Differentiation of Aspergillus flavus from Aspergillus oryzae Targeting the cyp51A Gene
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Fungal Isolates
2.2. Molecular Identification
2.2.1. DNA Extraction
2.2.2. PCR Amplification and Sequences Analysis of the ITS, benA, CaM, and cyp51A Genes
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of ITS Region, benA, CaM and cyp51A Genes
3.1.1. ITS Region
3.1.2. β-Tubulin Gene
3.1.3. CaM Gene
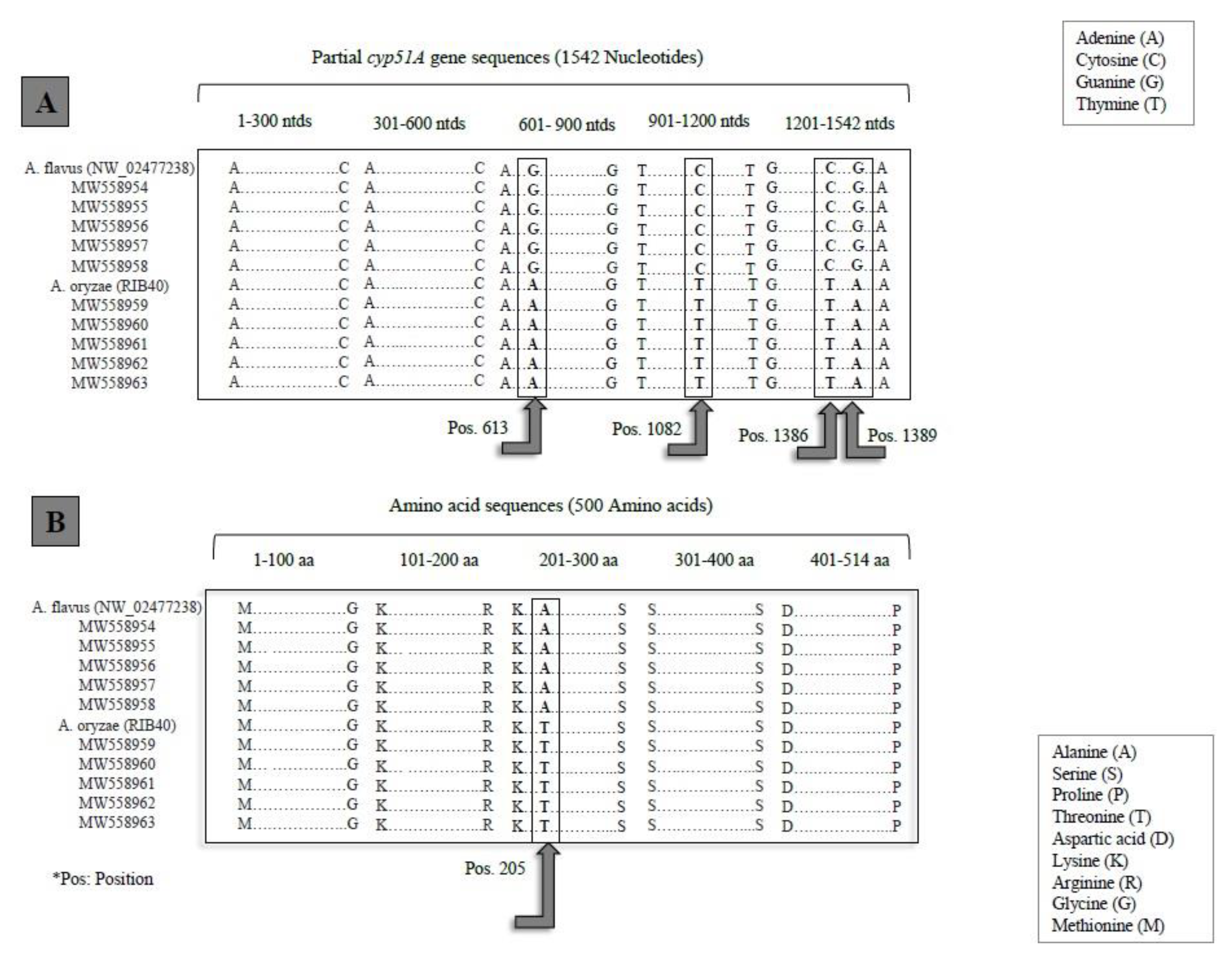
3.1.4. cyp51A Gene
3.2. Phylogenetic Diversity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MALDI-TOF MS | matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry |
| benA | β-tubulin |
| ITS | Internal Transcribed Spacer |
| CaM | calmodulin |
| BAL | bronchoalveolar lavage fluid |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| DW | distilled water |
| BLAST | Basic Local Alignment Search Tool |
| NCBI | National Center for Biotechnology Information |
| SP | sputum |
| IA | invasive aspergillosis |
| SNP | single nucleotide polymorphism |
References
- Frisvad, J.C.; Hubka, V.; Ezekiel, C.; Hong, S.-B.; Nováková, A.; Chen, A.; Arzanlou, M.; Larsen, T.; Sklenář, F.; Mahakarnchanakul, W. Taxonomy of Aspergillus section Flavi and their production of aflatoxins, ochratoxins and other mycotoxins. Stud. Mycol. 2019, 93, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjærbølling, I.; Vesth, T.; Frisvad, J.C.; Nybo, J.L.; Theobald, S.; Kildgaard, S.; Petersen, T.I.; Kuo, A.; Sato, A.; Lyhne, E.K. A comparative genomics study of 23 Aspergillus species from section Flavi. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonçalves, S.S.; Stchigel, A.M.; Cano, J.; Guarro, J.; Colombo, A.L. In vitro antifungal susceptibility of clinically relevant species belonging to Aspergillus section Flavi. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 1944–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hedayati, M.T.; Armaki, M.T.; Charati, J.Y.; Hedayati, N.; Seyedmousavi, S.; Denning, D.W. Burden of fungal infections in Iran. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2018, 12, 910–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, P.K.; Ehrlich, K.C. What does genetic diversity of Aspergillus flavus tell us about Aspergillus oryzae? Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 138, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, M.T.; Taghizadeh-Armaki, M.; Zarrinfar, H.; Hoseinnejad, A.; Ansari, S.; Abastabar, M.; Er, H.; Özhak, B.; Öğünç, D.; Ilkit, M. Discrimination of Aspergillus flavus from Aspergillus oryzae by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry. Mycoses 2019, 62, 1182–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, G.; Nierman, W.; Wortman, J.; Pritchard, B.; Brown, D.; Dean, R.; Bhatnagar, D.; Cleveland, T.; Machida, M.; Yu, J. Whole genome comparison of Aspergillus flavus and A. oryzae. Med. Mycol. 