Effect of the Initial Damage State on the Seismic Behavior of A Five-Story CLT Building
Abstract
1. Introduction
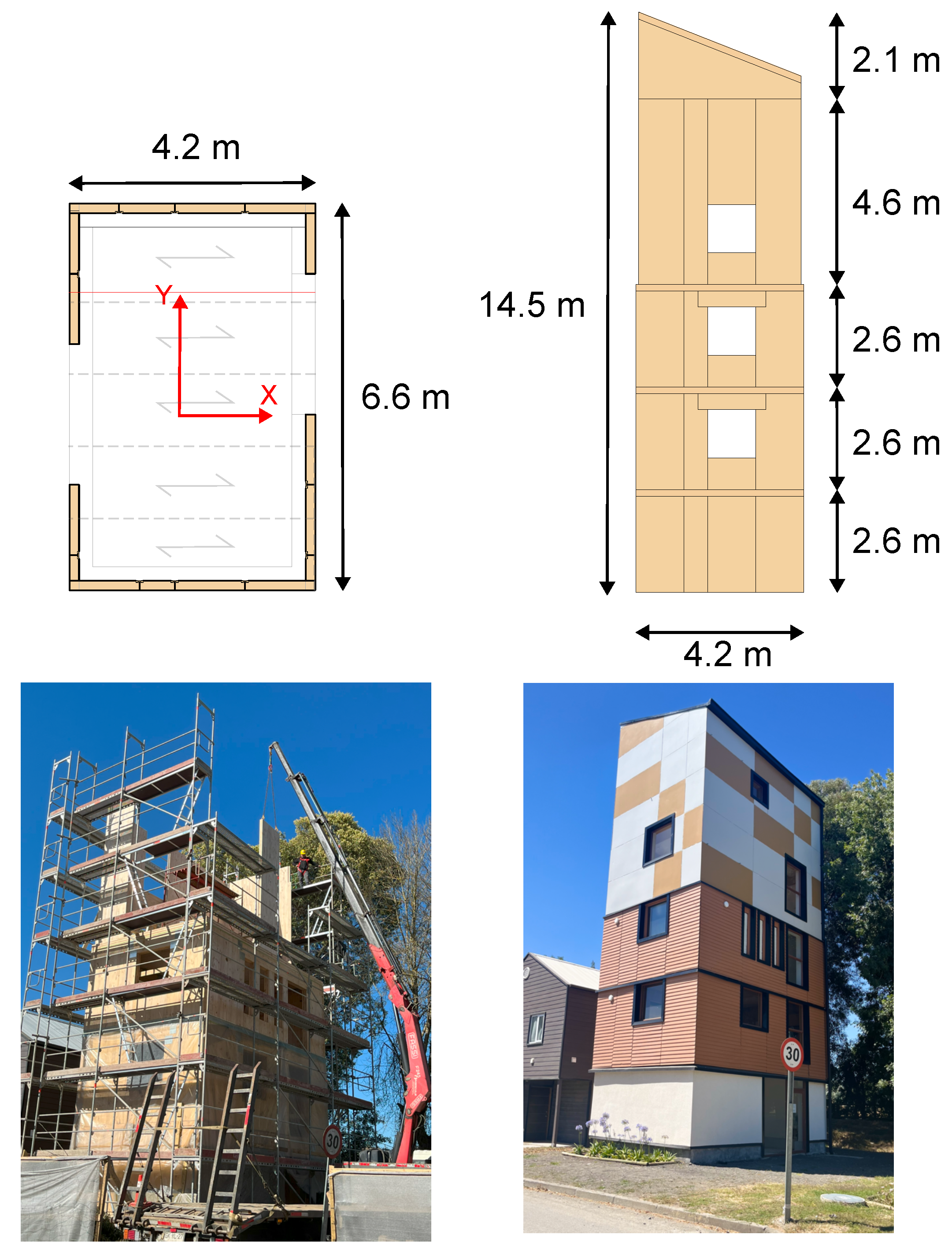
2. Prototype Building
2.1. Building Configuration
2.2. Seismic Design
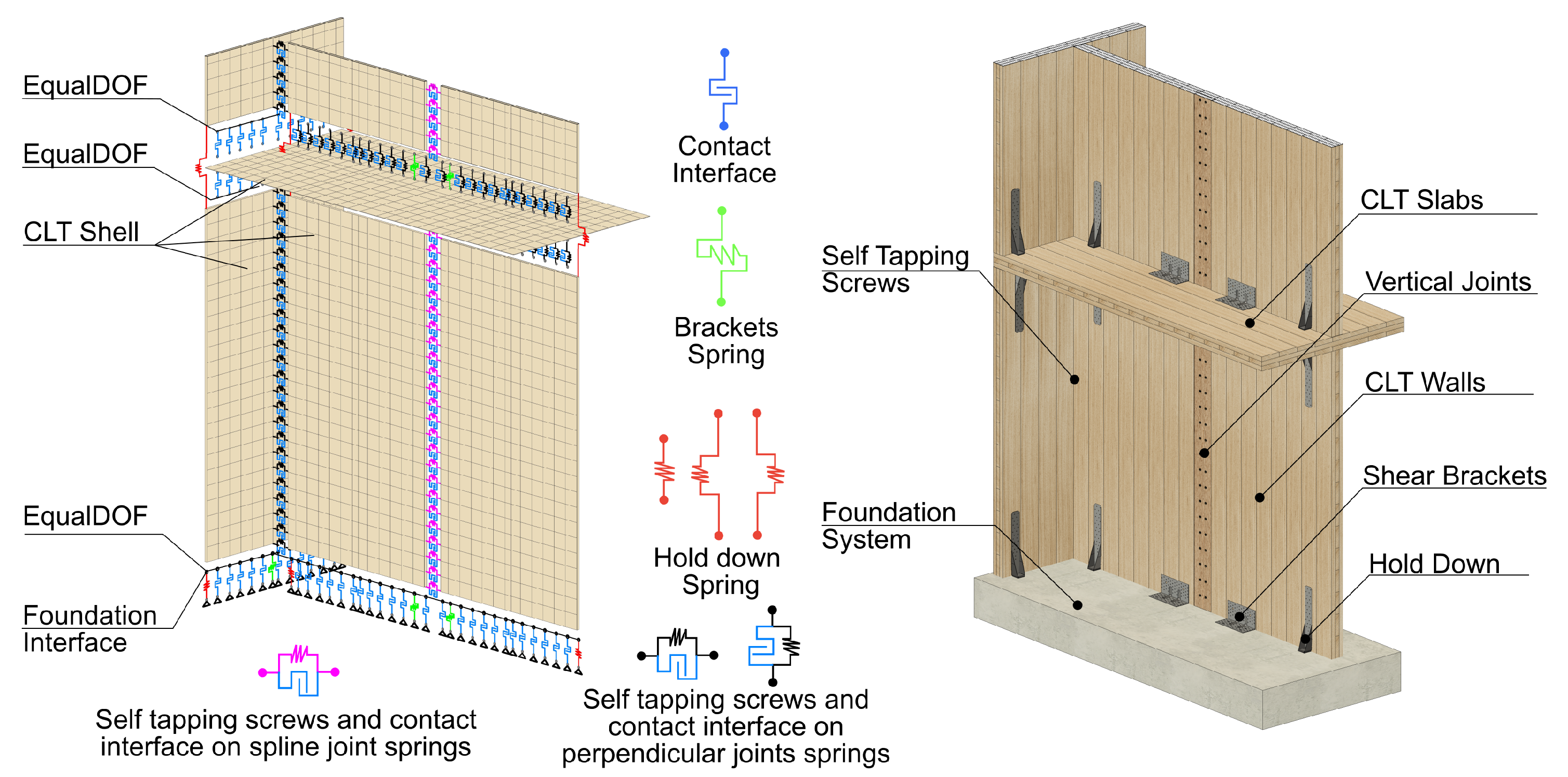
2.3. Construction Detailing
3. Model Development
3.1. Modeling Approach
3.2. Parallel Domain Decomposition
4. Model Validation
4.1. Lateral Deformation Mechanism
4.2. Global Dynamic Properties
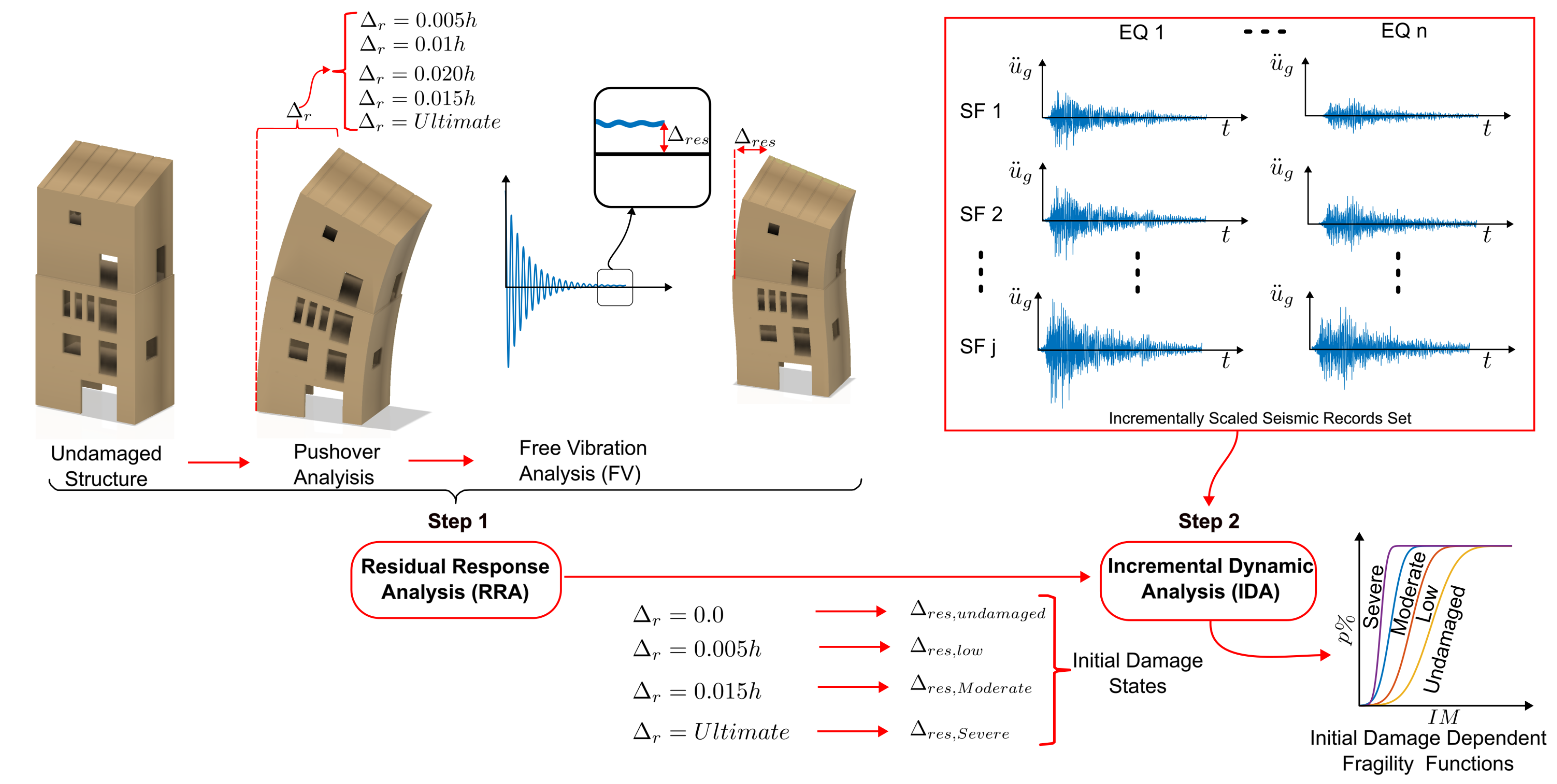
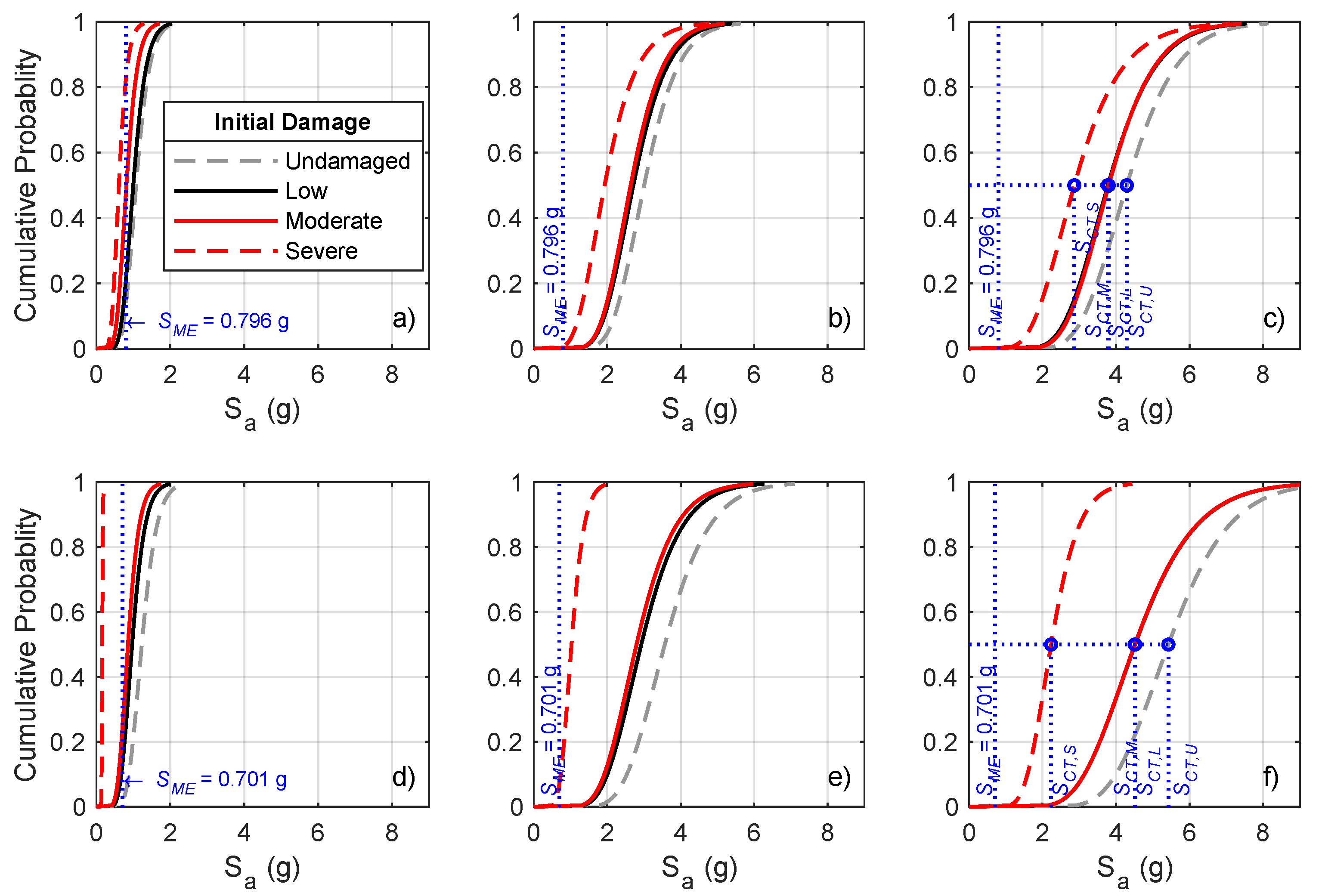
5. Initial Damage State Analysis Approach
5.1. Residual Response Analysis
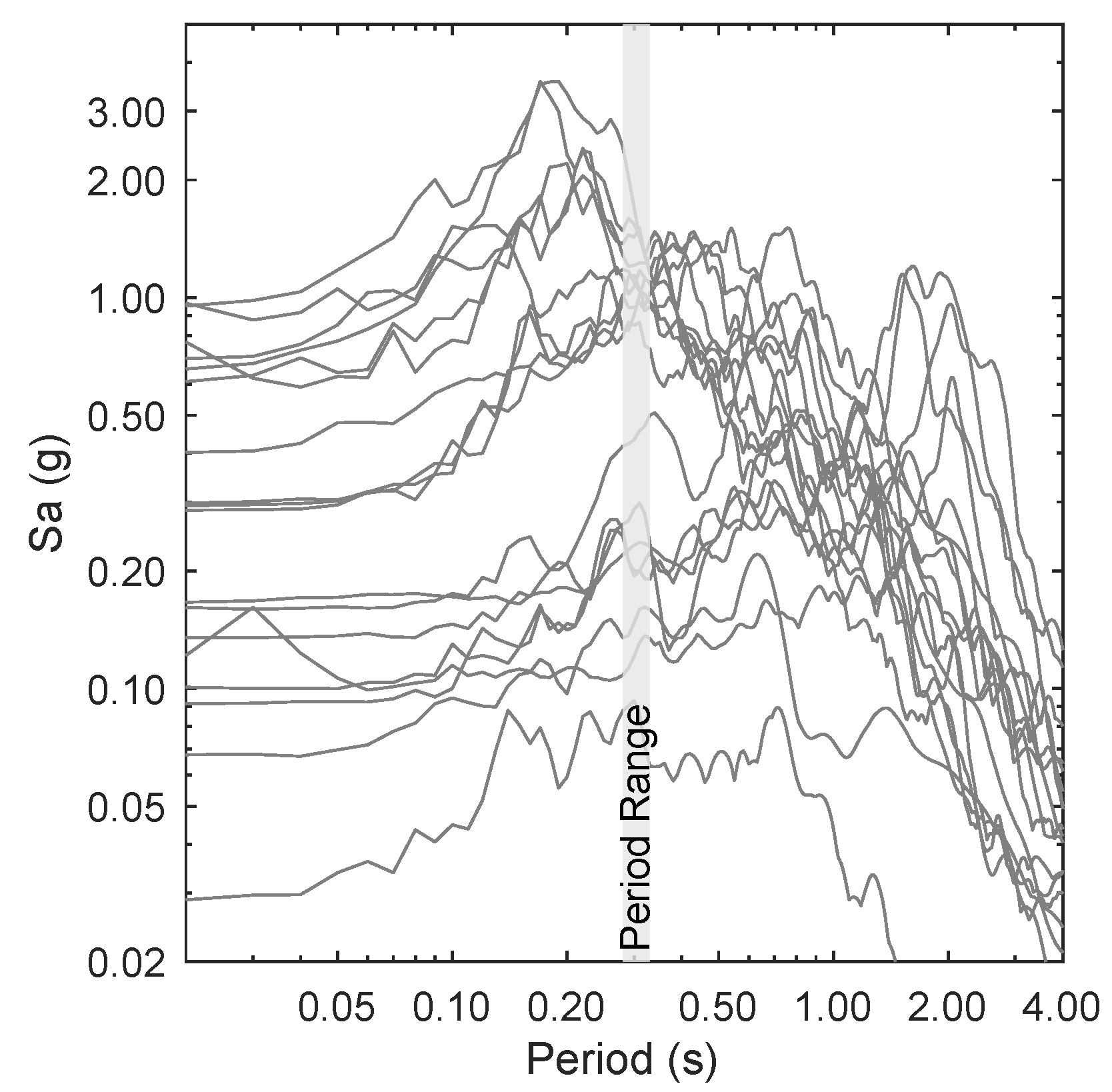
5.2. Seismic Fragility Evolution
6. Results and Discussion
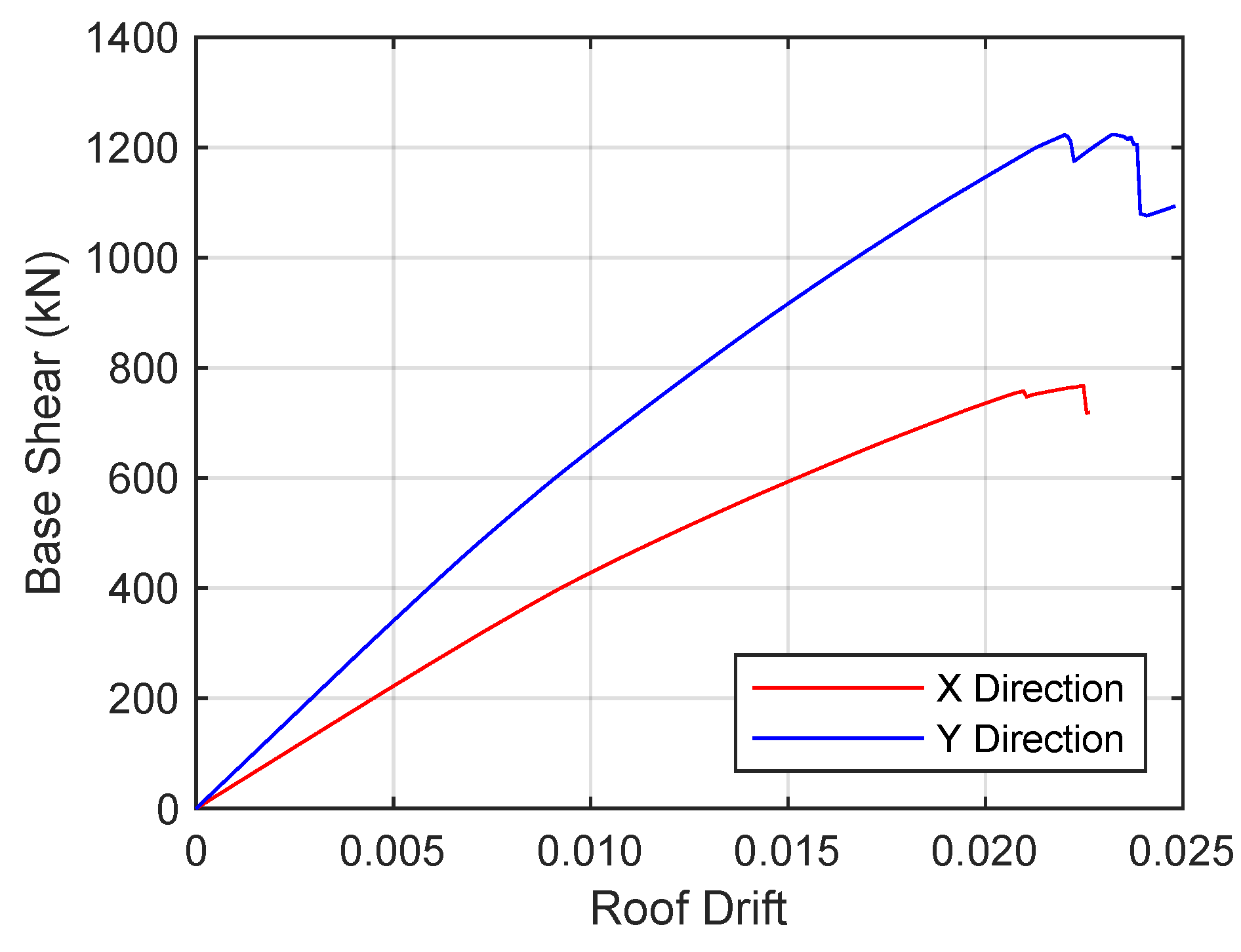
6.1. Global Lateral Load Response
6.2. Residual Response Results
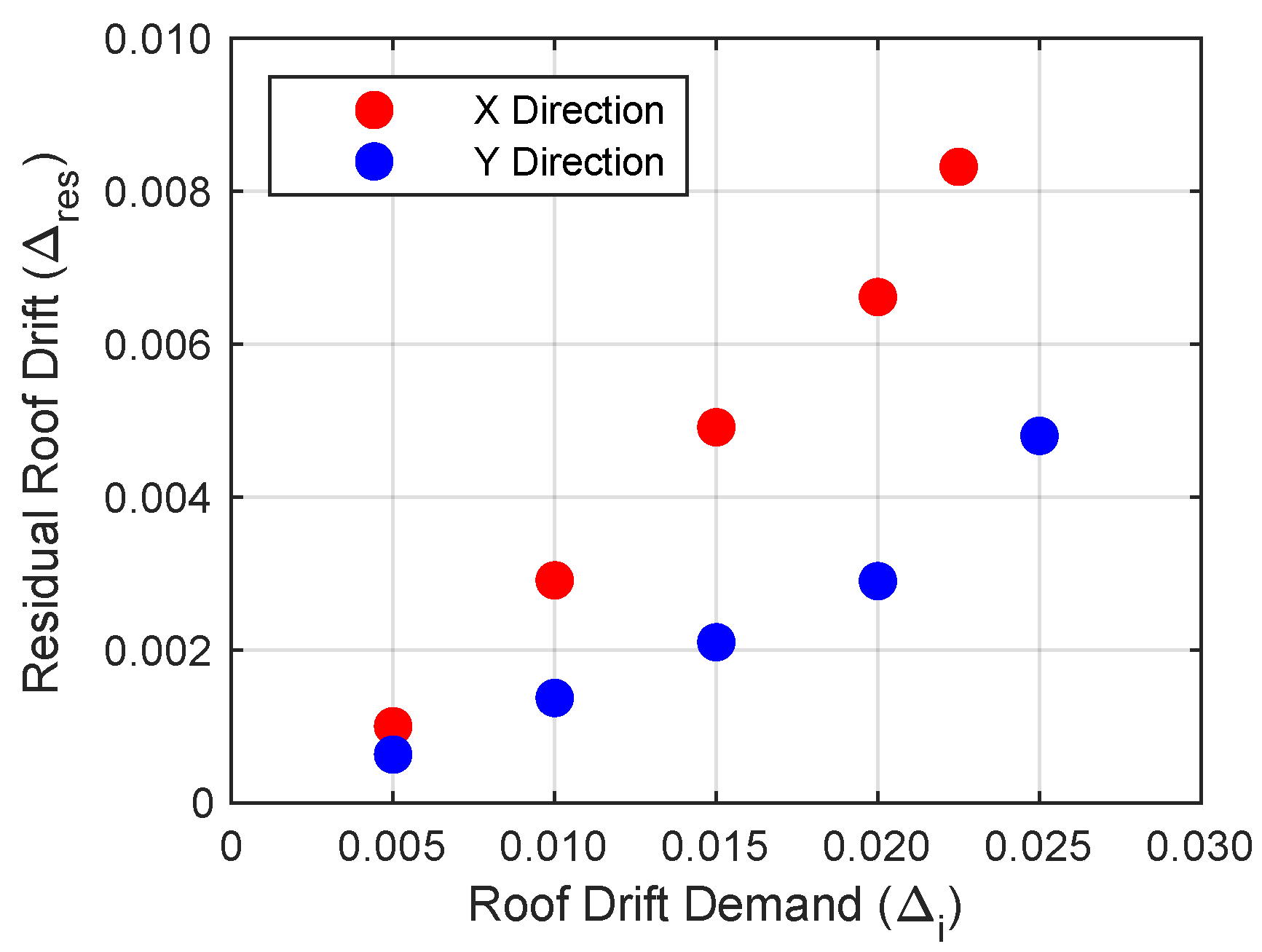
6.2.1. Static Nonlinear Analysis Residual Drift Response
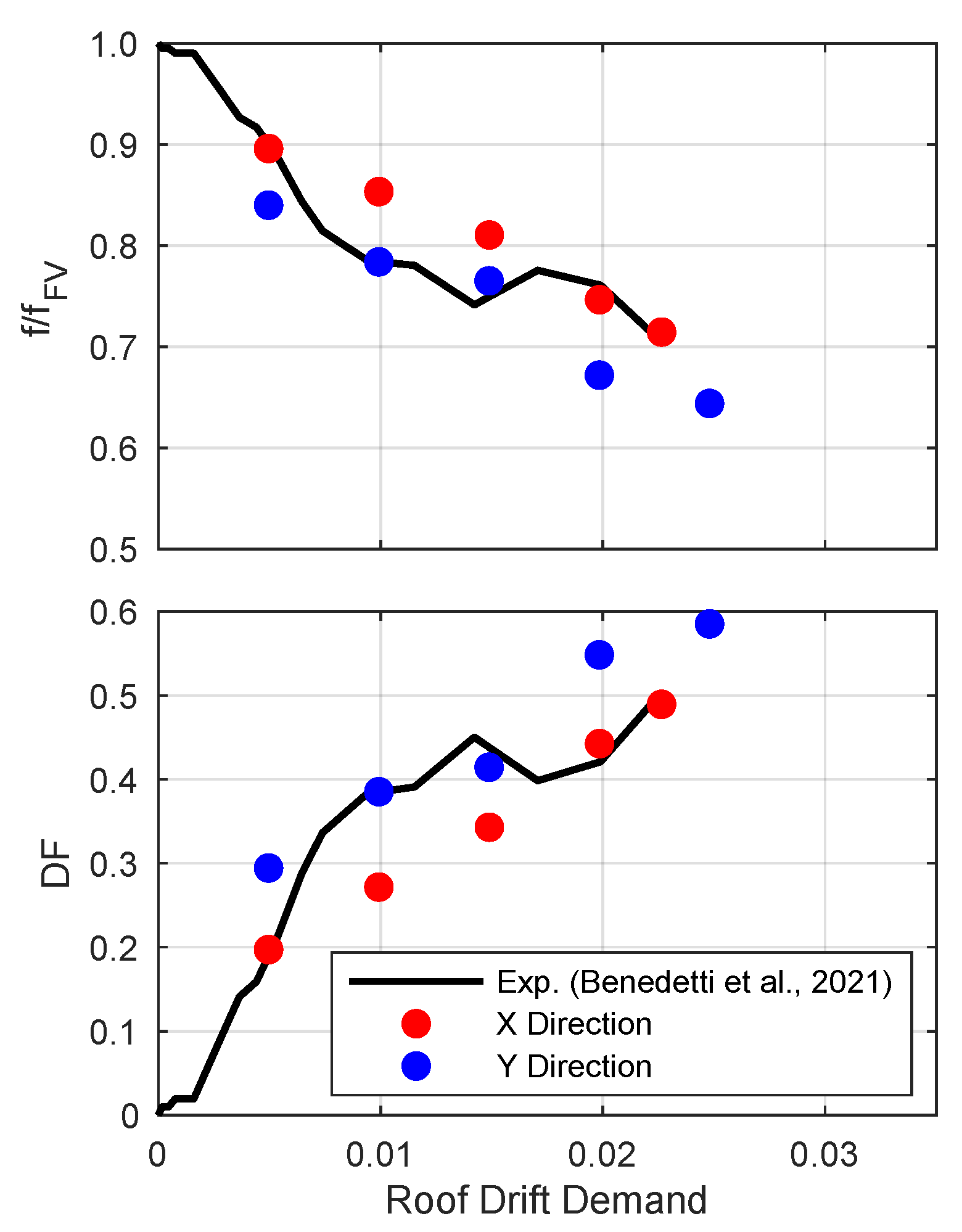
6.2.2. Fundamental Frequency Degradation
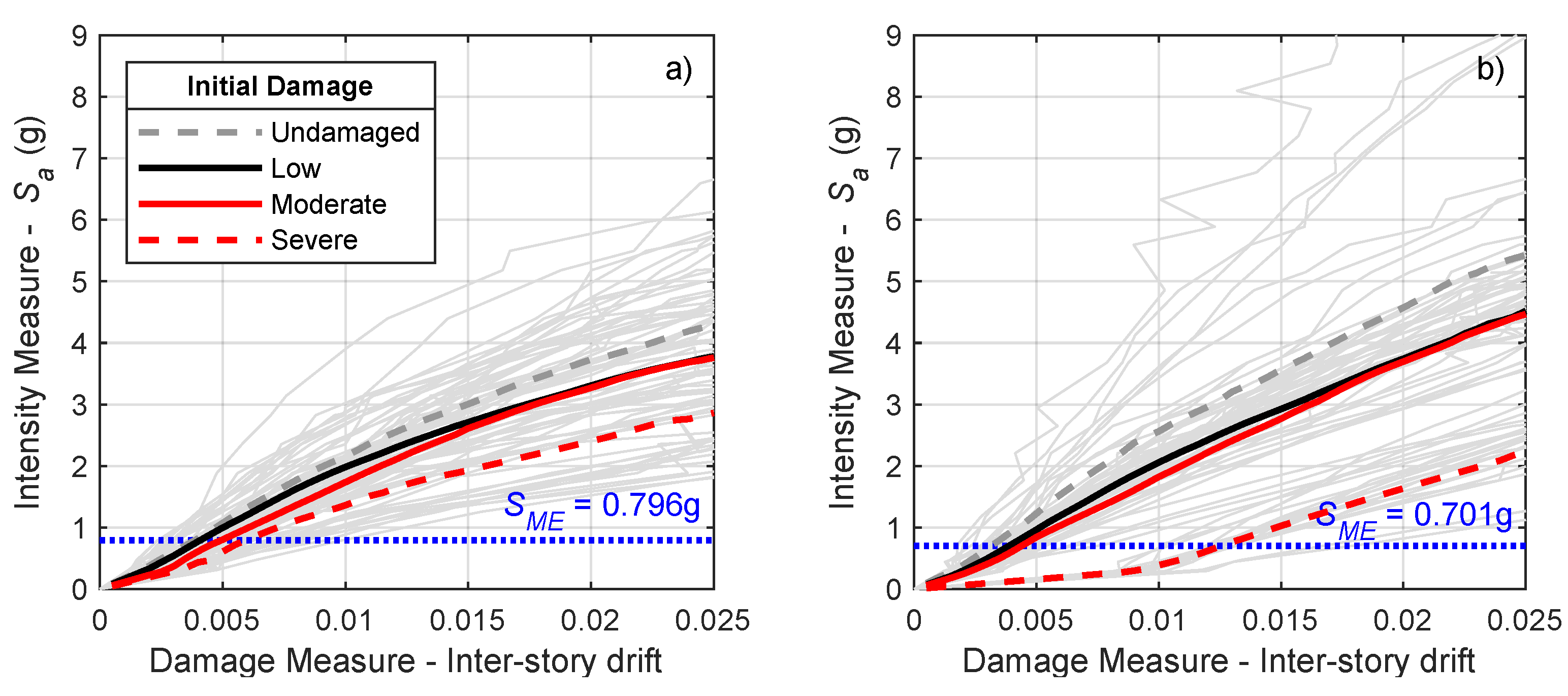
6.3. Seismic Fragility Assessment
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
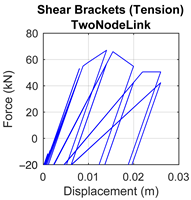
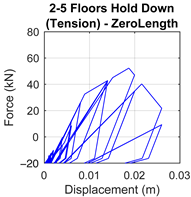
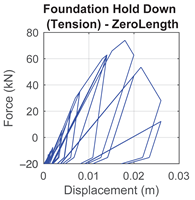
Appendix A. Summary of Connection Modeling Parameters
| Parameter | Connection Type | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Vertical Joints | Lintels |
Shear Brackets (Shear) |
Shear Brackets (Tension) |
2-5 Floors Hold Down |
Foundation Hold Down | |
| ePf1 (kN) | 7.38 | 105.12 | 92.62 | 71.20 | 52.52 | 50.0 |
| ePd1 (mm) | 3.88 | 2.460 | 6.11 | 7.24 | 8.92 | 7.0 |
| ePf2 (kN) | 11.50 | 147.00 | 105.00 | 78.00 | 62.42 | 80.0 |
| ePd2 (mm) | 12.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 13.81 | 13.0 |
| ePf3 (kN) | 13.29 | 174.84 | 110.11 | 88.19 | 72.33 | 94.0 |
| ePd3 (mm) | 26.60 | 15.00 | 12.20 | 14.50 | 18.70 | 18.0 |
| ePf4 (kN) | 5.00 | 139.88 | 98.35 | 70.57 | 12.48 | 25.0 |
| ePd4 (mm) | 35.00 | 16.30 | 18.30 | 21.70 | 32.93 | 30.0 |
| eNf1 (kN) | −7.38 | −105.12 | −92.62 | −71.20 | −52.52 | −50.0 |
| eNd1 (mm) | −3.88 | −2.460 | −6.11 | −7.24 | −8.92 | −7.0 |
| eNf2 (kN) | −11.50 | −147.00 | −105.00 | −78.00 | −62.42 | −80.0 |
| eNd2 (mm) | −12.00 | −10.00 | −10.00 | −10.00 | −13.81 | −13.0 |
| eNf3 (kN) | −13.29 | −174.84 | −110.11 | −88.19 | −72.33 | −94.0 |
| eNd3 (mm) | −26.60 | −15.00 | −12.20 | −14.50 | −18.70 | −18.0 |
| eNf4 (kN) | −5.00 | −139.88 | −98.35 | −70.57 | −14.46 | −25.0 |
| eNd4 (mm) | −35.00 | −16.30 | −18.30 | −21.70 | −32.93 | −30.0 |
