New Relationships Between Particle Meso-Mechanical Parameters and CBR of Graded Crushed Stone Pavement: Influence Factors Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
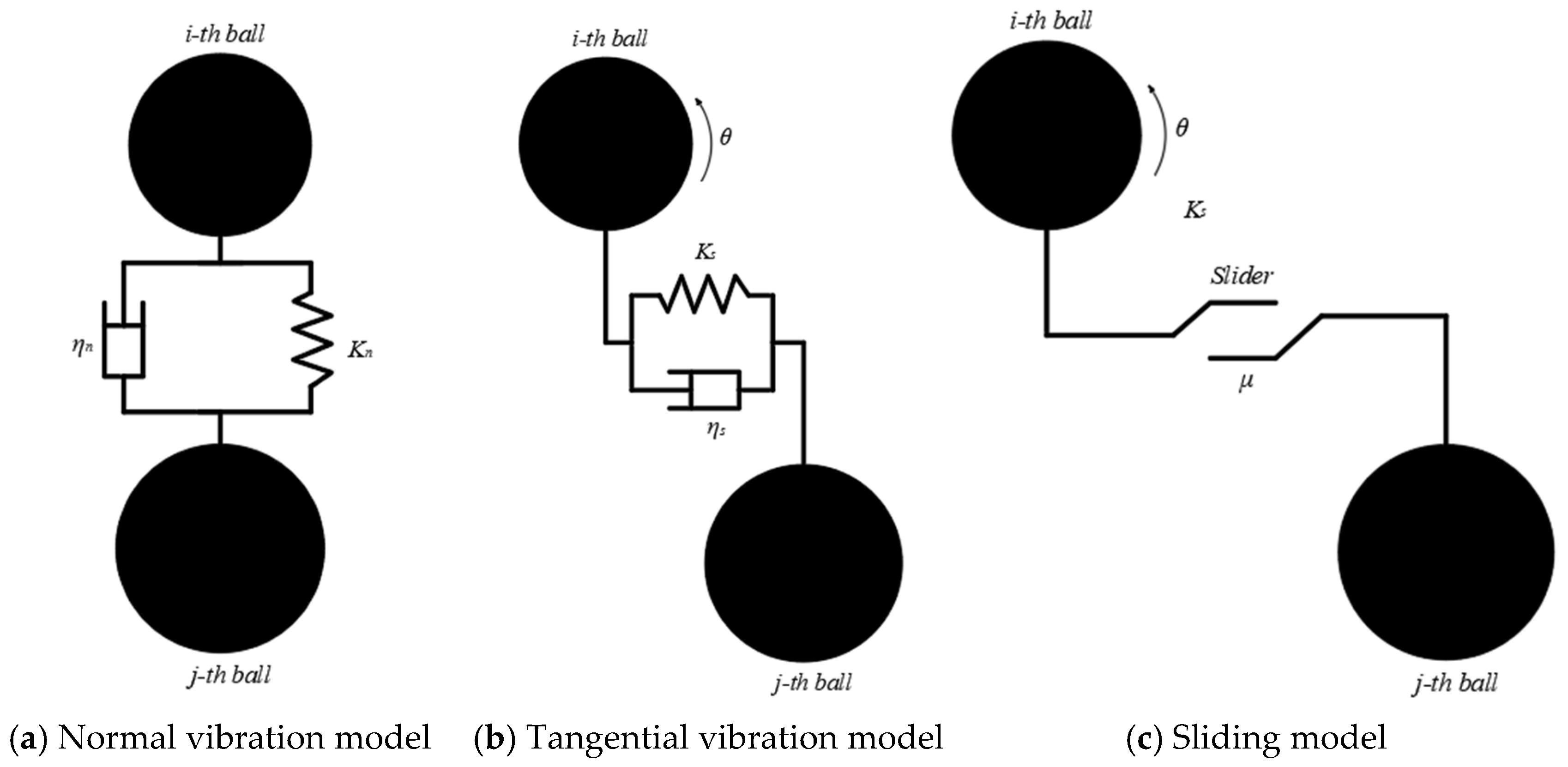
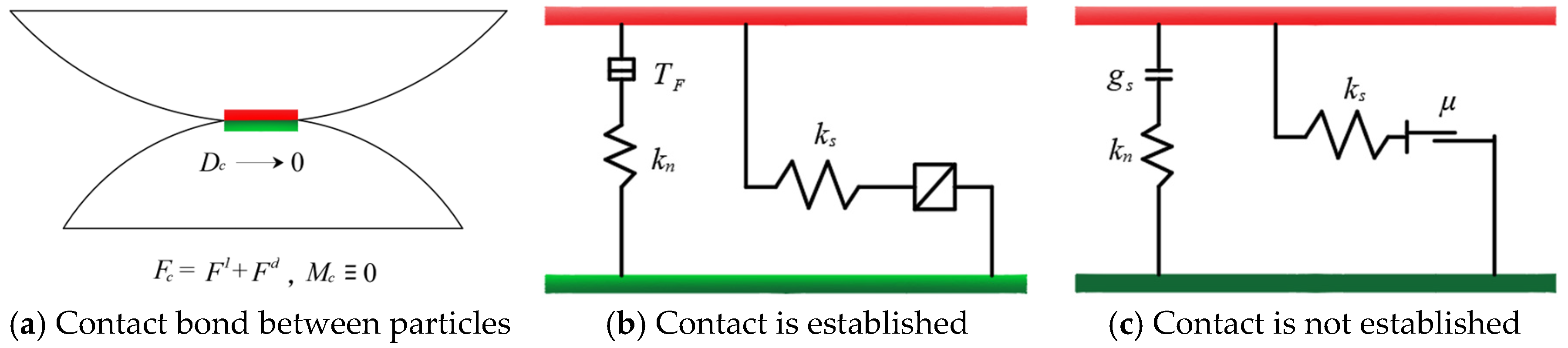
2.1. Theoretical Model
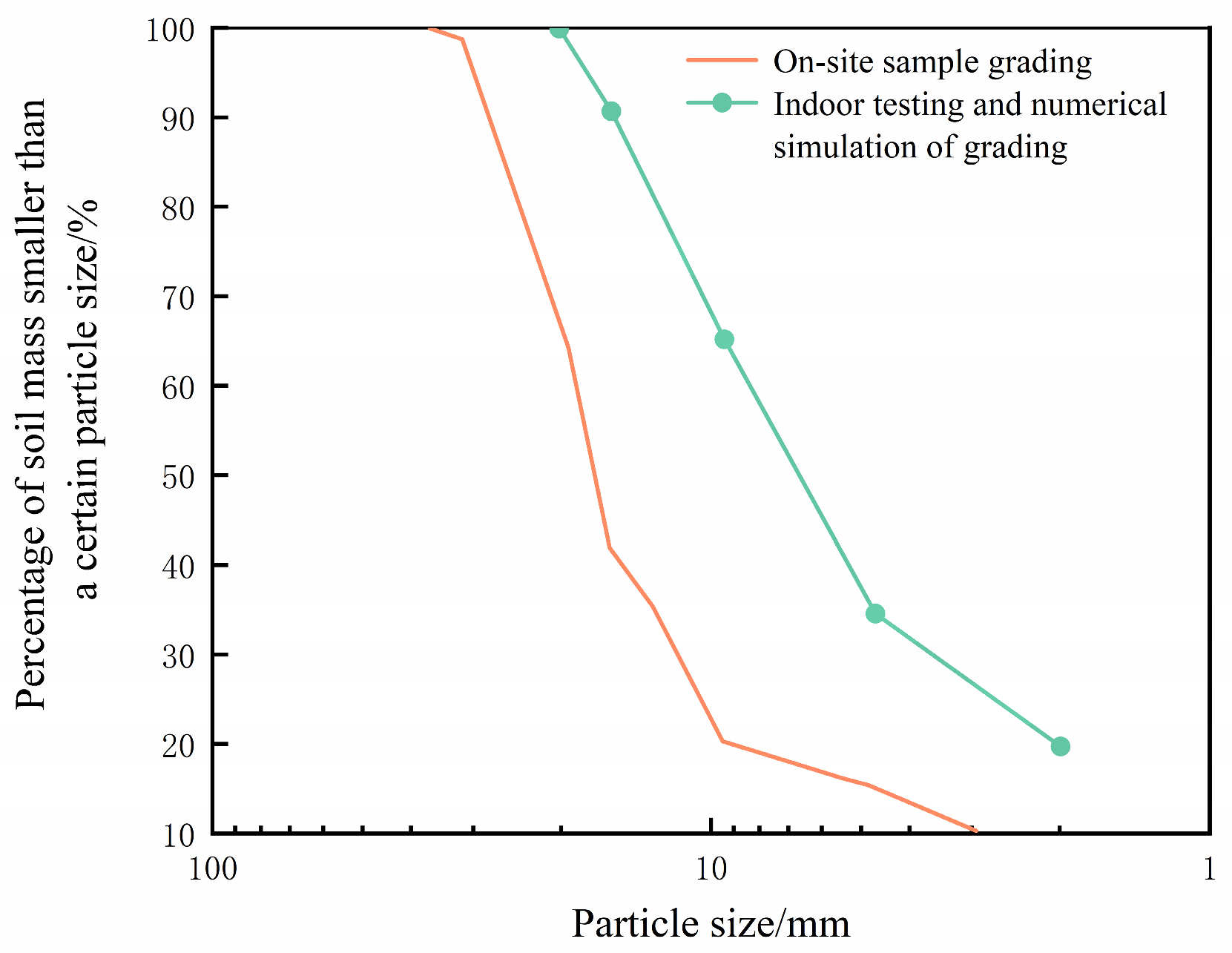
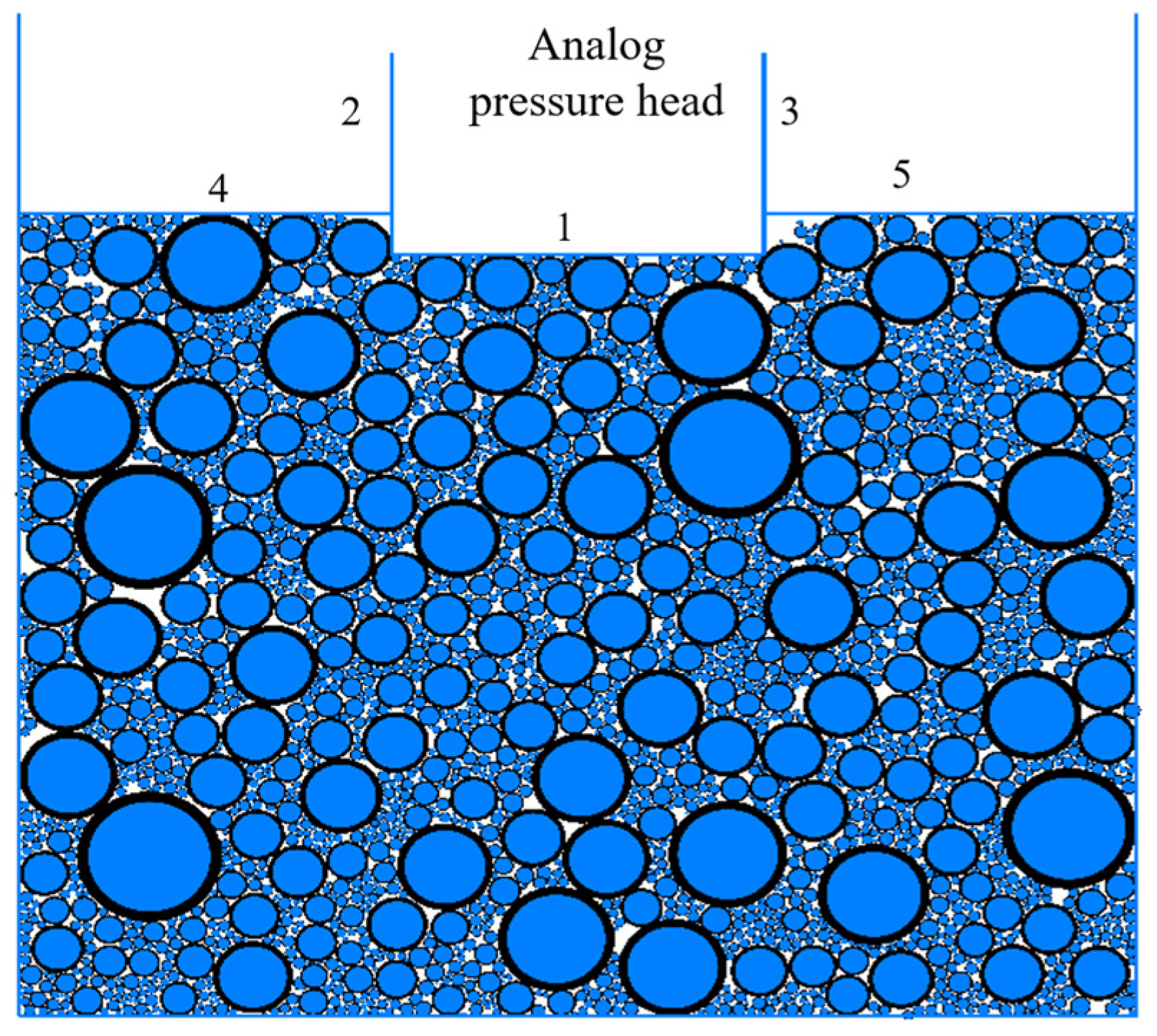
2.2. Model Initialization
2.3. CBR Model Design
2.3.1. Calibration of Meso-Mechanical Parameters
2.3.2. CBR Model Construction
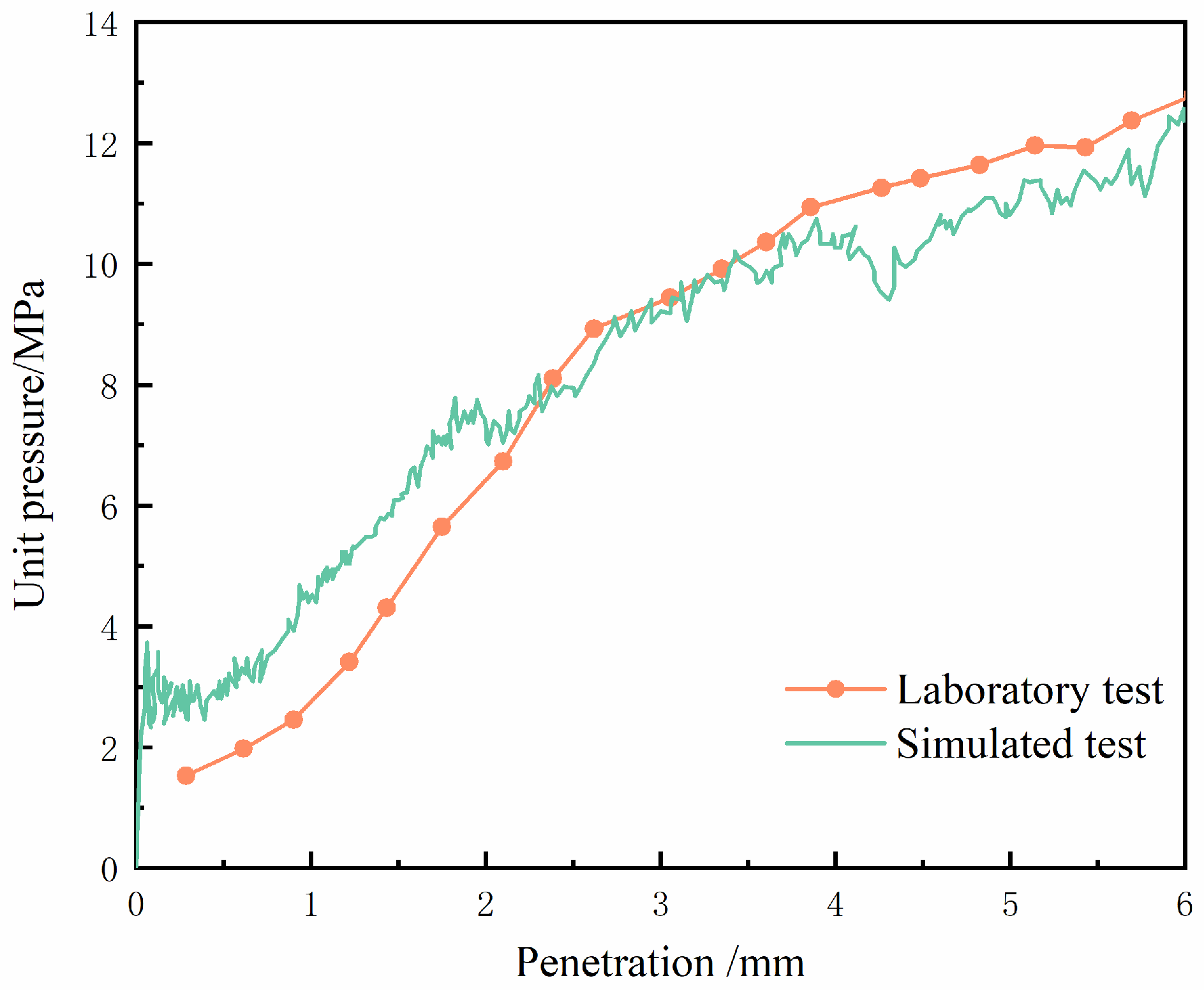
2.4. Model Validation
3. Analysis of Mesoscopic Mechanics Mechanism
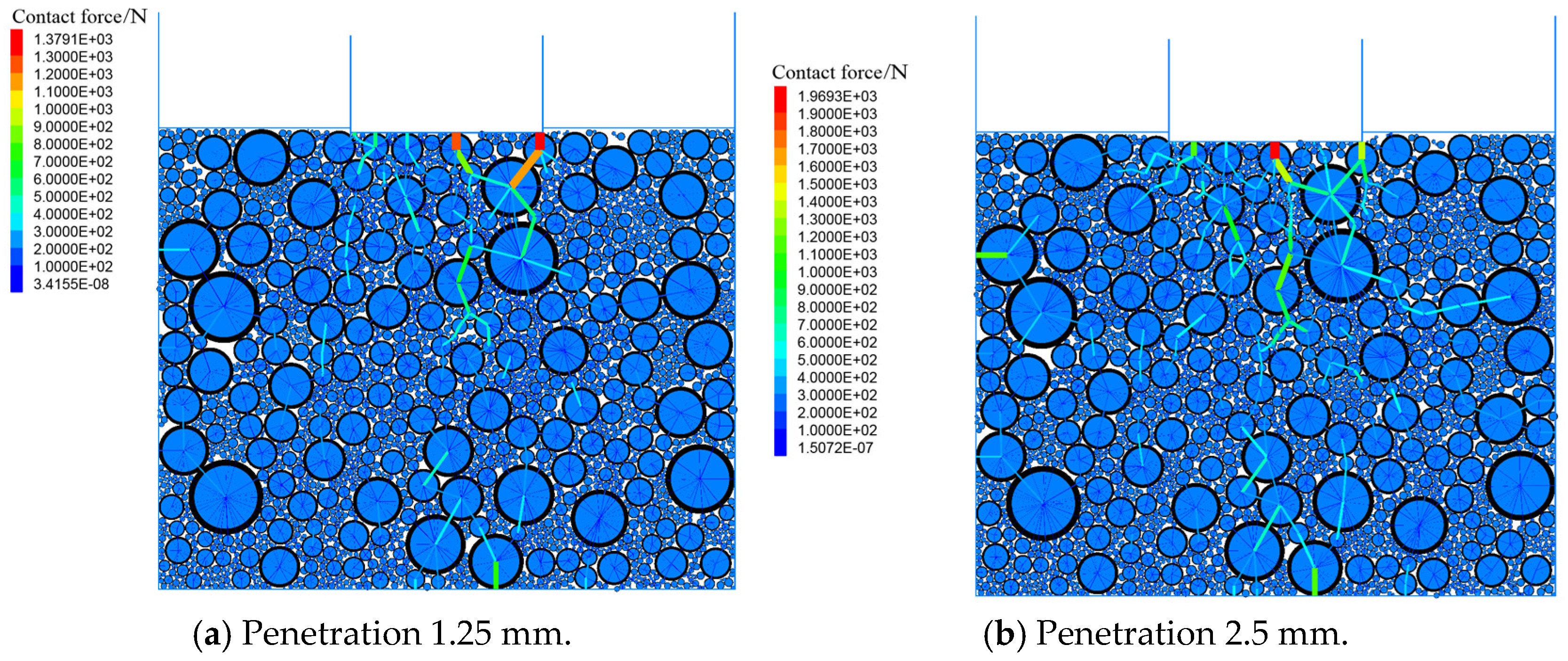
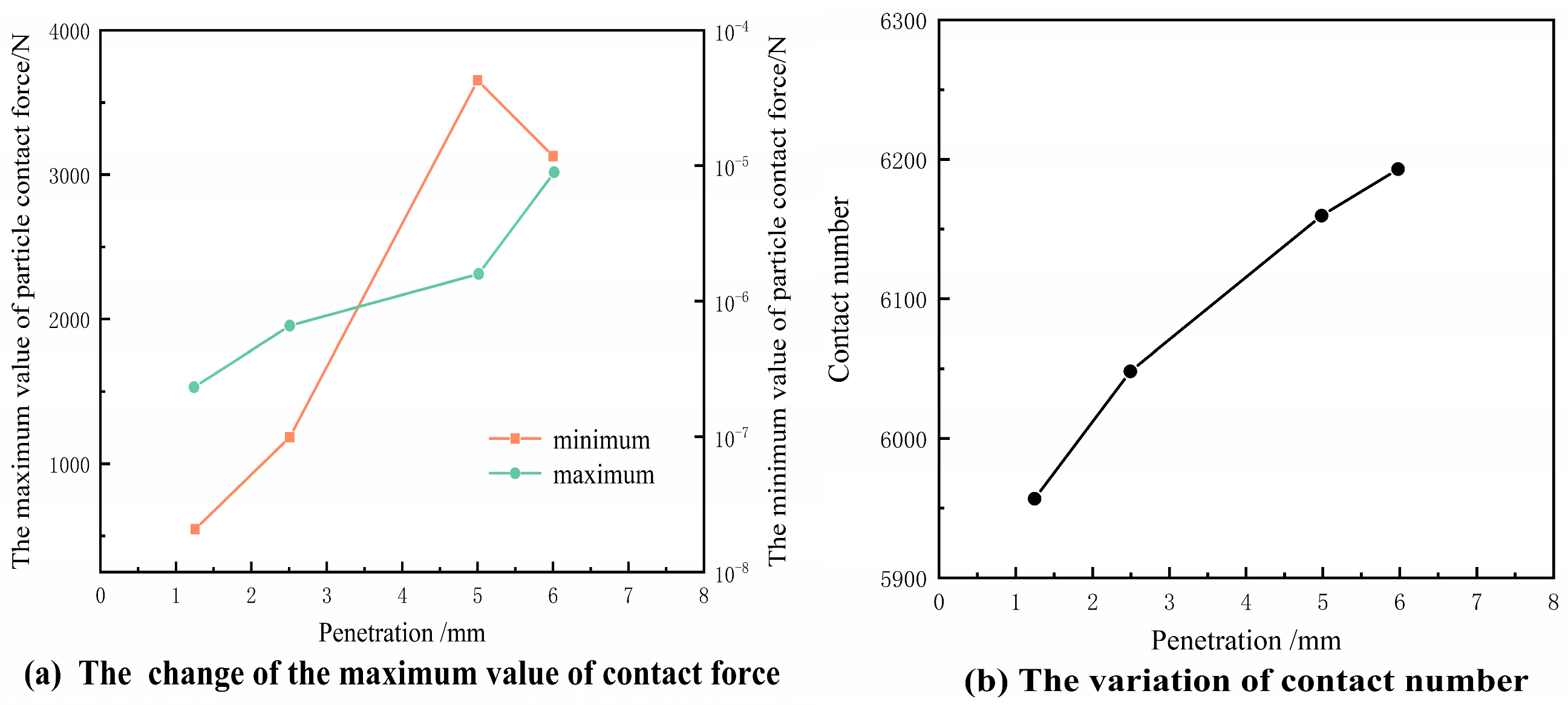
3.1. Contact Force Chain Distribution
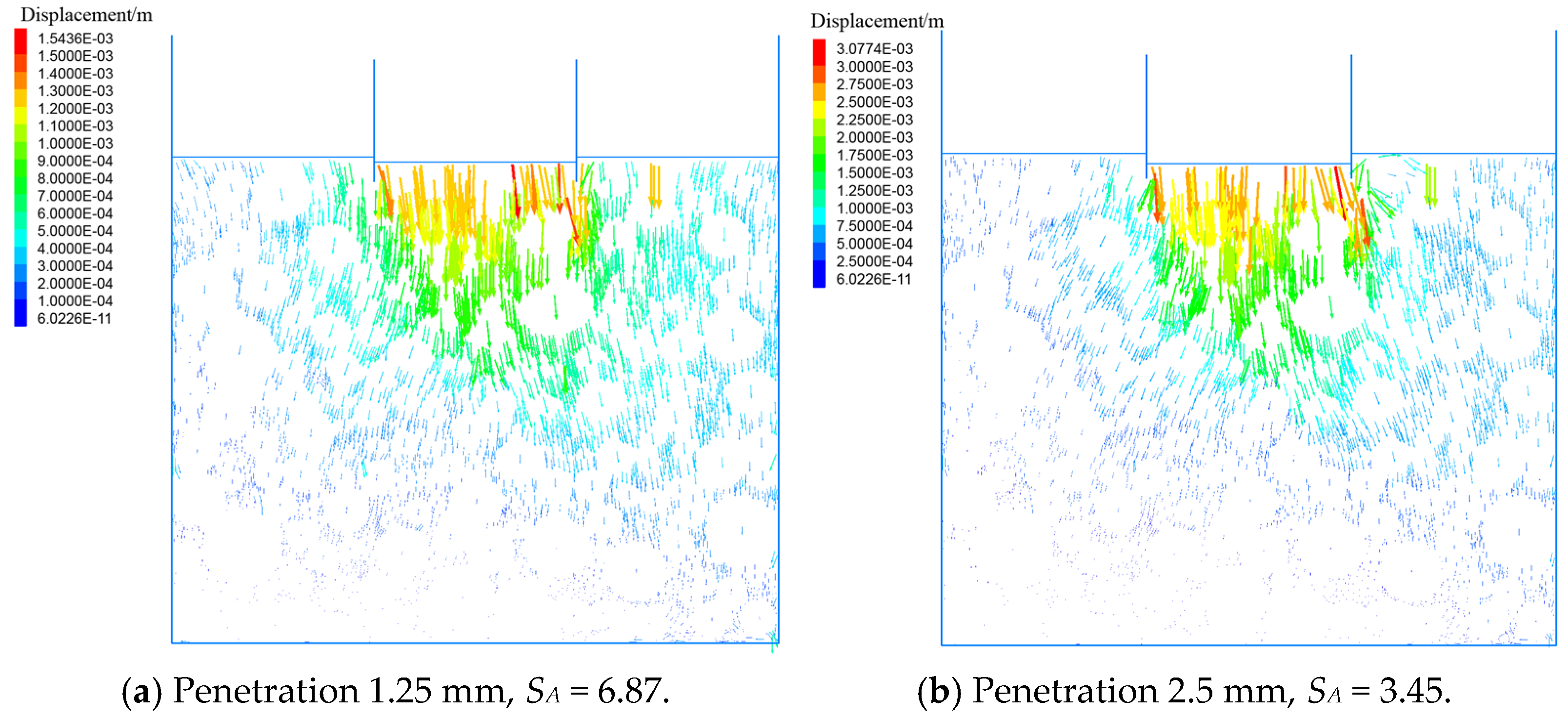
3.2. Particle Displacement Vector Field Distribution
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Correlation Between Meso-Mechanical Parameters and CBR Values
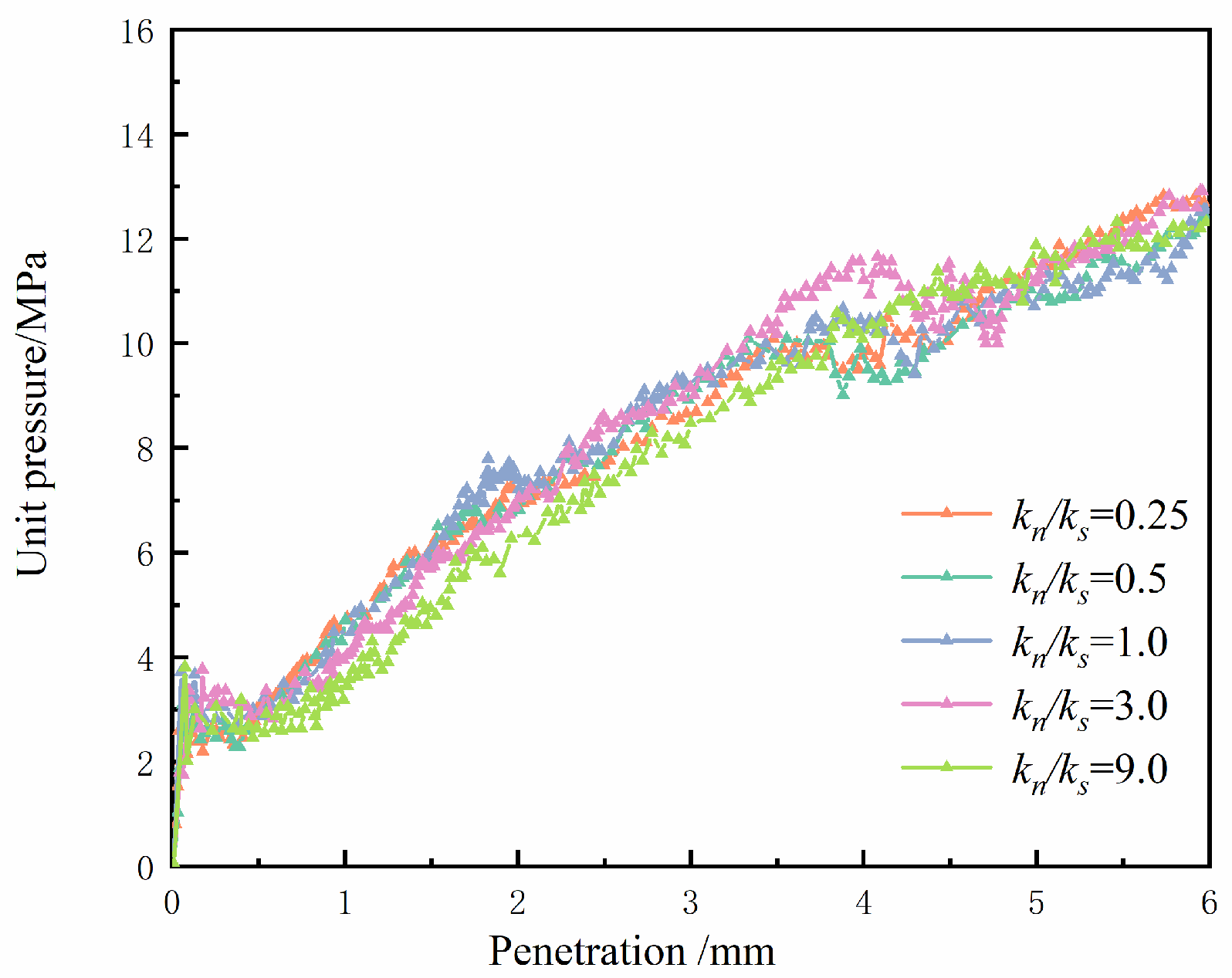
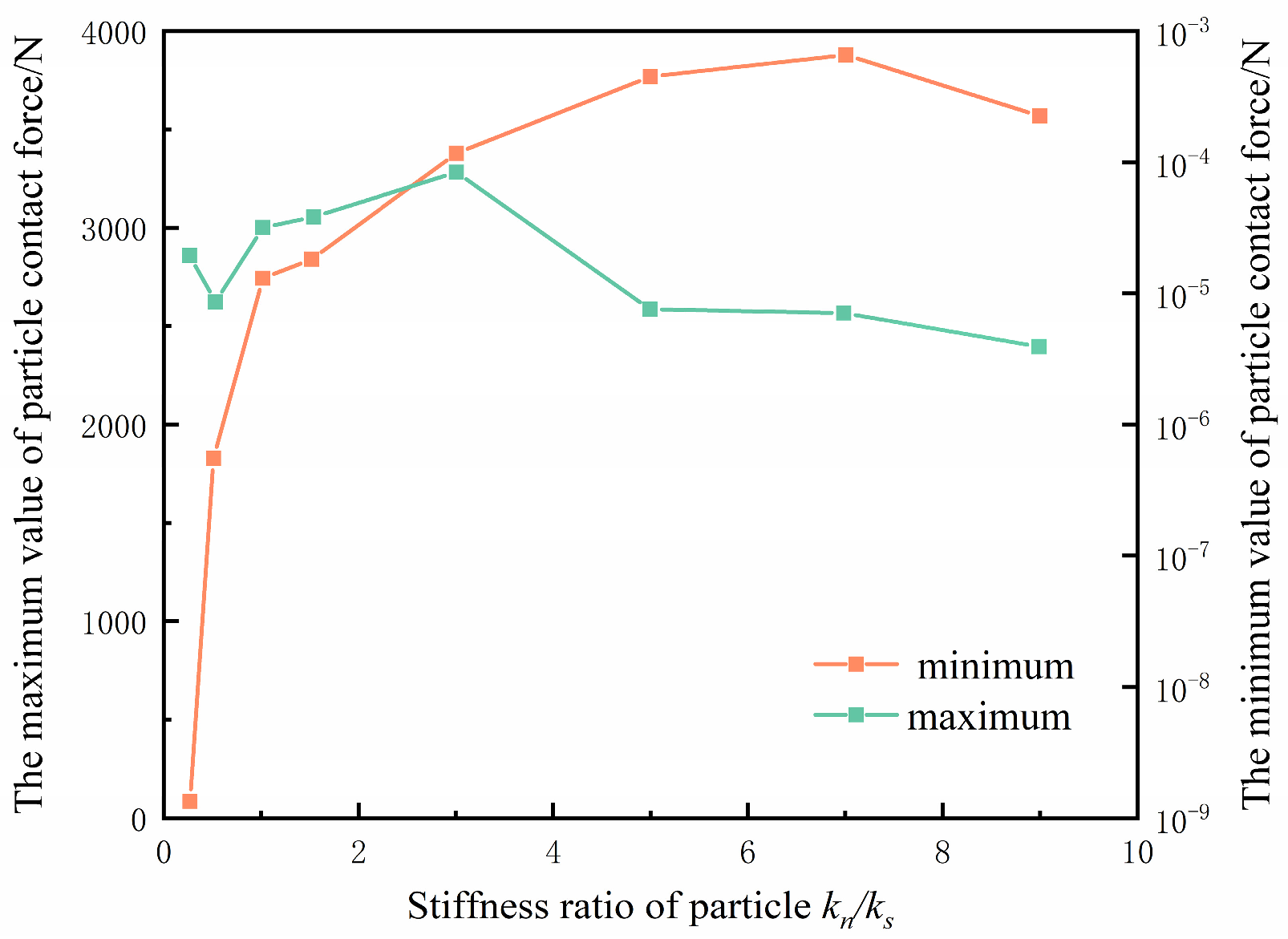
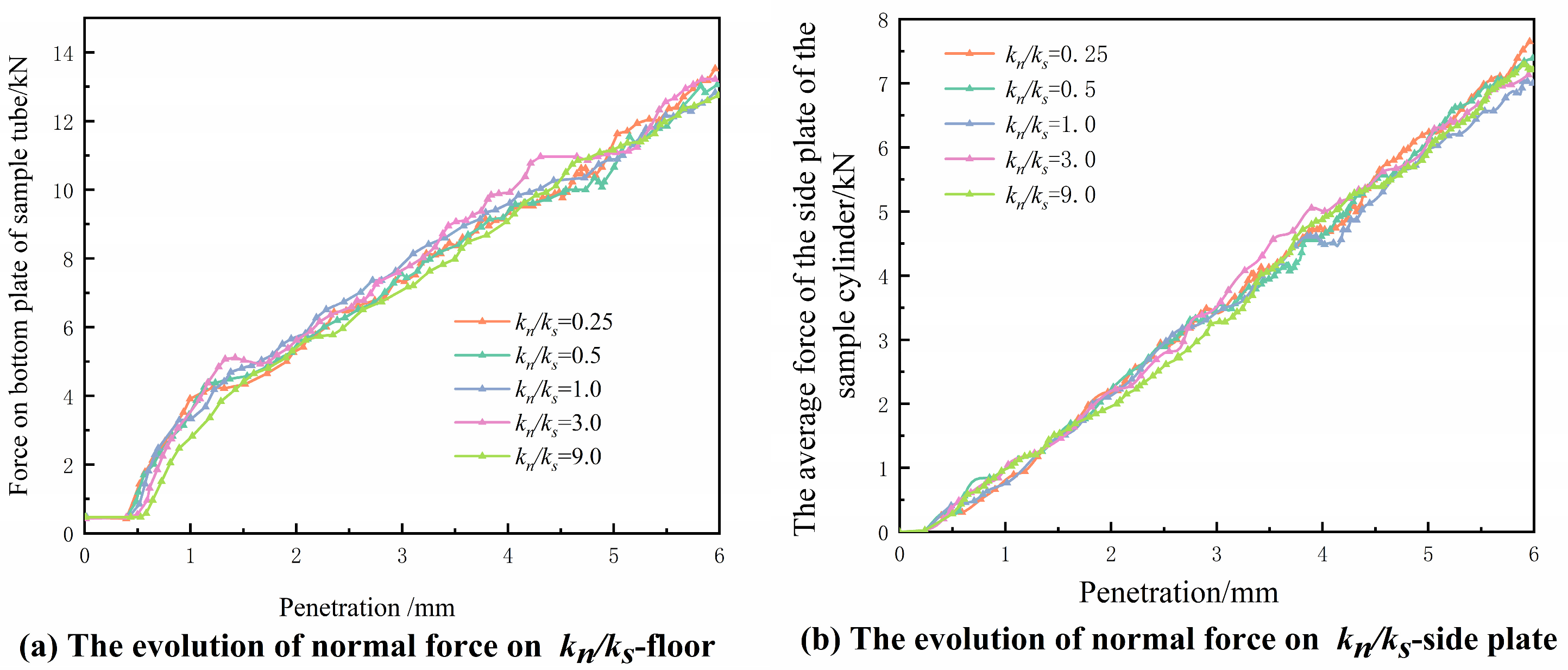
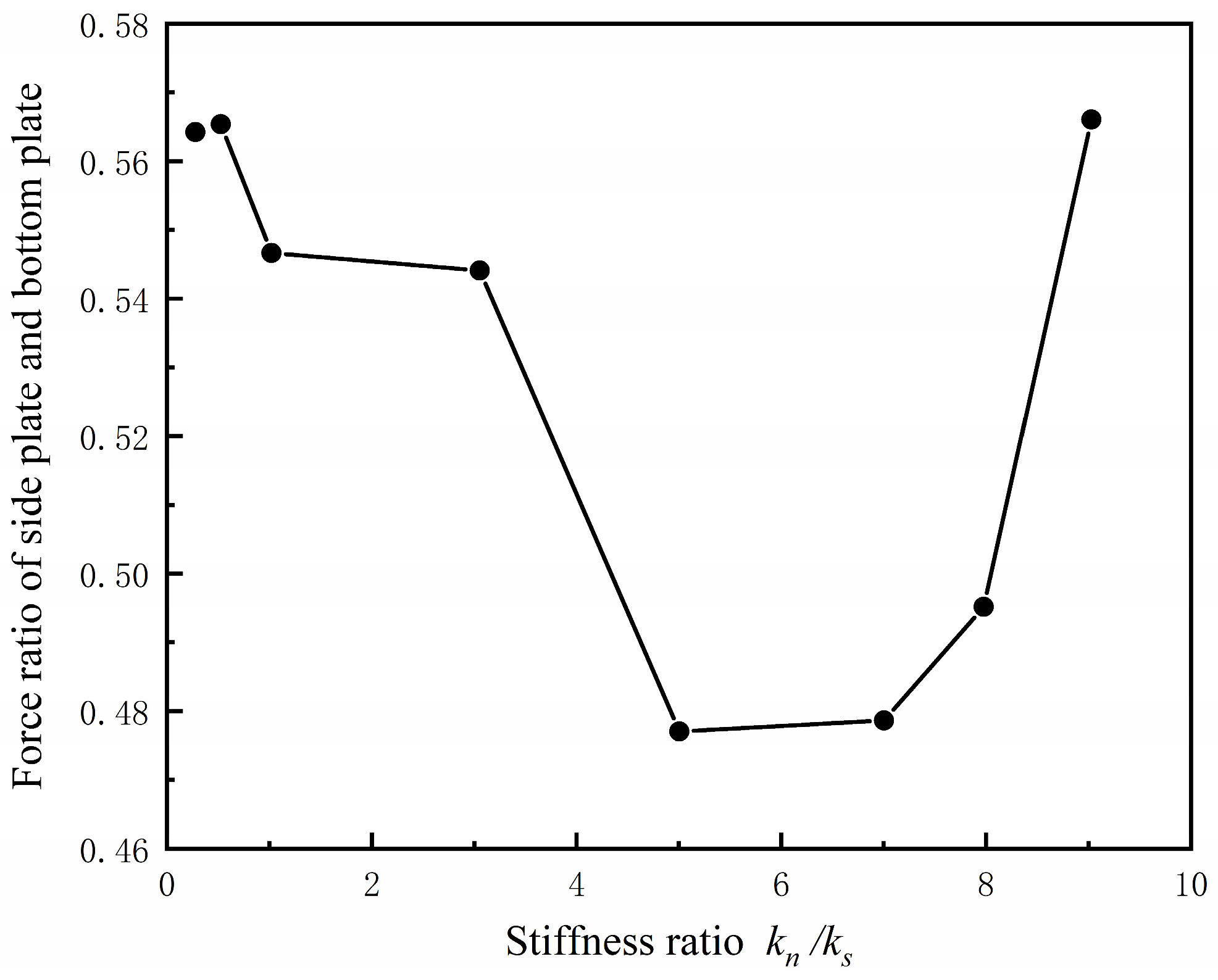
4.1.1. Stiffness Ratio
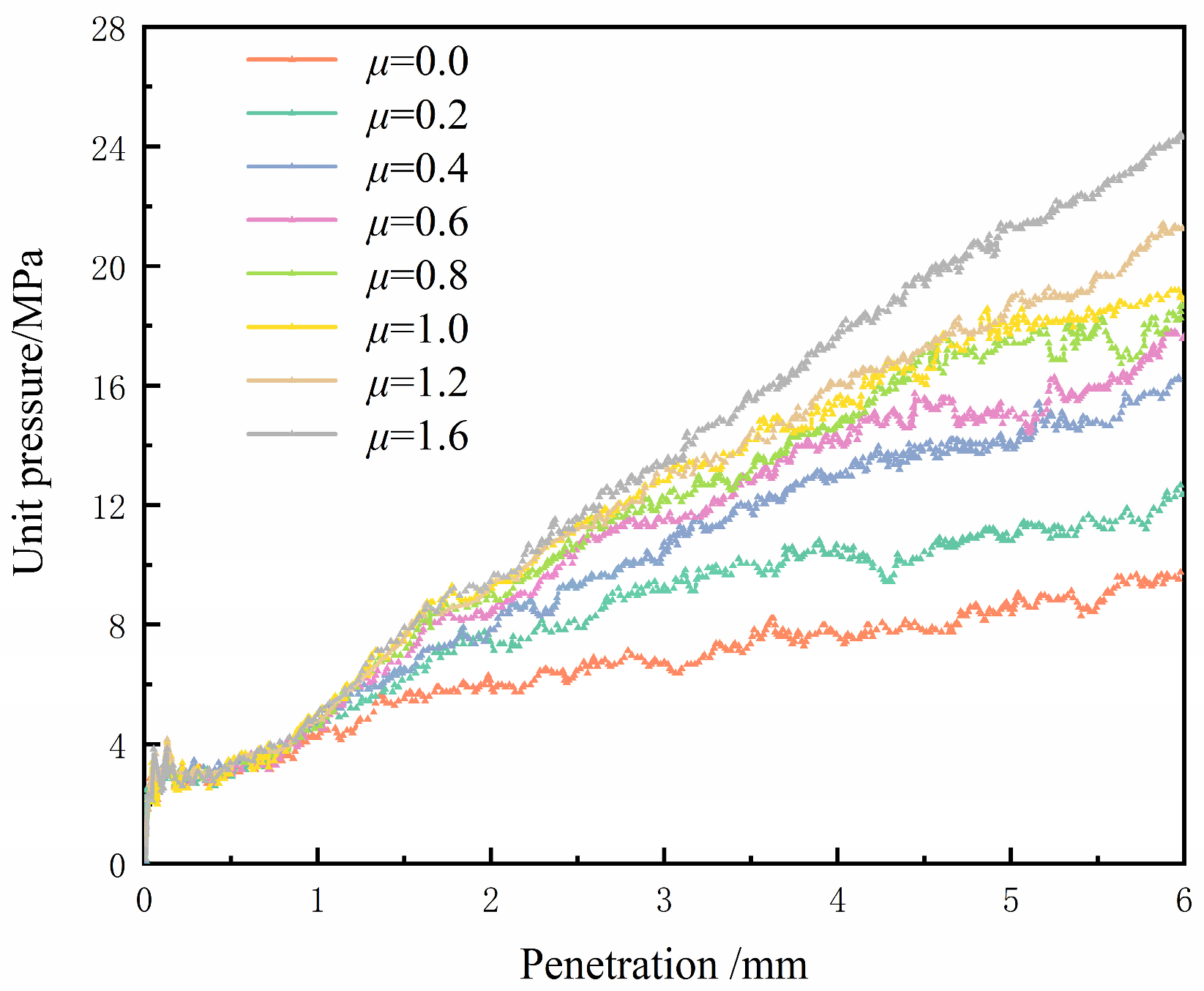
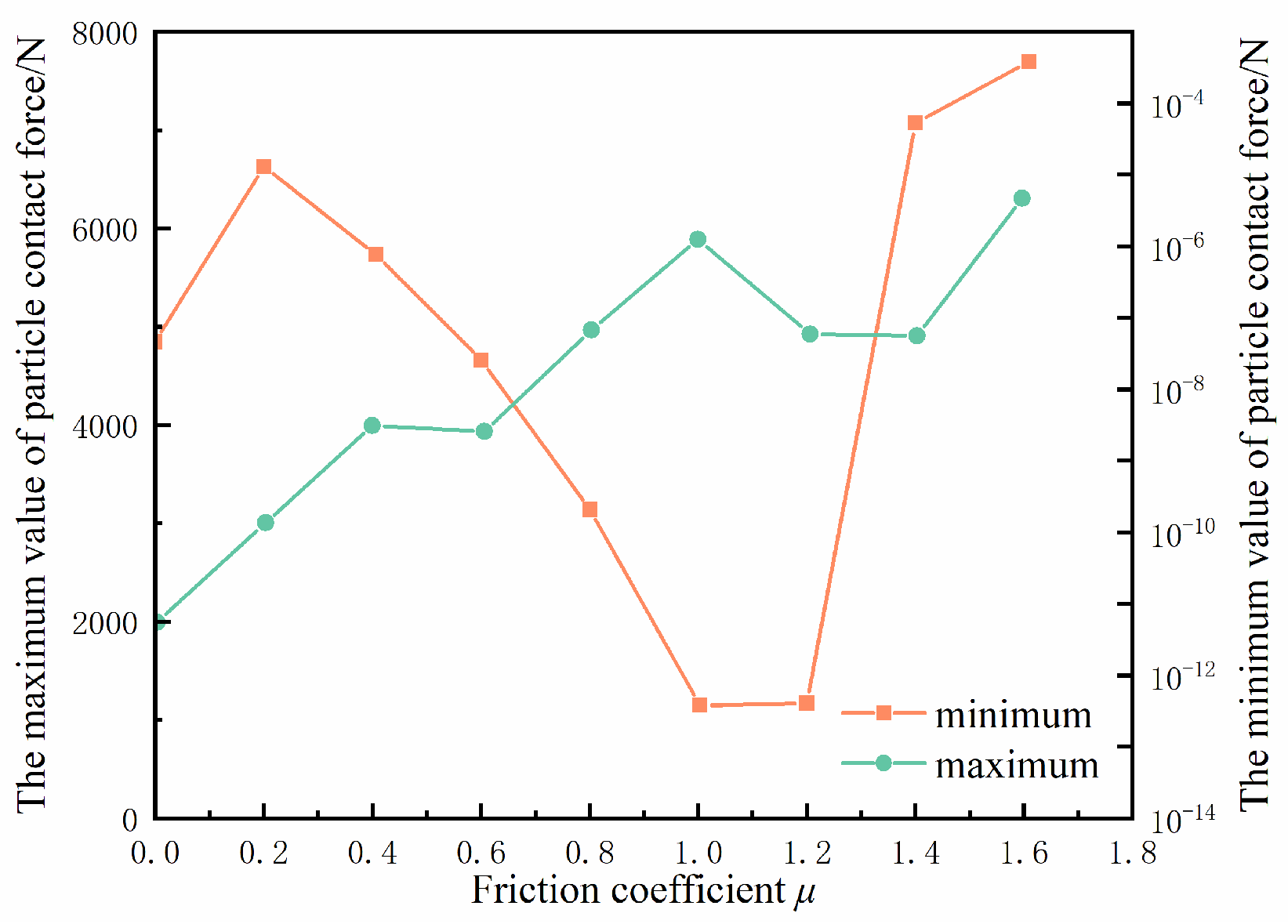
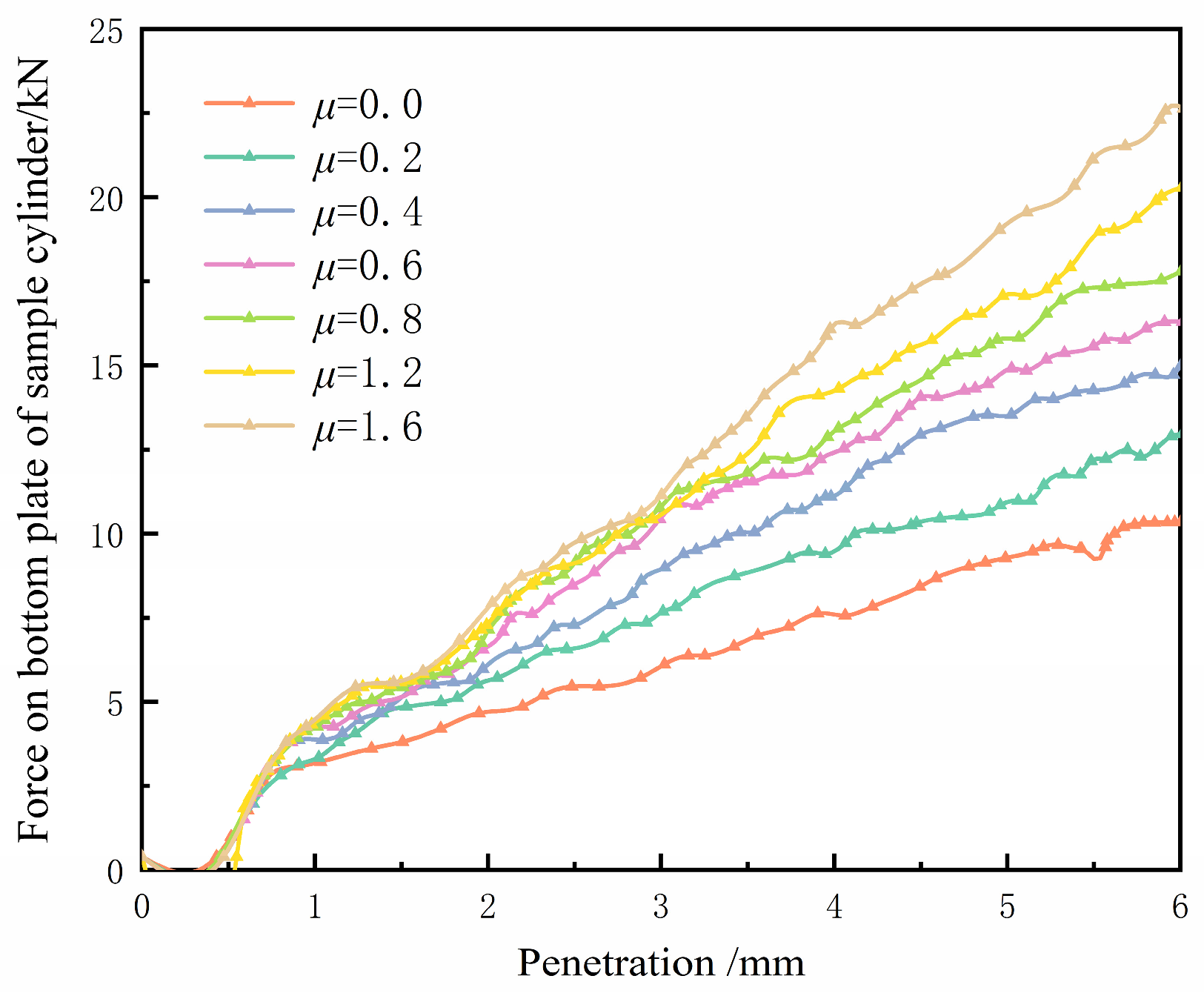
4.1.2. Friction Coefficient
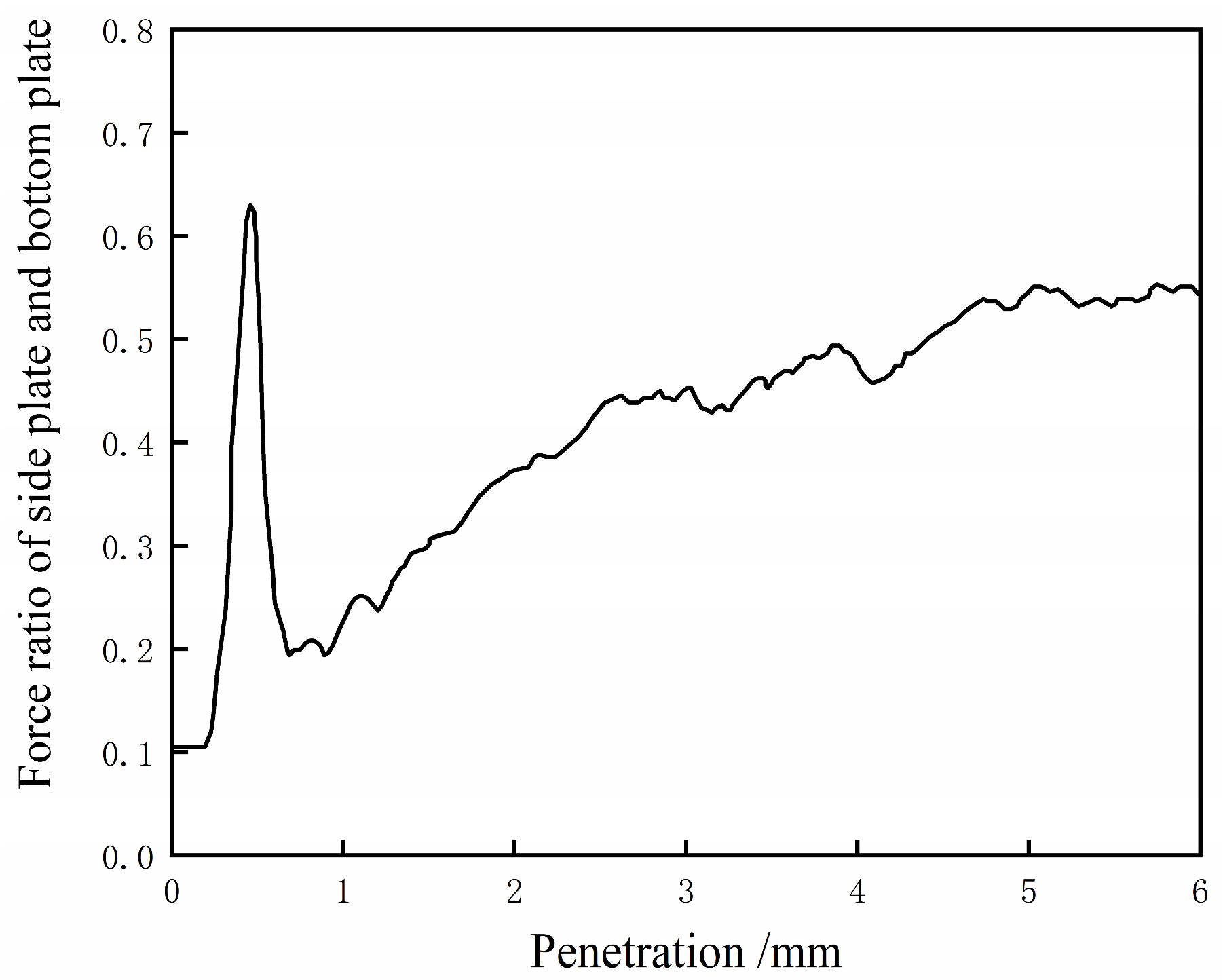
4.2. Influencing Factors on the Shape of Contact Force Field
