Abstract
Color contrast creates visual interest, increases attention, and enhances legibility in the indoor environment. Past studies have suggested that color contrast enhances visual clarity due to the color opponency mechanism of the visual system, especially when two opposing colored samples are seen side by side, such as red–green or yellow–blue. However, these studies were limited to solid single-colored samples, which falls short on representing the built environment with its complex distributions of colors and objects. This study explores the validity of the “color contrast–visual clarity” hypothesis for complex images of indoor built environments. Twenty images of indoor environments were selected from an image database to represent a wide range of colorfulness and spatial complexity (ranging from simple to complex). Forty new images were generated by increasing the colorfulness of either the red and green or blue and yellow sections of the original 20 images using an image editing software. Forty participants assessed the visual preference, clarity, colorfulness, and complexity of the 60 images. No statistically significant difference was found between red–green or yellow–blue enhanced images and original images. However, an observable trend indicated a linear relationship between visual clarity and colorfulness. In addition, participants preferred saturated images over original images. While the findings suggest potential trends, the lack of significant effects warrants cautious interpretation, and further research is needed to explore the impact of color contrast in more controlled settings.
1. Introduction
Color and color contrast play a pivotal role in architectural spaces, significantly impacting the overall design and experience of the built environment [1,2,3]. Understanding how color contrast influences visual clarity in indoor environments can inform lighting and interior design strategies, contributing to more visually comfortable and esthetically optimized architectural spaces [4,5,6]. For example, the careful selection of colors can evoke emotions, set moods, and influence the perception of space [7,8]. Color contrast aids in defining spatial boundaries, helping circulation, enhances visual interest, and fosters a greater understanding of visual composition. In addition, it has been suggested that color contrast can enhance visual interest and fosters a greater understanding of architectural composition [9,10,11,12]. The effective use of color and color contrast helps establish the identity of a place and enhance wayfinding, making it easier for occupants to navigate and interact with their surroundings [13,14]. Architects and designers utilize these principles to enrich the sensory experience within spaces, contributing to a more engaging, harmonious, and esthetically pleasing built environment.
Past research investigating the effect of color contrast found an intricate relationship between color contrast and visual clarity, namely a linear relationship between the two concepts [15,16,17]. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, the term “visual clarity” entered the lighting research lexicon in the late 1960s through Aston and Bellchambers’s study [15]. In the early studies, visual clarity was described as the perception of a distinct difference in surface colors of several objects illuminated by a test illuminant [18]. For example, Flynn et al. examined the effects of lighting conditions on people’s subjective impressions and overt behaviors using semantic differential rating scales and multidimensional scaling [19]. In a follow-up study, Flynn and Spencer investigated subjective responses to white fluorescent and high-intensity discharge (HID) sources in an interior space [20] and found that cool white (CW) fluorescent provided the highest visual clarity. In the following decades, others continued to examine the visual performance under various light sources with various spectral compositions that were frequently used in offices at the time (CW fluorescent, tri-phosphor fluorescent, high-grade halophosphor fluorescent, clear metal halide, and white HPS lamps) but found no difference [21]. Hashimoto and Nayatani associated visual clarity with brightness perception, somewhat arguably, while recognizing its ability to account for the effectiveness of visual design in prioritizing and expressing information [22]. Their study indicated that visual clarity could not be estimated by the average lightness but impacted by highly saturated red, green, and blue samples.
The relationship between color contrast and visual clarity has also been a subject of interest in vision research, particularly concerning border detection. Studies have shown that the human visual system is particularly sensitive to red–green contrasts, which play a vital role in the perception of edge detection [23,24,25,26]. The red–green contrast mechanism together with blue–yellow and achromatic channels constitute the opponent process theory of color vision [27] and has been an important part of the mathematical modeling of human color vision [28]. By investigating the influence of light sources on the rendering of red–green (RG) and blue–yellow (YB) mechanisms, researchers have found that greater red–green contrast can enhance visual clarity [23,24,25,26]. Inspired by vision research studies, Worthey investigated the relationship between an illuminant’s ability to render red–green contrast and its ability to provide visual clarity [29]. Using colored paper as stimuli with primarily red–green or blue–yellow contrast, subjects were asked to match the distinctness of borders under different lamps in the experiment. The study results indicated that the subjects required much lower illuminance under a prime color lamp to match the border distinctness of red–green papers illuminated by cool white lighting. Overall, these studies supported the hypothesis that greater red–green contrast can enhance visual clarity.
