Experimental Comparison of Ventilation Strategies for Condensation Risk in Underground Wheat Granaries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
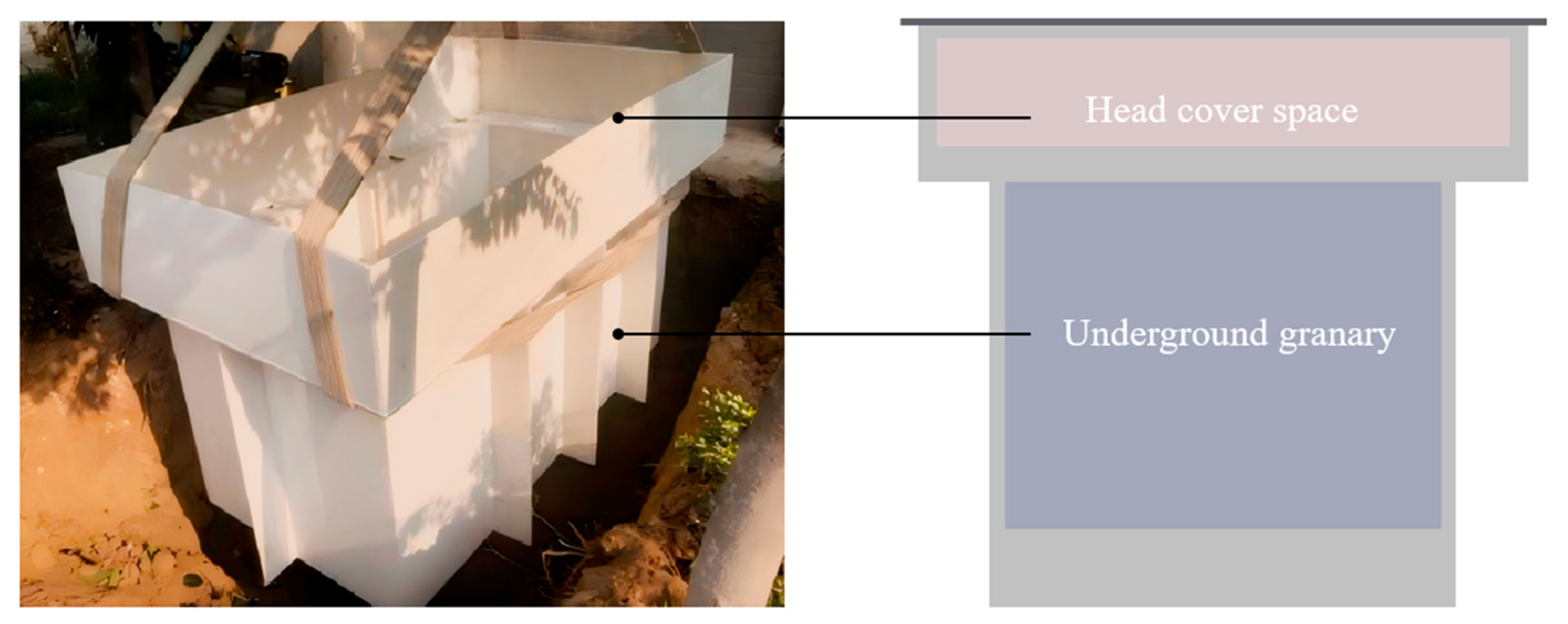
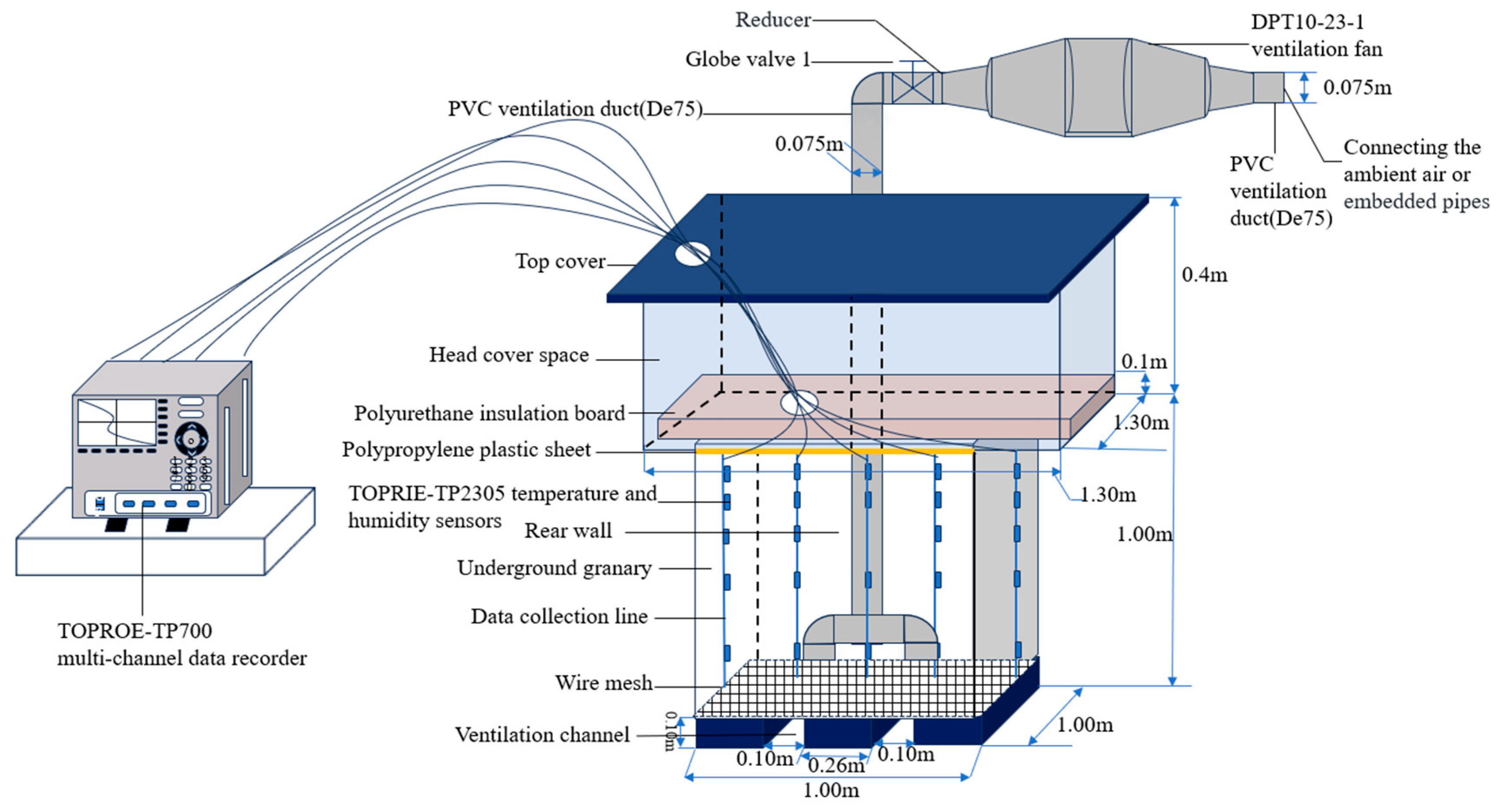
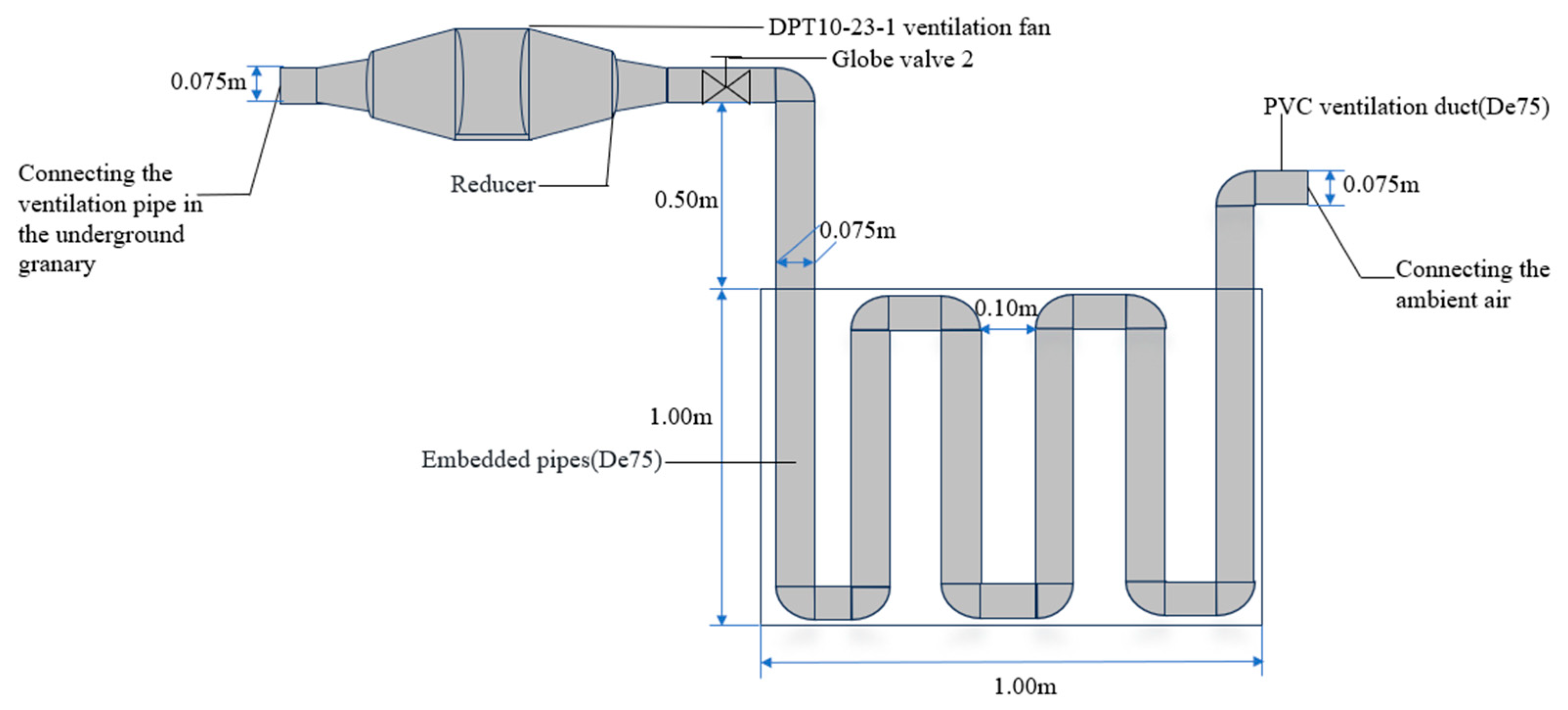
