Interpretation of Dominant Features Governing Compressive Strength in One-Part Geopolymer
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Multi-age compressive strength analysis. We provide systematic insights into 3-day, 7-day, 14-day, and 28-day compressive strengths of one-part geopolymers, enabling a more comprehensive understanding of their mechanical development.
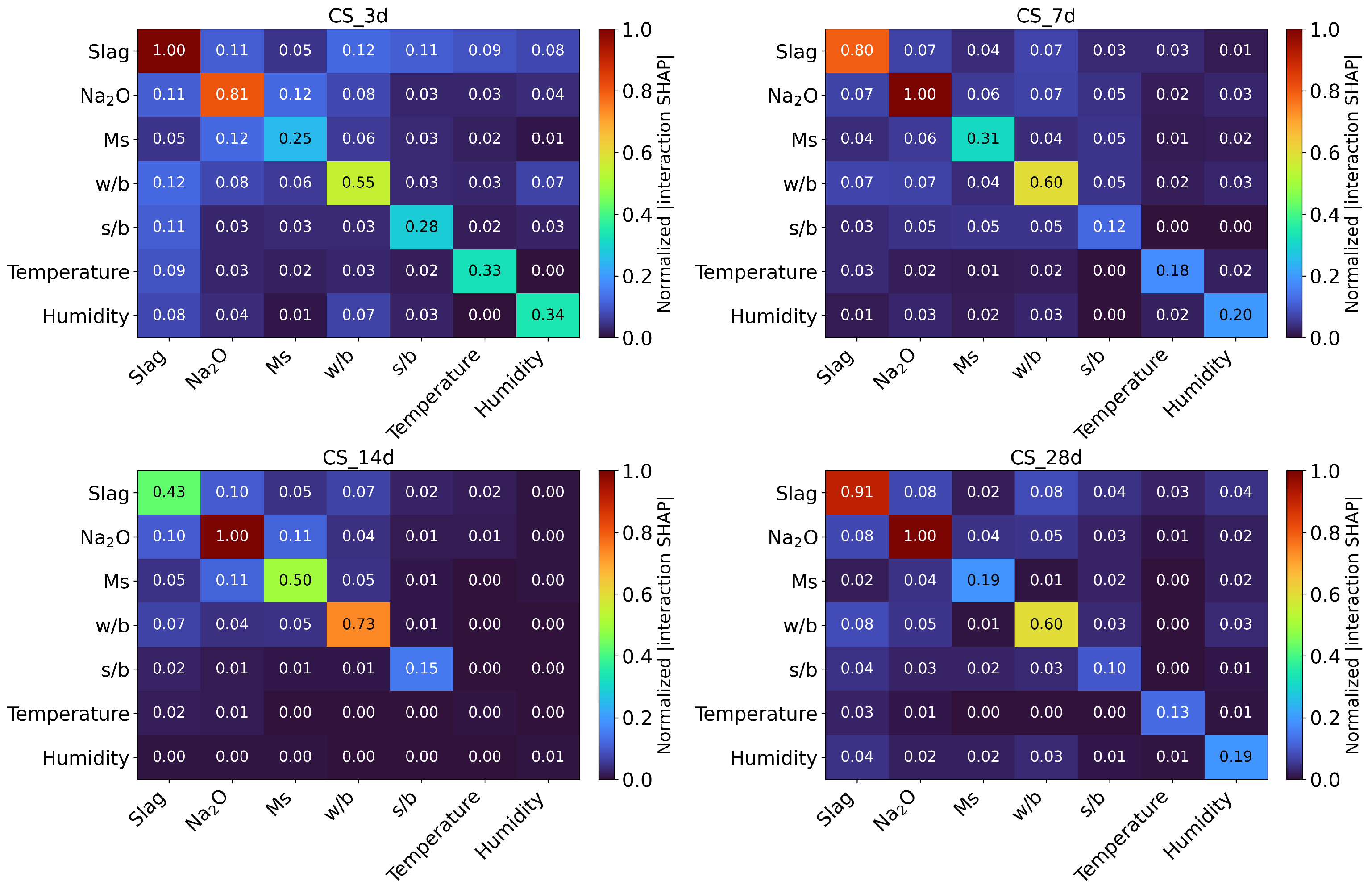
- Feature interaction interpretation. We move beyond individual variable sensitivity by analyzing the synergistic and antagonistic relationships among feature variables, thereby offering a more holistic interpretation of the governing mechanisms.
