How Restorative Design in Aquatic Center Enhances User Learning Engagement: The Critical Role of Attention Restoration: An Environmental Psychology Approach with Implications for Sports Buildings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Restorative Potential of Aquatic Centers
2.2. Attention Restoration Theory and Perceived Restorative Design
2.3. Flow Theory
2.4. Learning Engagement
3. Research Hypotheses
3.1. Being-Away, Extent, Fascination, and Compatibility and Learning Engagement in Aquatic Centers
3.2. Mediating Role of Psychological Flow
4. Research Design
4.1. Participants
4.2. Questionnaire Distribution
4.3. Variable Measurement
4.4. Research Procedures
5. Result
5.1. Common Method Bias Test
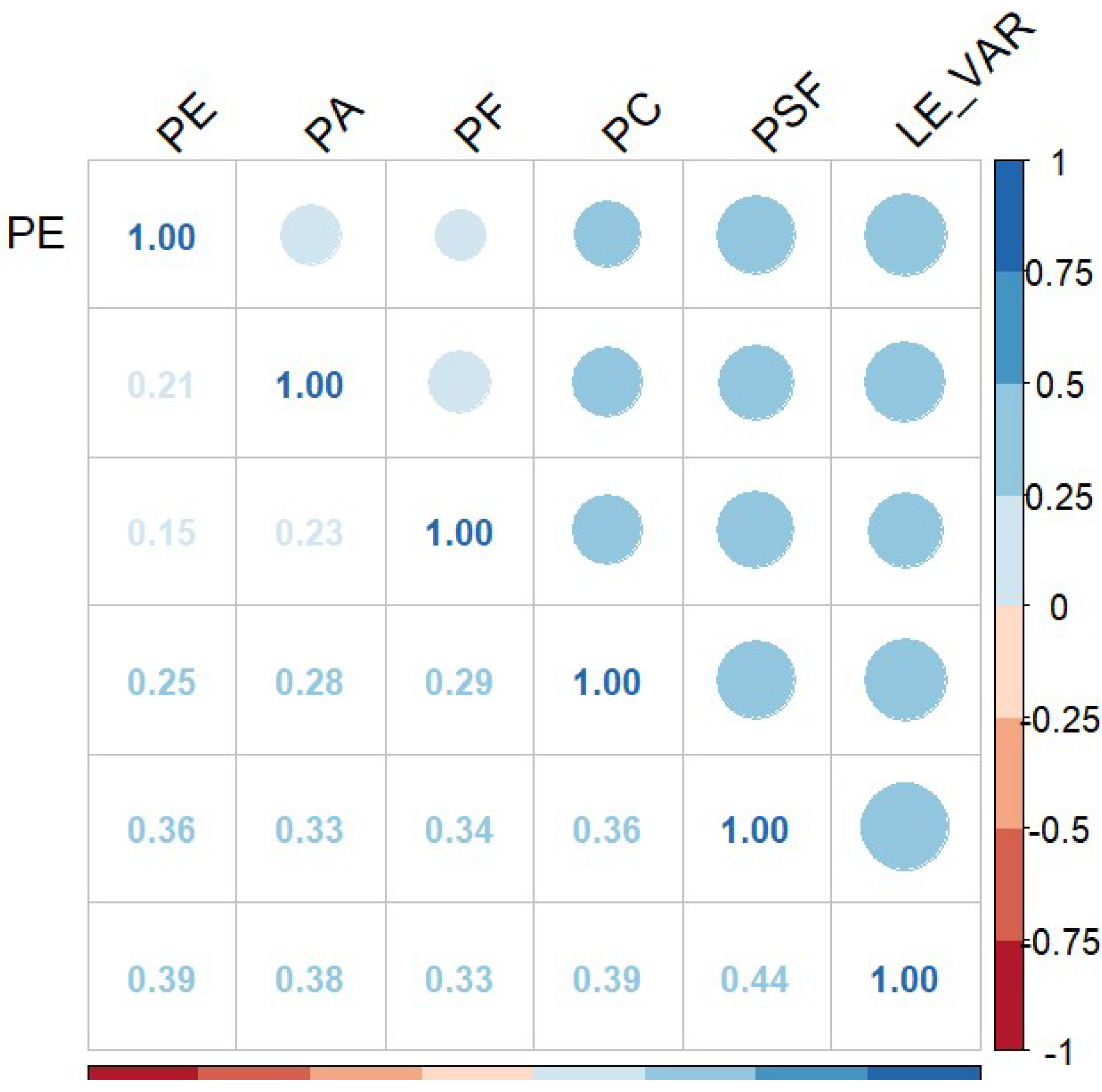
5.2. Correlation Analysis
5.3. Reliability Test
5.4. Validity Test
5.5. Validated Factor Analysis
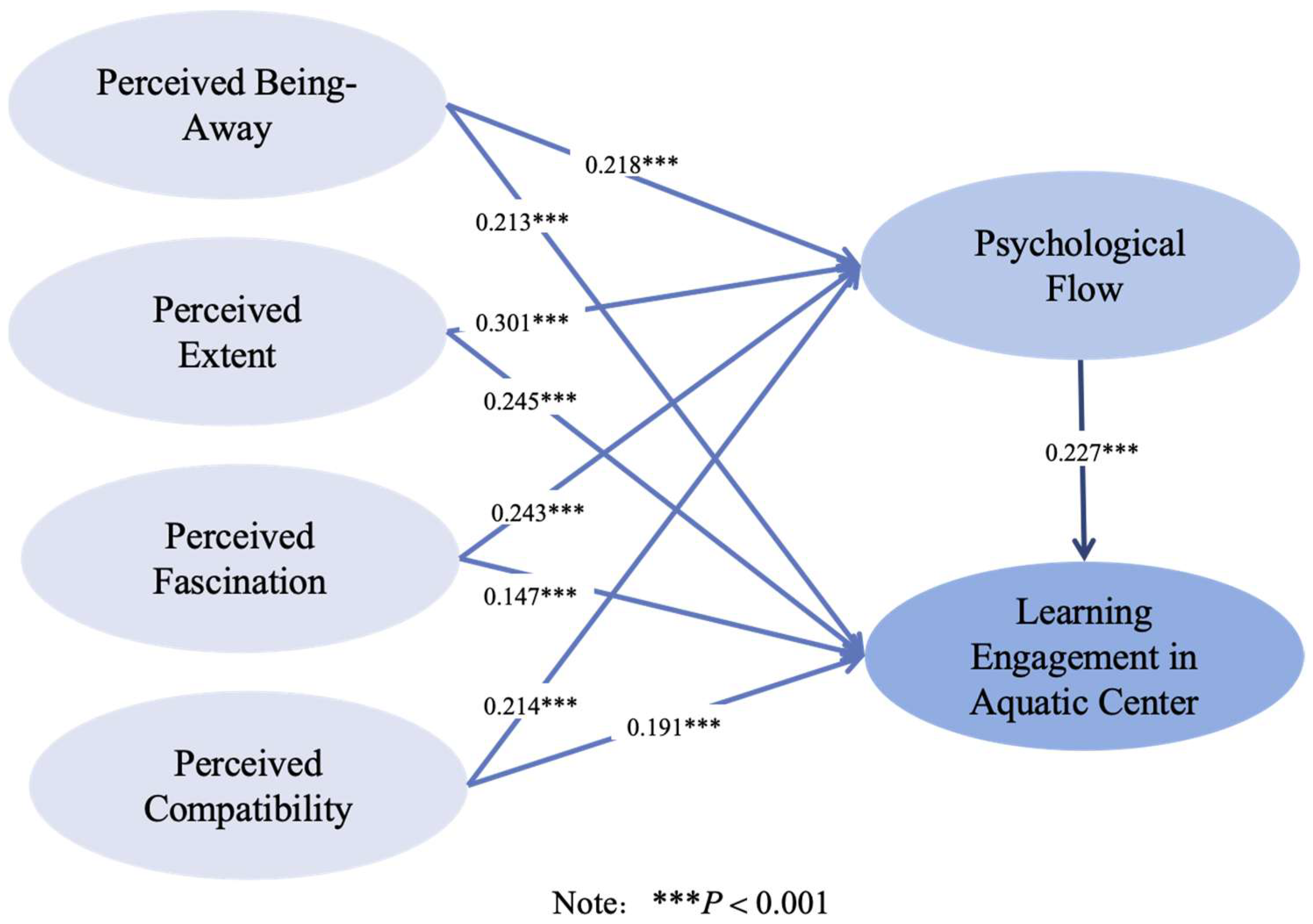
5.6. Structural Equation Modeling Analysis
5.7. Mediation Test
6. Discussion
6.1. Direct Effect
6.2. Mediation Effect
6.3. Research Comparison
6.4. Theoretical Contributions and Practical Implications
7. Conclusions
8. Limitations and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Chen, S.; Nah, K. Exploring the Mechanisms Influencing Users’ Willingness to Pay for Green Real Estate Projects in Asia Based on Technology Acceptance Modeling Theory. Buildings 2024, 14, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.; Mungall, G. Aquatics Centre, London 2012 Olympic and Paralympics Games. Bautechnik 2012, 89, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, O.; Berriman, M. Sydney International Aquatic Centre, Australia. Struct. Eng. Int. 1996, 6, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbu, M.C.R.; Tohăneanu, A.A.A.; Diaconescu, D.L.; Burcea, G.B.; Popescu, M.C.; Dragomir, M. The Creation of New Sports and Sports Venues. J. Sport Kinet. Mov. 2021, 1, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Van Bottenburg, M.; Salome, L. The indoorisation of outdoor sports: An exploration of the rise of lifestyle sports in artificial settings. Leis. Stud. 2010, 29, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Gromala, D. Touching light: A new framework for immersion in artistic environments. Technoetic Arts 2007, 5, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Li, C.P.; Lin, H.H.; Hung, S.T.; Tseng, C.H.; Hsu, C.H. Exploring the Flow Experience and Re-Experience Intention of Students Participating in Water Sports from the Perspective of Regional Tourism and Leisure Environment Suitability. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Du, L.; Pan, J. Mechanisms of Resident Satisfaction Enhancement Through Waterfront Sports Buildings: A Synergistic Perspective of Blue Space and Built Environment—Empirical Evidence from Nine Chinese Cases. Buildings 2025, 15, 2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, X.; Bao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wong, C.U.I. Adaptive Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning with Graph Neural Networks for Dynamic Optimization in Sports Buildings. Buildings 2025, 15, 2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łaskawiec, E.; Madej, M.; Dudziak, M.; Wyczarska-Kokot, J. The use of membrane techniques in swimming pool water treatment. J. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 18, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, G.; Tolis, E.I.; Panaras, G. Combined Investigation of Indoor Environmental Conditions and Energy Performance of an Aquatic Center. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanani, E.S. The study on value of recreational sports activity of urban communities. J. Kesehat. Masy. 2017, 12, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautenbach, F.; O’Connor, E.J.; Crozier, A.J.; Murphy, A.P.; Immink, M.A. Attention distraction and traction by task-irrelevant emotion information in Athletes: Evidence from the Sport Emotional Stroop Task-English. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2025, 80, 102913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetson, B.A.; Rahn, J.M.; Dubbert, P.M.; Wilner, B.I.; Mercury, M.G. Prospective evaluation of the effects of stress on exercise adherence in community-residing women. Health Psychol. 1997, 16, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodard, C.M.; Berry, M.J. Enhancing adherence to prescribed exercise: Structured behavioral interventions in clinical exercise programs. J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil. Prev. 2001, 21, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davydov, V.; Mankevych, A.; Iryna, L. Concentration and Distribution of Attention in Sports Swimming, Competitive and Rhythmic Gymnastics. Phys. Educ. Sport Health Cult. Mod. Soc. 2016, 1, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, S. What has influenced the growth and structural transformation of China’s cultural industry?—Based on the input-output bias analysis. Appl. Econ. 2025, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. The social benefits of water sports events and their impact on environmental pollution. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 104 (Suppl. S1), 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clashing, C.; Smith, I.; Montoya, M.F.; Patibanda, R.; Ananthanarayan, S.; Pell, S.J.; Mueller, F.F. Going into Depth: Learning from a Survey of Interactive Designs for Aquatic Recreation. In Proceedings of the 2022 ACM Designing Interactive Systems Conference, Online, 13–17 June 2022; pp. 1119–1132. [Google Scholar]
- Alasinrin, S.; Abubakar, I.L.; Adeleye, T.O. The Critical Role of Sports Facilities and Equipment in Optimizing Athletic Performance: A Sports Psychologist’s Perspective. KWASU Int. J. Educ. (KIJE) 2024, 7, 305–313. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, M.C. The Aquatic Center for XXVIII Olympiad. Ph.D. Dissertation, Texas Tech University, Lubbock, TX, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Panaras, G.; Markogiannaki, M.; Tolis, E.I.; Sakellaris, Y.; Bartzis, J.G. Experimental and theoretical investigation of air exchange rate of an indoor aquatic center. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 39, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, S. Aesthetics, affect, and cognition: Environmental preference from an evolutionary perspective. Environ. Behav. 1987, 19, 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, R.; Kaplan, S. The Experience of Nature: A Psychological Perspective; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, S.; Berman, M.G. Directed attention as a common resource for executive functioning and self-regulation. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2010, 5, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, S. The restorative benefits of nature: Toward an integrative framework. J. Environ. Psychol. 