Abstract
Within the context of urban sustainability, the renewal and activation of communities have received growing attention. Public art, as a common approach to community revitalization, has long been regarded as an effective means of addressing urban and community issues. Basic human senses serve as a bridge between residents and community spaces, offering an effective entry point for creating human-oriented spaces. This study addresses the challenge of insufficient spatial vitality in community spaces by examining how sensory interventions can enhance residents’ participation in public art and thereby contribute to the revitalization of communities. To guide this inquiry, a theoretical framework was constructed based on sensory marketing theory and the Stimulus–Organism–Response (SOR) model, focusing on three core dimensions: sensory stimuli, perceptual responses, and behavioral intention. The study further investigated the relationship between public art and residents’ willingness to participate through five types of sensory stimuli, using a measurement scale and Structural Equation Modeling (SEM), with eight public art installations in Shanghai serving as case references. It also assessed the relative strength of each effect. Participant interviews and non-participatory observations were subsequently conducted for validation and supplementary analysis. The results show that residents’ participation willingness in community public art is directly influenced by perceptual responses (emotional fluctuations, cognitive memory, and physiological responses), and indirectly influenced by different sensory stimuli. Cognitive memory, shaped mainly by olfactory and visual stimuli, emerged as the most important factor in encouraging participation. Participation willingness also varies across generations, and different sensory stimuli are associated with distinct participation patterns. Based on empirical data from Shanghai’s community activation practices, the study proposes implementation strategies guided by the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) to enhance spatial vitality, promote community activation, and support sustainable development.
1. Introduction
As the urbanization process in developing countries enters its later stages, the influx of large populations has made urban land resources increasingly scarce. With urban expansion no longer possible, aging neighborhoods face spatial constraints that limit their ability to support residents’ daily social interaction, community life, and participation in public spaces. Data from the World Bank and the United Nations indicate that more than half of the global population already lives in cities [1], and this trend is expected to continue with increasing demands for high-density spatial use. Such changes pose significant challenges to the capacity and governance of community public spaces. At the same time, the combined effects of population aging and heat risks have intensified demands for health and care at the community level. Moreover, the rise in online and virtual communities has altered patterns of offline participation, reducing residents’ perceived need for community spaces and gradually weakening spatial vitality. As these challenges accumulate, the role of public art and its social functions has begun to attract growing attention.
Against this backdrop, local governments have introduced a series of policies and sponsorship programs related to public art, aiming to create aesthetically pleasing and vibrant community spaces through the integration of public art into urban and community environments [2,3,4]. In recent years, with government support, the forms of public art have become increasingly diverse, shifting from traditional “street art” [5] placed in urban public spaces to new genre public art [6] that emphasize public participation and community building [5]. However, regardless of the form of creation, the most common public art remains primarily focused on visual appreciation, with the public often engaging through passive observation based on vision. As a result, a certain distance is consistently maintained between the artworks and the public. This phenomenon appears to overlook the perceptual capacity of other human senses and their potential role in participation. But, early 4th-century philosophy suggested that “touch” is the fundamental sense, the core of perceiving life. It appears earlier than other sensory perceptions and is also the last sense to fade with age [7]. Audition, like vision, is a non-utilitarian aesthetic sense and also possesses an independent aesthetic consciousness [8]. Liu argues that in Eastern aesthetics, the process of appreciating art is akin to the experience of tasting food. As a result, aesthetic experiences are often expressed through terms related to taste perception, such as Ziwei (flavor), Quwei (interest), and Chanwei (Zen taste), which have become common expressions for conveying aesthetic feelings in Eastern cultures [9]. Tourly and Milliman, from the perspective of sensory marketing, concluded that the five sensory stimuli in the spatial environment positively influence emotions, participation intentions, satisfaction, and purchase intentions [10]. It can thus be inferred that, in addition to Vision and Audition, the other human senses also have the capacity to influence human behavior. In addition, digital media art, interactive media, and immersive installations within the context of smart cities have all employed multiple senses to enhance the attractiveness of places [11,12]. It can therefore be inferred that, beyond vision, other human senses also carry the power to influence behavior. These insights lay the foundation for further refining the research framework.
In the context of countries worldwide actively promoting community activation, whether incorporating diverse sensory elements into community public art can enhance residents’ participation enthusiasm and thereby achieve the goal of spatial activation constitutes the primary research question of this study. It also examines the varying intensities of psychological, physiological, and cognitive responses triggered by different senses; whether residents’ responses to sensory stimulation differ across senses; and how to design public art based on different senses to stimulate residents’ participation behavior. Based on the above issues, this study selected Shanghai as the case site, a city that embodies typical characteristics of community activation in China, and examined eight public art installations located in central urban communities as the basic cases. These installations corresponded to sensory stimulation of Vision, Audition, Haptics, Olfaction, and Taste (some works could not be presented through a single sense and therefore required visual assistance). These eight public art cases were used as reference examples for respondents prior to the questionnaire survey, ensuring that they understood the forms of expression of different senses in public art and avoiding potential misunderstandings. The questionnaire adopted sensory marketing theory as an interdisciplinary framework, treating public art as a marketing product with artistic value. Together with the SOR model, it established a framework linking sensory stimulation, perceptual response, and behavior, aiming to extend theoretical boundaries in the art field. The collected data were tested using Structural Equation Modeling (SEM). Participants’ evaluations and non-participant observations were then incorporated to validate the data and supplement behavioral analysis.
The results reveal that sensory stimulations in public art facilitate residents’ participation indirectly, with perceptual responses serving as a mediating factor. In addition, residents’ behavioral intention to participate varies across generations, and different types of sensory stimulation present distinct participation characteristics. However, a gap remains between behavioral intention and actual participation. Based on these findings, and with reference to the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB), the study proposes relevant implementation recommendations aimed at enhancing the vitality of community spaces. This research highlights the significance of sensory stimulation in community public art for residents’ participation behavior and community activation, while providing optimization pathways. It addresses the research gap concerning the relationship between sensory stimulation in public art and residents’ participation behavior, and introduces sensory marketing theory into the field of public art research for the first time. The aim is to explore more diverse forms through which public art can contribute to sustainable community development and foster greater interaction between residents and community spaces.
This article is structured as follows: Section 2 presents the literature review. Section 3 describes the research framework and hypotheses. Section 4 introduces the case sites, methods, and data. Section 5 presents the empirical results. Section 6 discusses the empirical findings in detail, including participants’ evaluations and conclusions from non-participant observations, differences in residents’ preferences and participation characteristics during actual participation, as well as the practical value and implementation recommendations. Section 7 summarizes the research content and results, and reflects on the study’s limitations.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Community Activation
The concept of community was first defined in 1887 by German sociologist Ferdinand Tonnies and later expanded in American scholarship as a living collective formed through locality and social relations [13,14]. As the basic unit of a city, it not only shapes urban distinctiveness, comfort, and vitality but also directly affects residents’ quality of life [15,16]. When aging communities become disconnected from contemporary development and public spaces fail to meet functional needs, community activation emerges as a necessary agenda worldwide. Since the mid-20th century, after reflecting on the drawbacks of large-scale reconstruction, many Western countries have shifted toward micro-scale and incremental models of community renewal. In this process, public art has been widely introduced to enhance spatial quality and resident interaction. For example, in the 1960s the United States launched the Percent for Art Program, institutionalizing the integration of art into community renewal [17]. The United Kingdom, Japan, and other countries have also promoted small-scale renewal and policy support, regarding public art as a key tool to strengthen community identity and social cohesion [18].
In China, sociologist Fei Xiaotong introduced the concept of “community” in the 1930s, emphasizing its attributes of interaction and cooperation [19]. Over the past three decades, rapid urbanization has led to spatial scarcity, rising housing prices, and weakened neighborhood ties, making community renewal and vitality enhancement particularly urgent. In recent years, the Chinese government has proposed the concepts of the “15-Minute Community Life Circle” and “community micro-renewal,” gradually incorporating public art and civic participation into renewal practices. As a result, public art has become an important means to improve micro-spaces, rebuild neighborhood relations, and create livable communities. In this study, community activation mainly refers to fostering residents’ daily social interaction and participation through spatial construction and atmosphere building under conditions of spatial constraints and functional deficiencies.
2.2. Public Art
Public art emerged in the 1960s as a cultural policy with a distinct ideological orientation, aimed at reinforcing the social and public nature of art [20]. The term was first introduced by British writer John Willett in his 1967 book Art in a City [21]. In the same year, the National Endowment for the Arts established a public art program, marking its recognition as an established practice [22]. It is a physical expression in public spaces that conveys ideas, emotions, and information to the public, with the aim of strengthening the identity of a space or place. It includes functional, expressive, permanent, or temporary decorative forms within the landscape, not limited to sculptures, murals, and reliefs [23]. From its inception, public art has served as a cultural tool for many countries to address urban issues. Over time, it has gradually evolved into a comprehensive interdisciplinary field, integrating contributions from architecture, landscape architecture, urban design, and art history [22]. In the context of architecture and landscape, community public art often fulfills its social and spatial functions through architectural components, façade decorations, or site installations, thereby forming an organic whole with buildings and landscape structures within the built environment [24,25]. In this study, the scope of public art refers to all tangible artworks expressed through artistic means in community spaces, including sculptures, murals, art installations, structures, buildings, landscape environments, and others.
As urban artistic expression has shifted from street-level public spaces to inward-looking community domains, public art has become an essential component of community spaces. At the same time, the five human senses, as direct links between residents and their environment, have shown increasing relevance to health and quality of life. Yet research combining art, sensory experience, and resident participation remains limited, with most studies focusing on spatial healing and public health [26,27,28,29], and largely emphasizing vision and audition [30,31,32]. For example, Lu et al. demonstrated that the synergy between streetscapes and soundscapes significantly affects environmental satisfaction and emotional perception, providing quantitative evidence for audiovisual design in community public art [33]. Zhang et al. examined how olfactory and visual stimuli in “scented landscapes” influence heart rate, blood pressure, and emotional recovery [34]. Dehove et al. compared the visual appeal of urban art and greening interventions, finding public art more attractive [35]. Overall, these studies typically address single senses or specific combinations. While confirming links between sensory cues and emotional, cognitive, and physiological responses, few have compared all five senses within a single model or tested perceptual responses as mediators influencing interactive behavior. This gap forms the entry point and innovation of this study.