While local contrast has shown to impact the clarity of color samples, the perceived complexity of complex environments has hardly been investigated. In one rare study that investigated the visual clarity of complex stimuli, Durmus and Davis utilized a projector with a resolution of 3840 × 2160 pixels and an adjustable focal length between 21.4 mm and 42.8 mm to illuminate three paintings with low, medium, and high spatial complexity, as determined by a computational metric called spatial perceptual information (SI) [30]. Twenty-two observers were asked to rate visual clarity using a standard mean opinion score scale. The projector’s lens’s focal length was changed to produce five different lighting conditions for each test image. The circle of confusion (CoC) was raised by 1%, 3%, 5%, and 9%, where a 3% increase in the CoC considerably lowered the blur tolerance of illuminated images. With the increasing visual complexity of images, blur perception, and thus visual clarity, also varied.
Several studies have demonstrated the significance of color contrast in shaping visual clarity for simple color samples [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19], and others even developed computational image quality assessment tools based on color contrast [31]. However, color contrast’s influence on the visual clarity of complex indoor environments has not been widely explored. While prior research has primarily focused on simple visual stimuli, such as isolated color patches or uniform backgrounds, real-world environments often contain additional complexities, including texture, material properties, and ambient lighting variations. These factors interact with color contrast in ways that are not yet fully understood, necessitating further study in realistic indoor settings.
Recent advancements in digital image processing have allowed for a more nuanced examination of color perception in natural environments (e.g., [32,33,34]). Emerging techniques in computational modeling and machine learning now enable a more precise analysis of how color affects visual quality and selective attention in intricate environments [35,36,37]. Studies incorporating deep learning models and high-fidelity image processing have provided new insights into the role of color contrast in image perception [38,39], yet these advancements remain underutilized in architectural and lighting research. Additionally, studies in architecture and lighting design emphasize the role of color contrast in spatial perception and user experience, underscoring the need for interdisciplinary approaches [40,41,42,43,44]. Integrating findings from architecture, human factors, and computational vision research can help bridge the gap between controlled experimental studies and real-world applications.
This study aims to extend the existing body of knowledge by incorporating perspectives from multiple disciplines to explore how color contrast affects perception in designed spaces. Building upon past research findings, it can be hypothesized that the increase in color contrast for opponent channels (RG, YB) will increase the perceived visual clarity in complex images. To test this hypothesis, a visual experiment has been conducted in the Lighting Lab at Pennsylvania State University. Previous research on color contrast and visual clarity has largely been conducted using controlled, monochromatic stimuli, limiting its applicability to complex, real-world settings. The results of this study can extend the knowledge of the relationship between color contrast and visual clarity to complex indoor images. Understanding this relationship has significant implications for architectural lighting and interior design.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
Forty participants without a domain-relevant background (23 women and 17 men, mean age = 27, median age = 23, minimum age = 18, maximum age = 72) were involved in the experiment to rate images of ten types of architectural spaces by their perceived level of visual. The sample size was determined by G*Power software (v3.1) for an effect size of r = 0.40 (α = 0.05, 1 − β = 0.80) [45]. No participants were majoring in vision science. Participants were not pre-screened for expertise in color, vision, or design research; however, given their diverse backgrounds, it is unlikely that design or visual arts experience significantly influenced the results. Future studies could explore the role of expertise as a potential moderating factor. The experiment took approximately 60 min, including the training and vision tests. All participants were financially compensated for their participation. Participants’ color vision was tested using the Ishihara color blindness test. Participants had at least 20/25 visual acuity, tested by a Snellen chart and good contrast sensitivity (1.8/1.95 or better) tested using the Pelli–Robson test.
