Measurement and Prediction of Airborne Sound Insulation Performance of Different Vertical Partition Walls in Indoor Environments: A Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Experimental Determination of the Apparent Airborne Sound Insulation Index
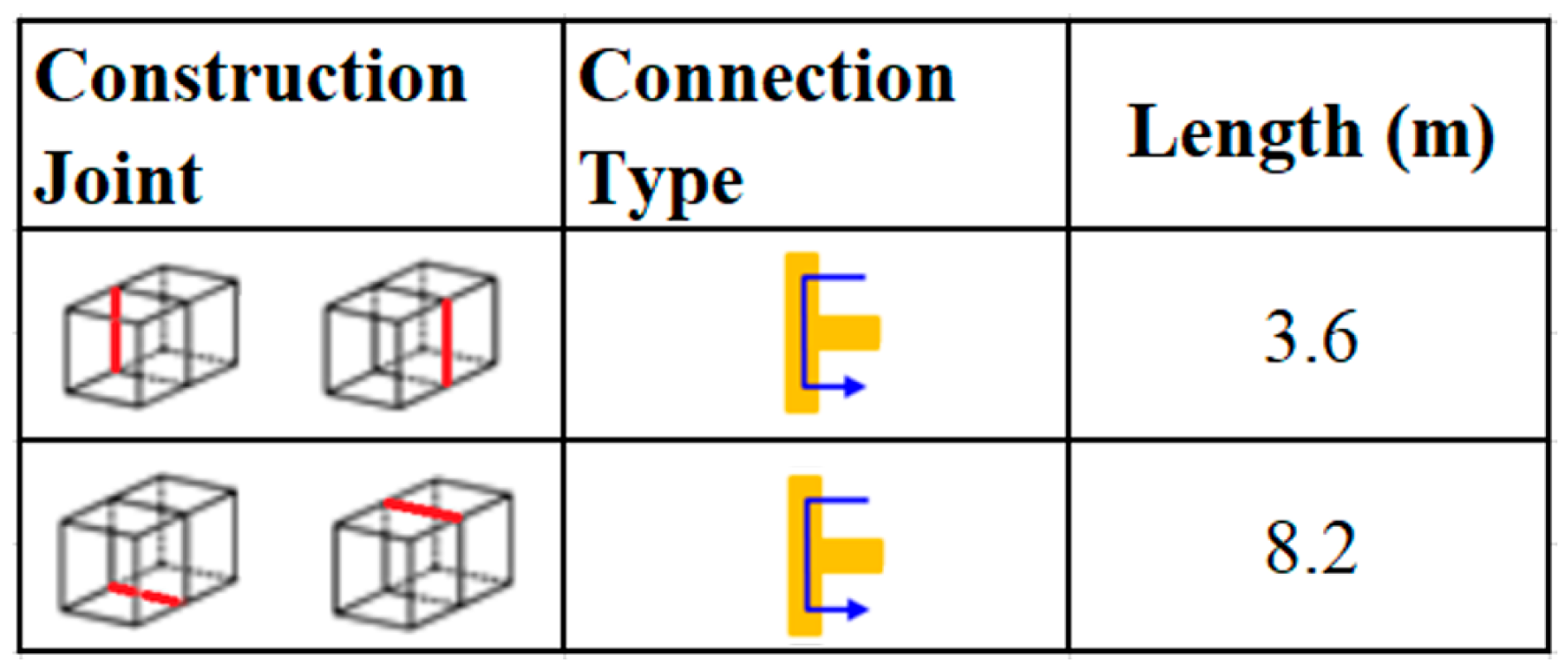
2.2. Prediction of the Apparent Airborne Sound Insulation Index
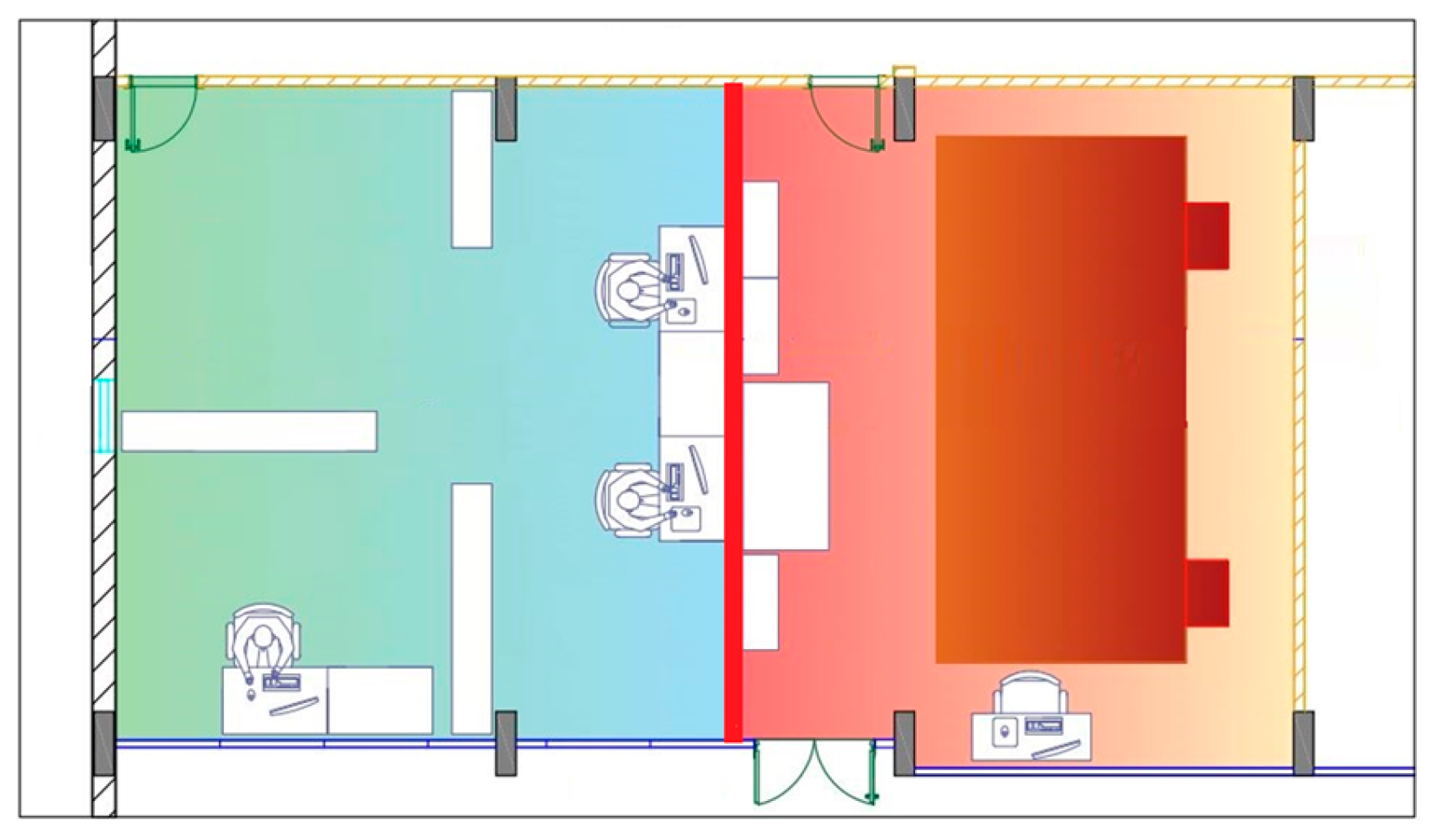
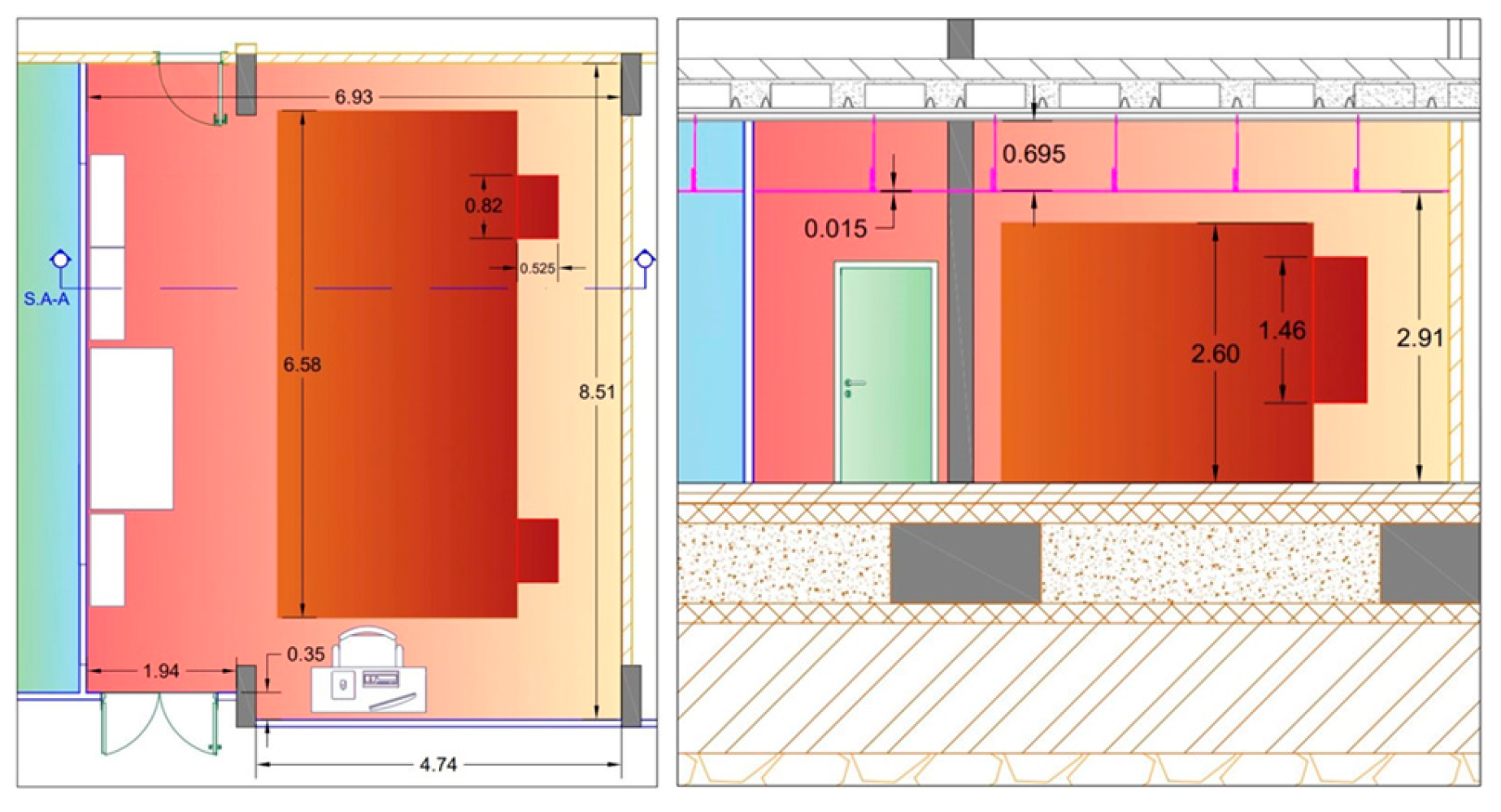
2.3. Case Study
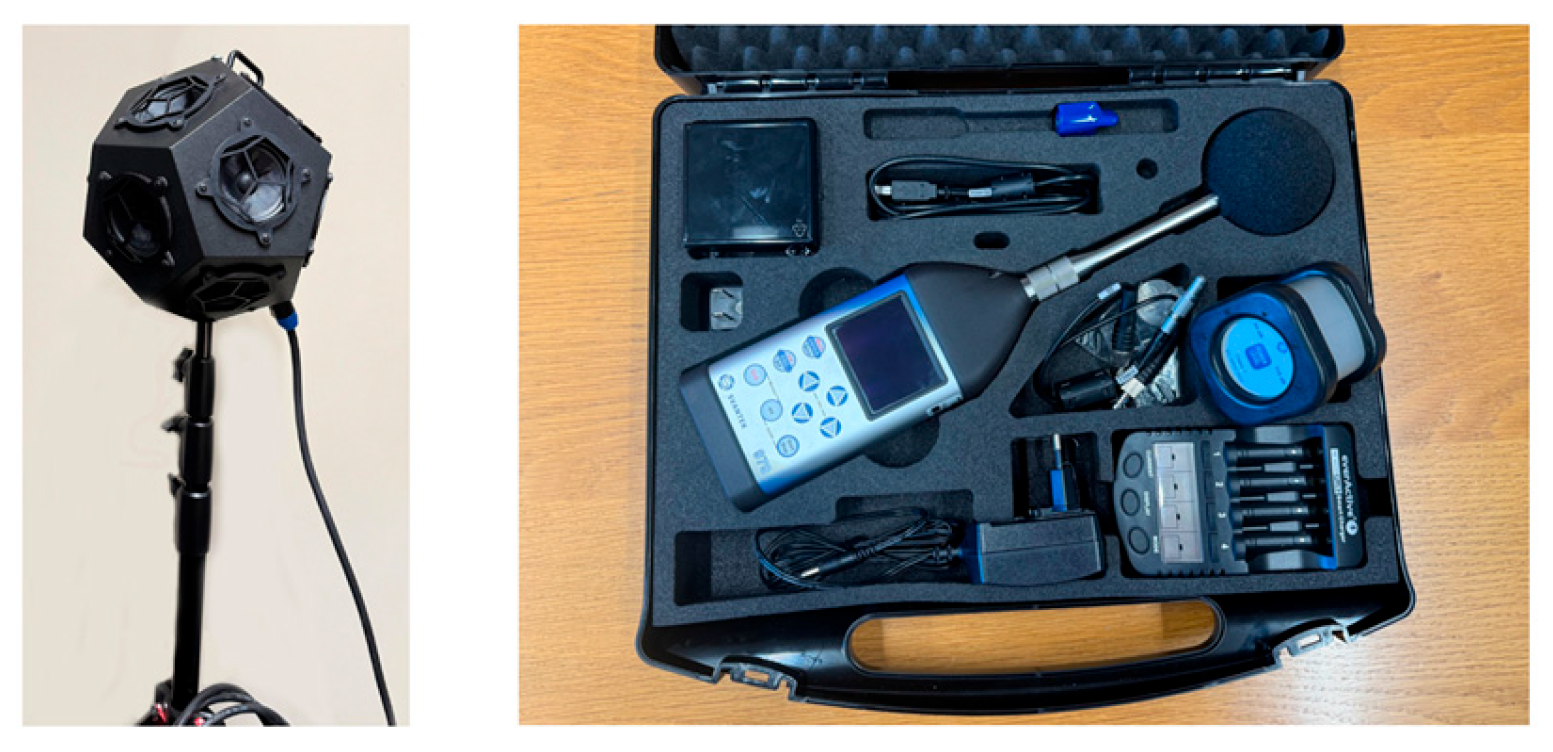
