Management of Microbiological Contamination of the Water Network of a Newly Built Hospital Pavilion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Physical and Chemical Parameters of Water Sample
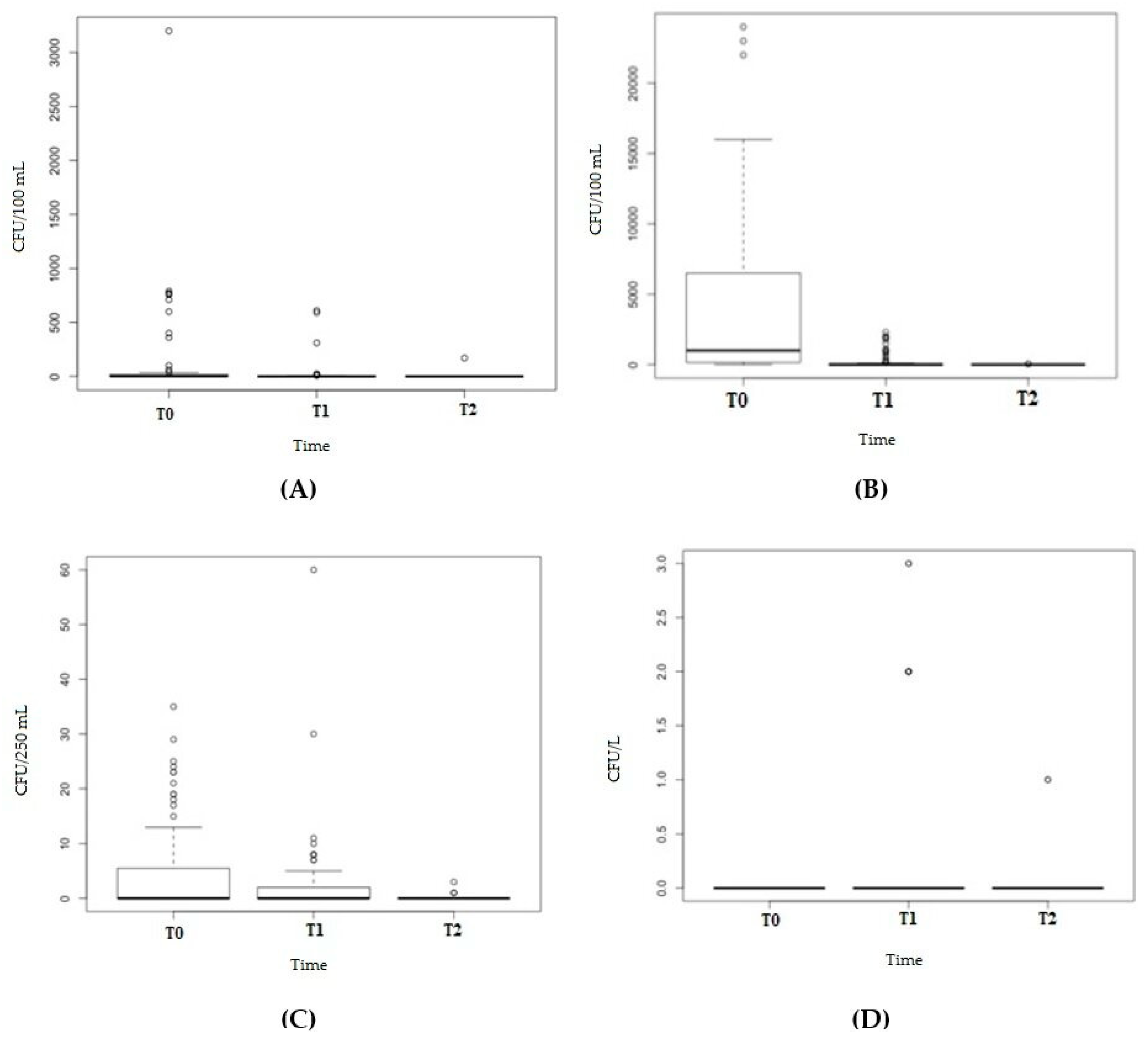
2.2. Bacterial Detection
2.3. Legionella Detection
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Water Disinfection
4.3. Physico-Chemical Parameters
4.4. Microbiological Investigation
4.5. Legionella Investigation
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Decreto Legislativo 2 Febbraio 2001, n. 31. “Attuazione della Direttiva 98/83/CE Relativa alla Qualità delle Acque Destinate al Consumo Umano”. GU n. 52 del 3 Marzo 2001-Supplemento Ordinario n. 41. Available online: https://www.camera.it/parlam/leggi/deleghe/01031dl.htm (accessed on 14 October 2020).
