Effects of Partially Hydrolyzed Guar Gum Supplementation on the Fecal Microbiotas of Piglets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
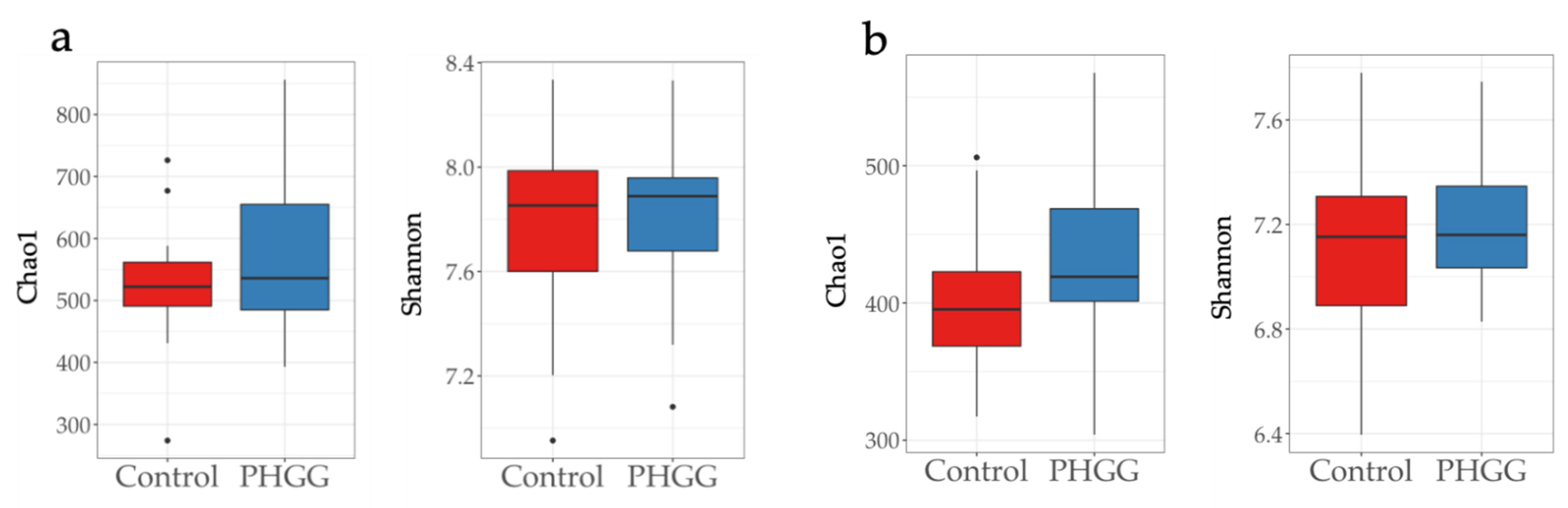
2.1. Alpha Diversity of Chao1 and Shannon Indices in the Fecal Samples of Piglets
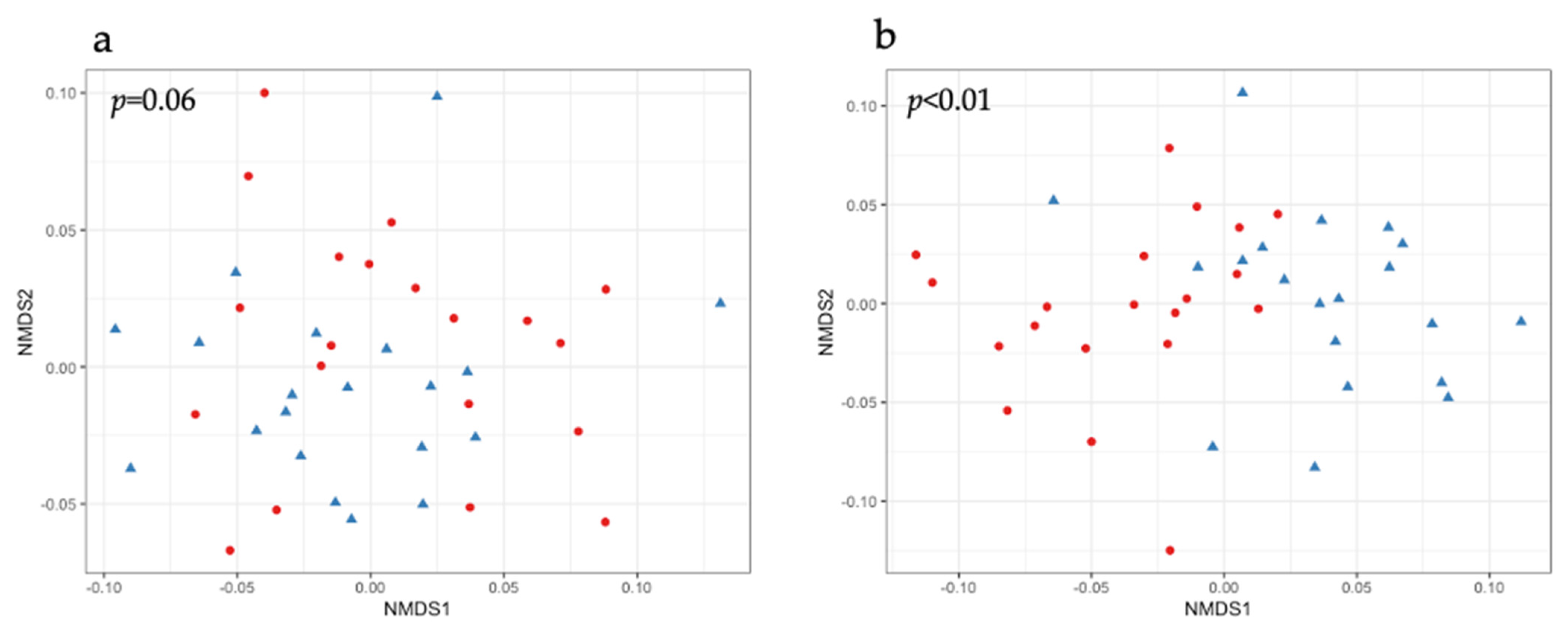
2.2. Beta Diversity in the Fecal Samples of Piglets
2.3. Bacterial Composition of Fecal Microbiota
2.4. Concentrations of Organic Acids in the Fecal Samples of Piglets
2.5. Body Weight at Slaughter and Mortality Rate
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Diets
4.2. Fecal Sampling
4.3. DNA Analysis
4.4. Analysis of the Concentrations of Organic Acids
4.5. Body Weights at Slaughter and Mortality Rates of Piglets
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karasova, D.; Crhanova, M.; Babak, V.; Jerabek, M.; Brzobohaty, L.; Matesova, Z.; Rychlik, I. Development of piglet gut microbiota at the time of weaning influences development of postweaning diarrhea—A field study. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 135, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Nieuwamerongen, S.E.; Soede, N.M.; van der Peet-Schwering, C.M.C.; Kemp, B.; Bolhuis, J.E. Gradual weaning during an extended lactation period improves performance and behavior of pigs raised in a multi-suckling system. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2017, 194, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluske, J.R. Feed- and feed additives-related aspects of gut health and development in weanling pigs. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayakawa, T.; Masuda, T.; Kurosawa, D.; Tsukahara, T. Dietary administration of probiotics to sows and/or their neonates improves the reproductive performance, incidence of post-weaning diarrhea and histopathological parameters in the intestine of weaned piglets. Anim. Sci. J. 2016, 87, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lallès, J.-P.; Bosi, P.; Smidt, H.; Stokes, C.R. Weaning—A challenge to gut physiologists. Livest. Sci. 2007, 108, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, B.; Kim, S.W.; Kwon, Y.M. Characterization of Microbiota Associated with Digesta and Mucosa in Different Regions of Gastrointestinal Tract of Nursery Pigs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCormack, U.M.; Curião, T.; Buzoianu, S.G.; Prieto, M.L.; Ryan, T.; Varley, P.; Crispie, F.; Magowan, E.; Metzler-Zebeli, B.U.; Berry, D.; et al. Exploring a Possible Link between the Intestinal Microbiota and Feed Efficiency in Pigs. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e00380-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mach, N.; Berri, M.; Estellé, J.; Levenez, F.; Lemonnier, G.; Denis, C.; Leplat, J.J.; Chevaleyre, C.; Billon, Y.; Doré, J.; et al. Early-life establishment of the swine gut microbiome and impact on host phenotypes. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2015, 7, 554–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suda, Y.; Sasaki, N.; Kagawa, K.; Elean, M.; Zhou, B.; Tomokiyo, M.; Islam, M.A.; Rajoka, M.S.R.; Kober, A.K.M.H.; Shimazu, T.; et al. Immunobiotic Feed Developed with Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. delbrueckii TUA4408L and the Soymilk By-Product Okara Improves Health and Growth Performance in Pigs. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadi, T.H.; Vahjen, W.; Zentek, J.; Melzig, M.F.; Granica, S.; Piwowarski, J.P. Lythrum salicaria L. herb and gut microbiota of healthy post-weaning piglets. Focus on prebiotic properties and formation of postbiotic metabolites in ex vivo cultures. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 261, 113073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigors, S.; O’Doherty, J.; Rattigan, R.; Sweeney, T. Effect of Supplementing Seaweed Extracts to Pigs until d35 Post-Weaning on Performance and Aspects of Intestinal Health. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, S.F.; Nyachoti, M. Using probiotics to improve swine gut health and nutrient utilization. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 3, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knecht, D.; Cholewińska, P.; Jankowska-Mąkosa, A.; Czyż, K. Development of Swine’s Digestive Tract Microbiota and Its Relation to Production Indices-A Review. Animals 2020, 10, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konstantinov, S.R.; Awati, A.; Smidt, H.; Williams, B.A.; Akkermans, A.D.; de Vos, W.M. Specific response of a novel and abundant Lactobacillus amylovorus-like phylotype to dietary prebiotics in the guts of weaning piglets. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 3821–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Sorrento, A.; Castillejos, L.; López-Colom, P.; Cifuentes-Orjuela, G.; Rodríguez-Palmero, M.; Moreno-Muñoz, J.A.; Luise, D.; Trevisi, P.; Martín-Orúe, S.M. Effects of the Administration of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis CECT 7210 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 and Their Synbiotic Combination With Galacto-Oligosaccharides Against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli F4 in an Early Weaned Piglet Model. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 642549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Sorrento, A.; Castillejos, L.; López-Colom, P.; Cifuentes-Orjuela, G.; Rodríguez-Palmero, M.; Moreno-Muñoz, J.A.; Martín-Orúe, S.M. Effects of Bifidobacterium longum Subsp. infantis CECT 7210 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001, Combined or Not With Oligofructose-Enriched Inulin, on Weaned Pigs Orally Challenged With Salmonella Typhimurium. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wei, X.; Xiao, M.; Han, Z.; Secundo, F.; Mou, H. Properties of hydrolyzed guar gum fermented in vitro with pig fecal inocula and its favorable impacts on microbiota. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 237, 116116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudgil, D.; Barak, S.; Patel, A.; Shah, N. Partially hydrolyzed guar gum as a potential prebiotic source. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, R.; Sakaue, Y.; Kawada, Y.; Tamaki, R.; Yasukawa, Z.; Ozeki, M.; Ueba, S.; Sawai, C.; Nonomura, K.; Tsukahara, T.; et al. Dietary supplementation with partially hydrolyzed guar gum helps improve constipation and gut dysbiosis symptoms and behavioral irritability in children with autism spectrum disorder. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2019, 64, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holscher, H.D. Dietary fiber and prebiotics and the gastrointestinal microbiota. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reider, S.J.; Moosmang, S.; Tragust, J.; Trgovec-Greif, L.; Tragust, S.; Perschy, L.; Przysiecki, N.; Sturm, S.; Tilg, H.; Stuppner, H.; et al. Prebiotic Effects of Partially Hydrolyzed Guar Gum on the Composition and Function of the Human Microbiota-Results from the PAGODA Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Chen, D.; Tian, G.; Zheng, P.; Mao, X.; Yu, J.; He, J.; Huang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Luo, J.; et al. Soluble Fiber and Insoluble Fiber Regulate Colonic Microbiota and Barrier Function in a Piglet Model. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 7809171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, A.P.; Al Za’abi, M.; Ali, B.H.; Terranegra, A. The influence of the prebiotic gum acacia on the intestinal microbiome composition in rats with experimental chronic kidney disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Q.; Li, P.; Hao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Kim, S.W.; Li, H.; Ma, X.; Gao, S.; He, L.; Wu, W.; et al. Dynamic distribution of the gut microbiota and the relationship with apparent crude fiber digestibility and growth stages in pigs. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, P.; Wu, Y.; Guo, P.; Liu, L.; Ma, N.; Levesque, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. Dietary Fiber Increases Butyrate-Producing Bacteria and Improves the Growth Performance of Weaned Piglets. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 7995–8004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera-Maillet, C.; Ribot, Y.; Forano, E. Fiber-degrading systems of different strains of the genus Fibrobacter. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 2172–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le Sciellour, M.; Labussiere, E.; Zemb, O.; Renaudeau, D. Effect of dietary fiber content on nutrient digestibility and fecal microbiota composition in growing-finishing pigs. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Peng, X.; Burrough, E.R.; Sahin, O.; Gould, S.A.; Gabler, N.K.; Loving, C.L.; Dorman, K.S.; Patience, J.F. Dietary Soluble and Insoluble Fiber With or Without Enzymes Altered the Intestinal Microbiota in Weaned Pigs Challenged With Enterotoxigenic E. coli F18. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Wang, M.; Xue, Y.; Duan, D.; Li, C.; Han, X.; Wang, K.; Qiao, R.; Li, X.L. Identification of microflora related to growth performance in pigs based on 16S rRNA sequence analyses. AMB Express 2020, 10, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, D.; Pan, H.