An Airborne and Impact Sound Insulation Analysis of 3D Woven Textiles on the Floor in Buildings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
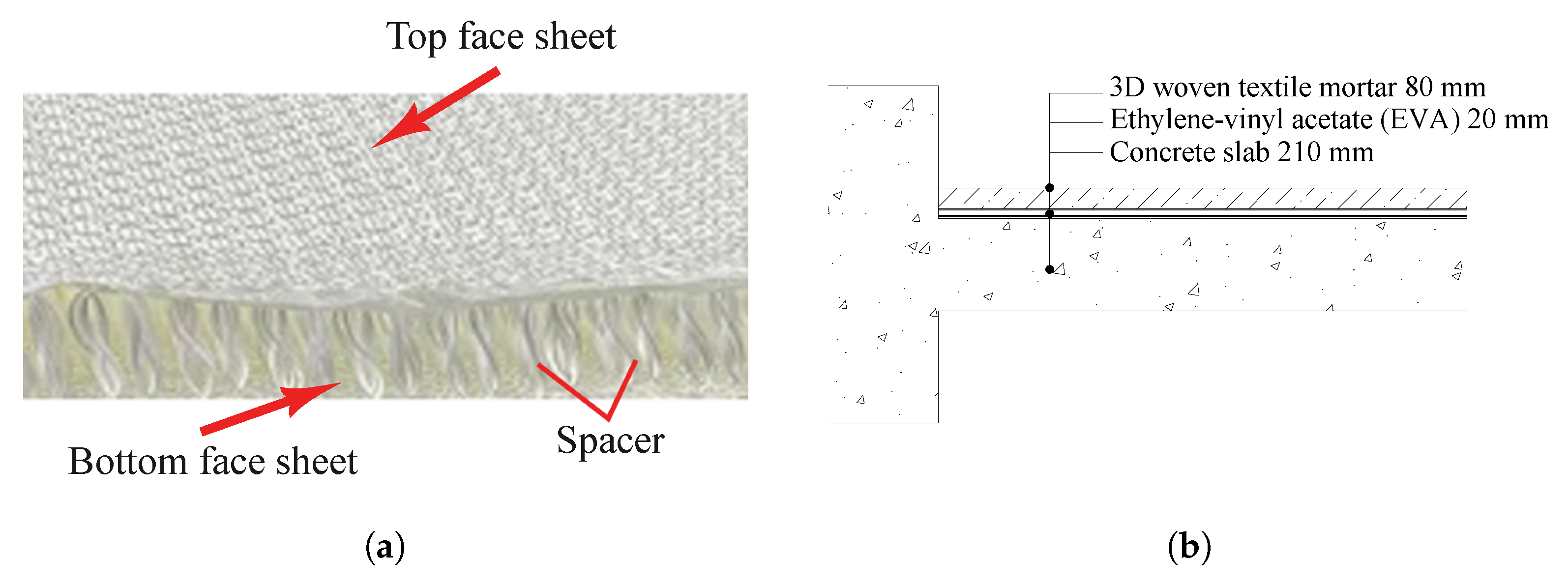
2.1. 3D Woven Textile Material
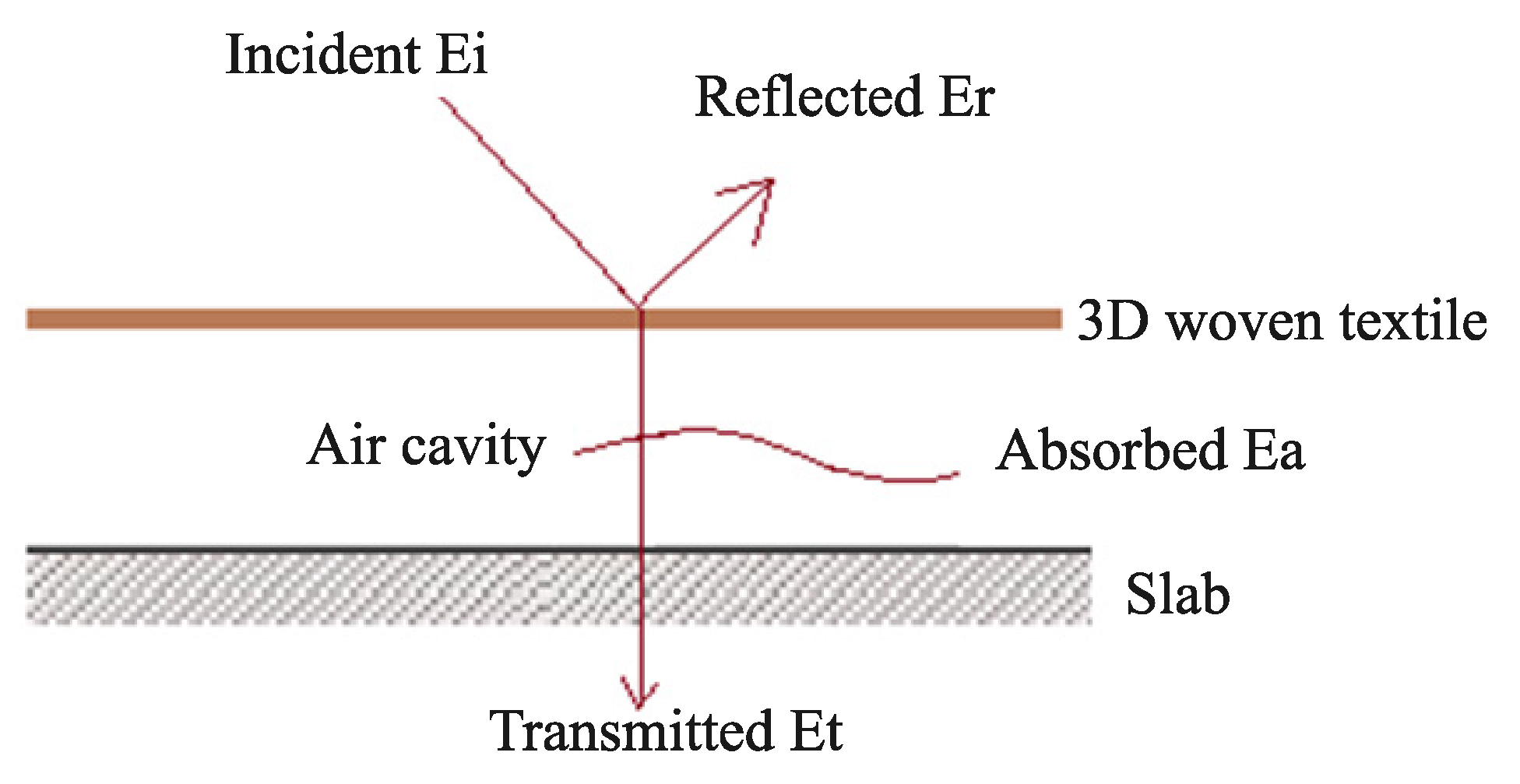
2.2. Sound Absorption Coefficient
2.2.1. Transfer Matrix Method
2.2.2. Measurement Method for SAC
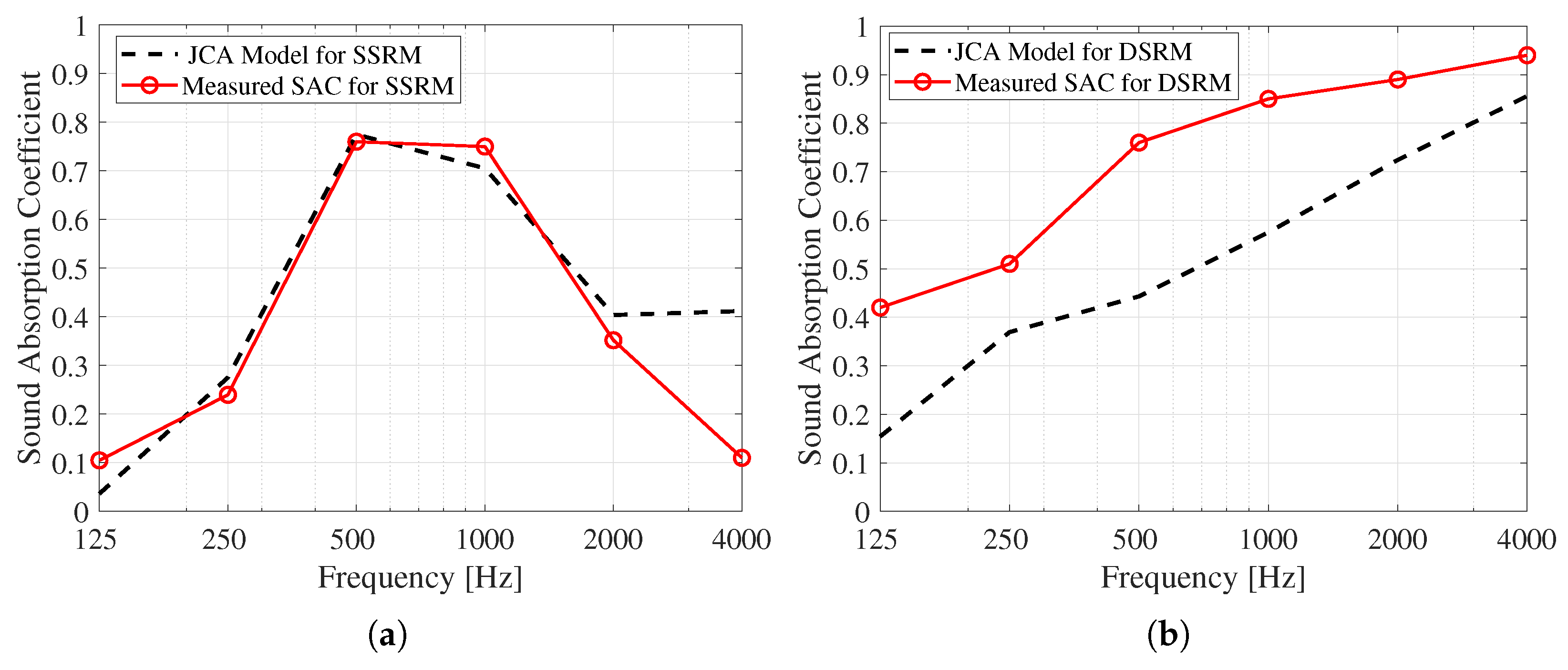
2.2.3. SAC Comparison and Calibration
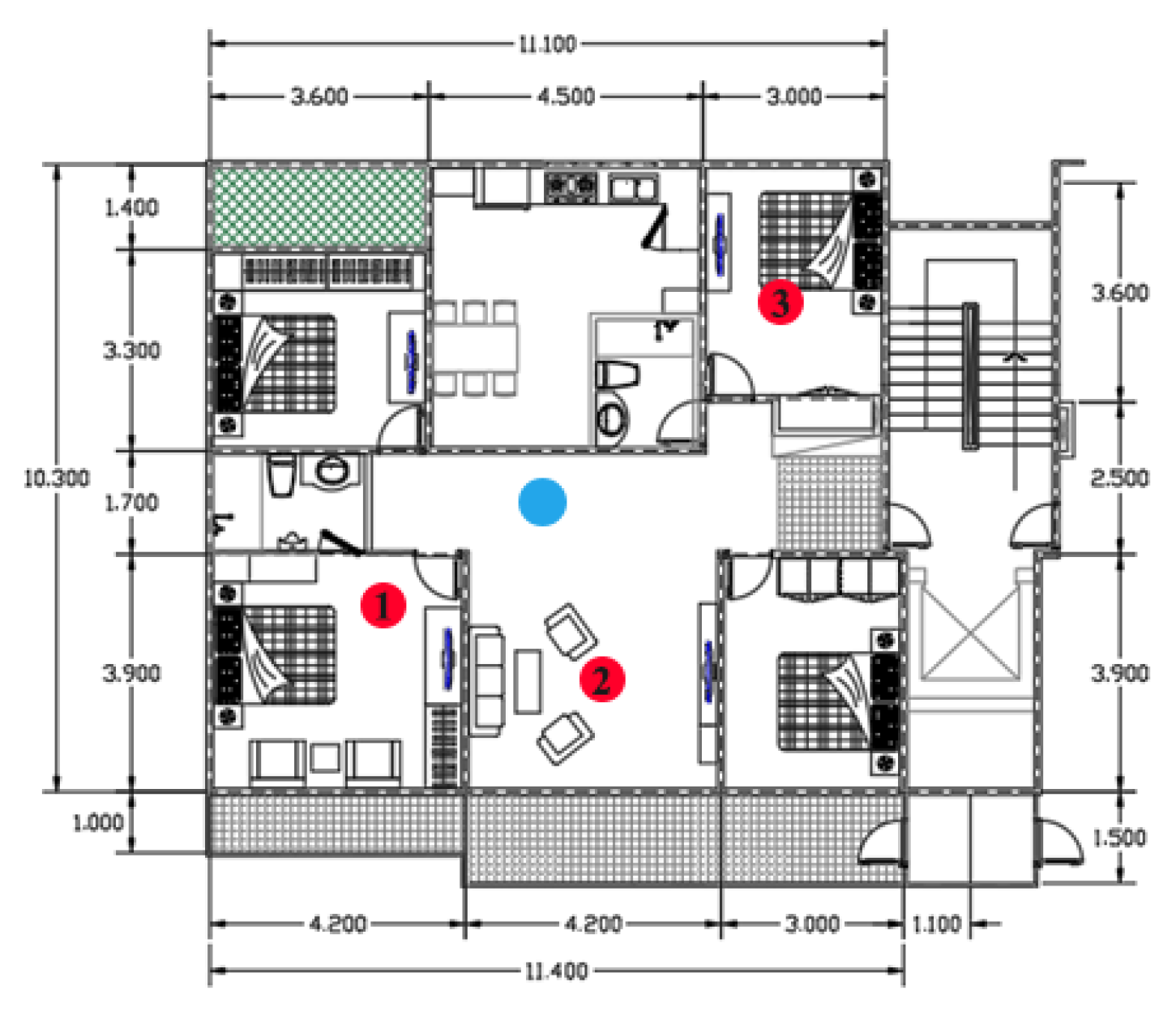
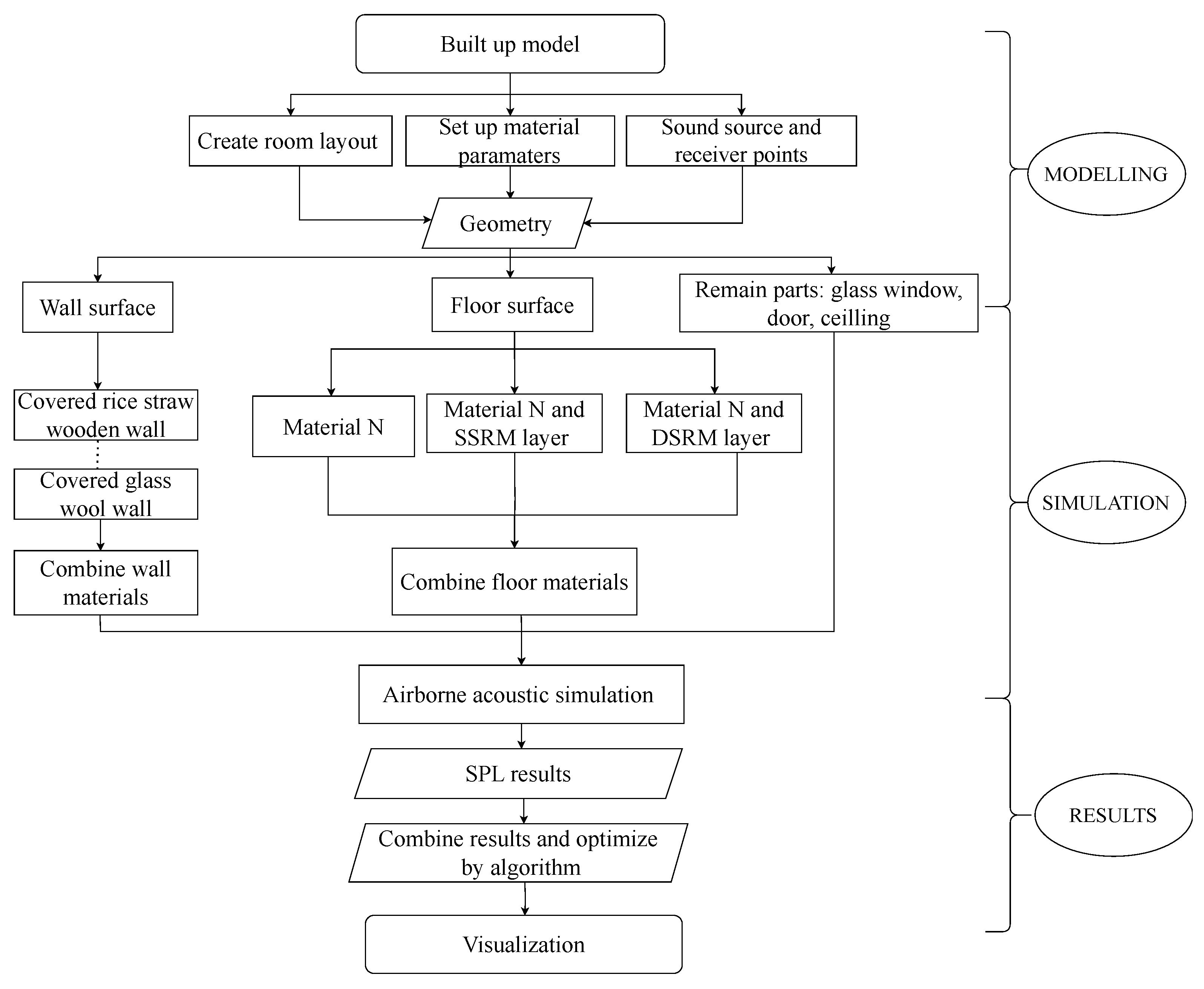
2.3. Airborne Sound Simulation
2.3.1. Parametric Study
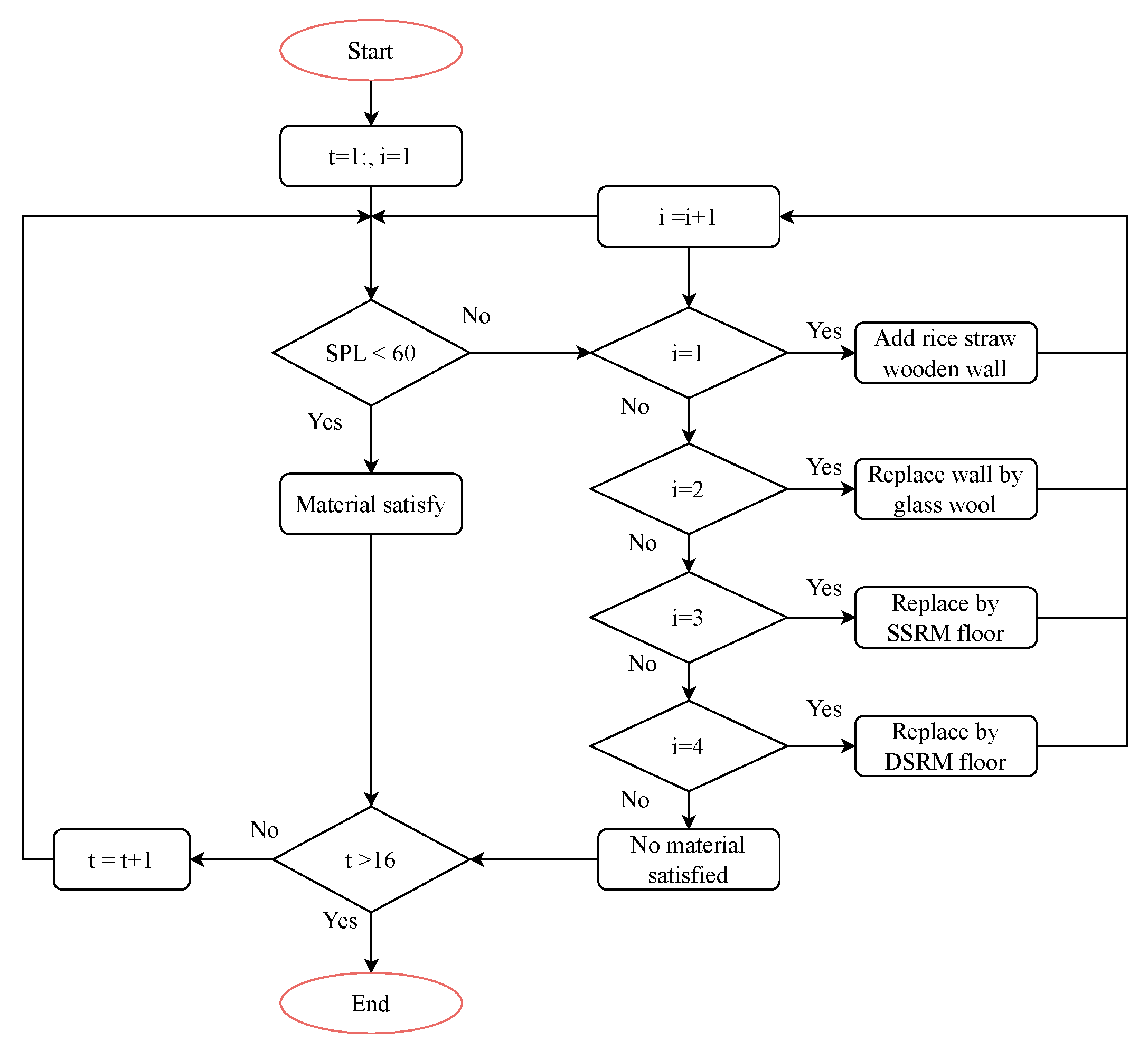
2.3.2. Control Strategy
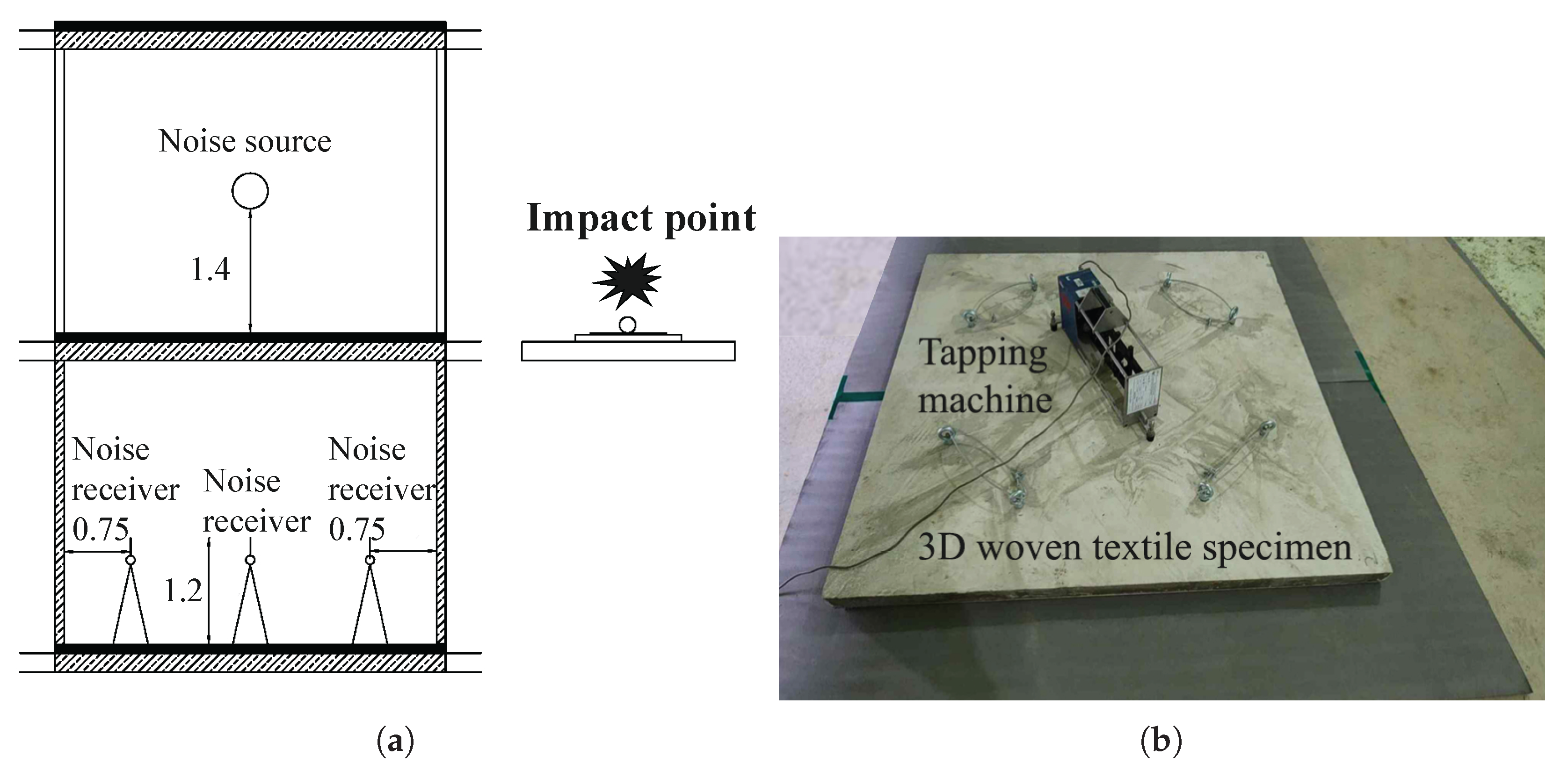
2.4. Floor Impact Sound Measurement
2.4.1. 3D Woven Textile Characteristics
2.4.2. Dynamic Stiffness
2.4.3. Measurement Method
2.5. Hybrid Approach
2.5.1. Airborne Sound Evaluation
2.5.2. Floor Impact Sound Evaluation
3. Results
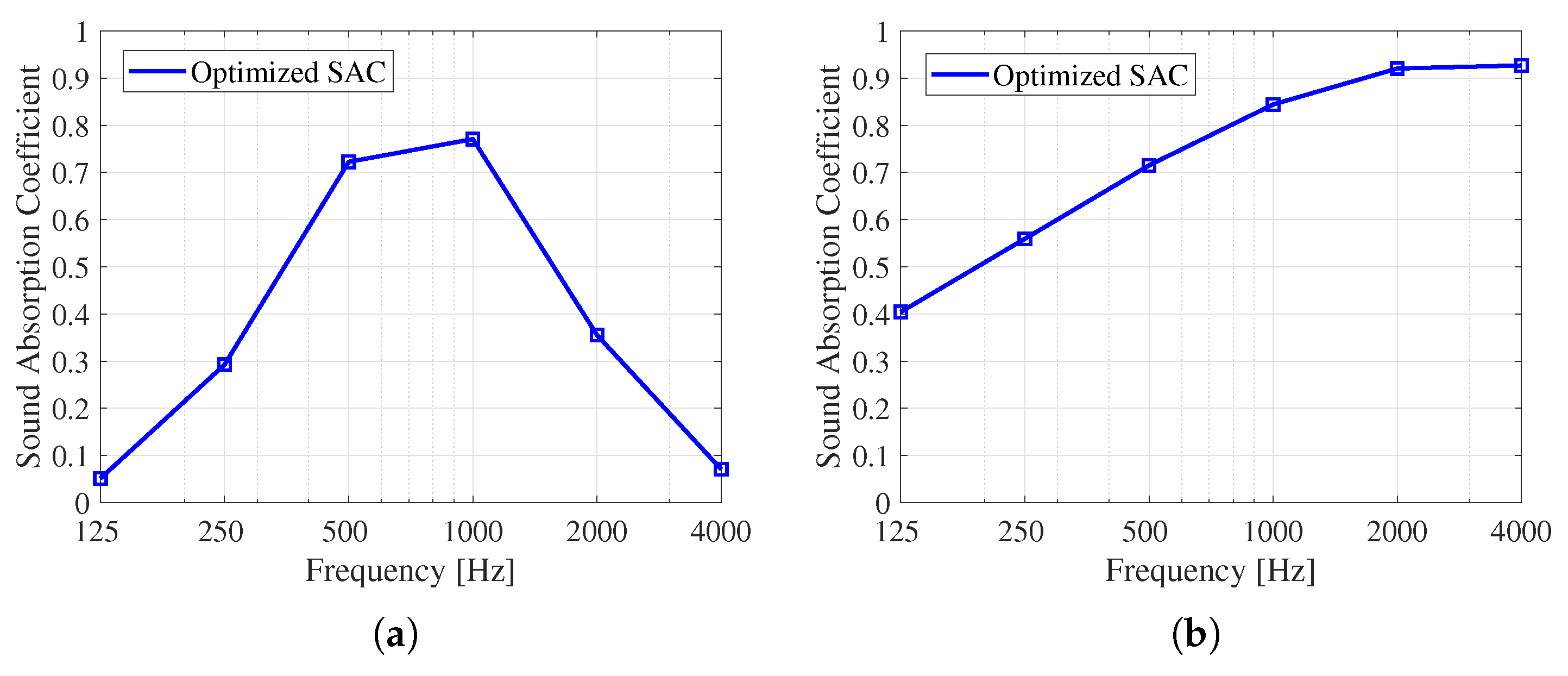
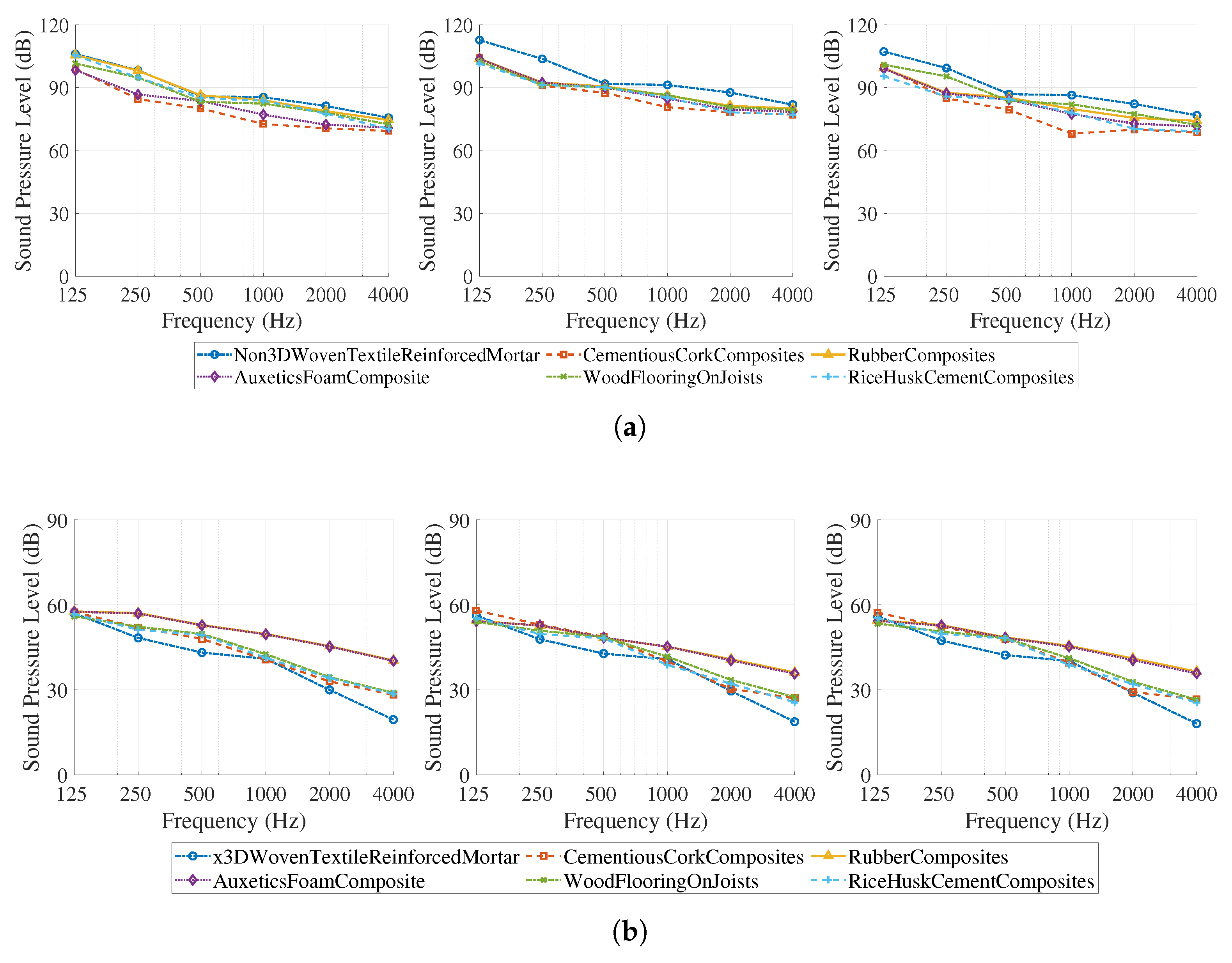
3.1. Airborne Sound Simulation Results
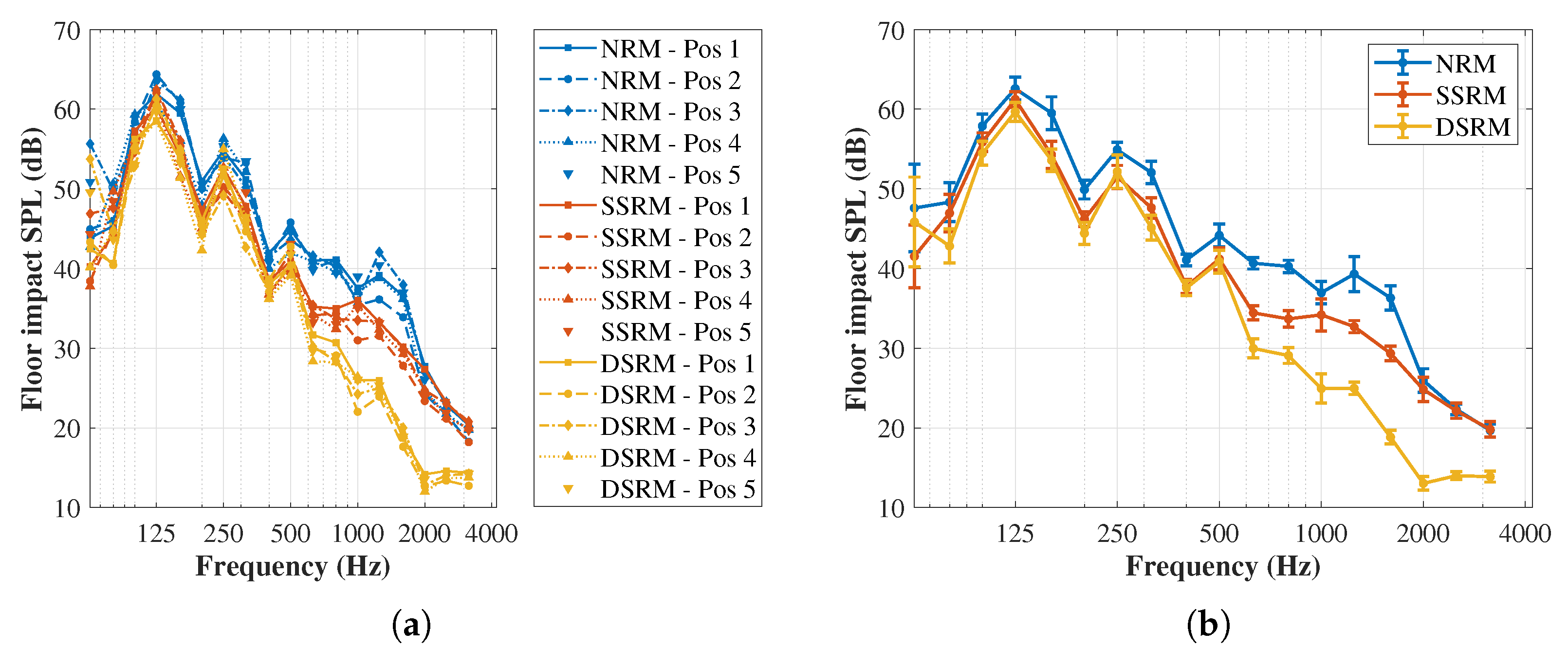
3.2. Floor Impact Sound Experimental Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Airborne Acoustic Reduction
4.2. Floor Impact Noise Reduction
4.3. Limitations
4.4. Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, S.H.; Lee, P.J. Reaction to floor impact noise in multi-storey residential buildings: The effects of acoustic and non-acoustic factors. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 150, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardaxis, N.G.; Bard, D.; Persson Waye, K. Review of acoustic comfort evaluation in dwellings—Part I: Associations of acoustic field data to subjective responses from building surveys. Build. Acoust. 2018, 25, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.W.; Jang, S.S.; Hashitsume, K.; Kolya, H. Estimation of impact sound reduction by wood flooring installation in a wooden building in Korea. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 64, 105708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.M.; Luo, W.; Xie, J.; Wen, G.; Lee, H.P. Studies on the sound absorption and transmission loss performances of wood-based, natural and waste materials. Acta Mech. Sin. 2021, 37, 861–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sair, S.; Mandili, B.; Taqi, M.; El Bouari, A. Development of a new eco-friendly composite material based on gypsum reinforced with a mixture of cork fibre and cardboard waste for building thermal insulation. Compos. Commun. 2019, 16, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, T.S.; Mo, K.H.; Putra, A.; Loo, S.C.; Alengaram, U.J.; Ling, T.C. Sound absorption performance of modified concrete: A review. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 30, 101219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awoyera, P.O.; Akinrinade, A.D.; de Sousa Galdino, A.G.; Althoey, F.; Kirgiz, M.S.; Tayeh, B.A. Thermal insulation and mechanical characteristics of cement mortar reinforced with mineral wool and rice straw fibers. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 53, 104568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.K.; Kim, K.W. Sound absorbing ceiling to reduce heavy weight floor impact sound. Build. Environ. 2020, 180, 107058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.H.; Kwak, J.H.; Park, J.; Kim, D. Floor-Impact Sound Insulation Performance of Acoustic Metamaterial Ceiling. In Proceedings of the 10th Convention of the European Acoustics Association, Torino, Italy, 11–15 September 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Sato, H.; Kurakata, K.; Hiramitsu, A.; Tanaka, M.; Hirota, T. Subjective ratings of heavy-weight floor impact sounds in wood frame construction. Acoust. Sci. Technol. 2010, 31, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Ha, Y.S.; Kim, C.K.; Cho, H.J.; Lee, S.J. Fundamental Natural Frequency and Floor Impact Sound Insulation Performance of CLT Slabs Based on Wood Species and Panel Connections: An Experimental Study. BioResources 2025, 20, 100–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, A.; Paoletti, I. Acoustic 3D Spacer Fabrics in the Frame of Acoustic Materials: Limitations and Potentialities. In Proceedings of the Forum Acusticum 2023: Proceedings of the 10th Convention of the European Acoustics Association, Turin, Italy, 11–15 September 2023; pp. 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouritz, A.P.; Bannister, M.K.; Falzon, P.J.; Leong, K.H. Review of applications for advanced three-dimensional fibre textile composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1999, 30, 1445–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Peng, X.; Xin, F.; Lu, T.J. A microstructure-based model of transport parameters and sound absorption for woven fabrics. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 227, 109607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, N.; Fan, X.; Gong, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, X. Investigation of effective factors of woven structure fabrics for acoustic absorption. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 161, 107081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barburski, M.; Blaszczak, J.R.; Pawliczak, Z. Influence of designs of weaves on acoustic attenuation of fabrics. J. Ind. Text. 2019, 49, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madushika, J.W.A.; Lanarolle, W.D.G. A review on novel approaches to enhance sound absorbing performance using textile fibers. J. Text. Inst. 2022, 113, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, V.; Mishra, R.; Militky, J.; Novak, J. Thermo-acoustic behaviour of 3D knitted spacer fabrics. Fibers Polym. 2015, 16, 2467–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeon, J.O.; Kim, K.W.; Yang, K.S. A correlation between a single number quantity and noise level of real impact sources for floor impact sound. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 125, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, K.; Tsianou, M.; Alexandridis, P. Recycling of Blended Fabrics for a Circular Economy of Textiles: Separation of Cotton, Polyester, and Elastane Fibers. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheurer, M.; Friese, D.; Penzel, P.; Dittel, G.; Bhat, S.; Overhage, V.; Hahn, L.; Heins, K.; Cherif, C.; Gries, T. Current and future trends in textiles for concrete construction applications. Textiles 2023, 3, 408–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, S.; Ivanova, T.A.; Mishra, R.K.; Müller, M.; Akhbari, M.; Hashjin, Z.E. Effect of natural fiber and biomass on acoustic performance of 3D hybrid fabric-reinforced composite panels. Materials 2024, 17, 5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayalath, A.; Navaratnam, S.; Gunawardena, T.; Mendis, P.; Aye, L. Airborne and impact sound performance of modern lightweight timber buildings in the Australian construction industry. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, C.M.; Wang, Z. Recent advances in building acoustics: An overview of prediction methods and their applications. Build. Environ. 2015, 91, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10140-3; Acoustics—Laboratory Measurement of Sound Insulation of Building Elements—Part 3: Measurement of Impact sound Insulation. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/79483.html (accessed on 16 April 2021).
