Dirofilaria spp. and Angiostrongylus vasorum: Current Risk of Spreading in Central and Northern Europe
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Dirofilaria spp.
2.1. Central Europe
2.1.1. Austria
2.1.2. Czechia
2.1.3. Germany
2.1.4. Hungary
2.1.5. Luxembourg
2.1.6. Poland
2.1.7. Slovakia
2.1.8. Slovenia
2.1.9. Switzerland
2.2. Northern Europe
2.2.1. Denmark
2.2.2. Finland
2.2.3. Iceland
2.2.4. Norway
2.2.5. Sweden
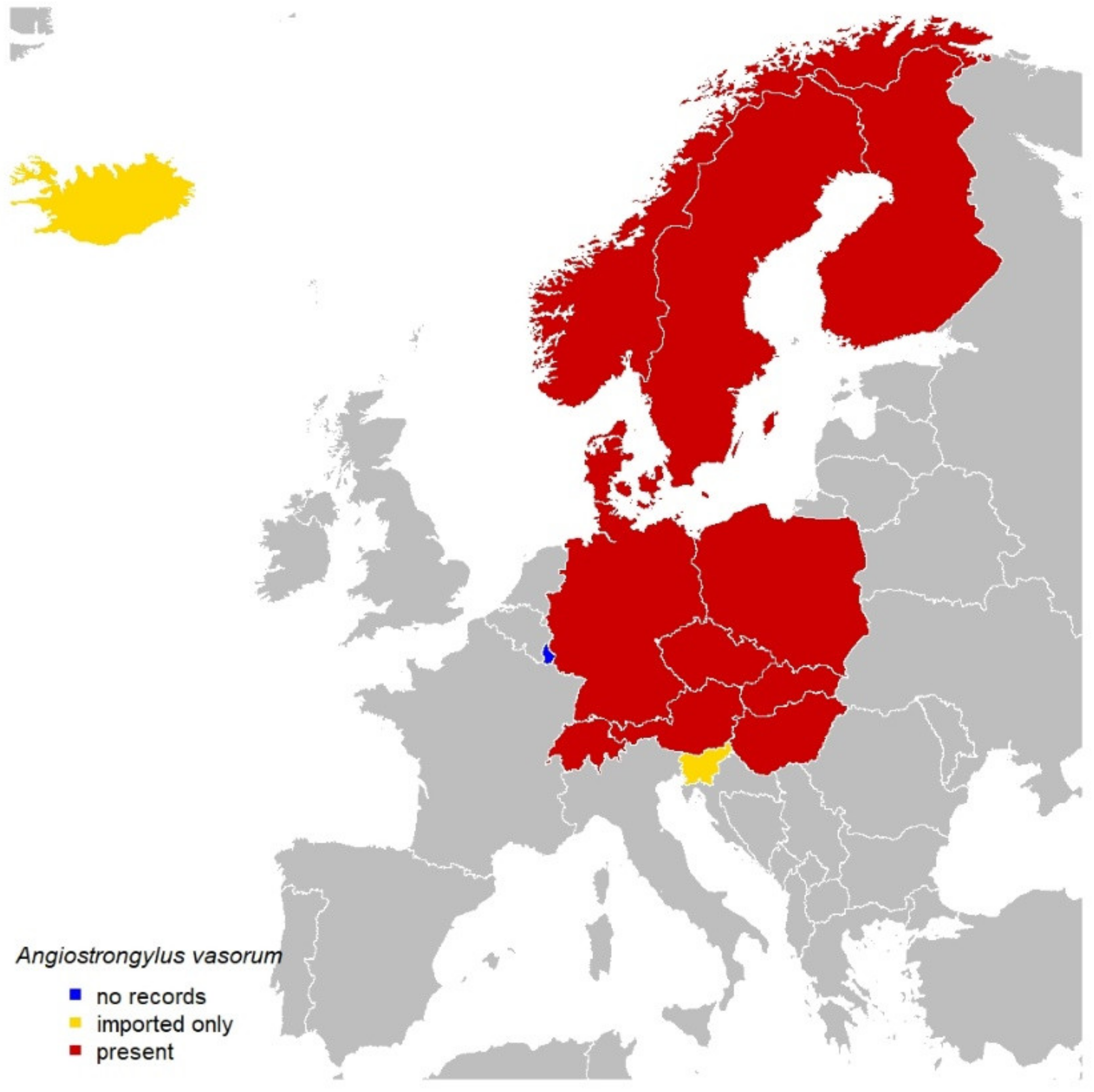
3. Angiostrongylus vasorum
3.1. Central Europe
3.1.1. Austria
3.1.2. Czechia
3.1.3. Germany
3.1.4. Hungary
3.1.5. Luxembourg
3.1.6. Poland
3.1.7. Slovakia
3.1.8. Slovenia
3.1.9. Switzerland
3.2. Northern Europe
3.2.1. Denmark
3.2.2. Finland
3.2.3. Iceland
3.2.4. Norway
3.2.5. Sweden
4. Factors Influencing the Prevalence and Establishment of D. immitis and D. repens
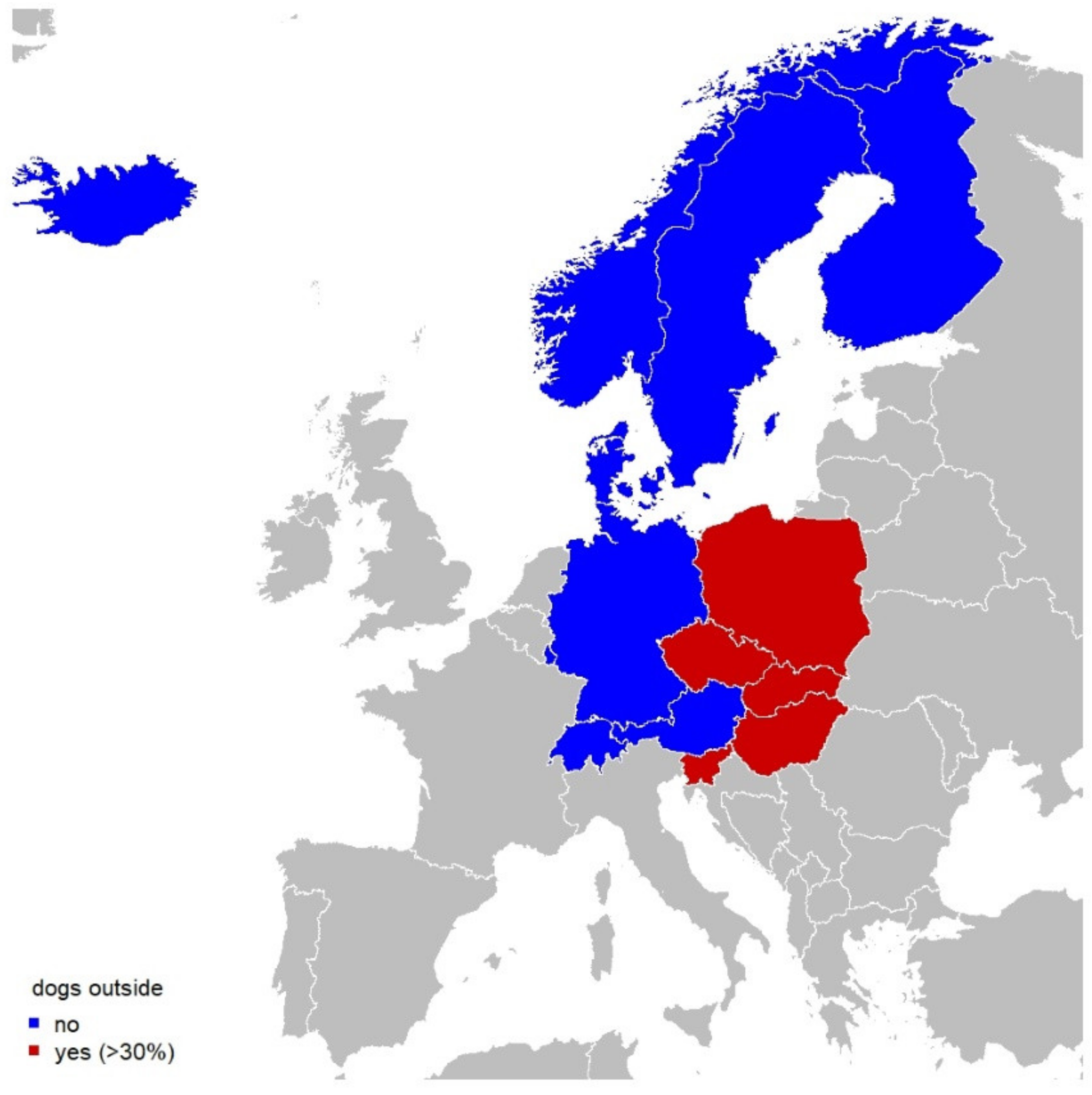
4.1. Dogs Staying Outside Overnight
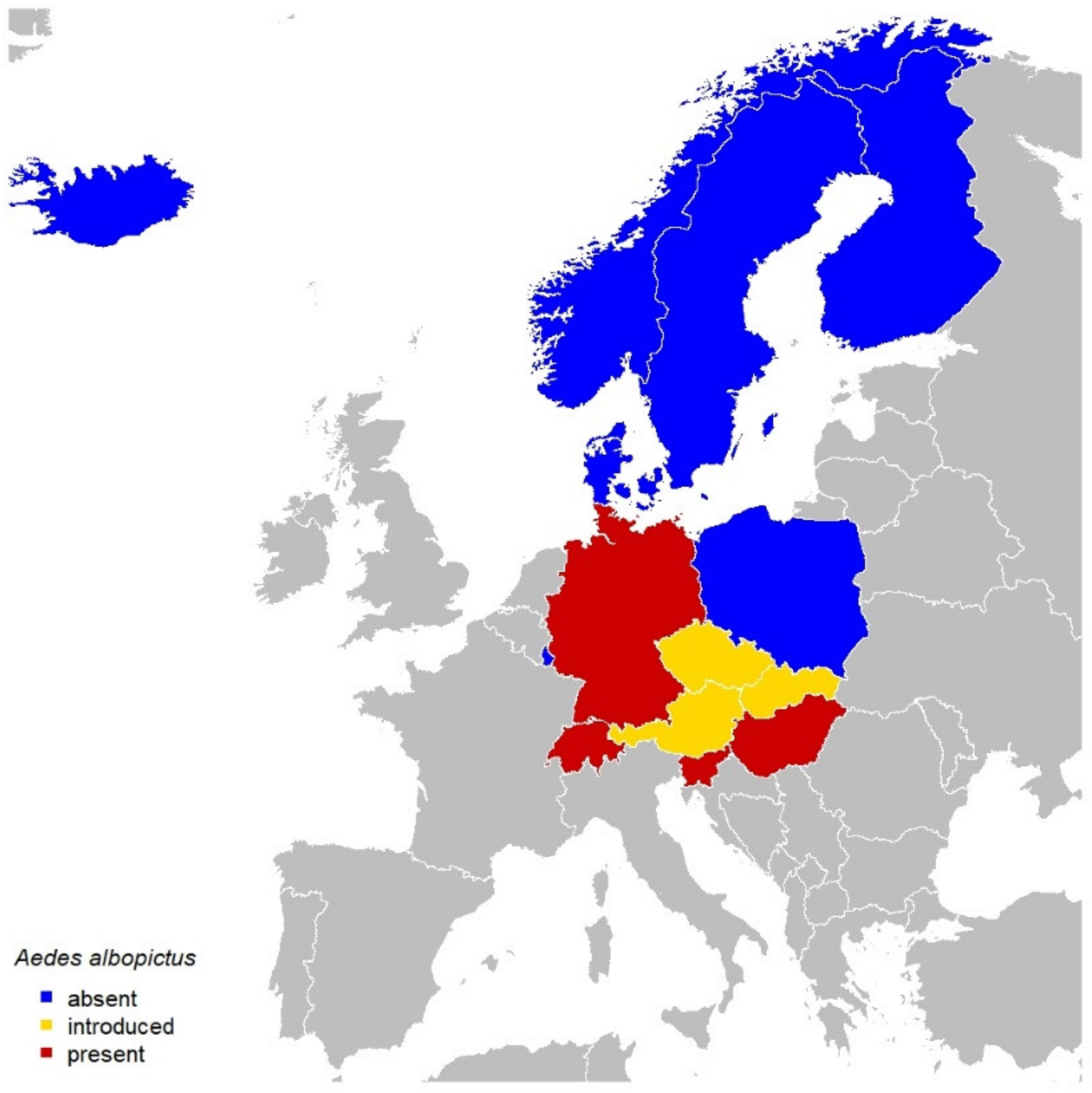
4.2. Diurnal Vector Activity
4.3. Climate Change
5. Factors Influencing the Prevalence and Distribution Dynamics of Angiostrongylus vasorum
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beugnet, F.; Chalvet-Monfray, K. Impact of climate change in the epidemiology of vector-borne diseases in domestic carnivores. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 36, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caminade, C.; McIntyre, K.M.; Jones, A.E. Impact of recent and future climate change on vector-borne diseases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1436, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, I.; Jongejan, F.; Marcondes, M.; Peregrine, A.; Baneth, G.; Bourdeau, P.; Bowman, D.D.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Capelli, G.; Cardoso, L.; et al. Parasites and vector-borne diseases disseminated by rehomed dogs. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillis-Germitsch, N.; Tritten, L.; Hegglin, D.; Deplazes, P.; Schnyder, M. Conquering Switzerland: The emergence of Angiostrongylus vasorum in foxes over three decades and its rapid regional increase in prevalence contrast with the stable occurrence of lungworms. Parasitology 2020, 147, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, L.; Schallig, H.; Persichetti, M.F.; Pennisi, M.G. New Epidemiological Aspects of Animal Leishmaniosis in Europe: The Role of Vertebrate Hosts Other Than Dogs. Pathogens 2021, 10, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, N.H.; Lindsay, L.R. Effects of Climate and Climate Change on Vectors and Vector-Borne Diseases: Ticks Are Different. Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traversa, D.; Morelli, S.; Di Cesare, A.; Diakou, A. Felid Cardiopulmonary Nematodes: Dilemmas Solved and New Questions Posed. Pathogens 2021, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikha, H.M.; Holmes, S.A.; Wright, I.; Morgan, E.R.; Lacher, D.W. Recent advances in the epidemiology, clinical and diagnostic features, and control of canine cardio-pulmonary angiostrongylosis. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelli, G.; Genchi, C.; Baneth, G.; Bourdeau, P.; Brianti, E.; Cardoso, L.; Danesi, P.; Fuehrer, H.-P.; Giannelli, A.; Ionică, A.M.; et al. Recent advances on Dirofilaria repens in dogs and humans in Europe. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, C.; Kramer, L.H. The prevalence of Dirofilaria immitis and D. repens in the Old World. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 280, 108995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsarraf, M.; Levytska, V.; Mierzejewska, E.J.; Poliukhovych, V.; Rodo, A.; Alsarraf, M.; Kavalevich, D.; Dwużnik-Szarek, D.; Behnke, J.M.; Bajer, A. Emerging risk of Dirofilaria spp. infection in Northeastern Europe: High prevalence of Dirofilaria repens in sled dog kennels from the Baltic countries. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deksne, G.; Davidson, R.K.; Buchmann, K.; Kärssin, A.; Kirjušina, M.; Gavarāne, I.; Miller, A.L.; Pálsdóttir, G.R.; Robertson, L.J.; Mørk, T.; et al. Parasites in the changing world—Ten timely examples from the Nordic-Baltic region. Parasite Epidemiol. Control 2020, 10, e00150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deksne, G.; Jokelainen, P.; Oborina, V.; Lassen, B.; Akota, I.; Kutanovaite, O.; Zaleckas, L.; Cīrule, D.; Tupīts, A.; Pimanovs, V.; et al. The Zoonotic Parasite Dirofilaria repens Emerged in the Baltic Countries Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania in 2008–2012 and Became Established and Endemic in a Decade. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2021, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCall, J.W.; Genchi, C.; Kramer, L.H.; Guerrero, J.; Venco, L. Heartworm disease in animals and humans. Adv. Parasitol. 2008, 66, 193–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón, F.; Siles-Lucas, M.; Morchón, R.; González-Miguel, J.; Mellado, I.; Carretón, E.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A. Human and animal dirofilariasis: The emergence of a zoonotic mosaic. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 507–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.A. Ursus americanus (Black Bear) a new host for Dirofilaria immitis. J. Parasitol. 1975, 61, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venco, L.; Marchesotti, F.; Manzocchi, S. Feline heartworm disease: A ‘Rubik’s-cube-like’ diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. J. Vet. Cardiol. 2015, 17 (Suppl. 1), S190–S201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajer, A.; Rodo, A.; Mierzejewska, E.J.; Tołkacz, K.; Welc-Falęciak, R. The prevalence of Dirofilaria repens in cats, healthy dogs and dogs with concurrent babesiosis in an expansion zone in central Europe. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alho, A.M.; Schnyder, M.; Schaper, R.; Meireles, J.; Belo, S.; Deplazes, P.; de Carvalho, L.M. Seroprevalence of circulating Angiostrongylus vasorum antigen and parasite-specific antibodies in dogs from Portugal. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 2567–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, M.K.; Atkins, C.E. Treatment of dogs with severe heartworm disease. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 283, 109131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, A.R.; Blagburn, B.L.; Tillson, M.; Brawner, W.; Welles, B.; Johnson, C.; Cattley, R.; Rynders, P.; Barney, S. Heartworm-associated respiratory disease (HARD) induced by immature adult Dirofilaria immitis in cats. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theis, J.H. Public health aspects of dirofilariasis in the United States. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 133, 157–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Society of Dirofilariosis and Angiostrongylosis. ESDA Guidelines for Clinical Management of Subcutaneous Dirofilariosis in Dogs and Cats. 2017. Available online: www.esda.vet (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Tarello, W. Clinical Aspects of Dermatitis Associated with Dirofilaria repens in Pets: A Review of 100 Canine and 31 Feline Cases (1990–2010) and a Report of a New Clinic Case Imported from Italy to Dubai. J. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 2011, 578385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocconi, F.; Di Tommaso, M.; Traversa, D.; Palmieri, C.; Pampurini, F.; Boari, A. Allergic dermatitis by Dirofilaria repens in a dog: Clinical picture and treatment. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 111, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potters, I.; Vanfraechem, G.; Bottieau, E. Dirofilaria repens Nematode Infection with Microfilaremia in Traveler Returning to Belgium from Senegal. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 1761–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, C.; Rinaldi, L.; Cascone, C.; Mortarino, M.; Cringoli, G. Is heartworm disease really spreading in Europe? Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 133, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, C.; Mortarino, M.; Rinaldi, L.; Cringoli, G.; Traldi, G.; Genchi, M. Changing climate and changing vector-borne disease distribution: The example of Dirofilaria in Europe. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 176, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, E.R.; Shaw, S.E.; Brennan, S.F.; de Waal, T.D.; Jones, B.R.; Mulcahy, G. Angiostrongylus vasorum: A real heartbreaker. Trends Parasitol. 2005, 21, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilhon, J.; Cens, B. Angiostrongilus vasorum (Baillet, 1866). Biological and morphological study. Ann. Parasitol. Hum. Comp. 1973, 48, 567–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozzer, L.R.; Lima, W.S. Gallus gallus domesticus: Paratenic host of Angiostrongylus vasorum. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 207, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, P.S.; Boag, A.K.; Guitian, J.; Boswood, A. Angiostrongylus vasorum infection in 23 dogs (1999–2002). J. Small Anim. Pract. 2004, 45, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traversa, D.; Torbidone, A.; Malatesta, D.; Guglielmini, C. Occurrence of fatal canine Angiostrongylus vasorum infection in Italy. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 152, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traversa, D.; Di Cesare, A.; Meloni, S.; Di Regalbono, A.F.; Milillo, P.; Pampurini, F.; Venco, L. Canine angiostrongylosis in Italy: Occurrence of Angiostrongylus vasorum in dogs with compatible clinical pictures. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 2473–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, S.A.; Paine, P.; Wright, I.; Morgan, E.R.; Elsheikha, H.M. Risk factors and predictors of angiostrongylosis in naturally infected dogs in the southeast of England. Companion Anim. 2020, 25, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becskei, C.; Willesen, J.L.; Schnyder, M.; Wozniakiewicz, M.; Miroshnikova, N.; Mahabir, S.P. Field safety and efficacy of an orally administered combination of sarolaner, moxidectin and pyrantel (Simparica Trio®) for the prevention of angiostrongylosis in dogs presented as veterinary patients. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillis-Germitsch, N.; Manser, M.B.; Hilbe, M.; Schnyder, M. Meerkats (Suricata suricatta), a new definitive host of the canid nematode Angiostrongylus vasorum. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2017, 6, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagardi, M.; Rabbogliatti, V.; Bassi, J.; Gioeni, D.; Oltolina, M.; Villa, L. Angiostrongylus vasorum in a Red Panda (Ailurus fulgens): Clinical Diagnostic Trial and Treatment Protocol. Acta Parasitol. 2021, 66, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelsen, M.F.; Meyland-Smith, F.; Willesen, J.L.; Jefferies, R.; Morgan, E.R.; Monrad, J. Diversity and prevalence of metastrongyloid nematodes infecting the red panda (Ailurus fulgens) in European zoos. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 172, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemming, L.; Jørgensen, A.C.; Nielsen, L.B.; Nielsen, S.T.; Mejer, H.; Chriél, M.; Petersen, H.H. Cardiopulmonary nematodes of wild carnivores from Denmark: Do they serve as reservoir hosts for infections in domestic animals? Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2020, 13, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueldner, E.K.; Schuppisser, C.; Borel, N.; Hilbe, M.; Schnyder, M. First case of a natural infection in a domestic cat (Felis catus) with the canid heart worm Angiostrongylus vasorum. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2019, 18, 100342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cesare, A.; Morelli, S.; Colombo, M.; Simonato, G.; Veronesi, F.; Marcer, F.; Diakou, A.; D’Angelosante, R.; Pantchev, N.; Psaralexi, E.; et al. Is Angiostrongylosis a Realistic Threat for Domestic Cats? Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diakou, A.; Dimzas, D.; Astaras, C.; Savvas, I.; di Cesare, A.; Morelli, S.; Neofitos, Κ.; Migli, D.; Traversa, D. Clinical investigations and treatment outcome in a European wildcat (Felis silvestris silvestris) infected by cardio-pulmonary nematodes. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2020, 19, 100357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segovia, J.M.; Torres, J.; Miquel, J. Helminth parasites of the red fox [Vulpes vulpes L., 1758] in the Iberian Peninsula: An ecological study. Acta Parasitol. 2004, 49, 67–79. [Google Scholar]
- Segovia, J.M.; Torres, J.; Miquel, J.; Llaneza, L.; Feliu, C. Helminths in the wolf, Canis lupus, from north-western Spain. J. Helminthol. 2001, 75, 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- Benda, T.; Csivincsik, Á.; Nemes, C.; Turbók, J.; Zsolnai, A.; Simonyai, E.; Majoros, G.; Nagy, G. Lethal Angiostrongylus vasorum infection in a Hungarian dog. Acta Parasitol. 2017, 62, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deak, G.; Gillis-Germitsch, N.; Ionică, A.M.; Mara, A.; Păstrav, I.R.; Cazan, C.D.; Ioniță, M.; Mitrea, I.L.; Răileanu, C.; Bărburaș, D.; et al. The first seroepidemiological survey for Angiostrongylus vasorum in domestic dogs from Romania. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čabanová, V.; Miterpáková, M.; Druga, M.; Hurníková, Z.; Valentová, D. GIS-based environmental analysis of fox and canine lungworm distribution: An epidemiological study of Angiostrongylus vasorum and Crenosoma vulpis in red foxes from Slovakia. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takács, A.; Szabó, L.; Juhász, L.; Lanszki, J.; Takács, P.; Heltai, M. Data on the parasitological status of golden jackal (Canis aureus L., 1758) in Hungary. Acta Vet. Hung. 2014, 62, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolnai, Z.; Széll, Z.; Sréter, T. Environmental determinants of the spatial distribution of Angiostrongylus vasorum, Crenosoma vulpis and Eucoleus aerophilus in Hungary. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 207, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuehrer, H.-P.; Morelli, S.; Bleicher, J.; Brauchart, T.; Edler, M.; Eisschiel, N.; Hering, T.; Lercher, S.; Mohab, K.; Reinelt, S.; et al. Detection of Crenosoma spp., Angiostrongylus vasorum and Aelurostrongylus abstrusus in Gastropods in Eastern Austria. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandi, G.; Lind, E.O.; Schaper, R.; Ågren, E.; Schnyder, M. Canine angiostrongylosis in Sweden: A nationwide seroepidemiological survey by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays and a summary of five-year diagnostic activity (2011–2015). Acta Vet. Scand. 2017, 59, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lempereur, L.; Martinelle, L.; Marechal, F.; Bayrou, C.; Dalemans, A.C.; Schnyder, M.; Losson, B. Prevalence of Angiostrongylus vasorum in southern Belgium, a coprological and serological survey. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiškina, V.; Lindqvist, E.-L.; Blomqvist, A.-C.; Orav, M.; Stensvold, C.R.; Jokelainen, P. Autochthonous Angiostrongylus vasorum in Finland. Vet. Rec. Open 2019, 6, e000314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikola, N.; Oborina, V.; Jokelainen, P. Knowledge About Emerging Zoonotic Vector-Borne Parasites Dirofilaria immitis and Dirofilaria repens in Finland: Questionnaire Survey to Medical Doctors and Veterinarians. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2020, 20, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiškina, V.; Jokelainen, P. Vector-borne parasitic infections in dogs in the Baltic and Nordic countries: A questionnaire study to veterinarians on canine babesiosis and infections with Dirofilaria immitis and Dirofilaria repens. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 244, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinaidy, H.K.; Bacowsky, H.; Hinterdorfer, F. Einschleppung der Hunde-Filarien Dirofilaria immitis und Dipetalonema reconditum nach Osterreich. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 1987, 34, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löwenstein, M.; Meissel, H.; Koller, J. Dirofilaria immitis in dogs in Austria. Wiener Tierarztliche Monatsschrift 1988, 75, 420–424. [Google Scholar]
- Kleiter, M.; Luckschander, N.; Willmann, M. Kutane Dirofilariose (Dirofilaria repens) bei zwei nach Österreich importierten Hunden. Kleintierpraxis 2001, 46, 283–288. [Google Scholar]
- Leschnik, M.; Löwenstein, M.; Edelhofer, R.; Kirtz, G. Imported non-endemic, arthropod-borne and parasitic infectious diseases in Austrian dogs. Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift 2008, 120, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duscher, G.G.; Feiler, A.; Wille-Piazzai, W.; Bakonyi, T.; Leschnik, M.; Miterpáková, M.; Kolodziejek, J.; Nowotny, N.; Joachim, A. Nachweis von Dirofilarien in österreichischen Hunden. Berliner und Munchener Tierarztliche Wochenschrift 2009, 122, 199–203. [Google Scholar]
