Detection of Anti-LipL32 Antibodies in Serum Samples from Horses with Chronic Intraocular Infection with Leptospira spp.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preliminary Examination and Classification of Equine Patients
2.2. Collection of the Serum Samples
2.3. Examination of Serum Samples
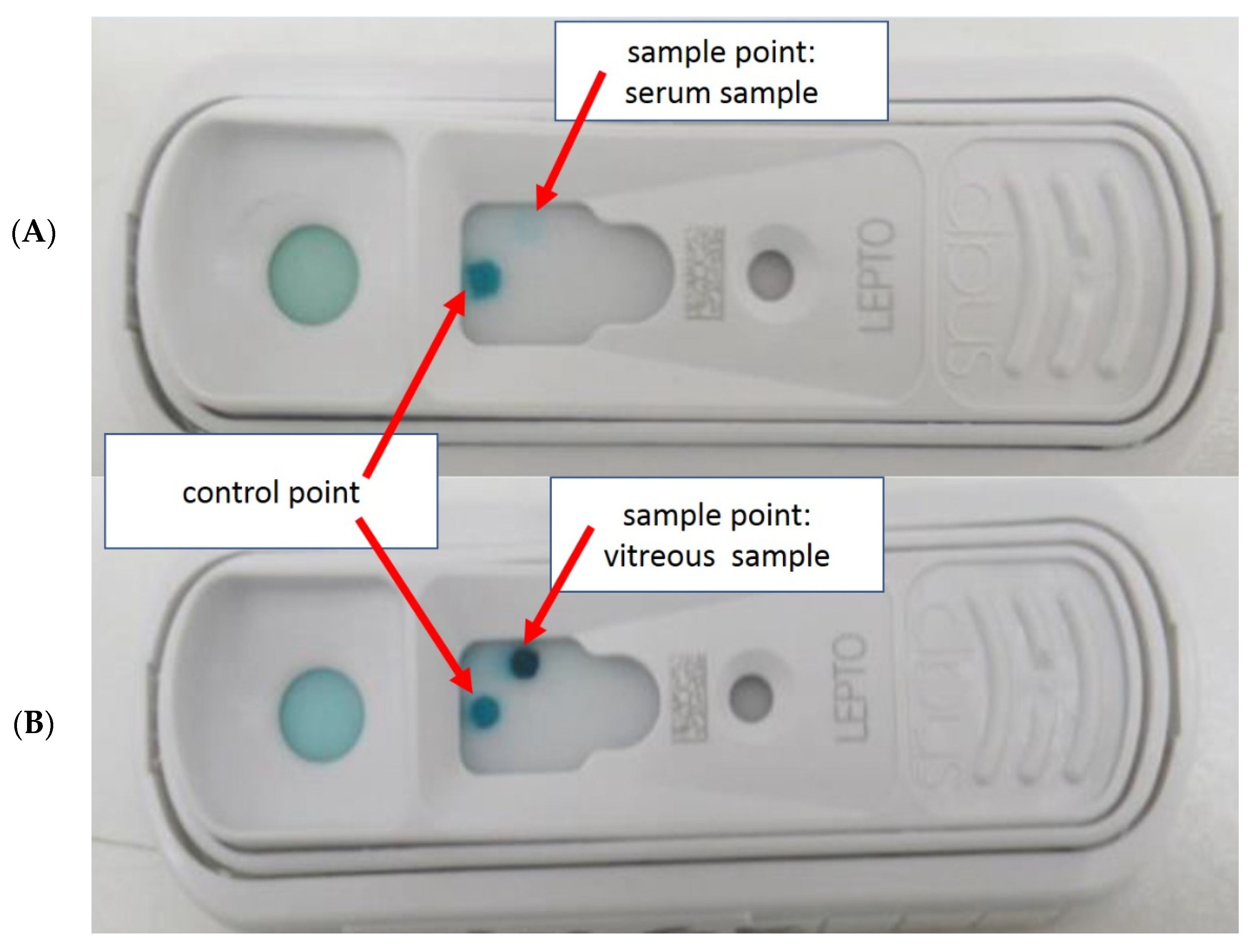
2.3.1. Preliminary Examination for the Use of SNAP Lepto
2.3.2. Examination of the 207 Horse Sera of this Study
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Preliminary Examination: Use of MAT and SNAP Lepto for Equine Serum Samples
3.2. Examination of the 207 Horse Sera of This Study
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wollanke, B.; Gerhards, H.; Brem, S.; Kopp, H.; Meyer, P. Intraocular and serum antibody titers to Leptospira in 150 horses with equine recurrent uveitis (ERU) subjected to vitrectomy. Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 1998, 111, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brem, S.; Gerhards, H.; Wollanke, B.; Meyer, P.; Kopp, H. 35 Leptospirenisolationen aus Glaskörpern von 32 Pferden mit rezidivierender Uveitis (ERU). Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 1999, 112, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wollanke, B.; Gerhards, H.; Brem, S.; Wolf, E.; Kopp, H.; Meyer, P. Zur Leptospirenaetiologie der equinen rezidivierenden Uveitis (ERU): Ergebnisse der Untersuchungen von Serum- und Glaskörperproben. Tieraerztl. Prax. 2000, 28, 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Wollanke, B.; Rohrbach, B.W.; Gerhards, H. Serum and vitreous humor antibody titers in and isolation of Leptospira interrogans from horses with recurrent uveitis. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2001, 219, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollanke, B. Die Equine Rezidivierende Uveitis (ERU) Als Intraokulare Leptospirose. Habilitation Thesis, Ludwig-Maximilians-University, Munich, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wollanke, B.; Gerhards, H.; Brem, S.; Meyer, P.; Kopp, H. Aetiologie der equinen rezidivierenden Uveitis (ERU): Autoimmunkrankheit oder intraokulare Leptospireninfektion? Pferdeheilkunde 2004, 20, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Von Borstel, M.V.; Oey, L.; Strutzberg-Minder, K.; Boevé, M.H.; Ohnesorge, B. Direct and indirect detection of leptospires in vitreal samples of horses with ERU. Pferdeheilkunde 2010, 26, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiehen, L.E. Retrospektive Analyse zum Vorkommen der Equinen Rezidivierenden Uveitis—Unter Beruecksichtigung der Leptospireninfektion—An der LMU München von 01/2005 bis 06/2010. Ph.D. Thesis, Ludwig-Maximilians-University, Munich, Germany, 2012. Ludwig-Maximilians-University Library, Electronic Publications. Available online: https://edoc.ub.uni-muenchen.de/14095/1/Wiehen_Lina_Elisabeth.pdf (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- Baake, E.; von Borstel, M.; Rohn, K.; Ohnesorge, B. Detection of intraocular leptospiral DNA, antibodies and Leptospira spp. in horses with equine recurrent uveitis in different laboratories. Pferdeheilkunde 2016, 32, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorrego-Keiter, E.; Tóth, J.; Dikker, L.; Sielhorst, J.; Schusser, G.F. Detection of leptospira by culture of vitreous humor and detection of antibodies against leptospira in vitreous humor and serum of 225 horses with equine recurrent uveitis. Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2016, 129, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollanke, B.; Gerhards, H.; Schinagl, C. Results of 654 trans-pars plana vitrectomies of equine eyes with recurrent uveitis-follow-up until 18 years after surgery. Pferdeheilkunde Equine Med. 2021, 37, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geißler, P.; Wollanke, B. Biofilm formation in persistent infections and its role in the pathogenesis of equine recurrent uveitis (ERU)—A literature review. Pferdeheilkunde Equine Med. 2021, 37, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, K.; Kenngott, R.; Settles, M.; Gerhards, H.; Maierl, J.; Wollanke, B. In Vivo Biofilm Formation of Pathogenic Leptospira spp. in the Vitreous Humor of Horses with Recurrent Uveitis. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gsell, O.; Rehsteiner, K.; Verrey, F. Iridocyclitis as a late consequence of Leptospirosis Pomona (porter’s disease): Agglutinin and lymphocytosis in the aqueous humor. Ophthalmologica 1946, 112, 320–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heusser, H. Zur Aetiologie der periodischen Augenentzündung. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilk. 1952, 94, 296–306. [Google Scholar]
