Study of Factors Influencing the Longitudinal Mechanical Performance of Shield Tunnels Traversing Soft–Hard Heterogeneous Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Engineering Background
3. Numerical Simulation
3.1. Establishment of Numerical Analysis Model
3.2. Material Properties
3.3. Interaction and Boundary Conditions
3.4. Loading Method and Conditions
4. Result Analysis
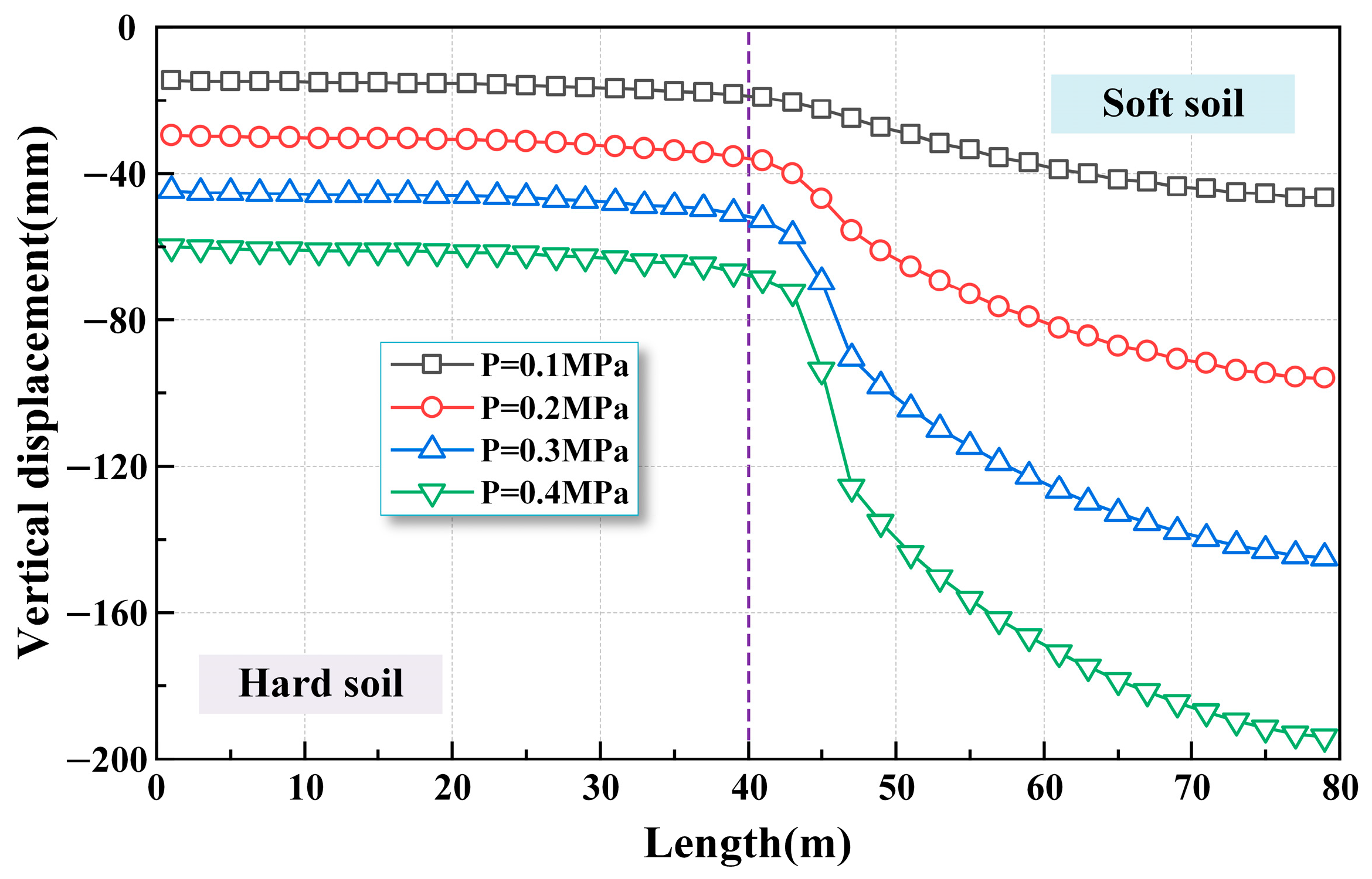