2. Materials and Dataset
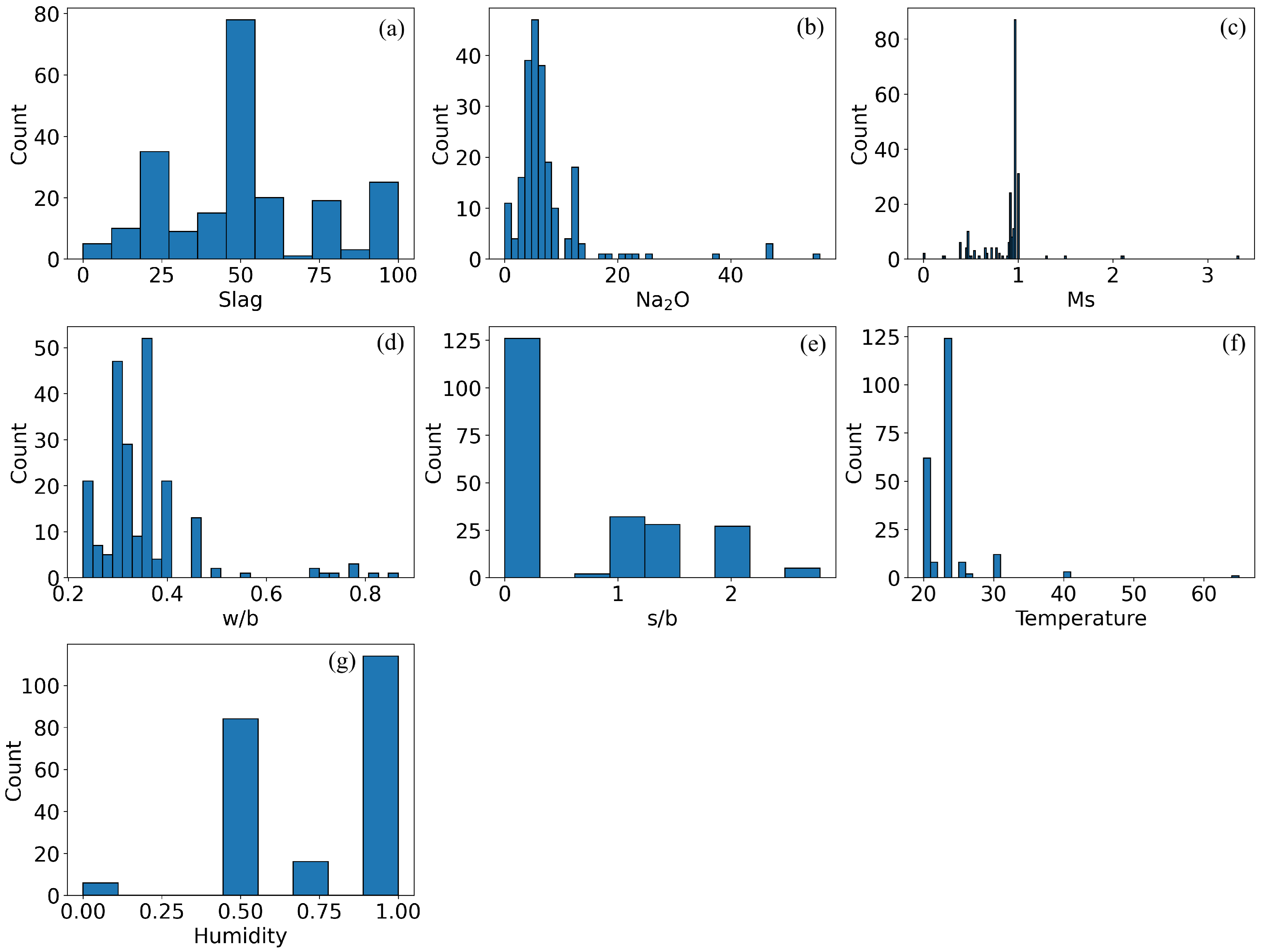
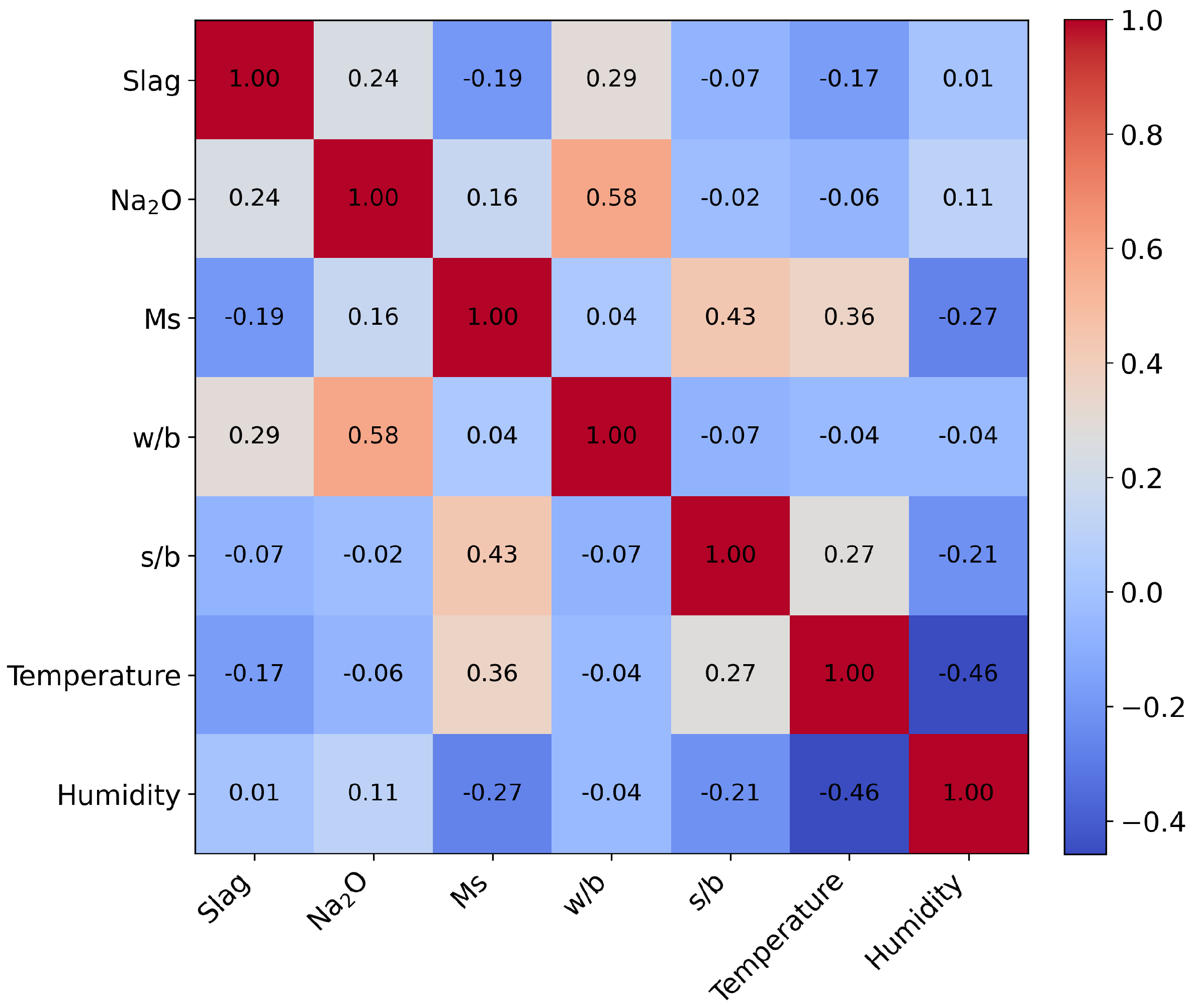
- Input variables: slag content (Slag, %), Na2O dosage in system (Na2O, %), activator modulus (molar ratio of SiO2/Na2O, denoted as Ms), water-to-binder ratio (w/b), sand-to-binder ratio (s/b), curing temperature (Temperature, °C), and curing humidity (Humidity, %).