- Hartwigk, H. Die periodische Augenentzündung des Pferdes als Spaetsymptom der Leptospirose. Tierarztl. Umsch. 1953, 8, 154–157. [Google Scholar]
- Bryans, J.T. Studies on equine leptospirosis. Cornell Veter. 1955, 45, 16–50. [Google Scholar]
- Kathe, J. Die Leptospirosen und ihre Verbreitung in der Deutschen Demokratischen Republik. Z. Hyg. 1955, 1, 39–62. [Google Scholar]
- Bolte, H.F. Uveitis, a Sequela to Experimentally Induced Leptospira Pomona Infection in the Shetland Pony. Master’s Thesis, Faculty of Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Zwierzchowski, J. Klinik und Therapie der Leptospirosen der Haus- und Nutztiere. In Leptospiren und Leptospirosen, Teil I.; Kathe, J., Mochmann, H., Eds.; Gustav Fischer Verlag: Jena, Germany, 1967; pp. 79–137. [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer, A.E.; Crockett, R.; Kalsow, C.M. Association of leptospiral seroreactivity and breed with uveitis and blindness in horses: 372 cases (1986–1993). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1995, 207, 1327–1331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.D. The Presence and Duration of Persistence of Leptospira Pomona in Equine Ocular Tissues Following Experimentally Induced Systemic Infection. Master’s Thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, R.D.; Morter, R.L.; Freeman, M.J.; Lavignette, A.M. Experimental chronic uveitis. Ophthalmic signs following equine leptospirosis. Investig. Ophthalmol. 1971, 10, 948–954. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, A.; Stevenson, B.; Adler, B. Leptospirosis in horses. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 167, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, W.A. 4. Disease in Animals. 4.4 Horses and Donkeys. In Leptospira and Leptospirosis, Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology; Adler, B., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 109–110. ISBN 978-3-662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malalana, F.; Stylianides, A.; McGowan, C. Equine recurrent uveitis: Human and equine perspectives. Vet. J. 2015, 206, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divers, T.J.; Schang, Y.F.; Irby, N.L.; Smith, J.L.; Carter, C.N. Leptospirosis: An important infectious disease in North American horses. Equine Vet. J. 2019, 51, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werry, H.; Gerhards, H. Technique and indications for surgical treatment of equine recurrent uveitis. Pferdeheilkunde 1991, 7, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werry, H.; Gerhards, H. Surgical treatment of equine recurrent uveitis: A preliminary report. Tierarztl. Prax. 1992, 20, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Winterberg, A.; Gerhards, H. Longterm-results of pars-plana-vitrectomy in equine recurrent uveitis. Pferdeheilkunde 1997, 13, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frühauf, B.; Ohnesorge, B.; Deegen, E.; Boevé, M. Surgical management of equine recurrent uveitis with single port pars plana vitrectomy. Vet. Ophthalmol. 1998, 1, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhards, H.; Wollanke, B.; Winterberg, A.; Werry, H. Technique for and results with vitrectomy in horses with recurrent uveitis. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual ACVO-Meeting, Seattle, WA, USA, 21–24 October 1998; p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- Gerhards, H.; Wollanke, B.; Brem, S. Vitrectomy as a diagnostic and therapeutic approach for equine recurrent uveitis (ERU). In Proceedings of the 45th Annual Convention AAEP, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 8 December 1999; Volume 45, pp. 