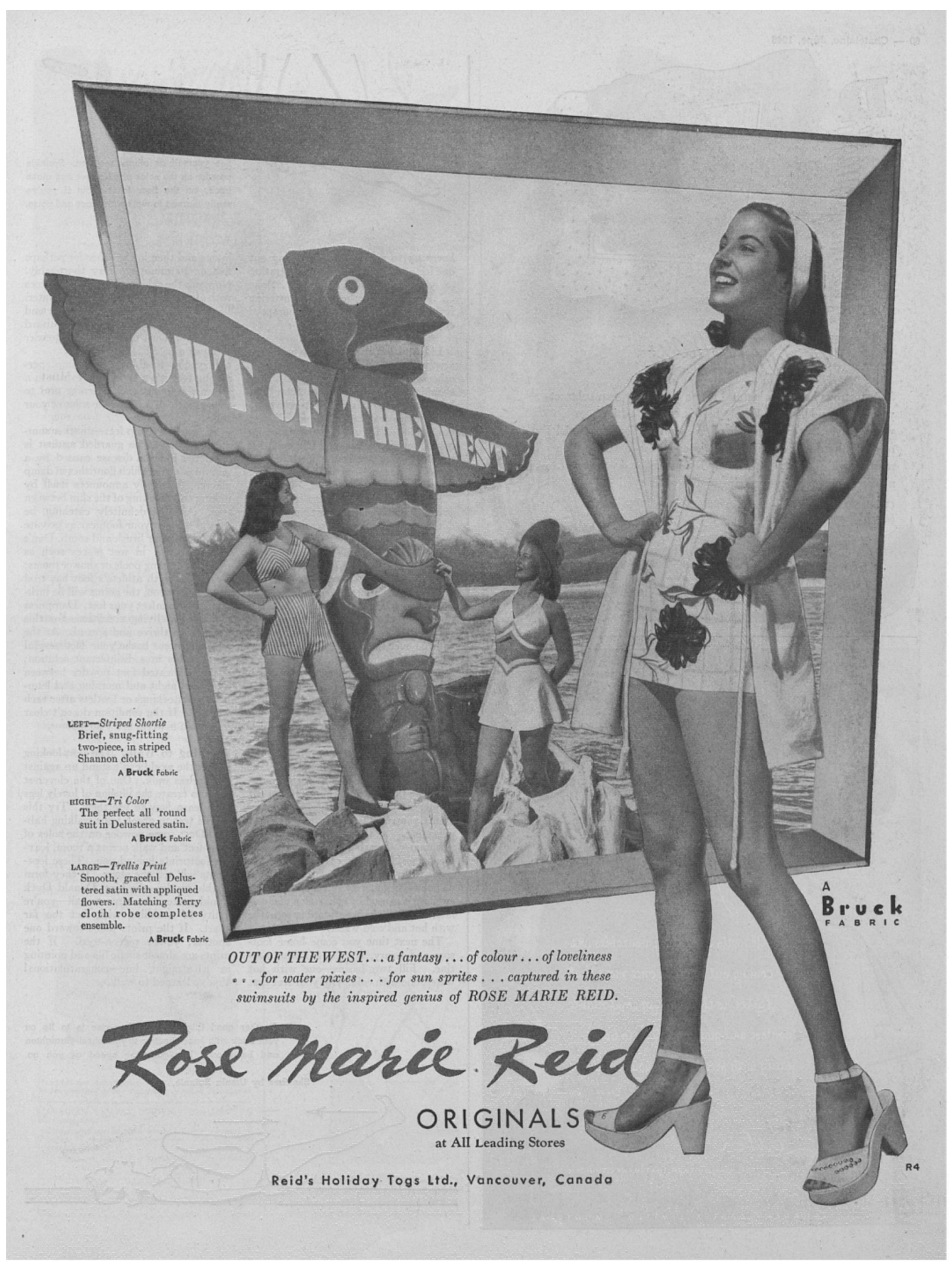Abstract
In the mid-twentieth century, growing North American textile and ready-to-wear industries vigorously appropriated Native American aesthetics to cultivate a commercial and design identity apart from Europe. Most studies of the circulation of Indigenous idioms in these industries focus on Southwestern or South Pacific regionalisms, and scholarship on studio and commercial fabric and fashion design from the Northwest Coast in the twentieth century is limited. This paper contributes by raising Indigenous and non-Indigenous use of Northwest Coast design forms during the politically turbulent 1940s–1960s and analyzing the impact of this aesthetic vocabulary within broader North American textiles and fashion. Throughout, I engage with the approaches of critical fashion theory and multiple modernisms, considering the frictions of property and power relations within settler-colonial states, then and now. Drawing from study of objects, periodicals, and archival materials as well as first-person perspectives, I contextualize these representations within entangled art, museum, and design worlds in the Northwest Coast, New York City, and the Southwest. My examination illustrates that Northwest Coast artists and art ideas asserted a peripheral but locatable role in mid-century textiles and fashion, facilitating the development of today’s robust Indigenous fashion network on the Northwest Coast and its cultural politics.
1. Prologue: Two Moments in Southeast Alaska
2021: On a rainy late summer day, a wool jacket knitted with geometric designs in bright yellow, white, and black burned in a ceremonial fire pit outside of Juneau’s Sealaska Heritage Institute. Tlingit clan leaders and community members circled the fire, holding cut strips of the fabric (Figure 1). The garment was not in fact a Northwest Coast Raven’s Tail robe (also spelled Ravenstail), customarily woven by Native artists with such colors and designs. Instead, it was an alleged unauthorized copy of a robe created in 1996 by Tlingit artist Clarissa Rizal titled Discovering the Angles of an Electrified Heart. The jacket on fire had been manufactured by the retailer Neiman Marcus and sold for $2550 as a “Ravenstail Knitted Coat”. Rizal’s family had copyrighted her robe and licensed it exclusively to the Sealaska Heritage Institute after the artist’s death in 2016 (Sealaska Heritage Institute 2020). Furthermore, regional weavers had asserted their “ownership of our traditional art forms” in a statement long before this (Weavers’s Circle 1993, reprinted in Kramer 2013, p. 746). Rizal’s family and the Sealaska Heritage Institute sued Neiman Marcus for alleged copyright infringement and violation of the Indian Arts and Crafts Act in a landmark action that rested on principles of both Western and Tlingit law protecting intellectual property (Sealaska Heritage Institute 2020, 2021). The ceremony marked the fact that the parties settled the suit before it went to court. During the gathering, one of Rizal’s daughters, the weaver Lily Hope, appealed to the industry, arguing for a more collaborative, cross-cultural approach: “Come to us”, she said. “Work with us. Help us to elevate our designs together” (Lockett 2021).

Figure 1.
Tlingit community members ceremonially burn a Neiman Marcus coat that allegedly copied a woven robe design by artist Clarissa Rizal, recognizing the settlement of a copyright infringement lawsuit brought to the company, 13 August 2021. Image by Michael S. Lockett/Juneau Empire. Used with permission of the Juneau Empire.
1947: A non-Native, New York City-based fabric stylist named Marjorie Holligan took a cruise to Southeast Alaska for inspiration (Women’s Wear Daily 1947). She traveled often in the Americas to seek rich vernacular aesthetics from places such as the Smoky Mountains, Mexico, and Guatemala for her work with Celanese, then the leading manufacturer of acetate fibers (synthetic silk) (Mara 1948). But this year, she went north, as tourism had returned to the Inside Passage after a wartime pause (Kiffer 2010). Holligan could have been motivated by the increasing calls for Alaskan statehood, or by the success of the 1946 exhibition Northwest Coast Indian Painting organized by Abstract Expressionist painter Barnett Newman at Betty Parsons Gallery in New York City. From Holligan’s cruise, Celanese debuted a line of 25 prints on Alluracel acetate rayon named “Northwest Passage” (Figure 2). Advertisements and articles noted that “Motifs have been culled from Indian carvings, Eskimo ivories, glaciers, and Flowers” and use “stripes … reproduced from Indian ceremonial robes and from topical motifs …”, likely referring to Chilkat blankets (Lichtenstein’s 1948; Women’s Wear Daily 1947).1 In one design, for example, a “totem pole” print was rendered in color on gray (Women’s Wear Daily 1947). While the Celanese designs appear to be loose inspirations and not straight reproductions, some almost certainly derived from crest motifs that were owned by particular Tlingit or Haida lineages. A year later, Holligan would hire painter Theodore Suina (Cochiti Pueblo) to directly design prints for Celanese (Mara 1948), but it appears that she did not consult nor collaborate with any Northwest Coast Native artists during or after her Alaska trip.

Figure 2.
An advertisement for prints in Celanese’s “Northwest Passage” line of textiles. Mauch Chunk Times-News, 16 March 1948 (Hess Brothers 1948).
These two vignettes—occurring in the same area and to the same ends yet 75 years apart—underscore the dominant fashion and textile industry’s persistent sense of entitlement to proprietary designs belonging to Native artists and/or their lineages. Customarily on the Northwest Coast, the rights to certain crest designs and other tangible and intangible prerogatives such as names, stories, and songs are acquired from ancestors and cannot be transferred to outsiders without permission. These cultural conditions can make appropriative practices like Neiman Marcus’s and Celanese’s particularly challenging to local Indigenous ethical and political structures, stymieing opportunities for Native artists and other culture-bearers to participate in and help determine the outcomes of design and distribution.2 To be sure, in 1947, there were Indigenous artists available in Alaska to work with Holligan, but the commercial market for Northwest Coast Native design was still nascent.
Within a few years, artist and entrepreneur Ka’kasolas [Ellen Neel] (Kwakwaka’wakw) would be the first Native artist from the coast to create printed fabrics and apparel with local designs, controlling her production and sales herself and inspiring greater involvement for Indigenous artists in this market (Kramer 2012, p. 40).3
In order to better understand the current climate of Northwest Coast Native fashion and textile design and its cultural politics, this paper looks at the mid-twentieth century as an uneven yet pivotal period of experimentation in these media. It raises and integrates Native and non-Native endeavors to bring Northwest Coast aesthetics to studio and commercial fabric and fashion from the 1940s to the mid-1960s, when the principles of Euro-American modernist art and design were being negotiated through paintings and through cloth.4 In this paper, I explore the aesthetic and ideological pull that Northwest Coast art had—and did not have—for textile and fashion designers, considering its formal properties of abstract space as well as its customary historical color range. I also attempt to narrate the tandem and co-constituted nature of Native and non-Native fabric experiments in relation to Indigenous concepts of property in this region, which shift over time.
2. Introduction
Although the primitivist interest in Northwest Coast and Alaska Native art by avant-garde artists and intellectuals in the early- and mid-twentieth century has been robustly treated by scholars (Cowling 1978; Rushing 1995; Anthes 2000; Mauzé 2006, 2008, 2013; Davis 2014; Junker 2014), the influence of these regional aesthetics in twentieth-century North American fabric media has not. Textile design and production was enmeshed with the activities of modernism and American artistic and nationalistic self-fashioning during the mid-twentieth century. At this time, fabric for apparel and interiors was frequently positioned as “fine art” in interlinked art, design, and museum worlds. Developments in modern art and architecture cross-pollinated with commercial design, and textile and fashion trends were conversant with those in exhibitions (Boydell 2002; Clifford 2003, p. 75). Furthermore, historical Northwest Coast art, particularly carving and painting, factored significantly in the visual and ideological development of American modernist art. In particular, American modernist painters favored the flattening of space and abstract forms of Northwest Coast formline painting (as well as of textiles such as Chilkat blankets), shaping their tendency to compress depth in their own work (Rushing 1995, pp. 121–68). Given these factors, one may expect to find a strong translation of Northwest Coast forms in printed fabric—painting’s corollary in cloth—as well as in three-dimensional dress objects made from fabric at this time.
Recently, scholars and curators such as Carolyn Butler Palmer, Christopher T. Green, Jennifer Kramer, Lou-ann Ika’wega Neel (Kwakwaka’wakw), and Solen Roth have investigated Northwest Coast Native artists who produced studio and commercial textiles and apparel in the mid-twentieth century, including Ellen Neel, Nathan Jackson (Tlingit), and Doug Cranmer (Kwakwaka’wakw) (Butler Palmer 2021; Green 2018, 2020; Kramer 2012; Neel 2020; Roth 2018). In this paper, I contextualize and expand upon their work, including research on primary sources such as objects, periodicals, and archival materials as well as interviews and oral histories. My analysis is framed by the approaches of critical fashion theory and multiple modernisms. The former seeks to disengage the Eurocentric/Western approach to fashion systems (Craik 1994; Lillethun et al. 2012; Gaugele and Titton 2019; Jansen 2020). The latter does the same for modernist histories, understanding “colonialism and conquest as the very condition of possibility for modernity and for aesthetic modernism” (Huyssen 2007, p. 191). New modernist studies redress the erasure of colonized peoples from modernism and emphasize that these histories are co-constituted (e.g., Duffek and Townsend-Gault 2004; Montiel 2005; Anthes 2006; NMAI 2006; Phillips 2015; Harney and Phillips 2018; Deloria 2019).
With this intercultural approach, this paper not only upholds the participation and innovation of Indigenous designers in mid-twentieth century North America, but also broadens the understanding and critique of the position of the Northwest Coast in settler consumer imaginaries at that time, attempting to conceptualize fashion and textiles “as moving actors and signifiers of entangled histories” (Gaugele and Titton 2019, p. 28). Studies of the cooptation and manipulation of Native aesthetics for North American clothing and textiles during this period tend to focus on far more visible South Pacific and Southwest/Western regionalisms, with little discussion of the Northwest Coast (e.g., Parezo 1999, 2007, 2013; Kerstein 2003; Parezo and Jones 2009; Jones and Parezo 2010; Stopp 2012, pp. 24–25; Bazylinski 2013; Navratil 2015; Abrego 2016; Carey 2020). Indeed, to this day, products with Native aesthetics from southerly realms remain much more widely circulated in North America than do designs from the North Pacific Coast (Duffek 2013, p. 603; Roth 2018, p. 76).
