Abstract
Canine angiostrongylosis by Angiostrongylus vasorum is increasingly reported in both enzootic and previously free areas. The complex pathogenesis of the disease makes the clinical workup challenging. Infected dogs show highly variable clinical pictures, characterized by subclinical to life-threatening general, cardio-respiratory, neurological and/or gastrointestinal signs. The present study reports the high variability of clinical pictures from 36 dogs across central and southern Italy that were naturally infected by A. vasorum. Of them, 23 (63.9%) presented at least one clinical sign, while 13 (36.1%) were subclinically infected and apparently healthy. Overall, 19 dogs (52.8%) showed cardiorespiratory signs, 14 (38.9%) had non-specific abnormalities, 2 (5.6%) presented coagulation disorders and 1 (2.8%) had a severe neurological condition. Importantly, four dogs presenting with clinical signs had neither cough nor dyspnea. These results underline that angiostrongylosis should be included in the differential diagnosis, even when dogs display only non-specific clinical signs. The proportion of apparently healthy dogs highlights the relevance of routine copromicroscopic and/or antigenic tests in enzootic areas to avoid the sudden onset of potentially life-threatening signs.
1. Introduction
The infection of companion animals with nematodes of the genus Angiostrongylus has recently gained attention in small animal clinical practices. While the role and importance of feline angiostrongylosis is yet to be understood [1,2,3], canine angiostrongylosis by Angiostrongylus vasorum is emerging as one of the most important parasitosis in canine medicine [4,5]. Adult stages of A. vasorum live in the pulmonary arteries and in the right heart of the definitive hosts, i.e., dogs, foxes and other animals [6,7,8]. After mating, A. vasorum females lay eggs that hatch and release first stage larvae (L1), which penetrate the alveolar/bronchial walls, reach the pharynx and are then swallowed and excreted with feces in the environment [9]. Dogs become infected ingesting either the intermediate (i.e., slugs and snails) or paratenic hosts (i.e., frogs and poultry) harboring the infective third stage larvae (L3) [7,10,11]. There is a recent hypothesis that dogs may acquire angiostrongylosis potentially via ingestion of infective L3 shed by slugs or snails onto vegetation in the environment [12].
The pathogenesis of the disease is complex and relies on different mechanisms [13,14,15] including (i) the presence of adults in the lungs with mechanic impairment of pulmonary arteries, (ii) lung inflammation as a response to eggs and migrating larvae, (iii) coagulation disorders, most probably due to hyperfibrinolysis and hypofibrinogenemia, as well as alterations in the coagulation cascade. Coagulation disorders cause hemorrhages in different body parts and when in the Central Nervous System (CNS), along with possible larval migrations, neurological clinical signs occur [16,17].
The clinical course is highly variable and unpredictable, and infected animals show varying pictures that can be subclinical, hyperacute/acute or chronic. Some dogs can be apparently healthy (Table 1) for a long period of time before an abrupt appearance of severe, and often fatal, clinical pictures [18,19,20,21].

Table 1.
Signalment of the dogs infected with Angiostrongylus vasorum involved in the study, along with presence (Y)/absence (N) of clinical signs.
Cardiopulmonary clinical signs, mainly cough and dyspnea, are most frequently reported [4,20,22]. Pulmonary hypertension and congestive right-sided heart failure can be fatal in more severe cases [23,24]. Bleeding disorders are frequent, and dogs may display epistaxis, hemoptysis, mucosal petechiae and ecchymosis [18,25,26]. Neurological signs include paresis/paralysis, ataxia and seizures [13,16,17]. Other clinical alterations are non-specific and include gastrointestinal signs, i.e., vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, weight loss [20,27] and ocular lesions [28].
In recent years A. vasorum has expanded its geographic distribution, from the Iberian Peninsula [29,30] to Central and Northern Europe [31,32,33], across the Mediterranean basin [27,34] to countries of Eastern Europe [35,36]. Though awareness on this life-threatening parasitosis is increasing [9,27], practitioners are still faced with a challenging and unexpected disease where A. vasorum is neglected and underestimated.
A continuous update on clinical features in naturally infected dogs is crucial for a timely diagnosis and prompt appropriate treatments. Hence, this study was conducted to evaluate the occurrence of different clinical presentations in dogs naturally infected by A. vasorum in enzootic areas of Italy.