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Liu, G.; Xia, L.C. Identifying Gut Microbiota Associated With Colorectal Cancer Using a Zero-Inflated Lognormal Model. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, S.I.; Sellin, J.H. Review article: Short chain fatty acids in health and disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1998, 12, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhao, J.B.; Tao, S.Y.; Zhou, X.J.; Pi, Y.; Gerrits, W.J.; Johnston, L.J.; Zhang, S.Y.; Yang, H.J.; Liu, L.; et al. Effect of dietary fiber fermentation on short-chain fatty acid production and microbial composition in vitro. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 4282–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, J.A.K.; Mullish, B.H.; Pechlivanis, A.; Liu, Z.; Brignardello, J.; Kao, D.; Holmes, E.; Li, J.V.; Clarke, T.B.; Thursz, M.R.; et al. Inhibiting Growth of Clostridioides difficile by Restoring Valerate, Produced by the Intestinal Microbiota. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1495–1507.e1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gardiner, G.E.; Metzler-Zebeli, B.U.; Lawlor, P.G. Impact of Intestinal Microbiota on Growth and Feed Efficiency in Pigs: A Review. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, M.; Inoue, R.; Tsuruta, T.; Hara, H.; Yajima, T. Long-term oral administration of cows’ milk improves insulin sensitivity in rats fed a high-sucrose diet. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 102, 1324–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inoue, R.; Sakaue, Y.; Sawai, C.; Sawai, T.; Ozeki, M.; Romero-Perez, G.A.; Tsukahara, T. A preliminary investigation on the relationship between gut microbiota and gene expressions in peripheral mononuclear cells of infants with autism spectrum disorders. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016, 80, 2450–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirarab, S.; Nguyen, N.; Warnow, T. SEPP: SATe-enabled phylogenetic placement. Pac. Symp. Biocomput. 2012, 2012, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsukahara, T.; Matsukawa, N.; Tomonaga, S.; Inoue, R.; Ushida, K.; Ochiai, K. High-sensitivity detection of short-chain fatty acids in porcine ileal, cecal, portal and abdominal blood by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anim. Sci. J. 2014, 85, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. STAMP: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| One Month Post-Supplementation | Control | PHGG | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phylum | Class | Order | Family | Genus | Abundance (%) | Abundance (%) | P-value | ||||
| Firmicutes | Bacilli | Lactobacillales | Streptococcaceae | Streptococcus | 4.63 | ± | 2.87 | 1.60 | ± | 0.98 | <0.01 |
| (3.97) | (1.43) | ||||||||||
| Firmicutes | Clostridia | Clostridiales | Ruminococcaceae | Unclassified | 11.03 | ± | 2.52 | 9.01 | ± | 2.64 | 0.04 |
| (11.11) | (9.33) | ||||||||||