1995, 15, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohly, H.; White, M.P.; Wheeler, B.W.; Bethel, A.; Ukoumunne, O.C.; Nikolaou, V.; Garside, R. Attention Restoration Theory: A systematic review of the attention restoration potential of exposure to natural environments. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2016, 19, 305–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, D. Back to nature? Attention restoration theory and the restorative effects of nature contact in prison. Health Place 2019, 57, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, M.G.; Jonides, J.; Kaplan, S. The cognitive benefits of interacting with nature. Psychol. Sci. 2008, 19, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, M.P.; Schilhab, T.; Bentsen, P. Attention Restoration Theory II: A systematic review to clarify attention processes affected by exposure to natural environments. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2018, 21, 227–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzog, T.R.; Maguire, P.; Nebel, M.B. Assessing the restorative components of environments. J. Environ. Psychol. 2003, 23, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, D.; Barbieri, B.; Barattucci, M.; Mascia, M.L.; Ramaci, T. The role of a restorative resource in the academic context in improving intrinsic and extrinsic motivation and flow within the job demands–resources model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wang, Z.; Meng, X.; Liu, M. A qualitative study on university students’ restorative experience of the Library Space Environment. Buildings 2024, 14, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norling, J.C.; Sibthorp, J.; Ruddell, E. Perceived restorativeness for activities scale (PRAS): Development and validation. J. Phys. Act. Health 2008, 5, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Chen, S.; Yao, Z.; Huang, Q.; Shen, X.; Cao, L.; Cheng, J.; Gui, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Green Building Consumption Perception and Its Impact on Fitness Service Purchasing Intentions: An Extended Institutional Analysis and Development Decision-Making Model Analysis. Buildings 2023, 13, 2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejati, A.; Shepley, M.; Rodiek, S.; Lee, C.; Varni, J. Restorative design features for hospital staff break areas: A multi-method study. HERD Health Environ. Res. Des. J. 2016, 9, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.; Gutowska, E. The role of restorative design in the achieving principles of Industry 5.0. Eur. Res. Stud. J. 2022, 25, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, Y.H.; Liu, K.Y.; Liu, T.H. A study of constructing the green indoors sustainable aquatic center. In Innovation, Communication and Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; p. 479. [Google Scholar]
- Csikszentmihalyi, M.; Abuhamdeh, S.; Nakamura, J. Flow. In Flow and the Foundations of Positive Psychology: The Collected Works of Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 227–238. [Google Scholar]
