The impact of Engineering, Procurement and Construction (EPC) Phases on Project Performance: A Case of Large-scale Residential Construction Project
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Management Practices in Construction Project Triangle Success
2.2. Factors Affecting Construction Project Triangle Success
2.3. Factors Affecting EPC Project Success
- Although several studies have highlighted the causes and effects of poor performance in the construction industry, only a limited number of them have focused on Iran’s construction industry, especially for residential buildings.
- Identification, prioritization, and interaction of factors causing poor construction performance with regard to engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) in constructing residential buildings in Iran has been far from the researcher’s attention.
- There is a significant need for up-to-date data.
3. Theoretical Framework
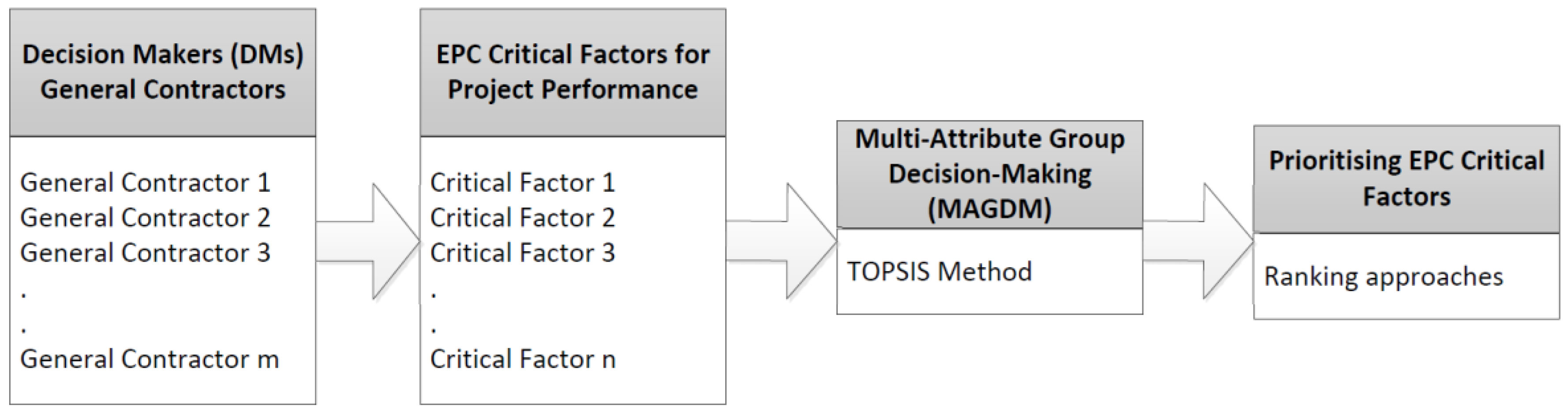
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Step 1: Identify Factors
4.2. Step 2: Collect Data and Evaluate EPC Contractors
4.3. Step 3: Develop a Group Decision-Making Model and Data Analysis
5. Results
6. Discussions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahmood, A.; Asghar, F.; Naoreen, B. “Success factors on research projects at university” an exploratory study. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 116, 2779–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, M.L.; Carvalho, M.M. Key factors of sustainability in project management context: A survey exploring the project managers’ perspective. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2017, 35, 1084–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joslin, R.; Müller, R. The relationship between project governance and project success. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2016, 34, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, E.W.; Gray, C.F. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge: Pmbok (®) Guide; Project Management Institute: Newtown Square, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kenny, C. Construction, Corruption and Developing Countries. Policy; Research Working Paper, No. WPS 4271; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, J.; Oliveira, R.; Abreu, M.I.J.P.E. The sustainability of the construction industry in sub-saharan africa: Some new evidence from recent data. Procedia Eng. 2017, 172, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavadskas, E.K.; Vainiūnas, P.; Turskis, Z.; Tamošaitienė, J. Multiple criteria decision support system for assessment of projects managers in construction. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Decis. Mak. 2012, 11, 501–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olanrewaju, A.L.; Abdul-Aziz, A.-R. Building maintenance processes, principles, procedures, practices and strategies; Springer: Singapore, 2015; Building Maintenance Processes and Practices; pp. 79–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussin, J.M.; Rahman, I.A.; Memon, A.H. The way forward in sustainable construction: Issues and challenges. Int. J. Adv. Appl. Sci. 2013, 2, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavadskas, E.K.; Vilutienė, T.; Turskis, Z.; Šaparauskas, J. Multi-criteria analysis of projects’ performance in construction. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2014, 14, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyestani, B.; Juanzon, J.B.P. Developing an Appropriate Performance Measurement Framework for Total Quality Management in Construction, and Other Industries; University Library of Munich: Munich, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Oakland, J.; Marosszeky, M. Total Construction Management: Lean Quality in Construction Project Delivery; Routledge: Abington, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Babalola, O.; Ibem, E.O.; Ezema, I.C. Implementation of lean practices in the construction industry: A systematic review. Build. Environ. 2018, 148, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peljhan, D.; Marc, M. Total quality management and performance management systems: Team players or lonely riders? Total Qual. Manag. Bus. Excell. 