| rDispP | 0.5 | 0.55 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| fForceP | 0.3 | 0.15 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| uForceP | −0.05 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.05 | −0.05 | −0.05 |
| rDispN | 0.5 | 0.55 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| fForceN | 0.4 | 0.15 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| uForceN | −0.05 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.05 | −0.05 | −0.05 |
| gK1 | −2.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −2.5 | −2.5 |
| gK2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| gK3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| gK4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| gKLim | −0.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −0.5 | −0.5 |
| gD1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| gD2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| gD3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| gD4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| gDLim | 0.08 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| gF1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| gF2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| gF3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| gF4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| gFLim | 0 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 |
| gE | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Damage Type | energy | energy | energy | energy | energy | energy |
References
- Shan, M.; Hwang, B.G.; Zhu, L. A Global Review of Sustainable Construction Project Financing: Policies, Practices, and Research Efforts. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Cui, X.; Yin, X.; Chen, Y.; Guo, H. Assessment of Energy Saving Potential by Replacing Conventional Materials by Cross Laminated Timber (CLT)—A Case Study of Office Buildings in China. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penfield, P.; Germain, R.; Smith, W.B.; Stehman, S.V. Assessing the adoption of Cross Laminated Timber by architects and structural engineers within the United States. J. Green Build. 2022, 17, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araujo, V.; Aguiar, F.; Jardim, P.; Mascarenhas, F.; Marini, L.; Aquino, V.; Santos, H.; Panzera, T.; Lahr, F.; Christoforo, A. Is Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT) a Wood Panel, a Building, or a Construction System? A Systematic Review on Its Functions, Characteristics, Performances, and Applications. Forests 2023, 14, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccotti, A.; Sandhaas, C.; Okabe, M.; Yasumura, M.; Minowa, C.; Kawai, N. SOFIE project—3D shaking table test on a seven-storey full-scale cross-laminated timber building. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2013, 42, 2003–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandner, R.; Flatscher, G.; Ringhofer, A.; Schickhofer, G.; Thiel, A. Cross laminated timber (CLT): Overview and development. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2016, 74, 331–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svatoš-Ražnjević, H.; Orozco, L.; Menges, A. Advanced Timber Construction Industry: A Review of 350 Multi-Storey Timber Projects from 2000 to 2021. Buildings 2022, 12, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baño, V.; Godoy, D.; Figueredo, D.; Vega, A. Characterization and Structural Performance in Bending of CLT Panels Made from Small-Diameter Logs of Loblolly/Slash Pine. Materials 2018, 11, 2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Lindt, J.W.; Amini, M.O.; Rammer, D.; Line, P.; Pei, S.; Popovski, M. Seismic Performance Factors for Cross-Laminated Timber Shear Wall Systems in the United States. J. Struct. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.L.; Schneider, J.; Tesfamariam, S.; Stiemer, S.F.; Mu, Z.G. Hysteresis behavior of bracket connection in cross-laminated-timber shear walls. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 48, 980–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavric, I.; Fragiacomo, M.; Ceccotti, A. Cyclic Behavior of CLT Wall Systems: Experimental Tests and Analytical Prediction Models. J. Struct. Eng. 2015, 141, e4015034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganey, R.; Berman, J.; Akbas, T.; Loftus, S.; Daniel Dolan, J.; Sause, R.; Ricles, J.; Pei, S.; Lindt, J.v.d.; Blomgren, H.E. Experimental Investigation of Self-Centering Cross-Laminated Timber Walls. J. Struct. Eng. 2017, 143, e4017135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, A.; Zarnani, P.; Masoudnia, R.; Quenneville, P. Experimental Testing of Rocking Cross-Laminated Timber Walls with Resilient Slip Friction Joints. J. Struct. Eng. 2018, 144, e4017180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumura, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Okabe, M.; Miyake, T.; Matsumoto, K. Full-Scale Tests and Numerical Analysis of Low-Rise CLT Structures under Lateral Loading. J. Struct. Eng. 2016, 142, E4015007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, F.; Rosales, V.; Opazo-Vega, A.; Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Jara-Cisterna, A. Experimental and numerical evaluation of hold-down connections on radiata pine Cross-Laminated-Timber shear walls: A case study in Chile. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2019, 77, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldin, G.; Amadio, C.; Fragiacomo, M. A component approach for the hysteretic behaviour of connections in cross-laminated wooden structures. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2013, 42, 2023–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavric, I.; Fragiacomo, M.; Ceccotti, A. Cyclic behaviour of typical metal connectors for cross-laminated (CLT) structures. Mater. Struct. 2014, 48, 1841–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietsch, P.; Brandner, R. Self-tapping screws and threaded rods as reinforcement for structural timber elements – A state-of-the-art report. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 97, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loss, C.; Piazza, M.; Zandonini, R. Connections for steel–timber hybrid prefabricated buildings. Part I: Experimental tests. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 122, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavric, I.; Fragiacomo, M.; Ceccotti, A. Cyclic behavior of typical screwed connections for cross-laminated (CLT) structures. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2015, 73, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Lindt, J.W.; Furley, J.; Amini, M.O.; Pei, S.; Tamagnone, G.; Barbosa, A.R.; Rammer, D.; Line, P.; Fragiacomo, M.; Popovski, M. Experimental seismic behavior of a two-story CLT platform building. Eng. Struct. 2019, 183, 408–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovski, M.; Gavric, I. Performance of a 2-Story CLT House Subjected to Lateral Loads. J. Struct. Eng. 2016, 142, e4015006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, F.T.; Branco, J.M.; Rocha, P.; Demschner, T.; Lourenço, P.B. Quasi-static tests on a two-story CLT building. Eng. Struct. 2019, 201, 109806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, S.; van de Lindt, J.W.; Barbosa, A.R.; Berman, J.W.; McDonnell, E.; Daniel Dolan, J.; Blomgren, H.E.; Zimmerman, R.B.; Huang, D.; Wichman, S. Experimental Seismic Response of a Resilient 2-Story Mass-Timber Building with Post-Tensioned Rocking Walls. J. Struct. Eng. 2019, 145, e4019120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugabo, I.; Barbosa, A.R.; Sinha, A.; Higgins, C.; Riggio, M.; Pei, S.; van de Lindt, J.W.; Berman, J.W. System Identification of UCSD-NHERI Shake-Table Test of Two-Story Structure with