- Output variables: compressive strength at different curing ages–3 days (CS_3d, MPa), 7 days (CS_7d, MPa), 14 days (CS_14d, MPa), and 28 days (CS_28d, MPa) of the OPGs.
3. Methods
3.1. Machine Learning Methods
3.1.1. Random Forest (RF)
3.1.2. Extremely Randomized Trees (Extra Trees)
3.1.3. Support Vector Regression (SVR)
3.1.4. Ridge Regression
3.1.5. K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) Regression
3.1.6. Extreme Gradient Boosting(XGBoost)
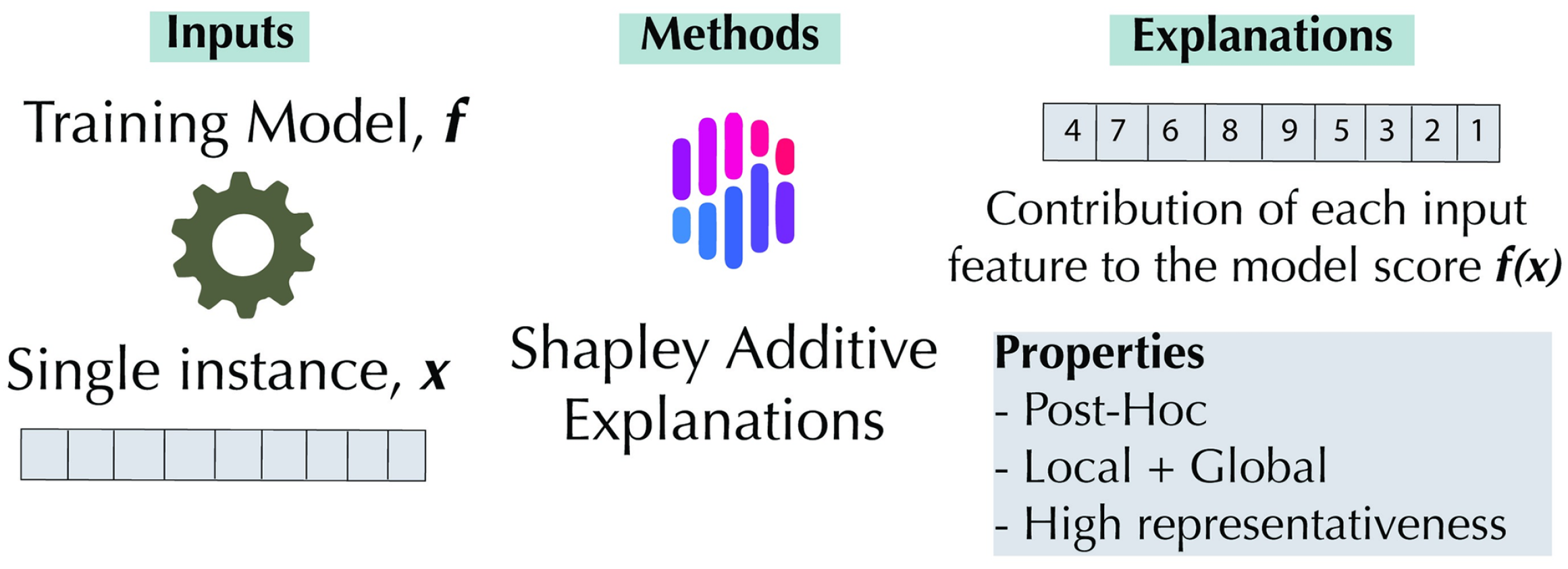
3.2. Shap Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Data Distribution Analysis
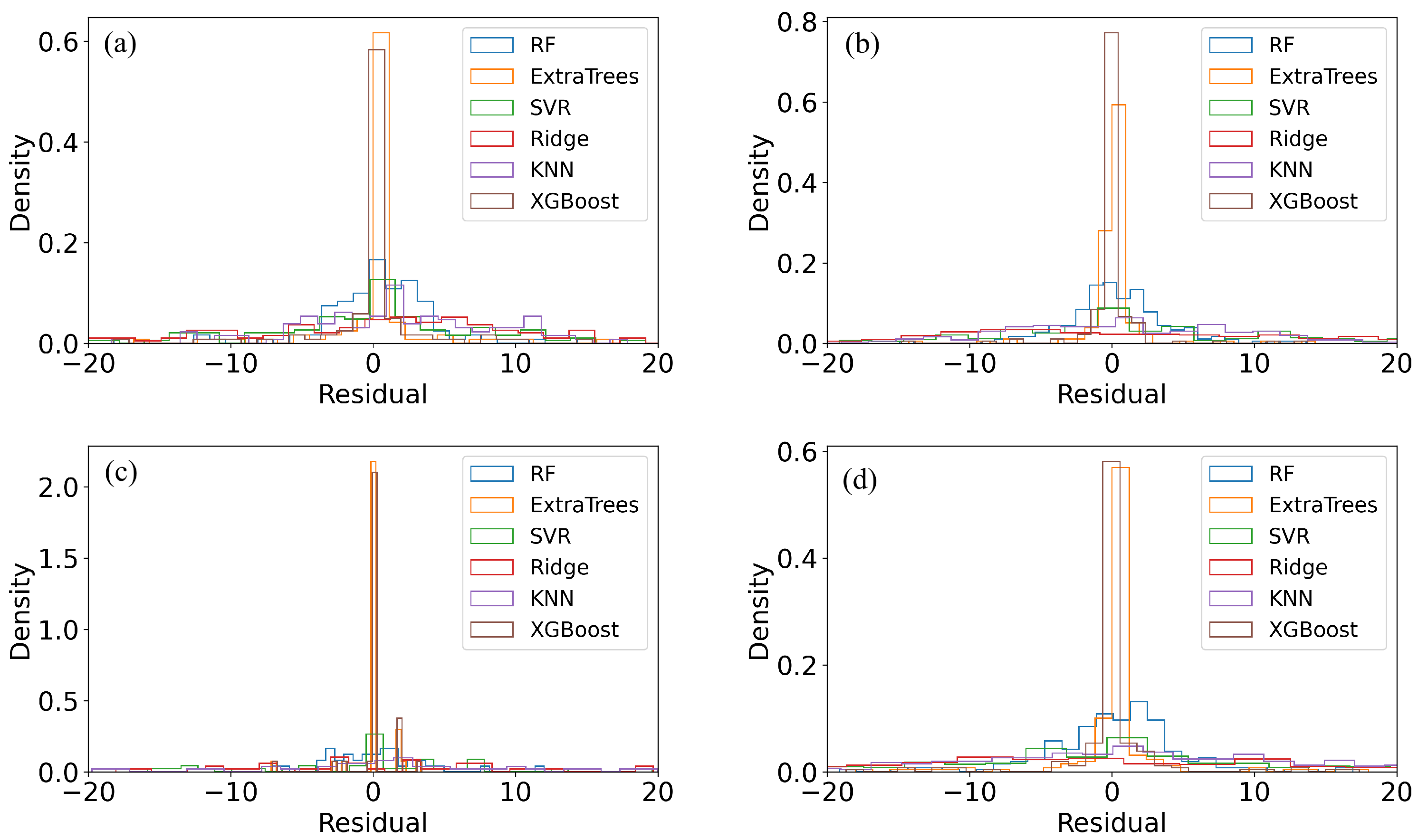
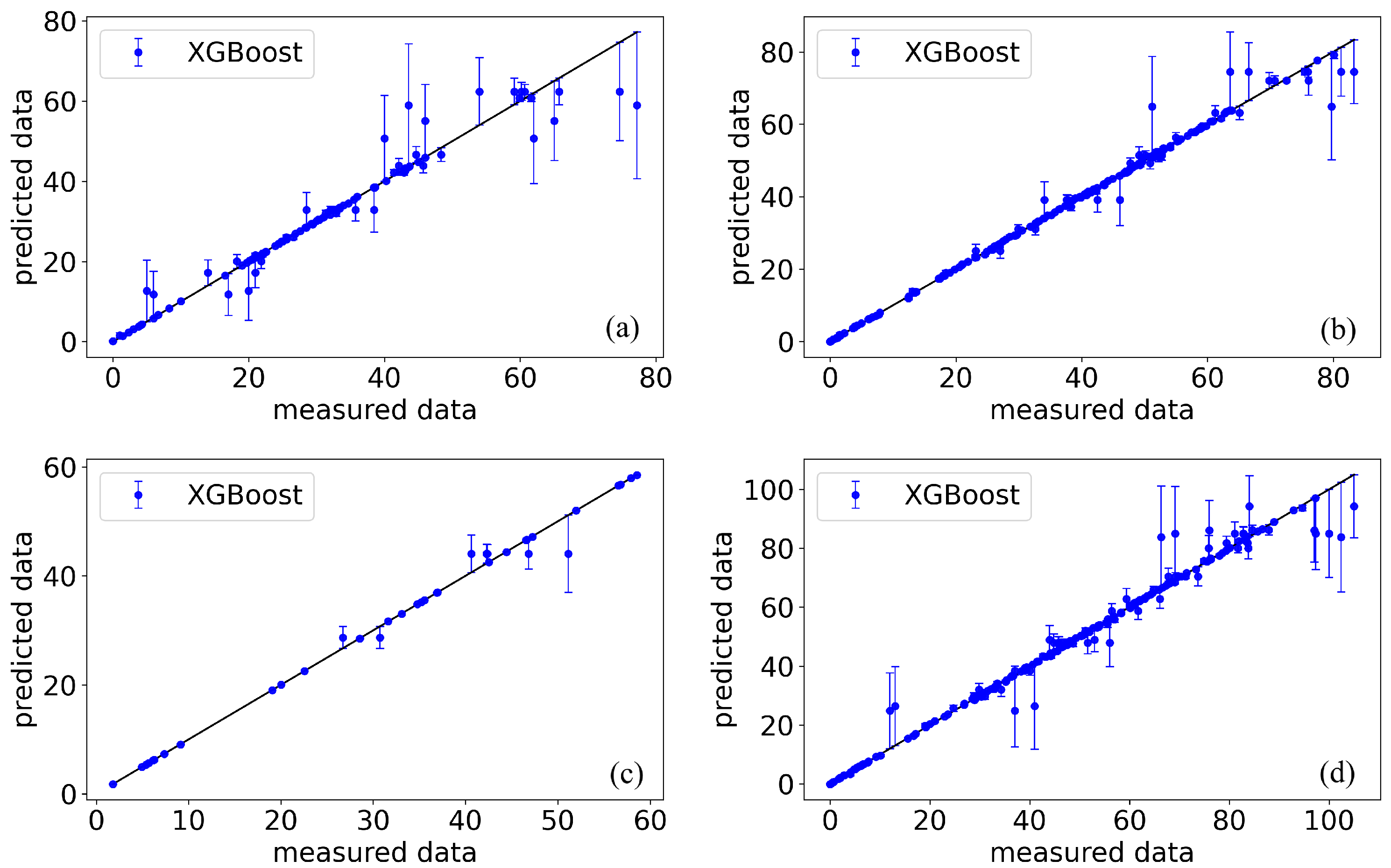
4.2. Machine Learning–Based Estimation of Material Properties
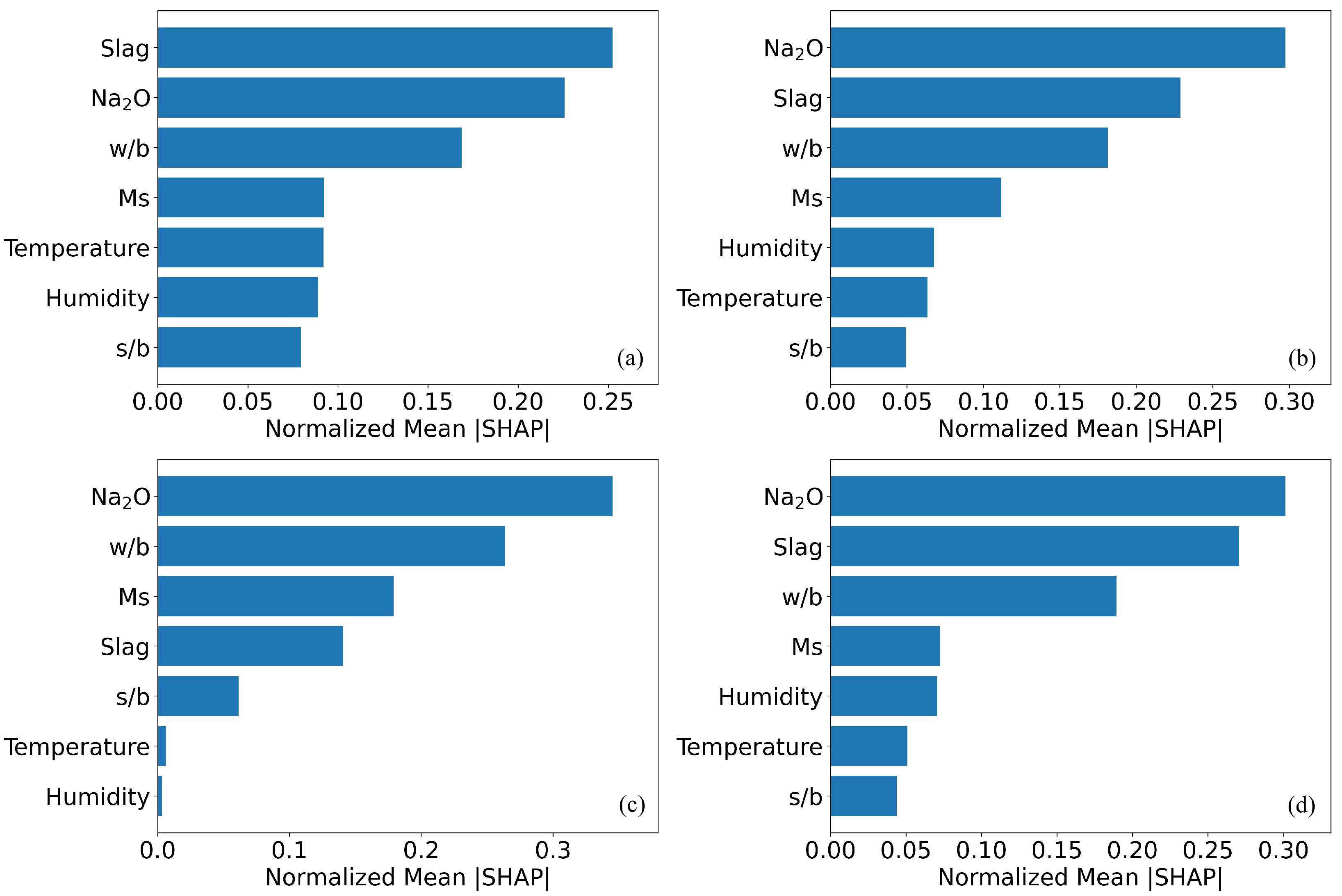
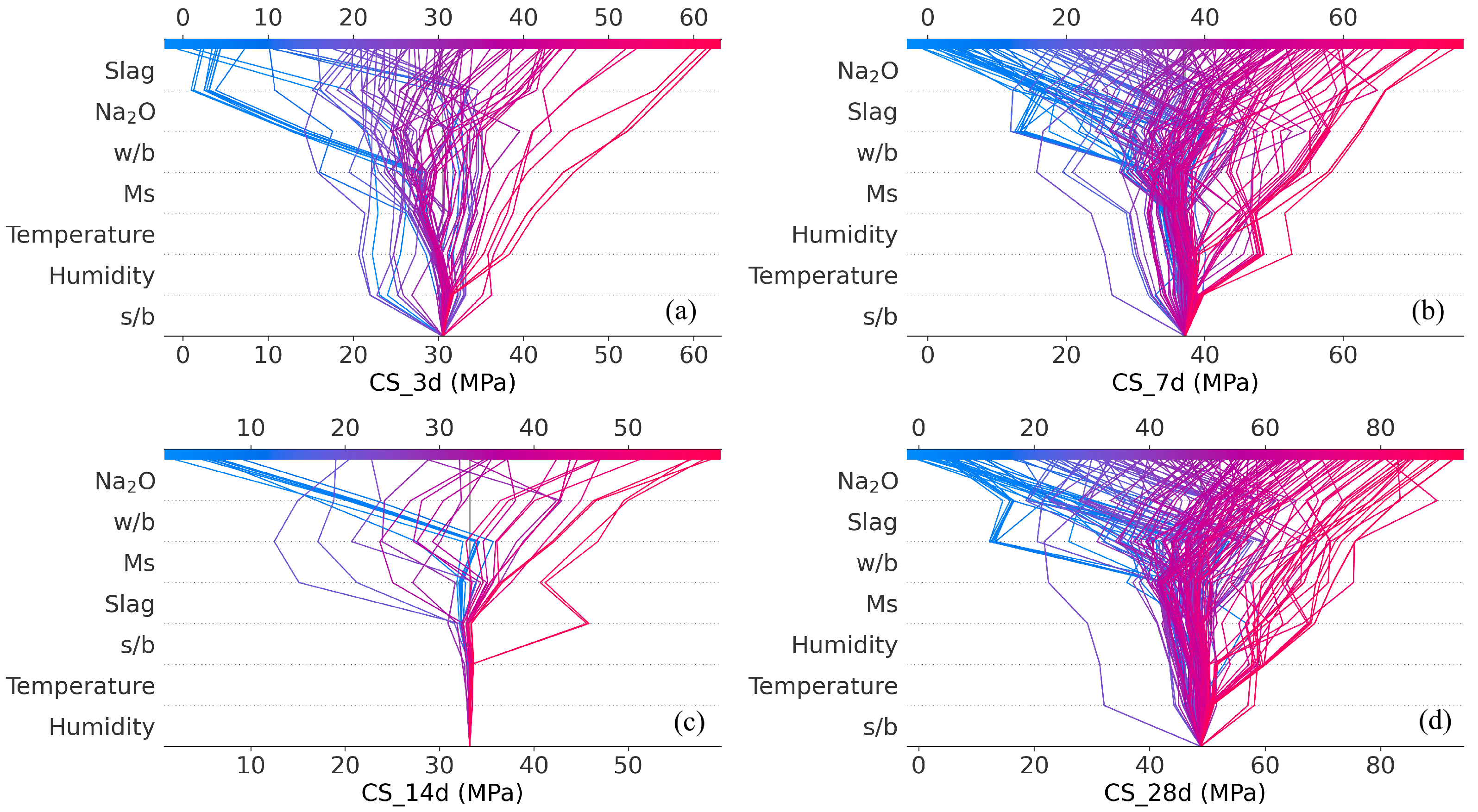
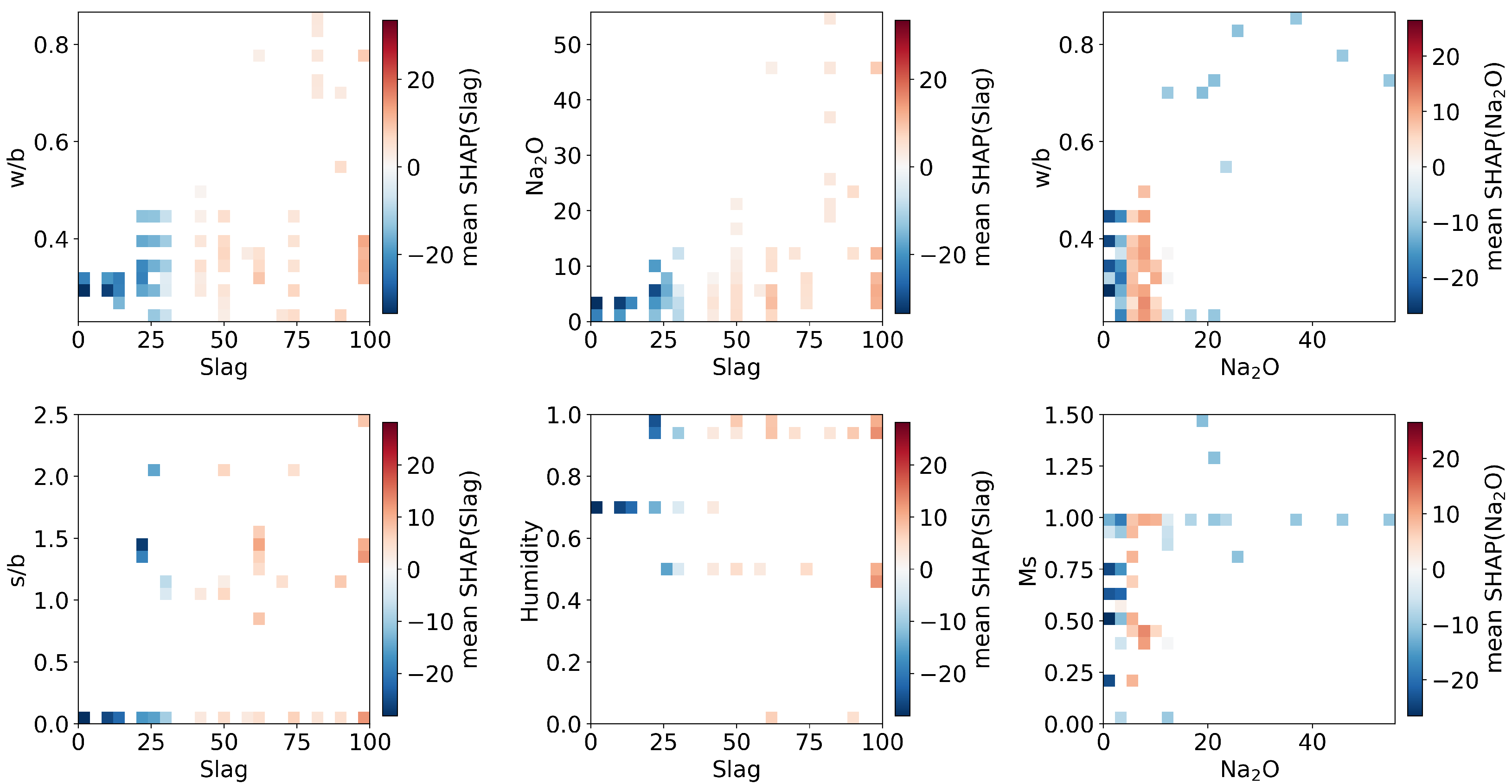
4.3. SHAP-Based Feature Importance Interpretation
5. Discussions
5.1. Strengths of the Present Study
5.2. Limitations
5.3. Future Works
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full form |
| FA | Fly Ash |
| GGBS | Ground Granulated Blast-furnace Slag |
| OPG | One-Part Geopolymer |
| OPC | Ordinary Portland Cement |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| SHAP | Shapley Additive Explanations |
| XGBoost | Extreme Gradient Boosting |
| RF | Random Forest |
| SVR | Support Vector Regression |
| KNN | K-Nearest Neighbors |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| Activator Modulus | |
| w/b | Water-to-Binder ratio |
| s/b | Sand-to-Binder ratio |
| Coefficient of Determination |
Appendix A. 2DDependence of Interacting Pairs



References
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Y.; Long, W.; Dong, B. Synthesis of one-part geopolymers from alkaline-activated molybdenum tailings: Mechanical properties and microstructural evolution. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 443, 141129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, T.; Abdollahnejad, Z.; Yliniemi, J.; Kinnunen, P.; Illikainen, M. One-part alkali-activated materials: A review. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 103, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Shenoy, S.; Li, L.; Tian, Q.; Zhang, H. Preparation of one-part geopolymers using coal gasification slag: Effect of alkali fusion product additive and liquid/solid ratio. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2024, 137, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiodun, Y.O.; Olanrewaju, O.A.; Gbenebor, O.P.; Ochulor, E.F.; Obasa, D.V.; Adeosun, S.O. Cutting cement industry CO2 emissions through metakaolin use in construction. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Saidur, R.; Hossain, M. A review on emission analysis in cement industries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 2252–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, G.; Bier, T.; Waida, S.; Dous, A.; Heinemann, S.; Herr, P.; Charitos, A. Treatment of Energy from Waste Plant fly-ash for blast furnace slag substitution as a Supplementary Cementitious Material. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 490, 144693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, K.H.; Zhou, Y.W.; Xu, H.; Zhao, C.H.; Yu, Y.; Li, Z.C. Nano-mechanism of graphene oxide reinforced fly ash-slag based geopolymer materials to form high polymerization degree C-(A)-SH: A new view of physical-chemical synergistic effect. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2025, 157, 105937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, A.İ.; Karalar, M.; Aksoylu, C.; Mydin, M.A.O.; Althaqafi, E.; Yılmaz, F.; Umiye, O.A.; Özkılıç, Y.O. Effect of GBFS ratio and recycled steel tire wire on the mechanical and microstructural properties of geopolymer concrete under ambient and oven curing conditions. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, A.I.; Tunc, U.; Karalar, M.; Şahan, M.F.; Özkılıç, Y.O. Study on mechanical, dynamic impact, and microstructural properties of eco-friendly geopolymer paving stones cured in ambient conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 464, 140132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, C.; Wang, H. Geopolymer from kaolin in China: An overview. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 119, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrefaei, Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Dai, J.G. Effect of mixing method on the performance of alkali-activated fly ash/slag pastes along with polycarboxylate admixture. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 117, 103917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasa, A.S.; Yaragal, S.C.; Swaminathan, K.; Reddy, R.R.K. Multi-objective optimization of one-part geopolymer mortars adopting response surface method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 409, 133772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Pavia, S.; Wang, X. Biomass ash waste from agricultural residues: Characterisation, reactivity and potential to develop one-part geopolymer cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 431, 136544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konduru, H.; Karthiyaini, S. Enhancing solidification in one-part geopolymer systems through alkali-thermal activation of bauxite residue and silica fume integration. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oderji, S.Y.; Chen, B.; Ahmad, M.R.; Shah, S.F.A. Fresh and hardened properties of one-part fly ash-based geopolymer binders cured at room temperature: Effect of slag and alkali activators. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Chen, K.; Yu, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Pan, C. Analyzing the compressive strength of one-part geopolymers using experiment and machine learning approaches. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 111429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaei, P.; Momenzadeh, A.; Hosseini, H.; Rajaei, S.; Ameri, F.; Pilehvar, S. One-part slag/zeolite geopolymer mortars under ambient and heat curing conditions. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e02677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wu, D.; Chen, K.; Liu, C.; Zhou, G.; Cheng, P. The effects of solid activator dosage and the liquid-solid ratio on the properties of FA-GGBS based one-part geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 463, 140067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, Y.J.; Heah, C.Y.; Liew, Y.M.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Lee, Y.S.; Kong, E.H.; Ong, S.W.; Ooi, W.E.; Ng, H.T.; Ng, Y.S. Strength optimization and key factors correlation of one-part fly ash/ladle furnace slag (FA/LFS) geopolymer using statistical approach. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 63, 105480. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Long, G.; Shi, Y.; Xie, Y. Preparation of cleaner one-part geopolymer by investigating different types of commercial sodium metasilicate in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 201, 636–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Su, J.; Wu, B. A hybrid Bayesian model updating and non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm framework for intelligent mix design of steel fiber reinforced concrete. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 161, 112071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasa, A.S.; Swaminathan, K.; Yaragal, S.C. Microstructural and optimization studies on novel one-part geopolymer pastes by Box-Behnken response surface design method. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e01946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Yao, J.; Li, X.; Qin, P.; Liu, X.; Cheng, C. Prediction of seawater intrusion run-up distance based on K-means clustering and ANN model. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, Z.; Yao, S. Slope Deformation Prediction Combining Particle Swarm Optimization-Based Fractional-Order Grey Model and K-Means Clustering. Fractal Fract. 2025, 9, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Huang, S.; Qiu, H.; Xu, Y.P.; Teegavarapu, R.S.; Guo, Y.; Nie, H.; Xie, H.; Xie, J.; Shao, Y.; et al. Assessment of ecological flow in river basins at a global scale: Insights on baseflow dynamics and hydrological health. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 178, 113868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xu, B.; Qiu, H.; Huang, S.; Teegavarapu, R.S.; Xu, Y.P.; Guo, Y.; Nie, H.; Xie, H. Adaptive assessment of reservoir scheduling to hydrometeorological comprehensive dry and wet condition evolution in a multi-reservoir region of southeastern China. J. Hydrol. 