- Fuehrer, H.-P.; Auer, H.; Leschnik, M.; Silbermayr, K.; Duscher, G.G.; Joachim, A. Dirofilaria in Humans, Dogs, and Vectors in Austria (1978–2014)-From Imported Pathogens to the Endemicity of Dirofilaria repens. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnberger, K.; Duscher, G.G.; Fuehrer, H.-P.; Leschnik, M. Current trends in canine dirofilariosis in Austria—do we face a pre-endemic status? Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnberger, K.; Fuehrer, H.-P.; Sonnberger, B.W.; Leschnik, M.; Fuehrer, H.-P.; Sonnberger, B.W.; Leschnik, M. The Incidence of Dirofilaria immitis in Shelter Dogs and Mosquitoes in Austria. Pathogens 2021, 10, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnberger, B.W.; Graf, B.; Straubinger, R.K.; Rackl, D.; Obwaller, A.G.; Peschke, R.; Barogh, B.S.; Joachim, A.; Fuehrer, H.-P. Vector-borne pathogens in clinically healthy military working dogs in eastern Austria. Parasitol. Int. 2021, 84, 102410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulmer, L.M.; Unterköfler, M.S.; Fuehrer, H.-P.; Janovska, V.; Pagac, M.; Svoboda, M.; Venco, L.; Leschnik, M. First Autochthonous Infection of a Cat with Dirofilaria immitis in Austria. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodžić, A.; Mrowietz, N.; Cézanne, R.; Bruckschwaiger, P.; Punz, S.; Habler, V.E.; Tomsik, V.; Lazar, J.; Duscher, G.G.; Glawischnig, W.; et al. Occurrence and diversity of arthropod-transmitted pathogens in red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in western Austria, and possible vertical (transplacental) transmission of Hepatozoon canis. Parasitology 2018, 145, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardach, H.; Heimbucher, J.; Raff, M. Sulkutane Dirofilaria (Nochtiella) repens. Infektion Beim Menschen. Erste Fallbeschreibung In Oesterreich Und Uebersicht Der Literatur. Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift 1981, 93, 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- Auer, H.; Susani, M. Der erste autochthone Fall einer subkutanen Dirofilariose in Osterreich. Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift 2008, 120, 104–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riebenbauer, K.; Weber, P.B.; Walochnik, J.; Karlhofer, F.; Winkler, S.; Dorfer, S.; Auer, H.; Valencak, J.; Laimer, M.; Handisurya, A. Human dirofilariosis in Austria: The past, the present, the future. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haim, A.; Kitchen, M.; Auer, H.; Rettenbacher, T.; Schmuth, M. A case of human Dirofilaria repens infection, causing an asymptomatic subcutaneous nodule. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 1703–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silbermayr, K.; Eigner, B.; Joachim, A.; Duscher, G.G.; Seidel, B.; Allerberger, F.; Indra, A.; Hufnagl, P.; Fuehrer, H.-P. Autochthonous Dirofilaria repens in Austria. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Übleis, S.S.; Cuk, C.; Nawratil, M.; Butter, J.; Schoener, E.; Obwaller, A.G.; Zechmeister, T.; Duscher, G.G.; Rubel, F.; Lebl, K.; et al. Xenomonitoring of Mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) for the Presence of Filarioid Helminths in Eastern Austria. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 2018, 9754695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoener, E.; Zittra, C.; Weiss, S.; Walder, G.; Barogh, B.S.; Weiler, S.; Fuehrer, H.-P. Monitoring of alien mosquitoes of the genus Aedes (Diptera: Culicidae) in Austria. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 1633–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuehrer, H.-P.; Schoener, E.; Weiler, S.; Barogh, B.S.; Zittra, C.; Walder, G. Monitoring of alien mosquitoes in Western Austria (Tyrol, Austria, 2018). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakran-Lebl, K.; Zittra, C.; Harl, J.; Barogh, B.S.; Grätzl, A.; Ebmer, D.; Schaffner, F.; Fuehrer, H.-P. Arrival of the Asian tiger mosquito, Aedes albopictus (Skuse, 1895) in Vienna, Austria, and initial monitoring activities. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svobodova, V.; Misonova, P. The potential risk of Dirofilaria immitis becoming established in the Czech Republic by imported dogs. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 128, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svobodová, Z.; Svobodová, V.; Genchi, C.; Forejtek, P. The first report of authochthonous dirofilariosis in dogs in the Czech Republic. Helminthologia 2006, 43, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miterpáková, M.; Hurníková, Z.; Valentová, D.; Borková, L.; Zuzana, H.; Lenka, B. Different epidemiological pattern of canine dirofilariosis in two neighboring countries in Cent0ral Europe-the Czech Republic and Slovakia. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolf, I.; Šebesta, O.; Mendel, J.; Betášová, L.; Bocková, E.; Jedličková, P.; Venclíková, K.; Blažejová, H.; Šikutová, S.; Hubálek, Z. Zoonotic Dirofilaria repens (Nematoda: Filarioidea) in Aedes vexans mosquitoes, Czech Republic. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 4663–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matějů, J.; Chanová, M.; Modrý, D.; Mitková, B.; Hrazdilová, K.; Žampachová, V.; Kolářová, L. Dirofilaria repens: Emergence of autochthonous human infections in the Czech Republic (case reports). BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebauer, J.; Ondruš, J.; Kulich, P.; Novotný, L.; Sałamatin, R.; Husa, P.; Novobilský, A. The first case of periorbital human dirofilariasis in the Czech Republic. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuterer, G.; Gothe, R. Die Herzwurmkrankheit des Hundes: Erregerbiologie und-okologie, Pathogenese, Klinik, Diagnose, Therapie und Prophylaxe. Canine heartworm disease: Biology and ecology of the causative agent, pathogenesis, clinical signs, diagnosis, therapy and prophylaxis. Kleintierpraxis 1993, 38, 633–646. [Google Scholar]
- Glaser, B.; Gothe, R. Importierte arthropodenübertragene Parasiten und parasitische Arthropoden beim Hund. Erregerspektrum und epidemiologische Analyse der 1995/96 diagnostizierten Fälle. Tierarztl. Prax. Ausg. K Kleintiere. Heimtiere. 1998, 26, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schrey, C.F. Epidemiologische Fallanalyse und Klinik der Kardiovaskulären Dirofilariose (Herzwurmerkrankung) bei Hunden in Deutschland; Free University of Berlin: Berlin, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wohlsein, P.; Vilafranca, M.; Brandes, B. Leishmaniose und Filariose bei einem Hund. Kleintierpraxis 1996, 25, 367–374. [Google Scholar]
- Zahler, M.; Glaser, B.; Gothe, R. Imported parasites in dogs: Dirofilaria repens and Dipetalonema reconditum. Tierarztliche Praxis 1997, 25, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hermosilla, C.; Pantchev, N.; Dyachenko, V.; Gutmann, M.; Bauer, C. First autochthonous case of canine ocular Dirofilaria repens infection in Germany. Vet. Rec. 2006, 158, 134–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassnau, R.; Dyachenko, V.; Pantchev, N.; Stockel, F.; Dittmar, K.; Daugschies, A. Dirofilaria-repens-Befall in einem Schlittenhunde-Rudel im Land Brandenburg. Diagnose und Therapie der kaninen kutanen Dirofilariose. Tierarztl. Prax. Ausg. K Kleintiere. Heimtiere. 2009, 37, 95. [Google Scholar]
- Pantchev, N.; Norden, N.; Lorentzen, L.; Rossi, M.; Rossi, U.; Brand, B.; Dyachenko, V. Current surveys on the prevalence and distribution of Dirofilaria spp. in dogs in Germany. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 105 (Suppl. 1), S63–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, M.; Pantchev, N. Vorkommenshäufigkeit der Reisekrankheiten Leishmaniose, Ehrlichiose, Babesiose und Dirofilariose bei in Deutschland lebenden Hunden. Kleintierpraxis 2008, 12, 154–165. [Google Scholar]
- Pantchev, N.; Etzold, M.; Daugschies, A.; Dyachenko, V. Diagnosis of imported canine filarial infections in Germany 2008–2010. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 109 (Suppl. 1), S61–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röhrig, E.; Hamel, D.; Pfister, K. Retrospective evaluation of laboratory data on canine vector-borne infections from the years 2004–2008. Berliner und Munchener Tierarztliche Wochenschrift 2011, 124, 411–418. [Google Scholar]
