Observations on a Novel Bacterial Pathogen of Root-Knot Nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
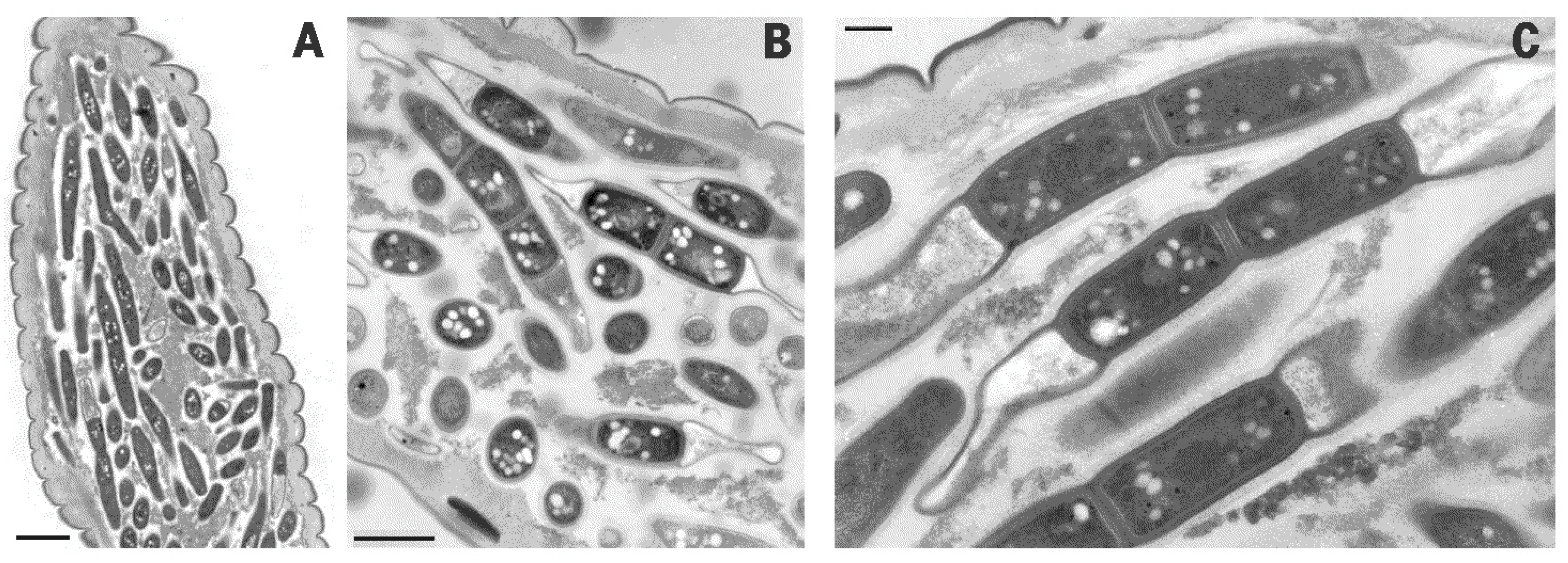
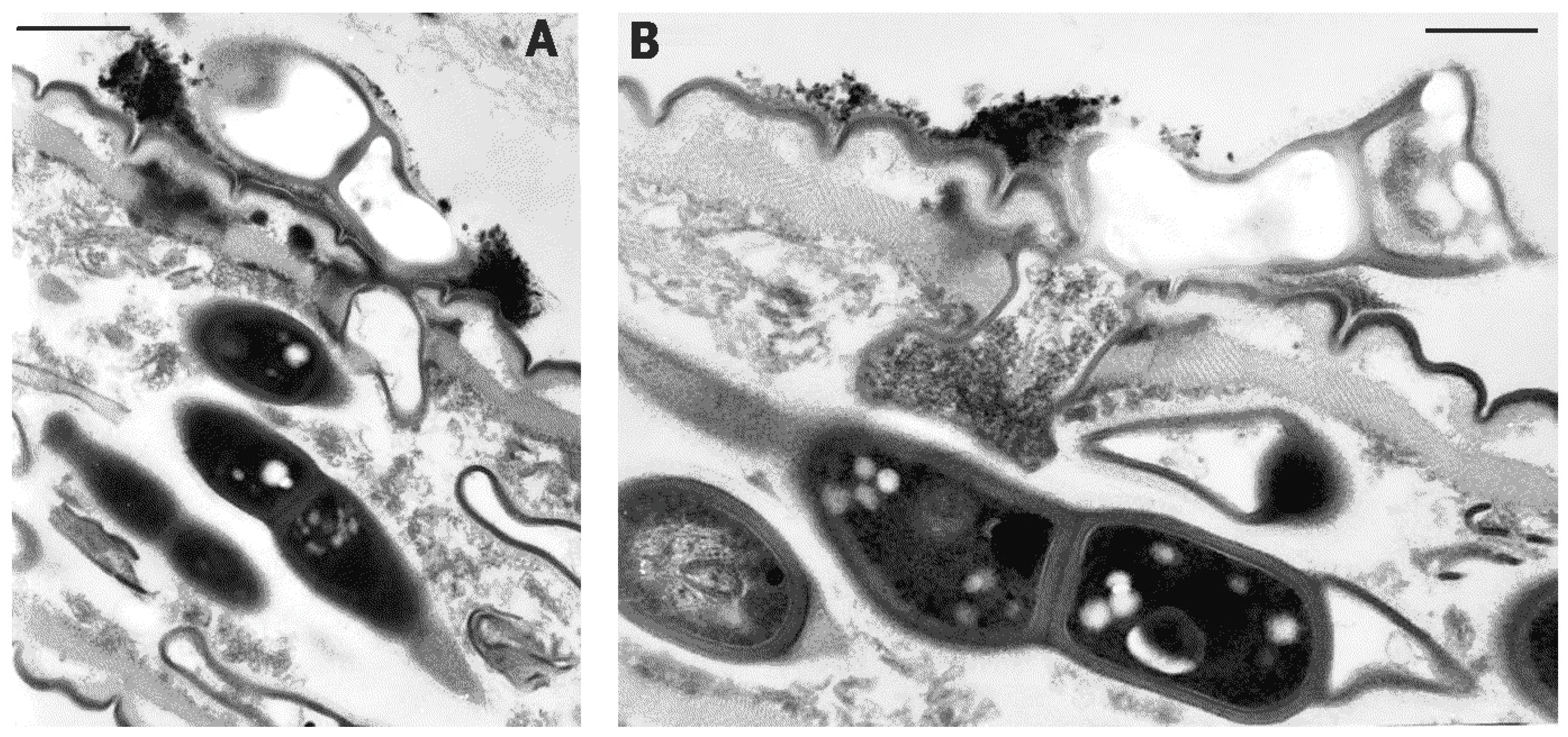
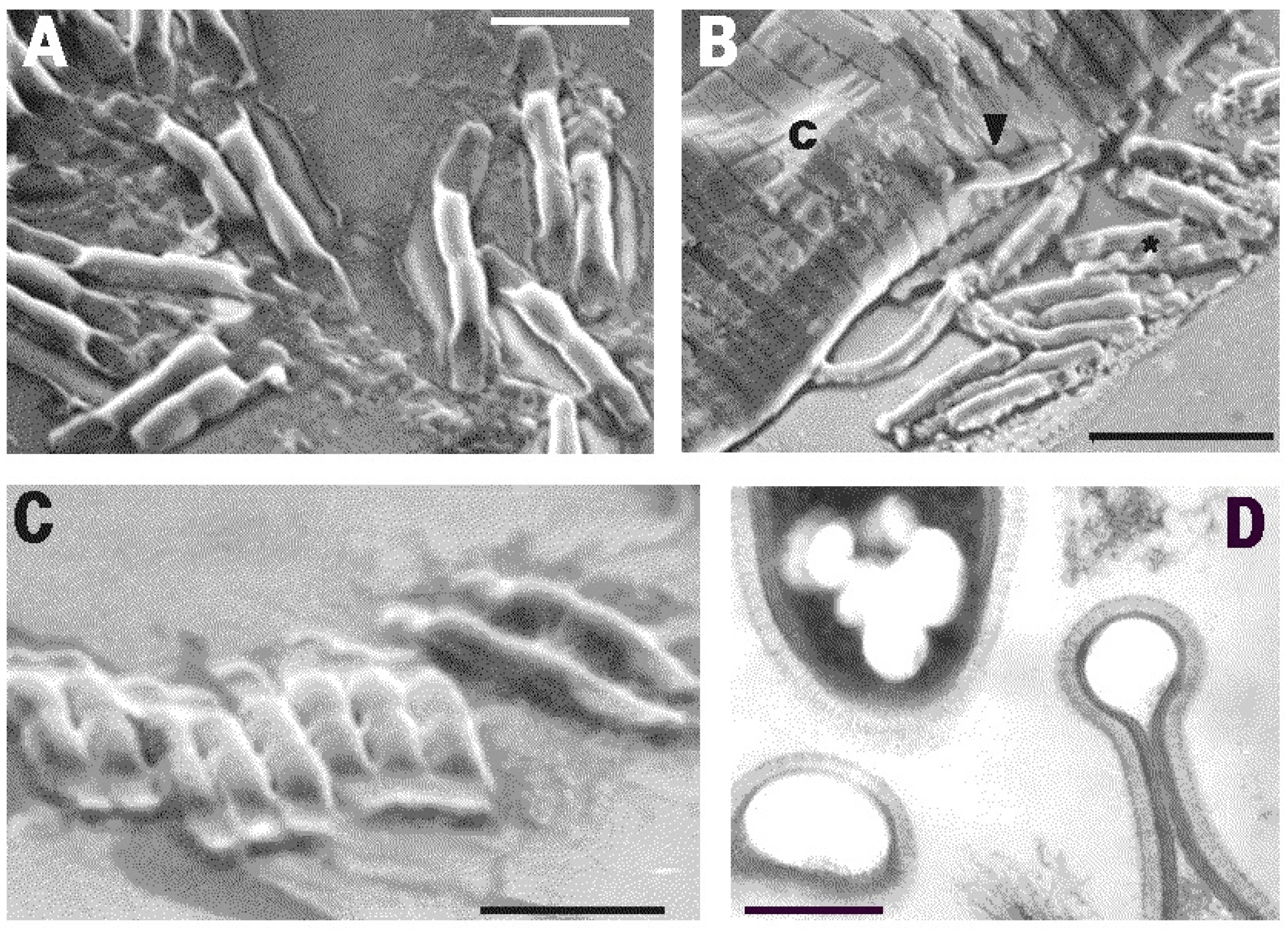
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sampling of the Host Populations
4.2. Light Microscopy (LM)
4.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.5. Culturing Assays
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poinar, G.O., Jr.; Hansen, E.L. Associations between nematodes and bacteria. Helminth. Abstr. Ser. B 1986, 55, 61–81. [Google Scholar]
- Bandi, C.; Anderson, T.J.; Genchi, C.; Blaxter, M.L. Phylogeny of Wolbachia in filarial nematodes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1998, 265, 2407–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, A.; Wasala, S.; Howe, D.; Peetz, A.B.; Zasada, I.A.; Denver, D.R. Genomic evidence for plant-parasitic nematodes as the earliest Wolbachia hosts. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomares-Rius, J.E.; Archidona-Yuste, A.; Cantalapiedra-Navarrete, C.; Prieto, P.; Castillo, P. Molecular diversity of bacterial endosymbionts associated with dagger nematodes of the genus Xiphinema (Nematoda: Longidoridae) reveals a high degree of phylogenetic congruence with their host. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 6225–6247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, Z.A.; Mahmood, I. Role of bacteria in the management of plant parasitic nematodes: A review. Biores. Technol. 1999, 69, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stirling, G. Biological Control of Plant-Parasitic Nematodes: Soil Ecosystem Management in Sustainable Agriculture; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bird, A.F.; Riddle, D.L. Effect of attachment of Corynebacterium rathayi on movement of Anguina agrostis larvae. Int. J. Parasitol. 1984, 14, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.E. Nematode interactions with other pathogens. