New Insights into Gastrointestinal and Pulmonary Parasitofauna of Wild Eurasian lynx (Lynx lynx) in the Harz Mountains of Germany
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Endoparasite Diversity and Prevalences
2.2. Molecular Analyses
2.2.1. Protozoa
2.2.2. Nematodes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
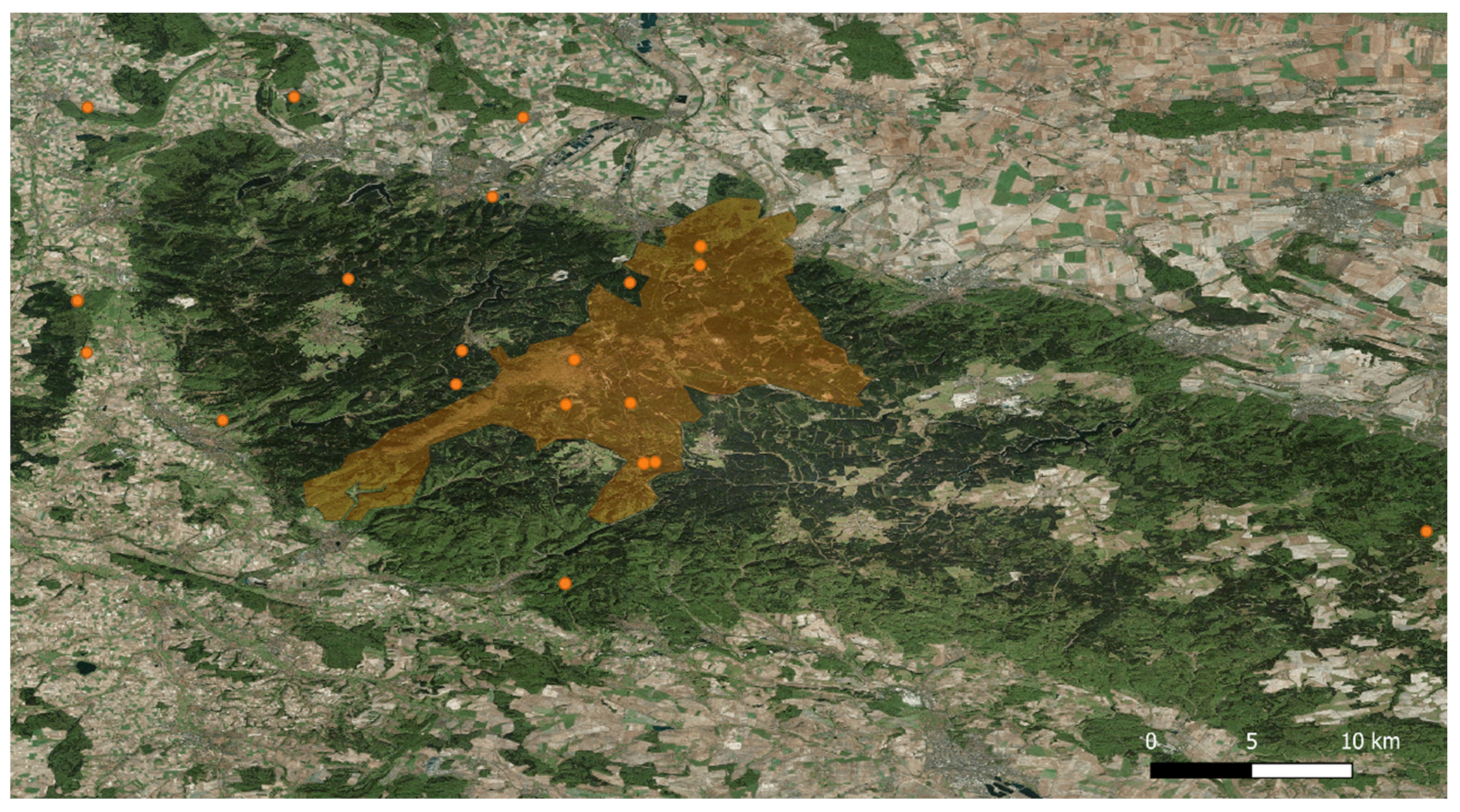
4.1. Study Area and Sampling Collection
4.2. Coprological Analyses
4.2.1. Microscopical Analyses
4.2.2. Coproantigen-ELISAs
4.2.3. Molecular Analyses
Protozoa
Nematodes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Port, M.; Henkelmann, A.; Schröder, F.; Waltert, M.; Middelhoff, L.; Anders, O.; Jokisch, S. Rise and Fall of a Eurasian Lynx (Lynx lynx) Stepping-Stone Population in Central Germany. Mammal Res. 2020, 66, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinig, H.; Boye, P.; Dähne, M.; Hutterer, R.; Lang, J. Rote Liste und Gesamtartenliste der Säugetiere (Mammalia) Deutschlands; Bundesamt für Naturschutz: Bonn-Bad Godesberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Reinhardt, I.; Kaczensky, P.; Knauer, F. Monitoring von Wolf, Luchs und Bär in Deutschland; BfN-Skripten; Bundesamt für Naturschutz: Bonn-Bad Godesberg, Germany, 2015; ISBN 978-3-89624-148-1. [Google Scholar]
- Bull, J.K.; Heurich, M.; Saveljev, A.P.; Schmidt, K.; Fickel, J.; Förster, D.W. The Effect of Reintroductions on the Genetic Variability in Eurasian Lynx Populations: The Cases of Bohemian–Bavarian and Vosges–Palatinian Populations. Conserv. Genet. 2016, 17, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchsvorkommen in Deutschland im Monitoringjahr 2019/2020 (1.5.2019–30.04.2020). 2021. Available online: https://www.bfn.de/sites/default/files/2021-04/2021_02_25_BfN_Luchs_kommentierte_Vorkommenskarte_bf.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Middelhoff, T.L.; Anders, O. Abundanz und Dichte des Luchses Im Östlichen Harz. Fotofallenmonitoring 2017; Nationalpark Harz: Wernigerode, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, S.A.; Reiners, T.E.; Middelhoff, T.L.; Anders, O.; Kasperkiewicz, A.; Nowak, C. The Rise of a Large Carnivore Population in Central Europe: Genetic Evaluation of Lynx Reintroduction in the Harz Mountains. Conserv. Genet. 2020, 21, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Posthaus, H.; Breitenmoser-Würsten, C.; Posthaus, H.; Bacciarini, L.; Breitenmoser, U. Causes of Mortality in Reintroduced Eurasian Lynx in Switzerland. J. Wildl. Dis. 2002, 38, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagrade, G.; Vismanis, K.; Kirjušina, M.; Ozoliņš, J. Preliminary Results on the Helminthofauna of the Eurasian Lynx (Lynx lynx) in Latvia. Acta Zool. Litu. 2003, 13, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagrade, G.; Králová-Hromadová, I.; Bazsalovicsová, E.; Radačovská, A.; Kołodziej-Sobocińska, M. The First Records of Spirometra erinaceieuropaei (Cestoda: Diphyllobothriidae), a Causative Agent of Human Sparganosis, in Latvian Wildlife. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 120, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdmann, H.; Moks, E.; Talvik, H. Helminth Fauna of Eurasian Lynx (Lynx lynx) in Estonia. J. Wildl. Dis. 2004, 40, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczęsna, J.; Popiołek, M.; Schmidt, K.; Kowalczyk, R. Coprological Study on Helminth Fauna in Eurasian Lynx (Lynx lynx) From the Białowieża Primeval Forest in Eastern Poland. J. Parasitol. 2008, 94, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deksne, G.; Laakkonen, J.; Näreaho, A.; Jokelainen, P.; Holmala, K.; Kojola, I.; Sukura, A. Endoparasites of the Eurasian Lynx (Lynx lynx) in Finland. J. Parasitol. 