2.4. Measurement Equipment
2.5. Acoustically Insulated Wall Configurations
- Perfetto Special 1 features a total thickness of 30 cm and consists of a 15 cm thick masonry block layer, a 5 cm air cavity containing 3 cm of insulating material, and a second masonry layer of 10 cm. Additionally, an elastic joint between the wall and the floor is provided by means of a perimeter acoustic decoupling strip, in order to reduce flanking sound transmission.
- Perfetto Special 2 has an overall thickness of 26 cm and is composed of a 12 cm thick masonry block layer, a 4 cm cavity with 3 cm of insulation, and a 10 cm thick masonry block layer.
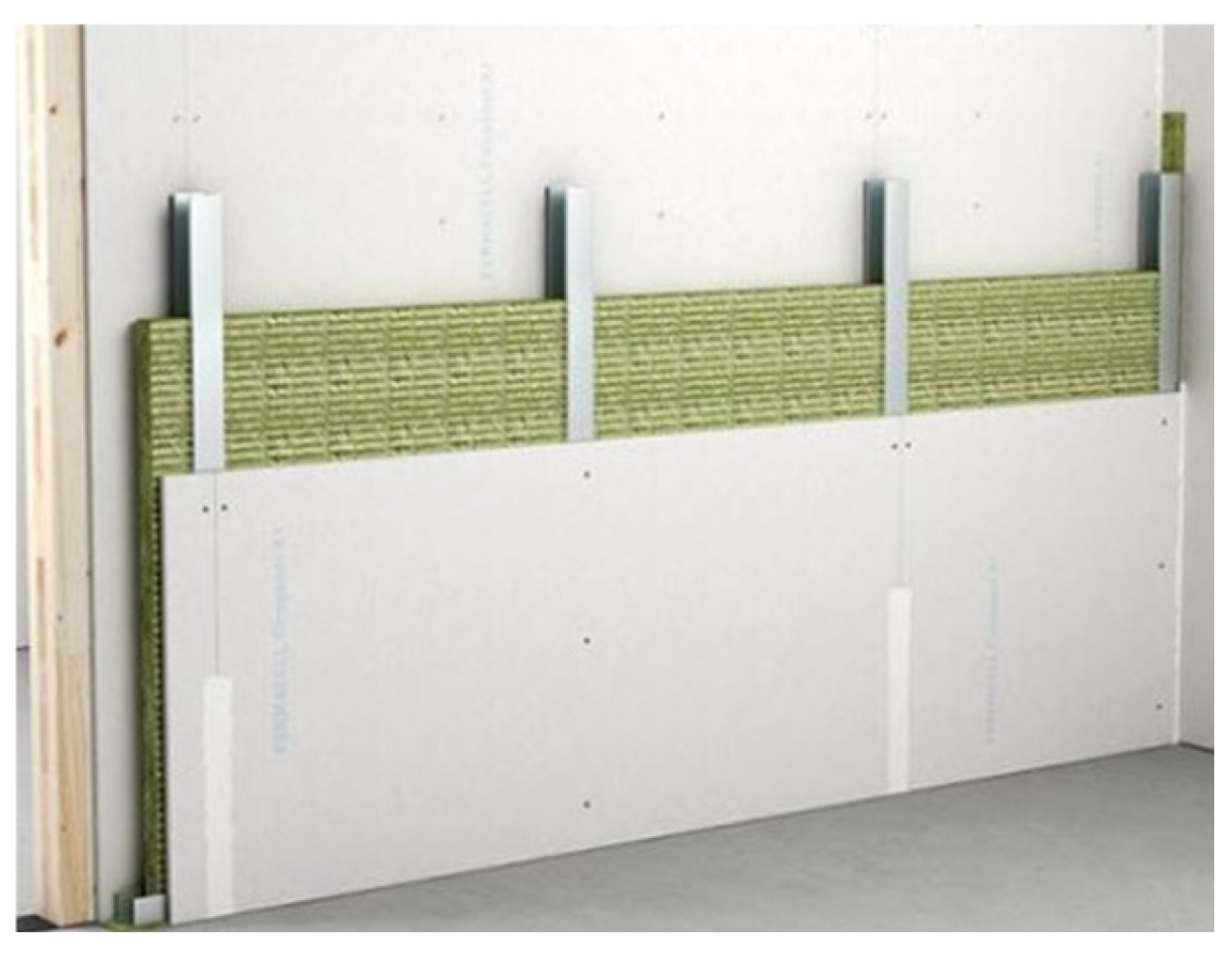
- Perfetto Special CG comprises a 2 cm plaster layer, 8 cm of hollow clay brick, a 2 cm base coat, and a 7.5 cm metal frame filled with 4.5 cm of insulation and covered with a double 2.5 cm gypsum board. The geometrical configuration of the metal support frame is illustrated in Figure 6.