2006, 44, S9–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, A.; Chatterjee, S.S.; Das, A.; Shivaprakash, M.R. Invasive aspergillosis in developing countries. Med. Mycol. 2011, 49, S35–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rudramurthy, S.M.; Paul, R.A.; Chakrabarti, A.; Mouton, J.W.; Meis, J.F. Invasive aspergillosis by Aspergillus flavus: Epidemiology, diagnosis, antifungal resistance, and management. J. Fungi 2019, 5, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tavakoli, M.; Yazdani Charati, J.; Hedayati, M.T.; Moosazadeh, M.; Badiee, P.; Seyedmousavi, S.; Denning, D.W. National trends in incidence, prevalence and disability-adjusted life years of invasive aspergillosis in Iran: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2019, 13, 1121–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazza, A.; Luciani, N.; Luciani, M.; Cammertoni, F.; Giaquinto, A.; Pavone, N.; Bruno, P.; Massetti, M. Fungal Endocarditis Due to Aspergillus oryzae: The First Case Reported in the Literature. J. Heart Valve Dis. 2017, 26, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M.R.; O’Donovan, B.D.; Gelfand, J.M.; Sample, H.A.; Chow, F.C.; Betjemann, J.P.; Shah, M.P.; Richie, M.B.; Gorman, M.P.; Hajj-Ali, R.A. Chronic meningitis investigated via metagenomic next-generation sequencing. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClenny, N. Laboratory detection and identification of Aspergillus species by microscopic observation and culture: The traditional approach. Med. Mycol. 2005, 43, S125–S128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balajee, S.; Houbraken, J.; Verweij, P.; Hong, S.; Yaghuchi, T.; Varga, J.; Samson, R. Aspergillus species identification in the clinical setting. Stud. Mycol. 2007, 59, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geiser, D.; Klich, M.; Frisvad, J.C.; Peterson, S.; Varga, J.; Samson, R.A. The current status of species recognition and identification in Aspergillus. Stud. Mycol. 2007, 59, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, T.; Iwen, P.C.; Hinrichs, S.H. Identification of Aspergillus species using internal transcribed spacer regions 1 and 2. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1510–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Makhlouf, J.; Carvajal-Campos, A.; Querin, A.; Tadrist, S.; Puel, O.; Lorber, S.; Oswald, I.P.; Hamze, M.; Bailly, J.