2018, 29, 920–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinade, O.O.; Oyedele, L.O.; Ajayi, S.O.; Bilal, M.; Alaka, H.A.; Owolabi, H.A.; Bello, S.A.; Jaiyeoba, B.E.; Kadiri, K.O. Design for deconstruction (dfd): Critical success factors for diverting end-of-life waste from landfills. Waste Manag. 2017, 60, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudienė, N.; Banaitis, A.; Podvezko, V.; Banaitienė, N. Identification and evaluation of the critical success factors for construction projects in lithuania: Ahp approach. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2014, 20, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Shen, G.Q.; Sun, M.; Kelly, J. Identification of key performance indicators for measuring the performance of value management studies in construction. J. Construct. Eng. Manag. 2011, 137, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghsoodi, A.I.; Khalilzadeh, M. Identification and evaluation of construction projects’ critical success factors employing fuzzy-topsis approach. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2018, 22, 1593–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, K.; Jha, K. An empirical study on performance measurement factors for construction organizations. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2018, 22, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, P.E.D.; Teo, P.; Morrison, J.; Grove, M. Quality and safety in construction: Creating a no-harm environment. J. Construct. Eng. Manag. 2016, 142, 05016006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramlee, N.; Tammy, N.J.; Raja Mohd Noor, R.N.H.; Ainun Musir, A.; Abdul Karim, N.; Chan, H.B.; Mohd Nasir, S.R. Critical success factors for construction project. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Penang, Malaysia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sibiya, M.; Aigbavboa, C.; Thwala, W. Construction projects’ key performance indicators: A case of the South African construction industry. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Construction and Real Estate Management, Lulea, Sweden, 11–12 August 2015; pp. 954–960. [Google Scholar]
- Haslinda, A.N.; Xian, T.W.; Norfarahayu, K.; Hanafi, R.M.; Fikri, H.M. Investigation on the Factors Influencing Construction Time and Cost Overrun for High-Rise Building Projects in Penang. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 995, 012043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tommelein, I.D. Journey toward lean construction: Pursuing a paradigm shift in the aec industry. J. Construct. Eng. Manag. 2015, 141, 04015005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, B.; Kubler, S.; Främling, K.; Koskela, L. Opportunities for enhanced lean construction management using internet of things standards. Autom. Construct. 2016, 61, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabehpour, N. An Investigation of the Implementation of Lean Philosophy within a Specialty Trade. Master’s Thesis, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chiarini, A.; Baccarani, C.; Mascherpa, V. Lean production, Toyota production system and kaizen philosophy: A conceptual analysis from the perspective of zen buddhism. TQM J. 2018, 30, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, L.H.; Ahmed, S.M. Modern Construction: Lean Project Delivery and Integrated Practices; Crc Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Goetsch, D.L.; Davis, S.B. Quality Management for Organizational Excellence; Pearson: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hanseth, O.; Lyytinen, K. Design theory for dynamic complexity in information infrastructures: The case of building internet. In Enacting Research Methods in Information Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 104–142. [Google Scholar]
- Bonham, D.R.; Goodrum, P.M.; Littlejohn, R.; Albattah, M.A. Application of data mining techniques to quantify the relative influence of design and installation characteristics on labor productivity. J. Construct. Eng. Manag. 2017, 143, 04017052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, C.; Cosenz, F.; Marinković, M. Designing dynamic performance management systems to foster sme competitiveness according to a sustainable development perspective: Empirical evidences from a case-study. Int. J. Bus. Perform. Manag. 2015, 16, 84–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunde, A.; Joshua, O.; Amusan, L.M.; Akuete, E. Project management a panacea to improving the performance of construction project. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2017, 8, 1234–1242. [Google Scholar]