- Csikszentmihalyi, M.; Csikzentmihaly, M. Flow: The Psychology of Optimal Experience; Harper & Row: New York, NY, USA, 1990; Volume 1990, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, J.; Csikszentmihalyi, M. Flow theory and research. In Oxford Handbook of Positive Psychology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Beard, K.S. Theoretically speaking: An interview with Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi on flow theory development and its usefulness in addressing contemporary challenges in education. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2015, 27, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.F. A flow theory perspective on learner motivation and behavior in distance education. Distance Educ. 2006, 27, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Che Tak, K.B.; Bailey, R.P.; Samsudin, N.; Ren, C. The effects of blended learning on learning engagement in physical education among university students in China: The mediating role of attitudes. Sustainability 2025, 17, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredricks, J.A.; Blumenfeld, P.C.; Paris, A.H. School engagement: Potential of the concept, state of the evidence. Rev. Educ. Res. 2004, 74, 59–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaufeli, W.B.; Bakker, A.B.; Salanova, M. The measurement of work engagement with a short questionnaire: A cross-national study. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2006, 66, 701–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammitt, W.E. The relation between being away and privacy in urban forest recreation environments. Environ. Behav. 2000, 32, 521–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laumann, K.; Gärling, T.; Stormark, K.M. Rating scale measures of restorative components of environments. J. Environ. Psychol. 2001, 21, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusli, N.A.N.M.; Roslan, S.; Zaremohzzabieh, Z.; Ghiami, Z.; Ahmad, N. Role of restorativeness in improving the psychological well-being of university students. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 646329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.K. Inflnuence of the Restorative Quality of Landscape on the Visiting Preference and Satisfaction for Tourist Destination-An Evaluation of Heritage Landscape of Kyongju by Americans. J. Korean Inst. Landsc. Archit. 2006, 34, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette, P.; Kaplan, R.; Kaplan, S. The monastery as a restorative environment. J. Environ. Psychol. 2005, 25, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, T.; Qiao, H.; Gao, Y.; Tao, Y.; Liu, J. Tourist rural destination restorative capacity: Scale development and validation. J. Travel Res. 2025, 64, 444–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.; He, L.; Li, J.; Hu, X. Optimizing light environments in aquatics center to enhance the performance of olympic champions and other elite swimmers: An experimental study. Build. Environ. 2025, 267, 112263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuper, R. Restorative potential, fascination, and extent for designed digital landscape models. Urban For. Urban Green. 2017, 28, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.; Smith, A.; Humphryes, K.; Pahl, S.; Snelling, D.; Depledge, M. Blue space: The importance of water for preference, affect, and restorativeness ratings of natural and built scenes. J. Environ. Psychol. 2010, 30, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, P. Affective priming of perceived environmental restorativeness. Int. J. Psychol. 2014, 49, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.C.; Irvine, K.N.; Bicknell, J.E.; Hayes, W.M.; Fernandes, D.; Mistry, J.; Davies, Z.G. Perceived biodiversity, sound, naturalness and safety enhance the restorative quality and wellbeing benefits of green and blue space in a neotropical city. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 143095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giusti, M.; Samuelsson, K. The regenerative compatibility: A synergy between healthy ecosystems, environmental attitudes, and restorative experiences. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagba, J.L. Perceived Coaches’ Attributes and Level of Fitness Skills Performance Among Student-Athletes. ACPES J. Phys. Educ. Sport Health (AJPESH) 2022, 2, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usra, M. Swimming learning model using rope as aid for beginners. In Proceedings of the First Indonesian Communication Forum of Teacher Training and Education Faculty Leaders International Conference on Education 2017 (ICE 2017), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 28–30 August 2017; Atlantis Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 388–393. [Google Scholar]
- Voloshynov, S.A.; Popova, H.V.; Dyagileva, O.S.; Bobrysheva, N.N.; Fedorova, O.V. Formation of professional competency in life saving appliances operation of future seafarers by means of online and simulation VR technologies. In Proceedings of the CTE Workshop Proceedings, Kyiv, Ukraine, 21–22 December 2022; Volume 9, pp. 365–380. [Google Scholar]
- Abkar, M.; Kamal, M.; Maulan, S.; Mariapan, M.; Davoodi, S.R. Relationship between the preference and perceived restorative potential of urban landscapes. HortTechnology 2011, 21, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Mao, Y.; Yang, R. Flow experience and city identity in the restorative environment: A conceptual model and nature-based intervention. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1011890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihara, H. Environmental Control and Information Design. Hist. Theory 2020, 3, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Du, X.; Wu, J. Revision of the Chinese version of the Perceived Restorativeness Scale (PRS-11). Chin. J. Health Psychol. 2024, 12, 1883–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasini, M.; Berto, R.; Brondino, M.; Hall, R.; Ortner, C. How to measure the restorative quality of environments: The PRS-11. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 159, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norsworthy, C.; Dimmock, J.A.; Miller, D.J.; Krause, A.; Jackson, B. Psychological flow scale (PFS): Development and preliminary validation of a new flow instrument that measures the core experience of flow to reflect recent conceptual advancements. Int. J. Appl. Posit. Psychol. 2023, 8, 309–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaufeli, W.B.; Salanova, M.; González-Romá, V.; Bakker, A.B. The measurement of engagement and burnout: A two sample confirmatory factor analytic approach. J. Happiness Stud. 2002, 3, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, Z.; Shen, X.; Cao, L.; Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Gui, F.; Cheng, J.; et al. The Multilevel Chain Mediating Mechanism of College Faculty’s Felt Responsibility on Students’ Engagement in Green Building Learning. Buildings 2024, 14, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén, F.; Martínez-Alvarado, J.R. The sport engagement scale: An adaptation of the Utrecht Work Engagement Scale (UWES) for the sports environment. Univ. Psychol. 2014, 13, 975–984. [Google Scholar]