2025, 648, 132392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.F.A.; Chen, B.; Zahid, M.; Ahmad, M.R. Compressive strength prediction of one-part alkali activated material enabled by interpretable machine learning. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 360, 129534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faridmehr, I.; Sahraei, M.A.; Nehdi, M.L.; Valerievich, K.A. Optimization of fly ash—slag one-part geopolymers with improved properties. Materials 2023, 16, 2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Mongy, M.; Iqbal, M.; Farag, M.; Yosri, A.; Alsharari, F.; Yousef, S.E.A. Artificial Intelligence Prediction of One-Part Geopolymer Compressive Strength for Sustainable Concrete. CMES-Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2024, 141, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematollahi, B.; Sanjayan, J.; Shaikh, F.U.A. Synthesis of heat and ambient cured one-part geopolymer mixes with different grades of sodium silicate. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 5696–5704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godani, P.; Priya, T.S.; Alengaram, U.J. Evaluation of chemo-physio-mechanical characteristics of GGBS-MBS-based ready-mix geopolymer under ambient curing condition. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 449, 138202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Liu, N.; Jiang, Z. Utilizing raw phosphogypsum to prepare one-part geopolymer: Mechanical properties, optimization, and hydration mechanisms. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 449, 138466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.P.; Sani, M.A.; Nguyen, T.N.; Ngo, T.D. Microstructure and pore structure of one-part geopolymer incorporating electrolytic copper powder and graphene oxide. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 456, 139331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Ma, C.; Long, G.; Xie, Y. Cleaner one-part geopolymer prepared by introducing fly ash sinking spherical beads: Properties and geopolymerization mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 219, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Zhao, B.; Guo, S.; Long, G.; Xie, Y. Properties and characterization of green one-part geopolymer activated by composite activators. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J. Experimental study of freeze–thaw resistance of a one-part geopolymer paste. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasa, A.S.; Swaminathan, K.; Yaragal, S.C. Effect of slag and solid activator on flowability and compressive strength of fly ash based one-part geopolymer pastes. Mater. Today Proc. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Zhu, Z.; Huo, W.