2.3. Multisensory Experiences of Healing Gardens
Healing gardens have become an important medium for sensory-based community therapy, gaining attention in the context of accelerating lifestyles and increasing stress [36]. Early approaches relied mainly on visual elements, such as plant layering, seasonal change, and color [37]. With the development of environmental psychology and restorative environment theory, it has been shown that healing extends beyond vision. It also includes auditory experiences such as flowing water and birdsong [38], olfactory stimulation from flowers and aromatic plants [39], tactile sensations of temperature, texture, and sunlight, as well as gustatory experiences provided by edible landscapes. Consequently, healing gardens have evolved from visual emphasis to multisensory design. At the community scale, healing gardens enhance residents’ health and well-being through multisensory engagement. Olfactory and haptic stimuli have been linked to reduced anxiety and improvements in sleep and heart rate [40]. Visual scenes, soundscapes, and edible gardens encourage residents to stay longer, communicate, and foster intergenerational integration [41]. Such multisensory spaces combine individual restoration with social connection, offering new insights into residents’ behavior under multisensory stimulation.
2.4. Development and Characteristics of Public Art in Shanghai
Shanghai is among the first cities in China to promote public art in community renewal. Guided by the “15-Minute Community Life Circle” strategy, which emphasizes building livable, elder-friendly, tourist-friendly, education-friendly, and employment-supportive neighborhoods, and supported by the Community Micro-Update Initiative, Shanghai has promoted the integration of public art into community renewal. Since 2015, the city has hosted the biennial Shanghai Urban Space Art Season (SUSAS) to encourage diverse forms of public art in urban and community contexts. With strong policy support, tens of thousands of projects have been completed, presenting distinct tendencies and distribution patterns. A review of works from the past three editions of SUSAS [42,43,44] highlights the following features:
In terms of spatial distribution, public artworks are concentrated in urban parks, plazas, waterfront spaces, and around cultural facilities, with the highest density in green parks and street plazas due to strong accessibility and foot traffic. However, works embedded in residents’ daily routines remain limited. Thematically, public art follows diverse paths such as ecology and nature, light-and-shadow technologies, community participation, and urban memory. Ecological themes are most prominent, reflecting sustained concern for green and healthy living under elder-friendly and livable goals. Technological expressions through light and digital media are also common, while civic participation and co-creation remain in the exploratory stage. From a sensory perspective, public art is still dominated by vision. Installations, sculptures, and facilities emphasize visual recognition and formal expression, but offer limited interaction with residents. Works involving audition, haptics, or olfaction are far fewer. This highlights the significance of this study, which underscores the need to expand sensory dimensions and deepen community integration, thereby enhancing residents’ everyday experiences.
2.5. Foundations and Recent Developments of the SOR Model
The SOR framework builds on the classic Stimulus–Response (S-R) theory, which viewed behavior as a direct reaction to external stimuli [45]. The S-R model, however, neglected the mediating role of internal psychological processes [46]. To address this, Robert S. Woodworth proposed the SOR model in Dynamic Psychology (1929), introducing the “organism” as an intermediary. He argued that cognitive and emotional processing of stimuli shapes the direction and intensity of behavioral responses, thereby embedding internal processes into behavioral explanation [47]. Building on this foundation, Mehrabian and Russell (1974) combined the SOR framework with the Pleasure-Arousal-Dominance (PAD) model to explain how environments evoke emotional states that drive approach or avoidance behavior [48]. Later, Bitner and Lin refined the framework, advancing its application in spatial experience research [49,50].
In recent years, the SOR model has been widely applied in art and environmental studies, including digital art exhibitions [51], art venues [52], public art spaces [53], urban forests [54], heritage sites [55], and parametric landscape design [56]. Stimuli often involve visual, auditory, interactive, and service-related factors, while the organism dimension typically focuses on aesthetic experience, emotional states, satisfaction, or perceived value. Behavioral responses cover participation willingness, revisit intention, and spatial use. Together, these studies provide structured theoretical support and variable references for examining how sensory stimulation in public art influences residents’ willingness to participate.
2.6. Foundations and Recent Developments of SEM
SEM is a comprehensive statistical method that tests hypotheses regarding the directional and non-directional relationships between a set of observed variables and latent variables [57]. It efficiently and quickly reveals the complex relationships between dependent and independent variables, and is particularly adept at addressing research issues such as motivation and attitudes [58]. Its origins trace back to Wright’s path analysis in the 1920s [59], later advanced by Jöreskog and Sörbom in the 1960s–70s into the LISREL framework, which integrated confirmatory factor analysis with structural modeling and laid the foundation for covariance-based SEM (CB-SEM) [60]. In the 1980s, Bollen systematized latent variable theory, shaping the modern form of SEM [61].
In recent years, SEM research has continued to evolve. Bollen’s review of fifty years of development emphasized theoretical advances in causal identification, model fit evaluation, and measurement invariance, highlighting SEM’s goals of explanation, prediction, and generalization [58]. In design and cultural studies, SEM has been widely applied to architecture, public space, and cultural research [62,63,64], while applications in art and design remain limited. Methodologically, most studies rely on questionnaire data combined with mediation or moderation models to reveal complex relationships among variables [62]. Some have introduced multi-group comparisons or social and ecological structures to capture group and contextual differences [65]. Others integrate digital tools or interdisciplinary frameworks, enhancing SEM’s predictive capacity while explaining causal mechanisms [66,67]. These developments provide robust methodological support for examining how sensory stimulation in public art influences residents’ participation.
3. Research Framework and Hypothesis
3.1. Theoretical Framework and Variables
The study’s framework draws on Krishna and Schwarz’s (2014) [68] sensory marketing theory. The theory posits that humans exchange information with their environment primarily through five senses (vision, haptics, audition, olfaction, and taste), which serve as external trigger variables. When external stimuli engage these senses, they elicit perceptual responses, leading to grounded emotion and grounded cognition. These processes ultimately generate individuals’ attitudes and behaviors toward a product [68].
This study draws on the structural model of sensory marketing theory, originally developed in commercial consumption contexts, and introduces it for the first time into research on public art and resident behavior. Public artworks are conceptualized as aesthetic products, and sensory marketing theory is applied to examine how external stimuli activate human senses, generate diverse perceptual responses, and increase the frequency of interaction between people and artworks. This cross-disciplinary integration provides both an innovative pathway and a more practical theoretical foundation for public art research. Building on the sensory marketing framework, this study also draws on the SOR model, originally proposed by Mehrabian and Russell [48]. Within this SOR paradigm, perceptual responses (comprising emotional fluctuations, cognitive memory, and physiological reactions) are considered key mediators in the relationship between sensory stimuli and behavioral outcomes. Accordingly, this study constructs a model (Figure 1) in which stimuli from the five senses serve as independent variables, and the intensity of perceptual responses is measured through emotional, cognitive, and physiological dimensions. These perceptual responses are then assessed as mediating variables to evaluate the impact of multisensory public art stimuli on the public’s willingness to engage and participate.
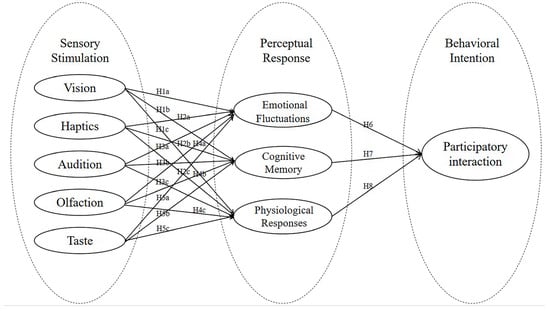
Figure 1.
Proposed research model diagram.
3.2. Hypotheses
In the context of community public art, multisensory cues collectively shape both the physical and perceptual environment of users. Different senses follow distinct perceptual pathways. First, visual factors such as the size, form, and color of public artworks influence emotions and aesthetic cognition. Numerous studies have confirmed the impact of visual art on mood and emotional states [69,70,71]. The inclusion of this hypothesis provides a reference for other senses and serves to validate the model. Second, audition and olfaction function as independent senses that can operate without visual support. Auditory stimuli are often used to regulate emotions, with observable variables including natural sounds, music, and human voices, and are hypothesized to have positive effects on participants’ emotions and cognition. Olfaction, strongly linked to memory, is represented by observable variables such as the scents of food, plants, or artificial blends, and is reasonably assumed to directly influence cognition and emotion. Third, haptics and taste usually depend on visual guidance, as material textures, temperature and humidity, or food associations evoke bodily and psychological perception.
Based on these considerations, we propose the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 1a (H1a):
Visual stimuli in public art have a significant positive effect on emotional fluctuation.
Hypothesis 1b (H1b):
Visual stimuli in public art have a significant positive effect on cognitive memory.
Hypothesis 1c (H1c):
Visual stimuli in public art have a significant positive effect on physiological responses.
Hypothesis 2a (H2a):
Haptic stimuli in public art have a significant positive effect on emotional fluctuation.
Hypothesis 2b (H2b):
Haptic stimuli in public art have a significant positive effect on cognitive memory.
Hypothesis 2c (H2c):
Haptic stimuli in public art have a significant positive effect on physiological responses.
Hypothesis 3a (H3a):
Auditory stimuli in public art have a significant positive effect on emotional fluctuation.
Hypothesis 3b (H3b):
Auditory stimuli in public art have a significant positive effect on cognitive memory.
Hypothesis 3c (H3c):
Auditory stimuli in public art have a significant positive effect on physiological responses.
