A Study on the Dynamic Strength and Index Model of Artificial Structural Loess
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Test Methods
3. Results and Discussion
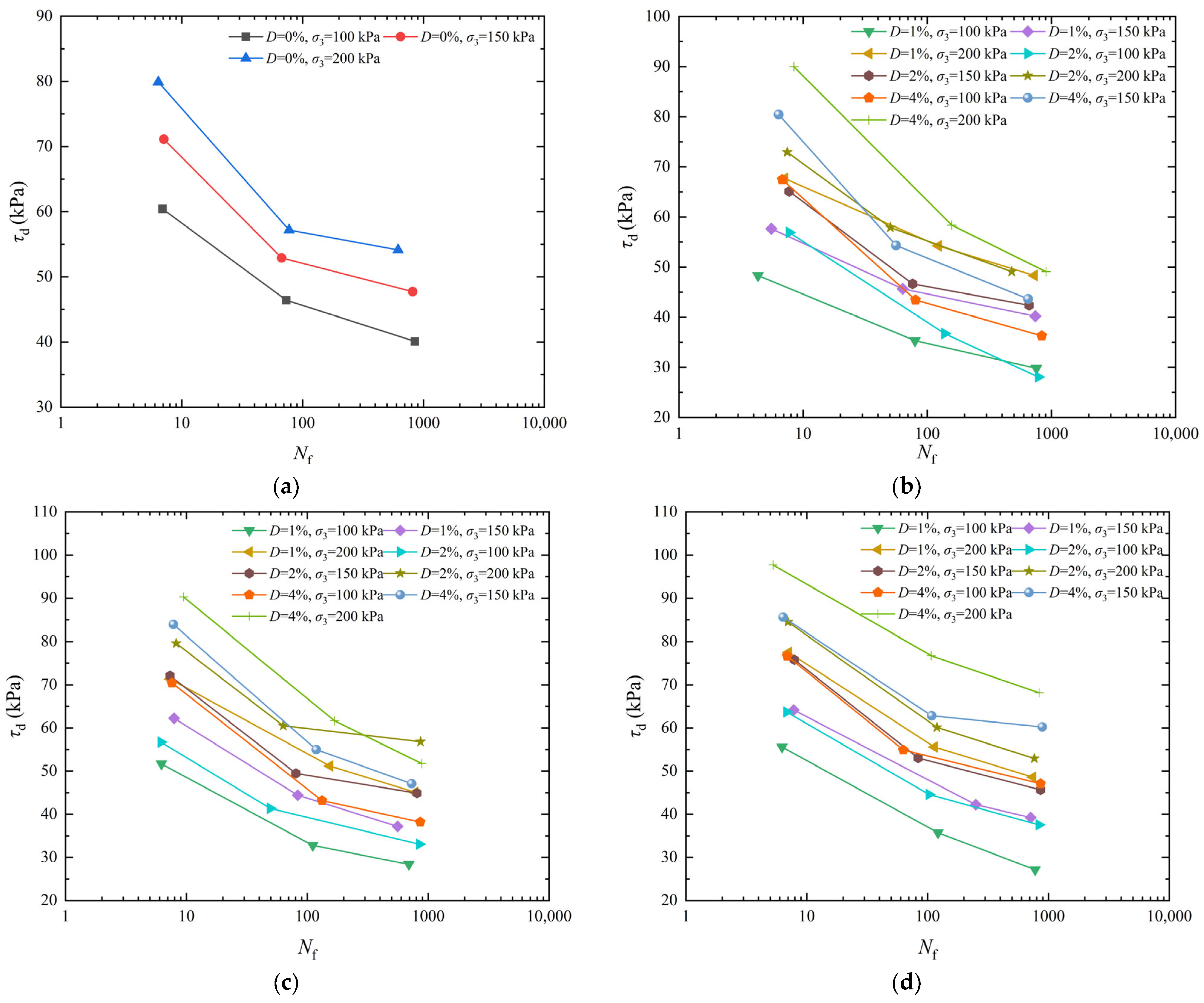
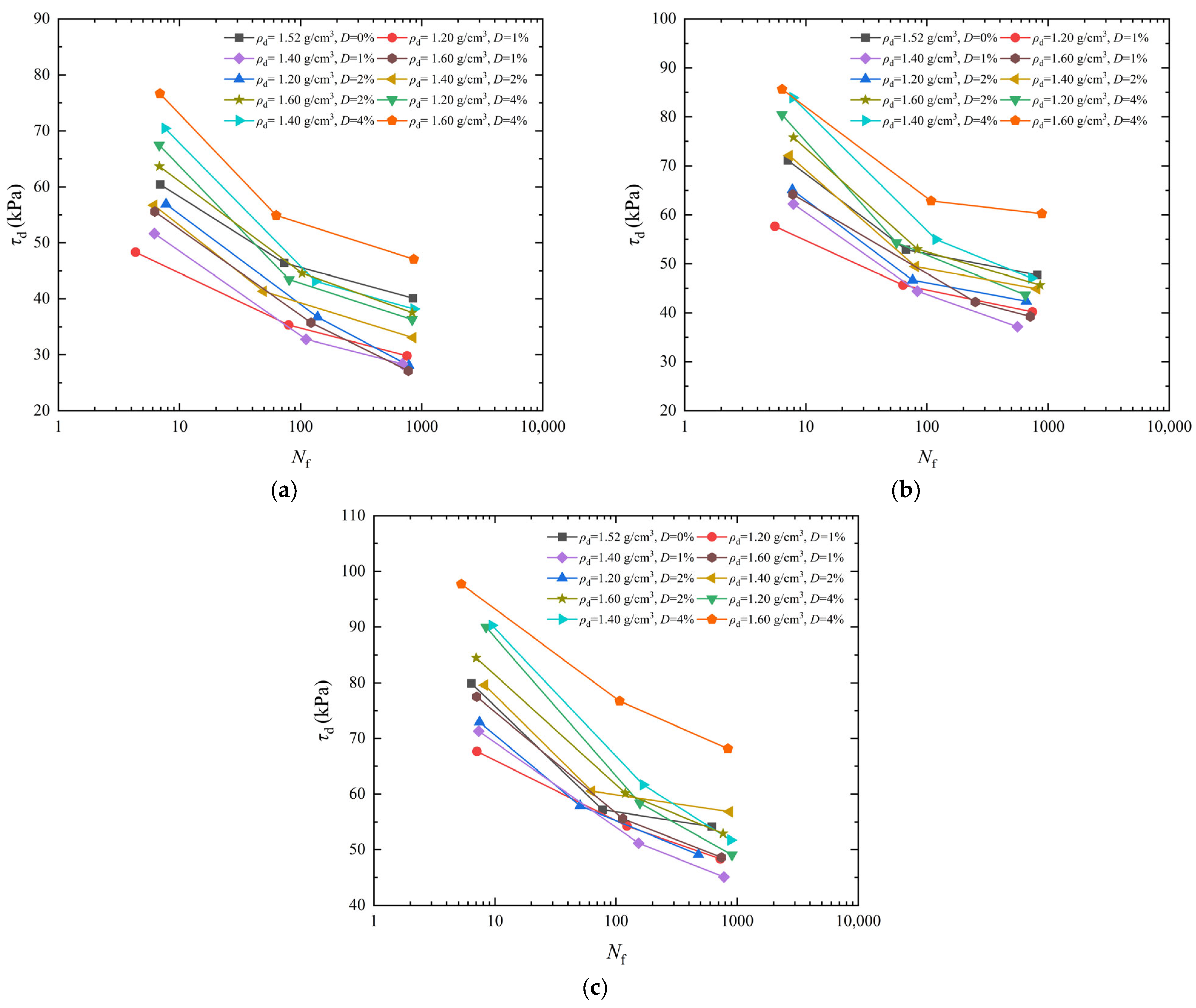
3.1. Analysis of the Effect of Dry Density on Dynamic Strength
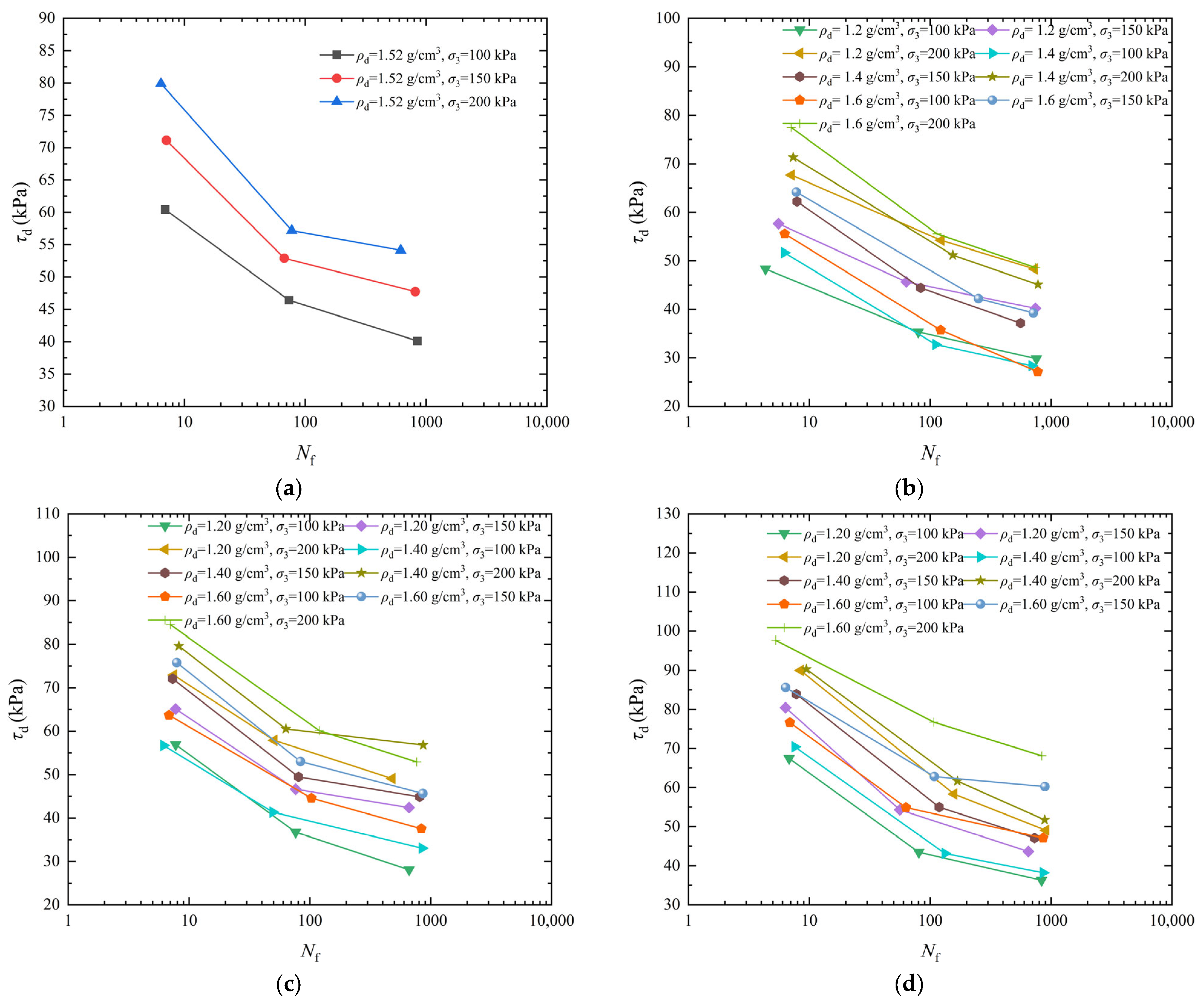
3.2. Analysis of the Effect of Confining Pressure on Dynamic Strength