2.1. Experimental Set-Up
2.2. Instruments and Parameters Measured
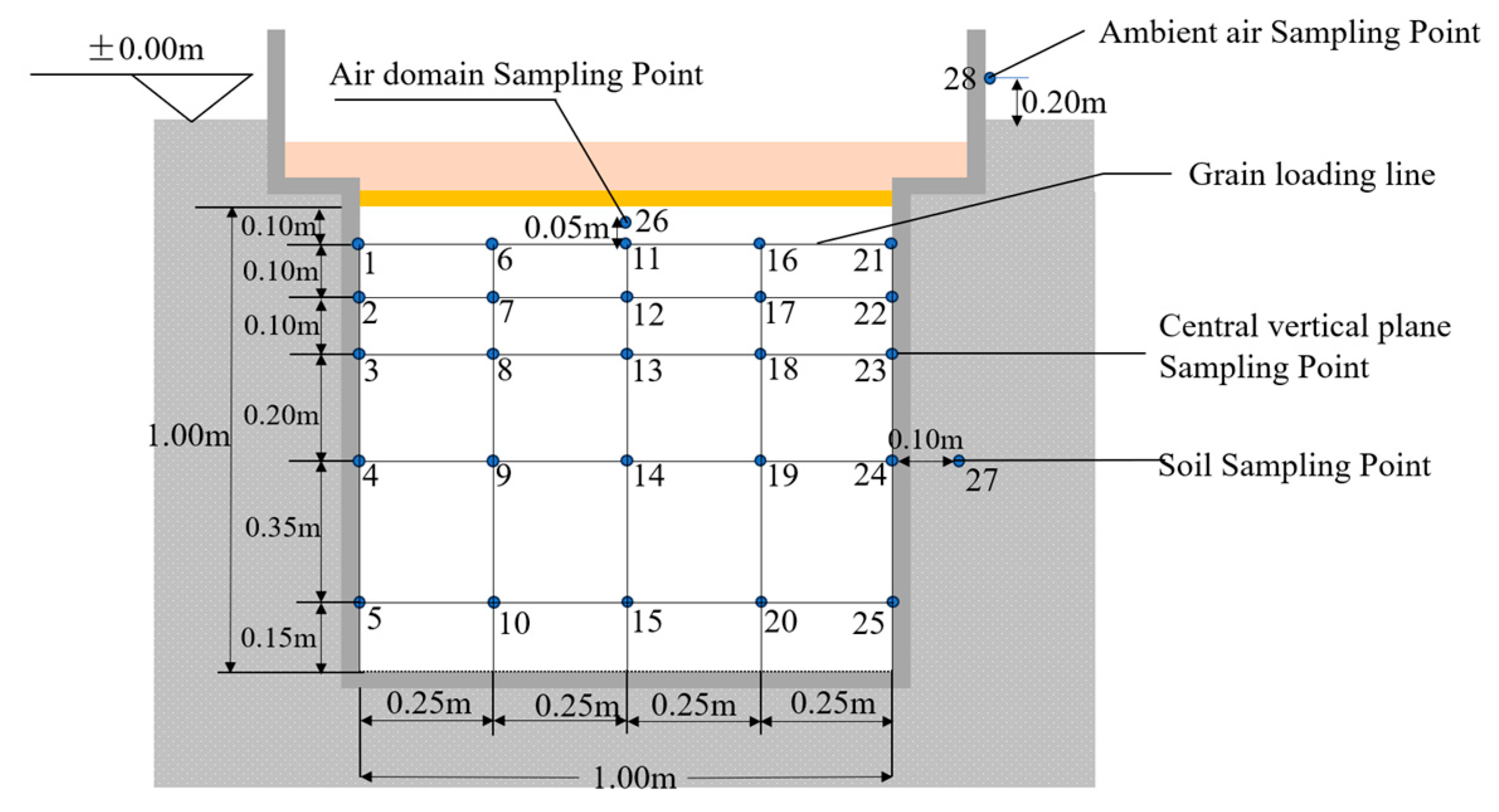
2.3. Distribution of Sampling Points
2.4. Description of Experimental Cases
2.5. Experimental Procedure
2.6. Definition of Temperature Difference
3. Results and Discussions