Cross-Laminated Timber Rocking Walls. J. Struct. Eng. 2021, 147, e4021018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, S.; Ryan, K.L.; Berman, J.W.; van de Lindt, J.W.; Pryor, S.; Huang, D.; Wichman, S.; Busch, A.; Roser, W.; Wynn, S.L.; et al. Shake-Table Testing of a Full-Scale 10-Story Resilient Mass Timber Building. J. Struct. Eng. 2024, 150, e4024183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Furuta, T.; Xiong, H. Full-scale shaking table tests of cross-laminated timber structures adopting dissipative angle brackets and hold-downs with soft-steel and rubber. Eng. Struct. 2024, 313, 118292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tsavdaridis, K.D. Design for Seismic Resilient Cross Laminated Timber (CLT) Structures: A Review of Research, Novel Connections, Challenges and Opportunities. Buildings 2023, 13, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Shahnewaz, M.; Tannert, T. Seismic Performance and Collapse Fragility of Balloon-Framed CLT School Building. J. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 27, 3115–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahnewaz, M.; Pan, Y.; Shahria Alam, M.; Tannert, T. Seismic Fragility Estimates for Cross-Laminated Timber Platform Building. J. Struct. Eng. 2020, 146, e4020256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloisio, A.; Alaggio, R.; Fragiacomo, M. Fragility functions and behavior factors estimation of multi-story cross-laminated timber structures characterized by an energy-dependent hysteretic model. Earthq. Spectra 2020, 37, 134–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, C.; Lopez-Caballero, F. Survival analysis of a liquefiable embankment subjected to sequential earthquakes. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 140, 106436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, E.M.; Admuthe, S.; Mahmoud, H. Response of semi-rigid steel frames to sequential earthquakes. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2020, 173, 106272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsenian, V.; Gharaei-Moghaddam, N.; Hajirasouliha, I. Seismic performance assessment of tunnel form concrete structures under earthquake sequences using endurance time analysis. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 40, 102327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.G.; Wu, G.; Feng, D.C.; Fan, J.J. Probabilistic multi-hazard fragility analysis of RC bridges under earthquake-tsunami sequential events. Eng. Struct. 