2. Results
The age of the infected dogs ranged from 4 months to 14 years. Within this group, 20 dogs were female, 16 dogs were male, 34 dogs lived outdoors (e.g., gardens and boxes) and 2 prevalently indoors (with up to 2–3 walks/day). Of the 36 clinically examined animals, 23 (63.9%) showed clinical signs, while 13 (36.1%) were apparently healthy. In detail, 19 (52.8%) had cardio-respiratory disorders while 4 (11.1%) had neither cough nor dyspnea. Non-specific abnormalities, including weight loss, diarrhea, anorexia, lethargy, exercise intolerance and fever, were present in 14 (38.9%) dogs, while 2 (5.6%) presented coagulation alterations, i.e., hematochezia and spontaneous hemorrhages (Figure 1), respectively, and 1 (2.8%) had severe neurological signs (Figure 2).
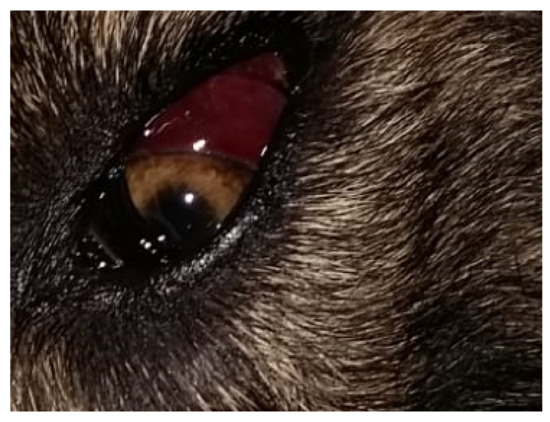
Figure 1.
Dog infected with Angiostrongylus vasorum showing a spontaneous subconjunctival hemorrhage.
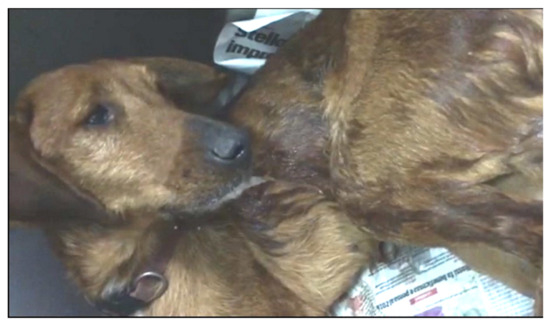
Figure 2.
Dog infected with Angiostrongylus vasorum showing shivering and hypersalivation.
The dogs showed variable clinical pictures with a high number of combinations of signs (Figure 3 and Figure 4). In particular, 7 (19.4%) of the 36 infected dogs had a combination of cardio-respiratory and non-specific signs, 2 (5.6%) showed cardio-respiratory signs in association with non-specific signs and coagulation disorders, 1 (2.8%) was brought to visit for cardio-respiratory, non-specific and neurological (Figure 2) signs and 9 (25%) and 4 (11.1%) dogs had only cardio-respiratory and non-specific signs, respectively. The remaining 13 had no evident clinical sign during the clinical examination. Overall, 17 infected dogs (47.2%), 13 clinically healthy and 4 with other conditions did not show cardio-respiratory signs. Detailed information on the clinical signs observed are listed in Table 2 and are shown by the frequency of observation in Figure 3.
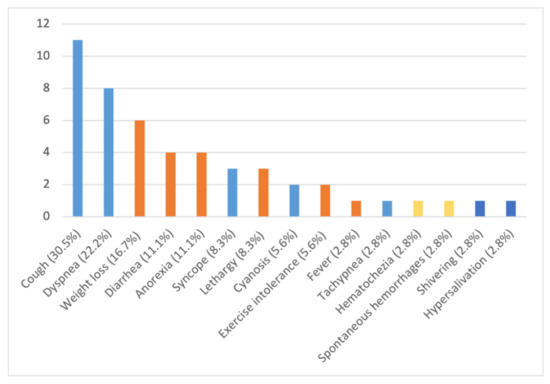
Figure 3.