- The FIBRAN B-040/A13—1 wall system has a total thickness of 10 cm and consists of two FIBRANgyps A13 plasterboards, each 1.3 cm thick, a 4 cm layer of FIBRANgeo B-040 rockwool, a 1 cm air cavity, and other two plasterboards, also 1.3 cm thick.
- The FIBRAN B-050/SUPER13 configuration follows the same stratigraphy as the previous one, while featuring two FIBRANgyps SUPER13 plasterboards, a 5 cm thick layer of FIBRANgeo B-050 rockwool, and a 2.5 cm air cavity.
- The FIBRAN B-040/A13—2 wall features the same materials as the first configuration, with a 5 cm thick air cavity, bordered this time by two layers of FIBRANgeo B-040 rockwool, each 4 cm thick.
2.6. Cost-Effective Insulated Walls
- Type A: masonry wall consisting of a 2 cm thick plaster layer, 8 cm thick hollow brick wall, and another 2 cm thick plaster layer.
- Type B: masonry wall of Type A with an additional partition on the side of the receiving room, consisting of 1.3 cm thick drywall layer, 5 cm thick layer of sintered expanded polystyrene, and 2 cm thick non-ventilated air cavity.
- Type C: partition wall consisting of two plasterboard layers, each 2.6 cm thick, enclosing a 5 cm thick rock wool panel and a 5 cm thick non-ventilated air cavity, and employing double metal studs for acoustic decoupling.
- Type D: metal stud partition wall consisting of two plywood layers, each 3 cm thick, enclosing a 5 cm thick rock wool panel and a 5 cm thick non-ventilated air cavity, and employing double metal studs for acoustic decoupling.
2.7. Cost Analysis
2.8. Software
2.8.1. On-Site Measurements Processing Software
2.8.2. Predictive Calculations Software
3. Results
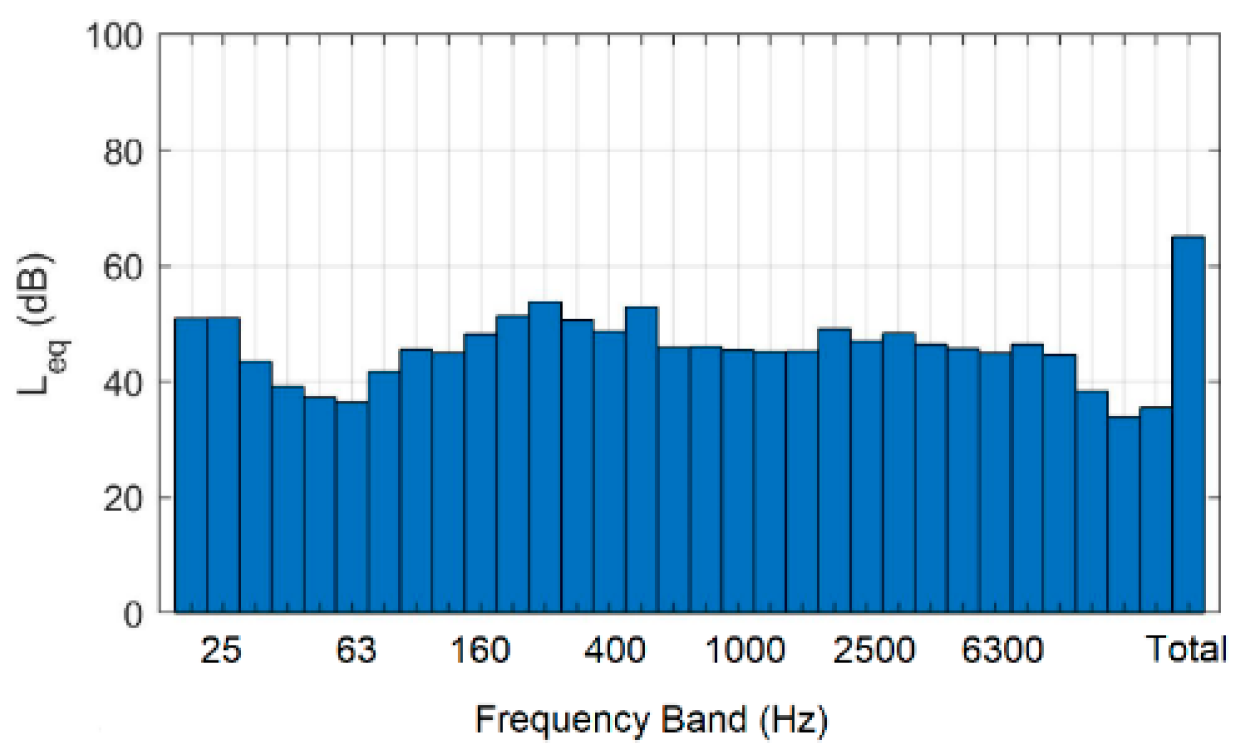
3.1. Experimental Measurement Results
3.2. Predictive Calculation Results
3.3. Acoustically Insulated Wall Configurations
3.4. Cost-Effective Insulated Walls
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Łapińska, A.; Grochowska, N.; Cieplak, K.; Płatek, P.; Wood, P.; Deuszkiewicz, P.; Dużyńska, A.; Sztorch, B.; Głowcka, J.; Przekop, R.; et al. Architecture influence on acoustic performance, EMI shielding, electrical and thermal, properties of 3D printed PLA/graphite/molybdenum disulfide composites. Mater. Des. 2024, 245, 113241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Cárdenas, B.; Lacasta, A.M.; Haurie, L. Bibliometric analysis of research on thermal, acoustic, and/or fire behaviour characteristics in bio-based building materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 432, 136569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorca-Bofí, J.; Heck, J.; Dreier, C.; Vorländer, M. Urban background sounds under various weather conditions categorized for virtual acoustics. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 371, 123081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haselhoff, T.; Schuck, M.; Lawrence, B.T.; Fiebig, A.; Moebus, S. Characterizing acoustic dimensions of health-related urban greenspace. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandiari, M.; Mohamed Zaid, S.; Ismail, M.A.; Reza Hafezi, M.; Asadi, I.; Mohammadi, S.; Vaisi, S.; Aflaki, A. Occupants’ Satisfaction toward Indoor Environment Quality of Platinum Green-Certified Office Buildings in Tropical Climate. Energies 2021, 14, 2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, D.; Menassa, C.C.; Kamat, V.R. Investigating the effect of indoor thermal environment on occupants’ mental workload and task performance using electroencephalogram. Build. Environ. 2019, 158, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluyssen, P.M.; Zhang, D.; Kurvers, S.; Overtoom, M.; Ortiz-Sanchez, M. Self-reported health and comfort of school children in 54 classrooms of 21 Dutch school buildings. Build. Environ. 2018, 138, 106–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarrazó-Serrano, D.; Castiñeira-Ibáñez, S.; Bautista, A.S.; Rubio, C.; Uris, A. Optimization of acoustic subwavelength slit barrier to control low-frequency noise in industrial buildings. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 103, 111926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ba, M.; Kang, J.; Meng, Q. Effect of soundscape dimensions on acoustic comfort in urban open public spaces. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 133, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X. Combined effects of dominant sounds, conversational speech and multisensory perception on visitors’ acoustic comfort in urban open spaces. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2023, 232, 104674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Kang, J.; Ma, H. Evaluation of healthy indoor acoustic environments in residential buildings by the occupants: A mixed-method approach. Build. Environ. 2023, 246, 110950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjunan, A.; Baroutaji, A.; Robinson, J.; Vance, A.; Arafat, A. Acoustic metamaterials for sound absorption and insulation in buildings. Build. Environ. 2024, 251, 111250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtrepi, L.; Prato, A. Towards a sustainable approach for sound absorption assessment of building materials: Validation of small-scale reverberation room measurements. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 165, 107304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, Q.; Fan, H.; Liu, L.; Yan, Z.; Chen, Y.; Luo, L.; Li, J. Lightweight, strong, and sound insulation bio-based structural material from discarded coconut wood. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 458, 139765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrzad, S.; Taban, E.; Soltani, P.; Samaei, S.E.; Khavanin, A. Sugarcane bagasse waste fibers as novel thermal insulation and sound-absorbing materials for application in sustainable buildings. Build. Environ. 2022, 211, 108753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Dauchez, N.; Nennig, B. A metaporoelastic structure that overcomes the sound insulation weaknesses of single and double panel partitions. Appl. Acoust. 2023, 210, 109409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Júnior, O.J.S.; Pinheiro, M.A.S.; Silva, J.J.R.; Pires, T.A.C.; Alencar, C.O.S. Sound insulation of gypsum block partitions: An analysis of single and double walls. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 39, 102253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo Alves, J.; Neto Paiva, F.; Torres Silva, L.; Remoaldo, P. Low-Frequency Noise and Its Main Effects on Human Health—A Review of the Literature between 2016 and 2019. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlaczyk-Luszczyńska, M.; Szymczak, W.; Dudarewicz, A.; Sliwińska-Kowalska, M. Proposed criteria for assessing low frequency noise annoyance in occupational settings. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2006, 19, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kempen, E.; Casas, M.; Pershagen, G.; Foraster, M. WHO Environmental Noise Guidelines for the European Region: A Systematic Review on Environmental Noise and Cardiovascular and Metabolic Effects: A Summary. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martellotta, F. Innovative Composite Materials for Sound Absorption and Insulation: Where We Are and Where We Are Going. Materials 2021, 14, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moravec, M.; Pinosova, M.; Badida, M.; Izarikova, G.; Badidova, M. Analysis of the Acoustic Parameters of Building Partition Structures of Varying Composition. Buildings 2024, 14, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, T.; Wang, B.; Min, H. Lightweight Composite Partitions with High Sound Insulation in Hotel Interior Spaces: Design and Application. Buildings 2022, 12, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Ren, M.; Zhang, H.; Peijs, T. Recent progress in acoustic materials and noise control strategies—A review. Appl. Mater. Today 2021, 24, 101141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Prasad, M.G. Acoustic Black Holes in Structural Design for Vibration and Noise Control. Acoustics 2019, 1, 220–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyelade, A.O.; Akano, T.T.; Odesanmi, G.A. Enhancing the sound transmission loss in double-leaf partitions with lateral local resonators substructure. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2022, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caniato, M.; Bettarello, F.; Gasparella, A. Energy and Acoustic Performances of Timber in Buildings. Encycl. Renew. Sustain. Mater. 2018, 2, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caniato, M.; Bettarello, F.; Schmid, C.; Fausti, P. The use of numerical models on service equipment noise prediction in heavyweight and lightweight timber buildings. Build. Acoust. 2018, 26, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caniato, M.; Bettarello, F.; Ferluga, A.; Marsich, L.; Schmid, C.; Fausti, P. Acoustic of lightweight timber buildings: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secchi, S.; Asdrubali, F.; Cellai, G.; Nannipieri, E.; Rotili, A.; Vannucchi, I. Experimental and environmental analysis of new sound-absorbing and insulating elements in recycled cardboard. J. Build. Eng. 2016, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Cao, Y.; Wu, M.; Albu, F.; Yang, J. Frequency-Domain Filtered-x LMS Algorithms for Active Noise Control: A Review and New Insights. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TEP s.r.l., ECHO 8. ANIT, Via Lanzone, 31-20123 Milano. Available online: https://www.anit.it/echo (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Zarastvand, M.; Ghassabi, M.; Talebitooti, R. Prediction of acoustic wave transmission features of the multilayered plate constructions: A review. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. 2022, 24, 218–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presidenza del Consiglio dei Ministri. DPCM 5 Dicembre 1997: Determinazione dei Requisiti Acustici Passivi Degli Edifici, Serie Generale n. 297. 22 December 1997. Available online: https://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/eli/id/1997/12/22/97A10190/sg (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- EN ISO 16283-1:2014; Acoustics—Field Measurement of Sound Insulation in Buildings and of Building Elements—Part 1: Airborne Sound Insulation. UNI: Milan, Italy, 2014.