2021, 238, 112250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrone, C.; Rossetto, T.; Baiguera, M.; la Barra Bustamante, C.D.; Ioannou, I. Fragility functions for a reinforced concrete structure subjected to earthquake and tsunami in sequence. Eng. Struct. 2020, 205, 110120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, V.; Benedetti, F.; Suazo, M.; Vargas, M.; Rojas, I.; Jara, A.; Rebolledo, A. Associativity between SMEs towards mid-rise building timber construction: PymeLab Project. In Proceedings of the World Conference on Timber Engineering, Santiago, Chile, 9–12 August 2021; pp. 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Nacional de Normalización. NCh433: 1996 Mod 2009: Diseño síSmico de Edificios; Instituto Nacional de Normalización: Santiago, Chile, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Nacional de Normalización. Nch 1198; Instituto Nacional de Normalización: Santiago, Chile, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Karacabeyli, E.; Gagnon, S. Canadian CLT Handbook, 2019; National Library of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Izzi, M.; Casagrande, D.; Bezzi, S.; Pasca, D.; Follesa, M.; Tomasi, R. Seismic behaviour of Cross-Laminated Timber structures: A state-of-the-art review. Eng. Struct. 2018, 170, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, F.; Valenzuela, T.; Jara-Cisterna, A.; Opazo-Vega, A.; Rosales, V. Incremental dynamic analysis of a five storeys CLT building designed through force-based methods. In Proceedings of the World Conference on Timber Engineering (WCTE 2023), Oslo, Norway, 19–22 June 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, F.; Jara-Cisterna, A.; Meza, S.; Castillo, J.; Casanova, E. Nonlinear Modeling of Midrise Cross-Laminated Timber Buildings Through Parallel and Sequential Computing Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2022 Eurasian OpenSees Days; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, F.; Scott, M.H.; Fenves, G.L. Nonlinear Finite-Element Analysis Software Architecture Using Object Composition. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2010, 24, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayegh, A.T.A.; Sotelino, E.D. A new row-wise parallel finite element analysis algorithm with dynamic load balancing. Int. J. Earthq. Impact Eng. 2020, 3, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, F.; Rosales, V.; Opazo-Vega, A.; Sepúlveda, S.; Jara-Cisterna, A. Experimental analysis of a two-story three-dimensional panelized CLT module. In Proceedings of the World Conference on Timber Engineering WCTE2020, Santiago, Chile, 9–12 August 2021; pp. 