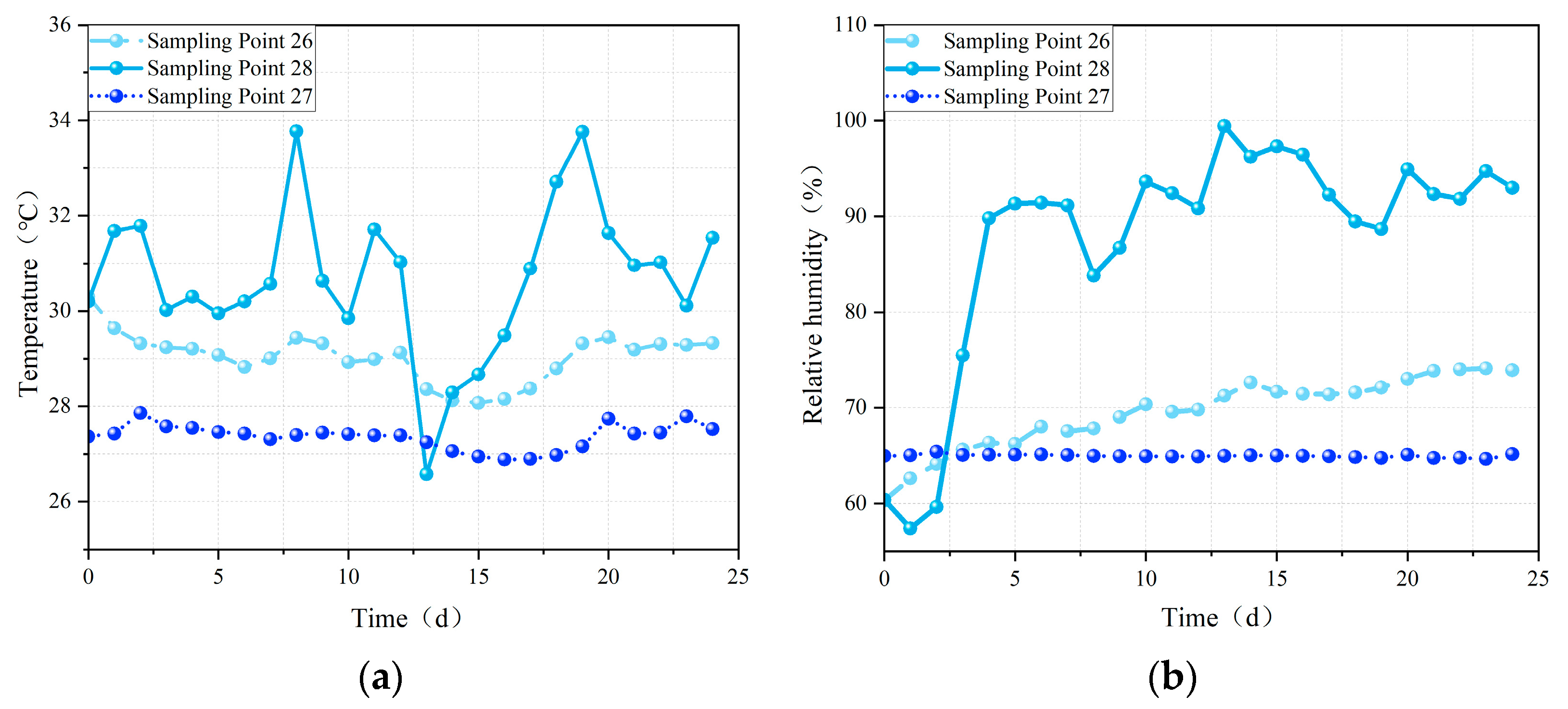
3.1. Influence of Ambient Air and Soil Conditions on Granary Air Domain
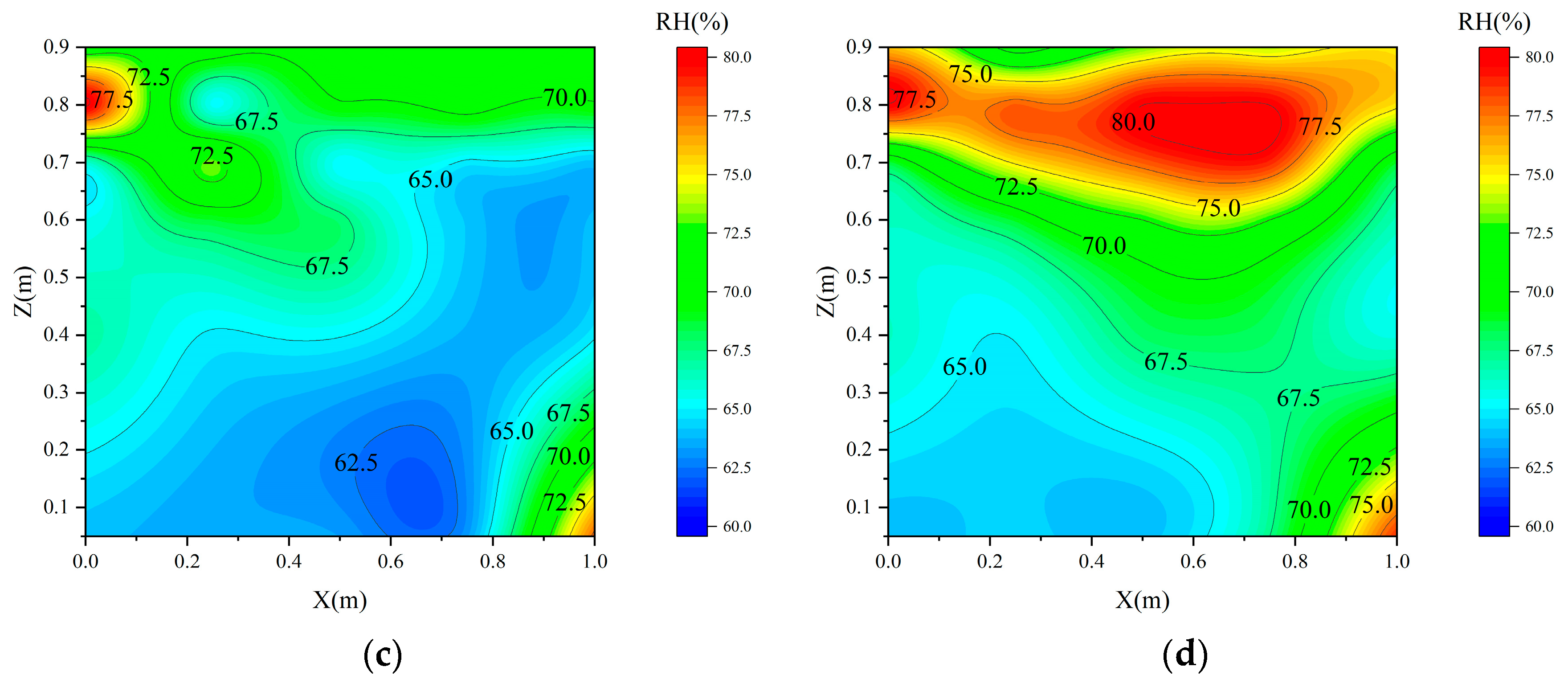
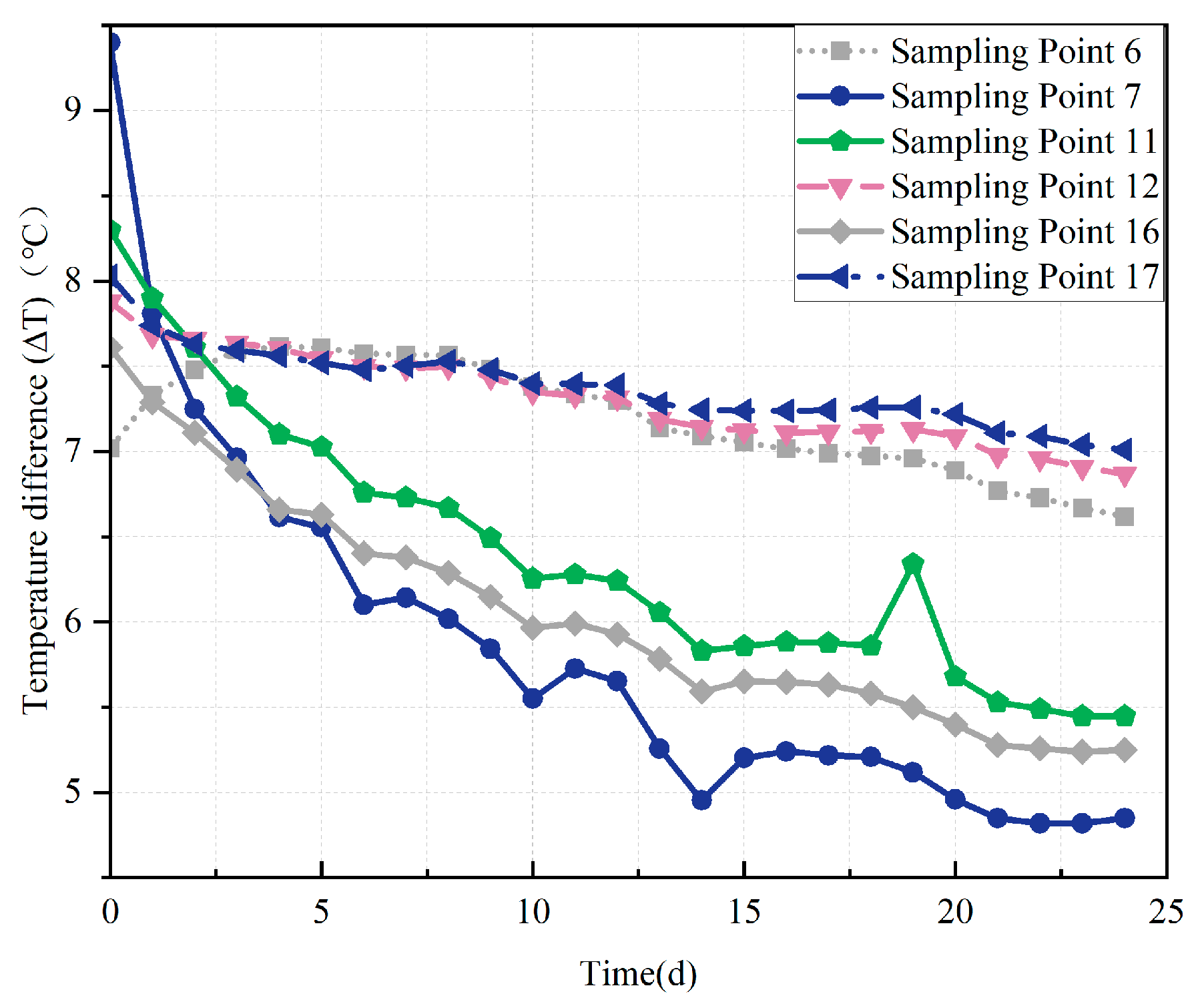
3.2. Temperature, Humidity, and Condensation in Grain Piles During Static Storage Phase
