. Bacteriol. 1965, 89, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A.; Picardeau, M.; Haake, D.A.; Sermswan, R.W.; Srikram, A.; Adler, B.; Murray, G.A. Flaa proteins in Leptospira interrogans are essential for motility and virulence but are not required for formation of the flagellum sheath. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 2019–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillot, J.; Ryter, A. Structure des spirochètes. 1. Etude des generes Treponema, Borrelia et Leptospira au microscope electronique [Structure of spirochetes. 1. Study of the genera Treponema, Borrelia and Leptospira by the electron microscope]. Ann. Inst. Pasteur 1965, 108, 791–804. [Google Scholar]
- Listgarten, M.A.; Socransky, S.S. Electron Microscopy of Axial Fibrils, Outer Envelope, and Cell Division of Certain Oral Spirochetes. J. Bacteriol. 1964, 88, 1087–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raddi, G.; Morado, D.R.; Yan, J.; Haake, D.A.; Yang, X.F.; Liu, J. Three-dimensional structures of pathogenic and saprophytic leptospira species revealed by cryo-electron tomography. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Norris, S.J.; Liu, J. Molecular architecture of the bacterial flagellar motor in cells. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 4323–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, K.H.; Zhao, X.; Manne, A.; Wang, J.; Yu, Z.; Liu, J.; Motaleb, M.A. Spirochetes flagellar collar protein FlbB has astounding effects in orientation of periplasmic flagella, bacterial shape, motility, and assembly of motors in Borrelia burgdorferi. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 102, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourhy, P.; Collet, L.; Clément, S.; Huerre, M.; Ave, P.; Giry, C.; Pettinelli, F.; Picardeau, M. Isolation and characterization of new Leptospira genotypes from patients in Mayotte (Indian Ocean). Plos Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e724:1–e724:10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogensen, T.H. Pathogen recognition and inflammatory signaling in innate immune defenses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 240–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isogai, E.; Isogai, H.; Kurebayashi, Y.; Ito, N. Biological activities of Leptospiral Lipopolysaccharide. Zent. Für Bakteriol. Mikrobiol. Und Hyg. Abt. 1 Orig. A 1986, 261, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulach, D.M.; Kalambaheti, T.; de la Peña-Moctezuma, A.; Adler, B. Lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis in Leptospira. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 2, 375–380. [Google Scholar]
- Nally, J.E.; Chow, E.; Fishbein, M.C.; Blanco, D.R.; Lovett, M.A. Changes in lipopolysaccharide O antigen distinguish acute versus chronic Leptospira interrogans infections. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 3251–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, Y.; Yanagawa, R. Inhibition of leptospiral agglutination by the type specific main antigens of leptospiras. Infect. Immun. 1977, 17, 466–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faine, S.; Vanderhoeden, J. Virulence-Linked Colonial and Morphological Variation in Leptospira. J. Bacteriol. 1964, 88, 1493–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, B.; Faine, S.; Yanagawa, R. Comparative studies on two antigens (F4 and TM) extracted from leptospires. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1980, 12, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinaiphat, A.; Thongboonkerd, V. Heat Shock Proteins in Leptospirosis. In Heat Shock Proteins in Veterinary Medicine and Sciences; Asea, A.A., Kaur, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Basel, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 361–374. [Google Scholar]
- Natarajaseenivasan, K.; Shanmughapriya, S.; Velineni, S.; Artiushin, S.C.; Timoney, J.F. Cloning, Expression, and Homology Modeling of GroEL Protein from Leptospira interrogans Serovar Autumnalis Strain N2. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2011, 9, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzingen, M.V.; Rodriguez, D.; Siqueira, G.H.; Leite, L.C.C.; Nascimento, A.L.T.O. Induction of boosted immune response in mice by leptospiral surface proteins expressed in fusion with DnaK. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 564285:1–564285:11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelista, K.V.; Coburn, J. Leptospira as an emerging pathogen: A review of its biology, pathogenesis and host immune responses. Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 1413–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-Pinheiro, M.P.; Schons-Fonseca, L.F.; Da Silva, J.B.; Domingos, R.H.; Santos Momo, L.H.; Quirino Simões, A.C.; Lee Ho, P.; Da Costa, R.M.A. Genomic survey and expression analysis of DNA repair genes in the genus Leptospira. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2016, 291, 703–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouts, D.E.; Matthias, M.A.; Adhikarla, H.; Adler, B.; Amorim-Santos, L.; Berg, D.E.; Bulach, D.; Buschiazzo, A.; Chang, Y.F.; Galloway, R.L.; et al. What Makes a Bacterial Species Pathogenic?:Comparative Genomic Analysis of the Genus Leptospira. PLos Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004403:1–e0004403:57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haake, D.A.; Levett, P.N. Leptospirosis in humans. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 387, 65–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charon, N.W.; Greenberg, E.P.; Koopman, M.B.H.; Limberger, R.J. Spirochete chemotaxis, motility, and the structure of the spirochetal periplasmic flagella. Res. Microbiol. 1992, 143, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, E.J.; Galloway, R.; Shadomy, S.V.; Wannemuehler, K.; Atrubin, D.; Blackmore, C.; Wofford, T.; Wilikins, P.P.; Ari, M.D.; Harris, L.; et al. Outbreak of leptospirosis among adventure race participants in Florida, 2005. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwachui, M.A.; Crump, L.; Hartskeerl, R.; Zinsstag, J.; Hattendorf, J. Environmental and Behavioural Determinants of Leptospirosis Transmission: A Systematic Review. PLos Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003843:1–e0003843:15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Khong, N.V.; Xuan, H.N.; Nghia, V.B.; Nguyen-Viet, H.; Grace, D. Sero-prevalence of specific Leptospira serovars in fattening pigs from 5 provinces in Vietnam. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 125:1–125:7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, B.Y.; Lee, K.W.; Ha, T.Y. Seroprevalence of Leptospira spp. in Clinically Healthy Racing Horses in Korea. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2010, 72, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Verma, A.; Stevenson, B.; Adler, B. Leptospirosis in horses. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 167, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, B.C.; Grapiglia, J.B.; Moreira, L.; Jaeger, L.H.; Carvalho-Costa, F.A.; Lilenbaum, W. Occurrence of uterine carriers for Leptospira interrogans on slaughtered cows. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 114, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant’Anna, R.; Vieira, A.S.; Grapiglia, J.; Lilenbaum, W. High number of asymptomatic dogs as leptospiral carriers in an endemic area indicates a serious public health concern. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 1852–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurilung, A.; Keeratipusan, C.; Suriyaphol, P.; Prapasarakul, N. Draft genome sequence of a Leptospira interrogans strain isolated from the urine of an asymptomatic dog in Thailand. Genome Announc. 2018, 6, e01140-17:1–e01140-17:2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levett, P.N.; Morey, R.E.; Galloway, R.L.; Steigerwalt, A.G. Leptospira broomii sp. nov., isolated from humans with leptospirosis. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 671–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, D.; Figueira, C.P.; Zhan, L.; Pertile, A.C.; Pedra, G.G.; Gusmão, I.M.; Wunder, E.A.; Rodrigues, G.; Ramos, E.A.G.; Ko, A.I.; et al. Leptospira in breast tissue and milk of urban Norway rats (Rattus norvegicus). Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 37, 3147–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, N.A.; Fitzgerald, W.R. Leptospirosis—Can it be a sexually transmitted disease? Postgrad. Med. J. 1988, 64, 163–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.L.; Townell, N.; Stephenson, E.; van den Berg, D.; Craig, S.B. Leptospirosis: An important zoonosis acquired through work, play and travel. Aust. J. Gen. Pract. 2018, 47, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharti, A.R.; Nally, J.E.; Ricaldi, J.N.; Matthias, M.A.; Diaz, M.M.; Lovett, M.A.; Levett, P.N.; Gilman, R.H.; Willig, M.R.; Gotuzzo, E.; et al. Leptospirosis: A zoonotic disease of global importance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2003, 3, 757–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banfi, E.; Cinco, M.; Bellini, M.; Soranzo, M.R. The role of antibodies and serum complement in the interaction between macrophages and leptospires. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1982, 128, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Que-Gewirth, N.L.S.; Ribeiro, A.A.; Kalb, S.R.; Cotter, R.J.; Bulach, D.M.; Adler, B.; Saint Girons, I.; Werts, C.; Raetz, C.R.H. A methylated phosphate group and four amide-linked acyl chains in Leptospira interrogans lipid A: The membrane anchor of an unusual lipopolysaccharide that activates TLR2. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 25420–25429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goris, M.G.A.; Wagenaar, J.F.P.; Hartskeerl, R.A.; van Gorp, E.C.M.; Schuller, S.; Monahan, A.M.; Nally, J.E.; van der Poll, T.; van’t Veer, C. Potent Innate Immune Response to Pathogenic Leptospira in Human Whole Blood. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18279:1–e18279:10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Li, S.; Ojcius, D.M.; Liao, S.; Li, L.; Xue, F.; Dong, H.; Yan, J. Replication or death: Distinct fates of pathogenic Leptospira strain Lai within macrophages of human or mouse origin. Innate Immun. 2010, 16, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, C.; Okura, N.; Takayama, C.; Suzuki, T. Characteristic features of intracellular pathogenic Leptospira in infected murine macrophages. Cell. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1783–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barocchi, M.A.; Ko, A.I.; Galvão Reis, M.; McDonald, K.L.; Riley, L.W. Rapid translocation of polarized MDCK cell monolayers by Leptospira interrogans, an invasive but nonintracellular pathogen. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 6926–6932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, G.L. The molecular basis of leptospiral pathogenesis. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 387, 139–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, L.G.; Siqueira, G.H.; Teixeira, A.R.F.; Silva, L.P.; Figueredo, J.M.; Cosate, M.R.; Vieira, M.L.; Nascimento, A.L.T.O. Leptospira spp.: Novel insights into host–pathogen interactions. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2016, 176, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, W.; Li, L.; Mao, Y.; Yan, J. Pathogenesis of leptospirosis: Interaction of Leptospira interrogans with in vitro cultured mammalian cells. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2007, 196, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Ojcius, D.M.; Sun, D.; Zhao, J.; Lin, X.; Li, L.; Li, L.; Yan, J. The mammalian cell entry (Mce) protein of pathogenic Leptospira species is responsible for RGD motif-dependent infection of cells and animals. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 83, 1006–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, B. Pathogenesis of leptospirosis: Cellular and molecular aspects. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 172, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satiya, J.; Gupta, N.M.; Parikh, M.P. Weil’s Disease: A Rare Cause of Jaundice. Cureus 2020, 12, e8428:1–e8428:4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, A.L.T.O.; Ko, A.I.; Martins, E.A.L.; Monteiro-Vitorello, C.B.; Ho, P.L.; Haake, D.A.; Verjovski-Almeida, S.; Hartskeerl, R.A.; Marques, M.V.; Oliveira, M.C.; et al. Comparative Genomics of Two Leptospira interrogans Serovars Reveals Novel Insights into Physiology and Pathogenesis. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 2164–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagliero, J.; Villanueva, S.Y.A.M.; Matsui, M. Leptospirosis Pathophysiology: Into the Storm of Cytokines. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 204:1–204:8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikarla, H.; Wunder, E.A.; Mechaly, A.E.; Mehta, S.; Wang, Z.; Santos, L.; Bisht, V.; Diggle, P.; Murray, G.; Adler, B.; et al. Lvr, a Signaling System That Controls Global Gene Regulation and Virulence in Pathogenic Leptospira. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 45:1–45:13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, N.M.P.; Galloway, R.; Blau, D.M.; Traxler, R.; Bhatnagar, J.; Zaki, S.R.; Rivera, A.; Torres, J.V.; Noyd, D.; Santiago-Albizu, X.E.; et al. Case report: Case series of fatal Leptospira spp./dengue virus co-infections - Puerto Rico, 2010–2012. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 91, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachu, A.; Madhavan, A.; Vasudevan, A.; Vasudevapanicker, J. Prevalence of dengue and leptospirosis co-infection in a tertiary care hospital in south india. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2018, 10, 227–232. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, K.; Latha, P.; Kalawat, U. Coinfection of leptospirosis and dengue fever at a tertiary care center in South India. Sch. Res. J. 2012, 2, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawal, G.; Yadav, S.; Kumar, R. Zika virus: An overview. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2016, 5, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neaterour, P.; Rivera, A.; Galloway, R.L.; Negrón, M.G.; Rivera-Garcia, B.; Sharp, T.M. Case report: Fatal Leptospira spp./Zika virus coinfection-Puerto Rico, 2016. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 97, 1085–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biron, A.; Cazorla, C.; Amar, J.; Pfannstie, A.; Dupont-Rouzeyrol, M.; Goarant, C. Zika virus infection as an unexpected finding in a leptospirosis patient. JMM Case Rep. 2016, 3, e005033:1–e005033:4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsrichanalai, C.; Murray, C.K.; Gray, M.; Miller, R.S.; McDaniel, P.; Liao, W.J.; Pickard, A.L.; Magill, A.J. Co-infection with malaria and leptospirosis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2003, 68, 583–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markotić, A.; Kuzman, I.; Babić, K.; Gagro, A.; Ksiazek, T.G.; Rabatić, S.; Dekaris, D.; Nichol, S. Double Trouble: Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome and Leptospirosis. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunil-Chandra, N.P.; Clement, J.; Maes, P.; De Silva, H.J.; Van Esbroeck, M.; Van Ranst, M. Concomitant leptospirosis-hantavirus co-infection in acute patients hospitalized in Sri Lanka: Implications for a potentially worldwide underestimated problem. Epidemiol. Infect. 2015, 143, 2081–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, C.D.; Yasuda, S.P.; Nishio, S.; Kularatne, S.A.; Weerakoon, K.; Rajapakse, J.; Nwafor-Okoli, C.; Lee, R.B.; Obayashi, Y.; Yoshimatsu, K.; et al. Serological evidence of Thailand virus-related hantavirus infection among suspected leptospirosis patients in Kandy, Sri Lanka. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 64, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Sonthayanon, P.; Chierakul, W.; Wuthiekanun, V.; Limmathurotsakul, D.; Amornchai, P.; Smythe, L.D.; Day, N.P.; Peacock, S.J. Short report: Molecular confirmation of co-infection by pathogenic leptospira spp. and orientia tsutsugamushi in patients with acute febrile illness in Thailand. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 89, 797–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, G.; Jongsakul, K.; Suttinont, C. Possible scrub typhus coinfections in Thai agricultural workers hospitalized with leptospirosis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2003, 68, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arean, V.M. The pathologic anatomy and pathogenesis of fatal human leptospirosis (Weil’s disease). Am. J. Pathol. 1962, 40, 393–423. [Google Scholar]
- Daher, E.F.; Lima, R.S.A.; Silva Júnior, G.B.; Silva, E.C.; Karbage, N.N.N.; Kataoka, R.S.; Carvalho Júnior, P.C.; Magalhães, M.M.; Mota, R.M.S.; Libório, A.B. Clinical presentation of leptospirosis: A retrospective study of 201 patients in a metropolitan city of Brazil. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 14, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koe, S.L.L.; Tan, K.T.; Tan, T.C. Leptospirosis in pregnancy with pathological fetal cardiotocography changes. Singap. Med. J. 2014, 55, e20–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, G.A. Human leptospirosis. Medicine 1960, 39, 117–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budihal, S.V.; Perwez, K. Leptospirosis diagnosis: Competancy of various laboratory tests. J. Clin. Diagnos. Res. 2014, 8, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaki, P. Clinical Laboratory Diagnosis of Human Leptospirosis. Int. J. Enteric Pathog. 2016, 4, e31859:1–e31859:7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Levett, P.N.; Branch, S.L.; Whittington, C.U.; Edwards, C.N.; Paxton, H. Two methods for rapid serological diagnosis of acute leptospirosis. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2001, 8, 349–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.D.; Carrington, D.G.; Gravekamp, C.; Van De Kemp, H.; Edwards, C.N.; Jones, S.R.; Prussia, P.R.; Garriques, S.; Terpstra, W.J.; Levett, P.N. Direct detection of leptospiral material in human postmortem samples. Res. Microbiol. 2003, 154, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysocki, J.; Liu, Y.; Shores, N. Leptospirosis with Acute Liver Injury. Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent. Proc. 2014, 27, 257–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thresiamma, K.C.; Biju, A.; Chaurasia, R.; Sritharan, M.; Jayaprakash, C.; Thomas, S.; Eapen, C.K. Proteinuria in early detection of human leptospirosis. Int. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2017, 5, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuerner, R.L. Host response to Leptospira infection. In Leptospira and Leptospirosis; Adler, B., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidenberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 223–250. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, J.; Suryavanshi, M. Thrombocytopenia in leptospirosis and role of platelet transfusion. Asian J. Transfus. Sci. 2007, 1, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galton, M.M.; Powers, D.K.; Hall, A.D.; Cornell, R.G. A rapid macroscopic slide screening test for the serodiagnosis of leptospirosis. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1958, 19, 505–512. [Google Scholar]
- Musso, D.; La Scola, B. Laboratory diagnosis of leptospirosis: A challenge. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2013, 46, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirathaworn, C.; Inwattana, R.; Poovorawan, Y.; Suwancharoen, D. Interpretation of microscopic agglutination test for leptospirosis diagnosis and seroprevalence. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 4, S162–S164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizer, J.; Grahlmann, M.; Hapke, H.; Velineni, S.; Lin, D.; Kohn, B. Evaluation of a rapid IgM detection test for diagnosis of acute leptospirosis in dogs. Vet. Rec. 2017, 180, 517:1–517:5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baburaj, P.; Nandkumar, V.S.; Khanna, L. Polymerase chain reaction in the diagnosis of leptospiral infection. J. Assoc. Phys. India 2006, 54, 339–340. [Google Scholar]
- Wynwood, S.J.; Burns, M.-A.A.; Graham, G.C.; Weier, S.L.; McKay, D.B.; Craig, S.B. Validation of a Microsphere Immunoassay for Serological Leptospirosis Diagnosis in Human Serum by Comparison to the Current Gold Standard. Plos Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003636:1–e0003636:13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpstra, W.J.; Ligthart, G.S.; Schoone, G.J. ELISA for the detection of specific IgM and IgG in human leptospirosis. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1985, 131, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, E.G.; van Houten, M.; van der Donk, J.A.; Frik, J.F. Serodiagnosis of canine leptospirosis by solid-phase enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1984, 7, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, B.; Murphy, A.M.; Locarnini, S.A.; Faine, S. Detection of specific anti-leptospiral immunoglobulins M and G in human serum by solid-phase enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1980, 11, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desakorn, V.; Wuthiekanun, V.; Thanachartwet, V.; Sahassananda, D.; Chierakul, W.; Apiwattanaporn, A.; Day, N.P.; Limmathurotsakul, D.; Peacock, S.J. Accuracy of a commercial IgM ELISA for the diagnosis of human leptospirosis in Thailand. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2012, 86, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekatkar, S.; Harish, B.N.; Parija, S.C. IgM Dot-ELISA Assay using prevalent Leptospira strain for diagnosis of leptospirosis. Parija Sc Int. J. Collab. Res. Intern. Med. Public Health 2010, 2, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, M.I.; dos Reis, M.F.; Simon, C.; Dondossola, E.; Alexandre, M.C.; Colonetti, T.; Meller, F.O. ELISA IgM para diagnóstico de leptospirose: Revisão sistemática e meta-análise. Cienc. E Saude Coletiva 2017, 22, 4001–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandão, A.P.; Camargo, E.D.; Da Silva, E.D.; Silva, M.V.; Abrão, R.V. Macroscopic agglutination test for rapid diagnosis of human leptospirosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 3138–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levett, P.N.; Whittington, C.U. Evaluation of the indirect hemagglutination assay for diagnosis of acute leptospirosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajani, M.D.; Ashford, D.A.; Bragg, S.L.; Woods, C.W.; Aye, T.; Spiegel, R.A.; Plikaytis, B.D.; Perkins, B.A.; Phelan, M.; Levett, P.N.; et al. Evaluation of four commercially available rapid serologic tests for diagnosis of leptospirosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatta, M.; Smits, H.L.; Gussenhoven, G.C.; Gooskens, J. Introduction of a rapid dipstick assay for the detection of leptospira-specific immunoglobulin M antibodies in the laboratory diagnosis of leptospirosis in a hospital in Makassar, Indonesia. Southeast. Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2000, 31, 515–520. [Google Scholar]