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Gerhards, H.; Wollanke, B. Uveitis bei Pferden-Diagnose und Therapie. Pferdeheilkunde 2001, 20, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerhards, H.; Wollanke, B. Surgical treatment of equine recurrent uveitis: Trans-pars-plana vitrectomy in horses. In Equine Ophthalmology, 1st ed.; Gilger, B.C., Ed.; Elsevier Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005; pp. 314–319. [Google Scholar]
- Von Borstel, M.; Von Oppen, T.; Glitz, F.; Frühauf, B.; Deegen, E.; Boevé, M.H.; Ohnesorge, B. Long-term results of pars-plana (double-port) vitrectomy in equine recurrent uveitis. Pferdeheilkunde 2005, 21, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tömördy, E.; Hässig, M.; Spiess, B.M. The outcome of pars plana vitrectomy in horses with equine recurrent uveitis with regard to the presence or absence of intravitreal antibodies against various serovars of Leptospira interrogans. Pferdeheilkunde 2010, 26, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorrego-Keiter, E.; Tóth, J.; Dikker, L.; Sielhorst, J.; Schusser, G.F. Long-term results of pars plana vitrectomy in relationship to leptospiral antibody detection in vitreous humor in 118 horses with equine recurrent uveitis (ERU). Pferdeheilkunde Equine Med. 2017, 33, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baake, E.I.A.; von Borstel, M.; Rohn, K.; Boevé, M.H.; Ohnesorge, B. Long-term ophthalmologic examinations of eyes with equine recurrent uveitis after pars plana vitrectomy. Pferdeheilkunde 2019, 35, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voelter, K.; Vial, Z.; Pot, A.S.; Spiess, B.M. Leptospiral antibody prevalence and surgical treatment outcome in horses with Equine Recurrent Uveitis (ERU) in Switzerland. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2020, 23, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollanke, B. Untersuchungen zur Aetiologie der Equinen Rezidivierenden Uveitis (ERU). Doctoral Thesis, Ludwig-Maximilians-University, Munich, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Båverud, V.; Gunnarsson, A.; Engvall, E.O.; Franzén, P.; Egenvall, A. Leptospira seroprevalence and associations between seropositivity, clinical disease and host factors in horses. Acta Vet. Scand. 2009, 51, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blatti, S.; Overesch, G.; Gerber, V.; Frey, J.; Hussy, D. Seroprevalence of Leptospira spp. in clinically healthy horses in Switzerland. Schweiz. Arch. Tierh. 2011, 153, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ebani, V.V.; Bertelloni, F.; Pinzauti, P.; Cerri, D. Seroprevalence of Leptospira spp. and Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in Italian horses. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2012, 19, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arent, Z.J.; Kedzierska-Mieszkowska, S. Seroprevalence study of leptospirosis in horses in northern Poland. Vet. Rec. 2013, 127, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habus, J.; Persic, Z.; Spicic, S.; Vince, S.; Stritof, Z.; Milas, Z.; Cvetnic, Z.; Perharic, M.; Turk, N. New trends in human and animal leptospirosis in Croatia, 2009–2014. Acta Trop. 2017, 168, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, E.; Taddei, S.; Cavirani, S.; Schiavi, J.; Angelone, M.; Cabassi, C.S.; Schiano, E.; Quintavalla, F. Leptospira Seroprevalence in Bardigiano Horses in Northern Italy 2019. Animals 2020, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wasinski, B.; Paschalis-Trela, K.; Trela, J.; Czopowicz, M.; Kita, J.; Zychska, M.; Cywinska, A.; Markowska-Daniel, I.; Carter, C.; Witkowski, L. Serological Survey of Leptospira Infection in Arabian Horses in Poland. Pathogens 2021, 10, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathaway, S.; Little, T.; Finch, S.; Stevens, A. Leptospiral infection in horses in England: A serological study. Vet. Rec. 1981, 108, 396–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, B.; de la Peña Moctezuma, A. Leptospira and leptospirosis. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamond, C.; Martins, G.; Lawson-Ferreira, R.; Medeiros, M.A.; Lilenbaum, W. The role of horses in the transmission of leptospirosis in an urban tropical area. Epidemiol. Infect. 2013, 141, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, A.P.; Hamond, C.; Lilenbaum, W. Leptospirosis in horses. Vet. Rec. 2013, 172, 479–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finger, M.A.; Filho, I.R.D.B.; Leutenegger, C.; Estrada, M.; Ullmann, L.S.; Langoni, H.; Kikuti, M.; Dornbush, P.T.; Deconto, I.; Biondo, A.W. Serological and molecular survey of Leptospira spp. among cart horses from an endemic area of human leptospirosis in Curitiba, Southern Brazil. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2014, 56, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsegay, K.; Potts, A.D.; Aklilu, N.; Loetter, C.; Gummow, B. Circulating serovars of Leptospira in cart horses of central and southern Ethiopia and associated risk factors. Prev. Vet. Med. 2016, 125, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sohail, M.; Khan, M.; Ijaz, M.; Fatima, Z.; Naseer, O.; Ahamad, W.; Ahmad, A. Seroprevalence of Leptospira spp. In Horses of Distinct Climatic Regions of Punjab, Pakistan. In Proceedings of the 10th International Leptospirosis Society Conferecnce (ILS 2017), Palmerston North, New Zealand, 27 November–1 December 2017; p. 237. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, T.M.P.; Correia, L.; Spohr, K.A.H.; Aguiar, D.M.; Martins, G.; de Sa Jayme, V. Risk Factors Associated with Seroreactivity Against Leptospira sp. in Horses from Brazilian Amazon. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2018, 68, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, J.C.; Astudillo, M.; Romero, M.H. Epidemiological characterization of Leptospira spp. infection in working horses and in an occupationally exposed population in six Colombian police stations. Biomedica 2019, 39, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolwell, C.F.; Rogers, C.W.; Benschop, J.; Collins-Emerson, J.M.; Adams, B.; Scarfe, K.R.; Gee, E.K. Seroprevalence of Leptospira in Racehorses and Broodmares in New Zealand. Animals 2020, 10, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, A.S.; Jaguezeski, A.M.; Laber, I.F.; von Laer, A.E.; Lovato, L.T.; da Silva, M.O.; de Moura, A.B. Leptospira spp. in horses in southern Brazil: Seroprevalence, infection risk factors, and influence on reproduction. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 73, 101551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagre, A.C.; Mayo, C.E.; Pabilonia, K.L.; Landolt, G.A. Seroprevalence of Leptospira spp. in Colorado equids and association with clinical disease. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2020, 32, 718–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirosh-Levy, S.; Baum, M.; Schvartz, G.; Kalir, B.; Pe’er, O.; Shnaiderman-Torban, A.; Bernstein, M.; Blum, S.E.; Steinman, A. Seroprevalence of Leptospira spp. in horses in Israel. Pathogens 2021, 10, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilger, B.C.; Salmon, J.H.; Yi, N.Y.; Barden, C.A.; Chandler, H.L.; Wendt, J.A.; Colitz, C.M.H. Role of bacteria in the pathogenesis of recurrent uveitis in horses from the southeastern United States. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2008, 69, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loibl, J. Immunologische und Mikrobiologische Untersuchungen zur Intraokular Persistierenden Leptospireninfektion bei Pferden mit Rezidivierender Uveitis. (Dissertation), LMU München. 