Number and percentage of clinical signs observed in 36 dogs naturally infected by Angiostrongylus vasorum: light blue: cardio-respiratory signs; orange: non-specific signs; yellow: coagulation disorders; blue: neurological signs.
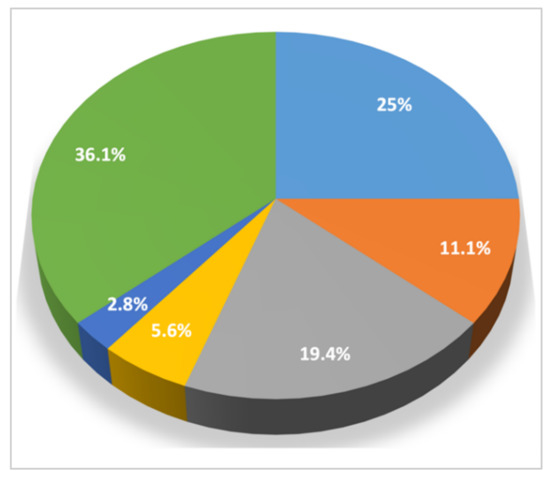
Figure 4.
Clinical pictures and association between different categories of clinical signs observed in 36 dogs with angiostrongylosis: light blue: cardio-respiratory signs; orange: non-specific signs; grey: cardio-respiratory signs + non-specific signs; yellow: cardio-respiratory signs + non specific signs + coagulation disorders; blue: cardio-respiratory signs + non-specific signs + neurological signs; green: no clinical signs.

Table 2.
Number and percentages of clinical signs in 36 dogs of the present study infected by Angiostrongylus vasorum.
3. Discussion
These data show that canine angiostrongylosis occurs with multiple and highly variable clinical presentations, and that the absence of cardio-respiratory signs should not preclude the inclusion of A. vasorum as a differential diagnosis in enzootic areas. In fact, almost half of the infected dogs did not exhibit any pulmonary condition, and some had other clinical signs that were not specific for a definitive diagnosis of A. vasorum infection.
Nonetheless, cardio-respiratory signs, i.e., cough, dyspnea, syncope, cyanosis and tachypnea, were present in several dogs in the present study, with cough being the most frequent. This is consistent with the results of other case series, where cardio-respiratory signs were present in the 63–65% of infected dogs, with cough in 42–65% of the cases [4,18,22,26].
Coagulopathies are common in canine angiostrongylosis. Past studies showed that they can be present in 15–45% of the cases [4,18,22,26,37], and that sometimes they are primary alterations in dogs with angiostrongylosis [4,38]. In contrast, bleeding was present only in a small proportion of dogs in this study. Indeed, blood disorders, e.g., anemia or higher activated partial thromboplastin time, can sometimes be mild and occur with no clinically evident hemorrhages or hematomas [39]. A coagulation profile or diagnostic imaging procedure would have been useful to identify bleedings (e.g., internal hematomas or mild hemoabdomen/hemothorax) undetected during the clinical examination [40,41]. As this was not performed with these study dogs, the proportion of coagulopathies in this paper may be underestimated. For instance, neurological signs could be elicited by both blood disorders and aberrant larval migrations in the CNS [16,17]. Shivering and hypersalivation in the single dog with evident neurological conditions (Figure 2) could have been caused by hemorrhages in the CNS. This would increase the number of dogs with coagulation disorders due to A. vasorum in this study. Another cause of neurological damage is the aberrant migration of A. vasorum larvae. Regardless, neurological signs were minimally represented in accordance with previous studies, which reported a 4–16% occurrence [4,18,22,26,37].
The high number of dogs with non-specific signs, i.e., weight loss, diarrhea, anorexia, lethargy and exercise intolerance, is unsurprising. These signs are frequently recorded in canine angiostrongylosis, and sometimes they are the only clinically evident alterations [4,20,26]. Fever is an infrequent non-specific alteration in dogs with angiostrongylosis [4,22,26,42,43,44]. In general, pyrexia can be present in up to 17% of the cases, though sometimes it is the only evident clinical manifestation [18,45]. Accordingly, increased body temperature and lethargy were the only clinical findings in one dog in the present study, confirming that, in enzootic areas, A. vasorum infection should be suspected in dogs presenting with fever as the sole/main alteration.