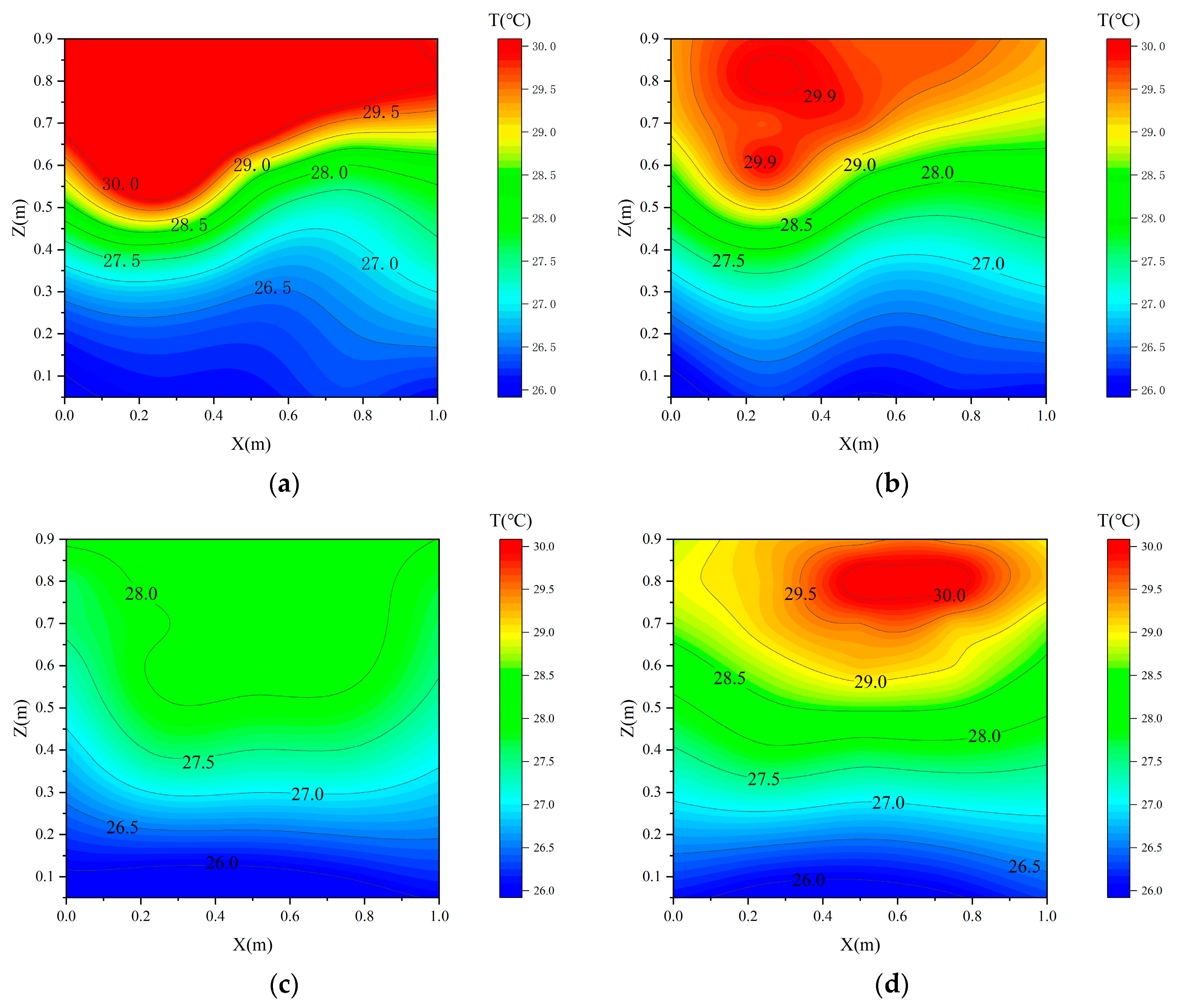
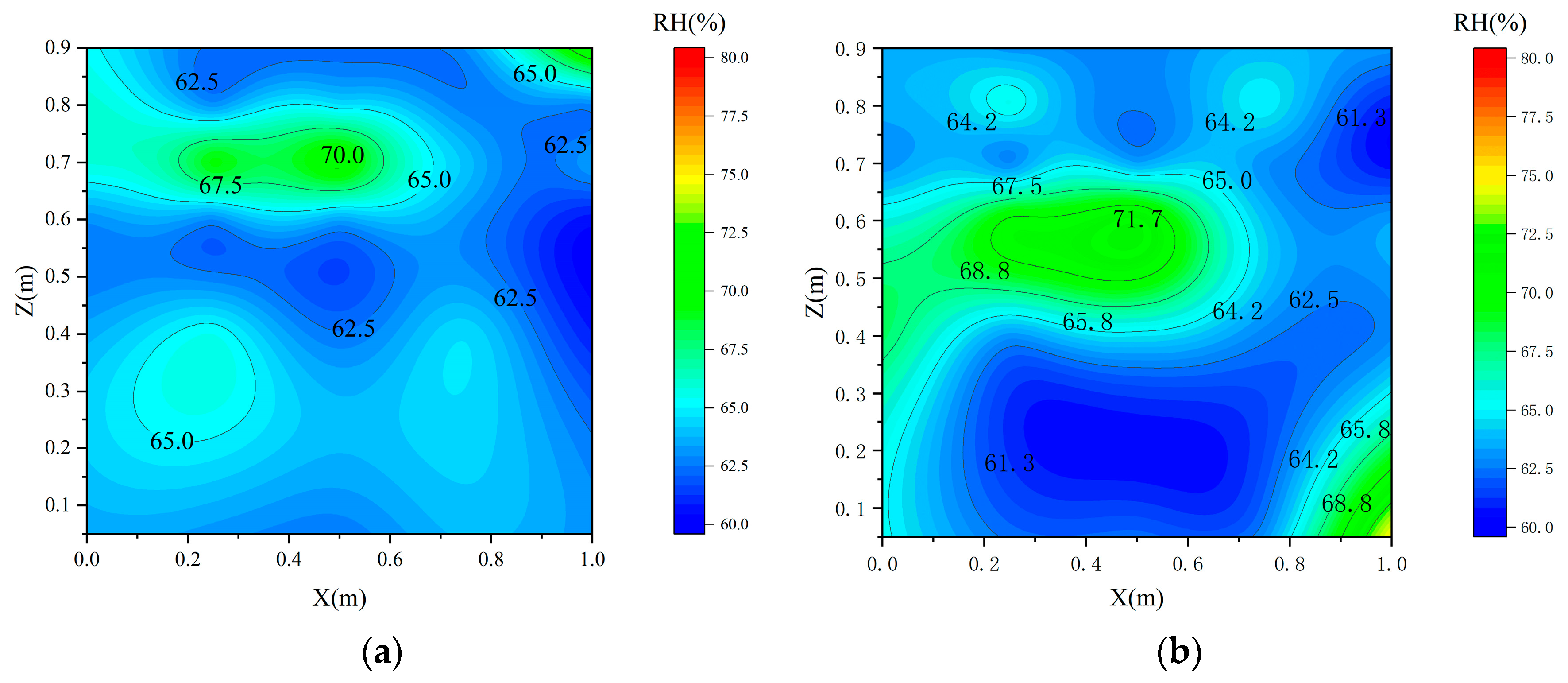
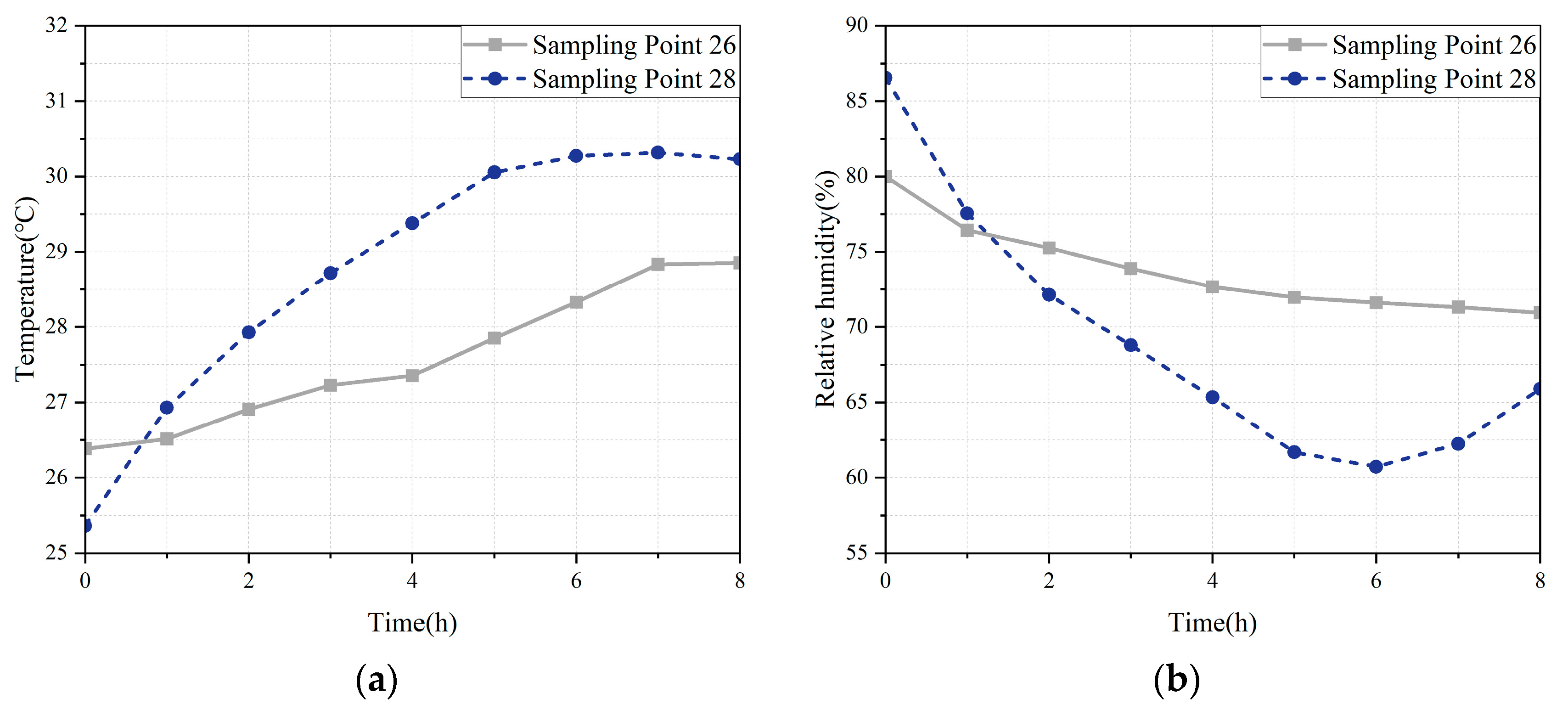
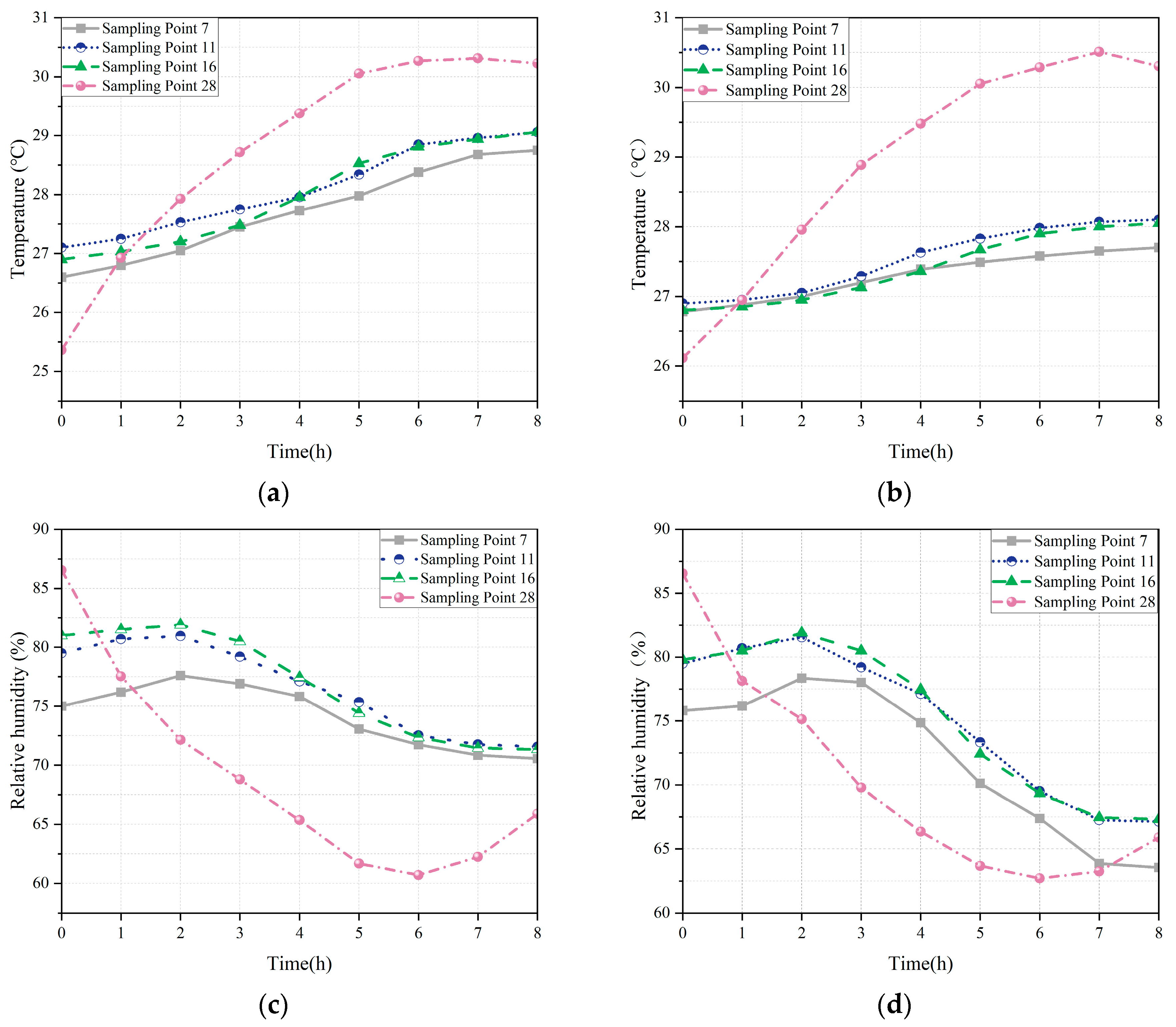
3.3. Effects of Ventilation Strategies on Grain Pile Temperature and Humidity