- Gussenhoven, G.C.; Van Der Hoorn, M.A.W.G.; Goris, M.G.A.; Terpstra, W.J.; Hartskeerl, R.A.; Mol, B.W.; Van Ingen, C.W.; Smits, H.L. LEPTO dipstick, a dipstick assay for detection of Leptospira-specific immunoglobulin M antibodies in human sera. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzur, A.; Moore, J.K.; Jorgensen, P.; Shapiro, H.M.; Kirschner, M.W. Optimizing Optical Flow Cytometry for Cell Volume-Based Sorting and Analysis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16053:1–e16053:9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adan, A.; Alizada, G.; Kiraz, Y.; Baran, Y.; Nalbant, A. Flow cytometry: Basic principles and applications. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headland, S.E.; Jones, H.R.; D’Sa, A.S.V.; Perretti, M.; Norling, L.V. Cutting-edge analysis of extracellular microparticles using imagestreamx imaging flow cytometry. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinnon, K.M. Flow cytometry: An overview. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2018, 2018, 5.1.1–5.1.11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yitzhaki, S.; Barnea, A.; Keysary, A.; Zahavy, E. New approach for serological testing for leptospirosis by using detection of leptospira agglutination by flow cytometry light scatter analysis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 1680–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lovitt, R.W.; Wright, C.J. Microscopy: Light Microscopy. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Batt, C.A., Tortorello, M.L., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 684–692. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekaran, S.; Gomathi, S. A standard screening test for the early and rapid diagnosis of leptospirosis. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 22, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gunasekara, C.P.; Sumaiha, M.H.F.; Damayanthi, M.K.S.; Weerasekera, M.M.; Fernando, S.S.N. Utility of a modified silver staining technique for detection of Leptospira. Sri Lankan J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 7, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, S.; Kheirandish, R.; Rahimi, E. Comparison of polymerase chain reaction and Warthin-Starry techniques to detect Leptospira spp. in kidneys of slaughtered cattle. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2014, 81, e1–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wild, C.J.; Greenlee, J.J.; Bolin, C.A.; Barnett, J.K.; Haake, D.A.; Cheville, N.F. An improved immunohistochemical diagnostic technique for canine leptospirosis using antileptospiral antibodies on renal tissue. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2002, 14, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mythri, B.A. Laboratory Diagnosis of Leptospirosis: A Review. J. Evol. Med. Dent. Sci. 2015, 4, 8759–8769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellinghausen, H.C.; Mccullough, W.G. Nutrition of Leptospira Pomona And Growth of 13 Other Serotypes: A Serum-Free Medium Employing Oleic Albumin Complex. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1965, 26, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Miraglia, F.; De Moraes, Z.M.; Melville, P.A.; Dias, R.A.; Vasconcellos, S.A. Emjh medium with 5-fluorouracil and nalidixic acid associated with serial dilution technique used to recover leptospira spp from experimentally contaminated bovine semen. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2009, 40, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bal, A.E.; Gravekamp, C.; Hartskeerl, R.A.; De Meza-Brewster, J.; Korver, H.; Terpstra, W.J. Detection of leptospires in urine by PCR for early diagnosis of leptospirosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 1894–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafighi, T.; Zahraei Salehi, T.; Abdollahpour, G.; Asadpour, L.; Akbarein, H.; Salehzadeh, A. Molecular detection of Leptospira spp. in the urine of cattle in northern Iran. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2014, 15, 402–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savio, M.L.; Rossi, C.; Fusi, P.; Tagliabue, S.; Pacciarini, M.L. Detection and identification of Leptospira interrogans serovars by PCR coupled with restriction endonuclease analysis of amplified DNA. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.D.; Gravekamp, C.; Carrington, D.G.; Van De Kemp, H.; Hartskeerl, R.A.; Edwards, C.N.; Everard, C.O.R.; Terpstra, W.J.; Levett, P.N. Evaluation of the polymerase chain reaction for early diagnosis of leptospirosis. J. Med. Microbiol. 