Subclinical infections with A. vasorum are generally less frequently described in the literature when compared to clinically manifested angiostrongylosis [4,22,46,47]. Nevertheless, a relatively high percentage of dogs included in this study did not show any clinical abnormality, as also previously shown [37]. False positive results may be due to the presence of larvae of cat lungworms in the feces of dogs [48], thus explaining the absence of clinical signs in dogs shedding larvae. Nonetheless, this is reasonably not the case of the present study, as all larvae were adequately examined microscopically, and feline metastrongyloid larvae have distinctive features that allow for their discrimination by expert operators [49].
The unpredictable nature of canine angiostrongylosis is hereby confirmed as having very highly variable clinical pictures. Although knowledge of clinical features has been greatly expanded in the last two decades, the full spectrum of clinical signs is yet to be completely elucidated, especially in the case of aberrant localizations of both adult and larval A. vasorum. Adult parasites have been found in the pericardial sac and in the urinary bladder of dogs [50], and intraocular localizations have also been reported [28]. Experimental studies have also shown that A. vasorum adults may migrate in the kidneys, causing renal cysts [51], and in the femoral arteries [52] or in the thoracic aorta [53], leading to their rupture and the subsequent death of infected animals. It has also been demonstrated that alive and active A. vasorum L1 can be retrieved in several organs and tissues other than blood and CNS, e.g., diaphragm, liver, pancreas and skin [50]. These ectopic localizations can cause unusual presentations, e.g., dermatitis [54], granulomatous hepatitis and multiple acquired portosystemic shunt [55], glomerulonephritis and granulomatous eosinophilic inflammation in the pancreas [56]. These data are still fragmentary and new studies aimed at exploring all possible clinical impacts of A. vasorum infection are advocated.
In conclusion, respiratory signs remain the predominant alteration in infected dogs even when more than one clinical alteration is found [4,18,20]. Nonetheless, the absence of cough or dyspnea should not prevent the inclusion of A. vasorum in the differential diagnosis for dogs with other compatible clinical signs, especially if living in enzootic areas. In fact, as shown here and in other studies [37], many infected dogs may display only non-respiratory signs or lack clinical signs entirely.
The presence of a high percentage of subclinical infections further underlines the primary importance of adequate routine parasitological examinations in the daily veterinary practice for all dogs living in endemic areas, as healthy dogs may present with a sudden onset of severe and life-threatening clinical angiostrongylosis [20,21,27,57]. Accordingly, the results presented here substantiate that A. vasorum may infect dogs more frequently than previously thought, despite the absence of compatible clinical signs, and suggest that, in the past, the lack of awareness and adequate routine parasitological tests may have led to an underestimation of subclinical infections.
4. Materials and Methods
Thirty-six privately owned dogs referred to veterinary facilities and practices in different regions of Italy for routine check-up or clinical examinations were included in the study. Overall, 9 dogs were from Abruzzo (Site A), 7 from Latium (Site B), 4 from Molise (Site C) and 16 from Campania (Site D) (Figure 5).
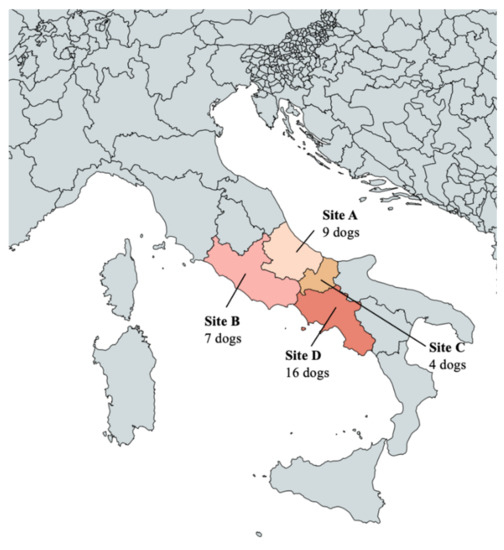
Figure 5.
Map of Italy showing the study sites of the present study: A (Abruzzo); B (Latium); C (Molise); D (Campania).