I ask: How were Northwest Coast aesthetics represented by various agents within mid-twentieth century textiles and apparel? What values—both Indigenous and non-Indigenous—were placed on these designed products and their reproduction and dissemination? How did the infrastructure available for mid-century modern commercial design and production factor into the selective uptake of Northwest Coast aesthetics in fabric media? Beyond deepening historical understanding, answers to these questions permit better interpretation of the activity of Indigenous fashion designers from this region in the decades afterward and the stakes at play in their work. Designers such as Betty David (Spokane, 1938–2007), Himikalas Pamela Baker (Squamish/Kwakwaka’wakw/Tlingit/Haida), and Dorothy Grant (Haida) began working in the 1980s and 1990s and have been vital to the efflorescence of contemporary Native fashion at large. However, scholarship on the history of Northwest Coast Native fashion in the twentieth and twenty-first centuries remains limited (Metcalfe 2010, p. 338; see Glass 2008; Baker and Tortora 2010; Willmott 2010, 2014; Green 2013, 2016; Kramer 2015; Allen, forthcoming). While this paper centers on the 1940s to the mid-1960s, it offers some reference points to contextualize North American and Northwest Coast fashion and textile design in the decades before and afterward, contributing to a more contiguous and intercultural design history of this region.
During the mid-twentieth century, across settler and Indigenous national borders, adherents and practitioners of Northwest Coast art attempted to promote the “local fabric”—both in literal and metaphorical terms—to serve personal, lineal, regional, and national agendas. Amid an urgency to define and grow domestic textile and clothing production apart from Europe, and buoyed by widening interest in and consumption of both textile and Native arts, Native and non-Native agents experimented with Northwest Coast aesthetics in the linked production centers of the Northwest Coast, the Southwest, and New York City. These agents include not only Neel, Jackson, Cranmer, and Holligan, but also the swimsuit designer Rose Marie Reid, architect Paul Thiry, and designer and educator Lloyd Kiva New (Cherokee), whom this paper will also address.
Organized chronologically, the first section that follows will situate the pre- and post-WWII growth of North American printed textiles and ready-to-wear fashion within the prevailing political climate. Here, I will explore how fabric and fashion that appropriated Native aesthetics was, like modern art broadly, both a strategy and outcome of specific social agendas. In the second section, I will identify the increasing interest in Northwest Coast aesthetics in the late 1940s and the 1950s, comparing non-Native projects with the efforts of Indigenous artists to explore and claim their own rights, regionalisms, and market potential through textiles. This section will highlight replication of motifs, the appeal of Northwest Coast visual forms, and tensions between Euro-American and Indigenous value systems. The third section will focus on Native artists working in commercial textiles and fashion through the mid-1960s, as the market for Northwest Coast art grew. Here, I will posit why design themes from the Northwest Coast were ultimately not as widely popular as those from other areas of Native America. The paper will conclude with a brief vantage on the mid-century period of cloth experimentation given the vigor and voice of Native fashion and textile designers on the Northwest Coast today.
3. Through the 1940s: Looking Inward
American fashion design and textile industries strove to create their own design identity independent of Paris after about 1910. That was when the American publication Women’s Wear (later Women’s Wear Daily) emerged, and American manufacturing firms began growing rapidly (Marcketti and Parsons 2007; Schweitzer 2008). During World War I, when French design ideas were not reaching North American designers, study programs in the collections of the Brooklyn Museum and the American Museum of Natural History (AMNH) in New York City exposed fashion and textile designers to Indigenous dress items from the Americas in order to seed new ideas (Tartsinis 2013). Outlets like Women’s Wear printed Indigenous designs in their pages, including “The Art of the Chilkat Indians” as early as 1916 (Quton 1916). In a 1917 article for a Canadian trade publication, anthropologist Harlan I. Smith lauded the AMNH program, commenting on the paucity of Native designs from Canada for industrial profit (Smith 1917). He later published an album of historical objects in museums to address this, with half of the works from British Columbia, but little came of his effort (Smith 1923; Dawn 2013, p. 313).
As sportswear emerged in the 1920s and 1930s, American and Canadian textile and fashion industries strengthened. American textile consumption tripled between 1920 and 1966, and by mid-century, the U.S. was the largest manufacturer and consumer of textiles in the world (Troy 2019, pp. 23, 26). Borrowing from Indigenous aesthetics across the Americas for fabric and fashion became a key strategy in national anxieties over self-definition. This strategy aligns with the long-standing phenomenon of settlers “playing Indian” or “going Native” to construct white Euro-American and Euro-Canadian identities that are distinctive from European ones (Green 1988; Deloria 1998; Huhndorf 2001). The appropriation of Native dress and design ideas was also related to contemporaneous federal and church policies that regulated Native dress. For example, forced attendance and abuse at residential schools in both countries deprived Indigenous children of their access to and pride in their customary clothing (Ottmann 2020). Until 1951, Canada’s Indian Act forbade the wearing of regalia outside one’s home reserve without the permission of the Indian Agent.
In the 1940s, North American designers and manufacturers increasingly drew from Native design patterns, silhouettes, and styles to rally domestic industries. After the German occupation of France in 1940, Paris was once again “blacked out as a style center”, while patriotism and propaganda about national capability became necessary to a successful war effort (Damon 1941, p. 16). Although Canadian fashion and textile designers had previously sought design guidance from Paris or New York (Caton 2004, pp. 258–59), in 1940, the Canadian women’s magazine Chatelaine raised a simple solution:
Where will [the ideas] come from? Mostly, right from where they’ve been coming from for a long time—Canada, and the rest of the British Empire … And as our Canadian designers develop strength and power, they’ll be turning their eyes on Canada for inspiration … just as the United States today looks at the costumes of its Indians and the landscape of its country for fashion ideas …(Chatelaine 1940)
In the United States, Vogue printed annual “Americana” issues from 1938 to 1970 that attest to these trends. In a fashion spread set in a Southwestern desert in the 1941 Americana issue, editor-in-chief Edna Woolman Chase remarked that fashion designers were “scouring South America, the Caribbean, California, and the Great Southwest for local colour and line” to develop “American taste” as “a real expression of our own land” (Woolman Chase 1941, pp. 78, 160). Designers interpreted “local colour and line” liberally, often producing amalgamated, impressionistic, stereotyped designs from their research that both reflected and shaped the white gaze (Bazylinski 2013, pp. 31–45). For example, “tiki style” became popular in the 1950s and 1960s (especially given Hawaii’s statehood in 1959) with products such as aloha shirts, batik-style prints, and printed cottons called “barkcloth” (Kerstein 2003). From the Southwest, Navajo design and silhouettes were often co-opted (Parezo and Jones 2009; Jones and Parezo 2010). More relevant to the West Coast is the “California casual” style that boomed in the postwar period, which favored bright colors and adaptations of Native Hawaiian and Mexican attire—anything regional that may have evoked a “relaxed” look and vacation lifestyles (Scott 2008).
Within this economy of appropriation, manufacturers and institutions eagerly positioned printed textiles as art. In the 1940s, for example, well-known artists such as Salvador Dalí, Marcel Vertès, and Cecil Beaton designed prints for textiles, scarves, and neckties (Rayner et al. 2012). Popular magazines regularly featured textiles, including the dedicated publication American Fabrics (1946–1972). Modern design became increasingly accessible through art exhibitions that also presented home goods and apparel for sale as essential to “modern living”, which fed back into the art/design system and its promotional potential (Riley and Eigen 1994; Troy 2019). As Marjorie Holligan wrote in 1938, “… it is the news of interest in a specific exhibition of paintings rather than a particular individual painting that we follow” (Clifford 2003, p. 75).
At this time, two exhibitions organized by Rene d‘Harnoncourt had a major impact on Euro-American exposure to Northwest Coast aesthetics that affected textile and fashion industries.5 The first was the display of historical objects from the Northwest Coast at the “Indian Court” exhibition at the 1939 Golden Gate International Exposition in San Francisco. Using this model, d’Harnoncourt followed in early 1941 with the landmark Indian Art of the United States at the Museum of Modern Art. The exhibitions’ goals were to align Native art and American modernism and to stimulate both production and broader consumption of Native art and designed goods; to aestheticize them and make them “fashionable” (Rushing 1992, p. 205; 1995, pp. 108–14). D’Harnoncourt also wished to build infrastructure by connecting Native artists and communities with New York City producers and retailers (Rushing 1992, p. 216; 1995, p. 114).
Fashion, textiles, and merchandising were key to the MoMA exhibition’s agenda, with the industry’s response as swift and profound as that of New York avant-garde artists (Rushing 1995, p. 118; Navratil 2015, p. 229).6 In a section of the exhibition called “Indian Art for Modern Living”, six garments that incorporated Native-made components and trimmings (but none from the Northwest Coast) were produced by Swiss designer Fred A. Picard (Rushing 1992, p. 215; Navratil 2015, pp. 212–13). Although the organizers aimed to promote Native-made work, the display nevertheless incentivized non-Native designers to keep drawing from Indigenous design ideas (Navratil 2015, pp. 234–42).
The year of the MoMA show, Frederic Douglas, d’Harnoncourt’s collaborator for both exhibitions, conceived of the idea of a fashion show of historical Native-made garments. This project impacted consumer fashion for middle-class, mostly suburban women at mid-century: Between 1942 and 1956, Douglas arranged more than 180 presentations for 300,000 spectators across the United States of the “Indian Fashion Show” featuring dress from the Denver Art Museum (DAM)’s collection, which he curated (Parezo 1999, pp. 244, 258).7 Included in its tour was a presentation at the University of British Columbia (UBC) in 1951 and at least three more in Seattle packed to “overflow” (Audrey Hawthorn to Frederic Douglas, 30 August 1955; UBC, “Notes on Indian Fashion Show”; UBC MOA Audrey Hawthorn fonds, box 26-6, series 7-C-2).8 The show’s 53 ensembles included several historical Northwest Coast garments (Parezo 2007, pp. 18–19). As with the New York City museum collection programs for industry professionals in the early twentieth century, the fashion show became a new method to introduce Native designs to invited industry designers as well as to home sewers. Anthropologist Nancy Parezo notes that almost every outfit in the show, including an 1890s Haida dance shirt (then attributed Tlingit by Douglas; DAM cat. no. 1951.90) as well as Tlingit hats, was adapted for commercial designs (Parezo and Blomberg 1997, pp. 51, 54; Parezo 1999, pp. 258–59).
Even with such exposure, Northwest Coast regionalisms remained limited in this design climate.9 In 1947, a representative of the New York City interior fabrics firm F. Schumacher complained to Victoria-based social reformer Alice Ravenhill, who was distributing some local motifs to manufacturers, that “the only Indian designs now available are those of the Navajo and Pueblo Indians” (Don Adams, letter to Provincial Libraries 1947, cited in Roth 2018, pp. 50–51).
In one case, however, Vancouver-based swimwear designer Rose Marie Reid attempted to brand herself with regional Native aesthetics, implying that her line was itself indigenous to Canada. By 1941, she was promoting her swimsuits with the tagline “Out of the West”, with a series of “Canadiana” prints that “had totem poles instead of the usual fish, and tepees and snowshoes instead of Hawaiian palm trees” (Burr and Petersen 1995, pp. 34–36). Her marketing and advertising utilized a totem pole logo and fanciful scenes (Figure 3). In the advertisement in Figure 3, the copy conspicuously reads “… a fantasy … of colour … of loveliness … for water pixies … for sun sprites”. The image and language link the exoticism of Northwest Coast carvings in the touristic market—which could sport bright shades of green, red, turquoise, yellow, and pink—to plucky, puckish summer beauty. However, by 1947, Reid’s marketing sited her line both in “Canada and California” (Reid 1947), and by 1951, she shifted her manufacturing to Los Angeles, abandoning her Vancouver factory and the nationalistic message (Burr and Petersen 1995, pp. 63–67).
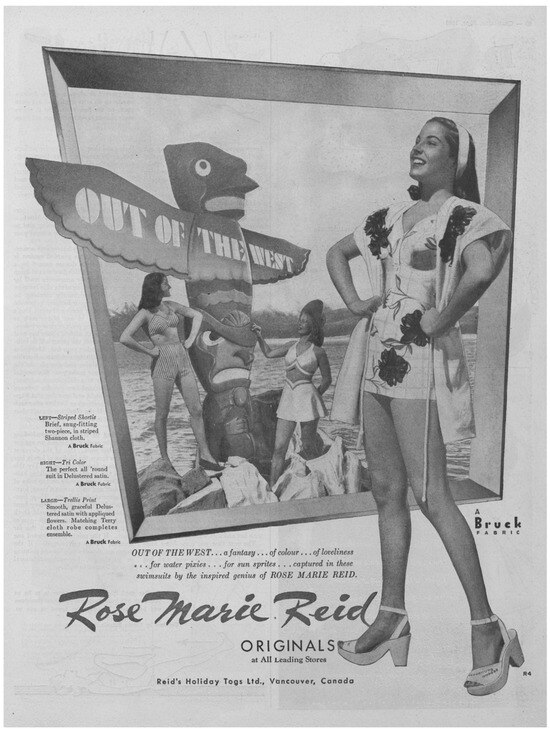
Figure 3.
Full-page advertisement for Rose Marie Reid swimwear in Chatelaine, June 1946 (Reid’s Holiday Togs Ltd. 1946).
These examples offer evidence that by the time Marjorie Holligan traveled to Alaska in 1947, “Northwest Coast art” held some appeal for the broader design community, but was still not a cohesive idea in that realm, despite its importance for modernist primitivist artists. Furthermore, Native designers from this region were apparently not involved in the commercial fashion and textile sector. However, in the later 1940s and early 1950s, Native and non-Native artists and museum professionals in Seattle, Vancouver, and New York increasingly promoted Northwest Coast aesthetics. The desire and opportunity to explore these motifs in textiles and fashion expanded.
4. Through the 1950s: “Our Art Continues to Live”
In April 1948, Ellen Neel, a Kwakwaka’wakw artist acclaimed in Vancouver for her woodcarving, made an influential speech for the Conference on Native Indian Affairs advocating for an expansion of Native-made design that was both commercial and verifiable, especially for home goods and apparel. She said: “Our art continues to live, for not only is it part and parcel of us, it can be a powerful factor in combining the best part of Indian culture into the fabric of a truly Canadian art form … I believe it can be used to stunning effect on tapestry, textiles, sportswear, and in jewelry” (Nuytten 1982, p. 50). The conference was organized by Ravenhill’s Society for the Furtherance of BC Indian Arts and Crafts, the University of British Columbia, and the British Columbia Provincial Museum. The society had been promoting commercial use of Northwest Coast Native designs, but inasmuch as it aimed to support Native makers, it also gave designs to non-Native corporations with little direct benefit to Native communities (Roth 2018, pp. 45–54). Since 1946, Neel had been experimenting with new media and techniques, and in the late 1940s and early 1950s, she designed a locally popular line of silk scarves with the crest designs and stories that she had the inherited rights to use. She also made bags and home goods with her designs silkscreened by hand. Neel sold these products at Vancouver shops, and gifted them to family and friends (Neel 2020; Butler Palmer 2021).