- Sears, S.K.; Sears, G.A.; Clough, R.H.; Rounds, J.L.; Segner, R.O. Construction Project Management; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Albliwi, S.A.; Antony, J.; Arshed, N.; Ghadge, A. Implementation of lean six sigma in Saudi Arabian organisations: Findings from a survey. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2017, 34, 508–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, F.A.; Pinnington, A.H. Exploring the value of project management: Linking project management performance and project success. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2014, 32, 202–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, P.; González, V.; Molenaar, K.; Orozco, F. Analysis of causes of delay and time performance in construction projects. J. Construct. Eng. Manag. 2013, 140, 04013027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Zaini, A.; Adnan, H.; Che Haron, R. Contractors’ Approaches to Risk Management at the Construction Phase in Malaysia. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Construction Project Management (ICCPM), Chengdu, China, 1 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, J.-S.; Irawan, N.; Pham, A.-D. Project management knowledge of construction professionals: Cross-country study of effects on project success. J. Construct. Eng. Manag. 2013, 139, 04013015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkesen, S.; Ozorhon, B. Impact of integration management on construction project management performance. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2017, 35, 1639–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X. The effect of relationship management on project performance in construction. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2012, 30, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngacho, C.; Das, D. A performance evaluation framework of development projects: An empirical study of constituency development fund (cdf) construction projects in Kenya. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2014, 32, 492–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, T.Y.; Fung, I.W.; Tung, K.C. Construction delays in Hong Kong civil engineering projects. J. Construct. Eng. Manag. 2006, 132, 636–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Ma, H.; Lin, H.; Zeng, R.; Tam, V.W. Social responsibility of major infrastructure projects in china. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2015, 33, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K. A method to measure success dimensions relating to individual stakeholder groups. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2016, 34, 480–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppong, G.D.; Chan, A.P.; Dansoh, A. A review of stakeholder management performance attributes in construction projects. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2017, 35, 1037–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunlana, S.O. Beyond the ‘iron triangle’: Stakeholder perception of key performance indicators (kpis) for large-scale public sector development projects. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2010, 28, 228–236. [Google Scholar]
- Arditi, D.; Nayak, S.; Damci, A. Effect of organizational culture on delay in construction. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2017, 35, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-M. An exploration into cost-influencing factors on construction projects. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2014, 32, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawale, Y.A.; Sun, M. Cost and time control of construction projects: Inhibiting factors and mitigating measures in practice. Construct. Manag. Econ. 2010, 28, 509–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, S.A. Construction Project Scheduling and Control; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kerzner, H.; Kerzner, H.R. Project Management: A Systems Approach to Planning, Scheduling, and Controlling; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tonchia, S. Industrial Project Management; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; Available online: https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007%2F978-3-662-56328-1#authorsandaffiliationsbook (accessed on 30 December 2018).