3.3. Analysis of the Effect of Cement Content on Dynamic Strength
3.4. Dynamic Strength Index of Artificial Structural Loess
4. Dynamic Strength Model of Artificial Structural Loess
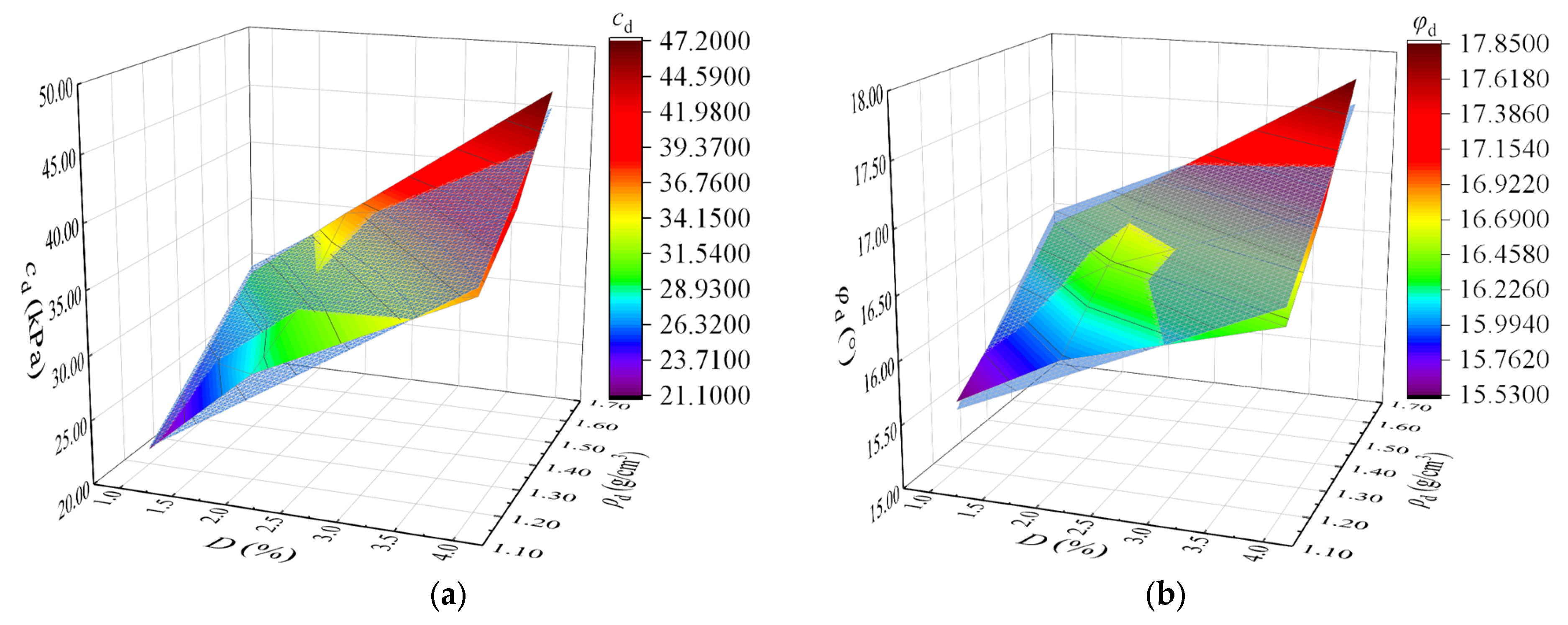
4.1. Model Establishment
4.2. Parameters Obtaining and Model Validation
5. Conclusions