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1990, 116, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esnard, J.; Potter, T.L.; Zuckerman, B.M. Streptomyces costaricanus sp. nov., isolated from nematode-suppressive soil. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1995, 45, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hackenberg, C.; Muehlchen, A.; Forge, T.; Vrain, T. Pseudomonas chlororaphis strain Sm3, bacterial antagonist of Pratylenchus penetrans. J. Nematol. 2000, 32, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Kluepfel, D.A.; Nyczepir, A.P.; Lawrence, J.E.; Wechter, W.P.; Leverentz, B. Biological control of the phytoparasitic nematode Mesocriconema xenoplax on peach trees. J. Nematol. 2002, 34, 120–123. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, S.L.F.; Roberts, D.P. Combinations of biocontrol agents for management of plant-parasitic nematodes and soilborne plant-pathogenic fungi. J. Nematol. 2002, 34, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, S.L.F.; Roberts, D.P.; Chitwood, D.J.; Carta, L.K.; Lumsden, R.D.; Mao, W. Application of Burkholderia cepacia and Trichoderma virens, alone and in combinations, against Meloidogyne incognita on bell pepper. Nematropica 2001, 31, 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.; Riggs, R.D.; Crippen, D.L. Control of soybean cyst nematode by chitinolytic bacteria with chitin substrate. J. Nematol. 2000, 32, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.W.; Niu, Q.H.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, K.Q. Bacillus nematocida sp. nov., a novel bacterial strain with nematotoxic activity isolated from soil in Yunnan, China. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 28, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, W.R.; Madden, P.A.; Tromba, F.G. Histopathologic and bacteriologic examinations of cuticular lesions of Ascaris suum. J. Parasitol. 1971, 57, 1010–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, W.R.; Madden, P.A.; Colglazier, M.L. Microbial flora of cuticular lesions on Strongylus edentatus. Proc. Helm. Soc. Wash. 1978, 45, 219–225. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, L.; Grewal, P.S. Pathogenicity of Moraxella osloensis, a bacterium associated with the nematode Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita, to the slug Deroceras reticulatum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 5010–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forst, S.; Nealson, K. Molecular biology of the symbiotic-pathogenic bacteria Xenorhabdus spp. and Photorhabdus spp. Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 60, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheperd, A.M.; Clark, S.A.; Kempton, A. An intracellular micro-organism associated with tissues of Heterodera spp. Nematologica 1973, 19, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Endo, B.Y. The ultrastructure and distribution of an intracellular bacterium-like microorganism in tissue of larvae of the soybean cyst nematode, Heterodera glycines. J. Ultrastr. Res. 1979, 67, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.A.; Lee, D.L.; Sheperd, A.M. The distribution and effect of intracellular rickettsia-like micro-organisms infecting adult males of the potato cyst-nematode Globodera rostochiensis. Nematologica 1983, 29, 227–239. [Google Scholar]
- Ferri, E.; Bain, O.; Barbuto, M.; Martin, C.; Lo, N.; Uni, S.; Landmann, F.; Baccei, S.G.; Guerrero, R.; Lima, S.D.S.; et al. New insights into the evolution of Wolbachia infections in filarial nematodes inferred from a large range of screened species. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wasala, S.K.; Brown, A.M.V.; Kang, J.; Howe, D.K.; Peetz, A.B.; Zasada, I.A.; Denver, D.R. Variable abundance and distribution of Wolbachia and Cardinium endosymbionts in plant-parasitic nematode field populations. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sironi, M.; Bandi, C.; Sacchi, L.; Di Sacco, B.; Damiani, G.; Genchi, C. Molecular evidence for a close relative of the arthropod endosymbiont Wolbachia in a filarial worm. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1995, 74, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, G.R.; Atibalentja, N. “Candidatus Paenicardinium endonii” an endosymbiont of the plant-parasitic nematode Heterodera glycines (Nemata: Tylenchida), affiliated to the phylum Bacteroidetes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 1697–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vandekerckhove, T.T.M.; Willems, A.; Gillis, M.; Coomans, A. Occurrence of novel verrucomicrobial species, endosymbiotic and associated with parthenogenesis in Xiphinema americanum-group species (Nematoda, Longidoridae). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50, 2197–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, A.M.V.; Howe, D.K.; Wasala, S.K.; Peetz, A.B.; Zasada, I.A.; Denver, D.R. Comparative genomics of a plant-parasitic nematode endosymbiont suggest a role in nutritional symbiosis. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 2727–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kellenberger, E. Exploring the unknown: The silent revolution of microbiology. EMBO Rep. 2001, 2, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overmann, J.; Abt, B.; Sikorski, J. Present and future of culturing bacteria. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 71, 711–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polz, M.F.; Harbison, C.; Cavanaugh, C.M. Diversity and heterogeneity of epibiotic bacterial communities on the marine nematode Eubostrichus dianae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 4271–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Els, H.J.; Krecek, R.C. Developmental stages of a smooth-walled filamentous bacterium associated with equine Cyathostomes. J. Helm. Soc. Wash. 1993, 60, 174–182. [Google Scholar]
- Krecek, R.C.; Sayre, R.M.; Els, H.J.; Van Niekerk, J.P.; Malan, F.S. Fine structure of a bacterial community associated with chyatostomes (Nematoda: Strongylidae) of zebras. Proc. Helm. Soc. Wash. 1987, 54, 212–219. [Google Scholar]
- Mackie, R.I.; Krecek, R.C.; Els, H.J.; Van Niekerk, J.P.; Kirschner, L.M.; Baecker, A.A.W. Characterization of the microbial community colonizing the anal vulvar pores of helminths from the hindgut of zebras. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1989, 55, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, B.; Valinsky, L.; Gao, X.; Becker, O.; Borneman, J. Bacterial rRNA genes associated with soil suppressiveness against the plant-parasitic nematode Heterodera schactii. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beveridge, T.J. Structures of Gram-negative cell walls and their derived membrane vesicles. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 4725–4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Southey, J.F. (Ed.) Laboratory Methods for Work with Plant and Soil Nematodes; Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food, Technical Bulletin No. 2; HMSO: London, UK, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Girard, H.; Rougieux, R. Techniques de Microbiologie Agricole; DUNOD: Paris, France, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Sher, S.A.; Bell, A.H. Scanning electron micrographs of the anterior region of some species of Tylenchoidea (Tylenchida: Nematoda). J. Nematol. 1975, 7, 69–83. [Google Scholar]
- Leadbetter, J.R. Cultivation of recalcitrant microbes: Cells are alive, well and revealing their secrets in the 21st century laboratory. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2003, 6, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciancio, A. Observations on a Novel Bacterial Pathogen of Root-Knot Nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.). Pathogens 2021, 10, 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101226
Ciancio A. Observations on a Novel Bacterial Pathogen of Root-Knot Nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.). Pathogens. 2021; 10(10):1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101226
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiancio, Aurelio. 2021. "Observations on a Novel Bacterial Pathogen of Root-Knot Nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.)" Pathogens 10, no. 10: 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101226
APA StyleCiancio, A. (2021). Observations on a Novel Bacterial Pathogen of Root-Knot Nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.). Pathogens, 10(10), 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10101226