- Nicholas, J.M.; Steyn, H. Project Management for Engineering, Business and Technology; Routledge: Abington, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zareei, S. Project scheduling for constructing biogas plant using critical path method. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 756–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvik, L.; Larsson, J. The Impact of Material Delivery-Deviations on Costs and Performance in Construction Projects. Master’s Thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Göteborg, Sweden, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jollands, S.; Akroyd, C.; Sawabe, N. Core values as a management control in the construction of “sustainable development”. Qual. Res. Account. Manag. 2015, 12, 127–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Lin, P.; Qiang, M.; Fan, Q. A labor consumption measurement system based on real-time tracking technology for dam construction site. Autom. Construct. 2015, 52, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamil, Y.; Rahman, I.A. Identification of causes and effects of poor communication in construction industry: A theoretical review. Emerg. Sci. J. 2018, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, T.; Sruthi, P.; Kavitha, M. Causes of cost overrun in construction. IOSR J. Eng. 2014, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enshassi, A.; Arain, F.; Al-Raee, S. Causes of variation orders in construction projects in the gaza strip. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2010, 16, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahnejad, M.H. Delay causes in iran gas pipeline projects. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2013, 31, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazaz, A.; Ulubeyli, S.; Tuncbilekli, N.A. Causes of delays in construction projects in turkey. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2012, 18, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunduz, M.; Nielsen, Y.; Ozdemir, M. Fuzzy assessment model to estimate the probability of delay in turkish construction projects. J. Manag. Eng. 2013, 31, 04014055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gündüz, M.; Nielsen, Y.; Özdemir, M. Quantification of delay factors using the relative importance index method for construction projects in turkey. J. Manag. Eng. 2012, 29, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane, P.J.; Caletka, A.F. Delay Analysis in Construction Contracts; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Naoum, S.G.; Alyousif, A.-R.T.; Atkinson, A.R. Impact of national culture on the management practices of construction projects in the united arab emirates. J. Manag. Eng. 2013, 31, 04014057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, P.X.; Zhang, G. Managing risks in construction projects: Life cycle and stakeholder perspectives. Int. J. Construct. Manag. 2009, 9, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, R.F.; Abdel-Hakam, A.A. Exploring delay causes of road construction projects in egypt. Alex. Eng. J. 2016, 55, 1515–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarkas, A.M.; Haupt, T.C. Major construction risk factors considered by general contractors in qatar. J. Eng. Des. Technol. 2015, 13, 165–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshodi Olalekan, S.; Rimaka, I. A comparative study on causes and effects of delay in nigerian and iranian construction projects. Asian J. Bus. Manag. Sci. 2013, 3, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Minaie, H. Identifying Success Factor in Mass Buildings Construction; Tehran University: Tehran, Iran, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shokouhinia, M. Analysis of Success Factor in Aria-Petro-Gas Company; Tehran University: Tehran, Iran, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Piran, M. Identifying Success Factor in Oil and Gas Project; Tehran University: Tehran, Iran, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Abolhasani, A. Assessment of Success Factor in Construction Project; Tehran University: Tehran, Iran, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dalirpour, A. Analysis of Success Factor on the Project-Based Organization; Tehran University: Tehran, Iran, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Doulabi, R.Z.; Asnaashari, E. Identifying success factors of healthcare facility construction projects in Iran. Proc. Eng. 2016, 164, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Hadikusumo, B. Impacts of human resource development on engineering, procurement, and construction project success. Built Environ. Proj. Asset Manag. 