| Three months post-supplementation | |||||||||||
| Bacteroidetes | Bacteroidia | Bacteroidales | Prevotellaceae | Prevotella | 11.15 | ± | 3.92 | 13.97 | ± | 3.51 | 0.04 |
| (10.58) | (13.98) | ||||||||||
| Firmicutes | Bacilli | Lactobacillales | Lactobacillaceae | Lactobacillus | 7.47 | ± | 5.13 | 15.21 | ± | 7.15 | <0.01 |
| (6.82) | (16.77) | ||||||||||
| Firmicutes | Bacilli | Lactobacillales | Streptococcaceae | Streptococcus | 12.13 | ± | 3.49 | 5.08 | ± | 3.56 | <0.01 |
| (11.97) | (4.82) | ||||||||||
| 1 Month Post-PHGG Supplementation | 3 Months Post-PHGG Supplementation | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mM | Control | PHGG | p-Value | Control | PHGG | p-Value | ||||||||
| Succinate | 0.67 | ± | 0.38 | 0.79 | ± | 0.29 | 0.25 | 1.18 | ± | 0.64 | 1.68 | ± | 0.98 | 0.07 |
| Lactate | 3.26 | ± | 2.68 | 1.24 | ± | 1.16 | <0.01 | 4.05 | ± | 3.56 | 3.34 | ± | 1.60 | 0.42 |
| Formate | 0.76 | ± | 0.46 | 0.62 | ± | 0.42 | 0.32 | 0.82 | ± | 0.44 | 0.58 | ± | 0.32 | 0.04 |
| Acetate | 132.17 | ± | 15.55 | 123.14 | ± | 18.70 | 0.11 | 128.45 | ± | 19.14 | 144.18 | ± | 17.36 | <0.01 |
| Propionate | 39.27 | ± | 5.32 | 40.12 | ± | 9.62 | 0.73 | 48.85 | ± | 11.41 | 59.39 | ± | 11.83 | <0.01 |
| iso-butyrate | 2.34 | ± | 1.10 | 2.15 | ± | 1.78 | 0.70 | 2.38 | ± | 0.99 | 3.26 | ± | 1.07 | <0.01 |
| n-butyrate | 18.01 | ± | 4.49 | 21.11 | ± | 9.93 | 0.21 | 20.46 | ± | 5.70 | 28.24 | ± | 7.02 | <0.01 |
| iso-valerate | 2.95 | ± | 1.68 | 3.37 | ± | 2.74 | 0.57 | 2.81 | ± | 1.35 | 4.36 | ± | 1.51 | <0.01 |
| n-valerate | 2.20 | ± | 1.03 | 2.93 | ± | 2.10 | 0.17 | 4.56 | ± | 1.63 | 6.62 | ± | 1.61 | <0.01 |
| Total organic acids | 201.62 | ± | 22.40 | 195.48 | ± | 40.55 | 0.56 | 213.55 | ± | 35.83 | 251.65 | ± | 31.32 | <0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Inoue, R.; Otabi, H.; Yamashita, T.; Takizawa, N.; Kido, T.; Sugiyama, A.; Ozeki, M.; Abe, A.; Tsukahara, T. Effects of Partially Hydrolyzed Guar Gum Supplementation on the Fecal Microbiotas of Piglets. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1420. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111420
Inoue R, Otabi H, Yamashita T, Takizawa N, Kido T, Sugiyama A, Ozeki M, Abe A, Tsukahara T. Effects of Partially Hydrolyzed Guar Gum Supplementation on the Fecal Microbiotas of Piglets. Pathogens. 2021; 10(11):1420. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111420
Chicago/Turabian StyleInoue, Ryo, Hikari Otabi, Taiga Yamashita, Naoya Takizawa, Toshinobu Kido, Akira Sugiyama, Makoto Ozeki, Aya Abe, and Takamitsu Tsukahara. 2021. "Effects of Partially Hydrolyzed Guar Gum Supplementation on the Fecal Microbiotas of Piglets" Pathogens 10, no. 11: 1420. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111420
APA StyleInoue, R., Otabi, H., Yamashita, T., Takizawa, N., Kido, T., Sugiyama, A., Ozeki, M., Abe, A., & Tsukahara, T. (2021). Effects of Partially Hydrolyzed Guar Gum Supplementation on the Fecal Microbiotas of Piglets. Pathogens, 10(11), 1420. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111420