4.2.1. CBR Test and Silo Effect
4.2.2. Stiffness Ratio
4.2.3. Friction Coefficient and Boundary Force
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deng, C.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, Y.; Tian, T.; Yuan, K.; Fan, J. Mechanical properties and influencing factors of vertical-vibration compacted unbound graded aggregate materials. Transp. Geotech. 2021, 28, 100538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, C.; Shi, W.; Wang, N.; Xue, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Meng, X. Laboratory investigation of solid wastes combined with tunnel slag in cement stabilized base of asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 392, 131807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.; Tian, G.; Chen, J.; Chen, G.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Liu, B.; Huang, T.; Qiang, M.; Satyanaga, A.; et al. Feasibility Studies on the Utilization of Recycled Slag in Grouting Material for Tunneling Engineering. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Qiu, W.; Liu, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, R. Experimental Study on the Properties of Mortar and Concrete Made with Tunnel Slag Machine-Made Sand. Materials 2022, 15, 4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Meng, F.; Feng, T.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Shi, J. Effect of stone powder content on the mechanical properties and microstructure of tunnel slag aggregate-based concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 388, 131692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.B. Study of dilatancy effect of redstong coarse grained soil by large sacle triaxial tests. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2010, 29, 3145–3149. [Google Scholar]
- Hardin, B.O.; Kalinski, M.E. Estimating the shear modulus of gravelly soils. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2005, 131, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indraratna, B.; Ionescu, D.; Christie, H.D. Shear behavior of railway ballast based on large-scale triaxial tests. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 1998, 124, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indraratna, B.; Nimbalkar, S.; Coop, M.; Sloan, S.W. A constitutive model for coal-fouled ballast capturing the effects of particle degradation. Comput. Geotech. 2014, 61, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Lin, H.; Guo, T. The complete stress-strain curve of recycled aggregate concrete under uniaxial compression loading. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mater. Sci. Ed. 2010, 25, 862–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, C.; Caicedo, B. Elastoplastic framework of relationships between CBR and Young’s modulus for fine grained materials. Transp. Geotech. 