- EN ISO 717-1:2013; Acoustics—Rating of Sound Insulation in Buildings and of Building Elements—Part 1: Airborne Sound Insulation. UNI: Milan, Italy, 2013.
- Svantek Italia. VibRum Plus—Software Modulare per Elaborazione dati Acustici. Available online: https://www.svantek.it/category/prodotti-rumore-vibrazioni/software/ (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- EN ISO 12354-1:2017; Building Acoustics—Estimation of Acoustic Performance of Buildings from the Performance of Elements—Part 1: Airborne Sound Insulation Between Rooms. UNI: Milan, Italy, 2017.
- Catalog Isolmant. Available online: https://www.isolmant.com/it/prodotti/rumore-aereo/isolamento-pareti-con-intercapedine/ (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- FIBRANgyps—500 Dry Construction Systems—Catalog. Available online: https://fibran.it/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2020/10/FIBRANgyps-catalogo-500-sistemi-a-secco.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Fermacell Catalog—Gypsum-Fibre Board. Available online: https://www.fermacell.it/it/prodotti/lastre-in-gessofibra-fermacell/lastra-gessofibra (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Isolmant—Pricing Catalog. Available online: https://www.isolmant.com/it/download/listini (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- “FIBRAN—Pricing Catalog,” 2025. Available online: https://fibran.it/downloads/listino-prezzi (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Fermacell Gypsum-Fibre Pricing. Available online: https://edilcommerce.com/67-fermacell (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Rockwool—Pricing Catalog 2025. Available online: https://www.rockwool.com/it/download-strumenti/listini (accessed on 1 March 2025).








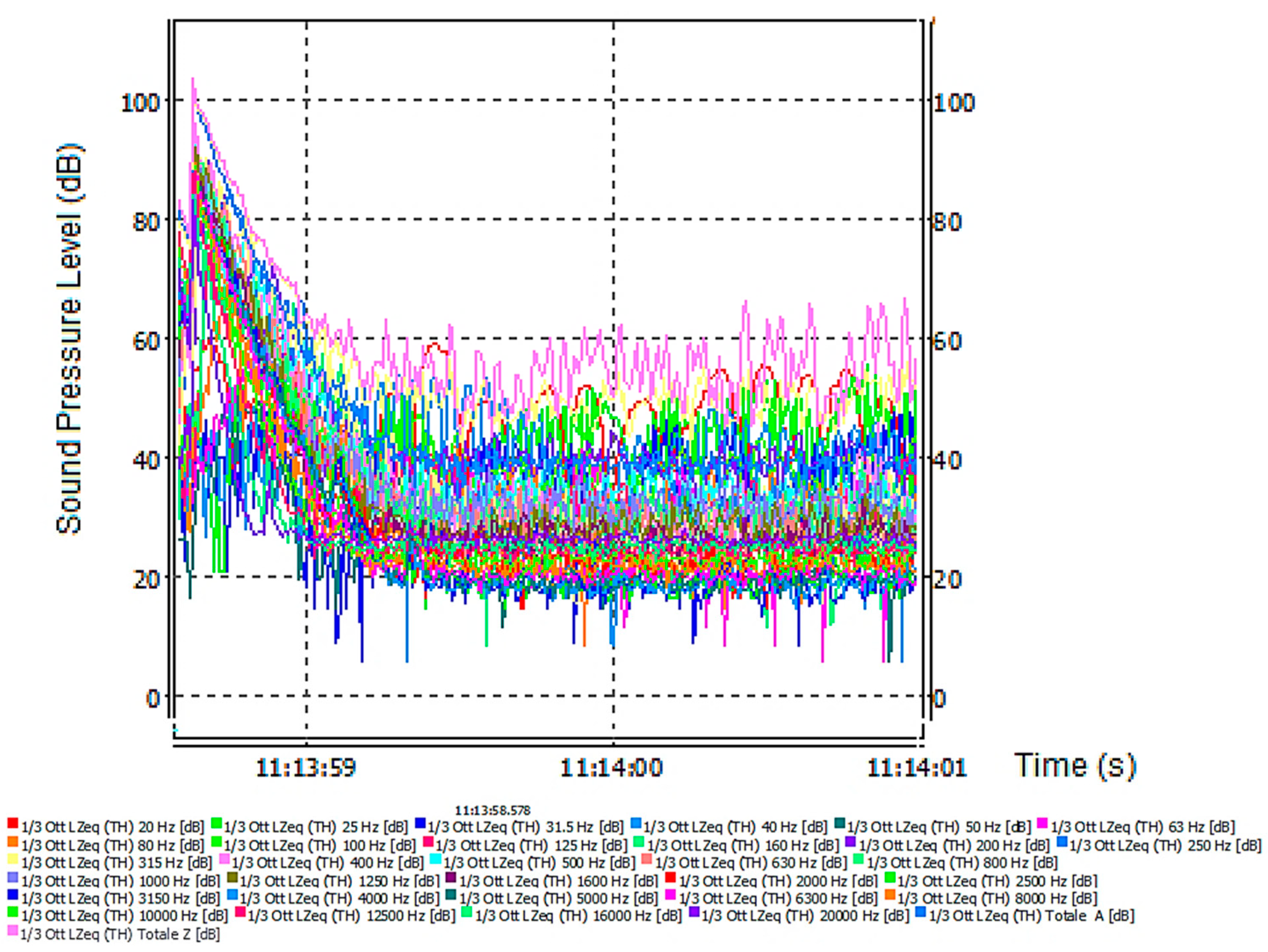

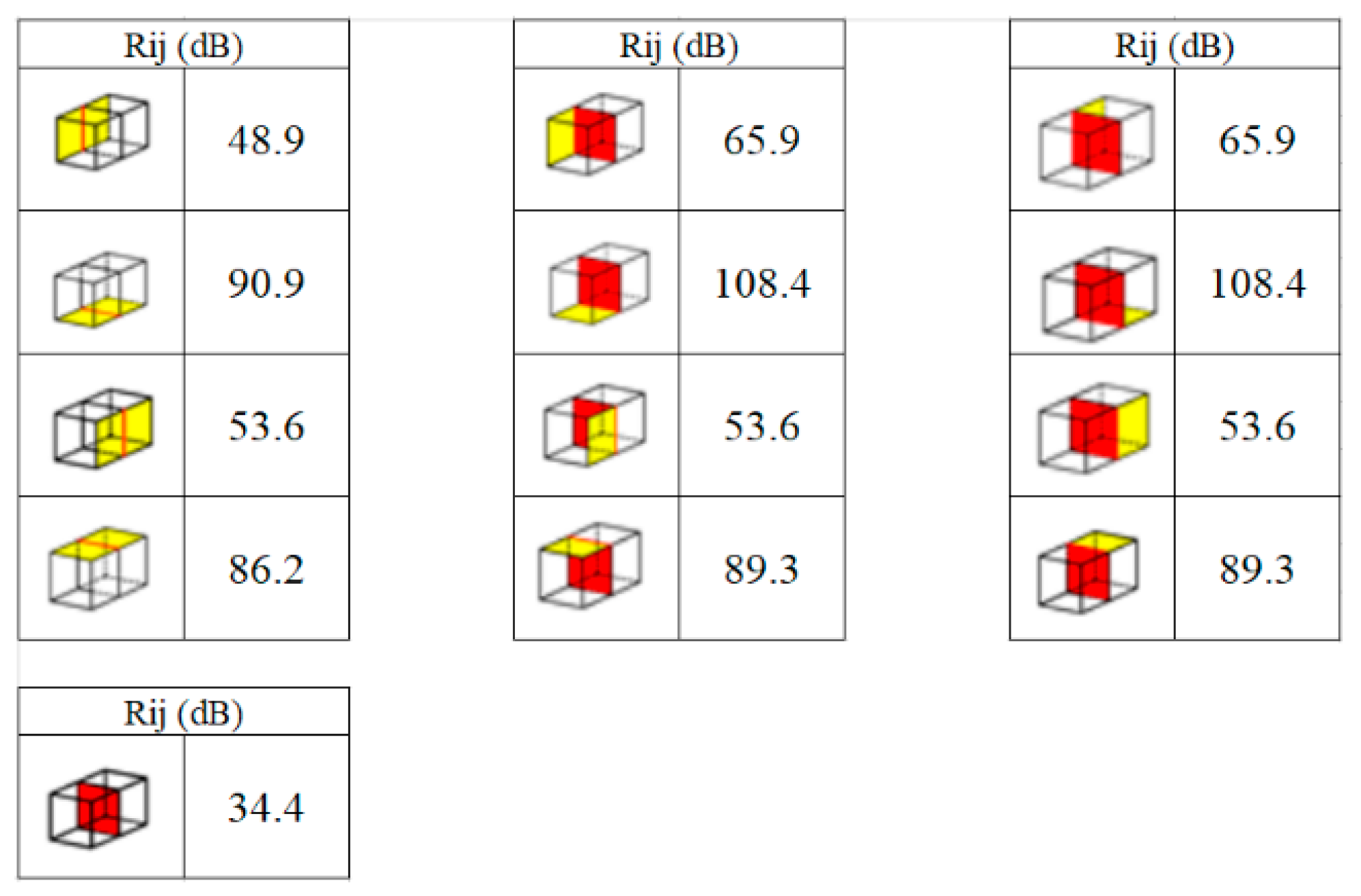

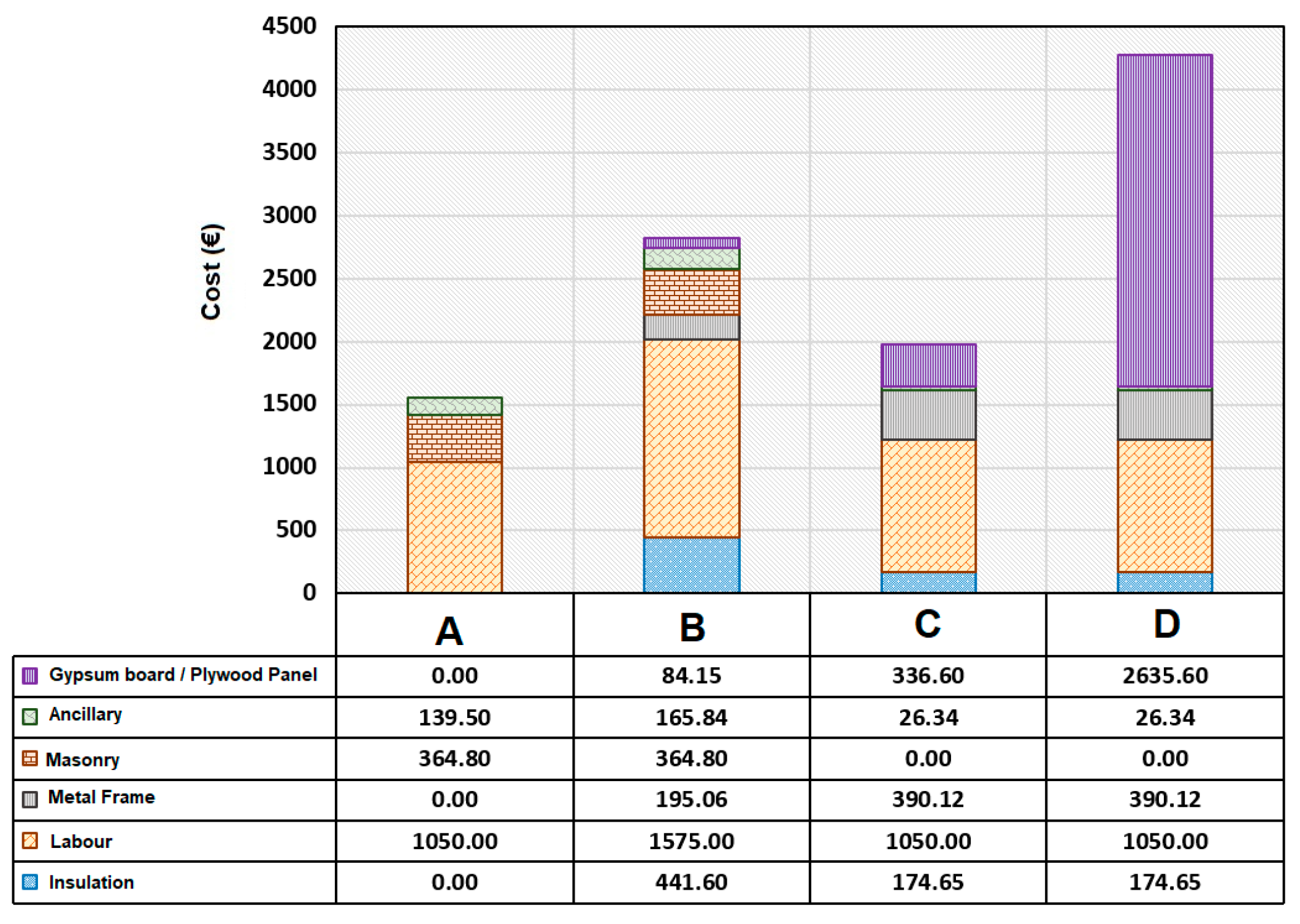