- Vrhovec, M.G.; Pantchev, N.; Failing, K.; Bauer, C.; Travers-Martin, N.; Zahner, H. Retrospective Analysis of Canine Vector-borne Diseases (CVBD) in Germany with Emphasis on the Endemicity and Risk Factors of Leishmaniosis. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Menn, B.; Lorentz, S.; Naucke, T.J. Imported and travelling dogs as carriers of canine vector-borne pathogens in Germany. Parasites Vectors 2010, 3, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, D.; Röhrig, E.; Pfister, K. Canine vector-borne disease in travelled dogs in Germany--a retrospective evaluation of laboratory data from the years 2004–2008. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 181, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czajka, C.; Becker, N.; Poppert, S.; Jöst, H.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Krüger, A. Molecular detection of Setaria tundra (Nematoda: Filarioidea) and an unidentified filarial species in mosquitoes in Germany. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czajka, C.; Becker, N.; Jöst, H.; Poppert, S.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Krüger, A.; Tannich, E. Stable transmission of Dirofilaria repens nematodes, northern Germany. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heym, E.C.; Kampen, H.; Krone, O.; Schäfer, M.; Werner, D. Molecular detection of vector-borne pathogens from mosquitoes collected in two zoological gardens in Germany. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 2097–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronefeld, M.; Kampen, H.; Sassnau, R.; Werner, D. Molecular detection of Dirofilaria immitis, Dirofilaria repens and Setaria tundra in mosquitoes from Germany. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassnau, R.; Daugschies, A.; Lendner, M.; Genchi, C. Climate suitability for the transmission of Dirofilaria immitis and D. repens in Germany. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 205, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassnau, R.; Czajka, C.; Kronefeld, M.; Werner, D.; Genchi, C.; Tannich, E.; Kampen, H. Dirofilaria repens and Dirofilaria immitis DNA findings in mosquitoes in Germany: Temperature data allow autochthonous extrinsic development. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 3057–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassnau, R.; Genchi, C. Qualitative risk assessment for the endemisation of Dirofilaria repens in the state of Brandenburg (Germany) based on temperature-dependent vector competence. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 2647–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassnau, R.; Kohn, M.; Demeler, J.; Kohn, B.; Müller, E.; Krücken, J.; von Samson-Himmelstjerna, G. Is Dirofilaria repens endemic in the Havelland district in Brandenburg, Germany? Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2013, 13, 888–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Härtwig, V.; Daugschies, A.; Dyachenko, V. Dirofilaria-repens-Befall bei einem Hund aus Mitteldeutschland ohne Reisevorbericht. Ein Fallbericht. Tierarztl. Prax. Ausg. K Kleintiere. Heimtiere. 2015, 43, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappe, D.; Plauth, M.; Bauer, T.; Muntau, B.; Dießel, L.; Tannich, E.; Herrmann-Trost, P. A case of autochthonous human Dirofilaria infection, Germany, March 2014. Euro Surveill. 2014, 19, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Härtwig, V.; Schulze, C.; Barutzki, D.; Schaper, R.; Daugschies, A.; Dyachenko, V. Detection of Angiostrongylus vasorum in Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes) from Brandenburg, Germany. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114 (Suppl. 1), S185–S192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liesner, J.M.; Krücken, J.; Schaper, R.; Pachnicke, S.; Kohn, B.; Müller, E.; Schulze, C.; Samson-Himmelstjerna, G. von. Vector-borne pathogens in dogs and red foxes from the federal state of Brandenburg, Germany. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 224, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, I.; Volkmann, M.; Beelitz, P.; Merle, R.; Müller, E.; Kohn, B. Retrospective evaluation of vector-borne infections in dogs imported from the Mediterranean region and southeastern Europe (2007–2015). Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, I.; Volkmann, M.; Beelitz, P.; Merle, R.; Müller, E.; Kohn, B. Retrospective analysis of vector-borne infections in dogs after travelling to endemic areas (2007–2018). Vet. Parasitol. X 2019, 2, 100015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, I.; Kohn, B.; Volkmann, M.; Müller, E. Retrospective evaluation of vector-borne pathogens in cats living in Germany (2012–2020). Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotlán, S. On a new case of human filarioidosis in Hungary. Acta Vet. Acad. Sci. Hung. 1951, 1, 69–79. [Google Scholar]
- Szénási, Z.; Kovács, A.H.; Pampiglione, S.; Fioravanti, M.L.; Kucsera, I.; Tánczos, B.; Tiszlavicz, L. Human dirofilariosis in Hungary: An emerging zoonosis in central Europe. Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift 2008, 120, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fodor, E.; Fok, É.; Maka, E.; Lukáts, O.; Tóth, J. Recently recognized cases of ophthalmofilariasis in Hungary. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 19, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dóczi, I.; Bereczki, L.; Gyetvai, T.; Fejes, I.; Skribek, Á.; Szabó, Á.; Berkes, S.; Tiszlavicz, L.; Bartha, N.; Bende, B.; et al. Description of five dirofilariasis cases in South Hungary and review epidemiology of this disease for the country. Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift 2015, 127, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fok, É.; Szabó, Z.; Farkas, R. Dirofilaria repens első hazai diagnosztizálása kutyában sebészeti beavatkozás sorá. Kisállatorvoslás 1998, 4, 218–219. [Google Scholar]
- Széll, Z.; Sréter, T.; Csikós, K.; Kátai, Z.; Dobos-Kovács, M.; Vetési, F. Dirofilaria repens fertőzöttség kutyákban. Magyar Állatorvosok Lapja 1999, 121, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Fok, É.; Kiss, G.; Majoros, G.; Jacsó, O.; Farkas, R.; Gyurkovszky, M. Preliminary results of an epidemiological survey on dirofilariosis of dogs and cats in Hungary. Mappe Parassitologiche 2007, 8, 195–196. [Google Scholar]
- Jacsó, O. Distribution and Veterinary Importance of Dirofilaria Species in Hungary, and Treatment Experience; Szent István University: Budapest, Hungary, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Farkas, R.; Mag, V.; Gyurkovszky, M.; Takács, N.; Vörös, K.; Solymosi, N. The current situation of canine dirofilariosis in Hungary. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemenesi, G.; Kurucz, K.; Kepner, A.; Dallos, B.; Oldal, M.; Herczeg, R.; Vajdovics, P.; Bányai, K.; Jakab, F. Circulation of Dirofilaria repens, Setaria tundra, and Onchocercidae species in Hungary during the period 2011–2013. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 214, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boros, G.; Janisch, M.; Sebesyén, G. Dirofilaria immitis fertőzöttség kutyában. Magyar Állatorvosok Lapja 1982, 122, 313–316. [Google Scholar]
- Vörös, K.; Kiss, G.; Baska, F.; Bagdi, N.; Széll, Z. Heartworm disease in dogs. Review article and case report. Magyar Állatorvosok Lapja 2000, 122, 707–716. [Google Scholar]
- Jacsó, O.; Mándoki, M.; Majoros, G.; Pétsch, M.; Mortarino, M.; Genchi, C.; Fok, É. First autochthonous Dirofilaria immitis (Leidy, 1856) infection in a dog in Hungary. Helminthologia 2009, 46, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, R.; Gyurkovszky, M.; Lukács, Z.; Aladics, B.; Solymosi, N. Seroprevalence of some vector-borne infections of dogs in Hungary. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014, 14, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Túri, Á.; Hetyey, C. Dirofilaria immitis elso magyarországi kimutatása a tüdo-artériában echokardiográfiás vizsgálattal. Magyar Állatorvosok Lapja 2014, 136, 231–233. [Google Scholar]
- Bacsadi, Á.; Papp, A.; Szeredi, L.; Tóth, G.; Nemes, C.; Imre, V.; Tolnai, Z.; Széll, Z.; Sréter, T. Retrospective study on the distribution of Dirofilaria immitis in dogs in Hungary. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 220, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vörös, K.; Becker, Z.; Arany-Tóth, A.; Gyurkovszky, M.; Farkas, R. Okkult Dirofilaria immitis szívférgesség kutyában: Esetismertetés és irodalmi áttekintés. Magyar Állatorvosok Lapja 2017, 139, 675–685. [Google Scholar]
- Tolnai, Z.; Széll, Z.; Sproch, T.; Szeredi, L.; Sréter, T. Dirofilaria immitis: An emerging parasite in dogs, red foxes and golden jackals in hungary. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 203, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnár, V.; Pazár, P.; Rigó, D.; Máthé, D.; Fok, T.; Glávits, R.; Vajdovich, P.; Jacsó, O.; Balogh, L.; Sós, E. Autochthonous Dirofilaria immitis infection in a ferret with aberrant larval migration in Europe. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2010, 51, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sréter, T.; Széll, Z.; Marucci, G.; Pozio, E.; Varga, I. Extraintestinal nematode infections of red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in Hungary. Vet. Parasitol. 2003, 115, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, C.; Schaffner, F. Krankheitsübertragende Stechmücken (Culicidae) in Luxemburg und Europa. Luxembourg, 7 November. 2019. Available online: https://mosquitoes.lu/posters/Poster%20A0%20Pest%20mosquitoes%20in%20LU%20and%20Eruope%202019%20with%20crop%20marks%20DE.pdf (accessed on 30 August 2021).