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Blass, H.J.; Fellmoser, P. Design of solid wood panels with cross layers. In Proceedings of the 8th World Conference on Timber Engineering, Lahti, Finland, 14–17 June 2004; Volume 14, p. 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Asparren, K. Characterization of the Mechanical Behavior of Screws in Cross Laminated Timber Walls. Bachelor’s Thesis, University of Bío-Bío, Concepción, Chile, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Casagrande, D.; Polastri, A.; Sartori, T.; Loss, C.; Chiodega, M. Experimental tests for mechanical characterization of timber buildings connections. In Proceedings of the World Conference on Timber Engineering (WCTE 2016), Vienna, Austria, 22–25 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jara-Cisterna, A.; Benedetti, F.; Rosales, V.; Almazán, J.L.; Opazo-Vega, A. Vibration-based monitoring of a cross-laminated timber building in a high seismicity zone. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiPasquale, E.; Ju, J.; Askar, A.; undefinedakmak, A.S. Relation between Global Damage Indices and Local Stiffness Degradation. J. Struct. Eng. 1990, 116, 1440–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobarah, A.; Abou-Elfath, H.; Biddah, A. Response-based damage assessment of structures. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1999, 28, 79–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamvatsikos, D.; Cornell, C.A. Incremental dynamic analysis. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2001, 31, 491–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACHISINA. Diseño Sísmico Basado en Desempeño. Un Procedimiento Alternativo para el Análisis y Diseño Sísmico de Edificios, 1st ed.; Chilean Association of Seismology and Earthquake Engineering: Santiago, Chile, 2017. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Ghobarah, A. On drift limits associated with different damage levels. In Proceedings of the Performance-Based Seismic Design Concepts and Implementation International Workshop, Bled, Slovenia, 28 June–1 July 2004; Fajfar, P., Krawinkler, H., Eds.; Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2004; pp. 321–332. [Google Scholar]
- FEMA. Quantification of Building Seismic Performance Factors; Federal Emergency Management Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.



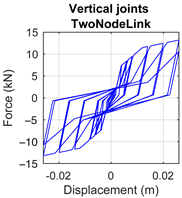 |  | 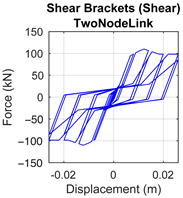 |
 |  |  |
| Mechanical Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Elastic Modulus Ex (3 layers) | 2750 MPa |
| Elastic Modulus Ey (3 layers) | 5250 MPa |