The scarves were not only a unique accessory, but also—in contrast to any designed by Dalí or Vertès—a reflection of internal cultural priorities and an assertion of Neel’s lineal prerogatives. For example, on one scarf (Figure 4), Neel illustrates a version of her family’s creation story as descendants of Thunderbird, a powerful supernatural being from the Sky World. In a series of comic-book style panels using both images and text arranged in concentric rings, she shares key moments from this history, starting with the cedar tree, the “Tree of Life” that sustains her people. Arrows guide the viewer through the narrative, which results in the crests that belong to these descendants (David A. Neel, email to author, 30 October 2023). The last sentence of the scarf’s story is an emphatic “So it is”, conveying the persistence of these privileges in the present tense. In creating this serialized work and others like it, Neel displayed and maintained her family’s property rights for her descendants.

Figure 4.
Ellen Neel, Scarf with lineage creation story, “An Original Totem-wear Design”, ca. 1950s. Serigraph on silk. Collection of David A. Neel. Photograph by David A. Neel. Used with permission.
Furthermore, the creation story scarf serves as an interactive educational tool for those outside the culture. It is notable that Neel’s drawing style for the scarf marshals the techniques of commercial illustration even more than it does the customary visual vocabulary of formline design. In remixing the colors and aesthetics of Kwakwaka’wakw art with comic art, Neel carefully gauged the unfamiliarity of her broader audience with her cultural art forms and content. She designed a popular accessory with mid-century modern cachet while minimizing its “foreignness” in both design and message. This approach helped her garner sales while subtly informing buyers about Indigenous cultural property.
In her speech, Neel invoked Canadian nationalist narratives that resonated with her audience. But she resisted non-Native exploitation, writing that “We need only to have some sort of organization to which architects, builders and manufacturers could go to guarantee authentic products” (Nuytten 1982, p. 50). Neel’s line came to include her designs on blouses, shirts, and skirts that she sold at her Stanley Park retail outlet, the Totem Art Studios, which operated from 1948 to 1957 (Kramer 2012, p. 33; Butler Palmer 2021, p. 12). Carolyn Butler Palmer points out that in a well-known image of Neel working in her studio in 1958, the artist wears a shirt that she probably designed herself (Figure 5). With buttons on the collar and crest forms stitched onto the shirt in contrasting fabric, the garment references button blankets and other cloth regalia that instantiate inherited rights in the potlatch system.
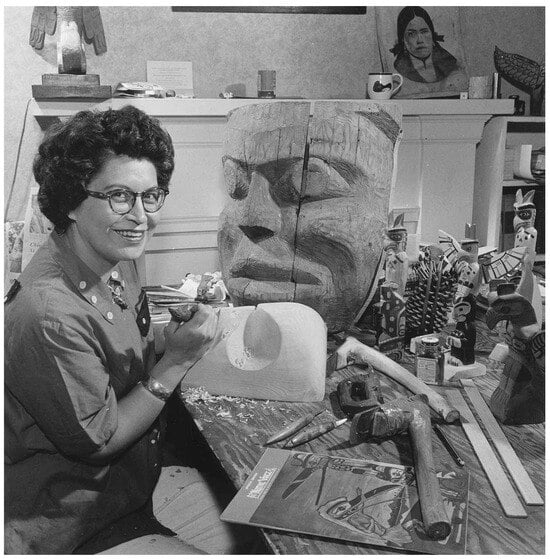

Figure 5.
Ellen Neel, Kwaguitl, from Alert Bay at Work in her Studio, 1958. Photograph by Gar Lunney courtesy of Library and Archives Canada/National Film Board fonds/e011176933.
It follows that this sort of culturally informed everyday dress for Native people on the Northwest Coast in the mid-twentieth century was more common than archival records might suggest.10 For example, Neel also wore clothes designed and sewn by her friend Mabel Stanley (Kwakwaka’wakw), a regalia maker and an advocate for Native culture based in Vancouver who sometimes worked in Neel’s shop (Carolyn Butler Palmer, personal communication, 14 September and 13 October 2023).11 Furthermore, the opportunities for local training in the fashion and beauty industries grew with the establishment of the Blanche Macdonald School and Modelling Agency in Vancouver in 1960 (Macdonald was Métis and a champion for Native empowerment, and her organization was where Indigenous designer Pamela Baker started her career) (Baker 2019).
As Neel was designing, Robert Bruce Inverarity—a Euro-American modernist artist, anthropologist, and federal arts promoter from Seattle—published a book that significantly raised the profile for Northwest Coast art and design. Called Art of the Northwest Coast Indians (1950), its text and hundreds of plates of mostly historical objects sought to remedy the fact that “the art of the Northwest Coast tribes is still relatively unknown” as compared to Navajo, Pueblo, Plains, and Ancient American art (Inverarity 1950, p. viii). The book served to keep Northwest Coast design ideas in circulation: Designs within it were copied or adapted by both Native and non-Native practitioners of textiles and fashion for decades to come, including Nathan Jackson, Paul Thiry, and Vera Neumann, as well as by designers more broadly.12
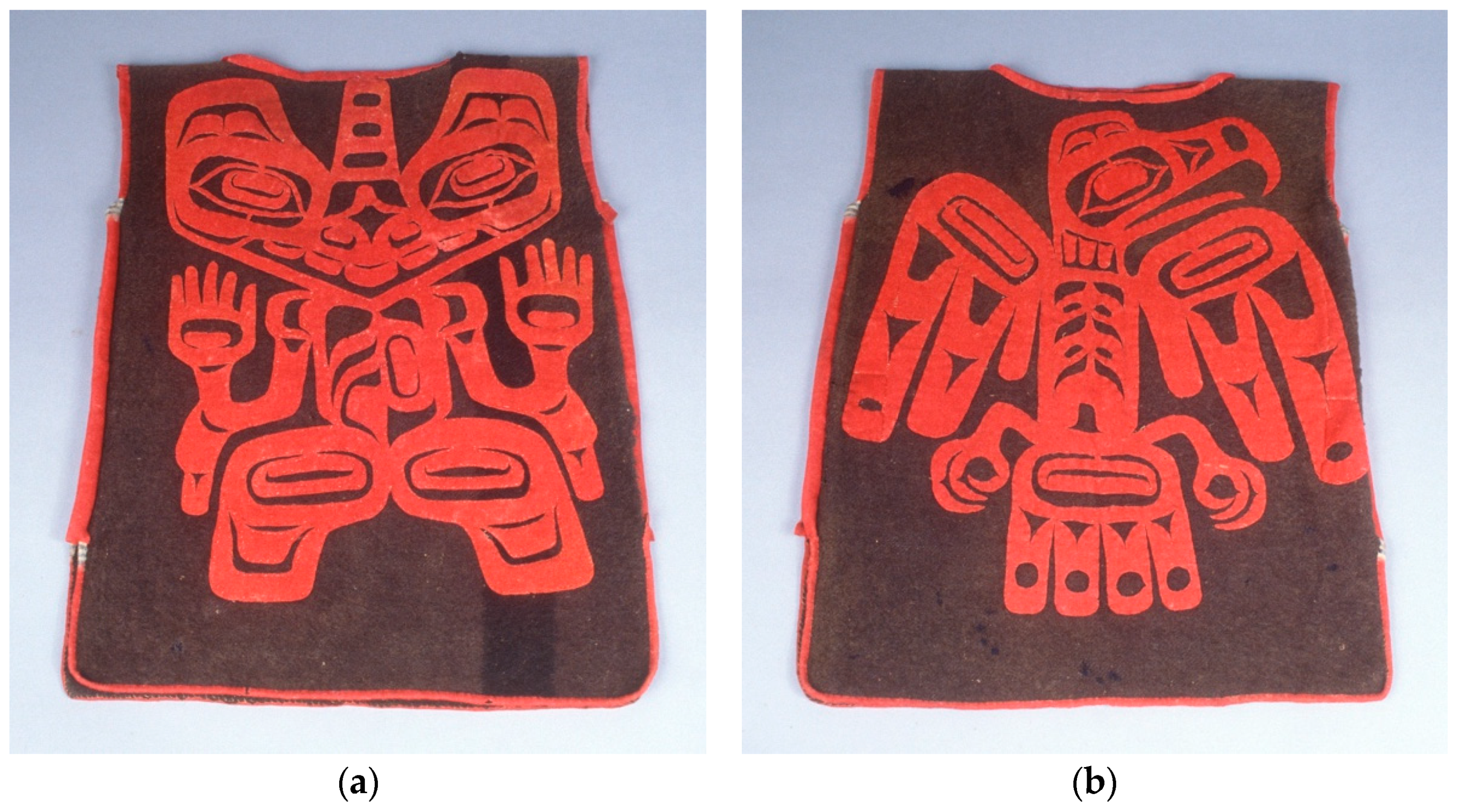
In particular, the book’s jacket art—a red Haida sea-bear crest ablaze on a yellow background—has been replicated and reinterpreted for printed textiles and much more (Figure 6). The cover’s sea-bear design was redrawn from the cloth appliqué on the front of a late-nineteenth century wool dance tunic in the collection of the Burke Museum in Seattle (Figure 7a). The front and the back of the tunic are reproduced in the book’s plate 4 (in black and white); the crest on the back is an eagle.13 The tunic’s motifs and its subsequent adaptations form a compelling case study of how both Native and non-Native artists and designers “were able to make demands on the objects and representations at their disposal”, in ways that were “entangled, mutually constitutive, and culturally situated” (Harney and Phillips 2018, pp. 4, 17). They also underscore the easy adaptability of Northwest Coast formline design from three-dimensional objects such as clothing to two-dimensional media, namely printing on paper and fabric, as well as the concomitant flattening of cultural meaning that can occur when doing so.

Figure 6.
Front cover of Art of the Northwest Coast Indians by Robert Bruce Inverarity, 1950, which depicts the crest design from the front of the Haida tunic in Figure 7. The back cover art is identical. Image by author.

Figure 7.
(a,b) Artists once known, Haida, 19th century. Tunic, (a) front crest: sea-bear (b) back crest: eagle. Wool. Burke Museum cat. no. 1. Collected 1891 by James G. Swan for exhibition in the Washington State Building at the 1893 World’s Columbian Exposition in Chicago. Courtesy of Burke Museum of Natural History and Culture, Seattle, WA.
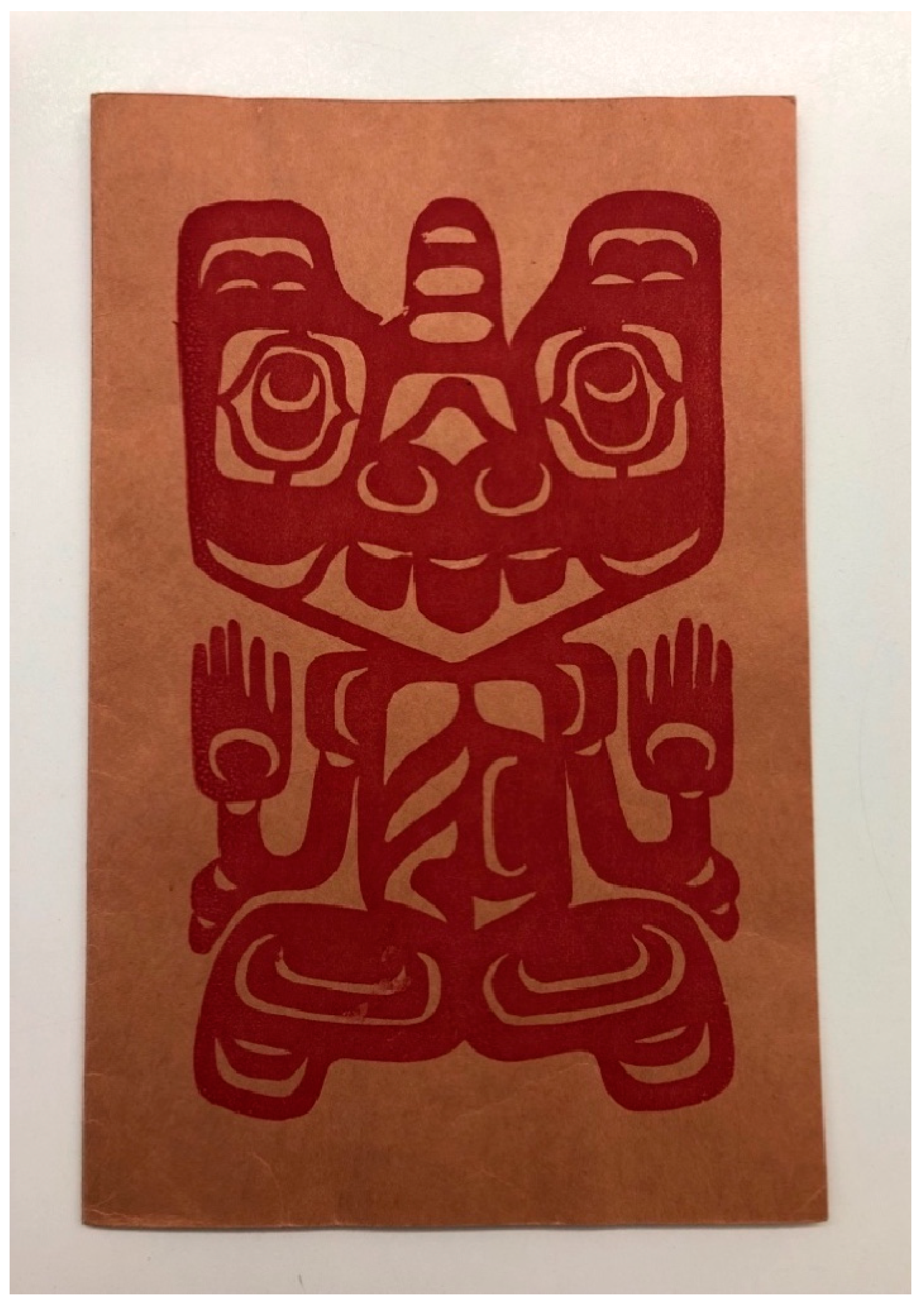
A 1956 replication of the tunic’s sea-bear occurred in a fashion-show context. That year, anthropologist Erna Gunther, the director of the Washington State Museum (the precursor of the Burke), presented a local version of Frederic Douglas’ popular program. Co-produced with the Seattle Art Teachers Association, this show featured 23 historical, “modern”, and “semi-modern” ensembles of only Northwest Coast and Alaska Native dress from the museum’s collection (MOA Audrey Hawthorn fonds, box 22-2, file 6-C-2). The program began with a potlatch regalia scene called “A Wealthy Puget Sound Man goes to a party with his Two Wives”. The clothes were mostly modeled by (non-Native) students and friends of Gunther, who narrated.14 Bill Holm, who was then a high school art teacher, danced Northwest Coast Native dances in an interlude between the modeled ensembles. The show’s program features a silkscreened version of the sea-bear (Figure 8). Holm did not remember the Haida tunic itself being part of the program (Holm, email to author, 27 October 2020), so it is unclear how aware participants and visitors were of the source and specific cultural context of the motif. While the replication of the sea-bear in this case is not entirely divorced from its lineage-based origins, the format of the fashion show positioned the crest as a “fashionable” design source and made it more available for commercial uptake.15
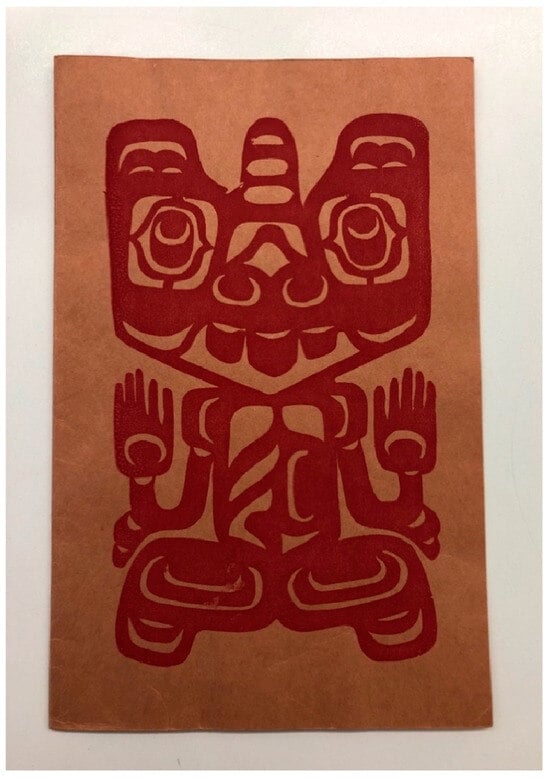

Figure 8.