Hypothesis 4a (H4a):
Olfactory stimuli in public art have a significant positive effect on emotional fluctuation.
Hypothesis 4b (H4b):
Olfactory stimuli in public art have a significant positive effect on cognitive memory.
Hypothesis 4c (H4c):
Olfactory stimuli in public art have a significant positive effect on physiological responses.
Hypothesis 5a (H5a):
Taste-related stimuli in public art have a significant positive effect on emotional fluctuation.
Hypothesis 5b (H5b):
Taste-related stimuli in public art have a significant positive effect on cognitive memory.
Hypothesis 5c (H5c):
Taste-related stimuli in public art have a significant positive effect on physiological responses.
Furthermore, we argue that perceptual responses are a key mediating factor linking sensory stimulation and interactive behavior. Emotional fluctuations (such as curiosity, pleasure, and desire) reflect immediate affective reactions; cognitive memory (including experience, recall, and association) represents deeper psychological processing; and physiological responses (changes in heart rate, skin, or muscles) indicate direct bodily feedback. We hypothesize that these responses actively promote residents’ participation in public art interactions. Thus, sensory stimulation is assumed to trigger multilayered perceptual responses, which ultimately enhance residents’ willingness to interact and their participation behavior.
Accordingly, the following hypotheses are proposed:
Hypothesis 6 (H6):
Emotional fluctuation has a significant positive effect on residents’ interactive behavior with public art.
Hypothesis 7 (H7):
Cognitive memory has a significant positive effect on residents’ interactive behavior with public art.
Hypothesis 8 (H8):
Physiological responses have a significant positive effect on residents’ interactive behavior with public art.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Case Site Description
As a high-density and compact international metropolis, Shanghai has an average population density of over 3000 people per square kilometer, with migrants accounting for 40.6% of its permanent residents. The influx of newcomers has intensified the tension between population and land, leading to a significant reduction in per capita public space. The contradiction between spatial constraints and rising demands for quality of life made Shanghai one of the first cities to promote public art in community renewal. Supported by policy, the city has completed tens of thousands of diverse public art projects, providing abundant cases and valuable references for studying the role of public art in community renewal.
This study selected eight public art installations, each representing one of the five sensory dimensions, as case references (Figure 2). We prioritized works with independent sensory attributes (some accompanied by necessary visual cues) to distinguish the varying effects of each sense on interaction. All cases are located in Shanghai’s central districts, Cases 2, 3, 4, and 6 in Jing’an, and Cases 1, 5, 7, and 8 in Changning (Figure 3). Jing’an, the historic city center of old Shanghai, retains rich architectural heritage, with dense population, convenient transport, and diverse cultural and commercial facilities, making it highly suitable for studying resident behavior. Adjacent to Jing’an, Changning has become a key demonstration area of Shanghai’s recent micro-renewal practices, offering numerous examples of art-based community interventions that support this research.

Figure 2.
Schematic Diagram of Case.
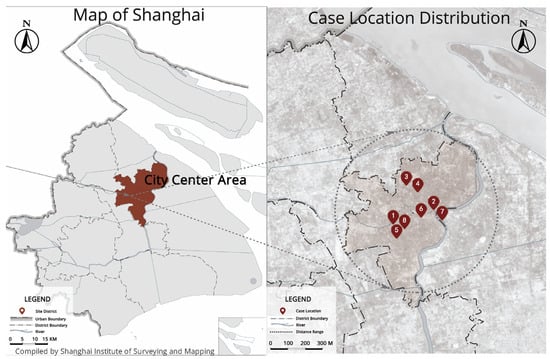
Figure 3.
Map of Shanghai and Case Locations.
In case selection, we focused on spaces frequently used by residents, ensuring diversity in location, including community parks, under-bridge spaces, residential areas, commercial zones, and waterfronts. The design themes align with the “15-Minute Community Life Circle” principles of building livable, elder-friendly, tourist-friendly, education-friendly, and employment-supportive communities, addressing needs of housing, elderly care, learning, leisure, and visual appreciation. The selected works also span different types, including functional facilities, interactive installations, and recreational structures (Table 1).

Table 1.
Description of Case.
4.2. Research Methodology
This study primarily employed quantitative methods, supplemented by qualitative approaches. In the quantitative stage, a measurement scale was designed across three dimensions—sensory stimuli, perceptual responses, and behavioral intention. The sensory stimuli included vision, hearing, touch, smell, and taste, while the perceptual responses covered physiological reactions, emotional fluctuations, and cognitive memory. The scale consisted of 26 items, measured through self-reported questionnaires (Table A1). The items focused on individuals’ self-assessment of multisensory elements and perceptual responses in public art spaces. They were developed based on literature review, field investigations, and interviews to ensure clarity and relevance. Before completing the questionnaire, participants were introduced to eight case sites through text and images to clarify how different sensory dimensions were represented in public art, avoiding misinterpretation and providing information reference. The questionnaire adopted a five-point Likert scale (1 = strongly disagree, 5 = strongly agree). The collected data were analyzed using SEM to test and verify the hypotheses.
Meanwhile, based on the questionnaire survey, this study also collected participation experiences and evaluations from 15 respondents at the case sites. The content focused on residents’ first impressions of the artworks, participation motivations, sensory experiences, and emotional fluctuations. These evaluations were used to further verify the hypothesized relationships mentioned above. In addition, non-participant observations conducted by the research team were incorporated to identify preference differences across groups and behavioral variations resulting from different types of Sensory Stimulation. As a contextual supplement to the quantitative findings, this section aims to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the complex behavioral patterns and underlying psychological mechanisms between Sensory Stimulation and residents’ participation behavior. Finally, the study summarizes the data, evaluations, and observations to propose implementation recommendations and optimization pathways guided by the TPB (Figure 4).
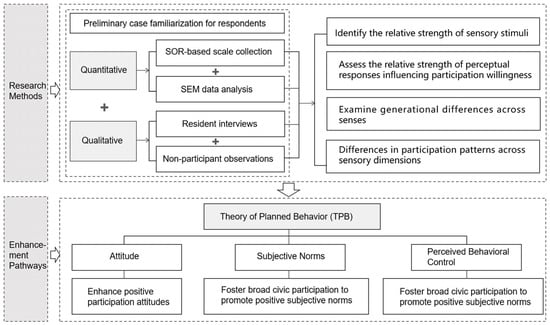
Figure 4.
Research Framework.
In this model, several single-item variables were used. Although past studies have raised concerns about measurement error, representativeness, and precision, suggesting limitations in reliability and explanatory power and unsuitability for complex constructs [72], prior research has nevertheless achieved successful results with such measures [73]. To mitigate these concerns, this study systematically assessed model fit through overall goodness-of-fit indices and supplemented the analysis with qualitative interviews to enhance robustness. Thus, the methodological approach is considered feasible.
4.3. Data Collection
Data for this study were collected between October 2024 and January 2025 through a combination of online and offline methods to ensure diversity and broad coverage of the sample. For the offline component, participant recruitment focused on the areas surrounding the selected case sites. The primary participants were residents who directly interacted with the artworks, those who paused or stayed near the installations, and residents living in nearby communities. The research team distributed paper-based questionnaires at designated public locations, such as plazas, parks, and community centers, through on-site invitations, oral communication, and assistance from community organizations. The questionnaires were also distributed along fitness trails, sidewalks, and plazas, with on-site guidance provided for completion.
For the online survey, a combination of purposive sampling and snowball recruitment was used, extending beyond Shanghai to include residents from nearby cities. Links to the questionnaire were distributed through community WeChat groups, message boards, and elderly contact networks, with participants invited to share them with family, neighbors, and acquaintances to broaden the age and social background coverage. In addition, limited promotion was carried out among university communities, community service platforms, and public art organizations to include a comparative sample of younger and professionally affiliated respondents. In total, 380 questionnaires were collected. After removing incomplete responses and those with uniform answers across all items, 332 valid questionnaires were retained for analysis.
Among the 332 respondents (Table A2), the largest group was aged 31–45, making up 35.84% of the total population, followed by the 46–60 age group, which accounted for 29.52%. The proportion of respondents under 45 years old was 57.83%, and 87.35% of respondents were under 60. The majority of respondents were middle-aged, between 31 and 60 years old. The smallest proportion of respondents were over 60 years old, which may be partly due to older individuals being less familiar with the skills needed to complete the online questionnaire. In terms of gender, there were slightly more female respondents than male. Additionally, 53.92% of the respondents had a bachelor’s degree or higher educational level. Among the respondents, 73.49% were permanent residents of Shanghai, while 24.69% were non-residents, primarily tourists. Based on the respondents’ age, gender, educational background, and residential status, the sample is generally consistent with the demographic proportions of Shanghai’s population, aligning with the characteristics and corresponding ratios of community residents in Shanghai.
5. Results
Using SPSS 24.0 and AMOS 22.0 software, we conducted reliability and validity analysis, exploratory factor analysis, and confirmatory factor analysis to verify the validity of the model and its factors. Subsequently, Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) was employed to examine the relationships among the variables.
5.1. Reliability and Validity Analysis
The results from Cronbach’s reliability analysis indicate that the scales for sensory stimulation, perceptual response, and behavioral intention, as well as their internal dimensions, demonstrate good to excellent internal consistency (Table 2). The total Cronbach’s α coefficient exceeds 0.9, suggesting that respondents’ perceptions of the scale dimensions, or how public art is influenced by these dimensions, show robust and reliable characteristics. This also indicates that the responses obtained from the questions in measuring these dimensions are consistent, providing a reliable foundation for the subsequent research work.

Table 2.
Cronbach Reliability Analysis.
According to the validity analysis of this questionnaire (Table 3), the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) value is 0.869, which falls between 0.8 and 0.9, indicating that factor analysis is suitable. Bartlett’s test of sphericity significance p-value is 0.000 ***, which is less than 1%, showing a high level of statistical significance. Furthermore, the approximate chi-square values are much greater than the degrees of freedom (df), which indicates a good model fit for the factor analysis, providing a solid statistical foundation for further factor analysis.