2.2. Stimuli
Images were randomly displayed on a calibrated 32-inch LCD monitor (Display ++, Cambridge Research Systems, UK) that were scaled to the same height (709 pixels) using MATLAB® Psychtoolbox (v3). The monitor was calibrated using Spyder 5 Pro (Datacolor, Lawrenceville, NJ, USA) before the experiment to ensure color accuracy. However, as the study used a single display and fixed viewing conditions, generalizability to other display settings may be limited. In front of a white wall, the display was set on a gray desk. The visual stimuli were presented around at a horizontal visual angle of 49° and a vertical visual angle of 30° while the participants were 0.635 m away from the screen, as shown in Figure 1. Flicker-free, neutral white fluorescent lighting (3869 K ± 3 K, Duv = 0.0077 ± 0.0001, CRI Ra = 85, R9 = 12) illuminated the experiment space to eliminate the effects of chromatic lighting [46]. The neutral background was chosen to minimize adaptation effects and ensure consistent contrast perception. The luminance distribution of the viewing environment was not explicitly measured, which is acknowledged as a limitation. The average vertical illumination was 82 lx ± 2 lx at the participants’ eye level, whereas the average horizontal illumination on the desk was 285 lx ± 4 lx at 0.7 m from the floor (1.2 m from the floor) measured using a calibrated CL-500A illuminance spectrophotometer (Konica Minolta, Ramsey, NJ, USA). The luminance of the gray background was 45 cd/m2 ± 4 cd/m2, the brightest point was 90 cd/m2 ± 2 cd/m2, and the dimmest point was 1.7 cd/m2 ± 0.9 cd/m2, measured using an LS-100 luminance meter (Konica Minolta, Ramsey, NJ, USA).

Figure 1.
Participants, positioned 0.64 m away from the calibrated display, made judgments using a 9-point scale.
Twenty images of indoor environments representing ten different types of indoor architectural settings (offices, homes, schools, sports arenas, restaurants, retail shops, industrial spaces, hospitals, museums, and places of worship) were obtained from an online database [47]. Images were selected to represent a range of indoor environments, including simple and complex spaces with diverse color distributions (from low to high colorfulness) using four image quality metrics, as shown in Table 1. Spatial information (SI) [48] and suprathreshold visual complexity (Rspt) [49] were used to quantify the visual complexity of images and to ensure that the images ranged from simple to complex environments. For reference, typical values for SI range between 0 and 110 and for Rspt range between 0 and 600. Similarly, two colorfulness metrices, CIELAB chroma C*ab [50] and colorfulness M [51], show that images widely varied in terms of colorfulness. Similarly, for reference, typical values for C*ab range between 0 and 80 and for M range between 0 and 110. The selection aimed to capture the visual diversity found in real-world architectural settings, ensuring relevance to practical applications in design and lighting.

Table 1.
Complexity and colorfulness distribution of the stimuli.
Forty new images were generated by increasing the colorfulness of either the red–green (RG) or yellow–blue (YB) parts of the original (OG) images using Adobe Photoshop® (v22.0). During the image processing procedure, the red, green, yellow, and blue portions of the images were selected using the Photoshop “color range” tool. The saturation of these selected sections was then increased by 100% twice (a total of 200% saturation increase). The 200% saturation increase was chosen based on preliminary testing to achieve a noticeable enhancement of color contrast while maintaining the overall realism of the images. The average pixel color difference between stimuli were calculated using MATLAB (v2019) functions for the CIELAB 1976 ΔE*ab and CIEDE2000 (ΔE00) [50]. The average OG-RG differences were ΔE*ab = 4.3 and ΔE00 = 2.4, and the average OG–YB differences were ΔE*ab = 4.4 and ΔE00 = 2.4, both above a just-noticeable difference (JND) [52], while the average grayscale brightness was maintained (OG = 113, RG = 111, YB = 113), as shown in Table 1.
A total of 60 images were used as stimuli in this experiment. The subjective evaluations of ten of them were collected in Part I of a previous experiment [53], and in Part II, the same participants were asked to rate their perception of fifty images (10 RG from Part I OG, 10 YB from Part I OG, 10 OG for Part II, 10 RG for Part II, 10 YB for Part II). The ten images used in Part I were set as the original (OG) images. While the spatial distribution of RG and YB colors (e.g., the location of reds in an image varied across images) was not explicitly quantified, images were manually selected to include both simple and complex indoor environments with varied color distributions to ensure a representative sample. To offer a range of values (extremely high and very low) for each evaluated image quality assessment metric, the image quality was calculated in advance. Images were chosen to depict a variety of perceived levels of visual complexity (simple vs. complicated) and color vibrancy (achromatic vs. colorful). Three examples of original images, RG-enhanced images, and YB-enhanced images are shown in Figure 2. Due to the complexity of the stimuli, subtle color differences may be challenging to discern in a small format. High-resolution versions of these images have been made available in an online data repository for detailed examination (see the Data Availability Statement for the link).