2013, 99, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kołodziej-Sobocińska, M.; Yakovlev, Y.; Schmidt, K.; Hurníková, Z.; Ruczyńska, I.; Bednarski, M.; Tokarska, M. Update of the Helminth Fauna in Eurasian Lynx (Lynx lynx) in Poland. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 2613–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kärssin, A.; Häkkinen, L.; Vilem, A.; Jokelainen, P.; Lassen, B. Trichinella spp. in Wild Boars (Sus scrofa), Brown Bears (Ursus arctos), Eurasian Lynxes (Lynx lynx) and Badgers (Meles meles) in Estonia, 2007–2014. Animals 2021, 11, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górski, P.; Zalewski, A.; Lakomy, M. Parasites of Carnivorous Mammals in Białowieza Primeval Forest. Wiad. Parazytol. 2006, 52, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Ryser-Degiorgis, M.-P.; Jakubek, E.-B.; Hård af Segerstad, C.; Bröjer, C.; Mörner, T.; Jansson, D.S.; Lundén, A.; Uggla, A. Serological Survey of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Free-Ranging Eurasian Lynx (Lynx lynx) from Sweden. J. Wildl. Dis. 2006, 42, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hurnikova, Z.; Miterpakova, M.; Chovancová, B. The Important Zoonoses in the Protected Areas of the Tatra National Park (TANAP). Wiad. Parazytol. 2009, 55, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ozoliņa, Z.; Bagrade, G.; Deksne, G. First Confirmed Case of Alaria alata Mesocercaria in Eurasian Lynx (Lynx lynx) Hunted in Latvia. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 759–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczęsna, J.; Popiołek, M.; Schmidt, K.; Kowalczyk, R. The First Record of Aelurostrongylus abstrusus (Angistrongylidae: Nematoda) in Eurasian Lynx (Lynx lynx L.) from Poland Based on Fecal Analysis. Wiad. Parazytol. 2006, 52, 321–322. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Crisi, P.E.; Di Cesare, A.; Boari, A. Feline Troglostrongylosis: Current Epizootiology, Clinical Features, and Therapeutic Options. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stunžėnas, V.; Binkienė, R. Description of Crenosoma vismani n. sp., Parasitic in the Lungs of Lynx lynx (L.) (Carnivora: Felidae), with Identification Key to the Species of the Genus Crenosoma Molin, 1861 (Nematoda: Crenosomatidae). Syst. Parasitol. 2020, 98, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traversa, D.; Morelli, S.; Di Cesare, A.; Diakou, A. Felid Cardiopulmonary Nematodes: Dilemmas Solved and New Questions Posed. Pathogens 2021, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, J.; Blasco-Costa, I. Molecular Evidence of Shared Hookworm Ancylostoma tubaeforme Haplotypes between the Critically Endangered Iberian Lynx and Sympatric Domestic Cats. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 186, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alić, A.; Traversa, D.; Duscher, G.G.; Kadrić, M.; Di Cesare, A.; Hodžić, A. Troglostrongylus brevior in an Eurasian Lynx (Lynx lynx) from Bosnia and Herzegovina. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deksne, G.; Segliņa, Z.; Jahundoviča, I.; Esīte, Z.; Bakasejevs, E.; Bagrade, G.; Keidāne, D.; Interisano, M.; Marucci, G.; Tonanzi, D.; et al. High Prevalence of Trichinella spp. in Sylvatic Carnivore Mammals of Latvia. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 231, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, C.F.; Schuppers, M.E.; Müller, N.; Ryser-Degiorgis, M.P.; Gottstein, B. Assessment of the Prevalence of Trichinella spp. in Red Foxes and Eurasian Lynxes from Switzerland. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 159, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajer, A.; Alsarraf, M.; Dwużnik, D.; Mierzejewska, E.J.; Kołodziej-Sobocińska, M.; Behnke-Borowczyk, J.; Banasiak, Ł.; Grzybek, M.; Tołkacz, K.; Kartawik, N.; et al. Rodents as Intermediate Hosts of Cestode Parasites of Mammalian Carnivores and Birds of Prey in Poland, with the First Data on the Life-Cycle of Mesocestoides melesi. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokelainen, P.; Deksne, G.; Holmala, K.; Näreaho, A.; Laakkonen, J.; Kojola, I.; Sukura, A. Free-Ranging Eurasian Lynx (Lynx lynx) as Host of Toxoplasma gondii in Finland. J. Wildl. Dis. 2013, 49, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, M. Feeding Ecology of Eurasian Lynx (Lynx lynx) in the Harz Mountains. Master’s Thesis, Faculty of Biology, Bielefeld University, Bielefeld, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Figueiredo, A.M.; de Carvalho, L.M.; González, M.J.P.; Torres, R.T.; Pla, S.; Núñez-Arjona, J.C.; Rueda, C.; Vallverdú-Coll, N.; Silvestre, F.; Peña, J.; et al. Parasites of the Reintroduced Iberian Lynx (Lynx pardinus) and Sympatric Mesocarnivores in Extremadura, Spain. Pathogens 2021, 10, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryser-Degiorgis, M.-P. Todesursachen und Krankheiten beim Luchs–Eine Übersicht; KORA Bericht Nr. 8; KORA: Bern, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Anders, O.; Middelhoff, T.L. The Development of the Harz Lynx Population. CATnews 2021, 14, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta, L.; Leon-Quinto, T.; Bornay-Llinares, F.; Simon, M.; Esteban, J. Helminth Parasites in Faecal Samples from the Endangered Iberian Lynx (Lynx pardinus). Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 179, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente, J.; Palomares, F.; Ruiz de Ibañez, R.; Ortiz, J. Epidemiology of Ancylostoma spp. in the Endangered Iberian Lynx (Lynx pardinus) in the Doñana National Park, South-West Spain. J. Helminthol. 2004, 78, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, J.; Naranjo, V.; Rodríguez, A.; de la Lastra, J.M.P.; Mangold, A.J.; de la Fuente, J. Prevalence of Infection and 18S RRNA Gene Sequences of Cytauxzoon Species in Iberian Lynx (Lynx pardinus) in Spain. Parasitology 2007, 134, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateo, M.; de Mingo, M.H.; de Lucio, A.; Morales, L.; Balseiro, A.; Espí, A.; Barral, M.; Lima Barbero, J.F.; Habela, M.Á.; Fernández-García, J.L.; et al. Occurrence and Molecular Genotyping of Giardia duodenalis and Cryptosporidium spp. in Wild Mesocarnivores in Spain. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 235, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, M.; Weckworth, J.; Wultsch, C.; Mesa, B.; Mills, L. Non-Invasive Sampling for Carnivores. In Carnivore Ecology and Conservation: A Handbook of Techniques; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 47–69. ISBN 978-0-19-955852-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ebmer, D.; Navarrete, M.J.; Muñoz, P.; Flores, L.M.; Gärtner, U.; Brabec, J.; Poppert, S.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C. Anthropozoonotic Parasites Circulating in Synanthropic and Pacific Colonies of South American Sea Lions (Otaria flavescens): Non-Invasive Techniques Data and a Review of the Literature. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dib, L.V.; Palmer, J.P.S.; de Souza Carvalho Class, C.; Pinheiro, J.L.; Ramos, R.C.F.; dos Santos, C.R.; Fonseca, A.B.M.; Rodríguez-Castro, K.G.; Gonçalves, C.F.; Galetti, P.M.; et al. Non-Invasive Sampling in Itatiaia National Park, Brazil: Wild Mammal Parasite Detection. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segeritz, L.; Cardona, A.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C.; Ruiz, A. Autochthonous Angiostrongylus cantonensis, Angiostrongylus vasorum and Aelurostrongylus abstrusus Infections in Native Terrestrial Gastropods from the Macaronesian Archipelago of Spain. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 2671–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Holland, C.V.; Wang, T.; Hofmann, A.; Fan, C.-K.; Maizels, R.M.; Hotez, P.J.; Gasser, R.B. Human Toxocariasis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, e14–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, M.; Payán, E.; Brabec, J.; Vélez, J.; Taubert, A.; Chaparro-Gutiérrez, J.J.; Hermosilla, C. Intestinal Parasites of Neotropical Wild Jaguars, Pumas, Ocelots, and Jaguarundis in Colombia: Old Friends Brought Back from Oblivion and New Insights. Pathogens 2021, 10, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Speer, C.A.; Fayer, R. Sarcocystosis of Animals and Man. In Sarcocystosis of Animals and Humans; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillova, V.; Prakas, P.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Gavarāne, I.; Fernández-García, J.L.; Martínez-González, M.; Rudaitytė-Lukošienė, E.; Martínez-Estéllez, M.Á.H.; Butkauskas, D.; Kirjušina, M. Identification and Genetic Characterization of Sarcocystis arctica and Sarcocystis lutrae in Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes) from Baltic States and Spain. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Rosenthal, B.M.; Sundar, N.; Velmurugan, G.V.; Beckmen, K.B. Sarcocystis arctosi sp. nov. (Apicomplexa, Sarcocystidae) from the Brown Bear (Ursus arctos), and Its Genetic Similarity to Schizonts of Sarcocystis canis-like Parasite Associated with Fatal Hepatitis in Polar Bears (Ursus maritimus). Acta Parasitol. 2007, 52, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjerde, B.; Schulze, J. Muscular Sarcocystosis in Two Arctic Foxes (Vulpes lagopus) Due to Sarcocystis arctica n. sp.: Sarcocyst Morphology, Molecular Characteristics and Phylogeny. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Liang, Y.; Hu, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y. First Isolation of Sarcocystis caninum Sarcocysts from Two Domestic Dogs (Canis familiaris) from China. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 3613–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, Y.L.; Chang, P.Y.; Tan, C.T.; Fong, M.Y.; Mahmud, R.; Wong, K.T. Sarcocystis nesbitti Infection in Human Skeletal Muscle: Possible Transmission from Snakes. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 90, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayer, R.; Esposito, D.H.; Dubey, J.P. Human Infections with Sarcocystis Species. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forest, T.W.; Abou-Madi, N.; Summers, B.A.; Tornquist, S.J.; Cooper, B.J. Sarcocystis neurona-like Encephalitis in a Canada Lynx (Felis lynx canadensis). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Zoo Vet. 2000, 31, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. A Review of Cystoisospora felis and C. rivolta-Induced Coccidiosis in Cats. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 263, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Houk, A.E.; Verma, S.K.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Humphreys, J.G.; Lindsay, D.S. Experimental Transmission of Cystoisospora felis-like Coccidium from Bobcat (Lynx rufus) to the Domestic Cat (Felis catus). Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 211, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diakou, A.; Psalla, D.; Migli, D.; Di Cesare, A.; Youlatos, D.; Marcer, F.; Traversa, D. First Evidence of the European Wildcat (Felis silvestris silvestris) as Definitive Host of Angiostrongylus chabaudi. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanović, O.; Diakou, A.; Morelli, S.; Paras, S.; Trbojević, I.; Nedic, D.; Sladojević, Ž.; Kasagić, D.; Di Cesare, A. Severe Verminous Pneumonia Caused by Natural Mixed Infection with Aelurostrongylus abstrusus and Angiostrongylus chabaudi in a European Wildcat from Western Balkan Area. Acta Parasitol. 2019, 64, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steeb, S.; Hirzmann, J.; Eskens, U.; Volmer, K.; Bauer, C. Lungenwurm-Infektionen bei der Europäischen Wildkatze. Kompakt Vet. 2014, 3, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Falsone, L.; Brianti, E.; Gaglio, G.; Napoli, E.; Anile, S.; Mallia, E.; Giannelli, A.; Poglayen, G.; Giannetto, S.; Otranto, D. The European Wildcats (Felis silvestris silvestris) as Reservoir Hosts of Troglostrongylus brevior (Strongylida: Crenosomatidae) Lungworms. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 205, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannelli, A.; Kirkova, Z.; Abramo, F.; Latrofa, M.S.; Campbell, B.; Zizzo, N.; Cantacessi, C.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Otranto, D. Angiostrongylus chabaudi in Felids: New Findings and a Review of the Literature. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 228, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimov, P.; Hermosilla, C.; Taubert, A.; Staubach, C.; Sauter-Louis, C.; Conraths, F.J.; Vrhovec, M.G.; Pantchev, N. GIS-Supported Epidemiological Analysis on Canine Angiostrongylus vasorum and Crenosoma vulpis Infections in Germany. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penagos-Tabares, F.; Lange, M.K.; Vélez, J.; Hirzmann, J.; Gutiérrez-Arboleda, J.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C.; Chaparro Gutiérrez, J.J. The Invasive Giant African Snail Lissachatina fulica as Natural Intermediate Host of Aelurostrongylus abstrusus, Angiostrongylus vasorum, Troglostrongylus brevior, and Crenosoma vulpis in Colombia. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Osorio, S.; Navarro-Ruiz, J.L.; Rave, A.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C.; Chaparro-Gutierrez, J.J. Aelurostrongylus abstrusus Infections in Domestic Cats (Felis silvestris catus) from Antioquia, Colombia. Pathogens 2021, 10, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jefferies, R.; Shaw, S.E.; Willesen, J.; Viney, M.E.; Morgan, E.R. Elucidating the Spread of the Emerging Canid Nematode Angiostrongylus vasorum between Palaearctic and Nearctic Ecozones. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2010, 10, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deak, G.; Gherman, C.M.; Ionică, A.M.; Vezendan, A.D.; D’Amico, G.; Matei, I.A.; Daskalaki, A.A.; Marian, I.; Damian, A.; Cozma, V.; et al. Angiostrongylus vasorum in Romania: An Extensive Survey in Red Foxes, Vulpes vulpes. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deak, G.; Ionică, A.M.; Mihalca, A.D.; Gherman, C.M. Troglostrongylus brevior: A New Parasite for Romania. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnyder, M.; Bilbrough, G.; Hafner, C.; Schaper, R. Angiostrongylus Vasorum, “The French Heartworm”: A Serological Survey in Dogs from France Introduced by a Brief Historical Review. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, M.K.; Penagos-Tabares, F.; Hirzmann, J.; Failing, K.; Schaper, R.; Van Bourgonie, Y.R.; Backeljau, T.; Hermosilla, C.; Taubert, A. Prevalence of Angiostrongylus vasorum, Aelurostrongylus abstrusus and Crenosoma vulpis Larvae in Native Slug Populations in Germany. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 254, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penagos-Tabares, F.; Groß, K.M.; Hirzmann, J.; Hoos, C.; Lange, M.K.