2017, 7, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, M.; Kermanshachi, S.; Safapour, E. Engineering, procurement and construction cost and schedule performance leading indicators: State-of-the-art review. In Proceedings of the Construction Research Congress, ASCE, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–4 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, R.; Wang, P.; Liang, X. The critical factors in managing relationships in international engineering, procurement, and construction (iepc) projects of chinese organizations. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2017, 35, 1225–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahantigh, F.F.; Malmir, B.; Avilaq, B.A. Engineering, S. Economic risk assessment of epc projects using fuzzy topsis approach. Int. J. Ind. Syst. Eng. 2017, 27, 161–179. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, W.; Hong, H.-U.; Han, S.H.; Baek, S.W. Optimal supply vendor selection model for lng plant projects using fuzzy-topsis theory. J. Manag. Eng. 2016, 33, 04016035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, M.; Toutounchian, S.; Dana, T.; Abedi, Z.; Toutounchian, S. Environmental parametric cost model in oil and gas epc contracts. Sustainability 2018, 10, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safa, M.; Shahi, A.; Haas, C.T.; Hipel, K.W. Supplier selection process in an integrated construction materials management model. Autom. Construct. 2014, 48, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jato-Espino, D.; Castillo-Lopez, E.; Rodriguez-Hernandez, J.; Canteras-Jordana, J.C. A review of application of multi-criteria decision making methods in construction. Autom. Construct. 2014, 45, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavadskas, E.K.; Turskis, Z.; Kildienė, S. State of art surveys of overviews on mcdm/madm methods. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2014, 20, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-T. Extensions of the TOPSIS for group decision-making under fuzzy environment. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2000, 114, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pournader, M.; Tabassi, A.A.; Baloh, P. A three-step design science approach to develop a novel human resource-planning framework in projects: The cases of construction projects in USA, Europe, and Iran. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2015, 33, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahdani, B.; Mousavi, S.M.; Mousakhani, M.; Hashemi, H. Time prediction using a neuro-fuzzy model for projects in the construction industry. J. Optim. Ind. Eng. 2016, 9, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Banihashemi, S.; Hosseini, M.R.; Golizadeh, H.; Sankaran, S. Critical success factors (csfs) for integration of sustainability into construction project management practices in developing countries. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2017, 35, 1103–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, B.; Sharifi, H.; Chaghouee, Y. Delay causes analysis in complex construction projects: A semantic network analysis approach. Prod. Plan. Control 2018, 29, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoddousi, P.; Hosseini, M.R. A survey of the factors affecting the productivity of construction projects in Iran. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2012, 18, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, M.M.; Patah, L.A.; de Souza Bido, D. Project management and its effects on project success: Cross-country and cross-industry comparisons. Int. J. Construct. Manag. 2015, 33, 1509–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha’ar, K.; Assaf, S.; Bambang, T.; Babsail, M.; Fattah, A.A.E. Design–construction interface problems in large building construction projects. Int. J. Construct. Manag. 2017, 17, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, V.; Yakhchali, S.H.; Khanzadi, M.; Mehrabanfar, E.; Šaparauskas, J. Proposing a neural network model to predict time and cost claims in construction projects. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2016, 22, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlNasseri, H.; Aulin, R. Assessing understanding of planning and scheduling theory and practice on construction projects. Eng. Manag. J. 2015, 27, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Factors | |