- Spector, P.E. Summated Rating Scale Construction: An Introduction; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1992; Volume 82. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.W.; Jones, P.S.; Mineyama, Y.; Zhang, X.E. Cultural differences in responses to a Likert scale. Res. Nurs. Health 2002, 25, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasanen, T.; Johnson, K.; Lee, K.; Korpela, K. Can nature walks with psychological tasks improve mood, self-reported restoration, and sustained attention? Results from two experimental field studies. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaggard, C.E. The Effect of Intentionally Engaging Attention When Viewing Restorative Environments: Exploring Attention Restoration Theory. Master’s Thesis, Indiana State University, Terre Haute, IN, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Farrokh, D.; Davids, K.; Araújo, D.; Strafford, B.W.; Rumbold, J.L.; Stone, J.A. Towards an ecological dynamics theory of flow in sport. Acta Psychol. 2025, 253, 104765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Wan, Q.; Chang, T.; Huang, R. A framework of learning activity design for flow experience in smart learning environment. In Foundations and Trends in Smart Learning, Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Smart Learning Environments, Denton, TX, USA, 18–20 March 2019; Springer: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar]

| Variables | Option | Frequency | Proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 445 | 51.45 |
| Female | 420 | 48.55 | |
| Age | 18–35 | 535 | 61.85 |
| 36–55 | 246 | 28.44 | |
| 56 and above | 84 | 9.71 | |
| Household registration | City | 330 | 38.15 |
| Suburbs | 232 | 26.82 | |
| Rural | 303 | 35.03 | |
| Educational background | Bachelor’s degree or above | 525 | 60.69 |
| Below Bachelor’s Degree | 340 | 39.31 | |
| Participants in this region | Eastern Coastal | 210 | 24.27 |
| Southern Coastal | 257 | 29.71 | |
| Central | 209 | 24.16 | |
| Western | 189 | 21.84 | |
| Number of times per month | 1–2 times | 244 | 28.21 |
| 3–4 times | 356 | 41.16 | |
| 5 times and above | 265 | 30.64 |
| Total Variance Explained | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component | Initial Eigenvalues | Extraction Sums of Squared Loadings | Rotation Sums of Squared Loadings | ||||||
| Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | |
| 1 | 8.806 | 29.352 | 29.352 | 8.806 | 29.352 | 29.352 | 2.417 | 8.058 | 8.058 |
| 2 | 2.663 | 8.876 | 38.228 | 2.663 | 8.876 | 38.228 | 2.397 | 7.991 | 16.048 |
| 3 | 1.862 | 6.206 | 44.434 | 1.862 | 6.206 | 44.434 | 2.396 | 7.986 | 24.034 |
| 4 | 1.632 | 5.440 | 49.874 | 1.632 | 5.440 | 49.874 | 2.385 | 7.951 | 31.985 |
| 5 | 1.589 | 5.297 | 55.171 | 1.589 | 5.297 | 55.171 | 2.377 | 7.925 | 39.910 |
| 6 | 1.426 | 4.755 | 59.926 | 1.426 | 4.755 | 59.926 | 2.288 | 7.627 | 47.537 |
| 7 | 1.360 | 4.532 | 64.458 | 1.360 | 4.532 | 64.458 | 2.191 | 7.302 | 54.839 |
| 8 | 1.269 | 4.229 | 68.687 | 1.269 | 4.229 | 68.687 | 2.161 | 7.203 | 62.043 |
| 9 | 1.205 | 4.016 | 72.702 | 1.205 | 4.016 | 72.702 | 2.160 | 7.199 | 69.242 |
| 10 | 1.048 | 3.493 | 76.196 | 1.048 | 3.493 | 76.196 | 2.086 | 6.954 | 76.196 |
| Variable | Mean | Standard Deviation | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA | 3.686 | 0.757 | 1 | |||||
| PE | 3.310 | 0.805 | 0.212 *** | 1 | ||||
| PF | 3.607 | 0.782 | 0.226 *** | 0.154 *** | 1 | |||
| PC | 3.523 | 0.812 | 0.278 *** | 0.254 *** | 0.287 *** | 1 | ||
| PSF | 3.581 | 0.687 | 0.335 *** | 0.361 *** | 0.342 *** | 0.364 *** | 1 | |
| LE | 3.475 | 0.713 | 0.376 *** | 0.390 *** | 0.325 *** | 0.394 *** | 0.440 *** | 1 |