Table 3.
Validity analysis.
5.2. Exploratory Factor Analysis
Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) is a multivariate statistical method used to understand the commonalities and relationships between multiple observed variables, thereby revealing underlying structures or factors [74]. It is mainly used in fields such as psychology, education, sociology, and market research. After conducting preliminary reliability and validity tests and confirming the feasibility of factor analysis, we proceeded with the analysis through total variance explained and the component matrix after exploratory factor rotation.
5.2.1. Total Variance Explained
Total variance explained refers to the proportion of the total variation in all variables explained by the extracted factors. It measures the extent to which the extracted factors account for the variability in the original data. In this exploratory factor analysis (Table 4), we used Principal Component Analysis (PCA) to extract factors. The analysis results showed that 26 factors were extracted, with the first 9 factors having eigenvalues greater than 1, and the cumulative variance explanation reached 78.419%, exceeding the 50% threshold. This indicates a strong explanatory power, suggesting that the first 9 factors effectively describe the primary structure of the data and explain its main variability. Moreover, the 26 variables selected for analysis exhibit good representativeness, making them suitable for further factor analysis.

Table 4.
Total Variance Explained.
5.2.2. Component Matrix After Factor Rotation
Factor rotation is an essential step in Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) used to simplify the factor structure and enhance the interpretability of factors. The rotated component matrix shows the relationships between each factor and the original variables, helping to identify which variables primarily load onto which factor. It is generally considered that loadings greater than 0.4 indicate significant correlations. From the data (Table 5), it is evident that all loadings exceed 0.7, which are relatively high values, suggesting that the model has good interpretability and each factor effectively represents a set of related variables.

Table 5.
Rotated Component Matrix.
5.3. Confirmatory Factor Analysis
Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) is an important component of Structural Equation Modeling (SEM), commonly used to test the consistency between theoretical models and data. It is used to verify whether the measurement model fits the expected factor structure. The data in this study aim to evaluate the relationships between several constructs, including five senses, physiological responses, cognitive memory, emotional fluctuations, and participatory interactions, as well as their respective observed variables (Figure 5). In Table 6, each latent variable (e.g., visual, tactile, auditory) is measured by multiple observed variables (e.g., shape, size, color). Latent variables represent theoretical constructs, while observed variables are used to measure the specific indicators of these constructs. All standardized factor loadings (Std. Estimate) in the table are significant (p < 0.001), and most are above 0.7, indicating that the latent variables have strong explanatory power for the observed variables. The Average Variance Extracted (AVE) for each latent variable is greater than 0.5, and the Composite Reliability (CR) is greater than 0.7, suggesting that the model has good convergent validity and internal consistency reliability. The results show that the measurement variables for each latent variable have good reliability and validity, and the latent variables can effectively explain their measurement variables. Furthermore, the contribution of each measurement variable to the latent variables is significant. Therefore, this model performs well in terms of latent variable measurement and exhibits strong statistical significance and reliability.
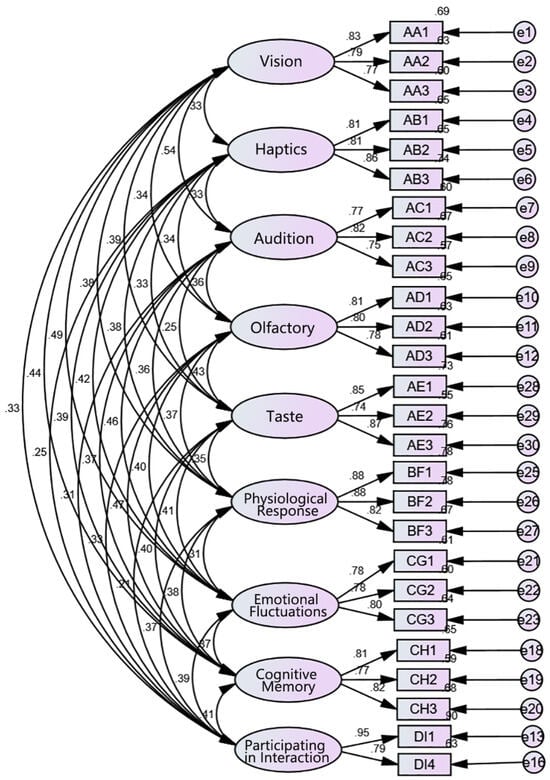
Figure 5.
Standardized estimate of the SEM model.

Table 6.
Measurement Model Diagram.
The table displays the correlation coefficients between a series of constructs (Figure 6), as well as the square roots of the average variance extracted (AVE) for each construct, which are commonly used in SEM to assess the discriminant validity of the structure. The correlation coefficients between constructs in the data are mostly below 0.85, indicating that these constructs exhibit good discriminant validity and can be measured independently. The AVE values for all constructs are greater than 0.7, indicating high values, particularly for the constructs of interaction participation, cognitive memory, emotional fluctuation, haptics, and taste. This suggests that these constructs have good internal consistency and meet acceptable measurement standards.
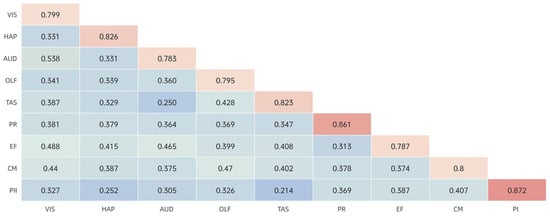
Figure 6.
Discriminant Validity Matrix.
5.4. Structural Equation Modeling Path Analysis
The path analysis table (Table 7) provides a detailed overview of the relationships between variables, including path coefficients (Estimate), standardized path coefficients (Std. Estimate), standard errors (S.E.), critical values (C.R.), and significance levels (p). Estimate refers to the path coefficient, which indicates the extent of influence that the independent variable has on the dependent variable. A higher value indicates a stronger effect. Std. Estimate is the standardized value of the path coefficient, making it easier to compare different path coefficients. The standardized path coefficient ranges from 0 to 1, and values closer to 1 indicate a greater influence. S.E. represents the uncertainty in the estimation of the path coefficient; smaller standard errors mean more precise estimates. C.R. is the ratio of the path coefficient estimate to the standard error, and it is used to test the significance of the path coefficient. The larger the C.R., the more significant the path coefficient is. p shows the significance of the path coefficient; the smaller the p-value, the more significant the path coefficient is. All p-values in Table 7 are below 0.05, indicating that all paths are statistically significant. In the path analysis diagram (Figure 7), the direction of the arrows indicates causal relationships between the variables, with the numbers representing the strength of these influences.

Table 7.
Path Analysis Results.
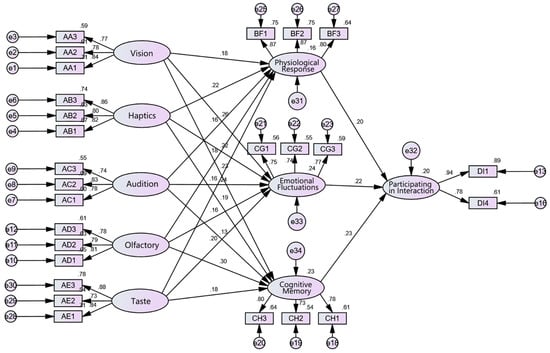
Figure 7.
Path analysis diagram.
The structural equation model fit indices (Table 8) show that the CMIN/DF value is 1.803, which is less than 3, indicating that the chi-square-to-degrees-of-freedom ratio is small, and the model fits well. The GFI (Goodness of Fit Index) value is 0.882, which is above the standard value of 0.8, suggesting good overall model fit. The AGFI (Adjusted Goodness of Fit Index) value is 0.853, greater than the standard value of 0.8, indicating that the model fits well even after adjustment. The RMSEA (Root Mean Square Error of Approximation) value is 0.049, which is below the standard value of 0.05, indicating small approximation errors and good fit. The IFI (Incremental Fit Index) value is 0.949, which is higher than the standard value of 0.9, suggesting a high degree of incremental fit. The TLI (Tucker–Lewis Index) value is 0.94, above the standard value of 0.9, indicating a good fit. The CFI (Comparative Fit Index) value is 0.948, above 0.9, indicating a high comparative fit index. Based on the data, all fit indices meet the recommended standards, and the values of GFI, AGFI, IFI, TLI, and CFI are all above 0.9, indicating that the model fits well. The model’s fit results are successful and can effectively explain the data, making it applicable for practical use.

Table 8.
Model fit indices.
According to the data shown in the table, first, all sensory variables have a significant impact on physiological responses, with path coefficients ranging from 0.154 to 0.263. Haptics (path coefficient 0.263) and visual (path coefficient 0.201) have the greatest impact on physiological responses (Figure 8a), indicating that the physiological responses based on skin stimulation and changes in heart rate, triggered by haptic and visual stimuli in public art, are the most significant. Next, all sensory variables have a direct and significant impact on emotional fluctuations, with visual (path coefficient 0.23) and auditory (path coefficient 0.23) having the greatest influence on emotional fluctuations (Figure 8b). Additionally, all sensory variables have a direct and significant impact on cognitive memory, with olfactory (path coefficient 0.244) having the stronger influence, followed by visual (path coefficient 0.203) (Figure 8c). Finally, cognitive memory, emotional fluctuations, and physiological responses all significantly influence participatory interaction. Cognitive memory has the most significant impact on participatory interaction (path coefficient 0.345), followed by emotional fluctuations, and lastly physiological responses (Figure 8d).