| Wall Type | Thickness (m) | Insulation Thickness (m) | Superficial Mass (kg/m2) | Total Area (m2) | Rw (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Perfetto Special 1 | 0.30 | 0.030 | 170 | 29.5 | 67 |
| Perfetto Special 2 | 0.26 | 0.030 | 160 | 29.5 | 63 |
| Perfetto CG | 0.22 | 0.045 | 122 | 29.5 | 55 |
| Wall Type | Thickness (m) | Insulation Thickness (m) | Superficial Mass (kg/m2) | Total Area (m2) | Rw (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIBRAN B-040/A13—1 | 0.10 | 0.04 | 38.6 | 29.5 | 51 |
| FIBRAN B-050/SUPER13 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 53.3 | 29.5 | 59 |
| FIBRAN B-040/A13—2 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 40.3 | 29.5 | 62 |
| Wall Type | Thickness (m) | Insulation Thickness (m) | Superficial Mass (kg/m2) | Total Area (m2) | Rw (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.12 | 0.00 | 118.0 | 29.5 | 41.4 |
| B | 0.20 | 0.05 | 130.7 | 29.5 | 41.4 |
| C | 0.15 | 0.05 | 51.8 | 29.5 | 59.3 |
| D | 0.16 | 0.05 | 67.0 | 29.5 | 61.5 |
| Wall Type | Cost (€/m2) |
|---|---|
| Perfetto Special 1 | 168.9 |
| Perfetto Special 2 | 147.5 |
| Perfetto CG | 111.7 |
| FIBRAN B-040/A13—1 | 115.6 |
| FIBRAN B-050/SUPER13 | 147.15 |
| FIBRAN B-040/A13—2 | 122.92 |
| Fermacell | 54.2 |
| A | 51.81 |
| B | 94.2 |
| C | 65.9 |
| D | 142.6 |
| Frequency (Hz) | EDT (s) | RT20 (s) | RT30 (s) | RT (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 0.801 | 0.637 | - | 0.637 |
| 125 | 1.218 | 0.606 | 0.511 | 0.511 |
| 160 | 1.009 | 0.782 | 0.797 | 0.797 |
| 200 | 0.458 | 0.796 | 0.685 | 0.685 |
| 250 | 0.843 | 0.759 | 0.713 | 0.713 |
| 315 | 0.620 | 0.636 | 0.708 | 0.708 |
| 400 | 0.482 | 0.582 | 0.592 | 0.592 |
| 500 | 0.485 | 0.640 | 0.679 | 0.679 |
| 630 | 0.577 | 0.434 | 0.526 | 0.526 |
| 800 | 0.394 | 0.482 | 0.561 | 0.561 |
| 1000 | 0.410 | 0.466 | 0.492 | 0.492 |
| 1250 | 0.459 | 0.461 | 0.466 | 0.466 |
| 1600 | 0.415 | 0.427 | 0.416 | 0.416 |