- Bonadonna, L.; De Grazia, M.C.; Capolongo, S.; Casini, B.; Cristina, M.L.; Daniele, G.; D’Alessandro, D.; De Giglio, O.; Di Benedetto, A.; Di Vittorio, G.; et al. Water safety in healthcare facilities. The Vieste Charter. Ann. Ig. 2017, 29, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caggiano, G.; Diella, G.; Triggiano, F.; Bartolomeo, N.; Apollonio, F.; Campanale, C.; Lopuzzo, M.; Montagna, M.T. Occurrence of Fungi in the Potable Water of Hospitals: A Public Health Threat. Pathogens 2020, 9, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exner, M.; Kramer, A.; Lajoie, L.; Gebel, J.; Engelhart, S.; Hartemann, P. Prevention and control of health care-associated waterborne infections in health care facilities. Am. J. Infect. Control 2005, 33, S26–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagna, M.T.; Caggiano, G.; Lovero, G.; De Giglio, O.; Coretti, C.; Cuna, T.; Iatta, R.; Giglio, M.; Dalfino, L.; Bruno, F.; et al. Epidemiology of invasive fungal infections in the intensive care unit: Results of a multicenter Italian survey (AURORA Project). Infection 2013, 41, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagna, M.T.; De Giglio, O.; Napoli, C.; Lovero, G.; Caggiano, G.; Delia, M.; Pastore, D.; Santoro, N.; Specchia, G. Invasive fungal infections in patients with hematologic malignancies (Aurora Project): Lights and shadows during 18-months surveil-lance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 774–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagna, M.T.; Lovero, G.; De Giglio, O.; Iatta, R.; Caggiano, G.; Montagna, O.; Laforgia, N. Invasive fungal Infections in neonatal intensive care units of Southern Italy: A multicenter regional active surveillance (AURORA Project). J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2010, 51, 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Montagna, M.T.; De Giglio, O.; Napoli, C.; Diella, G.; Rutigliano, S.; Agodi, A.; Auxilia, F.; Baldo, V.; Bisetto, F.; Arnoldo, L.; et al. Control and prevention measures for legionellosis in hospitals: A cross-sectional survey in Italy. Environ. Res. 2018, 166, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Water Safety in Buildings. 2011. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/76145 (accessed on 9 October 2020).
- Napoli, C.; De Giglio, O.; Bertamino, E.; Montagna, M.T. Legionellosis in health care facilities: State of the art in control and prevention in Italy. Ann. Ig. 2019, 31, 474–481. [Google Scholar]
- Napoli, C.; Fasano, F.; Iatta, R.; Barbuti, G.; Cuna, T.; Montagna, M.T. Legionella spp. and legionellosis in southeastern Italy: Disease epidemiology and environmental surveillance in community and health care facilities. BMC Public Health 2010, 10, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giglio, O.; Diella, G.; Lopuzzo, M.; Triggiano, F.; Calia, C.; Pousis, C.; Fasano, F.; Caggiano, G.; Calabrese, G.; Rafaschieri, V.; et al. Impact of lockdown on the microbiological status of the hospital water network during COVID-19 pandemic. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hase, R.; Miyoshi, K.; Matsuura, Y.; Endo, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Otsuka, Y. Legionella pneumonia appeared during hospitalization in a patient with hematological malignancy confirmed by sputum culture after negative urine antigen test. J. Infect. Chemother. 2018, 24, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzzi, A.; Cutti, S.; Bonadeo, E.; Lodola, L.; Monzillo, V.; Corbella, M.; Scudeller, L.; Novelli, V.; Marena, C. Prevention of nosocomial legionellosis by best water management: Comparison of three decontamination methods. J. Hosp. Infect. 2020, 105, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobin, J.O.; Beare, J.; Dunnill, M.S.; Fisher-Hoch, S.; French, M.; Mitchell, R.G.; Morris, P.J.; Muers, M.F. Legionnaires’ disease in a transplant unit: Isolation of the causative agent from shower baths. Lancet 1980, 2, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Direttiva (UE) 2020/2184 del Parlamento Europeo e del Consiglio del 16 Dicembre 2020 Concernente la Qualità delle Acque Destinate al Consumo Umano. G.U. dell’Unione Europea L 435/1 del 23 dicembre 2020. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/IT/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32020L2184&from=IT (accessed on 11 January 2020).