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C. Occurrence of Canine and Feline Lungworms in Arion vulgaris in a Park of Vienna: First Report of Autochthonous Angiostrongylus vasorum, Aelurostrongylus abstrusus and Troglostrongylus brevior in Austria. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diakou, A.; Migli, D.; Dimzas, D.; Morelli, S.; Di Cesare, A.; Youlatos, D.; Lymberakis, P.; Traversa, D. Endoparasites of European Wildcats (Felis silvestris) in Greece. Pathogens 2021, 10, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krone, O.; Guminsky, O.; Meinig, H.; Herrmann, M.; Trinzen, M.; Wibbelt, G. Endoparasite Spectrum of Wild Cats (Felis silvestris Schreber, 1777) and Domestic Cats (Felis catus L.) from the Eifel, Pfalz Region and Saarland, Germany. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2008, 54, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoli, E.; Anile, S.; Arrabito, C.; Scornavacca, D.; Mazzamuto, M.V.; Gaglio, G.; Otranto, D.; Giannetto, S.; Brianti, E. Survey on Parasitic Infections in Wildcat (Felis silvestris silvestris Schreber, 1777) by Scat Collection. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pence, D.B.; Samoil, H.P.; Stone, J.E. Spirocercid Stomach Worms (Nematoda: Spirocercidae) from Wild Felids in North America. Can. J. Zool. 1978, 56, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, J.A.; Woodberry, K.; Gillin, C.M.; Jackson, D.H.; Sanders, J.L.; Madigan, W.; Bildfell, R.J.; Kent, M.L. Cylicospirura Species (Nematoda: Spirocercidae) and Stomach Nodules in Cougars (Puma concolor) and Bobcats (Lynx rufus) in Oregon. J. Wildl. Dis. 2011, 47, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seguel, M.; Gottdenker, N. The Diversity and Impact of Hookworm Infections in Wildlife. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2017, 6, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otranto, D.; Deplazes, P. Zoonotic Nematodes of Wild Carnivores. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 9, 370–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.; Addison, E.; Joachim, D.; Smith, L.; Quinn, N. Helminth Parasites of Canada Lynx (Felis Canadensis) from Northern Ontario. Can. J. Zool. 2011, 64, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, J.; Casanova, J.C. Helminth Parasites of the Endangered Iberian Lynx (Lynx pardinus) and Sympatric Carnivores. J. Helminthol. 2007, 81, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, O.; Kaphegyi, T.; Kubik, F. Untersuchungen Zum Dispersionsverhalten Eines Männlichen Luchses (Lynx lynx) Im Dreiländereck Zwischen Thüringen, Niedersachsen Und Hessen. Säugetierkd. Inf. 2012, 8, 455–462. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Scholten, T. A Fixative for Intestinal Parasites Permitting the Use of Concentration and Permanent Staining Procedures. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1977, 67, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.H.; Bullock, S.L.; Melvin, D.M.; Spruill, C.L. Ethyl Acetate as a Substitute for Diethyl Ether in the Formalin-Ether Sedimentation Technique. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1979, 10, 852–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heine, J. Eine Einfache Nachweismethode Für Kryptosporidien Im Kot. Zent. Vet. 1982, 29, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilhon, J.; Cens, B. Angiostrongylus vasorum (Baillet, 1866). Etude biologique et morphologique. Ann. Parasitol. Hum. Comp. 1973, 48, 567–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, R.; Roy, S.; Siddique, A.; Mondal, U.; Rahman, S.M.M.; Mondal, D.; Houpt, E.; Petri, W.A. Multiplex Real-Time PCR Assay for Detection of Entamoeba histolytica, Giardia intestinalis, and Cryptosporidium spp. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 76, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schares, G.; Joeres, M.; Rachel, F.; Tuschy, M.; Czirják, G.