| 2000 | 0.414 | 0.418 | 0.436 | 0.436 |
| 2500 | 0.460 | 0.443 | 0.493 | 0.493 |
| 3150 | 0.391 | 0.491 | 0.490 | 0.490 |
| Wall Type | (dB) | Total Cost (€) |
|---|---|---|
| Perfetto Special 1 | 58.0 | 5068.0 |
| Perfetto Special 2 | 56.8 | 4424.6 |
| Perfetto CG | 52.5 | 3350.8 |
| FIBRAN B-040/A13—1 | 47.9 | 3468.3 |
| FIBRAN B-050/SUPER13 | 51.4 | 4414.5 |
| FIBRAN B-040/A13—2 | 50.9 | 3687.6 |
| Fermacell | 47.3 | 3250.6 |
| Wall Type | (dB) | Total Cost (€) |
|---|---|---|
| A | 41.2 | 1554.3 |
| B | 53.8 | 2826.4 |
| C | 51.4 | 1977.7 |
| D | 52.7 | 4276.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nicoletti, F.; Cristaudo, A.; Bruno, R.; Iorio, D.; Ferraro, V.; Kaliakatsos, D. Measurement and Prediction of Airborne Sound Insulation Performance of Different Vertical Partition Walls in Indoor Environments: A Case Study. Buildings 2025, 15, 3753. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203753
Nicoletti F, Cristaudo A, Bruno R, Iorio D, Ferraro V, Kaliakatsos D. Measurement and Prediction of Airborne Sound Insulation Performance of Different Vertical Partition Walls in Indoor Environments: A Case Study. Buildings. 2025; 15(20):3753. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203753
Chicago/Turabian StyleNicoletti, Francesco, Antonio Cristaudo, Roberto Bruno, Danilo Iorio, Vittorio Ferraro, and Dimitrios Kaliakatsos. 2025. "Measurement and Prediction of Airborne Sound Insulation Performance of Different Vertical Partition Walls in Indoor Environments: A Case Study" Buildings 15, no. 20: 3753. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203753
APA StyleNicoletti, F., Cristaudo, A., Bruno, R., Iorio, D., Ferraro, V., & Kaliakatsos, D. (2025). Measurement and Prediction of Airborne Sound Insulation Performance of Different Vertical Partition Walls in Indoor Environments: A Case Study. Buildings, 15(20), 3753. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203753