- Casini, B.; Aquino, F.; Totaro, M.; Miccoli, M.; Galli, I.; Manfredini, L.; Giustarini, C.; Costa, A.L.; Tuvo, B.; Valentini, P.; et al. Application of Hydrogen Peroxide as an Innovative Method of Treatment for Legionella Control in a Hospital Water Network. Pathogens 2017, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervero-Aragó, S.; Rodríguez-Martínez, S.; Canals, O.; Salvadó, H.; Araujo, R.M. Effect of thermal treatment on free-living amoeba inactivation. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 116, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giglio, O.; Napoli, C.; Apollonio, F.; Brigida, S.; Marzella, A.; Diella, G.; Calia, C.; Scrascia, M.; Pacifico, C.; Pazzani, C.; et al. Occurrence of Legionella in groundwater used for sprinkler irrigation in Southern Italy. Environ. Res. 2019, 170, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orkis, L.T.; Harrison, L.H.; Mertz, K.J.; Brooks, M.M.; Bibby, K.J.; Stout, J.E. Environmental sources of community-acquired legionnaires’ disease: A review. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2018, 221, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www.legionellaonline.it/Not%20ISS%20nov%202019.pdf (accessed on 14 October 2020).
- Facility Guidelines Institute; American Society for Healthcare Engineering. Guidelines for Design and Construction of Hospitals and Outpatient Facilities; American Hospital Association: Chicago, IL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www2.klenzoidinc.com/wp-content/themes/twentyfifteen-klenzoid/pdf/public-review-draft.pdf (accessed on 11 January 2020).
- Decker, B.K.; Palmore, T.N. Hospital Water and Opportunities for Infection Prevention. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2014, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartram, J.; Chartier, Y.; Lee, J.V.; Bond, K.; Surman-Lee, S. Legionella and the Prevention of Legionellosis; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Husband, S.; Boxall, J. Asset deterioration and discolouration in water distribution systems. Water Res. 2011, 45, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Chakhtoura, J.; Saikaly, P.E.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S. Impact of Distribution and Network Flushing on the Drinking Water Microbiome. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, C.R.; Reimann, M.; Vriens, B.; Hammes, F. Biofilms in shower hoses. Water Res. 2018, 131, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhoads, W.J.; Pruden, A.; Edwards, M.A. Convective Mixing in Distal Pipes Exacerbates Legionella pneumophila Growth in Hot Water Plumbing. Pathogens 2016, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, N.L.; Bass, P.; Liss, S.N. Antibacterial Properties and Mechanism of Activity of a Novel Silver-Stabilized Hydrogen Peroxide. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linee Guida per la Prevenzione ed il Controllo della Legionellosi. 2015. Available online: http://www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pubblicazioni_2362_allegato.pdf (accessed on 14 October 2020).
- Girolamini, L.; Dormi, A.; Pellati, T.; Somaroli, P.; Montanari, D.; Costa, A.; Savelli, F.; Martelli, A.; Grottola, A.; Serpini, G.F.; et al. Advances in Legionella Control by a New Formulation of Hydrogen Peroxide and Silver Salts in a Hospital Hot Water Network. Pathogens 2019, 8, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- British Standards Institution. Chemicals Used for Treatment of Water Intended for Human Consumption. Hydrogen Peroxide; British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Kim, D.; Lee, T. Microbial diversity in biofilms on water distribution pipes of different materials. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingender, J.; Flemming, H.-C. Contamination potential of drinking water distribution network biofilms. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 49, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsh, M.B.; Baron, J.L.; Mietzner, S.M.; Rihs, J.D.; Yassin, M.H.; Stout, J.E. Evaluation of Recommended Water Sample Collection Methods and the Impact of Holding Time on Legionella Recovery and Variability from Healthcare Building Water Systems. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hota, S.; Hirji, Z.; Stockton, K.; Lemieux, C.; Dedier, H.; Gideon, W.; Gardam, M.A. Outbreak of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa colonization and infection secondary to imperfect intensive care unit room design. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2009, 30, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara-López, S.; Domínguez, M.C.; Conejo, M.C.; Pascual, Á.; Rodríguez-Baño, J. Wastewater drainage system as an occult reservoir in a protracted clonal outbreak due to metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Klebsiella oxytoca. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, e490–e498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsanas, D.; Brett, J.; Kidd, T.J.; Stuart, R.L.; Korman, T.M.; Kidd, T.J. Disinfection of Burkholderia cepacia complex from non-touch taps in a neonatal nursery. J. Périnat. Med. 2008, 36, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines For Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Swtizerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Napoli, C.; Iatta, R.; Fasano, F.; Marsico, T.; Montagna, M.T. Variable bacterial load of Legionella spp. in a hospital water system. Sci. Total. Environ. 2009, 408, 242–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Giglio, O.; Napoli, C.; Lovero, G.; Diella, G.; Rutigliano, S.; Caggiano, G.; Montagna, M.T. Antibiotic susceptibility of Le-gionella pneumophila strains isolated from hospital water systems in Southern Italy. Environ. Res. 2015, 142, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM International. Standard Test. Methods for Ammonia Nitrogen in Water; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Methods for the Chemical Analysis of Water and Wastes (MCAWW)—EPA/600/4-79/020, 1983. EPA 600/4-79-020 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Water and Wastes. Available online: https://www.wbdg.org/ (accessed on 2 December 2020).