4.1. Vertical Displacement of Shield Tunnel
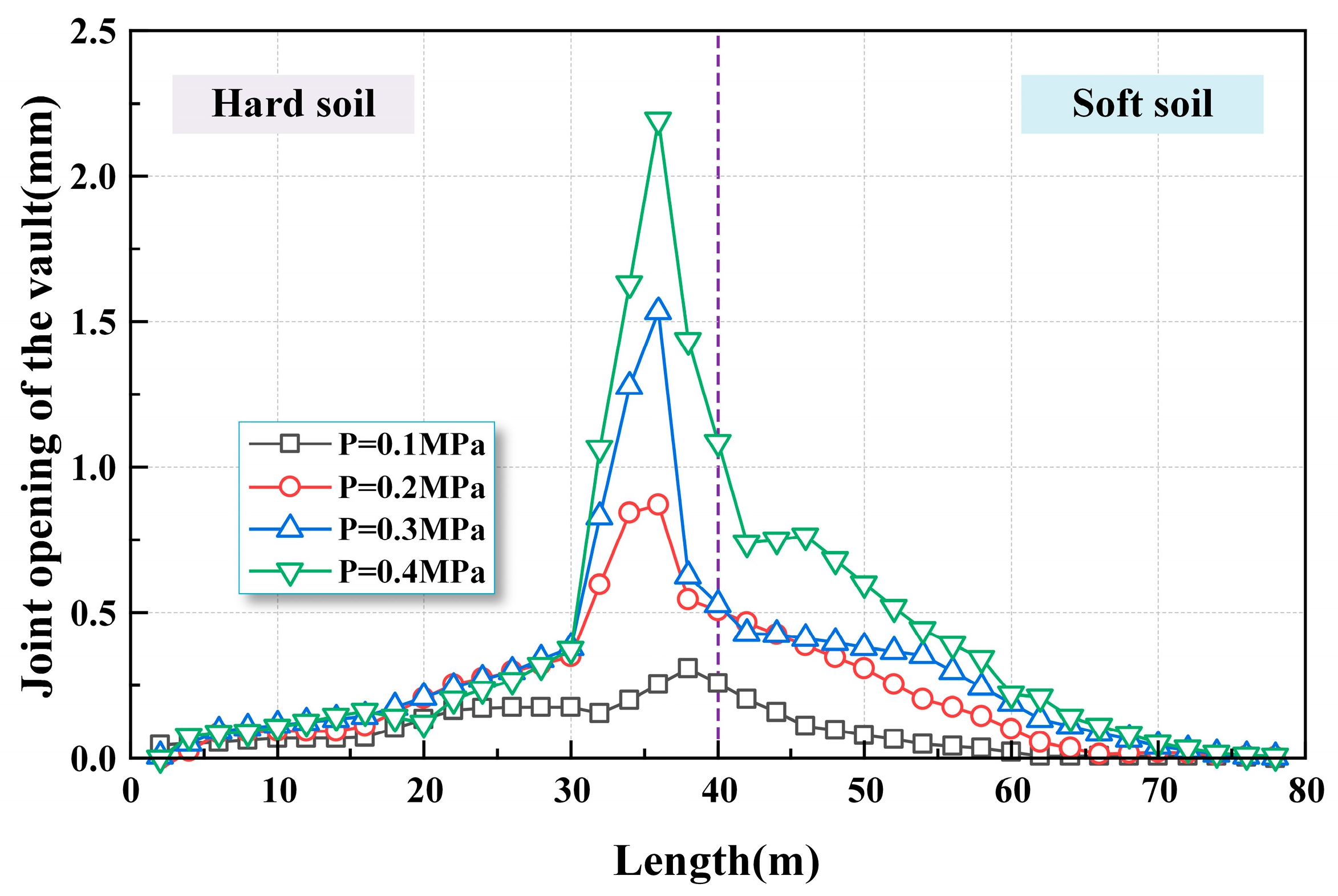
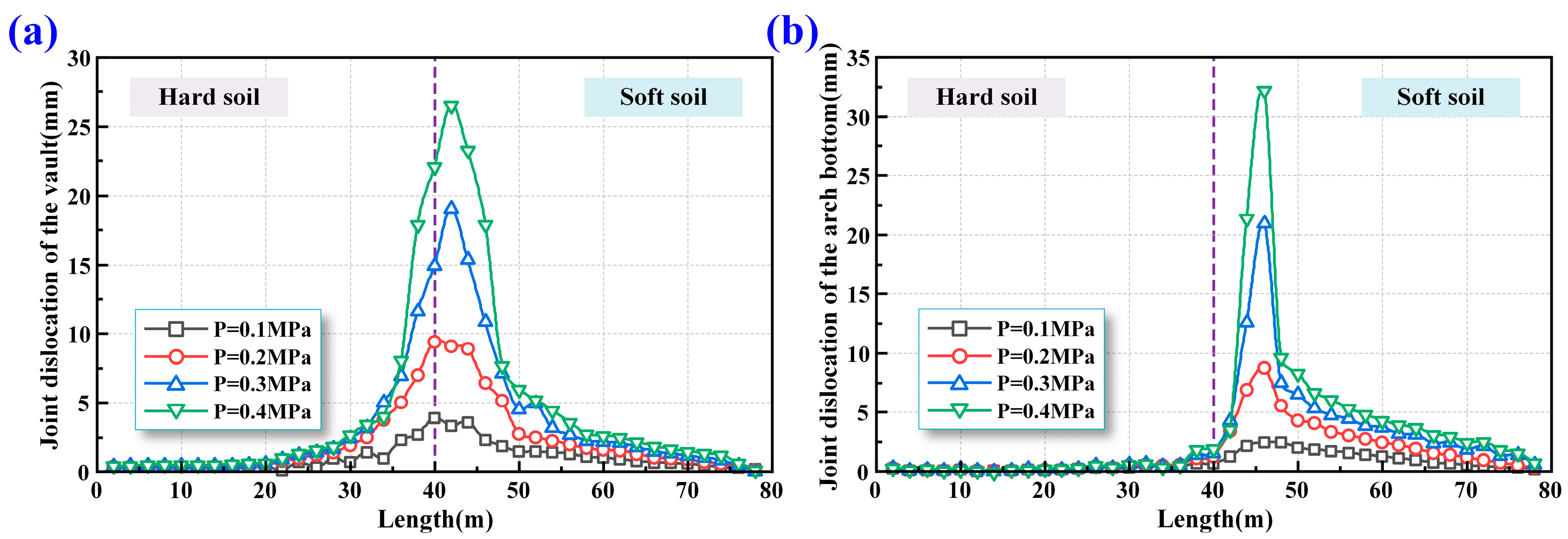
4.2. Deformation of Circumferential Joints
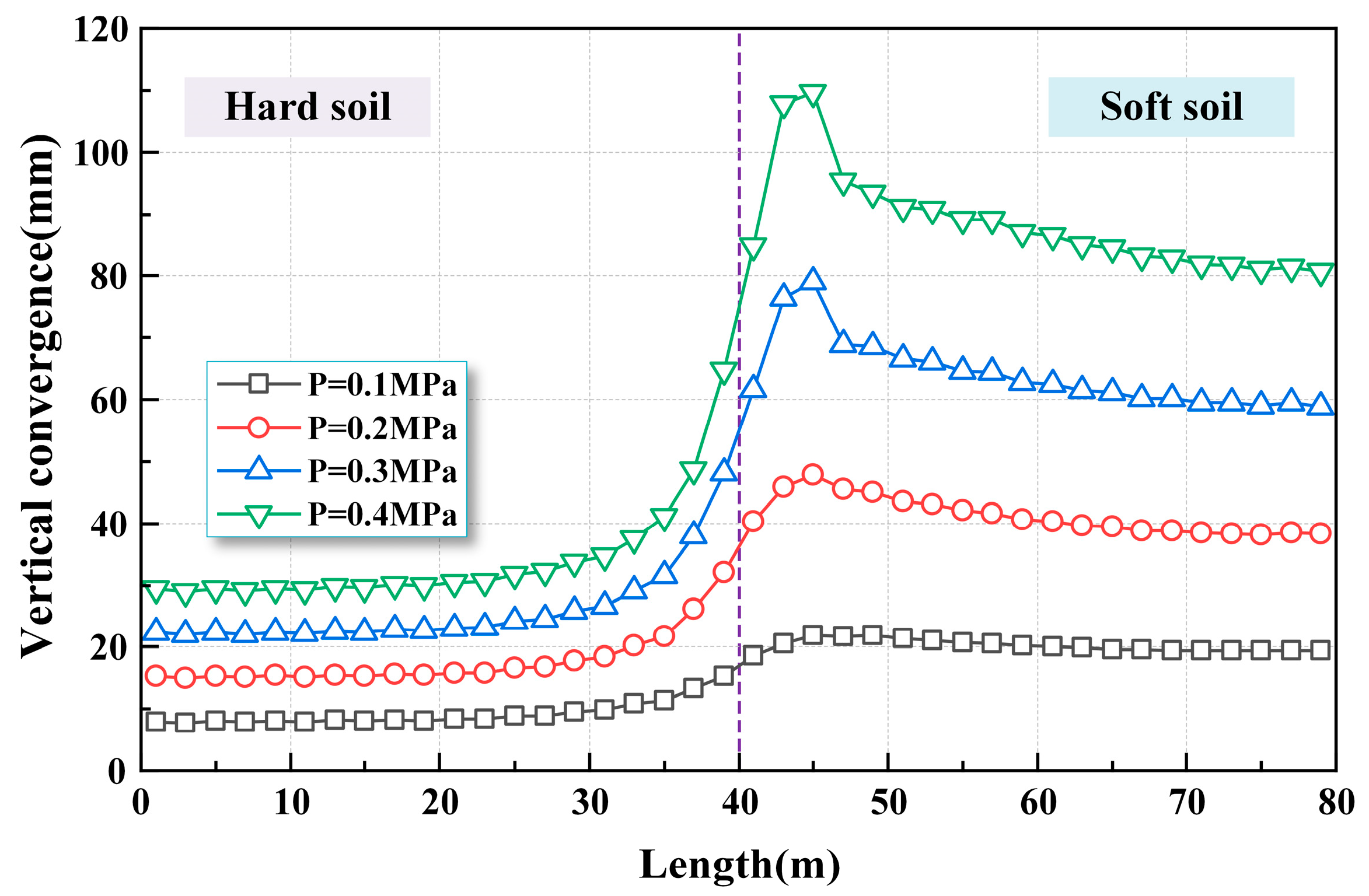
4.3. Vertical Convergence of Shield Tunnel
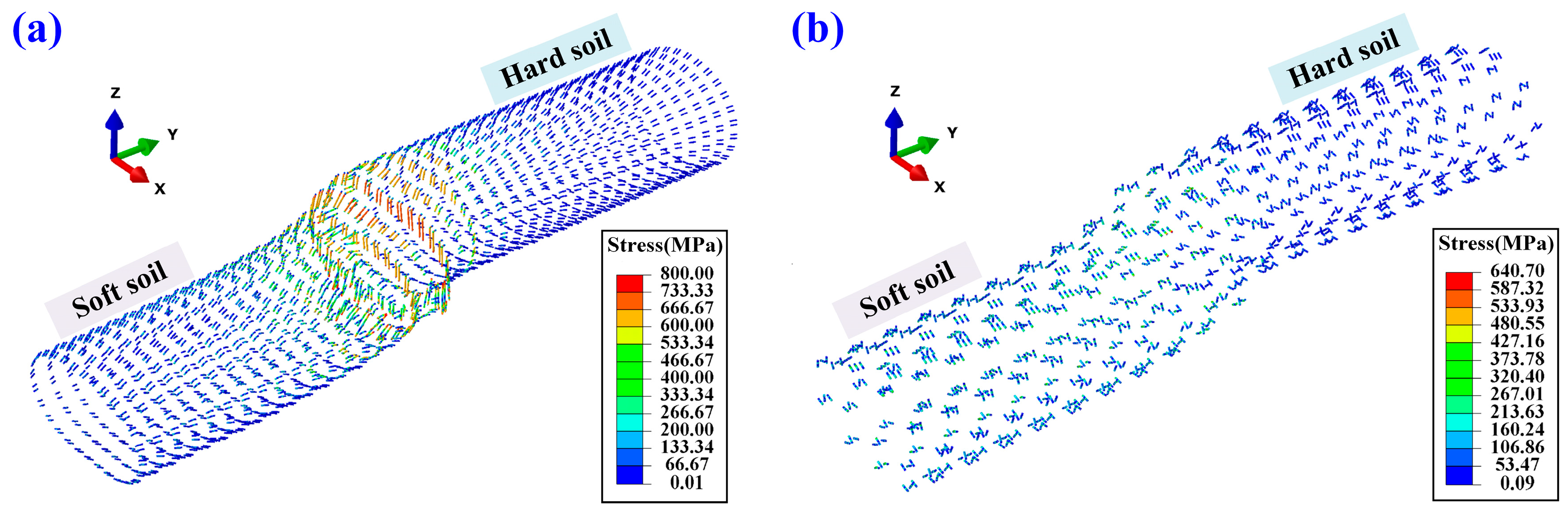
4.4. Reinforcement and Bolt Stresses
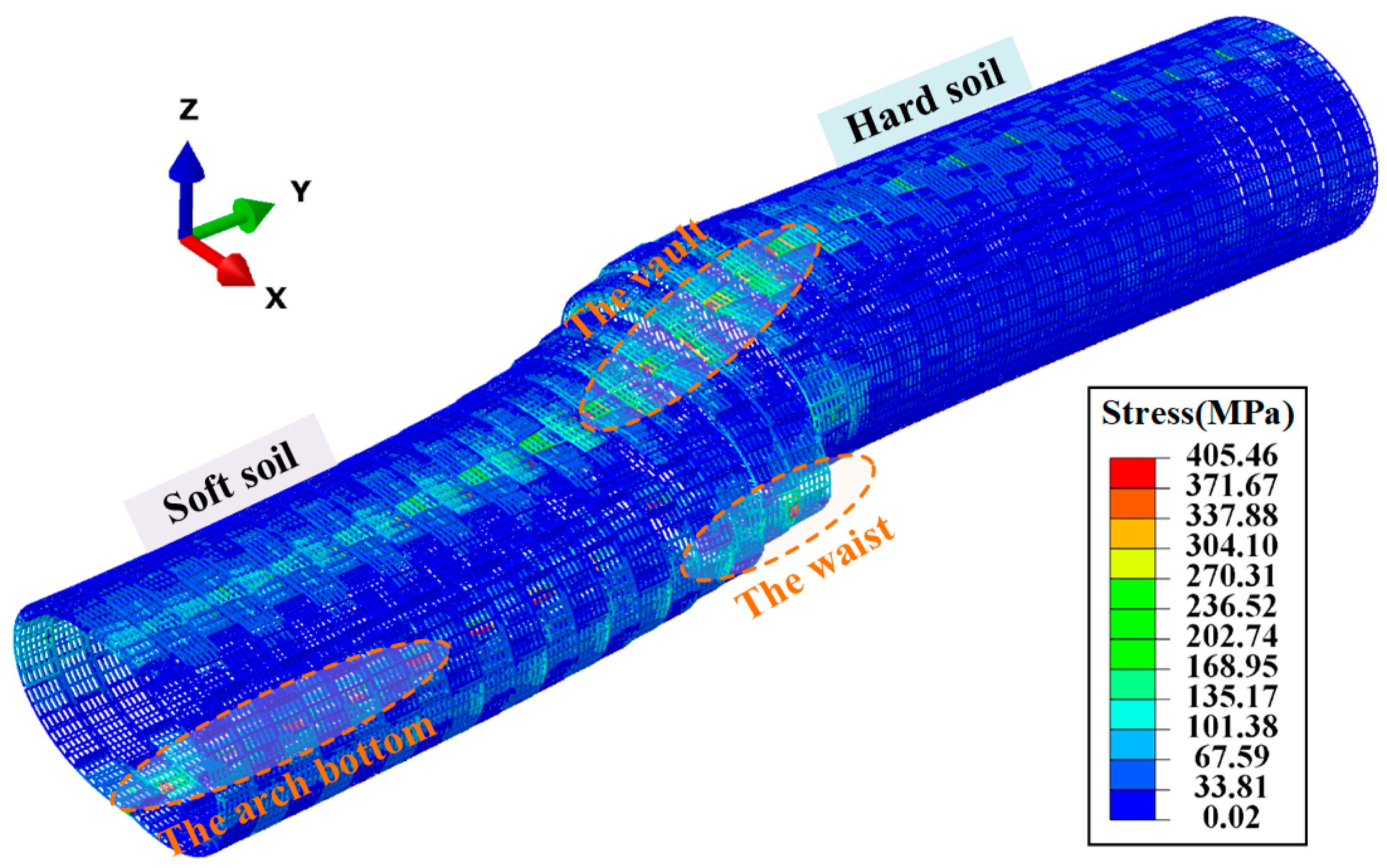