- KS F ISO 717-2; Acoustics—Rating of Sound Insulation in Buildings and of Building Elements—Part 2: Impact Sound Insulation. Korean Standards Association: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2022. Available online: https://www.kssn.net/en/search/stddetail.do?itemNo=K001010137978 (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Peled, A.; Bentur, A.; Mobasher, B. Textile Reinforced Concrete; Modern Concrete Technology Series; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, H.; Xu, J.; Feng, Y.; Liu, D.; Tang, P.; Feng, Y. Experimental Research and Theoretical Analysis of the Coupling Mechanism Between Microstructure and Acoustics in Porous Materials. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, M.J.; To, W.M. Acoustic properties of rigid-frame porous materials—An engineering perspective. Appl. Acoust. 2001, 62, 793–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Li, X.; Gai, X.; Zhang, B.; Xing, T. Optimization of Sound Absorption Performance of Woven Fabric. In Proceedings of the INTER-NOISE 2019: The 48th International Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering, Madrid, Spain, 16–19 June 2019; pp. 1323–1330. Available online: https://www.sea-acustica.es/INTERNOISE_2019/Fchrs/Proceedings/1323.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2025).
- Cai, Z.; Li, X.; Gai, X.; Zhang, B.; Xing, T. An empirical model to predict sound absorption ability of woven fabrics. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 170, 107483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.; Gaspar, A.; Godinho, L.; Amado Mendes, P.; Mateus, D.; Carbajo, J.; Ramis, J.; Poveda, P. On the use of perforated sound absorption systems for variable acoustics room design. Buildings 2021, 11, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN ISO 354:2003; Acoustics—Measurement of Sound Absorption in a Reverberation Room. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/34545.html (accessed on 9 June 2003).
- ASTM C423-22; Standard Test Method for Sound Absorption and Sound Absorption Coefficients by the Reverberation Room Method. ASTM Standard: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1990. [CrossRef]
- Soltani, P.; Zarrebini, M. The analysis of acoustical characteristics and sound absorption coefficient of woven fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2012, 82, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasina, M.; Monkova, K.; Monka, P.P.; Kozak, D.; Tkac, J. Study of the Sound Absorption Properties of 3D-Printed Open-Porous ABS Material Structures. Polymers 2020, 12, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taban, E.; Soltani, P.; Berardi, U.; Putra, A.; Mousavi, S.M.; Faridan, M.; Samaei, S.E.; Khavanin, A. Measurement, modeling, and optimization of sound absorption performance of Kenaf fibers for building applications. Build. Environ. 2020, 180, 107087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoruso, F.M.; Dietrich, U.; Schuetze, T. Development of a building information modeling-parametric workflow based renovation strategy for an exemplary apartment building in Seoul, Korea. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10534-2:2023; Acoustics—Determination of Acoustic Properties in Impedance Tubes—Part 2: Two-Microphone Technique for Normal Sound Absorption Coefficient and Normal Surface Impedance. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/81294.html (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Wijesinghe, K.; Gunasekara, C.; Law, D.W.; Hidallana-Gamage, H.; Wanasekara, N.; Wang, L. Thermal and acoustic performance in textile fibre-reinforced concrete: An analytical review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 412, 134879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KS F 2865:2020; Test Method for Impact Sound Insulation of Floors with Floor Coverings. Korean Standards Association: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2020. Available online: https://www.kssn.net/en/search/stddetail.do?itemNo=K001010129889 (accessed on 21 December 2020).
- Kim, Y.H.; Moon, S.S.; Yeon, J.O. Impact Sound Reduction Performances of Additional Floor Mats for the Retrofitting of an Existing Apartment Building in Accordance with Test-Bed Conditions. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 9052-1; Acoustics—Determination of Dynamic Stiffness—Part 1: Materials Used Under Floating Floors in Dwellings. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1989. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/16620.html (accessed on 25 February 1989).
- Carbajo, J.; Poveda, P.; Segovia, E.; Prieto, A.; Río-Martín, L.; Pastor, J.D.; Ramis, J. An Alternative Approach to Determine the Dynamic Stiffness of Resilient Materials under Low Prestatic Load. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Ha, Y.S.; Kim, C.K.; Chang, J.H.; Cho, H.J.; Lee, S.J. Effect of Concrete and EPS Layer on Stiffness and Floor Impact Sound Insulation Performance of CLT Slabs. SSRN 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KS F 2810-1:2020; Field Measurements of Impact Sound Insulation of Floors—Part 1: Method Using Standard Light Impact Source. Korean Standards Association: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2020. Available online: https://www.kssn.net/en/search/stddetail.do?itemNo=K001010129880 (accessed on 21 December 2020).
- KS F 2863-1:2022; Rating of Floor Impact Sound Insulation for Impact Source in Buildings and of Building Elements—Part 1: Floor Impact Sound Insulation Against Standard Light Impact Source. Korean Standards Association: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2022. Available online: https://www.kssn.net/en/search/stddetail.do?itemNo=K001010139589 (accessed on 12 October 2022).
- ISO 717-2:2020; Acoustics—Rating of Sound Insulation in Buildings and of Building Elements—Part 2: Impact Sound Insulation. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/69867.html (accessed on 25 December 2020).
- Zhang, D.; Tenpierik, M.; Bluyssen, P.M. Individual control as a new way to improve classroom acoustics: A simulation-based study. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 179, 10–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KS F 2809:2021; Field Measurements of Airborne Sound Insulation of Buildings. Korean Standards Association: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2021. Available online: https://www.kssn.net/en/search/stddetail.do?itemNo=K001010135119 (accessed on 12 October 2021).
- Long, M. Architectural Acoustics, 1st ed.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Available online: https://shop.elsevier.com/books/architectural-acoustics/long/978-0-08-052755-0 (accessed on 23 December 2005).