-D.; Bailly, S. Morphologic, molecular and metabolic characterization of Aspergillus section Flavi in spices marketed in Lebanon. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susca, A.; Stea, G.; Mulé, G.; Perrone, G. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) identification of Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus tubingensis based on the calmodulin gene. Food Addit. Contam. 2007, 24, 1154–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.-Y.; Guo, L.-N.; Xiao, M.; Zhou, M.-L.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, T.-S.; Ning, Y.-T.; Jia, P.-Y. Clinical and Microbiological Characterization of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Caused by Aspergillus lentulus in China. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Lv, Q.; Yan, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y. The fungal CYP51s: Their functions, structures, related drug resistance, and inhibitors. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Wu, Q.; He, B.; Zeng, B. Genome-Wide Analysis of the Cytochromes P450 Gene Family in Aspergillus oryzae. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, Bari, Italy, 11–13 October 2018; pp. 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Kim, J.-E.; Lee, Y.-W.; Son, H. Fungal cytochrome P450s and the P450 complement (CYPome) of Fusarium graminearum. Toxins 2018, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Lee, M.-K.; Jefcoate, C.; Kim, S.-C.; Chen, F.; Yu, J.-H. Fungal cytochrome p450 monooxygenases: Their distribution, structure, functions, family expansion, and evolutionary origin. Genome Biol. Evol. 2014, 6, 1620–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Phase | Primer | Temperature | Time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Denaturation | ITS | 94 °C | 5′ | |
| benA | 95 °C | 5′ | ||
| CaM | 94 °C | 5′ | ||
| cyp51A | 94 °C | 7′ | ||
| Denaturation | ITS | 95 °C | 30″ | |
| benA | 94 °C | 45″ | ||
| CaM | 95 °C | 30″ | ||
| cyp51A | 94 °C | 30″ | ||
| Annealing | ITS | 52 °C | 60″ | |
| benA | 60 °C | 45″ | ||
| CaM | 60 °C | 60″ | ||
| cyp51A | 52 °C | 30″ | ||
| Extension | ITS | 72 °C | 2′ | |
| benA | 72 °C | 1′ | ||
| CaM | 72 °C | 1′ | ||
| cyp51A | 72 °C | 2′ | ||
| Final Extension | ITS | 72 °C | 7′ | |
| benA | 72 °C | 6′ | ||
| CaM | 72 °C | 7′ | ||
| cyp51A | 72 °C | 7′ | ||
| Cycle (Χ) | ITS | benA | CaM | cyp51A |
| 28 | 35 | 30 | 35 | |
| Sample Code | Source | BenA Gene (Accession Number) | ITS (Accession Number) | CaM Gene (Accession Number) | cyp51A Gene (Accession Number) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BAL | 100% A. flavus (MZ305275) | 99.55% A. flavus, 99.55% A. oryzae (MZ055458) | 99.48% A. flavus, 99.48% A. oryzae (MZ291495) | 100% A. flavus (MW558954) |