Figure 2.
Three examples of original images (left column) with red–green (middle column) and yellow–blue (right column) enhanced images.
2.3. Procedure
Before the experiment, the participants were provided with a brief explanation of the protocol and the definition of each concept. The instructions were read from a script to reduce experimenter bias, and brief training was provided to address learning effects [54] and enable full chromatic adaptation [55]. The participants were asked to assess the visual preference, visual clarity, visual complexity, and colorfulness of each image (in this order) using a wireless number pad. The participants’ response time was also recorded. Figure 1 illustrates the interface with a 9-point Likert-type scale and progress indicator in the top-left corner. The bipolar scales ranged from “Extremely unclear” to “Extremely clear” for visual clarity and “Not colorful” to “Extremely colorful” for colorfulness. To decrease bias and improve the reliability of the scales, a separate “I do not know/I do not care” option was added [56].
3. Results
Parametric test assumptions were checked using the Shapiro–Wilk test for normality and Bartlett’s test for the homogeneity of variance. The statistical difference in visual clarity among OG, RG, and YB images was not apparent. The significance of the experimental factors was evaluated using a one-way ANOVA to test the effects of color contrast on the perceived preference, colorfulness, clarity, and complexity. The main effects of color contrast on the perceptual quality of preference (F(2,57) = 0.844, p > 0.05), colorfulness (F(2,57) = 0.810, p > 0.05), clarity (F(2,57) = 0.143, p > 0.05), and complexity (F(2,57) = 0.101, p > 0.05) were not statistically significant. There was no significant difference in visual clarity and visual colorfulness for original, RG, and YB images, as shown in Figure 3.
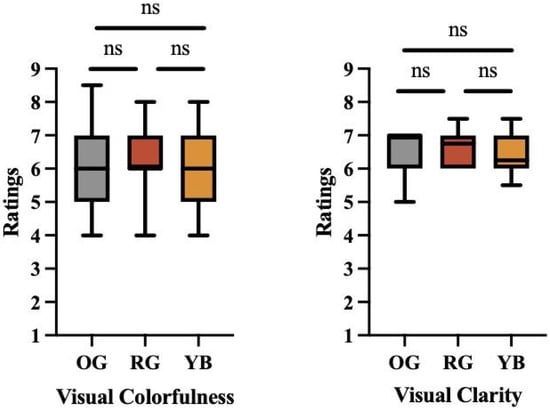
Figure 3.
There were no statistically significant differences in visual (perceived) colorfulness and visual clarity between original (OG), red–green (RG) enhanced, or yellow–blue (YB) enhanced images.
The distribution of visual clarity as a function of visual colorfulness is shown in Figure 4. The results indicated that overall visual clarity was not highly correlated with colorfulness, but there was an increasing trend. After removing data from four participants who were older than 52, the results did not change, indicating that age was not a major factor. Given that the majority of participants were young adults, the results primarily reflect the visual perceptions of this demographic.
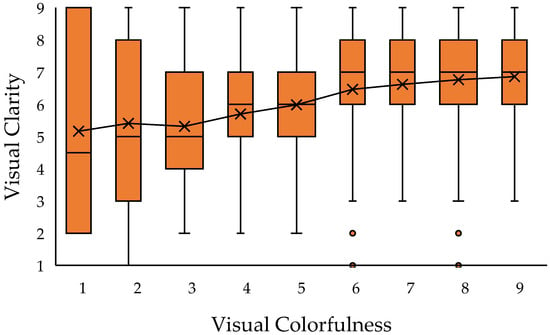
Figure 4.
The distribution of visual clarity scores across visual (perceived) colorfulness reveals an increasing trend for clarity with higher levels of colorfulness.
The limited range of color contrast adjustments, coupled with inherent variability in image characteristics, may have contributed to the lack of statistically significant differences. Variability in the effectiveness of the color selection tool may have introduced inconsistencies in contrast enhancement, as the software struggled to uniformly adjust hues across different saturation and lightness levels. This suggests that while the manipulated color contrast levels were not sufficient to produce statistically significant differences, colorfulness may still contribute to perceptual clarity in subtle ways. A summary of the key findings is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Summary of key findings across conditions.