4.5. Overall Lining Damage of Shield Tunnel
5. Influence of Key Parameters on Structural Behavior
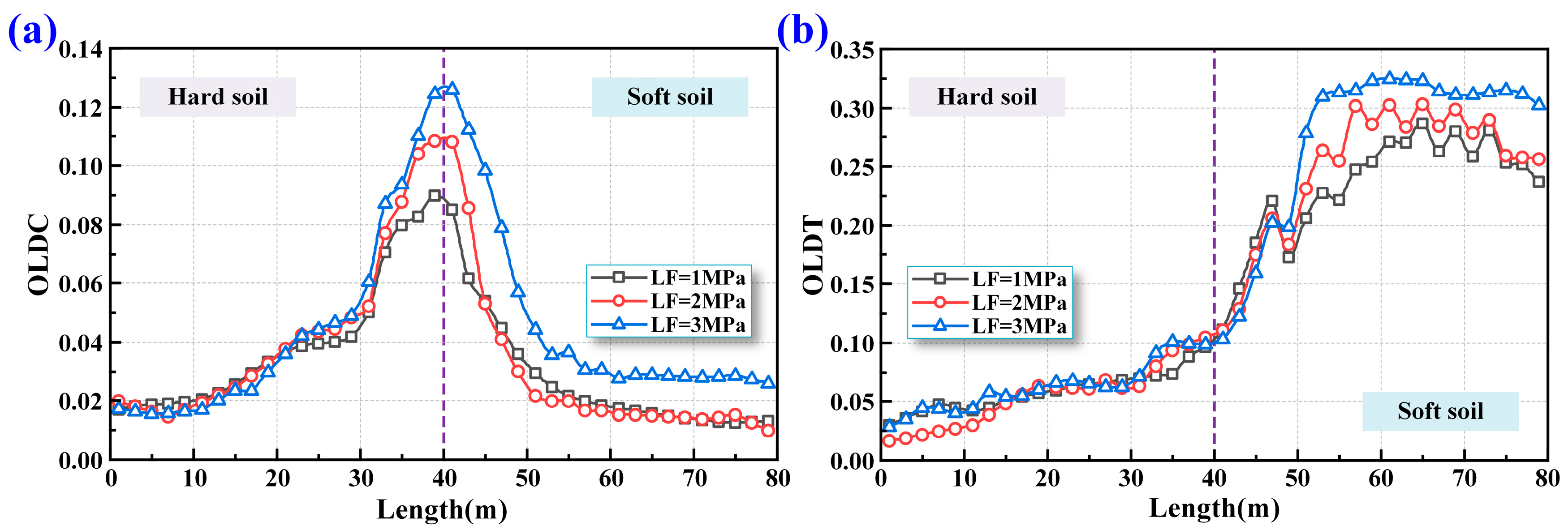
5.1. Effects of Longitudinal Force
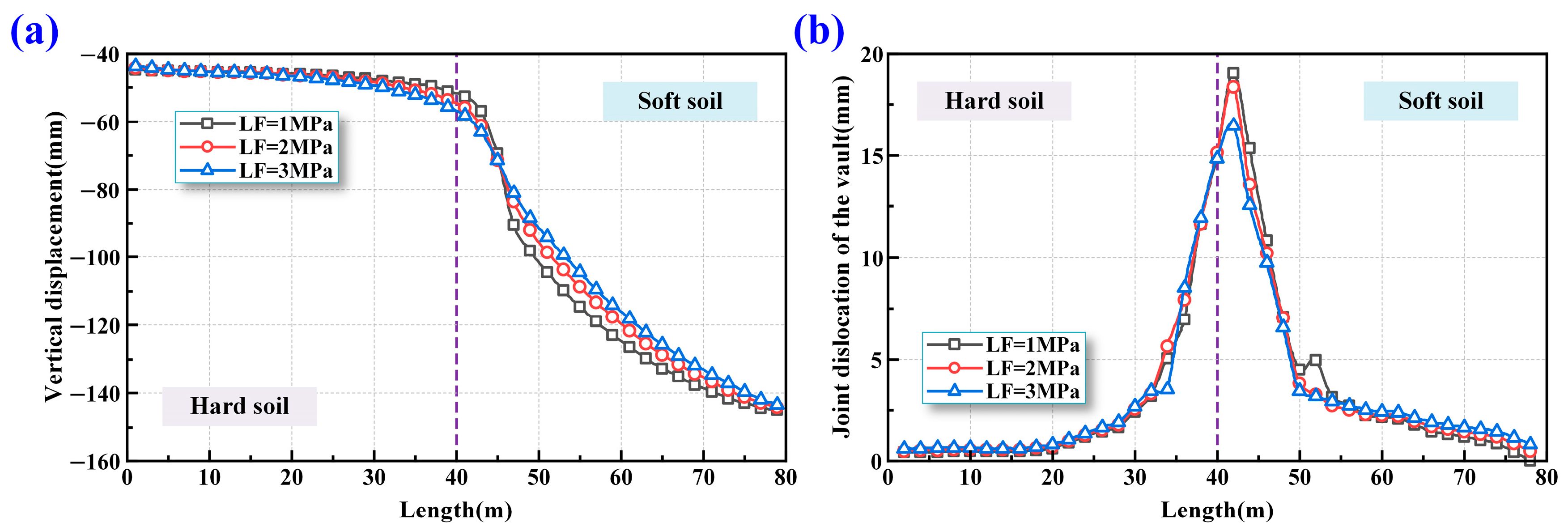
5.1.1. Deformation of Shield Tunnel
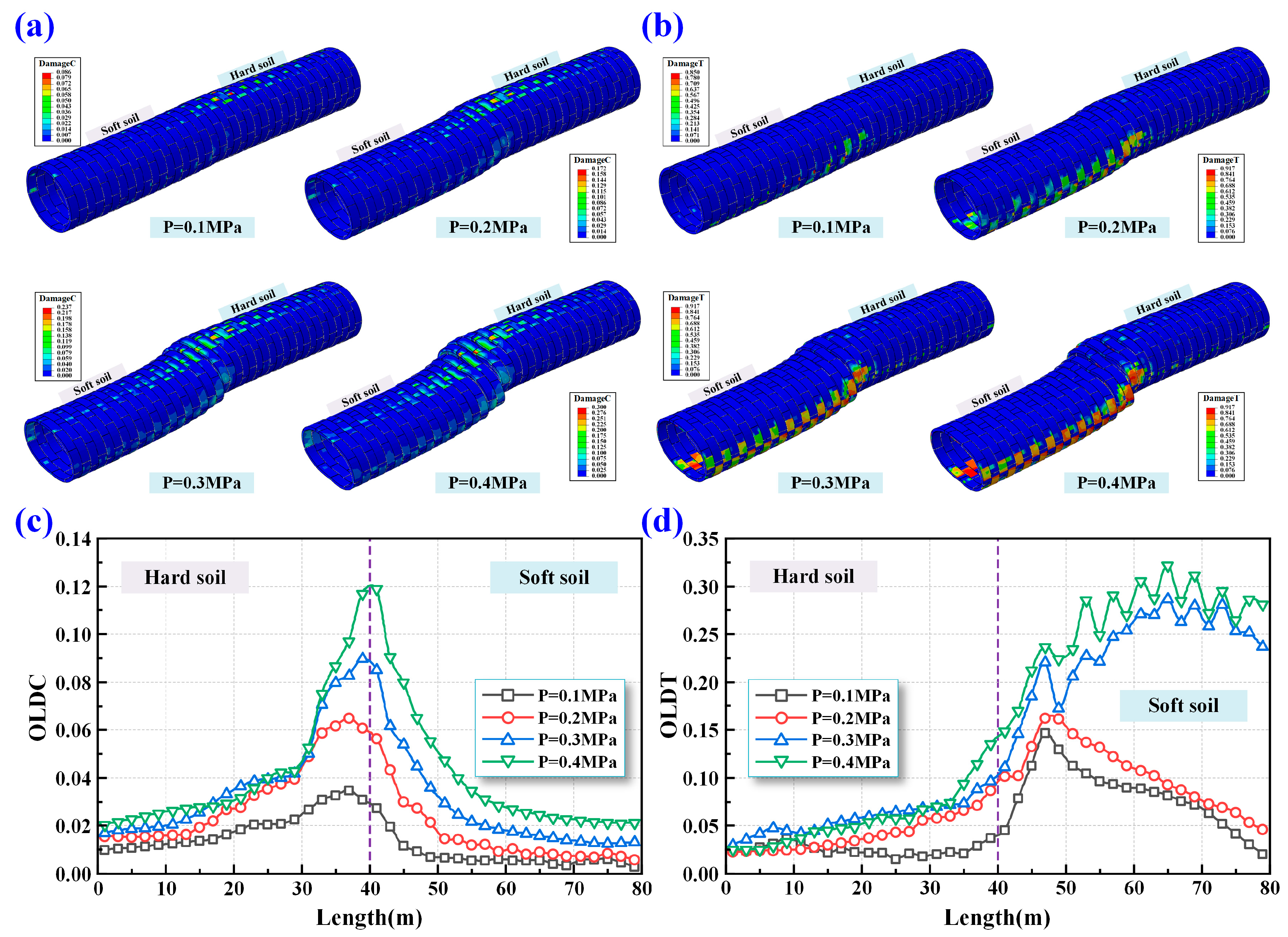
5.1.2. Overall Lining Damage of Shield Tunnel
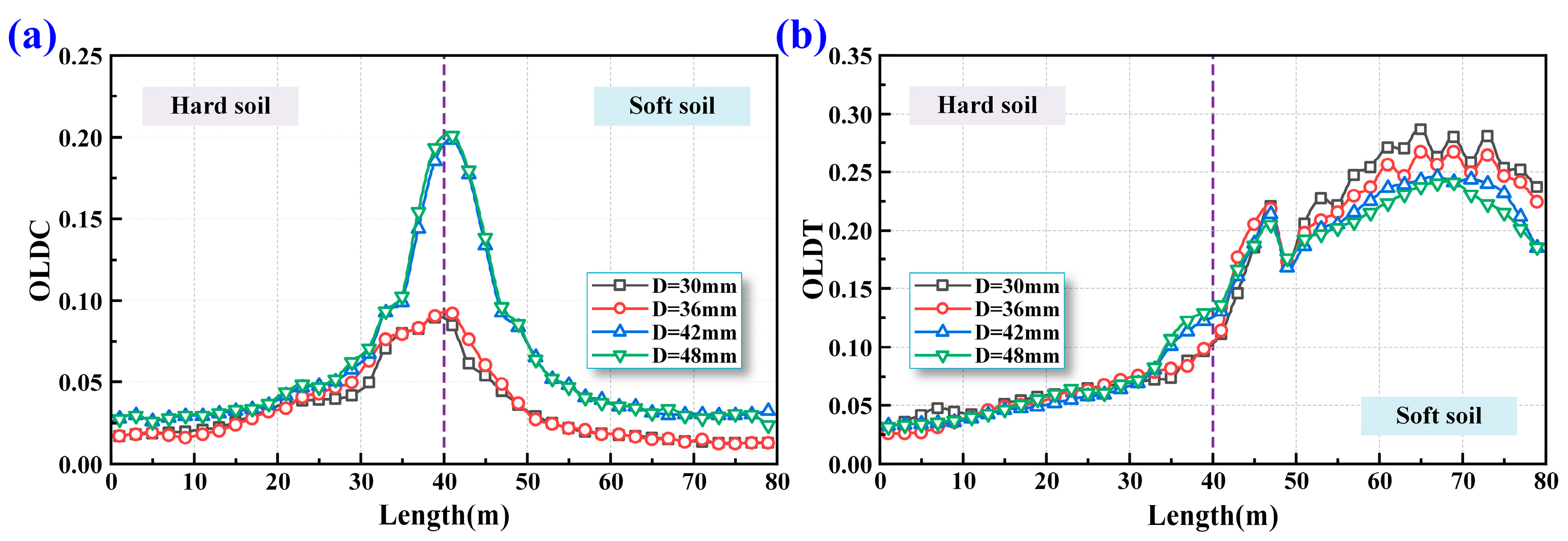
5.2. Effects of Oblique Bolt Diameter