2019, 21, 100280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes-Arvizu, M.E.; Chavez-Alegria, O.; Rojas-Gonzalez, E.; Gaxiola-Camacho, J.R.; Millan-Almaraz, J.R. CBR predictive models for granular bases using physical and structural properties. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Hu, Z.; Hu, Z.; Li, J. Strength characteristics and micro-scale mechanism of high liquid limit clay treated by recycled construction and demolition wastes (CDW) aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 332, 127367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narzary, B.K.; Ahamad, K.U. Estimating elastic modulus of California bearing ratio test sample using finite element model. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 175, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, A.; Cosentino, P. Characterizing structural performance of unbound pavement materials using miniaturized pressuremeter and California bearing ratio tests. J. Test. Eval. 2017, 45, 818–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Shu, Y.; Zhou, S. Finite-infinite element coupled analysis on the influence of material parameters on the dynamic properties of transition zones. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 148, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Gao, Z.; Shi, Y.; Lin, Y.; Li, J. Effect of large broken stone content on properties of roller compacted concrete based on fractal theory. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Ma, B.; Wang, H.; Sun, W. Development of elasto-plastic constitutive model for unbound granular materials under repeated loads. Transp. Geotech. 2020, 23, 100347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hao, P. Stress dependent and redistribution behaviour of unbound granular material. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2020, 21, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.F.; Wei, H.Z.; Meng, Q.S.; Wei, C.; Ai, D. Effects of shear rate on shear strength and deformation characteristics of coarse-grained soils in large-scale direct shear tests. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2013, 35, 728–733. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Huang, X.M. Resilient deformation behavior of unbound stone aggregates. J. Chang’an Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2007, 27, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, X.; Wu, G.; Jiang, S.; Xie, X.; Xie, Y.; Meng, J. Analysis of granular mechanical parameters characteristics in graded gravel triaxial test. Environ. Earth Sci. 2024, 83, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, D.K. A study of correlation between California Bearing Ratio (CBR) value with other properties of soil. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2014, 4, 559–562. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, X.; Li, J.; Cui, Z.; Li, S.; Xiong, Y.; Hu, J.; Jiang, Y. A Prediction Method for the California Bearing Ratio of Soil-Rock Mixture Based on the Discrete Element Method and CT Scanning. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 9794756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Q. Gradation Design of Phosphorus Tailing–Graded Waste Rock Subgrade Filling Using Discrete Element Method. Minerals 2022, 12, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, W.; Hei, T.; Ding, X.; Dong, Z. Evaluation of CBR of graded crushed stone of flexible base structural layer based on discrete element model. Materials 2022, 16, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wong, L.N.Y.; Ren, J. A numerical test method of California bearing ratio on graded crushed rocks using particle flow modeling. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. (Engl. Ed.) 2015, 2, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Ren, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, D. Simulation Method of Mechanical Properties of Graded Broken Stone Based on Particle Flow Code. J. Tongji Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2011, 39, 699–704. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, A.P.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z. Study on the meso-mechanical behavior of California bearing ratio of graded gravel with discrete element method. J. Railw. Sci. Eng. 2019, 16, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.L. CBR Simulation Test Method of Graded Broken Stone and Its Appliance. Master’s Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
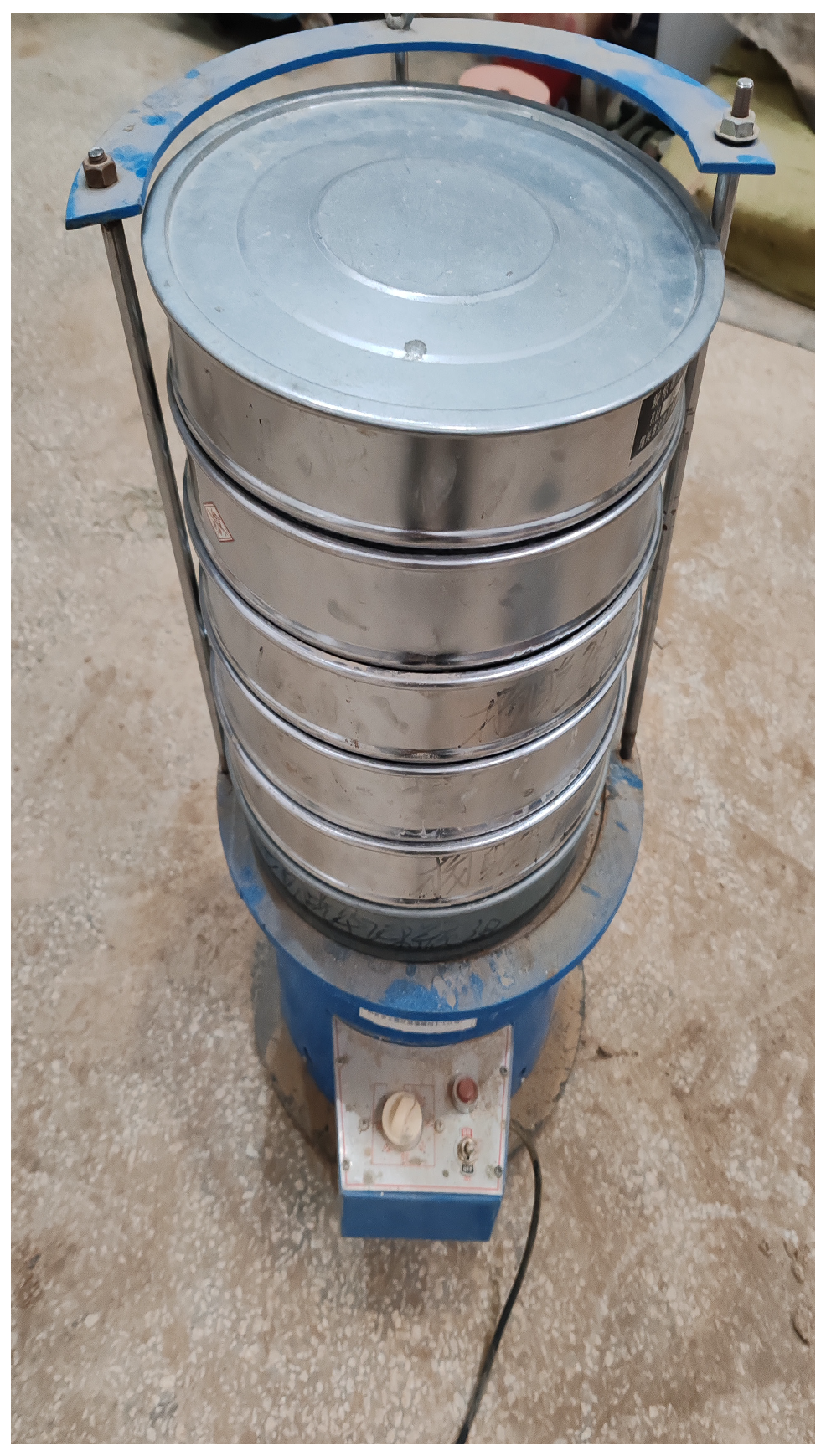
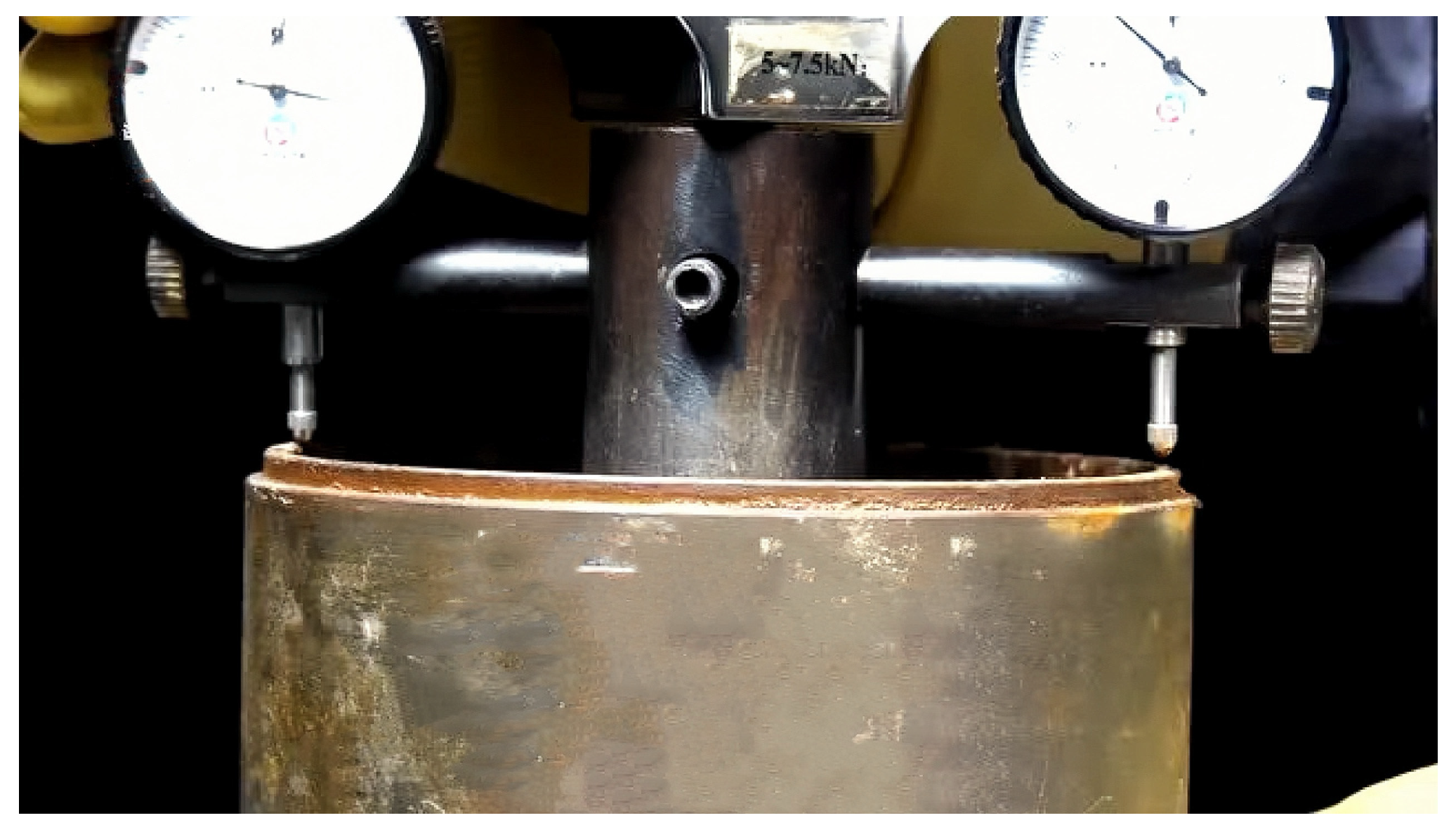




| Particle Size/mm | 19~16 | 16~9.5 | 9.5~4.75 | 4.75~2.36 | 2.36~1.18 | 1.18~0.6 | <0.6 |
| Content/% | 9.1 | 25.72 | 30.18 | 15.00 | 4.27 | 5.53 | 10.20 |
| Mesoscopic Constant | Symbol | The Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geometric parameter | Sample size/mm | 150 × 120 | ||
| Particle size range/mm | 1, 10 | |||
| Porosity | 0.30 | |||
| Physical parameters | Particles | Particle density/(kg/m3) | 2600 | |
| Normal stiffness/(N/m) | ||||
| Tangential stiffness/(N/m) | ||||
| Coefficient of friction | 0.2 | |||
| Wall | Normal stiffness (load board)/(N/m) | |||
| Normal stiffness (flexible film)/(N/m) | ||||
| Coefficient of friction | 0 | |||
| Local damping | 0.7 | |||
| Loading rate (mm/min) | 1.0 | |||