4. Discussion
The results of this study suggest that color contrast increases in opponent systems (red–green or yellow–blue) in complex visual indoor environmental images do not significantly impact visual clarity. However, an observable trend of increasing visual clarity was evident with the increase in perceived colorfulness (with a small effect size per Cohen’s d = 0.17), despite the lack of statistical significance. This trend aligns with the general notion indicating that increased colorful contrast can enhance visual discrimination and perceived structure in an environment. By expanding the range of colorfulness of the stimuli, a substantial correlation between visual clarity and colorfulness might be revealed in future studies. Similarly, reducing the complexity of observed images could potentially highlight a significant effect of color contrast on visual clarity. In summary, there is a need for more controlled studies to identify the threshold for both image complexity (using less complex images) and color contrast (using increased colorfulness) where a perceived effect takes place.
While there was no statistically significant impact of color contrast on visual clarity, the trend toward an increase in clarity with colorfulness indicated the importance of visual complexity in perceptual judgments. While past studies utilized solid color samples devoid of contextual information, it is likely that increasing visual complexity requires more cognitive load and reduces the relative importance of color contrast, echoing previous research [57,58]. Therefore, the non-significant study findings can be interpreted in the context of color perception and cognitive load theory. In simpler visual scenes, color contrast may play a more dominant role in clarity judgments, whereas in complex environments, other factors such as texture, luminance contrast, and object recognition demands may overshadow color-based effects. Since spatially complex images require analysis and judgments of a large number of borders, it is not surprising that participants’ higher-level perceptual responses to color contrast were muted.
In addition to color perception, border detection also plays a key role in this study. Border detection relies on specialized neurons in the visual cortex that are sensitive to edges and boundaries, enabling the recognition of objects and distinction from their background [59]. Visual perception involves intricate neural processes that integrate visual information from different parts of the retina, resulting in a coherent and meaningful representation of the surrounding world. Color contrast processing, in turn, plays a role in processing the differences in color and brightness in the field of view, influencing depth perception and the identification of object contours [60]. Understanding these mechanisms enhances our knowledge of human vision and holds implications in various fields, including architectural design, image processing, and computer vision.
Valuable insights were generated by this study, but it is vital to acknowledge its limitations. Notably, the color contrast ranges were limited due to the image editing software’s color selection operations. When prompted to select a color, the software encountered challenges in detecting the target hue across all saturation and lightness levels. The potential influence of demographic factors such as age and gender on color perception was not analyzed in this study. Given known variations in color vision across different populations, future research could investigate these effects in more detail. Additionally, it is worth noting that there was considerable variability in the proportion of RG and YB colors in each image, as expected from realistic visual environments. This variability implies a lack of constant spatial emphasis, which might impact saliency and other cognitive aspects. Also, some of the stimuli contained prominently RG and YB components, whereas the others exhibited a relatively lower prevalence of RG and YB channels, as most real-world architectural spaces do. In future studies, it would be advantageous to explore a wider range of color contrast values through the systematic desaturation of images. By deliberately manipulating the saturation levels, researchers can discern the impact of color contrast on perceptual attributes, including visual preference, clarity, complexity, colorfulness, and interest.
In summary, the human visual system is undeniably complex and exhibits a higher sensitivity to relative information rather than absolute values. By utilizing relative information, the human visual system can effectively make judgments of color contrast, brightness, and spatial relationships within a given scene. This comparison of relative intensities and color differences between objects and their surroundings allows viewers to perceive and interpret the visual world around them, playing a crucial role in tasks like object recognition, depth perception, and scene understanding. The results of this study emphasize the need for further exploration using complex visual environments to investigate the subjective and cognitive processes influenced by physical stimuli. Additionally, future work should explore whether different lighting conditions, material properties, or dynamic image stimuli could amplify the observed trends, offering new insights into the practical implications of color contrast in real-world settings. The improved understanding of visual clarity has implications in various fields, such as intelligent lighting systems based on image capturing devices [61], computer vision algorithms [62], and image processing techniques [63]. Future research holds the promise of providing deeper insights into the effects of color contrast, which may be impacted by factors such as the distance, composition, size, and texture of the elements within the visual field.