|---|---|
| 1. Manageable | 1.1 Flows (Resources and information inadequacy) 1.2 Conversion (Poor planning, poor design, improper implementation and execution, insufficient quality) 1.3 Management (Ineffective control, poor allocation, poor dispensation) |
| 2. Non-Manageable | 2.1 Failure in external methods 2.2 Environmental issues |
| Project Phase | Indicator | EPC Project Performance Attributes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engineering (X1) | X11 | 1. Poor design | [33,38,45,46] |
| X12 | 2. Poor project planning | ||
| X13 | 3. Poor estimation | ||
| X14 | 4. Design incompletion | ||
| Procurement (X2) | X21 | 5. Insufficient stakeholder engagement | [56,57,58,62] |
| X22 | 6. Dispute | ||
| X23 | 7. Reputation loss | ||
| X24 | 8. Long-lead item delivery | ||
| Construction (X3) | X31 | 9. Poor site supervision | [60,61,63,64,66,67,69] |
| X32 | 10. Poor project control | ||
| X33 | 11. Changes in project execution | ||
| X34 | 12. Late delivery of onsite construction materials (late or on time) | ||
| X35 | 13. Poor quality of construction materials | ||
| X36 | 14. Redo of deficient tasks | ||
| X37 | 15. Inadequate or inefficient equipment or machinery | ||
| X38 | 16. Sub-contractor’s poor conditions | ||
| X39 | 17. Skilled workforce | ||
| X40 | 18. Changes in workforce | ||
| X41 | 19. Accidents or incidents | ||
| X42 | 20. Excessive bureaucracy | ||
| X43 | 21. Inclement weather |
| Indicator | ID | EPC Performance Related Indicators | NC | ND | NCD | RANK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X11 | FR1 | Poor design | 0.82 | 0.75 | 0.79 | 3 |
| X12 | FR2 | Poor project planning | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 1 |
| X13 | FR3 | Poor estimation | 0.41 | 0.32 | 0.37 | 20 |
| X14 | FR4 | Design incompletion | 0.54 | 0.42 | 0.48 | 14 |
| X21 | FR5 | Insufficient stakeholder engagement | 0.76 | 0.54 | 0.65 | 6 |
| X22 | FR6 | Dispute | 0.5 | 0.33 | 0.42 | 15 |
| X23 | FR7 | Reputation loss | 0.31 | 0.44 | 0.38 | 18 |
| X24 | FR8 | Long-lead item delivery | 0.6 | 0.15 | 0.38 | 18 |
| X31 | FR9 | Poor site supervision | 0.34 | 0.75 | 0.55 | 11 |
| X32 | FR10 | Poor project control | 0.89 | 0.78 | 0.84 | 2 |
| X33 | FR11 | Changes in project execution | 0.37 | 0.45 | 0.41 | 16 |
| X34 | FR12 | Late delivery of onsite construction materials | 0.5 | 0.55 | 0.53 | 12 |
| X35 | FR13 | Poor quality of construction materials | 0.75 | 0.82 | 0.79 | 3 |
| X36 | FR14 | Redo of deficient tasks | 0.46 | 0.52 | 0.49 | 13 |
| X37 | FR15 | Inadequate or inefficient equipment or machinery | 0.35 | 0.45 | 0.4 | 17 |
| X38 | FR16 | Sub-contractor’s poor conditions | 0.46 | 0.66 | 0.56 | 10 |
| X39 | FR17 | Skilled workforce | 0.55 | 0.58 | 0.57 | 9 |
| X40 | FR18 | Changes in workforce | 0.79 | 0.35 | 0.57 | 8 |
| X41 | FR19 | Accidents or incidents | 0.66 | 0.89 | 0.78 | 5 |
| X42 | FR20 | Excessive bureaucracy | 0.55 | 0.69 | 0.62 | 7 |
| X43 | FR21 | Inclement weather | 0.48 | 0.24 | 0.36 | 21 |
| EPC Phase | NC | ND | NCD | RANK |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Engineering | 0.670 | 0.603 | 0.636 | 1 |
| Procurement | 0.655 | 0.550 | 0.454 | 3 |
| Construction | 0.553 | 0.403 | 0.572 | 2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kabirifar, K.; Mojtahedi, M. The impact of Engineering, Procurement and Construction (EPC) Phases on Project Performance: A Case of Large-scale Residential Construction Project. Buildings 2019, 9, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings9010015
Kabirifar K, Mojtahedi M. The impact of Engineering, Procurement and Construction (EPC) Phases on Project Performance: A Case of Large-scale Residential Construction Project. Buildings. 2019; 9(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings9010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleKabirifar, Kamyar, and Mohammad Mojtahedi. 2019. "The impact of Engineering, Procurement and Construction (EPC) Phases on Project Performance: A Case of Large-scale Residential Construction Project" Buildings 9, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings9010015
APA StyleKabirifar, K., & Mojtahedi, M. (2019). The impact of Engineering, Procurement and Construction (EPC) Phases on Project Performance: A Case of Large-scale Residential Construction Project. Buildings, 9(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings9010015