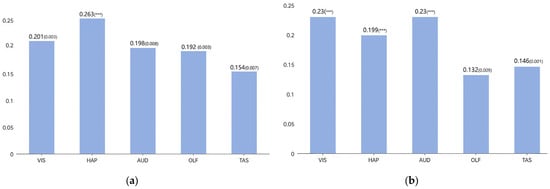
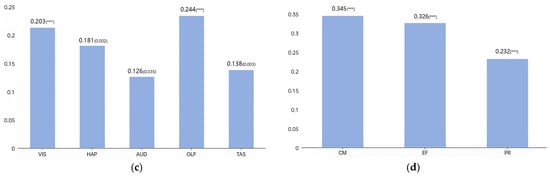
Figure 8.
(a)The impact of different senses on physiological responses; (b) the impact of different senses on emotional fluctuations; (c) the impact of different senses on cognitive memory; (d) the impact of different perceptual responses on participatory interaction. Note: *** represents p < 0.001.
6. Discussion
6.1. Empirical Analysis
Based on the empirical results of the measurement-scale data, the findings reveal how public art stimulates individual senses to generate Perceptual Responses, and how these responses influence residents’ Behavioral Intention. Incorporating sensory elements into public art significantly increased residents’ willingness to participate. The effect was strongest when driven by prior cognition and experience, such as recalling childhood memories of playground slides when encountering a smooth inclined surface. It was followed by emotions triggered during the interaction, including joy, curiosity, or sadness, and further supported by physiological responses to sensory stimulation.
The intensity of perceptual responses varies across different types of sensory stimulation, as detailed below:
Cognitive memory evoked through sensory stimuli is primarily influenced by Olfaction and Vision. Olfaction, regarded as the longest-lasting sense of memory, can retrieve more past experiences and even infer or associate with unfamiliar events [75]. Vision has also been repeatedly shown to be significantly linked to experience, memory, and association [76,77,78], supporting the explanatory validity of the model. Although taste is less directly represented in public art, taste-related associations triggered by visual cues can still encourage participation.
Physiological responses were primarily influenced by visual and haptic stimuli, followed by auditory cues. Haptics, often supported by vision, evoked bodily reactions to textures such as roughness, softness, smoothness, or coolness. Auditory elements like music and ambient sounds triggered heart rate and muscle changes, while olfactory and gustatory stimuli had weaker yet significant effects.
Emotional fluctuations were mainly shaped by visual and auditory stimuli. Sound, as an accessible and controllable medium, including natural sounds, voices, and music, could independently affect perception or complement vision, effectively triggering emotions. Compared with vision and audition, haptics, taste, and smell played a lesser role, but their significant impact indicates they can also serve as meaningful entry points in design.
Based on these findings, residents’ interaction with public art is directly influenced by emotional fluctuations, cognitive memory, and physiological responses, and indirectly shaped by sensory stimuli. Participation willingness can be strengthened through these three pathways. Visual stimuli generally exert the strongest influence, while other senses vary in impact but remain significant and should be considered in design to enhance interaction. Notably, olfaction, though often overlooked in public art, plays a major role in stimulating cognitive memory. Whether in the context of community healing or the rise in virtual spaces, olfaction deserves greater research attention [79,80].
6.2. Participant Feedback and Observational Insights
Through non-participatory observations of eight case sites and interviews with 15 participants (Table A3), supplementary data were collected to capture the complexity of community resident behavior.
(1) In terms of Vision, interviews confirmed that the renewed community environment significantly increased spatial reuse. Residents tended to rest near visually appealing artworks rather than in areas without art, showing that visual stimulation in public art can evoke pleasure and encourage lingering, photographing, sharing, and revisiting [81,82]. (2) For Audition, participants’ descriptions of the musical fountain demonstrated that auditory stimulation triggers curiosity and joy, often accompanied by physiological responses such as heart rate changes, encouraging people to approach and gather. Children’s preference for the mist highlighted the stronger appeal of haptics and audition working together to encourage their participation. (3) Regarding Haptics, tactile experiences stood out in artworks with specific forms and materials. Guided by visual cues, residents recalled memories through material textures and shapes, prompting active interaction. Observations also revealed a peer effect, where increased participation amplified group social behavior, underscoring the role of public art as a medium for social exchange. (4) For Olfaction, both interviews and observations showed dual functions. Natural floral scents evoked relaxation and comfort, while specific smells triggered memories and nostalgia, deepening emotional bonds with the place and motivating lingering, revisiting, and inviting others to join. These findings confirmed the role of olfaction in stimulating emotional fluctuations and cognitive memory. (5) Taste was mainly expressed through association and emotion. Residents often linked artworks’ forms to food, sparking appetite or pleasure, though this rarely translated into active interaction.
Overall, the interviews and observations reaffirmed the survey results and further highlighted the peer demonstration and conformity effects of certain senses. Together, these findings illustrate the mechanisms by which public art activates community vitality and fosters social interaction.
6.3. Generational Differences and Social Characteristics
However, observations and interviews revealed that individuals of different age groups exhibit varying responses and preferences toward Sensory Stimulation (Table 9). Vision, due to its immediacy and collective appeal, holds strong attractiveness across all age groups. It often becomes a social and interactive medium in public spaces, facilitating communication and connection among residents. Auditory stimulation is also effective for all age groups, but it tends to promote individual appreciation. Residents often experience emotional regulation through immersive soundscapes. Haptic stimulation is particularly prominent among children and typically exhibits a “one leads many” pattern. Children’s participation often encourages involvement from family members and even neighbors, thereby significantly enhancing community interaction. In contrast, olfactory stimulation resonates more strongly with older adults. Familiar scents often trigger memories and associations, offering emotional comfort and a sense of belonging through solitary experiences. As for taste-related stimulation, it shows a relatively stronger effect on middle-aged and younger adults. They tend to rely on visual cues to generate synesthetic and associative responses, resulting in individualized sensory experiences that exhibit a certain degree of subjectivity.

Table 9.
Generational Differences and Participation Characteristics by Sensory Dimension.
These generational differences and social expression not only highlight the distinct functional roles that each sensory modality plays in the design of community public art, but also offer insights into how sensory design can be tailored to enhance participation among residents of different age groups.
6.4. Practical Implications and Implementation Recommendations
Findings from both the scale and observational evaluations show that residents do not always use community spaces for functional needs. Emotional experiences and contextual atmospheres triggered by sensory elements often motivate them to “stay longer,” “get involved,” or “share with others.” This type of body-based, sensory-driven engagement represents an important dimension often overlooked in conventional spatial assessments.
The results further clarify the association between sensory stimulation in community public art and residents’ intention to participate. However, effective implementation is still required to translate intention into actual behavior. In 1985, Icek Ajzen proposed the TPB [83], which argues that actual participation depends not only on intention but also on the combined effects of Attitude, Subjective Norms, and Perceived Behavioral Control (Table 10). This framework provides a basis for exploring concrete implementation pathways.

Table 10.
Application of TPB Dimensions in Community Public Art Participation.
6.4.1. Enhancing Residents’ Positive Attitudes
Evidence from prior research provides support for strengthening residents’ willingness to participate in community life. This can be achieved by stimulating cognitive memory, emotional fluctuations, and physiological responses through sensory interventions. Specific implementation recommendations are as follows:
- Emphasize activating cognitive memory and emotional association, mainly through visual and olfactory stimuli. This includes cultural, childhood, taste-related, and auditory memories. For example, artworks may resemble familiar objects or evoke past experiences through cultural references. Scented plants, such as flowers, grasses, and fruits, can trigger memories, while herbs like verbena, mint, and lemongrass, known for mood-enhancing properties [39,84], may promote emotional well-being and spatial engagement. Residents may judge the healthiness of these smells from past experience, contributing to both spatial healing and willingness to participate.
- Encourage emotional fluctuations that lead to interaction, such as joy, sadness, desire, or curiosity, mainly through visual and auditory elements. This can be achieved by varying form, scale, and color, combined with soft sounds such as birdsong, flowing water, melodious music, nostalgic ambient audio, and other low-volume effects.
- Stimulate physiological responses through material and environmental design, using tactile, visual, and auditory elements. Public artworks may incorporate diverse materials offering distinct tactile sensations, such as plush textures, cool mist, or cobblestone paving. These features prompt participants to approach and interact with the space.
6.4.2. Fostering Positive Subjective Norms
Individual behavior is shaped by the atmosphere of community members and neighborhood groups, as residents often change their actions due to conformity and a sense of belonging. When many community members participate in public art, residents perceive it as “something everyone is doing.” This social recognition, formed through positive group influence, acts as a subjective norm that encourages individual participation. Specific implementation recommendations are as follows:
- Prioritize the creation of art facilities with collective participation features. Interviews and observations show that group activities are often linked to visual and haptic elements. Visually engaging installations, such as light projections, interactive displays, or appealing activity structures, can attract individuals and gradually stimulate group involvement. Haptic-friendly facilities, like climbing structures, dry fountains, or touch-based features, further enhance collective engagement.
- Design artworks that promote children’s participation to generate a “one leads many” effect. Children naturally identify with peers, and their social interactions often include family groups [85]. By integrating tactile and visual elements that appeal to children, social interaction can be stimulated, attracting family members and fostering wider resident participation.
- Provide opportunities for all age groups to improve inclusivity. Beyond high child engagement, facilities such as community canteens or small shared kitchens can support elderly residents in taste-oriented environments for health and wellness. Integrating art exhibitions with inclusive activities like flower arranging or gardening can also create emotional warmth and meaningful participation for residents of all ages.
6.4.3. Enhancing the Convenience and Feasibility of Participation
Building on existing public art facilities, more accessible pathways and comfortable experiences should be created to help residents perceive their ability to participate, thereby reducing psychological and environmental barriers to actual engagement.
- Provide accessible routes, barrier-free infrastructure, and user-friendly interfaces to create inclusive conditions for all residents. When individuals perceive that they are capable of participating, participation can extend to vulnerable groups within the community, including people with disabilities and those with limited mobility.
- Introduce supporting facilities around public artworks to make participation more convenient. For example, adding seating, shade structures, and lighting systems near installations can reduce psychological and environmental resistance to action, and lower the practical costs of participation for residents.