| Test Classification | CBR Value (Penetration 2.5 mm)/% | CBR Value (Penetration 5.0 mm)/% | Actual Value/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laboratory test | 117.56 | 112.45 | 117.56 |
| Simulation | 111.29 | 101.90 | 111.29 |
| Deviation | 5.33 | 9.38 | 5.33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, H.; Shan, L.; Zhao, X. New Relationships Between Particle Meso-Mechanical Parameters and CBR of Graded Crushed Stone Pavement: Influence Factors Analysis. Buildings 2026, 16, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings16010137
Wang X, Chen J, Liu H, Shan L, Zhao X. New Relationships Between Particle Meso-Mechanical Parameters and CBR of Graded Crushed Stone Pavement: Influence Factors Analysis. Buildings. 2026; 16(1):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings16010137
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xueying, Junwen Chen, Heng Liu, Liyan Shan, and Xin Zhao. 2026. "New Relationships Between Particle Meso-Mechanical Parameters and CBR of Graded Crushed Stone Pavement: Influence Factors Analysis" Buildings 16, no. 1: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings16010137
APA StyleWang, X., Chen, J., Liu, H., Shan, L., & Zhao, X. (2026). New Relationships Between Particle Meso-Mechanical Parameters and CBR of Graded Crushed Stone Pavement: Influence Factors Analysis. Buildings, 16(1), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings16010137