2009. Ludwig-Maximilians-University Library, Electronic Publications. Available online: https://edoc.ub.uni-muenchen.de/10508/1/Loibl_Julia.pdf (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- Malalana, F.; Blundell, R.J.; Pinchbeck, G.L.; McGowan, C.M. The role of Leptospira spp. in horses affected with recurrent uveitis in the UK. Equine Vet. J. 2017, 49, 706–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loibl, J.K.; Gerhards, H.; Brem, S.; Wollanke, B. Improving the laboratory diagnosis of leptospiral uveitis in horses by using an indirect ELISA for the detection of antibodies against Leptospira spp. in intraocular samples. Pferdeheilkunde Equine Med. 2018, 34, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wollanke, B.; Gerhards, H. Differential diagnosis of equine recurrent uveitis: The importance of a paracentesis of the anterior chamber and aqueous analysis. In Proceedings of the 30th WSAVA Congress, International Society of Veterinary Ophthalmology (IVO) Pre-Congress Programme, Mexico City, Mexico, 9–10 May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gesell, S.; Wollanke, B.; Brem, S.; Gerhards, H. Vergleich der Antikoerpertiter gegen Leptospiren in Kammerwasser- und Glaskoerperproben bei Pferden mit rezidivierender Uveitis. In Proceedings of the 19th DVG-Fachtagung Pferdekrankheiten, Hanover, Germany, 10–11 February 2006; 2006; pp. 239–241. [Google Scholar]
- Wollanke, B.; Geiger, T.; Gerhards, H. Evaluation of “SNAP® Lepto”-ELISA and comparison with MAT and PCR results for diagnosis of leptospiral uveitis in horses using intraocular samples. Pferdeheilkunde Equine Med. 2018, 34, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, T. Evaluierung eines ELISA-Schnelltests (SNAP-Lepto®) für den Nachweis von Antikörpern gegen LipL32 in Serum und Intraokularem Probenmaterial von Pferden als Diagnostikum der Equinen Rezidivierenden Uveitis. (Dissertation), LMU, München. 2019. Ludwig-Maximilians-University Library, Electronic Publications. Available online: https://edoc.ub.uni-muenchen.de/24938/1/Geiger_Tobias_Xaver.pdf (accessed on 18 September 2021).
- Guerreiro, H.; Croda, J.; Flannery, B.; Mazel, M.; Matsunaga, J.; Reis, M.G.; Levett, P.N.; Ko, A.I.; Haake, D.A. Leptospiral proteins recognized during the humoral immune response to leptospirosis in humans. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 4958–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haake, D.A.; Chao, G.; Zuerner, R.L.; Barnett, J.K.; Barnett, D.; Mazel, M.; Matsunaga, J.; Levett, P.N.; Bolin, C.A. The leptospiral major outer membrane protein LipL32 is a lipoprotein expressed during mammalian infection. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 2276–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baumgart, A.; Gerhards, H. Besonderheiten der Tigerschecken-Uveitis und möglicher Cyclosporin A-Einsatz in deren Therapie in Deutschland. Pferdeheilkunde 2014, 30, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faine, S. Guidelines for the Control of Leptospirosis; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Levett, P.N. Leptospirosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 14, 296–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haake, D.A.; Levett, P.N. Leptospirosis in humans. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 387, 65–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Day, N. Leptospirosis: Epidemiology, Microbiology, Clinical Manifestations, and Diagnosis. UpToDate® Home Page, Topic 5527, Version 27.0. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/leptospirosis-epidemiology-microbiology-clinical-manifestations-and-diagnosis (accessed on 14 September 2021).
- Limmathurotsakul, D.; Turner, E.L.; Wuthiekanun, V.; Thaipadungpanit, J.; Suputtamongkol, Y.; Chierakul, W.; Smythe, L.D.; Day, N.P.; Cooper, B.; Peacock, S.J. Fool’s gold: Why imperfect reference tests are undermining the evaluation of novel diagnostics: A reevaluation of 5 diagnostic tests for leptospirosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization and International Leptospirosis Society. Annex 10, Serological Techniques (MAT and ELISA). In Human Leptospirosis: Guidance for Diagnosis, Surveillance and Control; World Health Organisation, Ed.; WHO Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003; pp. 63–75. ISBN 92 4 154589 5. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/human-leptospirosis-guidance-for-diagnosis-surveillance-and-control (accessed on 15 September 2021).