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhang, X. Assessing the viability of a high performance one-part geopolymer made from fly ash and GGBS at ambient temperature. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 75, 106978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Hu, G.; Wu, J.; Min, Y.; Li, Y. Experimental Study on the Compressive Strength of Slag-fly Ash Based Geopolymer Activated by Solid Sodium Silicate. Spec. Struct. 2023, 40, 100–105. [Google Scholar]
- Oderji, S.Y.; Chen, B.; Shakya, C.; Ahmad, M.R.; Shah, S.F.A. Influence of superplasticizers and retarders on the workability and strength of one-part alkali-activated fly ash/slag binders cured at room temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 229, 116891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.F.A.; Chen, B.; Oderji, S.Y.; Haque, M.A.; Ahmad, M.R. Improvement of early strength of fly ash-slag based one-part alkali activated mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 246, 118533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarakoon, M.; Ranjith, P.; Duan, W.H.; De Silva, V. Properties of one-part fly ash/slag-based binders activated by thermally-treated waste glass/NaOH blends: A comparative study. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 112, 103679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Al-Damad, I.M.A.; Siddika, A.; Kim, T.; Foster, S.; Hajimohammadi, A. Enhancing the workability retention of one-part alkali activated binders by adjusting the chemistry of the activators. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2025, 157, 105928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajimohammadi, A.; van Deventer, J.S. Characterisation of one-part geopolymer binders made from fly ash. Waste Biomass Valorization 2017, 8, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Elchalakani, M.; Karrech, A. Development of high strength one-part geopolymer mortar using sodium metasilicate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 236, 117611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Alrefaei, Y.; Dai, J.G. Roles of hybrid activators in improving the early-age properties of one-part geopolymer pastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 306, 124880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almakhadmeh, M.; Soliman, A. Effects of mixing water temperatures on properties of one-part alkali-activated slag paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 266, 121030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Ref No. | Data Source | Tests Nbr |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Wei et al. (2024) [16] | 5 |
| 2 | Nematollahi et al. (2015) [30] | 2 |
| 3 | Srinivasa et al. (2023) [12] | 27 |
| 4 | Godani et al. (2024) [31] | 6 |
| 5 | Zhang et al. (2024) [32] | 1 |
| 6 | Tran et al.(2024) [33] | 1 |
| 7 | Chen et al. (2025) [18] | 9 |