Silkscreened cover (artist unidentified) for the program of a “fashion show” held at James Monroe Junior High School, Seattle, WA, 29 February 1956. Show sponsored by the Seattle Art Teachers Association and the Washington State Museum. MOA Audrey Hawthorn fonds, box 22-2, file 6-C-2. Photograph by author. Used with permission of UBC Museum of Anthropology, Vancouver, Canada.
In the 1950s and 1960s, the sea-bear and eagle motifs from the tunic depicted in Art of the Northwest Coast Indians circulated further off the page and onto clothing and textiles for home goods. Shortly after the book’s publication, non-Native architect and Northwest Coast art collector Paul Thiry, who was based in Seattle, designed a popular series of textile prints depicting regional Native designs for the New York City firm L. Anton Maix.16 Maix, a textile producer who got his start at Knoll, regularly invited leading designers to develop prints for his company. Thiry has been called “the father of Northwest [architectural] modernism” and designed buildings and interior features at Lewis and Clark College and the Museum of History and Industry (MOHAI) based on Northwest Coast forms (Follansbee 2012). In 1950, he catalogued Native belongings housed at MOHAI and became, in his words, “tremendously interested in the indigenous art of the country”. Thiry said, “Before, I had viewed all of these primitive things as more or less junk, but this was the first time I had come to realize that beyond this point there was great intrinsic value, I mean something that went beyond the primitive…this was sophistication” (Thiry 1983). His comments illustrate Ruth Phillips’ reflection that “The modernists … insisted on retaining the core meanings of ‘primitive’ as primal, simple, and natural, converting the negative charges associated with these terms … into a set of positive attributes” (Phillips 2015, p. 6). They also reveal the growing awareness and valuation of Northwest Coast forms within broader design worlds.
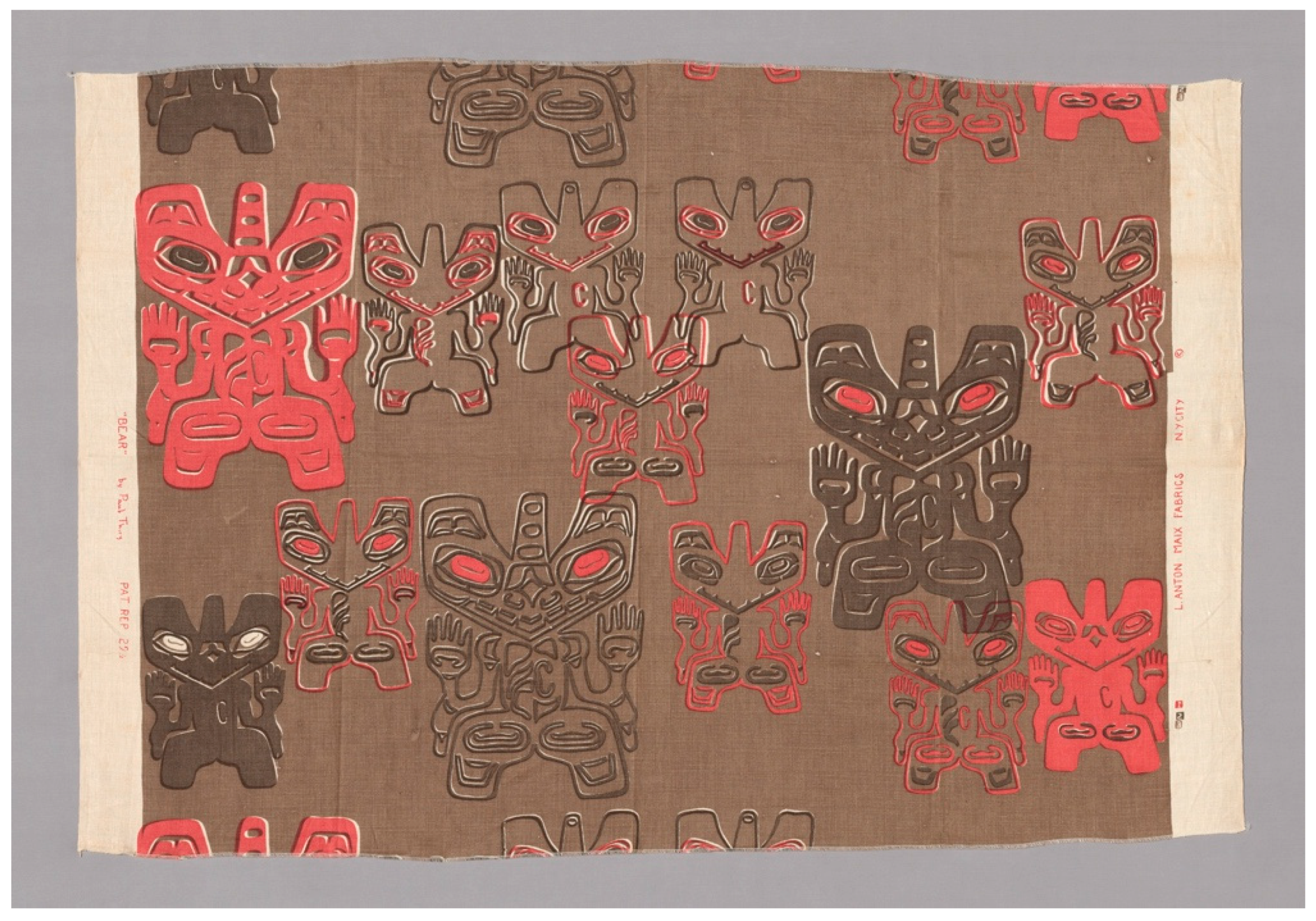
Thiry’s hand-printed textiles demonstrate his Euro-American modernist values. One textile in the series, called “Bear”, overprints the Haida tunic’s sea-bear motif in different scales and line treatments on Maix’s signature Belgian linen (Figure 9). Designers of printed textiles at mid-century often evoked handcraft aesthetics through overprinting, deliberately misaligned registers, and other intentional irregularities in the silkscreening process (Troy 2019, p. 35). “Bear” uses these approaches, with its brown and red colors probably referencing the weathered cedar wood and vermilion trade paint of totem poles, and its linen background suggesting hand-weaving with subtle slubs and texture. In this way, the print evokes the modernists’ stereotyped perception of Native cultures as primordial and timeless as an antidote to the complexities of modern civilization.

Figure 9.
“Bear” (furnishing fabric), ca. 1950–1955. Designer: Paul Thiry, Euro-American. Producer: L. Anton Maix, Inc., New York, NY. Linen, plain weave, screen printed. 37 12 × 54 ½ in. (93.3 × 138.5 cm), warp repeat: 29 ½ in. (75 cm). Christa C. Mayer Thurman Textile Endowment 1996.491, The Art Institute of Chicago, Chicago, USA. Photograph courtesy of Art Institute of Chicago/Art Resource, NY.
At the same time, the choice of the sea-bear as the motif in “Bear” seems to align with American modernist artists’ interest in the flatness of abstraction to convey psychological depth (See Joselit 2000). Unlike on the fashion-show cover, where the sea-bear’s potentially menacing gaze has been softened with larger eyes and fewer teeth—more like a teddy bear than a formidable supernatural being—Thiry’s repeated, fairly faithful rendering of the sea-bear on his textile results in an unnerving overall effect. Thiry’s recontextualized “bears”—no longer a hybrid supernatural being, but a land animal that consumers would recognize—widely cover the surface, akin to contemporaneous modern painting styles. This treatment makes the creature appear that it is closing in on the viewer, with paws that could attack (in northern Northwest Coast art, figures with their palms up to the viewer in fact signal welcome, respect, and/or gratitude [David Boxley, personal communication, 29 August 2018]). Thiry aestheticized this crest form away from its original context, flattened the cultural meaning, and designed it to maximize emotional content or impact. While Thiry clearly appreciated Northwest Coast art and architecture as “sophisticated”, he overlaid his own values in a way that obfuscated the complexity of the sea-bear’s original Haida basis.
Finally, as a white practitioner embedded in both the Northwest and New York design worlds, Thiry had privilege and access that few Native artists did at this time. His textiles were available at the Georg Jensen shop on Fifth Avenue and other retailers, and he noted that they became “a success all over the United States” (Thiry 1983). Asserting a Northwest regional modernism through local Indigenous art and architectural ideas, Thiry was able to leverage his position, demonstrating the extent of the production infrastructure available to non-Native designers in these industries amid glaring structural inequality for Native peoples across the continent.
In the postwar period, political conditions for Native people in Canada and the United States were uneven and turbulent. The patriotism of Native veterans in World War II prompted a reckoning over Canada’s enfranchisement policy (forced revocation of Indian status in order to obtain Canadian citizenship) alongside First Nations activism for self-determination. After a three-year parliamentary review of Canada’s prevailing Indian policy, the potlatch ban and its dress restrictions were lifted in 1951, among other adjustments to the Indian Act. Meanwhile, in the United States, federal termination policy and the urban relocation program brought a new wave of assimilation, discrimination, and other duress. It is in this climate that fashion designer Lloyd Kiva New began silkscreening fabric in his shop and studio in Scottsdale, Arizona in 1951 (The Arizona Republic “Lady Fare” 1961; cf. Metcalfe 2010, p. 94).17 Trained in art education at the Art Institute of Chicago, New found in art a means to shape his selfhood, promote cultural pride, and support Native prosperity. New’s work and personality attracted well-known clients and benefactors such as Eleanor Roosevelt and Frederic Douglas. New embraced modernist design aesthetics and promoted ideals such as artistic freedom and personal expression, innovation, and Native self-determination. In 1956, he was the only Native artist to have a textile in the MoMA’s popular exhibition Textiles U.S.A., a blue and purple striped print on Arizona cotton broadcloth for sportswear, a work that was chosen from more than 3500 entries (MoMA archives, Exhibitions 606.5 and 606.8, reproduction in IAIA archives).
Between 1954 and 1955, New developed the Kiva Craft Center, an expansive modernist court in Scottsdale that included his signature boutique and various studios and amenities. By 1959, New was employing 15 Indigenous artists to create leather bags and colorful, limited-edition, hand-dyed and printed textiles and fashions (Metcalfe 2010, pp. 97–98). His methodology included drawing from historical design idioms and Native landscapes. Similar to non-Native designers, he often named specific cultures when marketing the clothes, even if his inspirations were more diffuse.