| Item | PA | PE | PF | PC | PSF_A | PSF_B | PSF_C | LE_A | LE_B | LE_C | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reliability Value | 0.758 | 0.791 | 0.784 | 0.788 | 0.882 | 0.848 | 0.876 | 0.875 | 0.878 | 0.883 | 0.915 |
| Test | Value |
|---|---|
| KMO value | 0.887 |
| Approximate chi-square | 13,478.607 |
| Degrees of Freedom | 435 |
| Significance | 0.000 |
| Rotated Component Matrix a | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component | ||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | |
| PA1 | 0.055 | 0.134 | 0.059 | 0.037 | 0.081 | 0.130 | 0.084 | 0.065 | 0.095 | 0.785 |
| PA2 | 0.065 | 0.086 | 0.090 | 0.022 | 0.140 | 0.021 | 0.045 | 0.072 | 0.058 | 0.804 |
| PA3 | 0.109 | 0.076 | 0.062 | 0.145 | 0.053 | 0.078 | 0.047 | 0.121 | 0.051 | 0.771 |
| PE1 | 0.086 | 0.076 | 0.078 | 0.095 | 0.119 | 0.115 | 0.807 | 0.055 | 0.089 | 0.056 |
| PE2 | 0.083 | 0.118 | 0.070 | 0.081 | 0.073 | 0.074 | 0.800 | 0.104 | −0.010 | 0.064 |
| PE3 | 0.077 | 0.120 | 0.078 | 0.112 | 0.048 | 0.107 | 0.807 | 0.070 | 0.026 | 0.057 |
| PF1 | 0.057 | 0.019 | 0.111 | 0.056 | 0.050 | 0.101 | 0.018 | 0.094 | 0.795 | 0.045 |
| PF2 | 0.077 | 0.068 | 0.061 | 0.086 | 0.113 | 0.045 | 0.065 | 0.075 | 0.821 | 0.081 |
| PF3 | 0.126 | 0.115 | 0.078 | 0.093 | 0.057 | 0.057 | 0.016 | 0.112 | 0.798 | 0.077 |
| PC1 | 0.106 | 0.158 | 0.075 | 0.071 | 0.087 | 0.064 | 0.091 | 0.779 | 0.142 | 0.119 |
| PC2 | 0.062 | 0.080 | 0.098 | 0.111 | 0.111 | 0.093 | 0.053 | 0.787 | 0.070 | 0.068 |
| PC3 | 0.084 | 0.053 | 0.055 | 0.101 | 0.060 | 0.109 | 0.093 | 0.822 | 0.087 | 0.083 |
| PSF1 | 0.169 | 0.081 | 0.840 | 0.041 | 0.113 | 0.188 | 0.096 | 0.104 | 0.075 | 0.058 |
| PSF2 | 0.202 | 0.064 | 0.815 | 0.048 | 0.102 | 0.179 | 0.089 | 0.107 | 0.129 | 0.112 |
| PSF3 | 0.146 | 0.115 | 0.829 | 0.110 | 0.106 | 0.208 | 0.080 | 0.051 | 0.102 | 0.085 |
| PSF4 | 0.147 | 0.108 | 0.198 | 0.066 | 0.124 | 0.793 | 0.113 | 0.126 | 0.069 | 0.093 |
| PSF5 | 0.167 | 0.036 | 0.197 | 0.096 | 0.068 | 0.793 | 0.111 | 0.094 | 0.096 | 0.127 |
| PSF6 | 0.194 | 0.083 | 0.173 | 0.093 | 0.039 | 0.823 | 0.121 | 0.085 | 0.077 | 0.048 |
| PSF7 | 0.826 | 0.086 | 0.173 | 0.087 | 0.098 | 0.186 | 0.090 | 0.111 | 0.129 | 0.096 |
| PSF8 | 0.849 | 0.061 | 0.155 | 0.053 | 0.058 | 0.178 | 0.087 | 0.095 | 0.088 | 0.056 |
| PSF9 | 0.832 | 0.062 | 0.169 | 0.084 | 0.084 | 0.135 | 0.104 | 0.074 | 0.086 | 0.114 |
| LE1 | 0.065 | 0.183 | 0.074 | 0.794 | 0.242 | 0.092 | 0.108 | 0.102 | 0.137 | 0.095 |
| LE2 | 0.096 | 0.166 | 0.069 | 0.836 | 0.203 | 0.085 | 0.081 | 0.117 | 0.081 | 0.063 |
| LE3 | 0.069 | 0.175 | 0.056 | 0.822 | 0.162 | 0.085 | 0.155 | 0.110 | 0.071 | 0.080 |
| LE4 | 0.074 | 0.207 | 0.099 | 0.158 | 0.811 | 0.080 | 0.130 | 0.119 | 0.094 | 0.097 |
| LE5 | 0.098 | 0.173 | 0.111 | 0.217 | 0.826 | 0.052 | 0.069 | 0.114 | 0.114 | 0.124 |
| LE6 | 0.081 | 0.155 | 0.124 | 0.250 | 0.800 | 0.108 | 0.091 | 0.071 | 0.064 | 0.120 |
| LE7 | 0.048 | 0.844 | 0.078 | 0.172 | 0.121 | 0.111 | 0.128 | 0.095 | 0.084 | 0.101 |
| LE8 | 0.093 | 0.809 | 0.101 | 0.177 | 0.234 | 0.069 | 0.096 | 0.137 | 0.085 | 0.130 |
| LE9 | 0.080 | 0.816 | 0.087 | 0.180 | 0.183 | 0.051 | 0.156 | 0.102 | 0.071 | 0.132 |
| Dimension | PA | PE | PF | PC | PSF_A | PSF_B | PSF_C | LE_A | LE_B | LE_C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA | 0.716 | |||||||||
| PE | 0.273 | 0.751 | ||||||||
| PF | 0.294 | 0.197 | 0.741 | |||||||
| PC | 0.361 | 0.322 | 0.367 | 0.745 | ||||||