Á.; Maksimov, P.; Conraths, F.J.; Wachter, B. Molecular Analysis Suggests That Namibian Cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus) Are Definitive Hosts of a so Far Undescribed Besnoitia Species. Parasit. Vectors 2021, 14, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durant, J.-F.; Irenge, L.M.; Fogt-Wyrwas, R.; Dumont, C.; Doucet, J.-P.; Mignon, B.; Losson, B.; Gala, J.-L. Duplex Quantitative Real-Time PCR Assay for the Detection and Discrimination of the Eggs of Toxocara canis and Toxocara cati (Nematoda, Ascaridoidea) in Soil and Fecal Samples. Parasit. Vectors 2012, 5, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moré, G.; Schares, S.; Maksimov, A.; Conraths, F.J.; Venturini, M.C.; Schares, G. Development of a Multiplex Real Time PCR to Differentiate Sarcocystis spp. Affecting Cattle. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 197, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasser, R.B.; Chilton, N.B.; Hoste, H.; Beveridge, I. Rapid Sequencing of RDNA from Single Worms and Eggs of Parasitic Helminths. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 2525–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annoscia, G.; Latrofa, M.S.; Campbell, B.E.; Giannelli, A.; Ramos, R.A.N.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Brianti, E.; Otranto, D. Simultaneous Detection of the Feline Lungworms Troglostrongylus brevior and Aelurostrongylus abstrusus by a Newly Developed Duplex-PCR. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 199, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
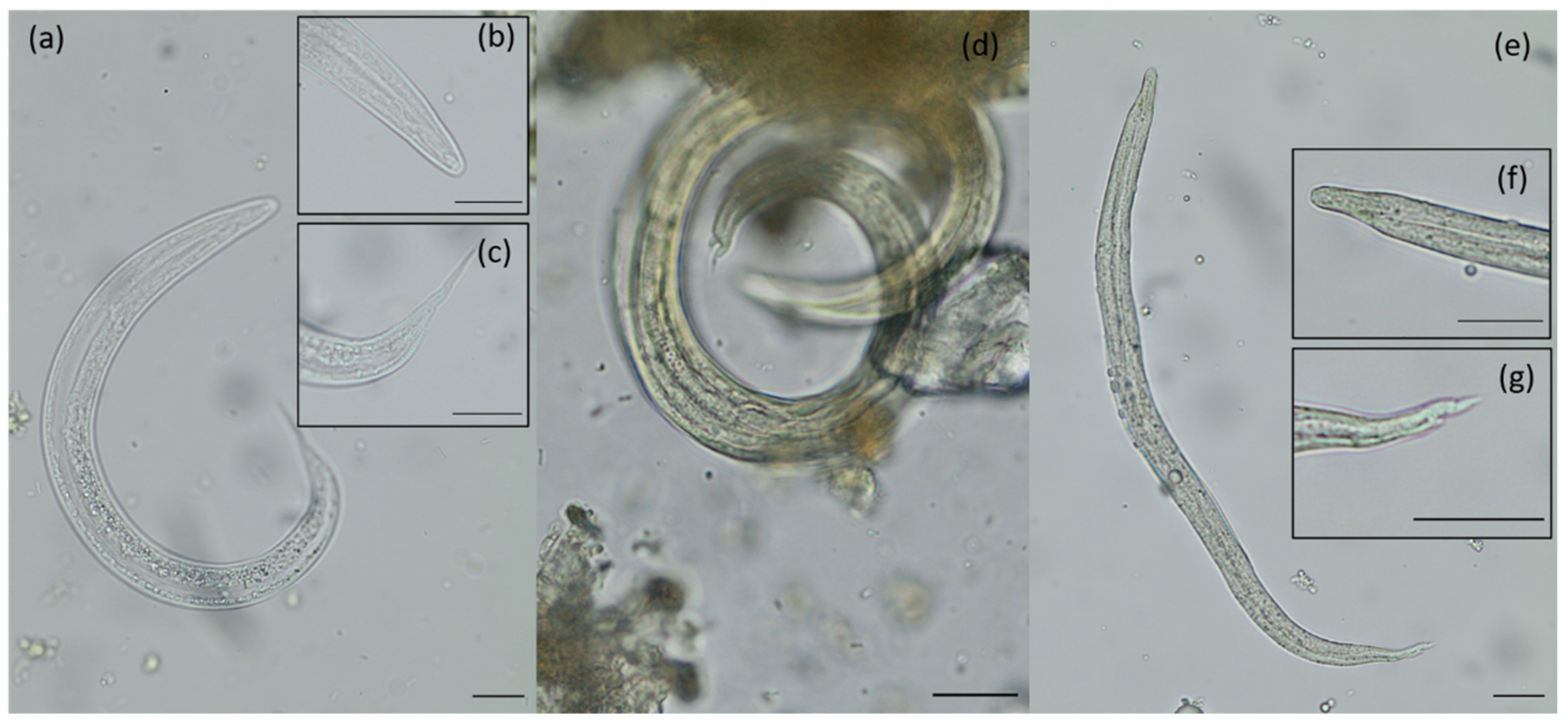


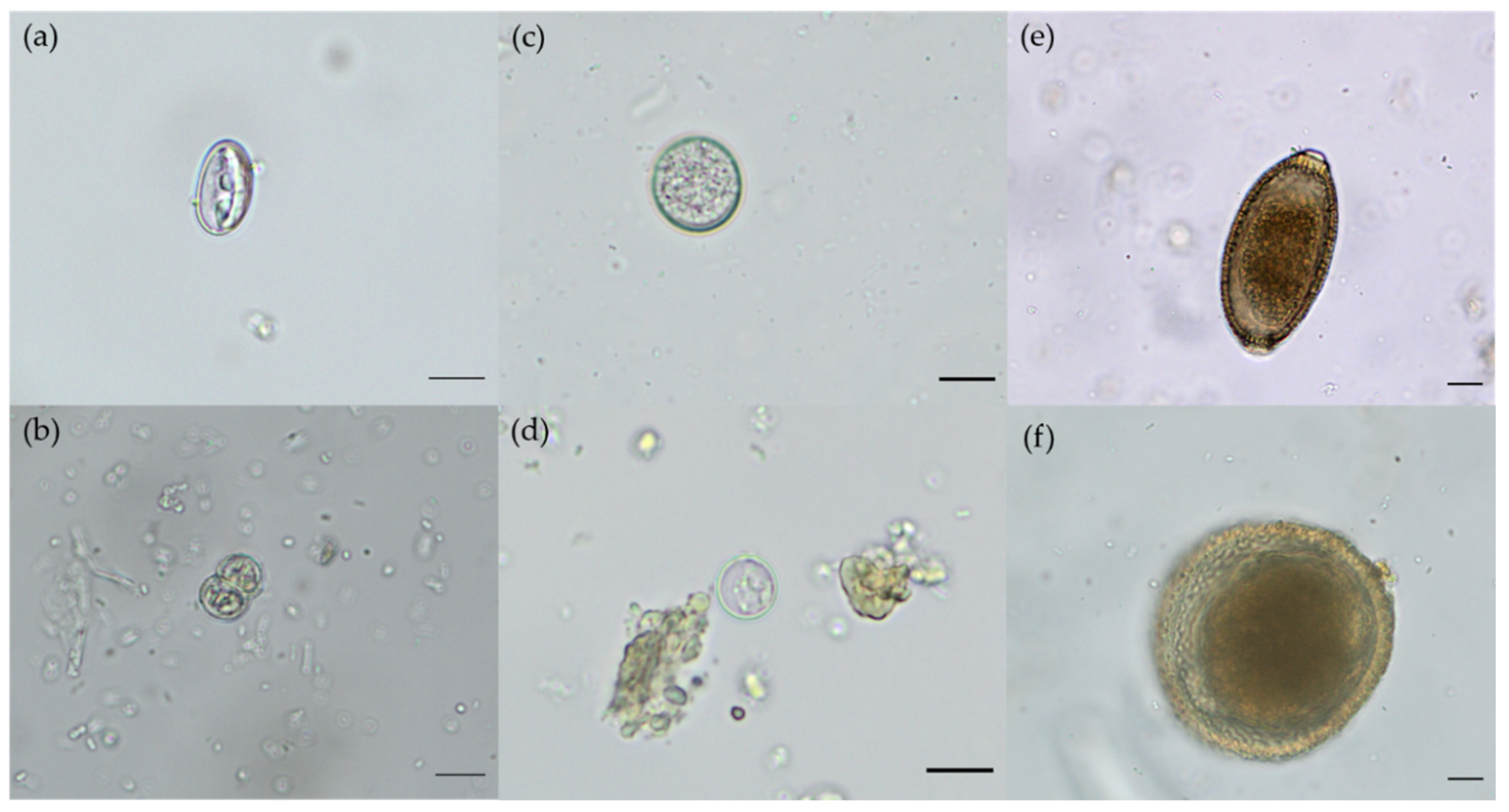

| Parasite | Country * | Prevalence Range in % | Prevalence Current Study in % (95%CI) | Literature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nematodes | ||||
| Toxocara cati/Toxocara sp. ** | P, B, L, F, E, G, Swi | 14.7–81.8 | 45.8 (25.9–65.7) | [8,9,11,12,13,14,16] |
| Toxascaris leonina ** | B, Swi, G | 1.7–9.1 | 4.2 (0–12.2) | [8,14] |
| Ancylostoma tubaeforme/Uncinaria spp. ** | P, B, F, Swi, G | 0.6–18.2 | 12.5 (0–25.7) | [8,12,13,14] |
| Aelurostrongylus abstrusus ** | P, Swi, G | 8.6–21.1 | 4.2 (0–12.2) | [8,20] |
| Troglostrongylus brevior | L | x | 0.0 (0) | [25] |
| Crenosoma vismani | L | x | 0.0 (0) | [22] |
| Angiostrongylus spp.-like larvae ** | G | - | 4.2 (0–12.2) | Current study |
| Metastrongylus sp. | P | 1 | 0.0 (0) | [12] |
| Protostrongylus pulmonalis ** | G | - | 4.2 (0–12.2) | Current study |
| Capillaria aerophilus/Capillaria sp. ** | F, Swi, E, G, L, P | 5–45.7 | 8.3 (0–19.3) | [8,9,11,12,13] |
| Trichuris sp. | Swi | 8.6 | 0.0 (0) | [8] |
| Capillaria felis-cati | L | 4 | not determined | [9] |
| Nematoda sp. | L | 3.1 | not determined | [9] |
| Nematodirus sp. | P, Swi | 1–1.7 | 0.0 (0) | [8,12] |
| Trichinella sp. | L, Swi, E | 29.6–46.4 | not determined | [8,9,11] |
| Trichinella nativa | L, E | 3–20 | not determined | [15,26] |
| Trichinella britovi | B, E, L, Swi, Sl | 27.3–97 | not determined | [14,15,18,26,27] |
| Trichinella spiralis | E | 4.4 | not determined | [15] |
| Cylicospirura spp. ** | G | - | 12.5 (0–25.7) | Current study |
| Cestodes | ||||
| Dibothriocephalus latus/Diphyllobothriidae ** | P, F, E, G | 3–5.4 | 4.2 (0–12.2) | [11,12,13] |
| Taenia sp. | P, F, Swi | 5.2–28 | 0.0 (0) | [8,12,13] |
| Taenia pisiformis | L, E | 100 | not determined | [9,11] |
| Taenia laticollis | E | 40.5 | not determined | [11] |
| Taenia lynciscapreoli | B | 72.7 | not determined | [14] |
| Taenia krabbei | B | 45.5 | not determined | [14] |
| Taenia taeniaeformis | E | 2.7 | not determined | [11] |
| Taenia hydatigena | E | 2.7 | not determined | [11] |