- Demiaszkiewicz, A.W.; Polańczyk, G.; Pyziel, A.M.; Kuligowska, I.; Lachowicz, J. Pierwsze ogniska dirofilariozy psow wywolanej przez Dirofilaria repens Railliet et Henry, 1911 w centralnej Polsce. Ann. Parasitol. 2009, 55, 367–370. [Google Scholar]
- Demiaszkiewicz, A.W.; Polańczyk, G. Pierwszy w Polsce przypadek inwazji Dirofilaria repens u psa. Magazyn Weterynaryjny 2010, 19, 254–256. [Google Scholar]
- Sapierzyński, R.; Fabisiak, M.; Sałamaszyńska, A. Several cases of dirofilariosis accidentally diagnosed in dogs from Poland, including two PCR positive Dirofilaria repens cases. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2010, 13, 545–547. [Google Scholar]
- Masny, A.; Lewin, T.; Sałamatin, R.V.; Gołąb, E. Autochthonous canine Dirofilaria repens in the vicinity of Warsaw. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2011, 14, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Demiaszkiewicz, A.W.; Pyziel, A.M. Przypadek dirofilariozy powiekowej u psa w Polsce. Magazyn Weterynaryjny 2012, 21, 342–344. [Google Scholar]
- Demiaszkiewicz, A.W.; Karamon, J.; Jasik, A. Przypadek wykrycia nicienia Dirofilaria repens w jądrze psa. Medycyna Weterynaryjna 2013, 69, 124–127. [Google Scholar]
- Demiaszkiewicz, A.W.; Polańczyk, G.; Osińska, B.; Pyziel, A.M.; Kuligowska, I.; Lachowicz, J.; Sikorski, A. Prevalence and distribution of Dirofilaria repens Railliet et Henry, 1911 in dogs in Poland. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2014, 17, 515–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajer, A.; Mierzejewska, E.J.; Rodo, A.; Bednarska, M.; Kowalec, M.; Welc-Falęciak, R. The risk of vector-borne infections in sled dogs associated with existing and new endemic areas in Poland: Part 1: A population study on sled dogs during the racing season. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 202, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demiaszkiewicz, A.W.; Polańczyk, G.; Osińska, B.; Pyziel, A.M.; Kuligowska, I.; Lachowicz, J.; Sikorski, A. The prevalence and distribution of Dirofilaria repens in dogs in the Mazovian Province of central-eastern Poland. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2014, 21, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Adaszek, L.; Janecki, R.; Lachowicz, K.; Teodorowski, O.; Winiarczyk, S. Czy zarażenia Dirofilaria immitis stanowią zagrożenie dla psów w Polsce? Magazyn Weterynaryjny 2021, 4, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Masny, A.; Gołąb, E.; Cielecka, D.; Sałamatin, R.V.; Cielecka, D. Vector-borne helminths of dogs and humans focus on central and eastern parts of Europe. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cielecka, D.; Szymanska, K.; Sałamatin, R.V.; Tomaszewska, A. Przypadek inwazji Dirofilaria repens (Leidy, 1856)(Nematoda: Filarioidea: Onchocercidae) u pacjenta w Warszawie. Wiadomości Parazytologiczne 2007, 53, 165. [Google Scholar]
- Żarnowska-Prymek, H.; Cielecka, D.; Sałamatin, R.V. Dirofilarioza—Dirofilaria repens, po raz pierwszy opisana u polskich pacjentów. Przegląd Epidemiologiczny 2008, 62, 547–551. [Google Scholar]
- Wesołowska, M.; Szaliński, M.; Zieliński, M.; Okulewicz, A.; Kisza, K.; Misiuk-Hojło, M. Dirofilaria repens–pierwszy przypadek dirofilariozy podspojówkowej w Polsce. Przewodnik Lekarza 2009, 12, 65. [Google Scholar]
- Cielecka, D.; Żarnowska-Prymek, H.; Masny, A.; Sałamatin, R.V.; Wesołowska, M.; Gołąb, E.; Cielecka, D.; Żarnowska-Prymek, H.; Masny, A.; Sałamatin, R.V.; et al. Human dirofilariosis in Poland: The first cases of autochthonous infections with Dirofilaria repens. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2012, 19, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Demiaszkiewicz, A.W. Dirofilaria repens Railliet et Henry, 1911-a new parasite acclimatized in Poland. Ann. Parasitol. 2014, 60, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kłudkowska, M.; Pielok, Ł.; Frąckowiak, K.; Masny, A.; Gołąb, E.; Paul, M. Dirofilaria repens infection as a cause of intensive peripheral microfilariemia in a Polish patient: Process description and cases review. Acta Parasitol. 2018, 63, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkowski, P.K.; Rymkiewicz, G.; Golebiewska, J.; Nestoros, N.; Romejko-Jarosinska, J.; Żarnowska-Prymek, H.; Masny, A.; Palucki, J.; Cielecka, D. The first case of human autochtonous subconjunctival dirofilariosis in Poland and MALT lymphoma as possible consequence of this parasitosis. Infect. Agents Cancer 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodziej, P.; Szostakowska, B.; Jarosz, B.; Pojasek, S.; Romak, M.; Kocki, J.; Bogucka-Kocka, A. The first case of elbow bursitis caused by Dirofilaria repens in humans. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świątalska, A.; Demiaszkiewicz, A.W. Pierwszy w Polsce rodzimy przypadek inwazji nicieni Dirofilaria immitis u psa. Życie Weterynaryjne 2012, 87, 685–686. [Google Scholar]
- Krämer, F.; Schaper, R.; Schunack, B.; Połozowski, A.; Piekarska, J.; Szwedko, A.; Jodies, R.; Kowalska, D.; Schüpbach, D.; Pantchev, N. Serological detection of Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato and Ehrlichia canis antibodies and Dirofilaria immitis antigen in a countrywide survey in dogs in Poland. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 3229–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svobodova, V.; Svobodova, Z.; Beladicova, V.; Valentová, D. First cases of canine dirofilariosis in Slovakia: A case report. Veterinární Medicína 2005, 50, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miterpáková, M.; Antolová, D.; Hurníková, Z.; Dubinský, P. Dirofilariosis in Slovakia-a new endemic area in Central Europe. Helminthologia 2008, 45, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miterpáková, M.; Antolová, D.; Hurníková, Z.; Dubinský, P.; Pavlačka, A.; Németh, J. Dirofilaria infections in working dogs in Slovakia. J. Helminthol. 2010, 84, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Miterpáková, M.; Iglódyová, A.; Čabanová, V.; Stloukal, E.; Miklisová, D. Canine dirofilariosis endemic in Central Europe-10 years of epidemiological study in Slovakia. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 2389–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čabanová, V.; Pantchev, N.; Hurníková, Z.; Miterpáková, M. Recent study on canine vector-borne zoonoses in southern Slovakia-serologic survey. Acta Parasitol. 2015, 60, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miterpáková, M.; Valentová, D.; Čabanová, V.; Berešíková, Ľ. Heartworm on the rise-new insights into Dirofilaria immitis epidemiology. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 2347–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miterpáková, M.; Zborovská, H.; Bielik, B.; Halán, M. The fatal case of an autochthonous heartworm disease in a dog from a non-endemic region of south-eastern Slovakia. Helminthologia 2020, 57, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miterpáková, M.; Hurníková, Z.; Zaleśny, G.; Chovancová, B. Molecular evidence for the presence of Dirofilaria repens in beech marten (Martes foina) from Slovakia. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 196, 544–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurníková, Z.; Miterpáková, M.; Zaleśny, G. Epidemiological coherency of vulpine dirofilariosis in environmental conditions of Slovakia. Helminthologia 2015, 52, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocková, E.; Rudolf, I.; Kočišová, A.; Betášová, L.; Venclíková, K.; Mendel, J.; Hubálek, Z. Dirofilaria repens microfilariae in Aedes vexans mosquitoes in Slovakia. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 3465–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocková, E.; Iglódyová, A.; Kočišová, A. Potential mosquito (Diptera: Culicidae) vector of Dirofilaria repens and Dirofilaria immitis in urban areas of Eastern Slovakia. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 4487–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čabanová, V.; Miterpáková, M.; Valentová, D.; Blažejová, H.; Rudolf, I.; Stloukal, E.; Hurníková, Z.; Dzidová, M. Urbanization impact on mosquito community and the transmission potential of filarial infection in central Europe. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilková, D.; Klisenbauer, D.; Juhas, T.; Moravec, F.; Uhlikova, M.; Hübner, J.; Konakova, G. Isolation of Dirofilaria repens in vitreoretinal findings. Ceskoslovenska Oftalmologie 1992, 48, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miterpáková, M.; Antolová, D.; Ondriska, F.; Gál, V. Human Dirofilaria repens infections diagnosed in Slovakia in the last 10 years (2007–2017). Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift 2017, 129, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miterpáková, M.; Antolová, D.; Ondriska, F.; Boldiš, V. Filarial infections in human medicine and public health. Lekársky obzor 2021, 70, 512–513. [Google Scholar]