5.2.1. Deformation of Shield Tunnel
5.2.2. Overall Lining Damage of Shield Tunnel
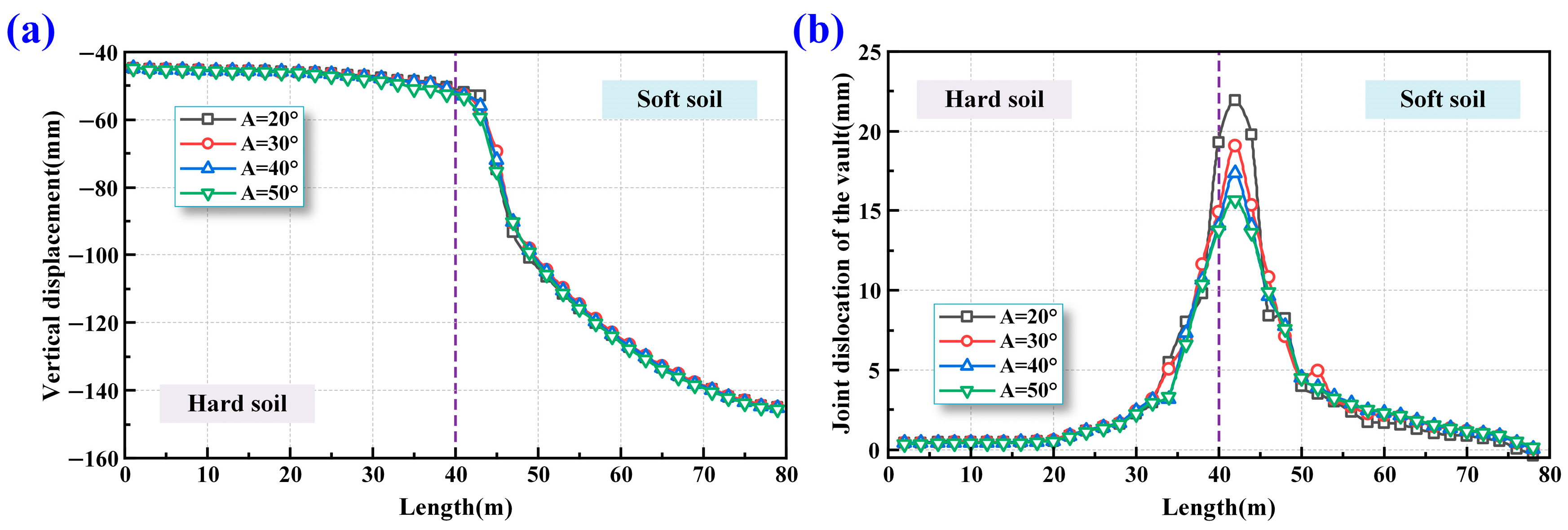
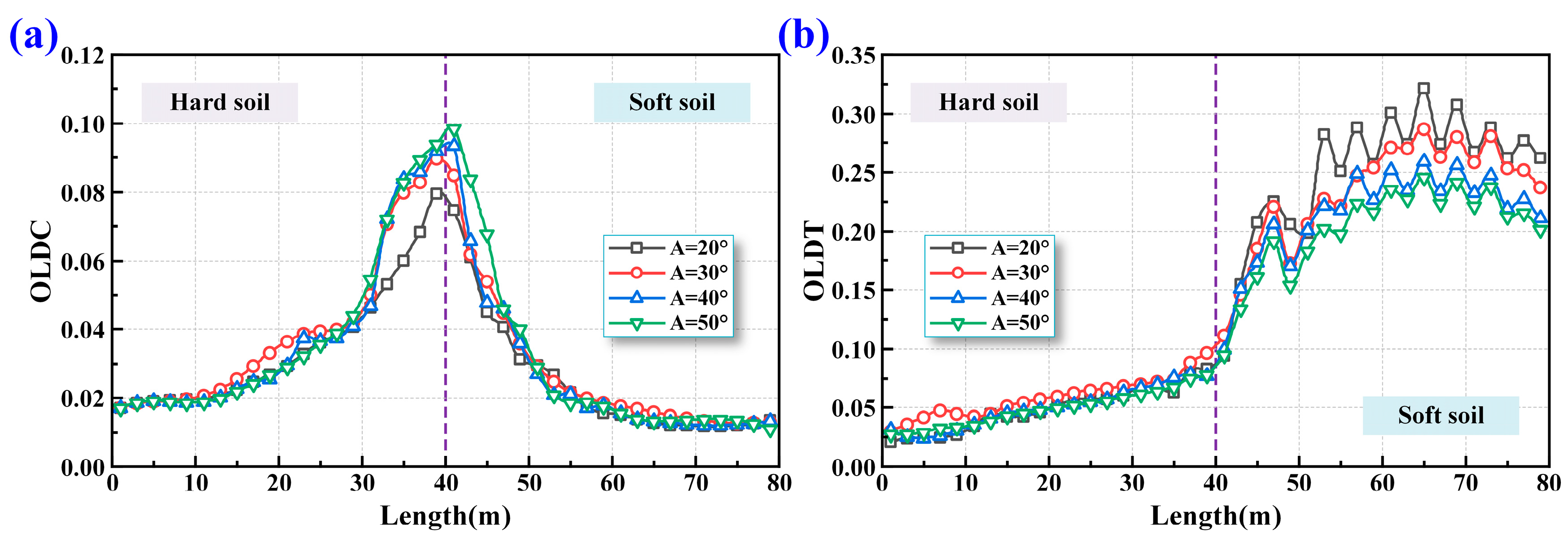
5.3. Effects of Inclination Angle of Oblique Bolt
5.3.1. Deformation of Shield Tunnel
5.3.2. Overall Lining Damage of Shield Tunnel
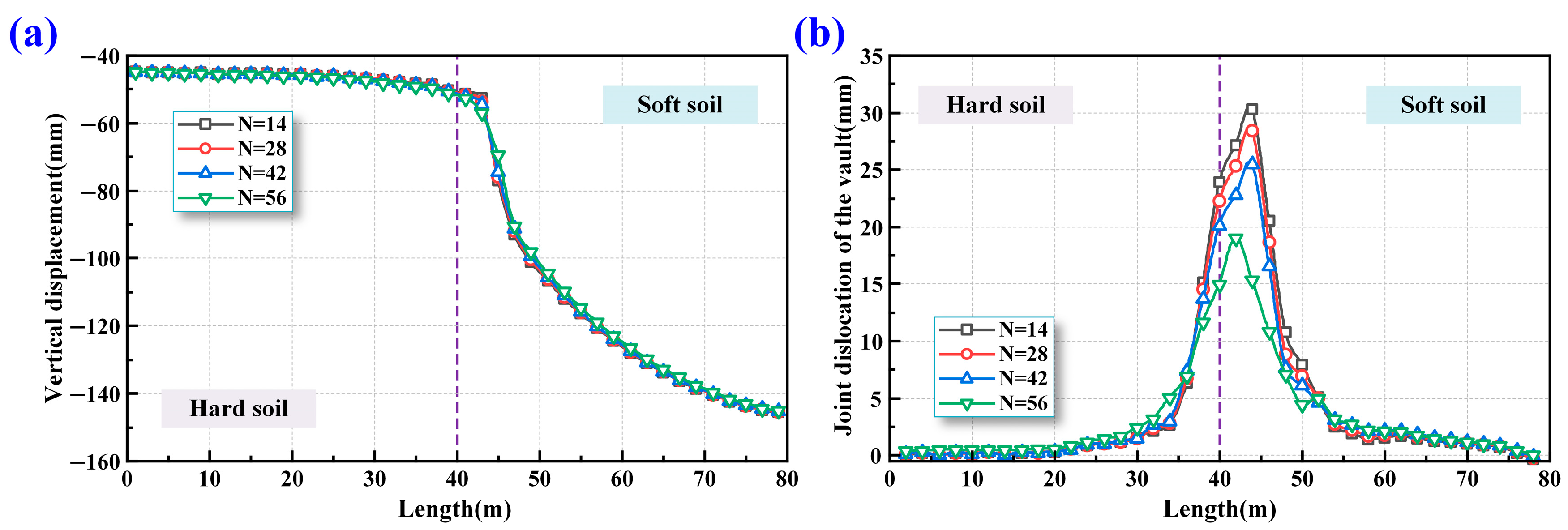
5.4. Effects of the Number of Oblique Bolts
5.4.1. Deformation of Shield Tunnel
5.4.2. Overall Lining Damage of Shield Tunnel
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
- (1)
- At the soft–hard interface, significant differential settlement occurs due to stiffness contrast. Joint opening is prominent on the hard soil side, while joint dislocation dominates on the soft soil side. Although the dislocation extent is larger at the vault, the maximum dislocation magnitude appears at the arch bottom.
- (2)
- Transverse deformation is more constrained in hard soil and more pronounced in soft soil near the interface. Compressive damage mainly concentrates at the interface, while tensile damage is more significant in soft soil zones. Fluctuations in tensile damage are linked to uneven interaction between segment rings.
- (3)
- Increasing longitudinal force enhances structural stiffness and reduces longitudinal deformation and joint dislocation but also intensifies compressive damage at the soft-hard interface and tensile damage in soft soils.
- (4)
- Enhancing bolt diameter, inclination angle, or quantity slightly reduces longitudinal deformation but more significantly improves joint coordination. In particular, bolt inclination is effective in limiting joint dislocation and transverse deformation.