| 2 | BAL | 100% A. flavus, 100% A. oryzae (MZ305264) | 99.55% A. flavus, 99.55% A. oryzae (MZ055461) | 100% A. flavus (MZ291482) | 100% A. flavus (MW558955) |
| 3 | SP | 100% A. flavus, 100% A. oryzae (MZ305267) | 99.55% A. flavus, 99.55% A. oryzae (MZ055465) | 99.28% A. flavus (MZ291484) | 100% A. flavus (MW558956) |
| 4 | BAL | 100% A. flavus (MZ305269) | 99.55% A. flavus, 99.55% A. oryzae (MZ055460) | 99.61% A. flavus (MZ291489) | 100% A. flavus (MW558957) |
| 5 | BAL | 100% A. flavus, 100% A. oryzae (MZ305271) | 99.55% A. flavus, 99.55% A. oryzae (MZ055468) | 99.65% A. flavus, 99.65% A. oryzae (MZ291491) | 100% A. flavus (MW558958) |
| 6 | SP | 100% A. flavus, 100% A. oryzae (MZ305262) | 99.55% A. flavus, 99.55% A. oryzae (MZ055459) | 98.99% A. flavus (MZ291480) | 100% A. oryzae (MW558959) |
| 7 | BAL | 100% A. flavus, 100% A. oryzae (MZ305265) | 99.55% A. flavus, 99.55% A. oryzae (MZ055462) | 99.65% A. flavus (MZ291483) | 100% A. oryzae (MW558960) |
| 8 | SP | 100% A. flavus, 100% A. oryzae (MZ305263) | 99.55% A. flavus, 99.55% A. oryzae (MZ055466) | 96.93% A. flavus (MZ291487) | 100% A. oryzae (MW558961) |
| 9 | BAL | 100% A. flavus (MZ305273) | 99.55% A. flavus, 99.55% A. oryzae (MZ055467) | 100% A. flavus (MZ291493) | 100% A. oryzae (MW558962) |
| 10 | SP | 100% A. flavus (MZ305272) | 99.55% A. flavus, 99.55% A. oryzae (MZ055469) | 97.82% A. flavus (MZ291492) | 100% A. oryzae (MW558963) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nargesi, S.; Abastabar, M.; Valadan, R.; Mayahi, S.; Youn, J.-H.; Hedayati, M.T.; Seyedmousavi, S. Differentiation of Aspergillus flavus from Aspergillus oryzae Targeting the cyp51A Gene. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101279
Nargesi S, Abastabar M, Valadan R, Mayahi S, Youn J-H, Hedayati MT, Seyedmousavi S. Differentiation of Aspergillus flavus from Aspergillus oryzae Targeting the cyp51A Gene. Pathogens. 2021; 10(10):1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101279
Chicago/Turabian StyleNargesi, Sanaz, Mahdi Abastabar, Reza Valadan, Sabah Mayahi, Jung-Ho Youn, Mohammad Taghi Hedayati, and Seyedmojtaba Seyedmousavi. 2021. "Differentiation of Aspergillus flavus from Aspergillus oryzae Targeting the cyp51A Gene" Pathogens 10, no. 10: 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101279
APA StyleNargesi, S., Abastabar, M., Valadan, R., Mayahi, S., Youn, J.-H., Hedayati, M. T., & Seyedmousavi, S. (2021). Differentiation of Aspergillus flavus from Aspergillus oryzae Targeting the cyp51A Gene. Pathogens, 10(10), 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101279