- ISO 226:2023; Acoustics—Normal Equal-Loudness-Level Contours. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/83117.html (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Kim, K.W.; Jeong, G.C.; Yang, K.S.; Sohn, J.Y. Correlation between dynamic stiffness of resilient materials and heavyweight impact sound reduction level. Build. Environ. 2009, 44, 1589–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.; Hsieh, M. Sound insulation performance of different built-in acoustic materials for new multifamily residential. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2025, 24, 1296–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
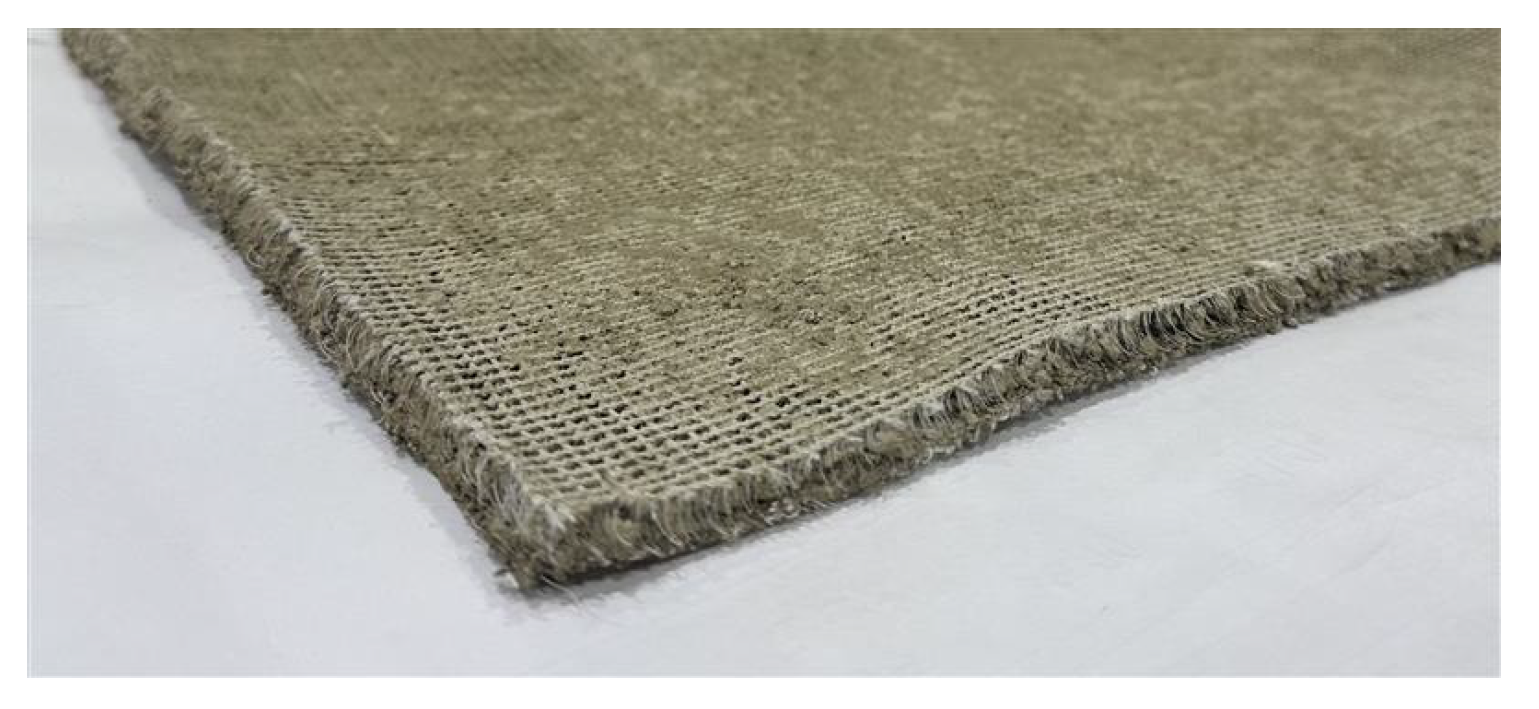
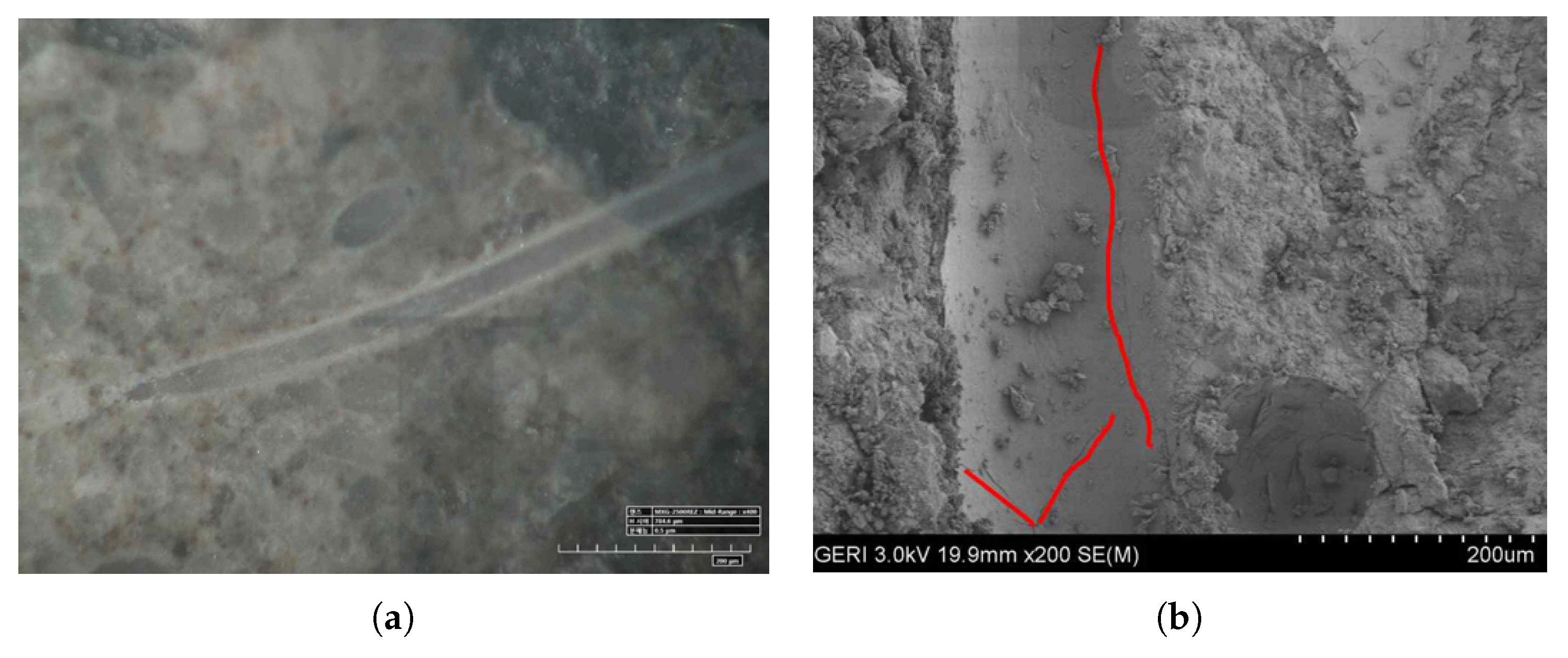
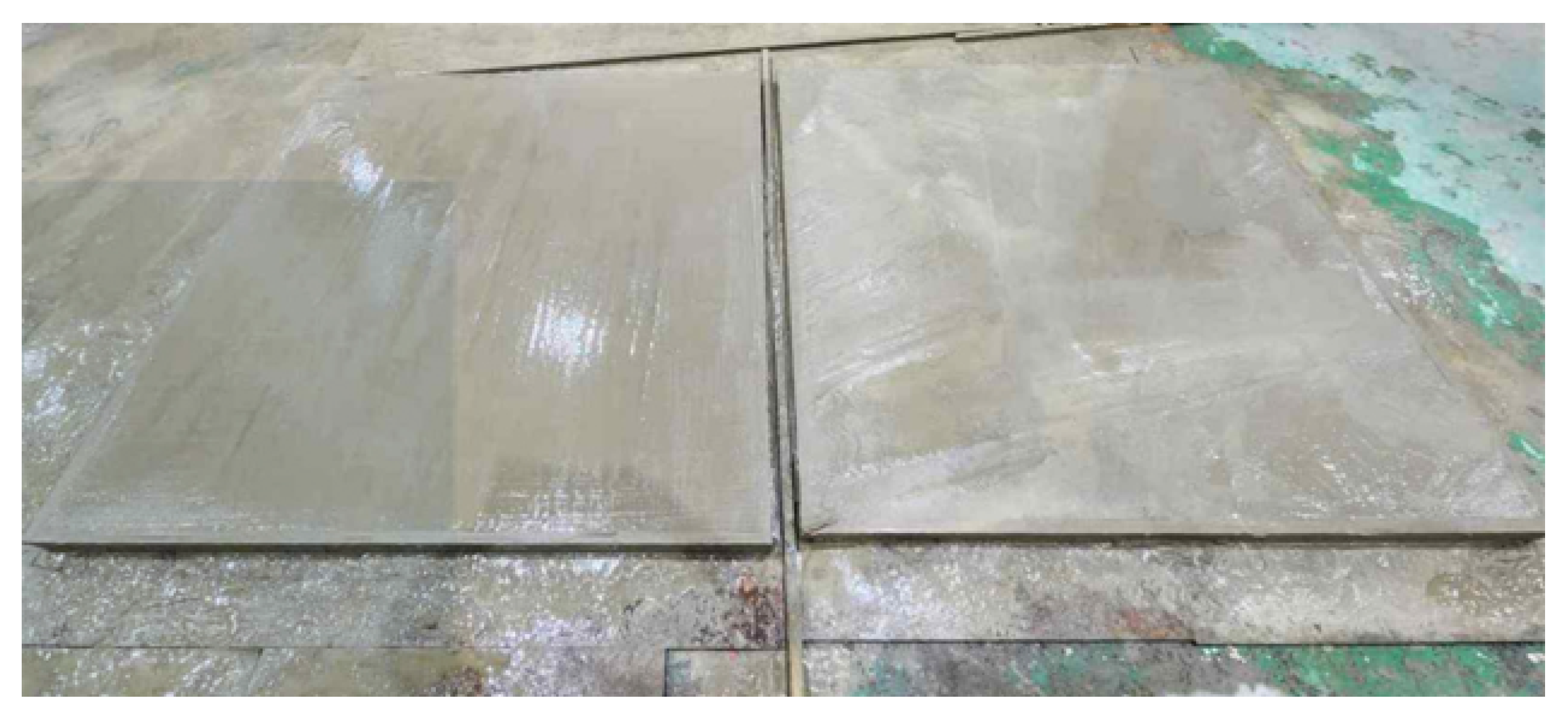










| Symbol | Parameters | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porosity | 0.86 | ||
| Tortuosity | 1.15 | ||
| Airflow resistivity | 56,000 | Pa.s/m2 | |
| Viscous characteristic length | 60 | µm | |
| Thermal characteristic length | 110 | µm |
| Materials | Coefficient | Frequency (Hz) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 125 | 250 | 500 | 1000 | 2000 | 4000 | ||
| Non-3D woven textile reinforced mortar (NRM) | 0.13 | 0.25 | 0.58 | 0.15 | 0.37 | 0.17 | |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | ||
| Single side-3D woven textile reinforced mortar (SSRM) | 0.05 | 0.29 | 0.72 | 0.77 | 0.36 | 0.07 | |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | ||
| Double side-3D woven textile reinforced mortar (SSRM) | 0.40 | 0.56 | 0.72 | 0.84 | 0.92 | 0.93 | |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | ||
| Cementious cork composites | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.86 | 0.3 | |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | ||
| Rubber composites | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.05 | |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | ||
| Auxetics foam composite | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.21 | 0.15 | |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | ||
| Wood flooring on joists | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.1 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.07 | |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | ||
| Rice husk cement composites | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.18 | 0.3 | |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | ||
| Gypsum ceiling | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.05 | |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | ||