Through these measures, enhancing sensory stimulation in community renewal not only increases residents’ willingness to interact in the short term, but also contributes to the formation of a positive attitude, a supportive social atmosphere, and accessible participation conditions under the framework of the TPB. This can further promote sustained resident engagement and strengthen community cohesion and momentum for sustainable development.
6.5. Research Limitations and Future Directions
6.5.1. Research Limitations
This study still has certain limitations. (1) Methodologically, data mainly relied on self-reported questionnaires. Although supplemented by observation and interviews, causal explanations remain limited. Future research could adopt longitudinal designs or contextual experiments and incorporate objective indicators such as environmental sensors and wearable devices, combined with subjective perceptions, to enhance reliability. (2) In terms of samples, participants were limited to residents aged 18 and above, leaving insufficient coverage of younger groups. Observations and interviews were used to supplement minors’ behavior. Future studies should expand through stratified random sampling to include diverse groups, especially adolescents and the elderly, to improve sample representation. (3) Regarding variables, only vision, hearing, touch, smell, and taste were examined, while complex senses such as proprioception and kinesthesia were excluded. Future work could explore their role in interactive and immersive art to further explain their impact on participation and social interaction.
6.5.2. Future Prospects of Technological Innovation and Policy Trends
The development of smart cities and digital art provides new directions for public art research. Future studies may incorporate augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and multisensory digital art to explore technology-driven modes of interaction. At the same time, international policies increasingly emphasize linking art with health, ecology, and social well-being. Future research could examine the potential of sensory-based public art under different institutional contexts. In addition, the rise in digital social networks offers new channels for resident participation, which may complement or amplify sensory stimulation effects, warranting further exploration.
7. Conclusions
This study examines cases of public art in Shanghai’s community renewal, employing a mixed-method approach that combines quantitative and qualitative research to explore how sensory-based public art can enhance residents’ frequency of spatial participation. The aim is to move beyond the limitation of public art as merely “to be viewed” and to reconstruct the interactive relationship between the public and artworks. By integrating sensory marketing theory with the SOR model, a research framework was developed based on sensory stimuli, perceptual responses, and behavioral intention, and the hypotheses were tested and analyzed using SEM. The data were used to verify the relationship between public art and residents’ participation intention under five types of sensory stimulation, as well as the relative strength of these effects. Second, interviews and observations with actual participants at the case sites are conducted to further examine variations in resident behavior within complex participatory processes. Finally, the TPB was introduced as an implementation framework to propose actionable pathways for supporting sustained resident participation in community settings.
The findings indicate that, according to the quantitative data, residents’ behavioral intention to participate is directly influenced by emotional fluctuations, cognitive experience, and physiological responses, and indirectly influenced by different types of sensory stimulation. Among these, cognitive memory has the strongest effect on behavioral intention, followed by emotional fluctuations, and then physiological responses. Cognitive memory is most strongly influenced by olfactory and visual stimulation. Emotional fluctuations are primarily affected by visual and auditory stimulation, while physiological responses are most notably triggered by visual and haptic stimulation. Although the effects of the other senses are somewhat lower in the data, they all play a significant role. Different senses can be effectively utilized in design to move beyond the visual dominance of public art. The qualitative results partially reaffirm the relationships identified in the structural model, while also revealing generational differences and varying participation patterns in response to different types of sensory stimulation. For example, children tend to respond more strongly to haptic stimulation, while elderly residents show a preference for olfactory stimulation. Vision and haptics are more likely to elicit collective forms of participation, whereas audition and olfaction are typically associated with individual appreciation. Taste-related stimulation is characterized by a higher degree of subjectivity. The findings not only confirm that senses beyond vision also play a role in driving behavior in artistic experiences, but also reveal the intrinsic linkage between material environmental factors and users’ emotional experiences. Specifically, the form, material, sound, and scent of public art act on individuals’ cognitive memory, emotional arousal, and bodily perception, which in turn trigger interactive behavior and social engagement.
Unlike existing studies that often focus on a single sense or on visual-auditory stimuli, this research constructs a comparative model of all five senses. In contrast to the current emphasis on technologically driven interactive installations, the study highlights the psychological–behavioral mechanism of stimuli–response–behavior, underscoring the value of interpreting urban art interventions through perspectives from environmental psychology and cognitive science. At the same time, this study introduces sensory marketing theory into the research on public art and resident behavior for the first time. By breaking through its traditional application in commercial consumption contexts, the study extends its theoretical applicability to participation mechanisms in urban communities and public spaces, demonstrating both novelty and theoretical significance.
The implementation recommendations derived from the findings are structured based on the TPB. (1) It is recommended to enhance residents’ positive participation attitude by activating experiential cognition and emotional memory, encouraging emotional fluctuations, and stimulating physiological responses. (2) Broad civic participation can be achieved by designing sensory categories with collective engagement characteristics, creating artworks that encourage high levels of participation among children, and providing public art facilities or activities that accommodate residents of all ages. These measures help shape positive subjective norms through the influence of collective atmosphere. (3) Improving the accessibility and feasibility of participation requires the provision of convenient, comfortable, easy-to-use, and barrier-free engagement pathways. This study offers insights into how to support sustained resident participation in community spaces, and provides practical references for enhancing spatial vitality and strengthening neighborhood ties.
These recommendations and findings carry cross-disciplinary applicability and practical value. At the practical level, they offer actionable design guidance for local governments, urban planners, and community organizers, particularly in micro-renewal contexts of high-density cities where public space is limited and participation remains low. Extending public art design toward multisensory experiences can enhance psychological well-being and social interaction, fostering neighborhood ties and revitalizing community vitality. The insights are also relevant to emerging urban practices that integrate technology and art, such as digital communities, online participation simulations, and multimodal urban experience design, providing future pathways for public art that are more immersive, interactive, and inclusive. At the policy level, the results support agendas in refined urban governance, old-community revitalization, and healthy city development. They are especially aligned with concepts such as the 15-Minute Community Life Circle, age-friendly cities, and equalization of public cultural services, offering policy-oriented guidance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.S.; methodology, Y.S. and R.T.; software, Y.S. and R.T.; validation, Y.S. and R.T.; formal analysis, Y.S. and S.L.; investigation, Y.S. and R.T.; resources, Y.S. and S.L.; data curation, Y.S. and S.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.S.; writing—review and editing, R.T. and S.L.; visualization, Y.S. and R.T.; supervision, S.L.; project administration, S.L.; funding acquisition, S.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
According to the requirements of our institution’s ethics approval documents, only studies involving human life sciences, medical research, or animal experiments require ethical approval. As our research does not fall into these categories, we determined that ethics approval was not necessary.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data and questionnaires used in this study are available from the corresponding author upon request. Data are not publicly available due to the privacy term signed by the respondents in the informed consent.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| VIS | Vision |
| HAP | Haptics |
| AUD | Audition |
| OLF | Olfactory |
| TAS | Taste |
| PR | Physiological Response |
| EF | Emotional Fluctuations |
| CM | Cognitive Memory |
| PII | Participating in Interaction |
| SEM | Structural Equation Modeling |
| SOR | Stimulus Organism Response |
| TPB | Theory of Planned Behavior |
Appendix A

Table A1.
Questionnaire Scale.
Table A1.
Questionnaire Scale.
| Scale | Dimensions | Items | References | Statements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensory Stimulation | Vision | V1 | [69,70,71] | The size and scale of public art give me a strong visual impact. |
| V2 | The form and shape of public art attract my attention. | |||
| V3 | The bright and vivid colors of public art draw my attention. | |||
| Haptics | H1 | [86,87] | Public art with temperature (fire, ice) stimulates my sense of touch. | |
| H2 | Moist or dry artworks (e.g., mist fountains) stimulate my skin. | |||
| H3 | Soft textures in public art provide a pleasant tactile experience. | |||
| Audition | A1 | [88,89,90] | Natural sounds (water, wind, birdsong) enhance my auditory experience. | |
| A2 | Public art with music strengthens my auditory perception. | |||
| A3 | Human sounds (discussion, laughter, vending) enrich my auditory experience. | |||
| Olfactory | O1 | [91,92,93] | The smell of healthy plants in public art makes me feel comfortable. | |
| O2 | Food-related smells in public art enrich my olfactory experience. | |||
| O3 | Mixed scents (perfume, fragrance) enhance my olfactory perception. | |||
| Taste | T1 | [94,95] | Visual cues or text evoke specific taste memories. | |
| T2 | Direct tasting related to public art provides a rich experience. | |||
| T3 | Flavors matched with the theme of the artwork improve the overall experience. | |||
| Perceptual Response | Physiological Response | 1 | [96,97,98] | Sensory stimuli in public art change my heart rate. |
| 2 | Multisensory public art triggers skin reactions. | |||
| 3 | Different sensory inputs in public art make my muscles relax or tense. | |||
| Emotional Fluctuations | 1 | [99,100,101] | Multisensory experiences in public art make me curious or interested. | |
| 2 | Multisensory experiences in public art bring feelings of joy, excitement, calmness, or happiness. | |||
| 3 | Sensory experiences in public art create a desire to approach, revisit, or share. | |||
| Cognitive Memory | 1 | [102,103] | Sensory experiences in public art evoke my past knowledge and experiences, helping me recognize interesting works. | |
| 2 | Sensory experiences in public art recall my memories of tastes, foods, or toys. | |||
| 3 | I can form sensory associations through images, shapes, or descriptions in public art. | |||
| Behavioral Intention | Participation in Interaction | 1 | [93,104] | Sensory elements in public art make me willing to participate (stay, interact, observe). |
| 2 | Sensory elements in public art make me resonate with the work, willing to interact, support, and share it. |

Table A2.
Respondent Demographic Characteristics.
Table A2.