| PSF_A | 0.323 | 0.325 | 0.338 | 0.335 | 0.845 | |||||
| PSF_B | 0.342 | 0.394 | 0.308 | 0.374 | 0.578 | 0.807 | ||||
| PSF_C | 0.327 | 0.332 | 0.343 | 0.351 | 0.514 | 0.531 | 0.845 | |||
| LE_A | 0.321 | 0.381 | 0.334 | 0.387 | 0.300 | 0.344 | 0.311 | 0.838 | ||
| LE_B | 0.393 | 0.348 | 0.332 | 0.374 | 0.386 | 0.336 | 0.330 | 0.605 | 0.842 | |
| LE_C | 0.406 | 0.404 | 0.308 | 0.396 | 0.341 | 0.329 | 0.305 | 0.544 | 0.558 | 0.847 |
| Item | PA | PE | PF | PF | PSF_A | PSF_B | PSF_C | LE_A | LE_B | LE_C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CR | 0.759 | 0.794 | 0.785 | 0.789 | 0.882 | 0.849 | 0.881 | 0.876 | 0.879 | 0.884 |
| AVE | 0.512 | 0.564 | 0.549 | 0.555 | 0.714 | 0.652 | 0.715 | 0.703 | 0.709 | 0.718 |
| Fit Index | Range of Fit | Results | Rating Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| GFI | >0.9 | 0.947 | Accept |
| AGFI | >0.9 | 0.931 | Accept |
| RMR | <0.05 | 0.021 | Accept |
| RMSEA | <0.05 | 0.031 | Accept |
| NFI | >0.9 | 0.952 | Accept |
| IFI | >0.9 | 0.977 | Accept |
| CFI | >0.9 | 0.977 | Accept |
| TLI | >0.9 | 0.972 | Accept |
| Path | Estimate | S.E. | C.R. | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSF←PA | 0.218 | 0.042 | 4.726 | *** |
| PSF←PE | 0.301 | 0.038 | 6.78 | *** |
| PSF←PF | 0.243 | 0.036 | 5.426 | *** |
| PSF←PC | 0.214 | 0.036 | 4.54 | *** |
| LE←PSF | 0.227 | 0.058 | 3.849 | *** |
| LE←PA | 0.214 | 0.041 | 4.69 | *** |
| LE←PE | 0.245 | 0.038 | 5.423 | *** |
| LE←PF | 0.147 | 0.035 | 3.359 | *** |
| LE←PC | 0.191 | 0.035 | 4.156 | *** |
| Path | Mediation Effect | Bootstrap 95% CI | SE | Direct Effect | Total Effect | Mediation Proportion | Significant? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA→PSF→LE | 0.049 | [0.023, 0.076] | 0.012 | 0.214 | 0.263 | 0.188 | Fit |
| PE→PSF→LE | 0.068 | [0.039, 0.098] | 0.014 | 0.245 | 0.313 | 0.218 | Fit |
| PF→PSF→LE | 0.055 | [0.030, 0.080] | 0.012 | 0.147 | 0.202 | 0.273 | Fit |
| PC→PSF→LE | 0.049 | [0.022, 0.075] | 0.012 | 0.191 | 0.240 | 0.203 | Fit |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Wong, C.U.I.; Qiu, J. How Restorative Design in Aquatic Center Enhances User Learning Engagement: The Critical Role of Attention Restoration: An Environmental Psychology Approach with Implications for Sports Buildings. Buildings 2025, 15, 3439. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15193439
Liu W, Chen X, Zhang H, Wong CUI, Qiu J. How Restorative Design in Aquatic Center Enhances User Learning Engagement: The Critical Role of Attention Restoration: An Environmental Psychology Approach with Implications for Sports Buildings. Buildings. 2025; 15(19):3439. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15193439
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wenyue, Xiaolong Chen, Hongfeng Zhang, Cora Un In Wong, and Jianguo Qiu. 2025. "How Restorative Design in Aquatic Center Enhances User Learning Engagement: The Critical Role of Attention Restoration: An Environmental Psychology Approach with Implications for Sports Buildings" Buildings 15, no. 19: 3439. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15193439
APA StyleLiu, W., Chen, X., Zhang, H., Wong, C. U. I., & Qiu, J. (2025). How Restorative Design in Aquatic Center Enhances User Learning Engagement: The Critical Role of Attention Restoration: An Environmental Psychology Approach with Implications for Sports Buildings. Buildings, 15(19), 3439. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15193439