- Brglez, J.; Senk, L. Dirofilaria immitis (Leidy, 1856) Railliet et Henry, 1911, pri psu: Zbornik Biotehniske Fakultete Univerze Edvardo Kardelja v Ljubljani. Veterinarstvo 1987, 24, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Brglez, J.; Verbančič, Š. Podkožna oblika dirofilarioze pri lisici: Zbornik Biotehniske Fakultete Univerze Edvardo Kardelja v Ljubljani. Veterinarstvo 1988, 25, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Logar, J.; Novsak, V.; Rakovec, S.; Stanisa, O. Subcutaneous infection caused by Dirofilaria repens imported to Slovenia. J. Infect. 2001, 42, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, G.F. Geographical distribution, vectors, and life cycle of Dirofilaria immitis. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1969, 154, 370–373. [Google Scholar]
- Savani, G. Distribuzione della microfilaria dei cani in Carpi, Novi, Concordia e dintorni. Scienze Mediche Colon 1933, 32, 357–364. [Google Scholar]
- Vlach, G. La filariosi nei cani di Trieste e Provincia. Archicio Italionao di Scienze Mediche Colon 1936, 77, 418–445. [Google Scholar]
- Depieds, R.; Remon, J. Etat actuel de l’endémicité à dirofilaria immitis chez le chien, dans la région d’hyères; apres les travaux récents de démoustiquation. Rev. Pathol. Gen. Physiol. Clin. 1955, 55, 824–826. [Google Scholar]
- Ranque, J.; Clayette, J. La distribution géographique de la filariose canine dans la région provençale; ses rapports avec les anciennes zones d’endémie palustre. J. Med. Bord. 1951, 128, 258–259. [Google Scholar]
- Kersten, W. Zum Vorkommen der Herzfilariose (Dirofilaria immitis) beim Hund. Dtsch Tieraerztl Wschr 1959, 66, 217–219. [Google Scholar]
- Thun, R. Die Herzwurmerkrankung des Hundes. Schweizer Archiv für Tierheilkunde 1975, 117, 99–111. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, P.; Deplazes, P.; Ruckstuhl, H.; Flückiger, M. Case report: Dirofilariasis in a dog. Schweizer Archiv für Tierheilkunde 1994, 136, 265–269. [Google Scholar]
- Deplazes, P.; Guscetti, F.; Wunderlin, E.; Bucklar, H.; Skaggs, J.; Wolff, K. Endoparasitenbefall bei Findel- und Verzicht-Hunden in der Südschweiz. Schweizer Archiv für Tierheilkunde 1995, 137, 172–179. [Google Scholar]
- Bucklar, H.; Scheu, U.; Mossi, R.; Deplazes, P. Breitet sich in der Südschweiz die Dirofilariose beim Hund aus? Schweizer Archiv für Tierheilkunde 1998, 140, 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- Petruschke, G.; Rossi, L.; Genchi, C.; Pollono, F. Sulle dirofilariosi canine nel Canton Ticino e in aree confinanti del Nord Italia. Schweizer Archiv für Tierheilkunde 2001, 143, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Suter, T.; Flacio, E.; Fariña, B.F.; Engeler, L.; Tonolla, M.; Müller, P. First report of the invasive mosquito species Aedes koreicus in the Swiss-Italian border region. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deplazes, P.; Staebler, S.; Gottstein, B. Reisemedizin parasitärer Erkrankungen des Hundes. Schweizer Archiv für Tierheilkunde 2006, 148, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Glaus, T.M.; Ivasovic, F.; Jörger, F.B.; Schreiber, N.; Baron Toaldo, M. Minimal invasive Extraktion von adulten Dirofilaria immitis bei einem Hund mit Kavalsyndrom. Schweizer Archiv für Tierheilkunde 2019, 161, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bausch, K.; Bosl, M.; Matter, M.; Gabrielli, S.; Neumayr, A. When you hear hoof beats … consider zebras—A diagnostic challenge. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2017, 19, 73–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitenbücher, A.; Gayer, R.; Giachino, D.; Mordasini, C. What is your diagnosis. Multiple pulmonary nodules. Respiration 1998, 65, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasler, S.; Grimm, F.; Thiel, M.A.; Müller, N.J.; Eberhard, R.; Bosch, M.M. Swiss patient with a subconjunctival Dirofilaria repens. Klin. Monbl. Augenheilkd. 2010, 227, 332–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokelainen, P.; Mõtsküla, P.F.; Heikkinen, P.; Ülevaino, E.; Oksanen, A.; Lassen, B. Dirofilaria repens Microfilaremia in Three Dogs in Estonia. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016, 16, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabūnas, V.; Radzijevskaja, J.; Sakalauskas, P.; Petkevičius, S.; Karvelienė, B.; Žiliukienė, J.; Lipatova, I.; Paulauskas, A. Dirofilaria repens in dogs and humans in Lithuania. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klintebjerg, K.; Petersen, E.; Pshenichnaya, N.Y.; Ermakova, L.A.; Nagorny, S.A.; Larsen, C.S. Periorbital Dirofilaria repens imported to Denmark: A human case report. IDCases 2015, 2, 25–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Genchi, C.; Rinaldi, L.; Mortarino, M.; Genchi, M.; Cringoli, G. Climate and Dirofilaria infection in Europe. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 163, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietikäinen, R.; Nordling, S.; Jokiranta, S.; Saari, S.; Heikkinen, P.; Gardiner, C.; Kerttula, A.-M.; Kantanen, T.; Nikanorova, A.; Laaksonen, S.; et al. Dirofilaria repens transmission in southeastern Finland. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, A. One Health. In Research on the Change in the North, Proceedings of the THULE SCIENCE DAYS 2015, Oulu, Finland, 27–28 October 2015; Highlights of the Thule Institute’s Research Program 2012–2015; Kamula, R., Taskinen, P., Pongrácz, E., Rautio, A., Strand, K., Eds.; University of Oulu: Oulu, Finland, 2015; pp. 10–11. ISBN 978-952-62-1008-0. [Google Scholar]
- Settnes, O.P.; Engebjerg, E. Human subcutaneous dirofilariasis caused by Dirofilaria repens. Report of a case in Norway and review of recent literature. APMIS 1991, 99, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredal, W.P.; Gjerde, B.; Eberhard, M.L.; Aleksandersen, M.; Wilhelmsen, D.K.; Mansfield, L.S. Adult Dirofilaria repens in a subcutaneous granuloma on the chest of a dog. J. Small Anim. Pract. 1998, 39, 595–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sævik, B.K.; Jörundsson, E.; Stachurska-Hagen, T.; Tysnes, K.; Brun-Hansen, H.; Wikström, H.C.; Robertson, L.J. Dirofilaria repens infection in a dog imported to Norway. Acta Vet. Scand. 2014, 56, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norwegian Veterinary Institute. Infectious Diseases in Dogs Imported to Norway. Available online: https://www.vetinst.no/en/surveillance-programmes/infectious-diseases-in-dogs-imported-to-norway (accessed on 16 July 2021).
- Swedisch Board of Agriculture. Årsrapport Över Anmälningspliktiga Djursjukdomar 2019: Annual Statistics on Notifiable Animal Diseases under the Regulations of the Swedish Board of Agriculture (SJVFS 2012: 24) on Notifiable Animal Diseases and Infectious Agents. 2019. Available online: http://djur.jordbruksverket.se/download/18.3a2a8b84171950f8cca80788/1587467632223/%C3%85rsstatistik%202019.pdf (accessed on 27 September 2021).
- Swedisch Board of Agriculture. Årsrapport Över Anmälningspliktiga Djursjukdomar 2018: Annual Statistics on Notifiable Animal Diseases under the Regulations of the Swedish Board of Agriculture (SJVFS 2012: 24) on Notifiable Animal Diseases and Infectious Agents. 2018. Available online: http://djur.jordbruksverket.se/download/18.3a2a8b84171950f8cca80788/1587467632223/%C3%85rsstatistik%202018.pdf (accessed on 27 September 2021).