| Single pane of glass window | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | ||
| Solid wood panels door | 0.1 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | ||
| Concrete block wall | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.08 | |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | ||
| Rice straw wood wall | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.46 | 0.3 | |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | ||
| Glass wool or rock wool wall 100 mm | 0.35 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 0.92 | 0.9 | 0.85 | |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | ||
| Material | Density | Poisson’s Ratio | Modulus of Elasticity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3D woven textiles | 0.44 | 1080 MPa |
| Airborne Sound Evaluation | Ordinary Room | Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Sound Pressure Level (SPL) [51] | dB | According to ISO 226:2023 [52], illustrates the threshold of hearing and a-weighting curve through the points at 60 dB. |
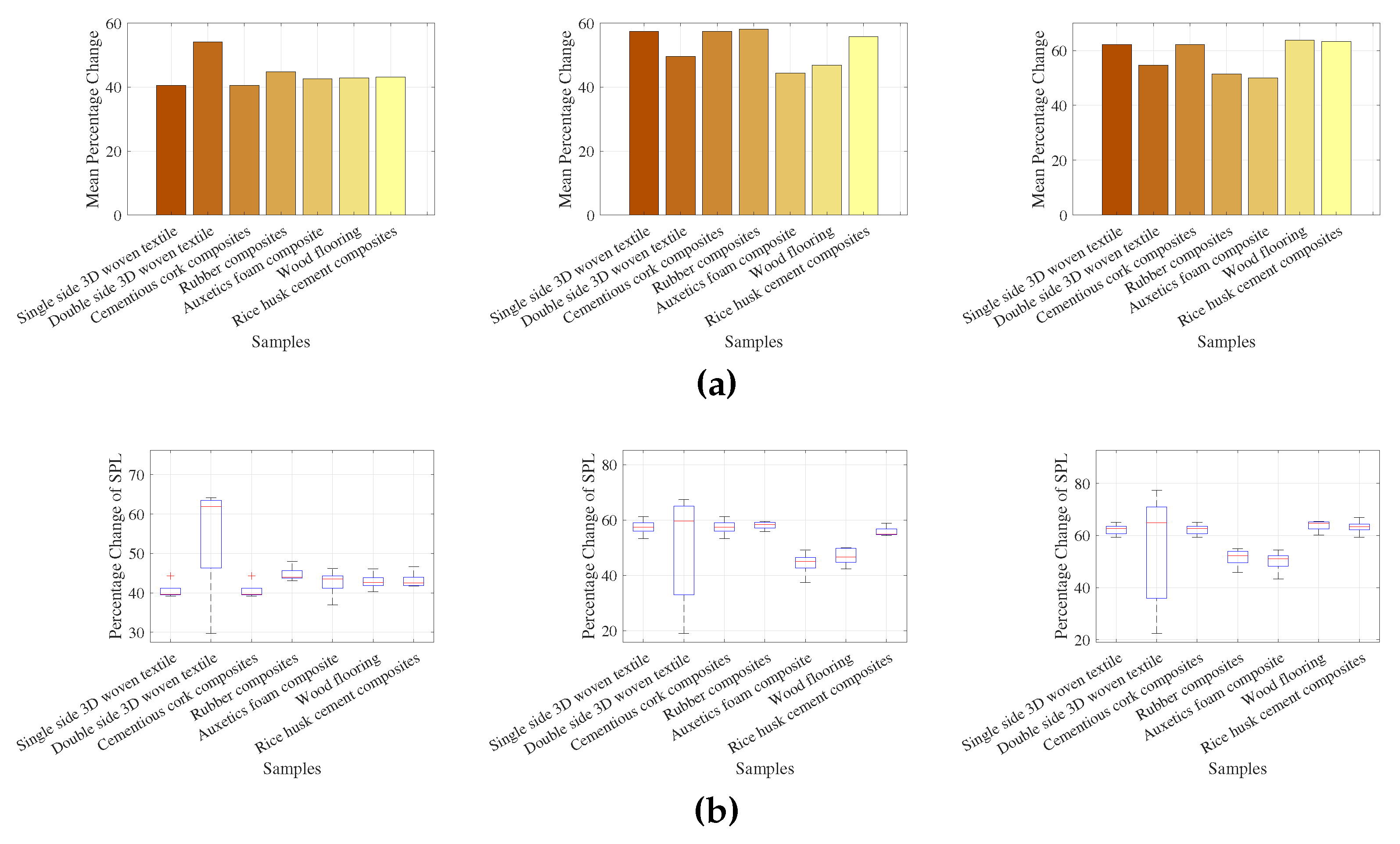
| No | Name of Materials | Mean of SPL Change at 5 Positions | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 Hz | 2000 Hz | 4000 Hz | ||
| 1 | Single side 3D woven textile (SSRM) | 40.57 | 57.42 | 62.23 |
| 2 | Double side 3D woven textile (DSRM) | 54.14 | 49.56 | 54.72 |
| 3 | Cementious cork composites | 40.57 | 57.42 | 62.23 |
| 4 | Rubber composites | 44.78 | 58.07 | 51.47 |
| 5 | Auxetics foam composite | 42.60 | 44.32 | 49.99 |
| 6 | Wood flooring on joists | 42.89 | 46.86 | 63.74 |
| 7 | Rice husk cement composites | 43.15 | 55.77 | 63.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vu, N.T.; Hong, W.-K.; Kim, S.-K. An Airborne and Impact Sound Insulation Analysis of 3D Woven Textiles on the Floor in Buildings. Buildings 2025, 15, 3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203643
Vu NT, Hong W-K, Kim S-K. An Airborne and Impact Sound Insulation Analysis of 3D Woven Textiles on the Floor in Buildings. Buildings. 2025; 15(20):3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203643
Chicago/Turabian StyleVu, Ngan Thanh, Won-Kee Hong, and Seong-Kyum Kim. 2025. "An Airborne and Impact Sound Insulation Analysis of 3D Woven Textiles on the Floor in Buildings" Buildings 15, no. 20: 3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203643
APA StyleVu, N. T., Hong, W.-K., & Kim, S.-K. (2025). An Airborne and Impact Sound Insulation Analysis of 3D Woven Textiles on the Floor in Buildings. Buildings, 15(20), 3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15203643