5. Conclusions
This study aims to investigate the effects of color contrast on diverse perceptual aspects, encompassing visual preference, clarity, complexity, and colorfulness. In this study, color contrast did not manifest any statistically significant impact on the visual clarity of the selected indoor environmental images. However, a trend was found, which implicates a linear relationship between perceived visual clarity and colorfulness. Given the methodological constraints, including image variability and software limitations, the findings should be interpreted with caution, and further controlled studies are necessary to validate the observed trends. Nonetheless, these findings align with earlier observational studies, such as the work by Richardson and Saunders, which suggested that detecting color changes in complex visual environments is more challenging [64]. While the null findings might seem discouraging for some, the results can be considered good news for advanced museum lighting systems designed to optimize light source spectra for a group of colors that have a similar hue to reduce damage to paintings [65]. This study extends prior research by testing the “color contrast–visual clarity” hypothesis in complex indoor environments rather than simplified stimuli. By sharing null results, it also contributes to addressing publication bias and highlights the need for refined methodologies in perceptual research. In addition, the authors believe that the findings from this study make an important contribution to the literature since sharing null results with the broader research community can help fight publication bias [66].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.D.; methodology, D.D.; software, Y.W.; validation, D.D. and Y.W.; formal analysis, Y.W.; investigation, Y.W.; resources, D.D.; data curation, Y.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.W.; writing—review and editing, D.D.; visualization, Y.W.; supervision, D.D.; project administration, D.D.; funding acquisition, D.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and the protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Pennsylvania State University (STUDY00017322) on [13 April 2021].
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in this study.
Data Availability Statement
The original data presented in this study are openly available in ScholarSphere at https://doi.org/10.26207/5av2-ya15 (accessed on 31 March 2025).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Cho, J.Y.; Suh, J. Spatial Color Efficacy in Perceived Luxury and Preference to Stay: An Eye-Tracking Study of Retail Interior Environment. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, J.; Gouaich, Y.; Manav, B. Preference for Accent and Background Colors in Interior Architecture in Terms of Similarity/Contrast of Natural Color System Attributes. Color Res. Appl. 2022, 47, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmus, D.; Wang, T.; Gonzalez, C.; Kore, R. Role of Lighting and Color in Microeconomics: Preference and Purchase Intent. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1320, 012024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Z.; Le, W.; Guo, B.; Yin, H. Analysis of Factors Affecting Visual Comfort in Hotel Lobby. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowska, A.; Olejnik-Krugly, A.; Jankowski, J.; Dziśko, M. Subjective and Objective User Behavior Disparity: Towards Balanced Visual Design and Color Adjustment. Sensors 2021, 21, 8502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, M.; Wang, C.; Li, L. Impact of Indoor Visual Environment on Emotional and Behavioral Symptoms of Older People with Dementia. Build. Environ. 2024, 265, 111980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomassoni, R.; Galetta, G.; Treglia, E. Psychology of Light: How Light Influences the Health and Psyche. PSYCH 2015, 6, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manav, B. Color-emotion Associations, Designing Color Schemes for Urban Environment-architectural Settings. Color Res. Appl. 2017, 42, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.H.; Jeon, J. A Study on Color Conspicuity and Color Harmony of Wayfinding Signs According to Outdoor Environment Types. Color Res. Appl. 2022, 47, 1259–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yao, Q.; Yang, Z.; Qin, B.; Chen, S.; Xu, W.; Wu, P.; Hao, K.; Shen, Y.; Wang, D.; et al. Spectrum Mapping Technology Based Creation of a Color-Contrast Reading Environment to Reach Comfort and Clarity. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 13208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.H.; Lee, S. Does Interior Color Contrast Enhance Spatial Memory? Color Res. Appl. 2020, 45, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpert, P.; Englund, J.-E.; Sang, Å.O. Shades of Green for Living Walls—Experiences of Color Contrast and Its Implication for Aesthetic and Psychological Benefits. Nat.-Based Solut. 2023, 3, 100067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLachlan, F.; Leng, X. Colour Here, There, and In-between—Placemaking and Wayfinding in Mental Health Environments. Color Res. Appl. 2021, 46, 125–139. [Google Scholar]
- Güneş, E.; Olguntürk, N. Color-emotion Associations in Interiors. Color Res. Appl. 2020, 45, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aston, S.M.; Bellchambers, H. Illumination, Colour Rendering and Visual Clarity. Light. Res. Technol. 1969, 1, 259–261. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.-L.; Yu, C.-Y. The Relationship between Visual Acuity and Color Contrast in the OSA Uniform Color Space. Color Res. Appl. 1996, 21, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Vrabel, P.L.; Bernecker, C.A.; Mistrick, R.G. Visual Performance and Visual Clarity under Electric Light Sources: Part 2—Visual Clarity. J. Illum. Eng. Soc. 1998, 27, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belichambers, H.; Godby, A. Illumination, Colour Rendering and Visual Clarity. Light. Res. Technol. 1972, 4, 104–106. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, J.E.; Spencer, T.J.; Martyniuk, O.; Hendrick, C. Interim Study of Procedures for Investigating the Effect of Light on Impression and Behavior. J. Illum. Eng. Soc. 1973, 3, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, J.E.; Spencer, T.J. The Effects of Light Source Color on User Impression and Satisfaction. J. Illum. Eng. Soc. 1977, 6, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrabel, P.; Bernecker, C.; Mistrick, R. Visual Performance and Visual Clarity under Electric Light Sources: Part 1—Visual Performance. J. Illum. Eng. Soc. 1995, 24, 69–80. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto, K.; Nayatani, Y. Visual Clarity and Feeling of Contrast. Color Res. Appl. 1994, 19, 171–185. [Google Scholar]