All dogs were subjected to a Baermann test performed by the examining veterinarian. All dogs scored positive for nematode L1 upon a Baermann test, and all larvae were identified as A. vasorum based on morphological and morphometric features [58,59]. In detail, A. vasorum L1 were identified based on their length (310–400 µm) and width (14–16 µm), on the presence of an anterior cephalic button and of a tip tail with a curve sinus wave and a dorsal spine (Figure 6) [9]. The 36 infected animals were clinically examined by the referring veterinarian, and a data sheet including signalment (age, sex and lifestyle) and presence of clinical signs was filled for each dog, none of whom was suffering from concomitant diseases.
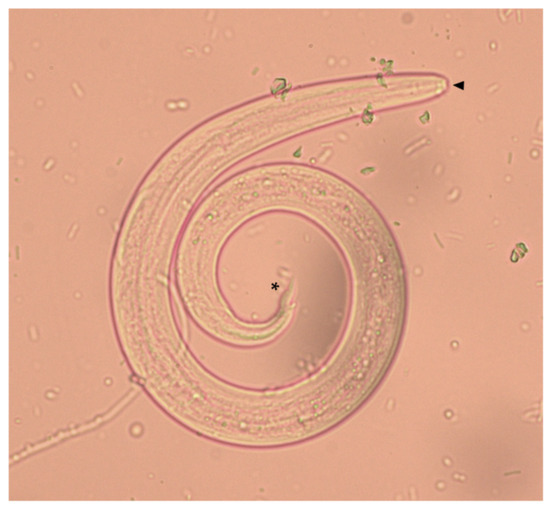
Figure 6.
First stage larva (L1) of Angiostrongylus vasorum collected from an infected dog included in the present study. The anterior cephalic button (arrowhead) and the tip tail with the dorsal spine (asterisk) are indicated.
Author Contributions
M.C. primarily participated in the field activities and clinical data interpretation. I.R., P.E.C., E.G., C.D.T. and C.P. were involved in the local sampling in various study areas and performed the clinical examinations of the infected dogs. A.D.C. and D.T. coordinated and supervised the whole study, drafted the article and finalized the submitted manuscript. F.P. and R.S. have supported the study and participated in the clinical design and interpretation. J.D. and M.R. have critically reviewed and revised the clinical data. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The study was supported by Bayer Animal Health (now part of Elanco Animal Health).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study, because dogs were sampled in the framework of their routine medical checks coordinated by local veterinarians. In addition, according to local laws and regulations, this was allowed by the consent form signed by each single dog owner or legal responsible.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all dog owners involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
All study data are presented in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The study was supported by Bayer Animal Health, of which F.P. and R.S. were employees. Bayer Animal Health has now been acquired by Elanco Animal Health, of which at present J.D. and M.R. are employees. F.P. was employee of Elanco when this manuscript was submitted.
References
- Vieira, F.M.; Muniz-Pereira, L.C.; Lima, S.D.S.; Neto, A.H.; Guimarães, E.V.; Luque, J.L. A new metastrongyloidean species (Nematoda) parasitizing pulmonary arteries of Puma (Herpailurus) yagouaroundi (É. Geoffroy, 1803) (Carnivora: Felidae) from Brazil. J. Parasitol. 2013, 99, 327–331, Erratum in: J. Parasitol. 2013, 99, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, A.; Morelli, S.; Colombo, M.; Simonato, G.; Veronesi, F.; Marcer, F.; Diakou, A.; D’Angelosante, R.; Pantchev, N.; Psaralexi, E.; et al. Is Angiostrongylosis a Realistic Threat for Domestic Cats? Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakou, A.; Dimzas, D.; Astaras, C.; Savvas, I.; Di Cesare, A.; Morelli, S.; Neofitos, Κ.; Migli, D.; Traversa, D. Clinical investigations and treatment outcome in a European wildcat (Felis silvestris silvestris) infected by cardio-pulmonary nematodes. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2020, 19, 100357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, E.R.; Jefferies, R.; van Otterdijk, L.; McEniry, R.B.; Allen, F.; Bakewell, M.; Shaw, S.E. Angiostrongylus vasorum infection in dogs: Presentation and risk factors. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 173, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikha, H.M.; Holmes, S.A.; Wright, I.; Morgan, E.R.; Lacher, D.W. Recent advances in the epidemiology, clinical and diagnostic features, and control of canine cardio-pulmonary angiostrongylosis. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolt, G.; Monrad, J.; Henriksen, P.; Dietz, H.H.; Koch, J.; Bindseil, E.; Jensen, A.L. The fox (Vulpes vulpes) as a reservoir for canine angiostrongylosis in Denmark. Field survey and experimental infections. Acta Vet. Scand. 