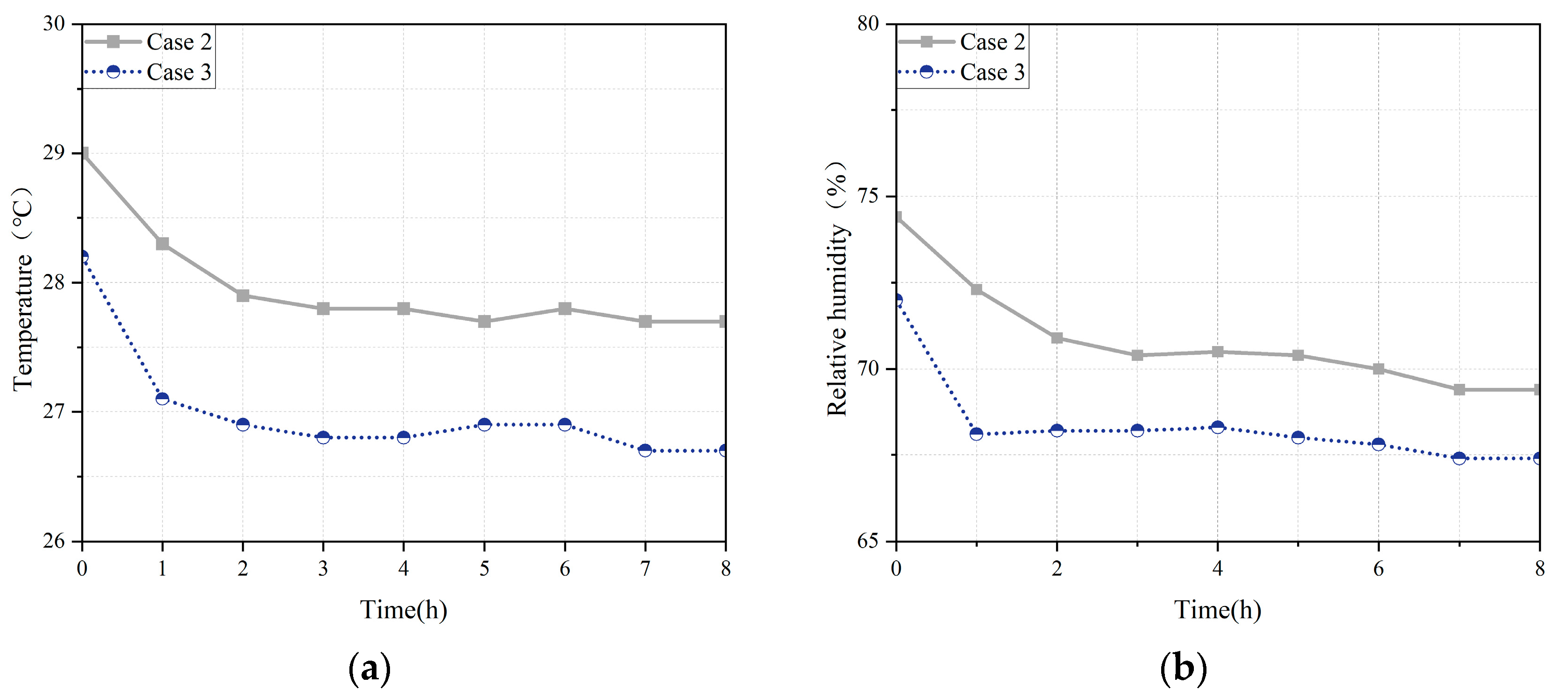
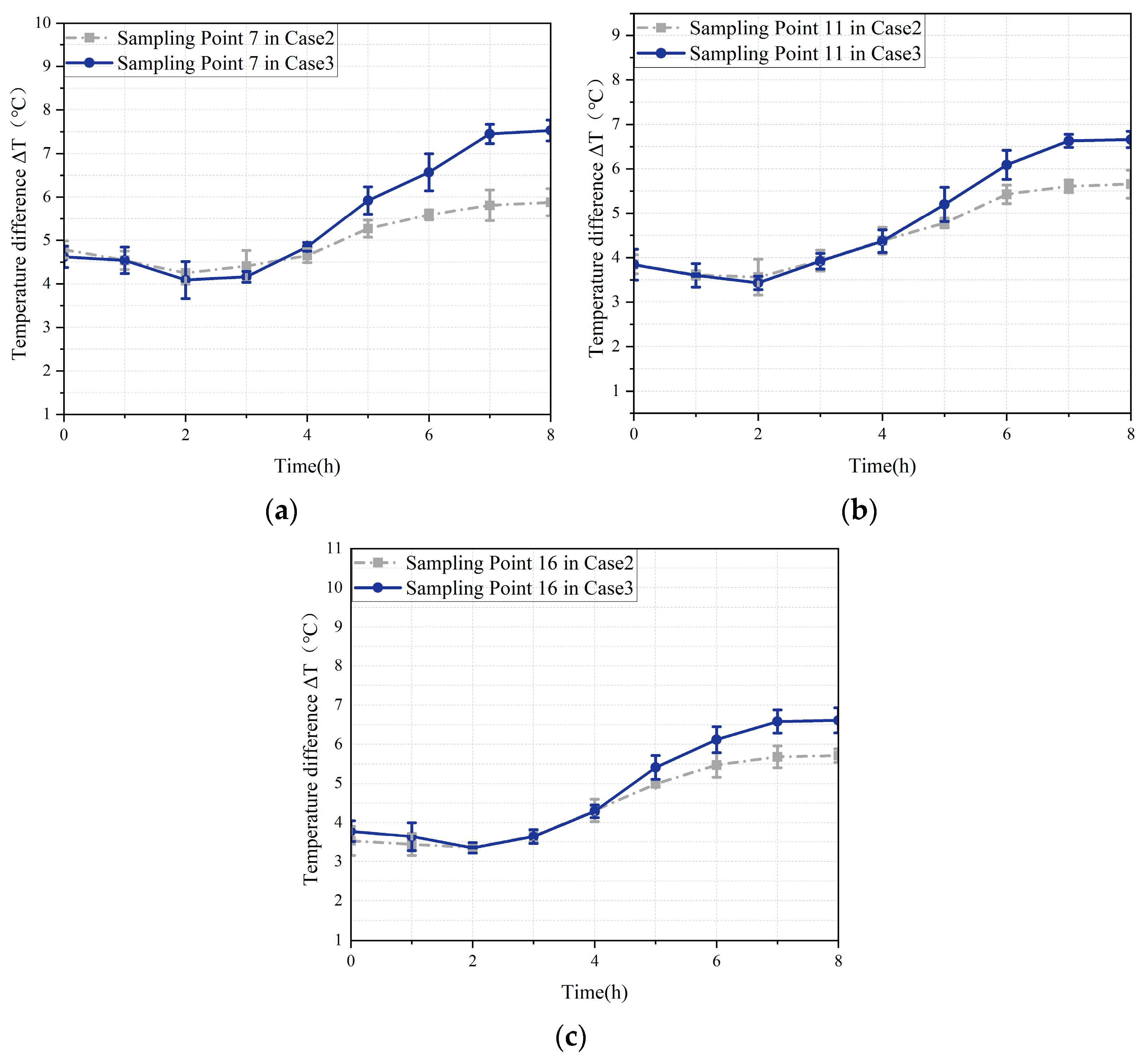
3.4. Comparison of Ventilation Strategies for Condensation Prevention in Grain Piles
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- During static storage, temperature stratification developed within the grain pile, with temperatures in the vertical profile initially decreasing and then increasing over time. Concurrently, relative humidity exhibited a continuous upward trend, resulting in a region of high temperature and humidity at the top center of the pile.