- McKeefry, D.J.; Murray, I.J.; Kulikowski, J.J. Red–Green and Blue–Yellow Mechanisms Are Matched in Sensitivity for Temporal and Spatial Modulation. Vis. Vision. Res. 2001, 41, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansley, B.W.; Boynton, R.M. A Line, Not a Space, Represents Visual Distinctness of Borders Formed by Different Colors. Science 1976, 191, 954–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansley, B.W.; Valberg, A. Chromatic Border Distinctness: Not an Index of Hue or Saturation Differences. J. Opt. Soc. Am. JOSA 1979, 69, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valberg, A.; Tansley, B.W. Tritanopic Purity-Difference Function to Describe the Properties of Minimally Distinct Borders. J. Opt. Soc. Am. JOSA 1977, 67, 1330–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurvich, L.M.; Jameson, D. An Opponent-Process Theory of Color Vision. Psychol. Rev. 1957, 64, 384. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, R.W.G.; Pointer, M.R. Measuring Colour; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 1-119-97537-9. [Google Scholar]
- Worthey, J.A. An Analytical Visual Clarity Experiment. J. Illum. Eng. Soc. 1985, 15, 239–251. [Google Scholar]
- Durmus, D.; Davis, W. Blur Perception and Visual Clarity in Light Projection Systems. Opt. Express 2019, 27, A216–A223. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Guo, W.; Ji, R. Image Quality Assessment for Color Correction Based on Color Contrast Similarity and Color Value Difference. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2018, 28, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maule, J.; Skelton, A.E.; Franklin, A. The Development of Color Perception and Cognition. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2023, 74, 87–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Wijntjes, M.; Eisemann, E.; Pont, S. Effects of Inter-Reflections on the Correlated Colour Temperature and Colour Rendition of the Light Field. Light. Res. Technol. 2023, 55, 772–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellia, L.; Fragliasso, F.; Stefanizzi, E. Effects of Light Source Spectrum and Background Colour on the Perception of Paintings. Light. Res. Technol. 2020, 52, 36–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charrier, C.; Lebrun, G.; Lezoray, O. A Machine Learning-Based Color Image Quality Metric. Conf. Colour Graph. Imaging Vis. 2006, 3, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weingerl, P.; Hladnik, A.; Javoršek, D. Development of a Machine Learning Model for Extracting Image Prominent Colors. Color Res. Appl. 2020, 45, 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Egger, R. Color and Engagement in Touristic Instagram Pictures: A Machine Learning Approach. Ann. Tour. Res. 2021, 89, 103204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, D.J.; Fang, L.; Ma, Z. Deep Learning for Camera Data Acquisition, Control, and Image Estimation. Adv. Opt. Photon. 2020, 12, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadler, E.O.; Darragh-Ford, E.; Desikan, B.S.; Conaway, C.; Chu, M.; Hull, T.; Guilbeault, D. Divergences in Color Perception between Deep Neural Networks and Humans. Cognition 2023, 241, 105621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaglarz, A. Perception of Color in Architecture and Urban Space. Buildings 2023, 13, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza-Sanhueza, C.; Hébert, M.; Lalonde, J.-F.; Demers, C. Evaluating Spatial Attributes of Surface Colors Under Daylight and Electrical Lighting in Sustainable Architecture. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Yan, W. Research on the Colour Preference and Harmony of the TWO-COLOUR Combination Buildings. Color Res. Appl. 2022, 47, 980–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, J.M.; Wilkerson, A.; Durmus, D.; Rodriguez-Feo Bermudez, E. Studying Response to Light in Offices: A Literature Review and Pilot Study. Buildings 2023, 13, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, Y.; Xing, L.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, X. Influence of Text Luminance, Text Colour and Background Luminance of Variable-Message Signs on Legibility in Urban Areas at Night. Light. Res. Technol. 2021, 53, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A Flexible Statistical Power Analysis Program for the Social, Behavioral, and Biomedical Sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmus, D. Correlated Color Temperature: Use and Limitations. Light. Res. Technol. 2022, 54, 363–375. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Lapedriza, A.; Khosla, A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Places: A 10 Million Image Database for Scene Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 1452–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ITU-T P.910; Subjective Video Quality Assessment Methods for Multimedia Applications. International Telecommunication Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- Durmus, D. Spatial Frequency and the Performance of Image-Based Visual Complexity Metrics. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 100111–100119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CIE 015:2018; Colorimetry. Commission Internationale de l’Eclairage: Vienna, Austria, 2018.