1992, 33, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolt, G.; Monrad, J.; Koch, J.; Jensen, A.L. Canine angiostrongylosis: A review. Vet. Rec. 1994, 135, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillis-Germitsch, N.; Manser, M.B.; Hilbe, M.; Schnyder, M. Meerkats (Suricata suricatta), a new definitive host of the canid nematode Angiostrongylus vasorum. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2017, 6, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cesare, A.; Traversa, D. Canine angiostrongylosis: Recent advances in diagnosis, prevention and treatment. Vet. Med. 2014, 5, 181–192. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, E.R.; Shaw, S.E.; Brennan, S.F.; De Waal, T.D.; Jones, B.R.; Mulcahy, G. Angiostrongylus vasorum: A real heartbreaker. Trends Parasitol. 2005, 21, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozzer, L.R.; Lima, W.S. Gallus gallus domesticus: Paratenic host of Angiostrongylus vasorum. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 207, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, W.; Conboy, G.; Greenwood, S.; Schaper, R. Infectivity of gastropod-shed third-stage larvae of Angiostrongylus vasorum and Crenosoma vulpis to dogs. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, J.; Willesen, J.L. Canine pulmonary angiostrongylosis: An update. Vet. J. 2009, 179, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigrist, N.E.; Hofer-Inteeworn, N.; Jud Schefer, R.; Kuemmerle-Fraune, C.; Schnyder, M.; Kutter, A.P.N. Hyperfibrinolysis and hypofibrinogenemia diagnosed with rotational thromboelastometry in dogs naturally infected with Angiostrongylus vasorum. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2017, 31, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tritten, L.; Gillis-Germitsch, N.; Kockmann, T.; Schnyder, M. Quantitative proteomics analysis of Angiostrongylus vasorum-induced alterations in dog serum sheds light on the pathogenesis of canine angiostrongylosis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garosi, L.S.; Platt, S.R.; McConnell, J.F.; Wrayt, J.D.; Smith, K.C. Intracranial haemorrhage associated with Angiostrongylus vasorum infection in three dogs. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2005, 46, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepri, E.; Veronesi, F.; Traversa, D.; Conti, M.B.; Marchesi, M.C.; Miglio, A.; Mandara, M.T. Disseminated angiostrongylosis with massive cardiac and cerebral involvement in a dog from Italy. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 109, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, P.S.; Boag, A.K.; Guitian, J.; Boswood, A. Angiostrongylus vasorum infection in 23 dogs (1999–2002). J. Small Anim. Pract. 2004, 45, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traversa, D.; Torbidone, A.; Malatesta, D.; Guglielmini, C. Occurrence of fatal canine Angiostrongylus vasorum infection in Italy. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 152, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traversa, D.; Di Cesare, A.; Meloni, S.; di Regalbono, A.F.; Milillo, P.; Pampurini, F.; Venco, L. Canine angiostrongylosis in Italy: Occurrence of Angiostrongylus vasorum in dogs with compatible clinical pictures. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 2473–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, A.; Traversa, D.; Manzocchi, S.; Meloni, S.; Grillotti, E.; Auriemma, E.; Pampurini, F.; Garofani, C.; Ibba, F.; Venco, L. Elusive Angiostrongylus vasorum infections. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, S.; Paine, P.; Wright, I.; Morgan, E.R.; Elsheikha, H.M. Risk factors and predictors of angiostrongylosis in naturally infected dogs in the southeast of England. Companion Anim. 2020, 25, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, J.N.; Malbon, A.; Dennler, M.; Glaus, T. Intrapulmonary arteriovenous anastomoses in dogs with severe Angiostrongylus vasorum infection: Clinical, radiographic, and echocardiographic evaluation. J. Vet. Cardiol. 2016, 18, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmári, V. Spontaneous tricuspid valve chordal rupture in a dog with severe, irreversible pulmonary hypertension caused by Angiostrongylus vasorum infection. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helm, J.R.; Morgan, E.R.; Jackson, M.W.; Wotton, P.; Bell, R. Canine angiostrongylosis: An emerging disease in Europe. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2010, 20, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, B.; Brennan, S.F.; Zarelli, M.; Mooney, C.T. Geographical, clinical, clinicopathological and radiographic features of canine angiostrongylosis in Irish dogs: A retrospective study. Ir. Vet. J. 2012, 65, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachmazidou, A.; Papaioannou, N.; Diakou, A.; Savvas, I.; Patsikas, M.; Stylianaki, I.; Morelli, S.; Di Cesare, A.; Mylonakis, M.E. First report of fatal autochthonous angiostrongylosis in a dog in Greece. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2021, 23, 100519. [Google Scholar]