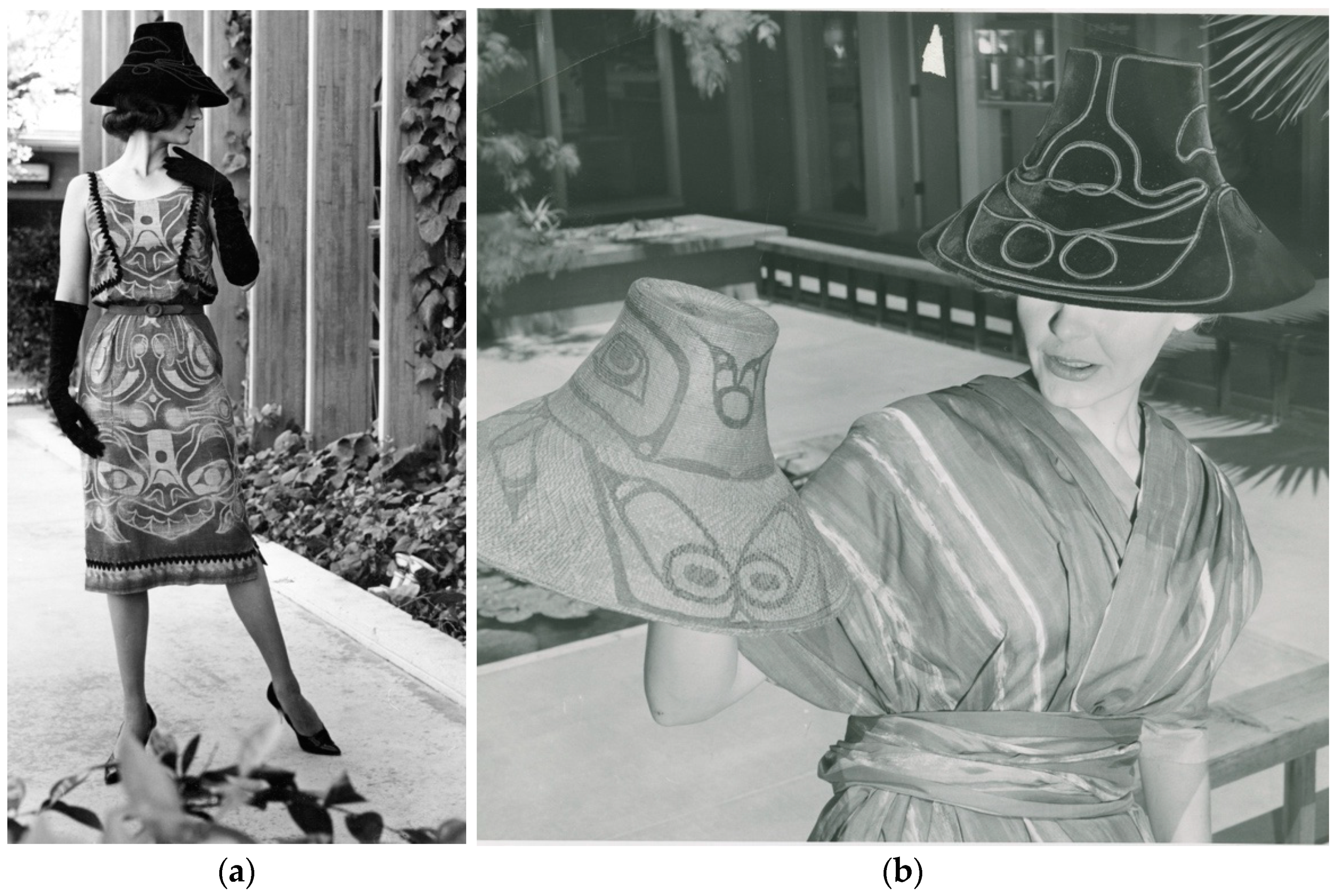
Promotional images from 1956 show a model in dresses by New at the Craft Center (Figure 10). For the shift dress (10a), New, or possibly a designer he hired, developed a bear or sea-bear motif that is similar to that on the Haida tunic in Inverarity’s book. The design was indeed adapted from an “old Indian dress”, meaning a dance tunic or shirt (Newspaper clipping, no date, IAIA archives, box 4, folder 7). Like the Haida tunic, the crest on New’s shift is aligned to the body, invoking its original context. The designer, who may have been Indigenous but not from the Northwest Coast, freely modified the customary forms of northern coastal art, adding a sinuous, rococo flair. The model also wears a northern-style hat fashioned in velvet based on a historical one woven in spruce root. As with Holligan and Thiry, the designer(s) of the shift dress and hat valued the abstraction and balance of Northwest Coast forms. But in New’s case, he acknowledged the original Indigenous designers and involved new ones, making a path for Native practitioners to contribute and grow in the broader design field.

Figure 10.
(a,b) Model in Lloyd Kiva New ensembles, Kiva Craft Center, Scottsdale, AZ, ca. 1956. Lloyd Kiva New collection, MS015 Addendum 16 & 17. Photograph by Stuart Weiner, courtesy of the IAIA Archives, Santa Fe, NM, www.iaia.edu.
New was also sensitive to issues of appropriation. For these two pieces, the designer did not attempt exact replication. Perhaps this was a deliberate choice in recognition of the original design forms belonging to Northwest Coast people. In recalling the launch of his business many years later, New reflected on his tendency to use and adapt Indigenous designs from across the continent: “Had I appropriated someone else’s design? Then like all thieves, or sharp business men (often interchangeable), I quickly justified my actions: if it was stealing, it was for a good cause, like the settlers whose Manifest Destiny rationale somehow made it all right to take Indian lands …” (New 2016, p. 154). Here, New saw his cross-cultural design projects as a necessary step in restorative justice for Native people and Native arts. Like many modernist artists at the time, New engaged with primitivism and cultural borrowing. But as a Native modernist, New explored aesthetics that Elizabeth Harney and Ruth Phillips describe as “rediscovered, reactivated, or reimagined … despite conditions of grossly unequal power” (Harney and Phillips 2018, p. 17). In doing so, he aligned modernist design principles with Indigenous cultural values. As with Neel before him, New expressed that his project was for Indigenous people to reclaim design, production, and marketing of commercial goods so that they could imagine and create an alternative future than one of unbridled colonialist consumption. The reworkings of the nineteenth-century Haida tunic’s sea-bear crest and similar designs described in this section demonstrate that, when Native determined, repetition and adaptation can rewrite design values themselves in ways that can feed back positively into Native art production and economic possibility.
5. The 1960s: Northwest Coast Textile Artists in Emerging Markets
Lloyd Kiva New did not create a cohesive body of textiles and fashion with Northwest Coast design ideas in his Scottsdale studio. However, after he co-founded the Institute of American Indian Arts (IAIA) in Santa Fe in 1962 and served as its first art director, a small number of Indigenous artists from the Pacific Northwest and Alaska were among those who learned textile printing techniques directly from New. One of them is the acclaimed Tlingit artist Nathan Jackson, who is renowned for his totem pole carving. Jackson was twenty-four when he joined IAIA’s first cohort between 1962 and 1964, receiving training from New as well as Seymour Tubis, an instructor of printmaking, painting, and design whose own mentor was Will Barnet, an artist whose work was informed by the spatial structures of Northwest Coast art. Art historian Christopher T. Green argues that Jackson’s career arc demonstrates an ambiguous embrace of both “traditionalist” and “modernist” modes that reveals the instability of a dialectic between them, emphasizing instead their bi-directionality (Green 2020, pp. 62, 130–31).
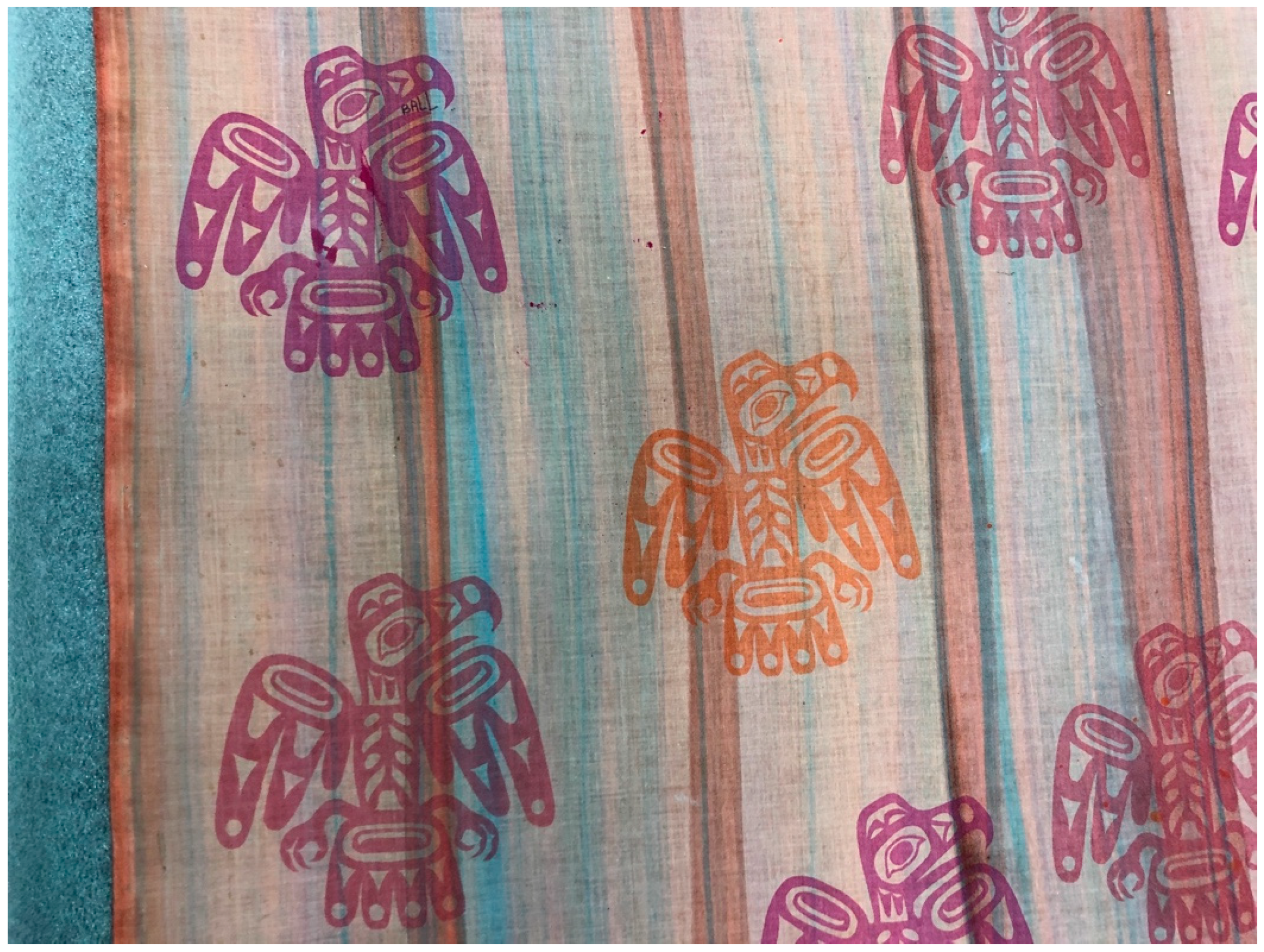
Such tensions are at play in a textile of Jackson’s in the IAIA collections, for which Jackson reworked the eagle motif from the Haida tunic in the Inverarity book in bright colors (Figure 11). The artist experimented with New’s signature “color clash” approach, which consists of muted, earth-and-sky dye tones applied as a background for the main silkscreened motif in more vivid colors (Myers et al. 2016, p. 48). Here, Jackson used the “canning” technique, in which he layered the dyes in tracks with a tin trough. While in Santa Fe, Jackson was learning two-dimensional crest design of Tlingit and neighboring cultures alongside these textile techniques, although he had already carved miniature crest poles by then. He recalled having no access to historical Northwest Coast objects in Santa Fe, only books, which were mostly black and white (Jackson 2020). With New’s influence, he had freedom to play with color. The magenta and orange eagles, poised for flight over the waterlike background, are more aligned with bright, playful California style than the customary palette of northern Northwest Coast painting. Unlike Thiry’s print, Jackson’s aesthetic choices synthesize handcraft and fidelity to customary forms with exuberant, contemporary color and innovative technique. The textile reveals Jackson’s experimental approach, not constraining “Northwest Coast style” to conventions, positioning the work as contemporary. As with New’s dress and hat, in this print, Indigenous value systems and the tenets of modernism work in concert.
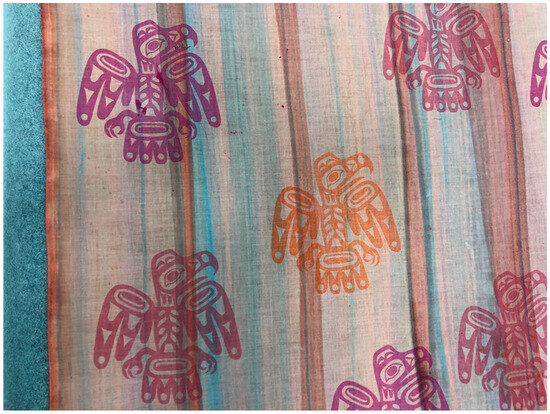

Figure 11.
Nathan Jackson (Tlingit), Untitled (detail), ca. 1963–1964, screen printed cotton, 57 × 27 in. IAIA Museum of Contemporary Native Arts (MoCNA) Collection: PROP-3; Honors Collection. Photograph by author, courtesy of the IAIA Museum of Contemporary Native Arts, Santa Fe, NM.