- Hasler, D.; Suesstrunk, S.E. Measuring Colorfulness in Natural Images. Int. Soc. Opt. Photonics 2003, 5007, 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, C.-H.; Hsu, Y.-H. Quality Assessment of Color Images Based on the Measure of Just Noticeable Color Difference. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Graphic and Image Processing, Hong Kong, China, 10 January 2014; p. 906925. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Durmus, D. Image Quality Metrics, Personality Traits, and Subjective Evaluation of Indoor Environment Images. Buildings 2022, 12, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, M.; Houser, K.; Durmus, D.; Esposito, T.; Wei, M. Recommended Methods for Conducting Human Factors Experiments on the Subjective Evaluation of Colour Rendition. Light. Res. Technol. 2022, 54, 199–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevell, S.K. The Time Course of Chromatic Adaptation. Color Res. Appl. 2001, 26, S170–S173. [Google Scholar]
- Chyung, S.Y.; Roberts, K.; Swanson, I.; Hankinson, A. Evidence-based Survey Design: The Use of a Midpoint on the Likert Scale. Perform. Improv. 2017, 56, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Harper, S.; Michailidou, E.; Stevens, R. Toward a Definition of Visual Complexity as an Implicit Measure of Cognitive Load. ACM Trans. Appl. Percept. TAP 2009, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Tan, Z.; Liu, J. Experimental Study on the Relationship between the Harmony and Cognitive Load of Business Intelligence Dashboard Color Combinations. Color Res. Appl. 2022, 47, 920–941. [Google Scholar]
- Craft, E.; Schutze, H.; Niebur, E.; von der Heydt, R. A Neural Model of Figure–Ground Organization. J. Neurophysiol. 2007, 97, 4310–4326. [Google Scholar]
- Roe, A.W.; Chelazzi, L.; Connor, C.E.; Conway, B.R.; Fujita, I.; Gallant, J.L.; Lu, H.; Vanduffel, W. Toward a Unified Theory of Visual Area V4. Neuron 2012, 74, 12–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Durmus, D. Variability in Image Quality Assessment Metrics with Different Image Capturing Devices. In Optical Devices and Materials for Solar Energy and Solid-State Lighting; Optica Publishing Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2022; p. PvM3H.5. [Google Scholar]
- Kruger, N.; Janssen, P.; Kalkan, S.; Lappe, M.; Leonardis, A.; Piater, J.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.J.; Wiskott, L. Deep Hierarchies in the Primate Visual Cortex: What Can We Learn for Computer Vision? IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 35, 1847–1871. [Google Scholar]
- Jobson, D.J.; Rahman, Z.; Woodell, G.A. A Multiscale Retinex for Bridging the Gap between Color Images and the Human Observation of Scenes. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1997, 6, 965–976. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, C.; Saunders, D. Acceptable Light Damage—A Preliminary Investigation. Stud. Conserv. 2007, 52, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kore, R.; Durmus, D. Optimizing Light Source Spectra for Art Conservation: Exploring Basic Color Groups. LEUKOS 2024, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munafò, M.; Neill, J. Null Is Beautiful: On the Importance of Publishing Null Results. J. Psychopharmacol. 2016, 30, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).