1995, 43, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villumsen, S.; Pedersen, R.; Krogfelt, K.A.; Jensen, J.S. Expanding the Diagnostic Use of PCR in Leptospirosis: Improved Method for DNA Extraction from Blood Cultures. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12095:1–e12095:7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merien, F.; Portnoi, D.; Bourhy, P.; Charavay, F.; Berlioz-Arthaud, A.; Baranton, G. A rapid and quantitative method for the detection of Leptospira species in human leptospirosis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 249, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajaseenivasan, K.; Raja, V.; Narayanan, R. Rapid diagnosis of leptospirosis in patients with different clinical manifestations by 16S rRNA gene based nested PCR. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 19, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassi, F.; Seixas, F.K.; Dorneles Jouglard, S.D.; Simionatto, S.; Silva, E.F.; Seyffert, N.; Brod, C.S.; Dellagostin, O.A. Leptospirosis diagnosis using nested-PCR. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2003, 34, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Blanco, R.M.; Romero, E.C. Evaluation of nested polymerase chain reaction for the early detection of Leptospira spp. DNA in serum samples from patients with leptospirosis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 78, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, V.K. Leptospirosis: A re-emerging infection. Malays. J. Pathol. 2011, 33, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gasem, M.H.; Hadi, U.; Alisjahbana, B.; Tjitra, E.; Hapsari, M.M.D.E.A.H.; Lestari, E.S.; Aman, A.T.; Lokida, D.; Salim, G.; Kosasih, H.; et al. Leptospirosis in Indonesia: Diagnostic challenges associated with atypical clinical manifestations and limited laboratory capacity. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 179:1–179:11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, N.; Nakajima, C.; Harunari, T.; Tanikawa, T.; Tokiwa, T.; Uchimura, E.; Furuya, T.; Mingala, C.N.; Villanueva, M.A.; Ohnishi, M.; et al. A new loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for rapid, simple, and sensitive detection of Leptospira spp. in urine. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2072–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasdell, K.R.; Morand, S.; Perera, D.; Firth, C. Association of rodent-borne Leptospira spp. with urban environments in Malaysian Borneo. Plos Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007141:1–e0007141:17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roqueplo, C.; Kodjo, A.; Demoncheaux, J.P.; Scandola, P.; Bassene, H.; Diatta, G.; Sokhna, C.; Raoult, D.; Davoust, B.; Mediannikov, O. Leptospirosis, one neglected disease in rural Senegal. Vet. Med. Sci. 2019, 5, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nozmi, N.; Samsudin, S.; Sukeri, S.; Shafei, M.N.; Wan Mohd, W.; Idris, Z.; Arifin, W.N.; Idris, N.; Saudi, S.; Abdullah, N.M.; et al. Low Levels of Knowledge, Attitudes and Preventive Practices on Leptospirosis among a Rural Community in Hulu Langat District, Selangor, Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierque, E.; Thibeaux, R.; Girault, D.; Soupé-Gilbert, M.E.; Goarant, C. A systematic review of Leptospira in water and soil environments. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227055:1–e0227055:22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samrot, A.V.; Sean, T.C.; Bhavya, K.S.; Sahithya, C.S.; Chan-drasekaran, S.; Palanisamy, R.; Robinson, E.R.; Subbiah, S.K.; Mok, P.L. Leptospiral Infection, Pathogenesis and Its Diagnosis—A Review. Pathogens 2021, 10, 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020145
Samrot AV, Sean TC, Bhavya KS, Sahithya CS, Chan-drasekaran S, Palanisamy R, Robinson ER, Subbiah SK, Mok PL. Leptospiral Infection, Pathogenesis and Its Diagnosis—A Review. Pathogens. 2021; 10(2):145. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020145
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamrot, Antony V., Tan Chuan Sean, Karanam Sai Bhavya, Chamarthy Sai Sahithya, SaiPriya Chan-drasekaran, Raji Palanisamy, Emilin Renitta Robinson, Suresh Kumar Subbiah, and Pooi Ling Mok. 2021. "Leptospiral Infection, Pathogenesis and Its Diagnosis—A Review" Pathogens 10, no. 2: 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020145
APA StyleSamrot, A. V., Sean, T. C., Bhavya, K. S., Sahithya, C. S., Chan-drasekaran, S., Palanisamy, R., Robinson, E. R., Subbiah, S. K., & Mok, P. L. (2021). Leptospiral Infection, Pathogenesis and Its Diagnosis—A Review. Pathogens, 10(2), 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020145