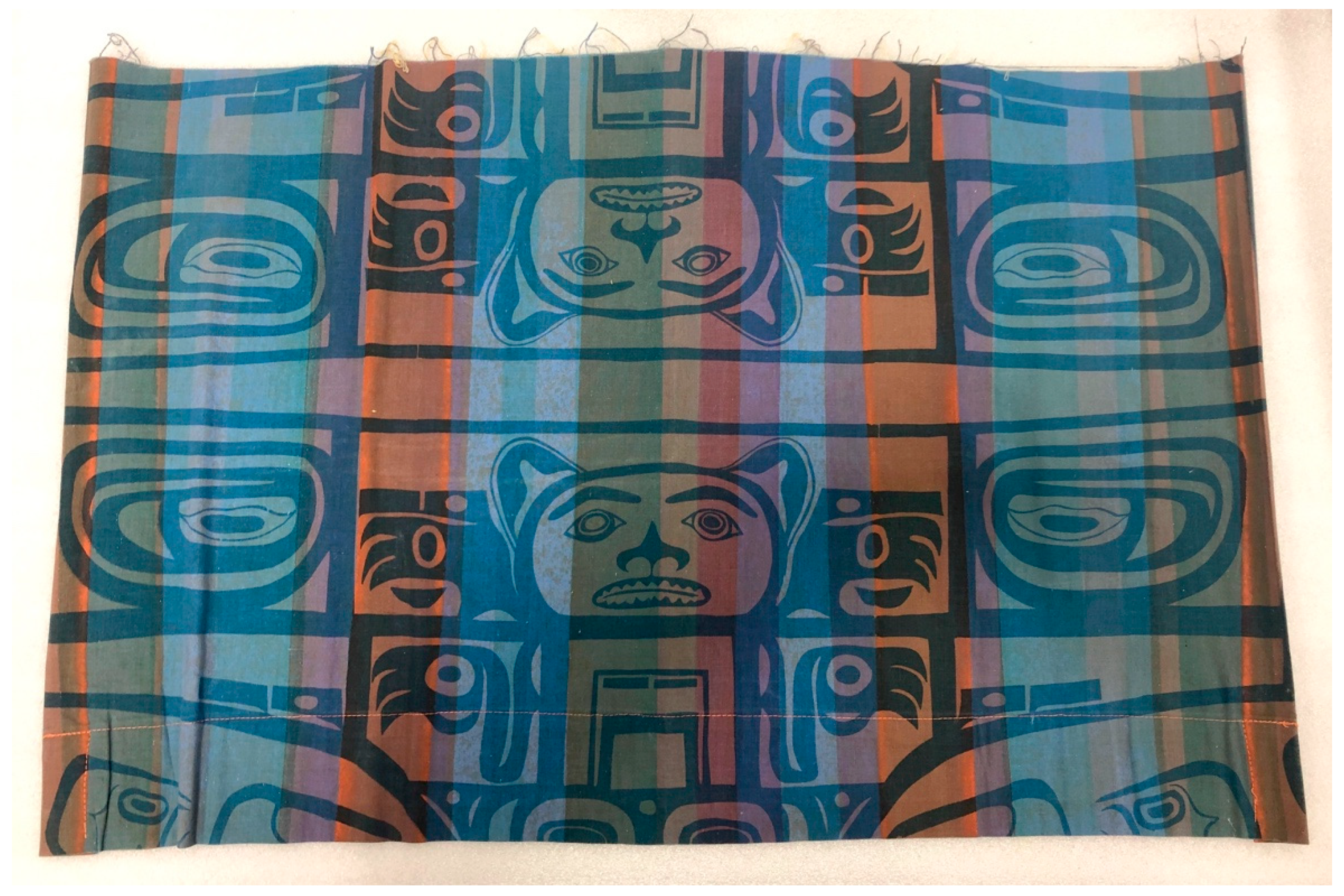
As Jackson was working, Athabascan artists at IAIA such as Bill Blackmore (a peer of Jackson’s from Haines, Alaska) and Charles Tega also created textile prints using formline styles and strong color statements (Green 2020, p. 66). These prints formed a cluster of Northwest Coast regional aesthetics in textiles. Many of the IAIA student prints were sewn into curtains, wall hangings, and table coverings for the school’s buildings, and into clothing and other items sold to support the organization (Myers et al. 2016, pp. 55–56; Green 2020, p. 64) (Figure 12). Although these artists did not utilize symbols of their specific cultures or clans in these works, their engagement with Northwest Coast forms affirms their identities as Indigenous artists exploring regional aesthetics for the purposes of cultural revitalization and resurgence, not exploitation. In this sense, the translation of these designs to printed fabric seeks to retain their cultural meanings, even if the specific origins were adjacent to the cultural contexts of these artists.

Figure 12.
Bill Blackmore (attr.) (Athabascan), Untitled (curtain), ca. 1963–1965, screen printed cotton, 21 × 31 ½ in. IAIA Museum of Contemporary Native Arts (MoCNA) Collection: NW-28; Honors Collection. Photograph by author, courtesy of the IAIA Museum of Contemporary Native Arts, Santa Fe, NM. “I.A.I.A. Boys Bldg 342 Room 228” is written in pen on the back of this curtain. (See Green 2020, p. 67, footnote 92).
In 1964, one of Jackson’s textile prints (Figure 13) won an award for outstanding student work by New York City-based Interior Design magazine. Jackson had met the editor through New and forged a friendship two years earlier (Green 2020, p. 92; Jackson 2020). Another booster of Jackson’s, Carl Heinmiller of the Haines-based workshop and cooperative Alaska Indian Arts (AIA), paid for Jackson’s travel from Santa Fe back to southeast Alaska and asked him to work as a screen-printing instructor for paper and textiles. Under Jackson’s guidance, some local artists created fabrics and clothing—including vests and miniskirts—bearing regional designs that AIA sold (Green 2020, p. 93). But Jackson noted that no other artists in his milieu were “plugged in” to textile work at that time (Jackson 2020). Green reports that Heinmiller asked New several times to come to Alaska to help develop a textile workshop with Jackson and Tega, but the records suggest that New and Tega did not travel there (Green 2020, pp. 113–14).
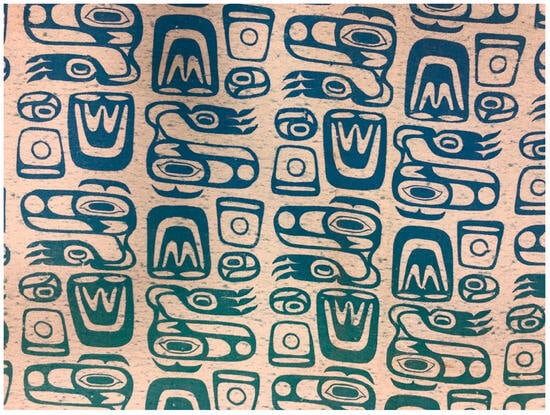

Figure 13.
Nathan Jackson (Tlingit), Untitled (detail), ca. 1963–1964, screen printed cotton and rayon, 80 × 41 in. IAIA Museum of Contemporary Native Arts (MoCNA) Collection: NW-35; Honors Collection. Photograph by author, courtesy of the IAIA Museum of Contemporary Native Arts, Santa Fe, NM.
Some of AIA’s fabrics reached urban centers. In 1965, “block printed cloth material” from AIA’s commercial output was included at gift shows in Los Angeles and New York City as a pilot. Later that same year, the director of the Southwest Museum (which became the Autry) indicated that at an exhibition that included Northwest Coast prints from the Los Angeles gift show, “many museum visitors were amazed to learn that various types of fine arts are still being produced in this area of North America, so famous for its arts and crafts” (Southwest Museum Director’s Report, cited in Green 2020, pp. 111–12). At the gift shows, silkscreened prints were favored over wood carvings and jewelry, but most of the interest and uptake was in prints on paper versus on fabric (Green 2020, pp. 109–10). Unlike textiles and clothing, paper prints could be readily and quickly made, distributed, and sold for museum, gallery, and home display, easily framed and understood as work for walls.
Jackson did not stay long in textiles, leaving AIA in 1967. He was deepening his talent for carving after Bill Holm came to teach in Haines in 1964, and the AIA effort was not sufficiently profitable (Green 2020, p. 124). Jackson noted that he was not sure such an undertaking in textiles from Alaska would be successful. “I thought, well, I don’t know if I can be able to make that kind of money”, he said. “Even getting started … I’d have to get a loan. I thought, ‘I’ll keep it simple.’ That is [one] reason why I am doing what I generally do” (Jackson 2020). Even with his short turn in cloth media, Jackson can be recognized as advancing space for Northwest Coast fabric arts and contributing to the continuity of Native practice within this design field in the way that Neel had advocated 17 years earlier.
Jennifer Kramer relates how Kwak’wakawakw artist Doug Cranmer, a relative of Ellen Neel, also created similar space at the same time. Cranmer had been experimenting with serialization by silkscreening on fabric and paper with his wife Judy Tweedie, a non-Native textile artist, in his Vancouver art gallery The Talking Stick. He started creating bags and wall hangings with his prints and sold some in his mother’s store in Alert Bay. They also became desirable potlatch gifts. Then, in 1964, he contracted with a firm called Industrial Bags to manufacture burlap bags with his screenprinted designs for royalties. With the closure of The Talking Stick in 1967, this product line ceased, owing to the limited profitability of the bags and Cranmer’s shift toward larger carving commissions as his notoriety grew (Kramer 2012, pp. 32–45). Cranmer’s story of textile experimentation was much like Jackson’s.
For these two artists, wood sculpture—which was typically men’s work—was more feasible, financially viable, and artistically invigorating than their forays into cloth printing for home goods and accessories. Furthermore, Northwest Coast designs on paper in the 1970s, with “the almost frenzied production and consumption of prints” at that time (Duffek 2013, p. 598), were also largely the work of male artists. While a productive investigation of the factor of gender in this design history is beyond the scope of this paper, it is clear that the public’s value of Northwest Coast carving and prints on paper far exceeded that of fiber arts in the mid-twentieth century, and remains so. Even with the creativity and agency of well-positioned Native artists exploring fabric media in the mid-twentieth century, production capacity and return on investment for textiles and fashion on the Northwest Coast was limited, major trade centers like New York were marginally accessible, and the appeal of Northwest Coast-specific design in the broader market was barely in place. Marcia Crosby writes that “Before the mid 1960s, there was no sustained economic or/and institutional or private support from patrons (including collectors of contemporary aboriginal art), nor an established intellectual discourse to create value for ‘modern Indian’ art” on the Northwest Coast (Crosby 2009). In the 1950s and 1960s, Northwest Coast textile arts did not have coordinated investment for economic development from government or private interests to build infrastructure for production and promotion that would generate artistic and market value.
These local conditions differed from those surrounding the range of Inuit-designed textiles from Kinngait Studios in Kinngait (Cape Dorset) in Nunavut during the same period. The Kinngait story is a useful comparative. Starting in 1938, the Canadian Handicrafts Guild, and then Canada’s Northern Affairs and National Resources office in 1956, initiated the development of a commercial art industry in Canadian Inuit communities. These agencies were motivated to stimulate economic development given collapses in subsistence livelihoods after the fur trade in the far north. In 1958, artists created the Inuit-led West Baffin Eskimo Cooperative, which produced a range of printed textiles for commercial sale with designs that represented Inuit cultural values. These were aligned with prevailing design sensibilities for apparel and interiors and maintained profits for local people. The textiles benefited from significant marketing, promotion, and acclaim across Canada. This included a major award by the Canada-Design ’67 program and sales through their “design marts” in Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver, as well as some inclusion at Expo ’67 in Montreal and museum display elsewhere. Even with this promising infrastructure, sales were limited. The studios could not accommodate the printing capacity necessary to fill large commercial orders. They eventually licensed their designs to other designers and companies to produce and adapt for apparel and accessories, with royalties going to the Inuit artists (Shaughnessy and Richard 2018). Today, while Inuit art more broadly is a multimillion-dollar industry and Kinngait has the highest number of artists per capita in Canada (Igloliorte 2018, p. 83), its textile industry flourished only during the mid-century period when these designed goods were accorded a value status of “fine art”.
Beyond the consideration of infrastructure, I speculate that in the arenas of dress and textiles, Northwest Coast design forms—and perhaps Inuit ones as well—did not conform as well to dominant visual tropes of “Indianness” for fashion and textile consumers at mid-century as compared with those further south or west. Solen Roth, in Incorporating Culture, notes the persistent locality of Northwest Coast “artware” (her term for modestly priced, serialized goods with Northwest Coast designs, including fashion and decor): “Northwest Coast artware has a very minimal presence east of the Pacific Coast Range”, she writes. It “has followed a much more restricted geographic path than the more global and less formal circuits of trade that have allowed other so-called ethnic products to be sold on the streets of New York, Paris, and elsewhere” (Roth 2018, p. 76). Roth attributes the circumstance to the art as not being seen as “generally ‘exotic’ or ‘ethnic’ to the same degree” as other Native North American aesthetic vocabularies or those from Africa or Asia.
Further reflection on prevailing mid-century aesthetics in fashion and textiles permits some speculation about the enduring localization of Northwest Coast design in these media. Northwest Native motifs based on hard-edged curvilinear crest and geometric designs are distinct from the amalgamated Indigenous cultural inputs to the California look that was popular at mid-century. Although also positioned as “West Coast”, “California casual” fabric prints and clothing adapted South Pacific “tiki style” and Southwestern Native design idioms, not Northwest Coast design. With its brilliant tropical colors and flowers, the California look symbolized warmth and leisure, and was disseminated by a significant manufacturing base in Los Angeles (Kerstein 2003, p. 68–69; Bazylinski 2013, pp. 29–30). “Carefree” fashion culture was particularly important during the post-war period, when consumers sought to dispel painful memories of loss and shed the commodity restrictions of wartime. The Northwest Coast art market was not only fledgling at this time, but what representations did exist in fabrics may have been an awkward fit aesthetically for social trends of escapism or exoticization, which relied on ebullient patterns and bright color. Rose Marie Reid, for example, could not build a swimsuit brand on totem poles and snowshoes, and Holligan’s “Northwest Passage” line included as many flowers as it did glacier tones and blanket prints. Perhaps the “Indian” stereotyping of Northwest Coast art that non-Native designers occasionally amplified in the 1940s became perceived as less exotic or relevant in the 1950s and 1960s. It is interesting that the tones that the IAIA textile artists tended to choose for their “color clash” approach aligned more with dominant market trends than (northern) Northwest Coast customary colors of red, black, and blue, and did not lean on nostalgia, even as they reworked historical designs.
Indeed, by the mid-1960s, American style trends drifted away from evoking the past and embraced futuristic looks, with mod, pop-art-inspired, and “Space Age” styles becoming more relevant in popular culture. Around this time, due to business and stylistic shifts, textiles also waned as the “face of modernity” and a site of nationalism (Troy 2019, pp. 36–37). Notably, Vogue’s “Americana” issues ceased production in 1970 and American Fabrics in 1972. Art and design historian Virginia Gardner Troy attributes the changing currency of textiles, in part, to the fact that companies began moving production outside the United States, which undercut North American industry.18 In conjunction, nationalist narratives adjusted to more global ones. Hierarchies of value for textile design shifted as well. Textiles, having been positioned prior as “art/design”, became increasingly valued as “craft” and took finished forms that were less often furnishings or clothing. Troy notes:
By the mid-1960s, American-designed and manufactured textiles … were no longer a consistent part of museum exhibition programming; rather, as more artists began exploring the medium of fibre, textiles began to be recognized as unique objects to be viewed for aesthetic value alone and categorized with terms such as ‘wall-hangings’ and ‘fibre-art’”(Troy 2019, p. 37)
The explorations in Northwest Coast fabric and fashion design in the mid-twentieth century, namely those by Native artists, extended and adapted long-standing regional dress and textile practices that declare identity through crest designs positioned on cloth. Sometimes the mid-century experiments were in tension with Indigenous values and property rights, while at other times, they were in alignment. Today, a vibrant regional Native fashion industry has expanded from these foundations, with its own Indigenous fashion week and a network of committed local designers and producers that still work on a small scale (Allen, forthcoming).