- (2)
- Mechanical ventilation effectively reduced relative humidity but was susceptible to fluctuations in ambient air temperature, thereby influencing the internal temperature distribution and the effectiveness of condensation control.
- (3)
- Pre-cooling the ambient air further enhanced the effectiveness of mechanical ventilation by reducing the internal temperature and creating a more uniform temperature distribution. This resulted in a lower relative humidity within the grain pile.
- (4)
- Ventilation pretreatment using embedded pipes is a highly effective strategy that significantly outperforms standard mechanical ventilation. By delivering cooler and more stable inlet air, it ensures a more uniform internal environment within the granary, effectively reducing the risk of condensation, particularly at the critical top layer of the grain pile. This method not only improves temperature and humidity control but also offers a practical solution for enhancing grain storage conditions, with direct implications for reducing spoilage and improving storage efficiency.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, E.; Hou, R.; Yu, J.; Niu, S.; Chen, X.; Han, B.; Zhang, P. Historical vicissitudes of grain storage environment of granaries in the North China Plain. J. Asian Archit. Build. 2024, 23, 220–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olorunfemi, B.J.; Kayode, S.E. Post-harvest loss and grain storage technology a review. Turk. J. Agric.-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 9, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Kalita, P. Reducing postharvest losses during storage of grain crops to strengthen food security in developing countries. Foods 2017, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manandhar, A.; Milindi, P.; Shah, A. An overview of the post-harvest grain storage practices of smallholder farmers in developing countries. Agriculture 2018, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Li, C.; Duan, H.; Wang, Z.; Xue, Y.; Wu, Q. On-site test and numerical analysis on temperature field of an underground grain silo under static storage. J. Food Process Eng. 2023, 46, e14306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtarovna, N.R.; Kizi, R.D.T.; Kholdorovich, A.K.; Botiraliyevich, U.N. Breathing of grain during storage and factors affecting the intensity of respiration. Acad. Int. Multidiscip. Res. J. 2021, 11, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y. Research on the temperature field of grain piles in underground grain silos lined with plastic. J. Food Process Eng. 2022, 45, e13971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, W.; Guo, H.; Wu, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, W.; Lu, Y. Smart Grain Storage Solution: Integrated Deep Learning Framework for Grain Storage Monitoring and Risk Alert. Foods 2025, 14, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Nunes, M.T.; Maldaner, V.; Coradi, P.C.; de Moraes, R.S.; Martens, S.; Marin, C.K. Rice drying, storage and processing: Effects of post-harvest operations on grain quality. Rice Sci. 2022, 29, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priesterjahn, E.M.; Geisen, R.; Schmidt-Heydt, M. Influence of Light and Water Activity on Growth and Mycotoxin Formation of Aspergillus flavus and A. parasiticus. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Melo Nazareth, T.; Pérez, E.S.; Luz, C.; Meca, G.; Quiles, J.M. Comprehensive Review of Aflatoxin and Ochratoxin A Dynamics: Emergence, Toxicological Impact, and Advanced Control Strategies. Foods 2024, 13, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqil, M. The effect of temperature and humidity of storage on maize seed quality. IOP Conf. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 484, 012116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yao, Q.; Wu, Z. The Temperature and Relative Humidity Change in Wheat Bulk under the Condition of Temperature Differences. In Proceedings of the International Conference of Fluid Flow, Heat and Mass Transfer, Toronto, ON, Canada, 21–23 August 2017; p. 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi, E.S.; Omodara, M.A.; Owoyele, S.N.; Ade, A.R.; Babarinsa, F.A. Temperature fluctuation inside inert atmosphere silos. Niger. J. Technol. 2016, 35, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, F.; Jayas, D.S.; White, N.D. Temperature fluctuations and moisture migration in wheat stored for 15 months in a metal silo in Canada. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2009, 45, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Chen, G.; Liu, C.; Zheng, D.; Liu, W. Effect of Vertical Pressure on Temperature Field Distribution of Bulk Paddy Grain Pile. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kechkin, I.; Ermolaev, V.; Belyaeva, M.; Tarakanova, V.; Gurkovskaya, E.; Buzetti, K. Processes of Heat and Mass Transfer During Grain Mass Storage in Metal Silos of Large Capacity. KnE Life Sci. 2021, 6, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, F.; Jayas, D.S.; White, N.D. Specific heat, thermal diffusivity, and bulk density of genetically modified canola with high oil content at different moisture contents, temperatures, and storage times. Trans. ASABE 2013, 56, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LoVetri, J.; Asefi, M.; Gilmore, C.; Jeffrey, I. Innovations in electromagnetic imaging technology: The stored-grain-monitoring case. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2020, 62, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asefi, M.; Gilmore, C.; Jeffrey, I.; LoVetri, J.; Paliwal, J. Detection and continuous monitoring of localised high-moisture regions in a full-scale grain storage bin using electromagnetic imaging. Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 163, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoa-Muñoz, F. Simulation of the temperature of barley during its storage in cylindrical silos. Math. Comput. Simul. 2019, 157, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shammi, S.; Hossen, M.A.; Al Mamun, M.R.; Soeb, M.J.A. Temporal and spatial representation of temperature and moisture in drying chamber and its impact on vertical vacuum dehumidifying rice seed dryer performance. J. Agric. Food Res. 2022, 10, 100424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pӑun, A.; Stroescu, G.; Zaica, A.; Khozamy, S.Y.; Zaica, A.; Cristea, O.; Stefan, V.; Bălţatu, C. Storage of grains and technical plants through active ventilation for the purpose of maintaining the quality of stored products. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 286, 03010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coradi, P.C.; de Oliveira, M.B.; de Oliveira Carneiro, L.; de Souza, G.A.C.; Elias, M.C.; Brackmann, A.; Teodoro, P.E. Technological and sustainable strategies for reducing losses and maintaining the quality of soybean grains in real production scale storage units. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2020, 87, 101624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, W.S.V.; Vanier, N.L.; Ziegler, V.; de Oliveira, M.; Dias, A.R.G.; Elias, M.C. Effects of using eolic exhausters as a complement to conventional aeration on the quality of rice stored in metal silos. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2014, 59, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnselvakumar, L.; Maier, D.E. Aeration strategies for wheat bulk storage in North India. In Proceedings of the ASABE Annual International Meeting, Providence, RI, USA, 29 June–2 July 2008; p. 084505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, F.; Ben Mabrouk, S.; Mami, A. Modelling and simulation of heat exchange and moisture content in a cereal storage silo. Math. Comput. Model. Dyn. 2016, 22, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behaeen, M.A.; Mahmoudı, A.; Ranjbar, S.F. An Evaluation of the Performance of Forced Air Cooling on Cooling Parameters in Transient Heat Transfer at Different Layers of Pomegranate. J. Agric. Sci. Sri Lanka 2018, 24, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kechkin, I.; Ermolaev, V.; Ivanov, M.; Yakovchenko, M.; Gurkovskaya, E.; Glebova, I. Ventilation of grain in metal silos of large capacity in the South of Russia. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 659, 012135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Li, X.; Xu, R.; Zhang, X. An adaptive grain-bulk aeration system for squat silos in winter: Effects on intergranular air properties and grain quality. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 3, 100121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, A.M.; Devilla, I.A.; Neto, A.C.B.; Alves, B.G.X.; Alves, G.R.; Santos, M.M. Development of an automated system of aeration for grain storage. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2016, 11, 4293–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho Lopes, D.; Martins, J.H.; Lacerda Filho, A.F.; de Castro Melo, E.; de Barros Monteiro, P.M.; de Queiroz, D.M. Aeration strategy for controlling grain storage based on simulation and on real data acquisition. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2008, 63, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañizares, L.D.C.C.; da Silva Timm, N.; Lang, G.H.; Gaioso, C.A.; Ferreira, C.D.; De Oliveira, M. Effects of using wind exhausters on the quality and cost of soybean storage on a real scale. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2021, 93, 101834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petravicius, D.; Binelo, M.O.; Binelo, M.D.F.; Faoro, V.; Da Silva, J.A. Genetic algorithm in the design of soybean silos for airflow homogenization. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agric. Amb. 2023, 27, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.N.; Prakash, O. Thermal performance of earth–air heat exchanger using an experimental test rig. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 48, 11665–11678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachim, D.M.; Al-Manea, A.; Al-Rbaihat, R.; Abed, Q.A.; Sadiq, M.; Homod, R.Z.; Alahmer, A. Enhancing the performance of photovoltaic solar cells using a hybrid cooling technique of thermoelectric generator and heat sink. J. Sol. Energy Eng. 2025, 147, 021011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Liu, J.; Zhao, J.; Qi, X.; Tai, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, A. Study of the application of solar chimneys combined with earth-air heat exchangers ventilation system (SEVS) in a solar greenhouse. Energy 2025, 334, 137537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Duan, H.; Zhang, H.; Fang, Z. Modeling on heat and mass transfer in stored wheat during forced cooling ventilation. J. Therm. Sci. 2010, 19, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, K.; Meng, Q.; Liu, X. A ventilation experimental study of thermal performance of an urban underground pipe rack. Energy Build. 2021, 241, 110852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, É.; Coradi, P.C. Applications of new technologies for monitoring and predicting grains quality stored: Sensors, internet of things, and artificial intelligence. Measurement 2022, 188, 110609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabane, F.; Moummi, N.; Brima, A. Forecast of relationship between a relative humidity and a dew point temperature. J. Power Technol. 2018, 98, 183. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, F.W. On the computation of saturation vapor pressure. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1967, 6, 203–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastón, A.; Abalone, R.; Bartosik, R.E.; Rodríguez, J.C. Mathematical modelling of heat and moisture transfer of wheat stored in plastic bags (silo bags). Biosyst. Eng. 2009, 104, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Zhu, L.; Dong, S.; Xie, G.; Li, J. Effect of Thermophysical Properties on Coupled Heat and Mass Transfer in Porous Material during Forced Convective Drying. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2014, 6, 830387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
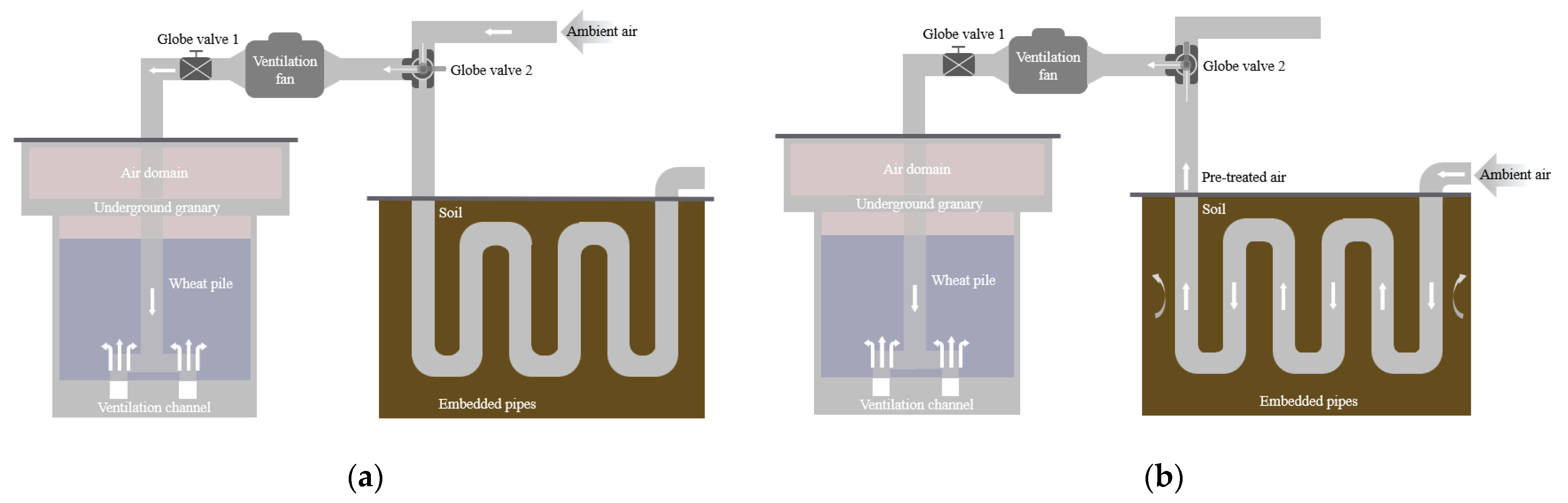

| Cases | Stages | Duration of Each Case | Total Days per Case | Airflow Rates | Ventilation Equipment Configuration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Static storage | 576 h | 24 d | 0 | None |
| 2 | Mechanical ventilation | 8 h | 3 d | 3.3 m3/min | Utilization of conventional ventilation equipment |
| 3 | Ventilation pretreatment | 8 h | 3 d | 3.3 m3/min | Utilization of conventional ventilation equipment with ambient air pre-cooled via the embedded pipe system |
| Time (d) | 0 | 1 | 13 | 24 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean differences (°C) | 0.68 | 0.37 | 0.034 | 0.31 |
| Standard deviation | 0.31 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.15 |
| Time (d) | 0 | 1 | 9 | 24 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean differences (%) | 0.70 | 0.86 | 1.53 | 2.34 |
| Standard deviation | 0.71 | 0.30 | 1.37 | 1.7 |
| Temperature Difference | Relative Humidity Difference | ΔT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean differences | 0.365 | 0.238 | 0.043 |
| Standard deviation | 1.117 | 2.060 | 0.504 |
| t-tests | 1.667 | 0.590 | 0.437 |
| p | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H. Experimental Comparison of Ventilation Strategies for Condensation Risk in Underground Wheat Granaries. Buildings 2025, 15, 3483. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15193483
Chen X, Li Y, Jiang S, Yang L, Liu Y, Gao Y, Zhang H. Experimental Comparison of Ventilation Strategies for Condensation Risk in Underground Wheat Granaries. Buildings. 2025; 15(19):3483. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15193483
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xi, Yaning Li, Shuai Jiang, Liu Yang, Yang Liu, Yahui Gao, and Hao Zhang. 2025. "Experimental Comparison of Ventilation Strategies for Condensation Risk in Underground Wheat Granaries" Buildings 15, no. 19: 3483. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15193483
APA StyleChen, X., Li, Y., Jiang, S., Yang, L., Liu, Y., Gao, Y., & Zhang, H. (2025). Experimental Comparison of Ventilation Strategies for Condensation Risk in Underground Wheat Granaries. Buildings, 15(19), 3483. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15193483