- Penagos-Tabares, F.; Groß, K.M.; Hirzmann, J.; Hoos, C.; Lange, M.K.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C. Occurrence of canine and feline lungworms in Arion vulgaris in a park of Vienna: First report of autochthonous Angiostrongylus vasorum, Aelurostrongylus abstrusus and Troglostrongylus brevior in Austria. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, K.; Löwenstein, M.; Duscher, G.; Leschnik, M.; Joachim, A. Angiostrongylus Vasorum, der “französische Herzwurm”: Auch ein Problem in Österreich? Wiener Tierarztliche Monatsschrift 2010, 97, 171. [Google Scholar]
- Reifinger, M.; Greszl, J. Pulmonale Angiostrongylose mit systemischer Ausbreitung und zentralnervaler Manifestation bei einem Hund. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 1994, 41, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Globokar, M.; Pantchev, N.; Hinney, B.; Leschnik, M.; Peschke, R.; Schaper, R.; Schnyder, M. Serological and faecal detection of Angiostrongylus vasorum in dogs from Austria. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2021, 26, 10064. [Google Scholar]
- Hajnalová, M.; Svobodová, V.; Schnyder, M.; Schaper, R.; Svoboda, M. Faecal detection of the lungworms Crenosoma vulpis and Angiostrongylus vasorum and serological detection of A. vasorum in dogs from the Czech Republic. Acta Veterinaria Brno 2017, 86, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schiefer, B.; Etreby, M.E. Zur Frage der sogenannten Riesenzellpneumonie und Riesenzellbronchitis bei Tieren. Pathol. Vet. 1965, 2, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallaske, G. Zur Angiostrongylose des Hundes. Deutsche Tierarztliche Wochenschrift 1967, 74, 166–171. [Google Scholar]
- Staebler, S.; Ochs, H.; Steffen, F.; Naegeli, F.; Borel, N.; Sieber-Ruckstuhl, N.; Deplazes, P. Autochthone Infektionen mit Angiostrongylus vasorum bei Hunden in der Schweiz und Deutschland. Schweizer Archiv für Tierheilkunde 2005, 147, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denk, D.; Matiasek, K.; Just, F.T.; Hermanns, W.; Baiker, K.; Herbach, N.; Steinberg, T.; Fischer, A. Disseminated angiostrongylosis with fatal cerebral haemorrhages in two dogs in Germany: A clinical case study. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 160, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pötz, C.; Peters, M. Der klinische Fall: Disseminierte Angiostrongylus-vasorum-Infektion bei einem aus Portugal importierten Junghund. Tierarztl. Prax. Ausg. K Kleintiere. Heimtiere. 2006, 34, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barutzki, D.; Schaper, R. Endoparasites in dogs and cats in Germany 1999–2002. Parasitol. Res. 2003, 90 (Suppl. 3), S148–S150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barutzki, D.; Dyachenko, V.; Schaper, R. Lungworms in Germany 2002–2016: Is there an Increase in Occurrence and Geographical Spread? Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barutzki, D.; Schaper, R. Results of parasitological examinations of faecal samples from cats and dogs in Germany between 2003 and 2010. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 109 (Suppl. 1), S45–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnyder, M.; Schaper, R.; Bilbrough, G.; Morgan, E.R.; Deplazes, P. Seroepidemiological survey for canine angiostrongylosis in dogs from Germany and the UK using combined detection of Angiostrongylus vasorum antigen and specific antibodies. Parasitology 2013, 140, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehbein, S.; Kaulfuß, K.-H.; Visser, M.; Sommer, M.F.; Grimm, F.; Silaghi, C. Parasites of sheep herding dogs in central Germany. Berliner und Munchener Tierarztliche Wochenschrift 2016, 129, 56–64. [Google Scholar]
- Barutzki, D.; Schaper, R. Natural infections of Angiostrongylus vasorum and Crenosoma vulpis in dogs in Germany (2007–2009). Parasitol. Res. 2009, 105 (Suppl. 1), S39–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimov, P.; Hermosilla, C.; Taubert, A.; Staubach, C.; Sauter-Louis, C.; Conraths, F.J.; Vrhovec, M.G.; Pantchev, N. GIS-supported epidemiological analysis on canine Angiostrongylus vasorum and Crenosoma vulpis infections in Germany. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, B.S.; Seybold, N.; Sauter-Louis, C.; Hartmann, K. Prevalence of Angiostrongylus vasorum and Crenosomo vulpis in dogs in Bavaria. Berliner und Munchener Tierarztliche Wochenschrift 2013, 126, 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Taubert, A.; Pantchev, N.; Vrhovec, M.G.; Bauer, C.; Hermosilla, C. Lungworm infections (Angiostrongylus vasorum, Crenosoma vulpis, Aelurostrongylus abstrusus) in dogs and cats in Germany and Denmark in 2003–2007. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 159, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schug, K.; Krämer, F.; Schaper, R.; Hirzmann, J.; Failing, K.; Hermosilla, C.; Taubert, A. Prevalence survey on lungworm (Angiostrongylus vasorum, Crenosoma vulpis, Eucoleus aerophilus) infections of wild red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in central Germany. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, M.K.; Penagos-Tabares, F.; Hirzmann, J.; Failing, K.; Schaper, R.; van Bourgonie, Y.R.; Backeljau, T.; Hermosilla, C.; Taubert, A. Prevalence of Angiostrongylus vasorum, Aelurostrongylus abstrusus and Crenosoma vulpis larvae in native slug populations in Germany. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 254, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlán, S. Helminthologie: Die Helminthosen der Haus-und Nutztiere unter Berücksichtigung der Helminthosen des Menschen; Akadémiai Kiadó: Budapest, Hungary, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Sólymos, P.; Fehér, Z. Conservation prioritization based on distribution of land snails in Hungary. Conserv. Biol. 2005, 19, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majoros, G.; Fukár, O.; Farkas, R. Autochtonous infection of dogs and slugs with Angiostrongylus vasorum in Hungary. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 174, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnyder, M.; Schaper, R.; Lukács, Z.; Hornok, S.; Farkas, R. Combined Serological Detection of Circulating Angiostrongylus vasorum Antigen and Parasite-specific Antibodies in Dogs from Hungary. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demiaszkiewicz, A.W.; Pyziel, A.M.; Kuligowska, I.; Lachowicz, J.; Demiaszkiewicz, A.W.; Pyziel, A.M. The first report of Angiostrongylus vasorum (Nematoda; Metastrongyloidea) in Poland, in red foxes (Vulpes vulpes). Acta Parasitol. 2014, 59, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczepaniak, K.; Tomczuk, K.; Buczek, K.; Komsta, R.; Łojszczyk-Szczepaniak, A.; Staniec, M.; Winiarczyk, S. Pierwszy rozpoznany bezpośrednio, kliniczny przypadek angiostrongylozy u psa w Polsce. Medycyna Weterynaryjna 2014, 70, 242. [Google Scholar]
- Schnyder, M.; Schaper, R.; Pantchev, N.; Kowalska, D.; Szwedko, A.; Deplazes, P. Serological detection of circulating Angiostrongylus vasorum antigen-and parasite-specific antibodies in dogs from Poland. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112 (Suppl. 1), 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczesna, J.; Popiolek, M.; Smietana, W. A study on the helminthfauna of wolves (Canis lupus L.) in the Bieszczady Mountains (south Poland)-preliminary results. Wiadomości Parazytologiczne 2007, 53 (Suppl. 1), 36. [Google Scholar]
- Hurníková, Z.; Miterpáková, M.; Mandelík, R. First autochthonous case of canine Angiostrongylus vasorum in Slovakia. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 3505–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miterpáková, M.; Hurníková, Z.; Zalewski, A.P. The first clinically manifested case of angiostrongylosis in a dog in Slovakia. Acta Parasitol. 2014, 59, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Miterpáková, M.; Schnyder, M.; Schaper, R.; Hurníková, Z.; Čabanová, V. Serological survey for canine angiostrongylosis in Slovakia. Helminthologia 2015, 52, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čabanová, V.; Hurníková, Z.; Miterpáková, M.; Dirbakova, K.; Bendova, A.; Kocak, P. Lungworm infections in dogs from Central Europe. Veterinární medicína 2018, 63, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurníková, Z.; Čabanová, V.; Karpjak, P.; Kasenčák, M.; Miterpáková, M. Rare case of Angiostrongylus vasorum intraocular infestation in an asymptomatic dog. Helminthologia 2019, 56, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čabanová, V.; Guimaraes, N.; Hurníková, Z.; Chovancová, G.; Urban, P.; Miterpáková, M. Endoparasites of the grey wolf (Canis lupus) in protected areas of Slovakia. Ann. Parasitol. 2017, 63, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, K.; Eckert, J.; Leemann, W. Beitrag zur Angiostrongylose des Hundes. Dtsch Vet-Med Ges Zürich 1969, 10, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Gottstein, B. Lungenwurm Angiostrongylus vasorum bei einem Fuchs in der Schweiz. BVET-Mag. 2001, 1, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Schnyder, M.; Jefferies, R.; Schucan, A.; Morgan, E.R.; Deplazes, P. Comparison of coprological, immunological and molecular methods for the detection of dogs infected with Angiostrongylus vasorum before and after anthelmintic treatment. Parasitology 2015, 142, 1270–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lurati, L.; Deplazes, P.; Hegglin, D.; Schnyder, M. Seroepidemiological survey and spatial analysis of the occurrence of Angiostrongylus vasorum in Swiss dogs in relation to biogeographic aspects. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 212, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, B.; Hegglin, D.; Schnyder, M. A grid-cell based fecal sampling scheme reveals: Land-use and altitude affect prevalence rates of Angiostrongylus vasorum and other parasites of red foxes (Vulpes vulpes). Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 2235–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deplazes, P.; Hegglin, D.; Gloor, S.; Romig, T. Wilderness in the city: The urbanization of Echinococcus multilocularis. Trends Parasitol. 2004, 20, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerup, E. Angiostrongylus vasorum hos hund. Dansk Veterinærtidsskrift 1983, 66, 338–340. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, J.; Bolt, G. Angiostrongylus vasorum hos hund (Canine angiostrongylosis). Dansk Veterinærtidsskrift 1990, 73, 1239–1243. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenlund, P.; Boserup, F.; Monrad, J. Angiostrongylus vasorum I forreste ojenkammer hos hund. Dansk-Vet Tidsskr 1991, 74, 451–453. [Google Scholar]
- Bolt, G.; Monrad, J.; Henriksen, P.; Dietz, H.H.; Koch, J.; Bindseil, E.; Jensen, A.L. The fox (Vulpes vulpes) as a reservoir for canine angiostrongylosis in Denmark. Field survey and experimental infections. Acta Vet. Scand. 1992, 33, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guildal, J.A.; Clausen, B. Endoparasites from one hundred Danish red foxes (Vulpes vulpes (L.)). Nor. J. Zool. 1973, 21, 329–330. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, I.; Maddox-Hyttel, C.; Monrad, J.; Kapel, C.M.O. Helminths of red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in Denmark. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 139, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, D.K.L. Prævalensundersøgelse af Crenosoma vulpis og Angiostrongylus Vasorum Hos ræv (Vulpes vulpes) og hund (Canis familiaris) i et område i Midtjylland-DK. Available online: https://www.ddd.dk/media/2130/2007-08-keld-loekkegaard-jacobsen.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2021).