- Halliwell, R.E.; Brim, T.A.; Hines, M.A.; Wolf, D.; White, F.H. Studies on equine recurrent uveitis. II: The role of infection with Leptospira interrogans serovar pomona. Curr. Eye Res. 1985, 4, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, C.; Keller, H. Aetiology and occurrence of periodic ophthalmia among horses in Berlin. Tierarztl. Prax. 1990, 18, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jung, B.Y.; Lee, K.W.; Ha, T.Y. Seroprevalence of Leptospira spp. in clinically healthy racing horses in Korea. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2010, 72, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pikalo, J.; Sattler, T.; Eichinger, M.; Loitsch, A.; Sun, H.; Schmoll, F.; Schusser, G.F. Occurrance of antibodies against Leptospira in horses in Middle Germany. Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2016, 129, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gesell, S. Gibt es eine Asymptomatische Intraokulare Leptospireninfektion beim Pferd? Ph.D. Thesis, LMU, Munich, Germany, 2004. Ludwig-Maximilians-University Library, Electronic Publications. Available online: https://edoc.ub.uni-muenchen.de/2527/1/Gesell_Stefan.pdf (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- Heusser, H. Die periodische Augenentzündung, eine Lepospirose? Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilk. 1948, 90, 287–312. [Google Scholar]
- Hupka, E.; Behrens, H. Untersuchungen über die Leptospirose des Pferdes. Dtsch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 1951, 58, 245–248. [Google Scholar]
- Kalisch, J. Leptospirose und periodische Augenentzündung. Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wschr. 1952, 65, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zaharija, J.; Maralt, J.; Cermak, K.; Andrasic, N.; Sanovic, I. Leptospirose und periodische Augenentzündung beim Pferd. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilk. 1960, 102, 400–408. [Google Scholar]
- World Organization of Animal Health—OIE. Chapter 3.1.12 Leptospirosis. Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals OIE Terrestrial manual 2021; Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals. OIE Terrestrial manual 2021: Paris, France OIE Home Page, most recent updates adopted 2021. Available online: https://www.oie.int/fileadmin/Home/eng/Health_standards/tahm/3.01.12_LEPTO.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2021).
- Himebaugh, N.E.; Gilger, B.C. Role of Leptospira spp. testing and ocular examination in horses with equine recurrent uveitis: A retrospective study of 63 horses. Equine Vet. Educ. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szemes, P.A.; Gerhards, H. Untersuchungen zur Prävalenz der equinen rezidivierenden Uveitis im Großraum Köln-Bonn. Prakt. Tierarzt 2000, 81, 408–420. [Google Scholar]
- Gesell-May, S.; Brem, S.; Wollanke, B.; Gerhards, H. Untersuchung gesunder Pferdeaugen auf eine intraokulare Leptospireninfektion. Pferdeheilkunde Equine Med. 2021, 37, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollanke, B.; Gerhards, H.; Kaufmann, S. Investigations on the Borrelia-etiology in equine recurrent uveitis (ERU). Pferdeheilkunde Equine Med. 2017, 33, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khurana, S.; Malik, P.; Nandal, A.; Srivastava, S. Seroprevalence of Leptospirosis in Equines in India. Indian J. Comp. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. Dis. 2003, 24, 93–95. [Google Scholar]
- Pissawong, T.; Maneewatchararangsri, S.; Ritthisunthorn, N.; Soonthornworasiri, N.; Reamtong, O.; Adisakwattana, P.; Kalambaheti, T.; Chaisri, U.; Doungchawee, G. Immunodominance of LipL3293–272 peptides revealed by leptospirosis sera and therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, 53, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, B.; Murphy, A.; Locarnini, S.; Faine, S. Detection of specific anti-leptospiral immunoglobulins M and G in human serum by solid-phase enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1980, 11, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leonard, F.; Quinn, P.; Ellis, W.; O’Farrell, K. Association between cessation of leptospiruria in cattle and urinary antibody levels. Res. Vet. Sci. 1993, 55, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, M.V.; Nakamura, P.M.; Camargo, E.D.; Batista, L.; Vaz, A.J.; Romero, E.C.; Brandao, A.P. Immunodiagnosis of human leptospirosis by dot-ELISA for the detection of IgM, IgG, and IgA antibodies. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1997, 56, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, Z.B.; Abutarbush, S.M.; Al-Majali, A.; Gharaibeh, M.H.; Al-Khateeb, B. Seroprevalence and risk factors of Leptospira serovar Pomona and Leptospira serovar Hardjo infection in dairy cows in Jordan. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2019, 13, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goris, M.G.A.; Leeflang, M.M.G.; Loden, M.; Wagenaar, J.F.P.; Klatser, P.R.; Hartskeerl, R.A.; Boer, K.R. Prospective Evaluation of Three Rapid Diagnostic Tests for Diagnosis of Human Leptospirosis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goris, M.G.A.; Leeflang, M.M.G.; Boer, K.R.; Goeijenbier, M.; van Gorp, E.C.M.; Wagenaar, J.F.P.; Hartskeerl, R.A. Establishment of Valid Laboratory Case Definition for Human Leptospirosis. J. Bacteriol. Parasitol. 2012, 3, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, X.T.; Amran, F.; Cheong, K.C.; Ahmad, N. In-house ELISA screening using a locallyisolated Leptospira in Malaysia: Determination of its cut-off points. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brockie, R.E.; Till, D.G. Leptospira ballum isolated from hedgehogs. New Zealand Vet. J. 1977, 25, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathaway, S.; Blackmore, D.K. Ecological aspects of the epidemiology of infection with leptospires of the Ballum serogroup in the black rat (Rattus rattus) and the brown rat (Rattus norvegicus) in New Zealand. J. Hyg. 1981, 87, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hartskeerl, R.A.; Goris, M.G.A.; Brem, S.; Meyer, P.; Kopp, H.; Gerhards, H.; Wollanke, B.J. Classification of Leptospira from the Eyes of Horses Suffering from Recurrent Uveitis. Vet. Med. B Infect. Dis. Vet. Public Health 2004, 51, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollanke, B.; Gerhards, H.; Brem, S.; Geiger, T.; Wiehen, L. Leptospira serovars in Germany and neighbouring countries in horses suffering from recurrent uveitis looking at intraocular and serum samples. In Proceedings of the 3rd ELS Scientific Meeting on Leptospirosis and Other Rodent Borne Haemorrhagic Fevers, Alghero, Sardinia, Italy, 24–26 May 2018; p. 51. [Google Scholar]
- Rathinam, S.R. Manifestations of ocular leptospirosis. J. Postgrad. Med. 2005, 51, 189–194. Available online: https://www.jpgmonline.com/article.asp?issn=0022-3859;year=2005;volume=51;issue=3;spage=189;epage=194;aulast=Rathinam (accessed on 17 September 2021). [PubMed]
- Shukla, D.; Rathinam, S.R.; Cunningham, E.T. Leptospiral uveitis in the developing world. Int. Ophthalmol. Clin. 2010, 50, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalogeropoulos, D.; Asproudis, I.; Stefaniotou, M.; Moschos, M.; Gartzonika, C.; Bassukas, I.; Konitsiotis, S.; Milionis, H.; Gaitanis, G.; Malamos, K.; et al. Spirochetal uveitis: Spectrum of clinical manifestations, diagnostic and therapeutic approach, final outcome and epidemiological data. Int. Ophthalmol. 2021. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs10792-021-01984-x (accessed on 17 September 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, H.R.; Cheong, M.Y.; Mustapha, M. Ocular leptospirosis in four patients: A diagnostic dilemma. Med. J. Malaysia 2021, 76, 569–572. Available online: http://www.e-mjm.org/2021/v76n4/ocular-leptospirosis.pdf (accessed on 17 September 2021). [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Stevenson, B. Leptospiral Uveitis—There Is More to It Than Meets the Eye! Zoonoses Public Health 2012, 59 (Suppl. 2), 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakolundu, S.; Sivakumar, R.R.; Chidambaranathan, G.P.; Sritharan, M. Serological diagnosis of leptospiral uveitis by HbpA IgG ELISA. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61, 1681–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bjarnsholt, T. The Role of Bacterial Biofilms in Chronic Infections. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. 2013, 121 (Suppl. 136), 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Høiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Moser, C.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Kolpen, M.; Qvist, T.; Aanaes, K.; Pressler, T.; Skov, M.; Ciofu, O. Diagnosis of biofilm infections in cystic fibrosis patients. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. 2017, 125, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moser, C.; Pedersen, H.T.; Lerche, C.J.; Kolpen, M.; Line, L.; Thomsen, K.; Høiby, N.; Jensen, P.Ø. Biofilms and host response—Helpful or harmful. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. 2017, 125, 320–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bjarnsholt, T.; Jensen, P.; Fiandaca, M.J.; Pedersen, J.; Hansen, C.R.; Andersen, C.B.; Pressler, T.; Givskov, M.; Høiby, N. Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms in the respiratory tract of cystic fibrosis patients. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2009, 44, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høiby, N. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis. Diagnostic and prognostic significance of pseudomonas aeruginosa precipitins determined by means of crossed immunoelectrophoresis. A survey. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. 1977, 262 (Suppl. C), 3–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Høiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Moser, C.; Bassi, G.L.; Coenye, T.; Donelli, G.; Hall-Stoodley, L.; Holá, V.; Imbert, C.; Kirketerp-Møller, K.; et al. ESCMID guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of biofilm infections 2014. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21 (Suppl. 1), S1–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedersen, S.S.; Espersen, F.; Høiby, N.; Jensen, T. Immunoglobulin A and immunoglobulin G antibody responses to alginates from Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aanaes, K.; Johansen, H.K.; Poulsen, S.S.; Pressler, T.; Buchwald, C.; Høiby, N. Secretory IgA as a diagnostic tool for Pseudomonas aeruginosa respiratory colonization. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2013, 12, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cibulski, S.; Wollanke, B. Investigations of wild small mammals and water samples from horse farms for DNA of pathogenic leptospires by real-time PCR. Pferdeheilkunde 2016, 32, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fritz, K.L.; Kaese, H.J.; Valberg, S.J.; Hendrickson, J.A.; Rendahl, A.K.; Bellone, R.R.; Dynes, K.M.; Wagner, M.L.; Lucio, M.A.; Cuomo, F.M.; et al. Genetic risk factors for insidious equine recurrent uveitis in Appaloosa horses. Anim. Genet. 2014, 45, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilger, B.C. Chapter 8 Diseases of the uvea, uveitis, and recurrent uveitis. In Equine Ophthalmology, 3rd ed.; Gilger, B.C., Ed.; Wiley Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2017; pp. 369–406. [Google Scholar]
- Rockwell, H.; Mack, M.; Famula, T.; Sandmeyer, L.; Bauer, B.; Dwyer, A.; Lassaline, M.; Beeson, S.; Archer, S.; McCue, M.; et al. Genetic investigation of equine recurrent uveitis in Appaloosa horses. Anim. Genet. 2020, 51, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandmeyer, L.S.; Bauer, B.S.; Feng, C.X.; Grahn, B.H. Equine recurrent uveitis in western Canadian prairie provinces: A retrospective study (2002–2015). Can. Vet. J. 2017, 58, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sandmeyer, L.S.; Kingsley, N.B.; Walder, C.; Archer, S.; Leis, M.L.; Bellone, R.R.; Bauer, B.S. Risk factors for equine recurrent uveitis in a population of Appaloosa horses in western Canada. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2020, 23, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| SNAP Lepto | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Negative | Positive | ||
| MAT 1 | negative | 86.5% | 13.5% |
| (titer < 1:100) | (32/37) | (5/37) | |
| positive | 43.3% | 56.7% | |
| (titer ≥ 1:100) | (45/104) | (59/104) | |
| MAT Using Serum Samples | SNAP Lepto Using Serum Samples | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | |
| no signs of ERU | 51.5% | 48.5% | 92.2% | 5.8% |
| (n = 103) | (53/103) | (50/103) | (97/103) | (6/103) |
| ERU | 17.8% | 82.2% | 21.1% | 78.9% |
| (n = 90) | (16/90) | (74/90) | (19/90) | (71/90) |
| uveitis in horses with leopard coat pattern | 57% | 43% | 100% | 0% |
| (n = 14) | (8/14) | (6/14) | (14/14) | (0/14) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geiger, T.; Gerhards, H.; Wollanke, B. Detection of Anti-LipL32 Antibodies in Serum Samples from Horses with Chronic Intraocular Infection with Leptospira spp. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101325
Geiger T, Gerhards H, Wollanke B. Detection of Anti-LipL32 Antibodies in Serum Samples from Horses with Chronic Intraocular Infection with Leptospira spp. Pathogens. 2021; 10(10):1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101325
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeiger, Tobias, Hartmut Gerhards, and Bettina Wollanke. 2021. "Detection of Anti-LipL32 Antibodies in Serum Samples from Horses with Chronic Intraocular Infection with Leptospira spp." Pathogens 10, no. 10: 1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101325
APA StyleGeiger, T., Gerhards, H., & Wollanke, B. (2021). Detection of Anti-LipL32 Antibodies in Serum Samples from Horses with Chronic Intraocular Infection with Leptospira spp. Pathogens, 10(10), 1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101325