- The dynamic strength of the specimen dropped as the vibration number rose at different ρd. The dynamic strength reduced as the vibration number rose for certain σ3.
- The dynamic strength rose significantly as the σ3 increased. The dynamic strength of artificial structural loess with the σ3 of 200 kPa was 20.01% and 41.10% higher than that with the σ3 of 150 kPa and 100 kPa, respectively, when the D was 1% and the ρd was 1.60 g/cm3.
- The higher the D, the larger the dynamic strength of artificial structural loess. The dynamic strength of artificial structural loess was closer to that of undisturbed loess when the ρd was 1.60 g/cm3 and the D was 2%.
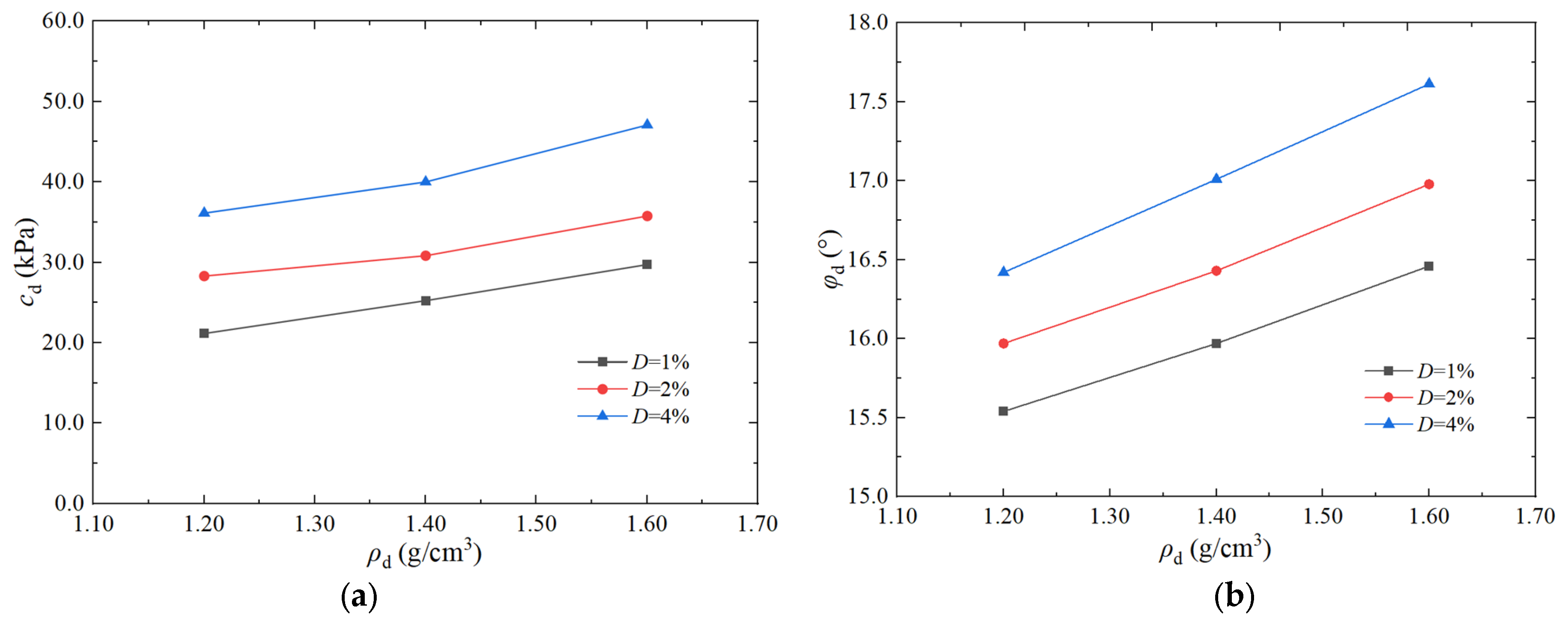
- As ρd and D increased, the cd and φd of artificial structural loess rose. The trend of cd with increasing D was relatively gentle.