Respondent Demographic Characteristics.
| Items | Index | Frequency | Percentage | Cumulative Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 15–30 | 73 | 21.99 | 21.99 |
| 31–45 | 119 | 35.84 | 57.83 | |
| 46–60 | 98 | 29.52 | 87.35 | |
| Over 60 | 42 | 12.65 | 100 | |
| Gender | Male | 134 | 40.36 | 40.36 |
| Female | 198 | 59.64 | 100 | |
| Educational background | Junior high school | 58 | 17.47 | 17.47 |
| Senior high school | 95 | 28.61 | 46.08 | |
| Bachelor degree | 125 | 37.65 | 83.73 | |
| Master degree | 46 | 13.86 | 97.59 | |
| Ph.D. degree | 8 | 2.41 | 100 | |
| Residential status | Permanent residents | 244 | 73.49 | 73.49 |
| Non-resident | 78 | 24.69 | 100 | |
| Total | 332 | 100 | 100 | |

Table A3.
Selected Interview Records.
Table A3.
Selected Interview Records.
| Gender | Age | Interview Content |
|---|---|---|
| Male | 31–45 | It used to be a mess here, nothing really to see, so I never came. But now it looks pretty cool, so I stopped to take a photo—and even posted it online. It’s nice enough that I’m thinking of bringing my kid here next time |
| Female | 18–30 | I heard they fixed up this place and it looked really nice, so I came just to check it out and snap some photos. |
| Male | 46–60 | I ended up standing here for a long time. The fountain moves with the music—it was honestly really exciting to watch. |
| Female | 31–45 | When I first got here, I couldn’t even see the fountain, but the sound of music and water immediately caught my attention, so I walked over to check it out. I also saw a bunch of kids running under the fountain and playing. It really pulls people in and makes you want to join. |
| Male | 31–45 | This thing really reminds me of the slides I used to play on as a kid. The surface is super smooth too, just like those. As soon as one kid tries to climb up, others want to join in. My kid has been playing here for a long time and doesn’t want to leave. |
| Female | 61+ | The scent of the flowers and plants here is just so comforting. I like to come here for a walk after dinner. |
| Male | 61+ | This smell takes me back to when my mom used to make noodles for me as a kid. |
| Male | 46–60 | I’m really sensitive to floral scents. As soon as I smelled it, I thought of my childhood in the countryside. It really hit home for me. I sat nearby for a while and figured I’d bring my friend next time. |
| Female | 31–45 | This ketchup bottle changes themes from time to time—last time it was a loaf of bread. I was super hungry at lunch, and just seeing it made me crave that taste immediately. |
References
- Group, W.B. Urban Development. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/urbandevelopment/overview?utm_source.com (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Peng, Z.; Wei, D. Street art as a way to enhance the vitality of Uurban public spaces: Inspiration based on the experience of Taipei. Int. Plan. Hist. Soc. Proc. 2018, 18, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.; Im, D.-U.; Lee, J. Promoting the Sustainability of City Communities through ‘Voluntary Arts Activities’ at Regenerated Cultural Arts Spaces: A Focus on the Combination of the ‘Democratization of Culture’ and ‘Cultural Democracy’ Perspectives. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, T.; Gadaloff, S. Public art for placemaking and urban renewal: Insights from three regional Australian cities. Cities 2022, 127, 103747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, V. Street Art and the Changing Urban Public Sphere. Public. Cult. 2017, 29, 385–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, S. Mapping the Terrain: New Genre Public Art; Bay Press: Seattle, WA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Purves, A.C. Touch and the Ancient Senses; Routledge: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.M. Subjectivity in Hegel’s Aesthetics. PhD. Thesis, University of Notre Dame, South Bend, IN, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.G. On “Sensory Aesthetics”: How Sensory Appreciation is Possible. Zhejiang Soc. Sci. 2017, 1, 119–126+159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turley, L.W.; Milliman, R.E. Atmospheric effects on shopping behavior: A review of the experimental evidence. J. Bus. Res. 2000, 49, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajadacz, A.; Lubarska, A. Sensory gardens as a new form of urban green space in smart sustainable cities. Czas. Geogr. 2023, 94, 125–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, A.R.G.; González-Carrasco, I.; Jasper, G.H.; Lopez, A.L.; Lopez-Cuadrado, J.L.; García-Crespo, A. Towards human smart cities: Internet of things for sensory impaired individuals. Computing 2017, 99, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonnies, F.; Loomis, C.P. Community and Society; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewkes, R.; Murcott, A. Meanings of community. Soc. Sci. Med. 1996, 43, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jiang, X.; Tan, L.; Chen, C.; Yang, S.; You, W. Analysis of Spatial Vitality Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Old Neighborhoods: A Case Study of Ya’an Xicheng Neighborhood. Buildings 2024, 14, 3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, J. Making a city: Urbanity, vitality and urban design. J. Urban. Des. 1998, 3, 93–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.R. Percent-for-art programs at public art’s frontier. Zoning Plan. Law. Rep. 2012, 35, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher, E.F. Small is Beautiful: Economics as if People Mattered; Blond & Briggs: London, UK, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, X.; Hamilton, G.G.; Zheng, W. From the Soil: The Foundations of Chinese Society; University of California Press: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Mulcahy, K.V. Public Culture, Cultural Identity, Cultural Policy: Comparative Perspectives; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, M. Art, Space and the City; Routledge: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartiere, C.; Willis, S. The Practice of Public Art; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, P.J. Public Art-Purpose and Benefits: Exploring Strategy in the New England City of Pittsfield, Ma. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Massachusetts Amherst, Amherst, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daglio, L.; Kousidi, S. From Ornament to Building Material: Revisiting the Aesthetics and Function of Green Architecture. Arts 2023, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska, J.; Telesińska, M.; Adamska, A.; Gronostajska, J. The Architectural Typology of Contemporary Façades for Public Buildings in the European Context. Arts 2022, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bone, T.A. Art and Mental Health Recovery: Evaluating the Impact of a Community-Based Participatory Arts Program Through Artist Voices. Community Ment. Health J. 2018, 54, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, E.; Barton, D. Blooming names: Nature-based art therapy and poetry honoring Black lives. Int. J. Art. Ther. 2025, 30, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, R.; Ortega, F.; Interrante, V. A multisensory approach to virtual reality stress reduction. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.00718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, H.; Mardani, A.; Basirinezhad, M.H.; Hamidzadeh, A.; Eskandari, F. The effects of Lavender and Chamomile essential oil inhalation aromatherapy on depression, anxiety and stress in older community-dwelling people: A randomized controlled trial. Explore 2022, 18, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.; Marshall, M.T. An Investigation of the Use of Augmented Reality in Public Art. Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2023, 7, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vi, C.T.; Ablart, D.; Gatti, E.; Velasco, C.; Obrist, M. Not just seeing, but also feeling art: Mid-air haptic experiences integrated in a multisensory art exhibition. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Stud. 2017, 108, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, P.-A.; Pasquier, P. Auditory Tactics: A Sound Installation in Public Space Using Beamforming Technology. Leonardo 2010, 43, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Hasegawa, Y.; Tan, J.K.A.; Lau, S.-K. Effect of audio-visual interaction on soundscape in the urban residential context: A virtual reality experiment. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 192, 108717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q. Physiological Effects of a Garden Plant Smellscape from the Perspective of Perceptual Interaction. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2023, 20, 5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehove, M.; Mikuni, J.; Podolin, N.; Moser, M.K.; Resch, B.; Doerrzapf, L.; Boehm, P.M.; Prager, K.; Leder, H.; Oberzaucher, E. Exploring the influence of urban art interventions on attraction and wellbeing: An empirical field experiment. Front. Psychol. 2024, 15, 1409086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, C.C.; Barnes, M. Healing Gardens: Therapeutic Benefits and Design Recommendations; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich, R.S. View Through a Window May Influence Recovery from Surgery. Science 1984, 224, 420–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratcliffe, E.; Gatersleben, B.; Sowden, P.T. Bird sounds and their contributions to perceived attention restoration and stress recovery. J. Environ. Psychol. 2013, 36, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.; Rodiek, S.; Fujii, E.; Miyazaki, Y.; Park, B.-J.; Ann, S.-W. Physiological and Psychological Response to Floral Scent. HortScience 2013, 48, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedblom, M.; Gunnarsson, B.; Iravani, B.; Knez, I.; Schaefer, M.; Thorsson, P.; Lundström, J.N. Reduction of physiological stress by urban green space in a multisensory virtual experiment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S. Therapeutic landscapes and healing gardens: A review of Chinese literature in relation to the studies in western countries. Front. Archit. Res. 2014, 3, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanghai Urban Planning and Natural Resources Bureau, Shanghai Municipal Administration of Culture and Tourism. Shanghai Urban Space Art Season 2021; Shanghai Urban Planning and Natural Resources Bureau, Shanghai Municipal Administration of Culture and Tourism: Shanghai, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Shanghai Urban Planning and Design Institute. Shanghai Urban Space Art Season 2023; Shanghai Urban Planning and Design Institute: Shanghai, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Shanghai Urban Planning and Design Institute. Shanghai Urban Space Art Season 2019; Shanghai Urban Planning and Design Institute: Shanghai, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, J.B. Psychology as the behaviorist views it. Psychol. Rev. 1913, 20, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foa, E.B.; Steketee, G.; Rothbaum, B.O. Behavioral/cognitive conceptualizations of post-traumatic stress disorder. Behav. Ther. 1989, 20, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppes, L.L. Historical Perspectives in Industrial and Organizational Psychology; Psychology Press: Hove, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrabian, A.; Russell, J.A. An Approach to Environmental Psychology; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Bitner, M.J. Servicescapes: The impact of physical surroundings on customers and employees. J. Mark. 1992, 56, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, I.Y. Evaluating a servicescape: The effect of cognition and emotion. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2004, 23, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Deng, Y.; Tao, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C. Digital art exhibitions and psychological well-being in Chinese Generation Z: An analysis based on the S-O-R framework. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H. Research on the underlying dynamics of leisure’s impact in arts venues. Front. Psychol. 