- UNI. Qualità dell’acqua—Conta di Escherichia coli e Batteri Coliformi—Parte 1: Metodo per Filtrazione su Membrana; UNI EN ISO 9308-1; UNI: Milan, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- UNI. Qualità dell’acqua-Ricerca ed Enumerazione di Enterococchi Intestinali—Metodo di Filtrazione su Membrana; UNI EN ISO 7899-2; UNI: Milan, Italy, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- UNI. Water Quality—Detection and Enumeration of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Membrane Filtration; UNI EN ISO 16266:2008; UNI: Milan, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- UNICHIM. Ricerca ed Enumerazione di Legionella spp e di Legionella pneumophila Nelle Acque; UNICHIM METHOD 1037:14; UNI: Milan, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, M.J.; Machin, D. Medical Statistics. A Common Sense Approach; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1993; p. 142. ISBN 0-471-93764-9. [Google Scholar]
| Parameters | Cold Water | Hot Water | Limit Value 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | Value | ||||
| Mean | Range | Mean | Range | ||
| pH | 8.13 | 7.9–9.0 | 8.16 | 7.9–9.0 | ≥6.5 to ≤9.5 |
| T (°C) | 15.8 | 13.4–16.3 | 56.5 | 50.1–57.2 | - |
| Conductivity (µS/cm) | 650 | 640–685 | 647 | 640–680 | 2500 |
| Hardness (°F) | 16.2 | 16–18 | 15.3 | 15–17 | 15–50 |
| Free Chlorine (mg/L) | 0.01 | 0.00–0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00–0.01 | 0.2 |
| Chlorides (mg/L) | 30 | 26–32 | 28 | 25–30 | 250 |
| Ammonium (mg/L) | <0.10 | - | <0.10 | - | 0.50 |
| Nitrites (mg/L) | <0.10 | - | <0.10 | - | 0.50 |
| Nitrates (mg/L) | 0.7 | 0.6–1.2 | 0.6 | 0.5–1.0 | 50 |
| Disinfectant residual (mg/L) | 21.0 | 20.0–28.0 | 23.7 | 20.0–29.7 | - |
| Flow rate (L/h) | 550 | 450–650 | 550 | 450–650 | - |
| Microorganism | Period | Tap (No./No.) | Shower (No./No.) | Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coliforms | T0 | 46.3 (31/67) | 50.0 (12/24) | χ2 = 0.0058, p-value = 0.94 |
| T1 | 35.8 (24/67) | 37.5 (9/24) | χ2 = 0.0101, p-value = 0.92 | |
| T2 | 4.5 (3/67) | 4.2 (1/24) | Fisher’s F test p-value = 1 | |
| T0 | 0 (0/67) | 0 (0/24) | Fisher’s F test p-value = 1 | |
| E. coli | T1 | 4.4 (4/67) | 0 (0/24) | Fisher’s F test p-value = 0.57 |
| T2 | 0 (0/67) | 0 (0/24) | Fisher’s F test p-value = 1 | |
| Enterococci | T0 | 0% (0/67) | 0% (0/24) | Fisher’s F test p-value = 1 |
| T1 | 13.4% (9/67) | 8.3% (2/24) | Fisher’s F test p-value = 0.72 | |
| T2 | 0% (0/67) | 8.3% (2/24) | Fisher’s F test p-value = 0.07 | |
| P. aeruginosa | T0 | 46.3% (31/67) | 62.5% (15/24) | χ2 = 1.2696, p-value = 0.26 |
| T1 | 29.9% (20/67) | 29.2% (7/24) | χ2 = 0.039, p-value = 0.84 | |
| T2 | 0% (0/67) | 4.2% (1/24) | Fisher’s F test p-value = 0.27 | |
| L. pneumophila | T0 | 85.1% (57/67) | 66.7% (16/24) | χ2 = 2.70, p-value = 0.10 |
| T1 | 37.3% (25/67) | 33.3% (8/24) | χ2 = 0.01, p-value = 0.91 | |