| Mesocestoides sp. | F | 0.3 | 0.0 (0) | [13] |
| Mesocestoides lineatus | B | 9.1 | not determined | [14] |
| Mesocestoides litteratus | P | x | not determined | [28] |
| Spirometra spp. | B | 9.1 | 0.0 (0) | [14] |
| Spirometra janickii | P | 40 | not determined | [12] |
| Spirometra erinaceieuropaei | F | x | not determined | [10] |
| Trematodes | ||||
| Alaria alata | P, F | 1.7–6 | not determined | [12,19] |
| Heterophyidae ** | G | - | 8.3 (0–19.3) | Current study |
| Protozoa | ||||
| Cystoisospora rivolta/C. felis ** | P, F, G | 0.6–14.7 | 25 (7.7–42.3) | [13,16] |
| coccidia | Swi | 12.1 | [8] | |
| Toxoplasma gondii | F, Swe | 75.4–86.1 ° | not determined | [17,29] |
| Toxoplasma/Hammodia spp. ** | G | - | 4.2 (0–12.2) | Current study |
| Giardia intestinalis ** | G | - | 16.7 (1.8–31.6) | Current study |
| Cryptosporidium spp. ** | G | - | 8.3 (0–19.3) | Current study |
| Sarcocystis spp. ** | G | - | 29.2 (11–47.4) | Current study |
| Primer | Probe | Orientation | Sequence 5′…3′, (Modifications) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gd-80F | Forward | GACGGCTCAGGACAACGGTT | [82] | |
| Gd-127R | Reverse | TTGCCAGCGGTGTCCG | [82] | |
| Gd-FT | (FAM)-CCCGCGGCGGTCCCTGCTAG-(DDQ1) | [82] | ||
| Cp-583F | Forward | CAAATTGATACCGTTTGTCCTTCTG | [82] | |
| Cp-733R | Reverse | GGCATGTCGATTCTAATTCAGCT | [82] | |
| Cp-TRT | (Texas Red)-TGCCATACATTGTTGTCCTGACAAATTGAAT-(DDQ2) | [82] | ||
| Tcanis-F | Forward | CAAATTGATACCGTTTGTCCTTCTG | [84] | |
| Tcati-F | Forward | GCGCCAATTTATGGAATGTGAT | [84] | |
| TCC-R | Reverse | GAGCAAACGACAGCSATTTCTT | [84] | |
| Tcanis-S | (FAM)-CCATTACCACACCAGCATAGCTCACCGA-(BHQ1) | [84] | ||
| Tcati-S | (Cy5)-TCTTTCGCAACGTGCATTCGGTGA-(BHQ3) | [84] | ||
| SarcoFext | Forward | GGTGATTCATAGTAACCGAACG | [85] | |
| SarcoRext | Reverse | GATTTCTCATAAGGTGCAGGAG | [85] | |
| SarcoFint | Forward | CGCAAATTACCCAATCCTGA | [85] | |
| SarcoRint | Reverse | ATCGTCTTCGAGCCCCTAAC | [85] | |
| NC1 | Forward | ACGTCTGGTTCAGGGTTGTT | [86] | |
| NC2 | Reverse | TTAGTTTCTTTTCCTCCGCT | [86] | |
| TrogloF | Forward | GCACTTGAAATCTTCGACA | [87] | |
| AeluroF | Forward | GCATTTATGCTAGTGATATC | [87] | |
| MetR | Reverse | CCGCTAAATGATATGCTTA | [87] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Segeritz, L.; Anders, O.; Middelhoff, T.L.; Winterfeld, D.T.; Maksimov, P.; Schares, G.; Conraths, F.J.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C. New Insights into Gastrointestinal and Pulmonary Parasitofauna of Wild Eurasian lynx (Lynx lynx) in the Harz Mountains of Germany. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10121650
Segeritz L, Anders O, Middelhoff TL, Winterfeld DT, Maksimov P, Schares G, Conraths FJ, Taubert A, Hermosilla C. New Insights into Gastrointestinal and Pulmonary Parasitofauna of Wild Eurasian lynx (Lynx lynx) in the Harz Mountains of Germany. Pathogens. 2021; 10(12):1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10121650
Chicago/Turabian StyleSegeritz, Lisa, Ole Anders, Tomma Lilli Middelhoff, Deliah Tamsyn Winterfeld, Pavlo Maksimov, Gereon Schares, Franz Josef Conraths, Anja Taubert, and Carlos Hermosilla. 2021. "New Insights into Gastrointestinal and Pulmonary Parasitofauna of Wild Eurasian lynx (Lynx lynx) in the Harz Mountains of Germany" Pathogens 10, no. 12: 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10121650
APA StyleSegeritz, L., Anders, O., Middelhoff, T. L., Winterfeld, D. T., Maksimov, P., Schares, G., Conraths, F. J., Taubert, A., & Hermosilla, C. (2021). New Insights into Gastrointestinal and Pulmonary Parasitofauna of Wild Eurasian lynx (Lynx lynx) in the Harz Mountains of Germany. Pathogens, 10(12), 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10121650