- Al-Sabi, M.N.S.; Halasa, T.; Kapel, C.M.O. Infections with cardiopulmonary and intestinal helminths and sarcoptic mange in red foxes from two different localities in Denmark. Acta Parasitol. 2014, 59, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderblom, A.; Saari, S.; Järvinen, A.-K. Angiostrongylus vasorum-tartunta tuontikoiralla: Ensimmäinen varmistettu tapaus Suomessa. Suomen eläinlääkärilehti 2008, 114, 199–208. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, R.S. Helminth parasites of the red fox in Finland 1963–1964. In Proceedings of the First International Congress of Parasitology, Roma, Italy, 21–26 September 1964; Corradetti, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Elsevier Science: Burlington, MA, USA, 1966; p. 482, ISBN 978-1-4832-2913-3. [Google Scholar]
- Isomursu, M.; Salin, N.; Oksanen, A. Rare canine parasites survive in the wild fox population. Acta Vet. Scand. 2010, 52, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Skírnisson, K.; Pálsdóttir, G.R.; Eydal, M. Parasites of dogs and cats imported to Iceland during 1989–2017 with remarks on parasites occurring in the native populations. IAS 2018, 31, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, R.K.; Gjerde, B.; Vikøren, T.; Lillehaug, A.; Handeland, K. Prevalence of Trichinella larvae and extra-intestinal nematodes in Norwegian red foxes (Vulpes vulpes). Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 136, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norwegian Veterinary Institute. Angiostrongylus Vasorum in Red Foxes. Available online: https://www.vetinst.no/en/surveillance-programmes/angiostrongylus-vasorum-in-red-foxes (accessed on 16 July 2021).
- Norwegian Food Safety Authority. The Surveillance Programme for Angiostrongylus Vasorum in Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in Norway 2019: Annual Report; Norwegian Veterinary Institute: Ås, Norway, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Åblad, B.; Christensson, D.; Osterman-Lind, E.; Ågren, E.; Mörner, T. Angiostrongylus vasorum etablerad i Sverige. Svensk Veterinartidning 2003, 12, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Sabi, M.N.S. Gastrointestinal helminths of gray wolves (Canis lupus lupus) from Sweden. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 1891–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silaghi, C.; Beck, R.; Capelli, G.; Montarsi, F.; Mathis, A. Development of Dirofilaria immitis and Dirofilaria repens in Aedes japonicus and Aedes geniculatus. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionică, A.M.; Zittra, C.; Wimmer, V.; Leitner, N.; Votýpka, J.; Modrý, D.; Mihalca, A.D.; Fuehrer, H.-P. Mosquitoes in the Danube Delta: Searching for vectors of filarioid helminths and avian malaria. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancrini, G.; Magi, M.; Gabrielli, S.; Arispici, M.; Tolari, F.; Dell’Omodarme, M.; Prati, M.C. Natural vectors of dirofilariasis in rural and urban areas of the Tuscan region, central Italy. J. Med. Entomol. 2006, 43, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancrini, G.; Gabrielli, S. Vectors of Dirofilaria nematodes: Biology, behaviour and host/parasite relationships. In Dirofilaria Immitis and D. Repens in Dog and Cat and Human Infections; Rolando Editore: Naples, Italy, 2007; pp. 48–58. [Google Scholar]
- Pollono, F.; Cancrini, G.; Rossi, L. Survey on Culicidae attracted to bait dog in piedmont. Parassitologia 1998, 40, 439–445. [Google Scholar]
- Ahid, S.M.; Vasconcelos, P.S.; Lourenço-de-Oliviera, R. Vector competence of Culex quinquefasciatus say from different regions of Brazil to Dirofilaria immitis. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2000, 95, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.F.; Main, A.J.; Ferrandino, F.J.; Andreadis, T.G. Nocturnal activity of mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) in a West Nile virus focus in Connecticut. J. Med. Entomol. 2007, 44, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medlock, J.M.; Hansford, K.M.; Schaffner, F.; Versteirt, V.; Hendrickx, G.; Zeller, H.; van Bortel, W. A review of the invasive mosquitoes in Europe: Ecology, public health risks, and control options. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012, 12, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholte, E.-J.; Schaffner, F. Waiting for the tiger: Establishment and spread of the Aedes albopictus mosquito in Europe. Emerg. Pests Vector-Borne Dis. Eur. 2007, 1, 241. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, N.; Petric, D.; Zgomba, M.; Boase, C.; Madon, M.; Dahl, C.; Kaiser, A. Mosquitoes and Their Control; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; ISBN 354092874X. [Google Scholar]
- Giangaspero, A.; Marangi, M.; Latrofa, M.S.; Martinelli, D.; Traversa, D.; Otranto, D.; Genchi, C. Evidences of increasing risk of dirofilarioses in southern Italy. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 1357–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrobelli, M. Importance of Aedes albopictus in veterinary medicine. Parassitologia 2008, 50, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, H.E.; Harrington, L.C.; Kaufman, P.E.; McKay, T.; Bowman, D.D.; Nelson, C.T.; Wang, D.; Lund, R. Key factors influencing canine heartworm, Dirofilaria immitis, in the United States. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, E.R.; Tomlinson, A.; Hunter, S.; Nichols, T.; Roberts, E.; Fox, M.T.; Taylor, M.A. Angiostrongylus vasorum and Eucoleus aerophilus in foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in Great Britain. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 154, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirk, L.; Limon, G.; Guitian, F.J.; Hermosilla, C.; Fox, M.T. Angiostrongylus vasorum in Great Britain: A nationwide postal questionnaire survey of veterinary practices. Vet. Rec. 2014, 175, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, E.R. Canine pulmonary angiostrongylosis: Can a worm change its spots? Vet. Rec. 2014, 175, 116–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blancou, J. Ecology and epidemiology of fox rabies. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1988, 10 (Suppl. 4), S606–S609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolsey, I.D.; Webster, P.; Thamsborg, S.; Schnyder, M.; Monrad, J.; Kapel, C.M.O. Repeated inoculations with the lung and heartworm nematode Angiostrongylus vasorum result in increasing larval excretion and worm burden in the red fox (Vulpes vulpes). Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2017, 6, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnyder, M. Slugs and Angiostrongylus vasorum--how much do we know? Vet. Rec. 2015, 177, 44–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdushy, T.; Kapel, C.M.O.; Webster, P.; Al-Sabi, M.N.S.; Grønvold, J.R. The effect of temperature and host age on the infectivity and development of Angiostrongylus vasorum in the slug Arion lusitanicus. Parasitol. Res. 2010, 107, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, A.; Crisi, P.E.; Di Giulio, E.; Veronesi, F.; Di Regalbono, A.F.; Talone, T.; Traversa, D. Larval development of the feline lungworm Aelurostrongylus abstrusus in Helix aspersa. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 3101–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, S.; Traversa, D.; Colombo, M.; Raue, K.; Strube, C.; Pollmeier, M.; Di Cesare, A. The effect of the hibernation on the larval development of Troglostrongylus brevior in the land snail Cornu aspersum. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 282, 109123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morelli, S.; Colombo, M.; Diakou, A.; Traversa, D.; Grillini, M.; Di Regalbono, A.F.; Di Cesare, A. The Influence of Temperature on the Larval Development of Aelurostrongylus abstrusus in the Land Snail Cornu aspersum. Pathogens 2021, 10, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivieri, E.; Zanzani, S.A.; Gazzonis, A.L.; Giudice, C.; Brambilla, P.; Alberti, I.; Romussi, S.; Lombardo, R.; Mortellaro, C.M.; Banco, B.; et al. Angiostrongylus vasorum infection in dogs from a cardiopulmonary dirofilariosis endemic area of Northwestern Italy: A case study and a retrospective data analysis. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traversa, D.; Morelli, S.; Cassini, R.; Crisi, P.E.; Russi, I.; Grillotti, E.; Manzocchi, S.; Simonato, G.; Beraldo, P.; Viglietti, A.; et al. Occurrence of canine and feline extra-intestinal nematodes in key endemic regions of Italy. Acta Trop. 2019, 193, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, J.; Parrish, R. Dog importation and changes in canine intestinal nematode prevalence in Colorado, USA, 2013–2017. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, A.W.; Hertling, R.; Kennedy, M.J. Angiostrongylosis with disseminated larval infection associated with signs of ocular and nervous disease in an imported dog. Can. Vet. J. 1991, 32, 430–431. [Google Scholar]
- Tebb, A.I.; Johnson, V.S.; Irwin, P.J. Angiostrongylus vasorum (French heartworm) in a dog imported into Australia. Aust. Vet. J. 2007, 85, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.F.; Lindemann, B.; Padgett, G.A.; Smith, O.L. Angiostrongylosis in a greyhound. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1985, 186, 1101–1103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fuehrer, H.-P.; Morelli, S.; Unterköfler, M.S.; Bajer, A.; Bakran-Lebl, K.; Dwużnik-Szarek, D.; Farkas, R.; Grandi, G.; Heddergott, M.; Jokelainen, P.; et al. Dirofilaria spp. and Angiostrongylus vasorum: Current Risk of Spreading in Central and Northern Europe. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101268
Fuehrer H-P, Morelli S, Unterköfler MS, Bajer A, Bakran-Lebl K, Dwużnik-Szarek D, Farkas R, Grandi G, Heddergott M, Jokelainen P, et al. Dirofilaria spp. and Angiostrongylus vasorum: Current Risk of Spreading in Central and Northern Europe. Pathogens. 2021; 10(10):1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101268
Chicago/Turabian StyleFuehrer, Hans-Peter, Simone Morelli, Maria Sophia Unterköfler, Anna Bajer, Karin Bakran-Lebl, Dorota Dwużnik-Szarek, Róbert Farkas, Giulio Grandi, Mike Heddergott, Pikka Jokelainen, and et al. 2021. "Dirofilaria spp. and Angiostrongylus vasorum: Current Risk of Spreading in Central and Northern Europe" Pathogens 10, no. 10: 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101268
APA StyleFuehrer, H.-P., Morelli, S., Unterköfler, M. S., Bajer, A., Bakran-Lebl, K., Dwużnik-Szarek, D., Farkas, R., Grandi, G., Heddergott, M., Jokelainen, P., Knific, T., Leschnik, M., Miterpáková, M., Modrý, D., Petersen, H. H., Skírnisson, K., Vergles Rataj, A., Schnyder, M., & Strube, C. (2021). Dirofilaria spp. and Angiostrongylus vasorum: Current Risk of Spreading in Central and Northern Europe. Pathogens, 10(10), 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101268