| Elastic Modulus Ex (5 layers) | 1755 MPa |
| Elastic Modulus Ey (5 layers) | 6250 MPa |
| Shear Modulus | 324 MPa |
| Poisson Coefficient | 0.3 |
| Density | 450 kg/m3 |
| (s) | (s) | (hz) | (hz) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FE Model | 0.32 | 0.28 | 3.12 | 3.57 |
| Measurement Results | 0.32 | 0.27 | 3.13 | 3.66 |
| Earthquake | Station | Direction | PGA (g) | PGV (m/s) | Sig. Duration (s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maule 2010 | 8.8 | CCP | L | 0.40 | 0.67 | 80.7 |
| T | 0.28 | 0.51 | 88.1 | |||
| CSP | EO | 0.60 | 0.43 | 72.8 | ||
| NS | 0.65 | 0.37 | 69.5 | |||
| Angol | NS | 0.69 | 0.37 | 50.8 | ||
| EO | 0.93 | 0.33 | 49.8 | |||
| Peñalolén | NS | 0.29 | 0.22 | 33.7 | ||
| EO | 0.29 | 0.29 | 34.2 | |||
| Valdivia | NS | 0.13 | 0.18 | 33.9 | ||
| EO | 0.09 | 0.13 | 29.0 | |||
| Algarrobo 1985 | 8.0 | Llolleo | 10 | 0.71 | 0.40 | 35.9 |
| 100 | 0.44 | 0.23 | 40.8 | |||
| Mexico City 1985 | 8.1 | SCT | EO | 0.16 | 0.58 | 39.0 |
| NS | 0.09 | 0.35 | 71.1 | |||
| Loma Prieta 1989 | 6.9 | Treasure Island | 0 | 0.09 | 0.15 | 6.0 |
| 90 | 0.15 | 0.33 | 4.4 | |||
| Yerba buena | 0 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 18.7 | ||
| 90 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 8.0 |
| Direction | Undamaged | Low | Moderate | Severe |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X (Transverse) | 5.39 | 4.75 | 4.74 | 3.60 |
| Y (Longitudinal) | 6.81 | 5.68 | 5.66 | 2.80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benedetti, F.; Álvarez M., J.; Jara-Cisterna, A.; Opazo-Vega, A.; Rosales, V. Effect of the Initial Damage State on the Seismic Behavior of A Five-Story CLT Building. Buildings 2025, 15, 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15050727
Benedetti F, Álvarez M. J, Jara-Cisterna A, Opazo-Vega A, Rosales V. Effect of the Initial Damage State on the Seismic Behavior of A Five-Story CLT Building. Buildings. 2025; 15(5):727. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15050727
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenedetti, Franco, Julieta Álvarez M., Alan Jara-Cisterna, Alexander Opazo-Vega, and Víctor Rosales. 2025. "Effect of the Initial Damage State on the Seismic Behavior of A Five-Story CLT Building" Buildings 15, no. 5: 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15050727
APA StyleBenedetti, F., Álvarez M., J., Jara-Cisterna, A., Opazo-Vega, A., & Rosales, V. (2025). Effect of the Initial Damage State on the Seismic Behavior of A Five-Story CLT Building. Buildings, 15(5), 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15050727