| T2 | 0% (0/67) | 8.3% (2/24) | Fisher’s F test p-value = 0.07 |
| Microorganism | Period | Tap–Median load (Range) | Shower–Median load (Range) | Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coliforms (CFU/100 mL) | T0 | <1 (<1–35) | <1 (<1–19) | W = 784, p-value = 0.76 |
| T1 | <1 (<1–60) | <1 (<1–10) | W = 827.5, p-value = 0.91 | |
| T2 | <1 (<1–3) | <1 | W = 768, p-value = 0.23 | |
| E. coli | T1 | <1 (<1–2) | <1 | W = 1140, p-value = 0.30 |
| (CFU/100 mL) | ||||
| Enterococci (CFU/100 mL) | T1 | <1 (<1–3) | 0 (0–2) | W = 847, p-value = 0.49 |
| T2 | <1 | <1 (<1–1) | W = 737, p-value = 0.018 | |
| P. aeruginosa (CFU/250 mL) | T0 | <1 (<1–790) | 2 (<1–3200) | W = 687, p-value = 0.26 |
| T1 | <1 (<1–610) | <1(<1–26) | W = 823.5, p-value = 0.83 | |
| T2 | <1 | <1 (<1–170) | W = 770.5, p-value = 0.099 | |
| L. pneumophila (CFU/L) | T0 | 1700 (<50–24,000) | 325 (<50–22,000) | W = 1091.5, p-value = 0.009 |
| T1 | <50 (<50–2300) | <50 (<50–2000) | W= 868, p-value = 0.5058 | |
| T2 | <50 | <50 (<50–50) | W = 737, p-value = 0.018 |
| Indipendent Variables | B | (eβ-1) = RR (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 7.06 | <0.0001 | |
| Coliforms | 7.28 | 1449.99 | <0.0001 |
| E. coli | −2.277 | −1.00 | <0.0001 |
| Enterococci | −4.78 | −0.99 | <0.0001 |
| P. aeruginosa | 0.07 | 0.08 | <0.0001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Giglio, O.; Diella, G.; Lopuzzo, M.; Triggiano, F.; Calia, C.; Pousis, C.; Fasano, F.; Calabrese, G.; Rafaschieri, V.; Carpagnano, L.F.; et al. Management of Microbiological Contamination of the Water Network of a Newly Built Hospital Pavilion. Pathogens 2021, 10, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10010075
De Giglio O, Diella G, Lopuzzo M, Triggiano F, Calia C, Pousis C, Fasano F, Calabrese G, Rafaschieri V, Carpagnano LF, et al. Management of Microbiological Contamination of the Water Network of a Newly Built Hospital Pavilion. Pathogens. 2021; 10(1):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10010075
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Giglio, Osvalda, Giusy Diella, Marco Lopuzzo, Francesco Triggiano, Carla Calia, Chrysovalentinos Pousis, Fabrizio Fasano, Giuseppe Calabrese, Vincenza Rafaschieri, Lucia Federica Carpagnano, and et al. 2021. "Management of Microbiological Contamination of the Water Network of a Newly Built Hospital Pavilion" Pathogens 10, no. 1: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10010075
APA StyleDe Giglio, O., Diella, G., Lopuzzo, M., Triggiano, F., Calia, C., Pousis, C., Fasano, F., Calabrese, G., Rafaschieri, V., Carpagnano, L. F., Carlucci, M., Gesualdo, L., Ricci, M. L., Scaturro, M., Rota, M. C., Bonadonna, L., Lucentini, L., & Montagna, M. T. (2021). Management of Microbiological Contamination of the Water Network of a Newly Built Hospital Pavilion. Pathogens, 10(1), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10010075