- A dynamic strength mechanical index model for artificial structural loess was established, which presents a “slope type”. The R2 values of the artificial structural loess cd model and φd model were 0.98 and 0.97, respectively. The model is suitable for the prediction of indexes of dynamic strength.
- This study mainly replicated the structural characteristics of Chang’an loess. Future research will combine numerical methods to explore its micro mechanisms in depth and will expand the study of artificial structural loess to different regions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.H.; Shen, Z.J. Study on mechanism of micro-failure of structured soils. Rock Soil Mech. 2007, 28, 1525–1532. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Luo, A.Z.; Shao, S.J.; Chen, C.L. Progressive failure analysis of soil slopes considering the influences of humidity and loading. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1256041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.A.; Li, H.; Jiang, Y.L.; Yu, Q.B.; Yao, M.; Shan, W.C. Feasibility study on artificial preparation of structured loess. Geosci. Lett. 2022, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.Y.; Lei, Z.S.; Wang, A.G. Additional textual criticism of southern Tianshui M8 earthquake in Gansu province in 1654. Chin. Earthq. Eng. J. 2017, 39, 509–520. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, C.Y.; Qi, Y.F.; Meng, K.; You, Z.J.; Liang, Z.M.; Xu, C.S. A new analytical solution for horizontal vibration of floating pile in saturated soil based on FSSP method. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2024, 187, 108960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.Y.; Xu, M.Z.; Xu, C.S.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, J.T. An ontology-based probabilistic framework for comprehensive seismic risk evaluation of subway stations by combining Monte Carlo simulation. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 135, 105055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.R.; Liang, H.N. Study on the difference of mechanical properties of artificial structured loess with different binders. Rock Soil Mech. 2023, 44, 1416–1424. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.C.; Qiu, G.R. Constitutive relation of seismic subsidence of loess based on microstructure. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2011, 33, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, E.L.; Shen, Z.J. Strength criterion for structured soils. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2006, 28, 1248–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.J.; Chen, F.; Dai, Y.F.; Lu, Y. Shear band mechanism and strength characteristics of structural loess tested by true triaxial apparatus. Rock Soil Mech. 2015, 36, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Hong, B.; Wang, L.; Li, L.C.; Sun, J.Q. Microscopic anisotropy and preferred orientation of grains and aggregates (POGA) of the Malan loess in Yan’an, China: A profile study. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2020, 79, 1893–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.J.; Hu, H.J.; Liu, F. Summary of collapsible behaviour of artificially structured loess in oedometer and triaxial wetting tests. Can. Geotech. J. 2012, 49, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinou, C.; Biscontin, G.; Jiang, N.J.; Soga, K. Application of microbially induced carbonate precipitation to form bio-cemented artificial sandstone. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2021, 13, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.M.; Sridharan, A.; Ramanath, K.P. Collapse behaviour of an artificially cemented clayey silt. Geotech. Test. J. 1995, 18, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diambra, A.; Ibraim, E.; Peccin, A.; Consoli, N.C.; Festugato, L. Theoretical derivation of artificially cemented granular soil strength. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2017, 143, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Xiao, H.W.; Chen, D.H.; Liu, Y. A direct assessment for the stiffness development of artificially cemented clay. Géotechnique 2018, 69, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharatii, S.K.; Chew, S.H. Geotechnical behavior of recycled copper slag-cement-treated Singapore marine clay. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2016, 34, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Shao, S.J.; Wang, Q.; Yu, Q.G. Relation of structural index to changes of structural parameters for Q2-loess from Daqing mountain. Chin. J. Geol. Hazard Control. 2015, 26, 130–137. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Kong, J.; Zheng, J.; Mu, J.Q.; Wang, J.; Zhuang, J.Q. The dynamic characteristics of saturated remolded loess under cyclic load. Earthq. Res. Adv. 2024, 4, 100235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tang, Y.Q.; Yang, P.; Liu, Q. Dynamic properties of freezing-thawing muddy clay surrounding subway tunnel in Shanghai. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 5341–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosallamy, M.E.; Fattah, T.T.A.E.; Khouly, M.E. Experimental study on the determination of small strain-shear modulus of loess soil. HBRC J. 2016, 12, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Luo, T.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y. Effects of cyclic freezing-thawing on dynamic properties of Loess reinforced with polypropylene fiber and fly ash. Water 2022, 14, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.M.; Wang, J.D.; Gu, T.F.; Li, P.P.; Chen, P. Experimental research on the dynamic strength characteristics of compacted loess and its impact factor. J. Lanzhou Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2016, 52, 735–740. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, T.F.; Wang, J.D.; Liu, Y.M. Dynamic strength characteristics of compacted loess under cyclic loads. J. Eng. Geol. 2015, 23, 604–608. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.; Li, R.J.; Liu, J.D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.E. Structure and dynamic strength attenuation of Pan’an structural loess characteristic features. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2016, 34, 74–78. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.L.; Chen, H.E.; Leng, G.J. Dynamic elastic modulus of Xianyang loess based on microscopic analysis: A qualitative evaluation. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2022, 26, 3331–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tian, K.; Ma, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, R.; Li, D. Study on the dynamic structural parameters and dynamic structural constitutive relation of intact Loess. Soil Mech. Found. Eng. 2021, 58, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.J.; Xu, S.M.; Chen, D.W.; Zhao, D.Y.; Zhang, D. An experimental study of the influence of structural parameters on dynamic characteristics of loess. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 132, 106067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, F.; Chang, C.Y.; Bo, J.S.; Wang, L.; Wang, J. Study on the dynamic characteristics of loess. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhang, X.D. Dynamic deformation characteristics and modeling of loess. J. Changjinag River Sci. Res. Inst. 2018, 35, 114–120. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.Y.; Liang, Q.G.; Ou, E.F.; Yan, S.H.; Zhang, Y.W. Comparative experimental study on tensile strength of undisturbed and remolded Q2 loess from Yan’an Shanxi. Chin. Civ. Eng. J. 2015, 48, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T50123-2019; Standard for Geotechnical Testing Method. Construction Ministry of PRC: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Chen, Z.M.; Li, J.P.; Fan, C.H.; Zhou, F. Dynamic characteristics of salted soft soil. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2021, 43, 208–212. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.J.; Zhang, W.Y.; Ma, Y.X.; Liu, L.X.; Su, Y.G. Experimental study on microstructure change of intact loess based on GDS dynamic triaxial test. J. Qinghai Univ. 2018, 36, 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.H.; Liu, Y.M. Dynamic strength properties of compacted Loess based on dynamic triaxial test. Chin. Earthq. Eng. J. 2016, 38, 439–444. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.M.; Lu, Q.; Guo, S.L.; Gao, M.; Shen, Z.T. Dynamic behavior of soil with fiber and cement under cyclic loading. Rock Soil Mech. 2018, 39, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.W.; Ji, J.W.; Dong, X.L.; Jia, J. Analysis of dynamic strength and settlement characteristics of cement-lime composite stabilized soil under traffic loading. Archit. Archit. Technol. 2023, 54, 2301–2304. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, W.; Yun, W.; Dang, K.X.; Li, T. Study on dynamic characteristics of subgrade Loess improved by EICP solution with different calcium sources. Mater. Rep. 2024, 38, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.R.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, T. Dynamic strength characteristics and microscopic analysis of modified loess with xanthan gum. J. Basic Sci. Eng. 2024, 32, 900–909. [Google Scholar]
- Tiam, K.L.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhang, B.P.; Luo, Y.S. Research on structural characteristics and strength of loess. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2005, 1, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W. Analysis of cement improvement for railway collapsible loess roadbed. Sichuan Build. Mater. 2018, 44, 183–184. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Mou, X.Y.; Li, H.; Mao, Y.X.; Song, H.Z. Study on influencing factors and prediction model of strength and compression index of sandy silt on bank under freeze-thaw cycles. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, H.C.; Cheng, M.Y.; Lu, H.W.; Wang, Z.J.; Feng, P.Y. Dynamic triaxial test and microscopic study of solidified muddy soil with different mixing ratios and curing Ages. Front. Mater. 2021, 8, 731449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.P.; Ma, T.; Yang, X.H.; Yang, K.B.; Wang, H.M. Shear strength tests and regression analysis of red sandstone-improved soils based on orthogonal design. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2018, 40, 87–92. [Google Scholar]