| 8 | Guo et al. (2019) [34] | 18 |
| 9 | Ma et al. (2019) [35] | 6 |
| 10 | Oderji et al. (2019) [15] | 8 |
| 11 | Min et al. (2022) [36] | 2 |
| 12 | Srinivasa et al. [22] | 17 |
| 13 | Shoaei et al. (2024) [17] | 2 |
| 14 | Srinivasa et al. (2023) [37] | 10 |
| 15 | Ma et al. (2023) [38] | 16 |
| 16 | Gao et al. (2023) [39] * | 8 |
| 17 | Oderji et al.(2019) [40] | 3 |
| 18 | Shah et al. (2020) [41] | 14 |
| 19 | Samarakoon (2020)[42] | 2 |
| 20 | Alrefaei et al. (2021) [11] | 8 |
| 21 | Gao et al. (2025) [43] | 2 |
| 22 | Ma et al. (2018) [20] | 6 |
| 23 | Hajimohammadi et al. (2017) [44] | 3 |
| 24 | Dong et al. (2020) [45] | 30 |
| 25 | Wang et al. (2021) [46] | 8 |
| 26 | Almakhadmeh et al. (2021) [47] | 6 |
| Total number of tests | 220 | |
| Model | CS_3d | CS_7d | CS_14d | CS_28d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ExtraTrees | 0.9464 | 0.9888 | 0.9918 | 0.9804 | |
| KNN | 0.8141 | 0.8100 | 0.7304 | 0.8061 | |
| RF | 0.9325 | 0.9671 | 0.9572 | 0.9648 | |
| Ridge | 0.5794 | 0.4671 | 0.7304 | 0.4312 | |
| SVR | 0.7022 | 0.7151 | 0.8132 | 0.6978 | |
| XGBoost | 0.9462 | 0.9889 | 0.9918 | 0.9810 | |
| RMSE | ExtraTrees | 3.7715 | 2.1520 | 1.5378 | 3.5557 |
| KNN | 7.0253 | 8.8473 | 8.8329 | 11.1718 | |
| RF | 4.2327 | 3.6825 | 3.5211 | 4.7606 | |
| Ridge | 10.5668 | 14.8159 | 8.8329 | 19.1363 | |
| SVR | 8.8910 | 10.8330 | 7.3523 | 13.9485 | |
| XGBoost | 3.7796 | 2.1695 | 1.5384 | 3.5723 | |
| MAE | ExtraTrees | 1.6148 | 0.6360 | 0.6328 | 1.2395 |
| KNN | 5.5770 | 6.9305 | 6.6341 | 8.7905 | |
| RF | 2.8452 | 2.6556 | 2.6092 | 3.3540 | |
| Ridge | 8.2062 | 11.7629 | 7.1553 | 15.0461 | |
| SVR | 6.0249 | 7.7845 | 5.1732 | 10.0671 | |
| XGBoost | 1.6692 | 0.7875 | 0.6517 | 1.4226 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Wang, C.; He, W.; Ding, Q.; Wang, F.; Wang, M.; Fang, K. Interpretation of Dominant Features Governing Compressive Strength in One-Part Geopolymer. Buildings 2025, 15, 3661. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203661
Wang Y, Jia Y, Wang C, He W, Ding Q, Wang F, Wang M, Fang K. Interpretation of Dominant Features Governing Compressive Strength in One-Part Geopolymer. Buildings. 2025; 15(20):3661. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203661
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yiren, Yihai Jia, Chuanxing Wang, Weifa He, Qile Ding, Fengyang Wang, Mingyu Wang, and Kuizhen Fang. 2025. "Interpretation of Dominant Features Governing Compressive Strength in One-Part Geopolymer" Buildings 15, no. 20: 3661. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203661
APA StyleWang, Y., Jia, Y., Wang, C., He, W., Ding, Q., Wang, F., Wang, M., & Fang, K. (2025). Interpretation of Dominant Features Governing Compressive Strength in One-Part Geopolymer. Buildings, 15(20), 3661. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203661