- Hurníková, Z.; Čabanová, V.; Karpjak, P.; Kasenčák, M.; Miterpáková, M. Rare Case of Angiostrongylus vasorum intraocular infestation in an asymptomatic dog. Helminthologia 2019, 56, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alho, A.M.; Schnyder, M.; Schaper, R.; Meireles, J.; Belo, S.; Deplazes, P.; de Carvalho, L.M. Seroprevalence of circulating Angiostrongylus vasorum antigen and parasite-specific antibodies in dogs from Portugal. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 2567–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morchón, R.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A.; Sánchez-Agudo, J.Á.; de Vicente-Bengochea, J.; Murcia-Martínez, X.; Carretón, E. Angiostrongylus vasorum in domestic dogs in Castilla y León, Iberian Peninsula, Spain. Animals 2021, 11, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lempereur, L.; Martinelle, L.; Marechal, F.; Bayrou, C.; Dalemans, A.C.; Schnyder, M.; Losson, B. Prevalence of Angiostrongylus vasorum in southern Belgium, a coprological and serological survey. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandi, G.; Lind, E.O.; Schaper, R.; Ågren, E.; Schnyder, M. Canine angiostrongylosis in Sweden: A nationwide seroepidemiological survey by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays and a summary of five-year diagnostic activity (2011–2015). Acta Vet. Scan. 2017, 59, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiškina, V.; Lindqvist, E.L.; Blomqvist, A.C.; Orav, M.; Stensvold, C.R.; Jokelainen, P. Autochthonous Angiostrongylus vasorum in Finland. Vet. Rec. Open 2019, 6, e000314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traversa, D.; Morelli, S.; Cassini, R.; Crisi, P.E.; Russi, I.; Grillotti, E.; Manzocchi, S.; Simonato, G.; Beraldo, P.; Viglietti, A.; et al. Occurrence of canine and feline extra-intestinal nematodes in key endemic regions of Italy. Acta Trop. 2019, 193, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benda, T.; Csivincsik, Á.; Nemes, C.; Turbók, J.; Zsolnai, A.; Simonyai, E.; Majoros, G.; Nagy, G. Lethal Angiostrongylus vasorum infection in a Hungarian dog. Acta Parasitol. 2017, 62, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deak, G.; Gillis-Germitsch, N.; Ionică, A.M.; Mara, A.; Păstrav, I.R.; Cazan, C.D.; Ioniță, M.; Mitrea, I.L.; Răileanu, C.; Bărburaș, D.; et al. The first seroepidemiological survey for Angiostrongylus vasorum in domestic dogs from Romania. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tieri, E.; Pomilio, F.; Di Francesco, G.; Saletti, M.A.; Totaro, P.; Troilo, M.; Menna, S.; Tampieri, M.P.; Morelli, D. Angiostrongylus vasorum in 20 dogs in the province of Chieti, Italy. Vet. Ital. 2011, 47, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Glaus, T.; Sigrist, N.; Hofer-Inteeworn, N.; Kuemmerle-Fraune, C.; Mueller, C.; Geissweid, K.; Beckmann, K.; Wenger, M.; Matos, J.N. Unexplained bleeding as primary clinical complaint in dogs infected with Angiostrongylus vasorum. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilkd. 2016, 158, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnyder, M.; Fahrion, A.; Riond, B.; Ossent, P.; Webster, P.; Kranjc, A.; Glaus, T.; Deplazes, P. Clinical, laboratory and pathological findings in dogs experimentally infected with Angiostrongylus vasorum. Parasitol. Res. 2010, 107, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, S.F.; McCarthy, G.; McAllister, H.; Bassett, H.; Jones, B.R. Clinical signs, diagnosis and treatment of three dogs with angiostrongylosis in Ireland. Ir. Vet. J. 2004, 57, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willesen, J.; Bjornvad, C.; Koch, J. Acute haemoabdomen associated with Angiostrongylus vasorum infection in a dog: A case report. Ir. Vet. J. 2008, 61, 591–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasanelli, M.; Paradies, P.; Otranto, D.; Lia, R.P.; de Caprariis, D. Haemothorax associated with Angiostrongylus vasorum infection in a dog. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2008, 49, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradies, P.; Schnyder, M.; Capogna, A.; Lia, R.P.; Sasanelli, M. Canine angiostrongylosis in naturally infected dogs: Clinical approach and monitoring of infection after treatment. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 702056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miterpáková, M.; Hurníková, Z.; Zalewski, A.P. The first clinically manifested case of angiostrongylosis in a dog in Slovakia. Acta Parasitol. 2014, 59, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Olivieri, E.; Zanzani, S.A.; Gazzonis, A.L.; Giudice, C.; Brambilla, P.; Alberti, I.; Romussi, S.; Lombardo, R.; Mortellaro, C.M.; Banco, B.; et al. Angiostrongylus vasorum infection in dogs from a cardiopulmonary dirofilariosis endemic area of Northwestern Italy: A case study and a retrospective data analysis. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barutzki, D.; Schaper, R. Endoparasites in dogs and cats in Germany 1999–2002. Parasitol. Res. 2003, 90, S148–S150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barutzki, D.; Schaper, R. Natural infections of Angiostrongylus vasorum and Crenosoma vulpis in dogs in Germany (2007–2009). Parasitol. Res. 2009, 105, S39–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, G.T.; DeBess, E. Detection of parasites in canine feces at three off-leash dog parks in Portland, Oregon 2014. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 22, 100494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traversa, D.; Morelli, S.; Di Cesare, A.; Diakou, A. Felid cardiopulmonary nematodes: Dilemmas solved and new questions posed. Pathogens 2021, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira-Júnior, S.D.; Barçante, J.M.; Barçante, T.A.; Ribeiro, V.M.; Lima, W.S. Ectopic location of adult worms and first-stage larvae of Angiostrongylus vasorum in an infected dog. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 121, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cury, M.C.; Lima, W.S. Ocorrência de Angiostrongylus vasorum no rim de cäo experimentalmente infectado. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 1995, 47, 593–595. [Google Scholar]
- Cury, M.C.; Lima, W.S. Rupture of femoral artery in a dog infected with Angiostrongylus vasorum. Vet. Parasitol. 1996, 65, 313–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozzer, L.R.; Lima, W.S. Rupture of the thoracic aorta associated with experimental Angiostrongylus vasorum infection in a dog. Parasite 2012, 19, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavana, P.; Bensignor, E.; Blot, S.; Carlus, M.; Chermette, R.; Crosaz, O.; Grimm, F.; Hurion, M.; Jeandel, A.; Polack, B. Nematode dermatitis due to Angiostrongylus vasorum infection in a dog. Vet. Dermatol. 2015, 26, 293-e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, S.; Priestnall, S.L.; Blake, D.; Meeson, R.L. Angiostrongylus vasorum causing severe granulomatous hepatitis with concurrent multiple acquired PSS. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2015, 51, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, L.; Cortese, L.; Meomartino, L.; Pagano, T.B.; Pepe, P.; Cringoli, G.; Papparella, S. Angiostrongylus vasorum: Epidemiological, clinical and histopathological insights. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traversa, D.; Guglielmini, C. Feline aelurostrongylosis and canine angiostrongylosis: A challenging diagnosis for two emerging verminous pneumonia infections. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 157, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traversa, D.; Di Cesare, A.; Conboy, G. Canine and feline cardiopulmonary parasitic nematodes in Europe: Emerging and underestimated. Parasites Vectors 2010, 3, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, D.D. Georgi’s Parasitology for Veterinarians, 6th ed.; W.B. Saunders Company: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1995; pp. 295–296. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).