As anthropologist Solen Roth has demonstrated, contemporary local design and production are increasingly operating as “culturally modified capitalism”, integrating Indigenous values with commercialization to help maintain the cultural and political goals of Native communities (Roth 2018, p. 5). Furthermore, the discourse of cultural property rights on the Northwest Coast has shifted since the mid-twentieth century, with emphasis on the limitations of European-derived property law alone at resolving issues of ownership and protection. Anthropologist Jennifer Kramer wrote in 2013 that “What has been commonly valued aesthetically by non-Native people is now more and more being asserted as cultural property by Native people” to, among other aims, “fight appropriation and secure greater control over the proliferation of others claiming their designs, stories, songs, etc.” (Kramer 2013, p. 722). As demonstrated by the two vignettes that begin this paper, appropriations that went uncontested in the 1940s are today being challenged by Indigenous legal structures grounded in concepts of obligation, ownership, and reciprocity. The cultural values, property, and opportunities that were lost, maintained, or gained in the mid-century modernist explorations in textiles and dress remain on a course of resurgence and reclamation, ever more bound to their communities in constant adjustment of what “local fabric” can mean. This is a design climate that Ellen Neel foresaw, and remains complex and unfinished business.
Funding
Travel to conduct some of the research in this article was supported by the Bonnie Cashin Fund at the Bard Graduate Center, New York, NY.
Data Availability Statement
Some of the collection items and images researched in this article are available online.
Acknowledgments
Earlier iterations of some content in this paper were shared in my 2019 Qualifying Paper for Bard Graduate Center, as well as at the University of Oklahoma New Perspectives in Native American Art Symposium in 2020. I thank the many individuals who generously shared their knowledge and experiences with me and/or offered feedback on this research or versions of the text, including Aaron Glass, Michele Majer, Nathan and Dorica Jackson, Christopher T. Green, Carolyn Butler Palmer, David Neel, Katie Bunn-Marcuse, Amanda Thompson, Leonie Treier, Emily Hayflick, Pamela Baker, Ryan Flahive, and Karen Kramer, as well as the colleagues who facilitated access to collections, archives, and imagery. I also appreciate the incisive comments by an anonymous reviewer that strengthened the scope and arguments of this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Notes
| 1 | While Chilkat weaving has an unbroken history of manufacture, weavers stopped producing Raven’s Tail robes in the early-to-mid 1800s, then revived the practice in the 1980s. |
| 2 | In this article, I employ Jennifer Ayres’ broad definition of appropriation: “an umbrella term that encapsulates different degrees of borrowing, ranging from inspiration to theft” (Ayres 2017, p. 152). |
| 3 | Ellen Neel is credited as the first Northwest Coast printmaker in any medium. |
| 4 | In this paper, I distinguish “studio and commercial fabric and fashion design” from more historically embedded types of Northwest Coast fiber arts such as weavings, appliqued button blankets, beadwork, and Cowichan sweaters. The paper chiefly focuses on silkscreened fabrics, which can be utilized for interior design items such as curtains and upholstery as well as for cut and sewn apparel and accessories. |
| 5 | Before d’Harnoncourt’s two exhibitions, the 1927 Exposition d’Art Canadien in Paris and the 1927–1928 Exhibition of Canadian West Coast Art, Native and Modern in Ottawa, Toronto, and Montreal juxtaposed Northwest Coast art and works by artists such as members of the Group of Seven (Dawn 2013). The latter exhibition included Emily Carr’s hooked rugs with Native motifs. In 1952, after d’Harnoncourt’s exhibitions, Erna Gunther, the director of the Washington State Museum in Seattle who had participated in developing the Northwest Coast art display at the 1939 San Francisco exposition, developed two exhibitions at the Seattle and Colorado Springs art museums that also promulgated Northwest Coast Native art (Garfield and Amoss 1984, p. 396). |
| 6 | For example, Vogue printed fashion spreads set in the MoMA exhibition with models wearing non-Native-inspired styles (Crowninshield 1941). |
| 7 | Frederic Douglas’ Indian Fashion Show paused during wartime between 1942 and 1947. After Douglas’ death in 1956, it continued through 1972 in modified forms. |
| 8 | Erna Gunther was dubbed the “Western Secretary” of the Indian Fashion Show and would sometimes narrate in Douglas’ stead (Audrey Hawthorn to Erna Gunther, 28 November 1950, MOA Audrey Hawthorn fonds, box 26-6, series 7-C-2). |
| 9 | Some examples of “Native-inspired” designs relating to the Northwest Coast appear in periodicals and other publications in the 1950s, often drawing upon the cachet of the totem pole. |
| 10 | An overlooked area of research in mid-to-late twentieth century fashion is the networks of Native women sewing and designing for themselves and their friends. In Canada, these activities became especially relevant after the lifting of potlatch ban in 1951: after this time, Native women in communities where regalia making had gone underground or had been entirely suppressed gradually felt more comfortable creating and wearing ceremonial or outwardly “cultural” clothing once again for themselves and their families. This type of research is challenging because of the persistent values that determine which types of dress materials and narratives are archived in museums across art, anthropological, and fashion collections. For example, fancy regalia and non-Native dress are favored for preservation, and not everyday wear that may nonetheless be informed by Indigenous aesthetics and cultural values. |
| 11 | A to-do list in one of Ellen Neel’s notebooks indicates needing to purchase “nylon chiffon for Mabel”, for example (Nuytten 1982, p. 63). |
| 12 | As a well-known example, in 1975, a Kwakwaka’wakw eagle transformation mask on plate 90 in Inverarity’s book was the inspiration for the Seattle Seahawks logo (Wright 2014). |
| 13 | The Haida tunic’s sea-bear crest had in fact already been re-signified as modernist design before the publication of Art of the Northwest Coast Indians: The crest was redrawn by Euro-American artist Louis Siegriest for one of the advertising posters for the Golden Gate International Exposition’s Indian Court in 1939, commissioned by Rene d’Harnoncourt (DeNoon 1987, p. 55). Given that Erna Gunther was also involved in the Northwest Coast art display there, the tunic was probably on view at the exposition as well. The visibility of the Siegriest posters may have influenced the selection of the Haida crest for Inverarity’s 1950 book and the 1956 fashion show cover. |
| 14 | Very few models in Douglas’s fashion show were Indigenous. At the 1951 presentation at UBC, undergraduate Gloria Cranmer Webster (Kwakwaka’wakw), Doug Cranmer’s sister, in fact modeled an 1885 Apsáalooke (Crow) dress from the Denver Art Museum collection (Photograph in MOA Audrey Hawthorn fonds, box 22-2, file 6-C-2). |
| 15 | It is worth noting that non-Natives involved in the mid-century Native fashion shows could momentarily inhabit Northwest Coast Indigeneity—including gender and marital structures—while Native people were generally not present to self-represent. As Rayna Green articulates, such an opportunity allowed temporary escape from “the conventional and often highly restrictive boundaries of…fixed cultural identities based on gender or race”. The perceived potential of an embodied transcultural experience was part of the allure of the popular commercial clothing styles that derived from historical Native antecedents (Green 1988, pp. 31, 43–44). |
| 16 | Among Paul Thiry’s prints are “Tlingit”, with a repeating motif he took from a nineteenth-century Tlingit bentwood box at the American Museum of Natural History that was illustrated by Franz Boas in “The Chilkat Blanket” (New York Times 1950, p. 27; Cora Ginsburg W3455a catalog entry, 10 June 2019). |
| 17 | In 1952, Lloyd Kiva New met textile designer Leslie Tillett while at the International Fashion Show in Atlantic City, then trained with him for several months to learn how to scale up production (Myers et al. 2016, p. 48). |
| 18 | The Celanese Corporation itself expanded its production beyond the U.S. as early as 1947, when it began manufacturing acetate fibers in Ocotlan, Mexico. |
References
- Abrego, Sonya. 2016. Westernwear and the Postwar American Lifestyle, 1945–65. Ph.D. dissertation, Bard Graduate Center, New York, NY, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, Laura J. Forthcoming. Sovereignty Every Day: Mobilizing Indigenous Fashion from the Northwest Coast. In Fashion in American Life. Edited by Hazel Clark and Lauren Downing Peters. London: Bloomsbury Visual Arts.
- Anthes, Bill. 2006. Native Moderns: American Indian Painting, 1940–60. Objects/Histories. Durham: Duke University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Anthes, William Louis, Jr. 2000. Indian Style: Primitivism, Nationalism, and Cultural Sovereignty in Twentieth Century American Art. Ph.D. dissertation, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, USA. Available online: http://search.proquest.com/docview/304615072/abstract/C4A37E49690446C7PQ/1 (accessed on 27 April 2019).
- Ayres, Jennifer. 2017. Inspiration or Prototype? Appropriation and Exploitation in the Fashion Industry. Fashion, Style & Popular Culture 4: 151–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, Pamela. 2019. Interview with author. September 9. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, Pamela C., and Phyllis G. Tortora. 2010. Influence of North American Indian and First Nations Dress on Mainstream Fashion. In Berg Encyclopedia of World Dress and Fashion: The United States and Canada. Oxford: Bloomsbury Academic, pp. 467–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazylinski, Alison Rose. 2013. Dressing Indian: Appropriation, Identity, and American Design, 1940–68. Master’s thesis, University of Nevada, Las Vegas, NV, USA. Available online: http://search.proquest.com/docview/1466640213/abstract/5C07292D12A741FCPQ/1 (accessed on 29 April 2019).
- Boydell, Christine. 2002. Textiles in the Modern Home. In Disentangling Textiles: Techniques for the Study of Designed Objects. Edited by Mary Schoeser and Christine Boydell. London: Middlesex University Press, pp. 81–94. [Google Scholar]
- Burr, Carole Reid, and Roger K. Petersen. 1995. Rose Marie Reid: An Extraordinary Life Story. American Fork: Covenant Communications. [Google Scholar]
- Butler Palmer, Carolyn, ed. 2021. Ellen Neel: The First Woman Totem Pole Carver. Victoria: Flask. Available online: https://curatorialincubator.ca/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/Ellen-Neel-Book-PRINT-FINAL-03-2021.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Carey, Lucille. 2020. A Story of Connections: Gilbert Adrian and Thomas Dorsey. Master’s thesis, S.U.N.Y. Fashion Institute of Technology, New York, NY, USA. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/openview/db504ee1ca517319f051bd524888c2cd/1 (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Caton, Susan Turnbull. 2004. Fashion and War in Canada. In Fashion: A Canadian Perspective. Edited by Alexandra Palmer. Toronto: University of Toronto Press, pp. 249–69. [Google Scholar]
- Chatelaine. 1940. The Canadian Woman and Her Fashion Formula. Chatelaine, October 5. [Google Scholar]
- Clifford, Marie. 2003. Working with Fashion: The Role of Art, Taste, and Consumerism in Women’s Professional Culture, 1920–40. American Studies 44: 59–84. [Google Scholar]
- Cowling, Elizabeth. 1978. The Eskimos, the American Indians and the Surrealists. Art History 1: 484–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craik, Jennifer. 1994. The Face of Fashion: Cultural Studies in Fashion. London: Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Crosby, Marcia. 2009. Making Indian Art ‘Modern.’ Ruins in Process: Vancouver Art in the Sixties. Available online: http://vancouverartinthesixties.com/essays/making-indian-art-modern (accessed on 25 October 2020).
- Crowninshield, Frank. 1941. American Indian Art. Vogue 97: 96, 97, 150, 151, 152. [Google Scholar]
- Damon, Carolyn. 1941. How Do We Dress from Here? Chatelaine, February. 16. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, Karl J. 2014. Objects of Desire: Surrealist Collecting and the Art of the Pacific Northwest Coast. Ph.D. dissertation, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/docview/1783597951/7CA203A7CC3B4E59PQ/2 (accessed on 13 September 2023).