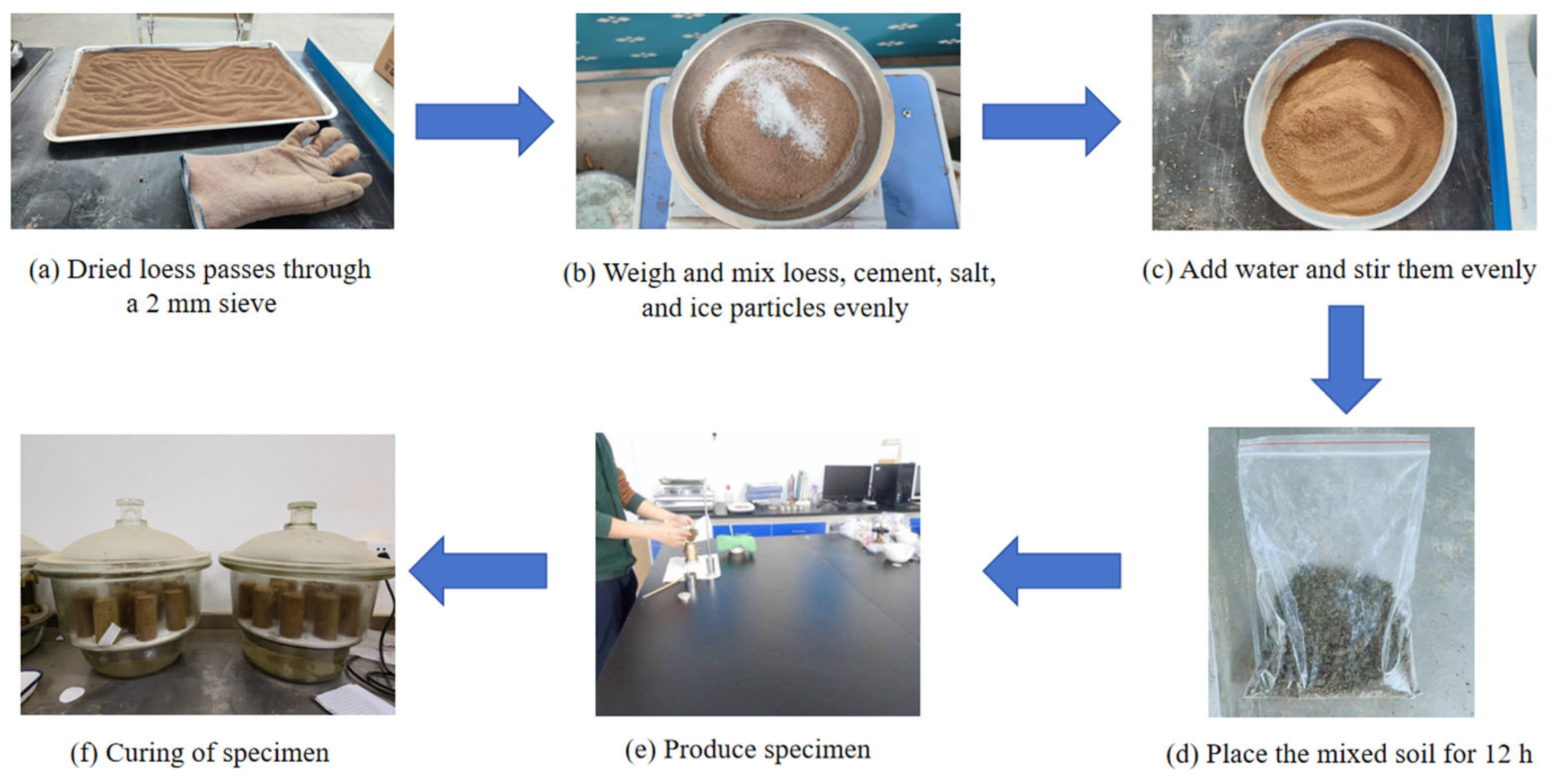
| Specific Gravity Gs | Dry Density ρd (g/cm3) | Water Content w (%) | Density ρ (g/cm3) | Liquid Limit wL (%) | Plastic Limit wp (%) | Porosity Ratio e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.71 | 1.52 | 19.41 | 1.62 | 35.78 | 20.54 | 0.97 |
| Cement Content D (%) | Dry Density ρd (g/cm3) | Confining Pressure σ3 (kPa) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.52 | 100, 150, 200 |
| 1 | 1.20 | 100, 150, 200 |
| 1.40 | 100, 150, 200 | |
| 1.60 | 100, 150, 200 | |
| 2 | 1.20 | 100, 150, 200 |
| 1.40 | 100, 150, 200 | |
| 1.60 | 100, 150, 200 | |
| 4 | 1.20 | 100, 150, 200 |
| 1.40 | 100, 150, 200 | |
| 1.60 | 100, 150, 200 |
| Cement Content D (%) | Dry Density ρd (g/cm3) | Confining Pressure σ3 (kPa) | Dynamic Shear Stress τd (kPa) | Dynamic Cohesive Force cd (kPa) | Dynamic Friction Angle φd (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.52 | 100 | 68.21 | 37.79 | 16.92 |
| 150 | 83.42 | ||||
| 200 | 98.63 | ||||
| 1 | 1.20 | 100 | 48.99 | 21.19 | 15.54 |
| 150 | 62.90 | ||||
| 200 | 76.81 | ||||
| 1.40 | 100 | 53.89 | 25.27 | 15.97 | |
| 150 | 68.20 | ||||
| 200 | 82.51 | ||||
| 1.60 | 100 | 59.30 | 29.75 | 16.46 | |
| 150 | 74.07 | ||||
| 200 | 88.84 | ||||
| 2 | 1.20 | 100 | 56.94 | 28.32 | 15.97 |
| 150 | 71.24 | ||||
| 200 | 85.56 | ||||
| 1.40 | 100 | 60.34 | 30.86 | 16.43 | |
| 150 | 75.09 | ||||
| 200 | 89.83 | ||||
| 1.60 | 100 | 66.13 | 35.79 | 16.88 | |
| 150 | 81.31 | ||||
| 200 | 96.48 | ||||
| 4 | 1.20 | 100 | 65.62 | 36.15 | 16.42 |
| 150 | 80.35 | ||||
| 200 | 95.09 | ||||
| 1.40 | 100 | 70.61 | 40.02 | 17.01 | |
| 150 | 85.90 | ||||
| 200 | 101.20 | ||||
| 1.60 | 100 | 79.31 | 47.11 | 17.85 | |
| 150 | 95.41 | ||||
| 200 | 111.51 |
| Number | Cement Content D (%) | Dry Density ρd(g/cm3) | Experimental Values | Predicted Values | Experimental Values | Predicted Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Friction Angle φd (°) | Friction Angle φd (°) | Dynamic Cohesive Force cd (kPa) | Dynamic Cohesive Force cd (kPa) | |||
| 1 | 1 | 1.20 | 15.54 | 15.59 | 21.19 | 21.34 |
| 2 | 1 | 1.40 | 15.97 | 15.96 | 25.27 | 25.84 |
| 3 | 1 | 1.60 | 16.46 | 16.43 | 29.75 | 30.34 |
| 4 | 2 | 1.20 | 15.97 | 15.93 | 28.32 | 26.50 |
| 5 | 2 | 1.40 | 16.43 | 16.39 | 30.86 | 30.99 |
| 6 | 2 | 1.60 | 16.88 | 16.96 | 35.79 | 35.50 |
| 7 | 4 | 1.20 | 16.42 | 16.41 | 36.15 | 36.81 |
| 8 | 4 | 1.40 | 17.01 | 17.06 | 40.02 | 41.31 |
| 9 | 4 | 1.60 | 17.85 | 17.81 | 47.11 | 45.81 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xi, Y.; Hua, X.; Sun, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Y. A Study on the Dynamic Strength and Index Model of Artificial Structural Loess. Buildings 2025, 15, 1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15081227
Xi Y, Hua X, Sun M, Zhang Y, Yuan Y. A Study on the Dynamic Strength and Index Model of Artificial Structural Loess. Buildings. 2025; 15(8):1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15081227
Chicago/Turabian StyleXi, Yu, Xueqing Hua, Mingming Sun, Yao Zhang, and Ye Yuan. 2025. "A Study on the Dynamic Strength and Index Model of Artificial Structural Loess" Buildings 15, no. 8: 1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15081227
APA StyleXi, Y., Hua, X., Sun, M., Zhang, Y., & Yuan, Y. (2025). A Study on the Dynamic Strength and Index Model of Artificial Structural Loess. Buildings, 15(8), 1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15081227