2025, 16, 1401922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, S. Walking in Tandem with the City: Exploring the Influence of Public Art on Encouraging Urban Pedestrianism within the 15-Minute Community Living Circle in Shanghai. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Sun, Y.; Sun, B.; Huang, Y. The Impact of the Urban Forest Park Recreation Environment and Perceived Satisfaction on Post-Tour Behavioral Intention—Using Tongzhou Grand Canal Forest Park as an Example. Forests 2024, 15, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, P. Unraveling Tourist Behavioral Intentions in Historic Urban Built Environment: The Mediating Role of Perceived Value via SOR Model in Macau’s Heritage Sites. Buildings 2025, 15, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.-H.; Guo, S.; Yan, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Hong, P.; Chen, Y. Parametric Landscape Facilities Aesthetic Design Method Based on SOR Model and Hybrid Kansei Engineering: A Case of Landscape Corridors. Buildings 2025, 15, 3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyle, R.H. The structural equation modeling approach: Basic concepts and fundamental issues. In Structural Equation Modeling: Concepts, Issues, and Applications; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1995; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Bollen, K.A.; Fisher, Z.; Lilly, A.; Brehm, C.; Luo, L.; Martinez, A.; Ye, A. Fifty years of structural equation modeling: A history of generalization, unification, and diffusion. Soc. Sci. Res. 2022, 107, 102769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S. On the nature of size factors. Genetics 1918, 3, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jöreskog, K.G.; Sörbom, D. PRELIS 2 User’s Reference Guide: A Program for Multivariate Data Screening and Data Summarization: A Preprocessor for LISREL; Scientific Software International: Chicago, IL, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Bollen, K.A. Structural Equations with Latent Variables; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández Rojas, R.; Jimber del Río, J.A.; Ibáñez Fernández, A.; Vergara-Romero, A. The cultural and heritage tourist, SEM analysis: The case of The Citadel of the Catholic King. Herit. Sci. 2021, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olanrewaju, A. Application of structural equation modelling (SEM) to evaluate reworks in sustainable buildings. Front. Eng. Built Environ. 2025, 5, 86–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, R.; Chatterjee, S.; Mariani, M.M.; Wamba, S.F. Assessing the influence of emerging technologies on organizational data driven culture and innovation capabilities: A sustainability performance perspective. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2024, 200, 123165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ling, G.H.T.; Misnan, S.H.b.; Fang, M. A Systematic Review of Factors Influencing the Vitality of Public Open Spaces: A Novel Perspective Using Social–Ecological Model (SEM). Sustainability 2023, 15, 5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kineber, A.F.; Massoud, M.M.; Hamed, M.M.; Alhammadi, Y.; Al-Mhdawi, M.K.S. Impact of Overcoming BIM Implementation Barriers on Sustainable Building Project Success: A PLS-SEM Approach. Buildings 2023, 13, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Rodríguez, A.L.; Sanchís-Pedregosa, C.; Moreno-Moreno, A.M.; Leal-Millán, A.G. Digitalization beyond technology: Proposing an explanatory and predictive model for digital culture in organizations. J. Innov. Knowl. 2023, 8, 100409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, A.; Schwarz, N. Sensory marketing, embodiment, and grounded cognition: A review and introduction. J. Consum. Psychol. 2014, 24, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Watanabe, K. Effect of colour–shape associations on visual feature discrimination. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 2023, 76, 2285–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinna, B. The organization of shape and color in Vision and Art. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 11502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelowski, M.; Leder, H.; Mitschke, V.; Specker, E.; Gerger, G.; Tinio, P.P.L.; Vaporova, E.; Bieg, T.; Husslein-Arco, A. Capturing Aesthetic Experiences with Installation Art: An Empirical Assessment of Emotion, Evaluations, and Mobile Eye Tracking in Olafur Eliasson’s “Baroque, Baroque!”. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, C.; Diamantopoulos, A. Using single-item measures for construct measurement in management research: Conceptual issues and application guidelines. Die Betriebswirtschaft 2009, 69, 195. [Google Scholar]
- Bettencourt, L.A.; Brown, S.W.; MacKenzie, S.B. Customer-oriented boundary-spanning behaviors: Test of a social exchange model of antecedents. J. Retail. 2005, 81, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, M.W. Exploratory factor analysis: A guide to best practice. J. Black Psychol. 2018, 44, 219–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebb, D.O. The Organization of Behavior: A Neuropsychological Theory; Psychology Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Cui, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Liu, H. Biophilic environment with visual-olfactory stimuli contributes to psychophysiological restoration and cognitive enhancement. Build. Environ. 2024, 250, 111202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pylyshyn, Z. Is vision continuous with cognition? The case for cognitive impenetrability of visual perception. Behav. Brain Sci. 1999, 22, 341–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, J.; Brascamp, J. Sensory memory for ambiguous vision. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2008, 12, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doukakis, E.; Debattista, K.; Bashford-Rogers, T.; Dhokia, A.; Asadipour, A.; Chalmers, A.; Harvey, C. Audio-visual-olfactory resource allocation for tri-modal virtual environments. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2019, 25, 1865–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, T.; Souto, D.; Barrett, D.; Lok, B.; Bocian, M.; Soczawa-Stronczyk, A.; Vavoula, G.; Long, P.; Bhangaonkar, A.; Bowry, S. Sight, Sound and Smell in Immersive Experiences of Urban History: Virtual Vauxhall Gardens Case Study. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.13612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, P.; Li, L.; Liu, J. The influence of architectural heritage and tourists’ positive emotions on behavioral intentions using eye-tracking study. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; You, C.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Tan, M.; Zhang, G.; Zhong, Y. Influence of Environmental Aesthetic Value and Anticipated Emotion on Pro-Environmental Behavior: An ERP Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzen, I. The theory of planned behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 1991, 50, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, P.; García, A.; Villa, R.; Nobile, V.; Parisi, O.I.; Lirangi, C.; Amone, F.; D’Ambrosio, E.; Caturla, N.; Jones, J. Lippia citrodora (Lemon Verbena) Extract Helps Reduce Stress and Improve Sleep Quality in Adolescents in a Double-Blind Randomized Intervention Study. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zöggeler-Burkhardt, L.; Embacher, E.-M.; Smidt, W. Social relationships, interactions and learning in early childhood—Theoretical approaches, empirical findings and challenges. Early Child. Dev. Care 2023, 193, 1199–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.Y.; Choo, C.M.; Lin, Y.; Ho, H.N.; Kitada, R. The Effect of Temperature on Tactile Softness Perception. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2022, 15, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.; Prativa, S.; Likova, L.T. Perception and Appreciation of Tactile Objects: The Role of Visual Experience and Texture Parameters. J. Percept. Imaging 2022, 5, 000405-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, J.; Kang, J. Effects of Soundscape on the Environmental Restoration in Urban Natural Environments. Noise Health 2017, 19, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carles, J.; Barrio, I.; de Lucio, J. Sound influence on landscape values. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 1999, 43, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, C.; Xie, H.; Yang, W.; He, Y. Perception of National Park Soundscape and Its Effects on Visual Aesthetics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 5721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lygum, V.L.; Xiao, J. Creating Smellscapes with Plants: A Landscape Architectural Framework. Urban. Sci. 2025, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, C. Using Ambient Scent to Enhance Well-Being in the Multisensory Built Environment. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 598859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Gómez, F.I.; Miranda-Gonzalez, F.J.; Pérez Mayo, J.; González-López, Ó.R.; Pascual-Nebreda, L. The Scent of Art. Perception, Evaluation, and Behaviour in a Museum in Response to Olfactory Marketing. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koczanowicz, D. Taste as a Medium of Memory in Anna Królikiewicz’s Installations. Arts 2021, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhang, P.; Xing, L.; Hu, J.; Feng, R.; Zhong, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, Y. Insights into brain perceptions of the different taste qualities and hedonic valence of food via scalp electroencephalogram. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, M.; Karulkar, N.; Broadbent, E. Evidence for the effects of viewing visual artworks on stress outcomes: A scoping review. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e043549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschacher, W.; Greenwood, S.; Kirchberg, V.; Wintzerith, S.; van den Berg, K.; Martin, T. Physiological Correlates of Aesthetic Perception of Artworks in a Museum. Psychol. Aesthet. Creat. Arts 2011, 6, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiblum-Itskovich, S.; Czamanski-Cohen, J.; Galili, G. Emotional Response and Changes in Heart Rate Variability Following Art-Making With Three Different Art Materials. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikuni, J.; Dehove, M.; Dörrzapf, L.; Moser, M.K.; Resch, B.; Böhm, P.; Prager, K.; Podolin, N.; Oberzaucher, E.; Leder, H. Art in the city reduces the feeling of anxiety, stress, and negative mood: A field study examining the impact of artistic intervention in urban public space on well-being. Wellbeing Space Soc. 2024, 7, 100215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trupp, M.D.; Howlin, C.; Fekete, A.; Kutsche, J.; Fingerhut, J.; Pelowski, M. The impact of viewing art on well-being—A systematic review of the evidence base and suggested mechanisms. J. Posit. Psychol. 2025, 4, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühnapfel, C.; Fingerhut, J.; Pelowski, M. The Role of the Body in the Experience of Installation Art: A Case Study of Visitors’ Bodily, Emotional, and Transformative Experience in Tomás Saraceno’s “in orbit”. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1192689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, A.; Grabowecky, M.; Suzuki, S. In the working memory of the beholder: Art appreciation is enhanced when visual complexity is compatible with working memory. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2015, 41, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, S.E.; Yonelinas, A.P.; Ghetti, S.; Geng, J.J. Multisensory processing impacts memory for objects and their sources. Mem. Cogn. 2025, 53, 646–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jégo, J.-F.; Meneghini, M.B. Let’s Resonate: How to Elicit Improvisation and Letting Go in Interactive Digital Art. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Movement and Computing, New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 15–17 July 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).