- Dawn, Leslie. 2013. Northwest Coast Art and Canadian National Identity, 1900–1950. In Native Art of the Northwest Coast: A History of Changing Ideas. Edited by Charlotte Townsend-Gault, Jennifer Kramer and Ki-ke-in. Vancouver: University of British Columbia Press, pp. 304–47. [Google Scholar]
- Deloria, Philip J. 1998. Playing Indian. Yale Historical Publications. New Haven: Yale University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Deloria, Philip J. 2019. Native to Modern. In Becoming Mary Sully: Toward an American Indian Abstract. Seattle: University of Washington Press, pp. 3–23. [Google Scholar]
- DeNoon, Christopher. 1987. Posters of the WPA. Los Angeles: Wheatley Press. Seattle: University of Washington Press. [Google Scholar]
- Duffek, Karen. 2013. Value Added: The Northwest Coast Art Market since 1965. In Native Art of the Northwest Coast: A History of Changing Ideas. Edited by Charlotte Townsend-Gault, Jennifer Kramer and Ki-ke-in. Vancouver: University of British Columbia Press, pp. 590–604. [Google Scholar]
- Duffek, Karen, and Charlotte Townsend-Gault, eds. 2004. Bill Reid and Beyond: Expanding on Modern Native Art. Vancouver: Douglas & McIntyre. Seattle: University of Washington Press. [Google Scholar]
- Follansbee, Joe. 2012. The Lasting Impact of Seattle’s World’s Fair Architects. Seattle Magazine. April 8. Available online: https://seattlemag.com/lasting-impact-seattles-worlds-fair-architects/ (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Garfield, Viola E., and Pamela T. Amoss. 1984. Erna Gunther (1896–1982). American Anthropologist 86: 394–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaugele, Elke, and Monica Titton, eds. 2019. Fashion and Postcolonial Critique. Publication Series of the Academy of Fine Arts Vienna. Berlin: Akademie der Bildenden Künste, Wien: Sternberg Press, vol. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Glass, Aaron. 2008. Crests on Cotton: ‘Souvenir’ T-Shirts and the Materiality of Remembrance among the Kwakwaka’wakw of British Columbia. Museum Anthropology 31: 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, Rayna. 1988. The Tribe Called Wannabee: Playing Indian in America and Europe. Folklore 99: 30–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, Denise Nicole. 2013. Stella Blum Grant Report: Nuu-Chah-Nulth First Nations’ Huulthin (Shawls)—Historical and Contemporary Practices. Dress 39: 153–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, Denise Nicole. 2016. Fashion(s) from the Northwest Coast: Nuu-Chah-Nulth Design Iterations. In Ethnic Fashion. Edited by Miguel Angel Gardetti and Subramanian Senthilkannan Muthu. Singapore: Springer, pp. 19–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, Christopher T. 2018. ‘Rather Unusual Stuff’: Nathan Jackson’s Early Advent of a Tlingit Modern. ab-Original 2: 300–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, Christopher T. 2020. Northwest Coast Native Art Beyond Revival, 1962–92. Ph.D. dissertation, City University of New York, New York, NY, USA. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/dissertations-theses/northwest-coast-native-art-beyond-revival-1962/docview/2455909512/se-2 (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Harney, Elizabeth, and Ruth B. Phillips, eds. 2018. Mapping Modernisms: Art, Indigeneity, Colonialism. Objects/Histories: Critical Perspectives on Art. Material Culture, and Representation. Durham: Duke University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Hess Brothers. 1948. Advertisement for Hess Brothers Department Stores. Mauch Chunk: Mauch Chunk Times-News, March 16, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Huhndorf, Shari M. 2001. Going Native: Indians in the American Cultural Imagination. Ithaca: Cornell University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Huyssen, Andreas. 2007. Geographies of Modernism in a Globalizing World. New German Critique 100: 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igloliorte, Heather. 2018. ‘Hooked Forever on Primitive Peoples’: James Houston and the Transformation of ‘Eskimo Handicrafts’ to Inuit Art. In Mapping Modernisms: Art, Indigeneity, Colonialism. Edited by Elizabeth Harney and Ruth B. Phillips. Objects/Histories: Critical Perspectives on Art, Material Culture, and Representation. Durham: Duke University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Inverarity, Robert Bruce. 1950. Art of the Northwest Coast Indians. Berkeley: University of California Press. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, Nathan. 2020. Interview with author. October 25. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, M. Angela. 2020. Fashion and the Phantasmagoria of Modernity: An Introduction to Decolonial Fashion Discourse. Fashion Theory: The Journal of Dress, Body & Culture 24: 815–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, Angelina R., and Nancy J. Parezo. 2010. Tucson’s Squaw Dress Industry. The Journal of Arizona History 51: 299–320. [Google Scholar]
- Joselit, David. 2000. Notes on Surface: Toward a Genealogy of Flatness. Art History 23: 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junker, Patricia A. 2014. Modernism in the Pacific Northwest: The Mythic and the Mystical: Masterworks from the Seattle Art Museum. Seattle: Seattle Art Museum. Seattle: University of Washington Press. [Google Scholar]
- Kerstein, Melinda Webber. 2003. Tiki Style: Pacific Influences on American Dress and Textiles of the 1950s and 1960s. Master’s thesis, Fashion Institute of Technology, New York, NY, USA. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/docview/1685023933/A3AEB3DE427E4694PQ/1 (accessed on 16 January 2020).
- Kiffer, David. 2010. A Steady ‘Boom’ in Tourism Post World War II. SitNews. December 29. Available online: http://www.sitnews.us/Kiffer/Tourism3/122910_tourism_pt3.html (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Kramer, Jennifer. 2012. esu’: The Art and Life of Doug Cranmer. Vancouver: Douglas & McIntyre. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, Jennifer. 2013. ‘Fighting with Property’: The Double-Edged Character of Ownership. In Native Art of the Northwest Coast: A History of Changing Ideas. Edited by Charlotte Townsend-Gault, Jennifer Kramer and Ki-ke-in. Vancouver: University of British Columbia Press, pp. 720–56. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, Karen. 2015. Native Fashion Now: North American Indian Style. Salem: Peabody Essex Museum. [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein’s. 1948. Advertisement for Lichtenstein’s department store. Corpus Christi: The Corpus Christi Caller-Times, March 22, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Lillethun, Abby, Linda Welters, and Joanne B. Eicher. 2012. CSA Forum: (Re)Defining Fashion. Dress 38: 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockett, Michael S. 2021. Saga over Garment Design Copyright Infringement Ends with Ceremonial Fire. Juneau Empire. August 12. Available online: https://www.juneauempire.com/news/saga-over-garment-design-copyright-infringement-ends-in-ceremonial-fire/ (accessed on 19 November 2023).
- Mara, Margaret. 1948. Resort Wear in Celanese Will Reproduce Beauty of Santa Fe. Brooklyn Eagle, August 25, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Marcketti, Sara B., and Jean L. Parsons. 2007. American Fashions for American Women: Early Twentieth Century Efforts to Develop an American Fashion Identity. Dress 34: 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauzé, Marie. 2006. Surrealists in Exile. In Collection Robert Lebel. Paris: Calmels Cohen, pp. 16–29. [Google Scholar]
- Mauzé, Marie. 2008. Totemic Landscapes and Vanishing Cultures through the Eyes of Wolfgang Paalen and Kurt Seligmann. Journal of Surrealism and the Americas 2: 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Mauzé, Marie. 2013. Surrealists and the New York Avant-Garde, 1920–1960. In Native Art of the Northwest Coast: A History of Changing Ideas. Edited by Charlotte Townsend-Gault, Jennifer Kramer and Ki-ke-in. Vancouver: University of British Columbia Press, pp. 404–43. [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe, Jessica RheAnn. 2010. Native Designers of High Fashion: Expressing Identity, Creativity, and Tradition in Contemporary Customary Clothing Design. Ph.D. dissertation, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/docview/577639724/FE3F30FFE87348D8PQ/1 (accessed on 6 April 2019).
- Montiel, Anya. 2005. The Art of George Morrison and Allan Houser: The Development and Impact of Native Modernism. The American Indian Quarterly 29: 478–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, Jhane, Ryan S. Flahive, Antonio R. Chavarria, Tatiana Lomahaftewa-Singer, and Carmen Vendelin. 2016. Lloyd Kiva New: A New Century: The Life and Legacy of Cherokee Artist and Educator Lloyd Kiva New, 1st ed. Santa Fe: Art Guild Press. [Google Scholar]
- National Museum of the American Indian (NMAI), ed. 2006. Essays on Native Modernism: Complexity and Contradiction in American Indian Art. NMAI Editions. Washington, DC: National Museum of the American Indian, Smithsonian Institution. [Google Scholar]
- Navratil, Emily Schuchardt. 2015. Native American Chic: The Marketing of Native Americans in New York between the World Wars. Ph.D. dissertation, City University of New York, New York, NY, USA. Available online: http://search.proquest.com/docview/1658532777/abstract/95EDF51C9F114F02PQ/1 (accessed on 29 April 2019).
- Neel, Lou-ann Ika’wega. 2020. Ellen Neel and Carving on the Coast. In Unsettling Native Art Histories on the Northwest Coast. Seattle: University of Washington Press, pp. 133–49. [Google Scholar]
- New, Lloyd Kiva. 2016. The Sound of Drums: A Memoir of Lloyd Kiva New. Edited by Ryan Flahive. Santa Fe: Sunstone Press. [Google Scholar]
- New York Times. 1950. For the Home: New Fabrics Show Ancient Motifs. New York Times, December 27, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Nuytten, Phil. 1982. The Totem Carvers: Charlie James, Ellen Neel, and Mungo Martin. Vancouver: Panorama Publications. [Google Scholar]
- Ottmann, Shawkay. 2020. Indigenous Dress Theory and Dress in Canadian Residential Schools. Fashion Studies 3: 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parezo, Nancy J. 1999. The Indian Fashion Show. In Unpacking Culture: Art and Commodity in Colonial and Postcolonial Worlds. Edited by Ruth B. Phillips and Christopher B. Steiner. Berkeley: University of California Press, pp. 243–63. [Google Scholar]
- Parezo, Nancy J. 2007. The Indian Fashion Show: Manipulating Representations of Native Attire in Museum Exhibits to Fight Stereotypes in 1942 and 1998. American Indian Culture & Research Journal 31: 5–48. [Google Scholar]
- Parezo, Nancy J. 2013. The Indian Fashion Show: Fighting Cultural Stereotypes with Gender. Journal of Anthropological Research 69: 317–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parezo, Nancy J., and Angelina R. Jones. 2009. What’s in a Name?: The 1940s-1950s ‘Squaw Dress’. American Indian Quarterly 33: 373–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parezo, Nancy J., and Nancy J. Blomberg. 1997. Indian Chic: The Denver Art Museum’s ‘Indian Style Show’. American Indian Art Magazine 23: 44–55. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, Ruth B. 2015. Aesthetic Primitivism Revisited: The Global Diaspora of ‘Primitive Art’ and the Rise of Indigenous Modernisms. Journal of Art Historiography 12: 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Quton. 1916. The Art of the Chilkat Indians. Women’s Wear, June 21. [Google Scholar]
- Rayner, Geoffrey, Richard Chamberlain, and Annamarie Stapleton. 2012. Artists’ Textiles: Artist Designed Textiles 1940–76. Woodbridge: Antique Collectors’ Club. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, Rose Marie. 1947. Advertisement for Rose Marie Reid. Chatelaine, July. 48. [Google Scholar]
- Reid’s Holiday Togs Ltd. 1946. Advertisement for Rose Marie Reid Originals. Chatelaine, June. [Google Scholar]
- Riley, Terence, and Edward Eigen. 1994. Between the Museum and the Marketplace: Selling Good Design. In The Museum of Modern Art at Mid-Century: At Home and Abroad, Studies in Modern Art. New York: Museum of Modern Art, vol. 4, pp. 150–79. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, Solen. 2018. Incorporating Culture: How Indigenous People Are Reshaping the Northwest Coast Art Industry. Vancouver: University of British Columbia Press. [Google Scholar]
- Rushing, W. Jackson. 1992. Marketing the Affinity of the Primitive and the Modern: René d’Harnoncourt and ‘Indian Art of the United States’. In The Early Years of Native American Art History: The Politics of Scholarship and Collecting. Edited by Janet Catherine Berlo. Seattle: University of Washington Press, pp. 191–236. [Google Scholar]
- Rushing, W. Jackson. 1995. Native American Art and the New York Avant-Garde: A History of Cultural Primitivism. American Studies Series; Austin: University of Texas Press. [Google Scholar]
- Schweitzer, Marlis. 2008. American Fashions for American Women: The Rise and Fall of Fashion Nationalism. In Producing Fashion: Commerce, Culture, and Consumers. Edited by Regina Lee Blaszczyk. Hagley Perspectives on Business and Culture. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, pp. 130–49. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, William R. 2008. California Casual: Lifestyle Marketing and Men’s Leisurewear, 1930–1960. In Producing Fashion: Commerce, Culture, and Consumers. Edited by Regina Lee Blaszczyk. Hagley Perspectives on Business and Culture. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, pp. 169–86. [Google Scholar]
- Sealaska Heritage Institute. 2020. Sealaska Heritage Sues Neiman Marcus Alleging Unlawful Use of Term “Ravenstail”, Copyright Infringement. April 20. Available online: https://www.sealaskaheritage.org/node/1211 (accessed on 21 December 2023).
- Sealaska Heritage Institute. 2021. Sealaska Heritage, Rizal Family Settle Lawsuit against Several Defendants. March 3. Available online: https://www.sealaskaheritage.org/node/1367 (accessed on 21 December 2023).
- Shaughnessy, Roxane, and Anna Richard. 2018. The Untold Story of Inuit Printed Fabrics from Kinngait Studios, Kinngait (Cape Dorset), Nunavut, Canada. In Textile Society of America Symposium Proceedings. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Digital Commons. Available online: https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/tsaconf/1106 (accessed on 30 October 2023).
- Smith, Harlan I. 1917. Distinctive Canadian Designs: How Manufacturers May Profit by Introducing Native Designs into Their Products. Industrial Canada 17: 729–33. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, Harlan I. 1923. An Album of Prehistoric Canadian Art. In Bulletin No. 37. Anthropological Series 8; Ottawa: National Museum of Canada. Available online: https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=uc1.31822007179245 (accessed on 9 May 2019).
- Stopp, Marianne. 2012. The Coast Salish Knitters and the Cowichan Sweater: An Event of National Historic Significance. Material Culture Review 76: 9–29. [Google Scholar]
- Tartsinis, Ann Marguerite. 2013. An American Style: Global Sources for New York Textile and Fashion Design, 1915–1928. New York: Bard Graduate Center: Decorative Arts, Design History, Material Culture. [Google Scholar]
- The Arizona Republic “Lady Fare”. 1961. Designers Set Fashion Mood. The Arizona Republic, January 29, F1. [Google Scholar]
- Thiry, Paul. 1983. Oral History Interview by Meredith Clausen. Northwest Oral History Project. Archives of American Art, Smithsonian Institution. Available online: https://www.aaa.si.edu/collections/interviews/oral-history-interview-paul-thiry-11659 (accessed on 30 October 2019).
- Troy, Virginia Gardner. 2019. Textiles as the Face of Modernity: Artistry and Industry in Mid-Century America. Textile History 50: 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, Cory. 2010. Designing, Producing and Enacting Nationalisms: Contemporary Amerindian Fashions in Canada. In The Force of Fashion in Politics and Society: Global Perspectives from Early Modern to Contemporary Times. Edited by Beverly Lemire. Farnham: Ashgate Publishing Ltd., pp. 167–90. [Google Scholar]
- Willmott, Cory. 2014. Radical Entrepreneurs: First Nations Designers’ Approaches to Community Economic Development. Anthropology of Work Review 35: 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Women’s Wear Daily. 1947. Cool Alaskan Colors, Prints Shown by Celanese for Resorts. Women’s Wear Daily, August 20, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Woolman Chase, Edna, ed. 1941. American Fashion on Its Own. Vogue 97: 78–83, 160. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, Robin K. 2014. The Mask That Inspired the Seahawks Logo. Burke Museum (Blog). January 28. Available online: https://www.burkemuseum.org/news/mask-inspired-seahawks-logo (accessed on 30 October 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).