- (5)
- The extent of compressive and tensile damage is closely related to longitudinal and transverse stiffness, respectively. Optimizing longitudinal force and bolt configuration is essential for improving tunnel integrity and minimizing damage in variable ground conditions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berthoz, N.; Branque, D.; Subrin, D.; Wong, H.; Humbert, E. Face Failure in Homogeneous and Stratified Soft Ground: Theoretical and Experimental Approaches on 1g EPBS Reduced Scale Model. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2012, 30, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Bonini, M.; Debernardi, D.; Janutolo, M.; Barla, G.; Chen, G. Computational Modelling of the Mechanised Excavation of Deep Tunnels in Weak Rock. Comput. Geotech. 2015, 66, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Feng, K.; Fang, Y.; Jiang, Y. Surface Settlement Caused by Twin-Parallel Shield Tunnelling in Sandy Cobble Strata. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2012, 13, 858–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.-L.; Wu, H.-N.; Cui, Y.-J.; Yin, Z.-Y. Long-Term Settlement Behaviour of Metro Tunnels in the Soft Deposits of Shanghai. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2014, 40, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-N.; Shen, S.-L.; Chen, R.-P.; Zhou, A. Three-Dimensional Numerical Modelling on Localised Leakage in Segmental Lining of Shield Tunnels. Comput. Geotech. 2020, 122, 103549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, A.; Murakami, H.; Nishino, K. Study on the Analytical Model of Shield Tunnel in Longitudinal Direction. Proc. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1988, 394, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiba, Y.; Kawashima, K.; Obinata, N.; Kano, T. An Evaluation Method of Longitudinal Stiffness of Shield Tunnel Linings for Application to Seismic Response Analyses. Proc. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1988, 398, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Jiang, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Li, L.; Wang, R. Time-Dependent Longitudinal Responses of a Shield Tunnel Induced by Surcharge Load: Theoretical Prediction and Analysis. Undergr. Space 2024, 14, 219–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Xia, T.; Huang, M.; Lin, C. Simplified Analytical Method for Evaluating the Effects of Adjacent Excavation on Shield Tunnel Considering the Shearing Effect. Comput. Geotech. 2017, 81, 167–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, X.; Hong, B.; Zhu, H. Experimental and Analytical Study on Longitudinal Bending Behavior of Shield Tunnel Subjected to Longitudinal Axial Forces. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 86, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, S.; Tang, Y.; Ye, Z. Experimental Study on the Longitudinal Mechanical Behavior of Shield Tunnel in Soft-Hard Uneven Strata and the Reinforcement Effect of Longitudinal Channel Steel. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2024, 28, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Jiang, H.; Xu, C.; Li, X.; Zhan, T. Analytical Algorithm of Longitudinal Bending Stiffness of Shield Tunnel Considering Longitudinal Residual Jacking Force. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 137, 105146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Zhang, X.; He, S.-H.; Qi, Y.-J.; Lin, C.-G. Experimental and Theoretical Study on Longitudinal Deformation and Internal Force of Shield Tunnel under Surcharge. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2024, 144, 105506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Y.; Huang, Q.; Jia, S.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y. Navigating the Depths: Experimental Study on the Influence of Ground Fissures on Metro Shield Tunnels Considering Different Intersection Angles. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 162, 108425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Wang, J. Failure Mechanism of Tunnel Lining Joints and Bolts with Uneven Longitudinal Ground Settlement. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2014, 40, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Cao, C.; Lei, M.; Peng, L.; Ai, H. Effects of Lateral Unloading on the Mechanical and Deformation Performance of Shield Tunnel Segment Joints. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 51, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Fu, H.; Ma, S.; Liu, Y. Deformation Response Induced by Surcharge Loading above Shallow Shield Tunnels in Soft Soil. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 24, 2533–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, C.; Wang, Z.; Lei, M.; Zhao, D.; Cao, C. Damage Mechanism Modelling of Shield Tunnel with Longitudinal Differential Deformation Based on Elastoplastic Damage Model. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 113, 103952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, C.; Lei, M.; Wang, Z.; Cao, C.; Lin, Y. A Study on Damage Mechanism Modelling of Shield Tunnel under Unloading Based on Damage-Plasticity Model of Concrete. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 123, 105261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Geng, P.; Li, P.; He, D.; Shen, H. Failure Analysis of Circumferential Joints and Preferable Bolt Form of Shield Tunnel under Normal Fault Dislocation. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2024, 146, 105648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Chai, S.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Fu, X.; Zhou, Y. Longitudinal Mechanical Properties of Shield Tunnels Crossing Soft and Hard Mutation Strata. Int. J. Geomech. 2023, 23, 04023225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galván, A.; Peña, F.; Moreno-Martínez, J.Y. Effect of TBM Advance in the Structural Response of Segmental Tunnel Lining. Int. J. Geomech. 2017, 17, 04017056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Feng, K.; Lu, X.; Qi, M.; Liu, X.; Fang, Y.; He, C.; Xiao, M. Model Test Investigation on the Longitudinal Mechanical Property of Shield Tunnels Considering Internal Structure. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 140, 105293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Feng, K.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, X.; Qi, M.; He, C.; Xiao, M. Experimental and Numerical Investigation on the Shear Behavior and Damage Mechanism of Segmental Joint under Compression-Shear Load. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 139, 105238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Feng, K.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhao, L. Investigation on the Shear Performance of Circumferential Joints of Segments in Super-large Cross-section Shield Tunnels. Struct. Concr. 2023, 24, 4978–4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB50010-2010; Code for Design of Concrete Structures. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Sidoroff, F. Description of Anisotropic Damage Application to Elasticity. In Physical Non-Linearities in Structural Analysis; Hult, J., Lemaitre, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981; pp. 237–244. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, C.-L.; Ma, S.-K.; Zhang, J.-B.; Zhu, Q.-X. Study of the Mechanical Behaviour and Damage Characteristics of Three New Types of Joints for Fabricated Rectangular Tunnels Using a Numerical Approach. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 118, 104184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Shen, Y.; Gao, B.; Zheng, Q.; Fan, K.; Huang, H. Damage Evolution of Tunnel Lining with Steel Reinforced Rubber Joints under Normal Faulting: An Experimental and Numerical Investigation. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2020, 97, 103223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Feng, K.; Xu, P.; He, C.; Zhang, H. Refined Three-dimensional Numerical Model for Segmental Joint and Its Application. Struct. Concr. 2020, 21, 1612–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-N.; Chen, S.; Chen, R.-P.; Cheng, H.-Z.; Feng, D.-L. Deformation Behaviors and Failure Mechanism of Segmental RC Lining under Unloading Condition. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 130, 104687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wei, J. Correlation between Ground Motion Parameters and Lining Damage Indices for Mountain Tunnels. Nat. Hazards 2013, 65, 1683–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Ang, A.H.-S. Mechanistic Seismic Damage Model for Reinforced Concrete. J. Struct. Eng. 1985, 111, 722–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; He, C.; Fang, Y.; Jiang, Y. Study on the Mechanical Behavior of Lining Structure for Underwater Shield Tunnel of High-Speed Railway. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2013, 16, 1381–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
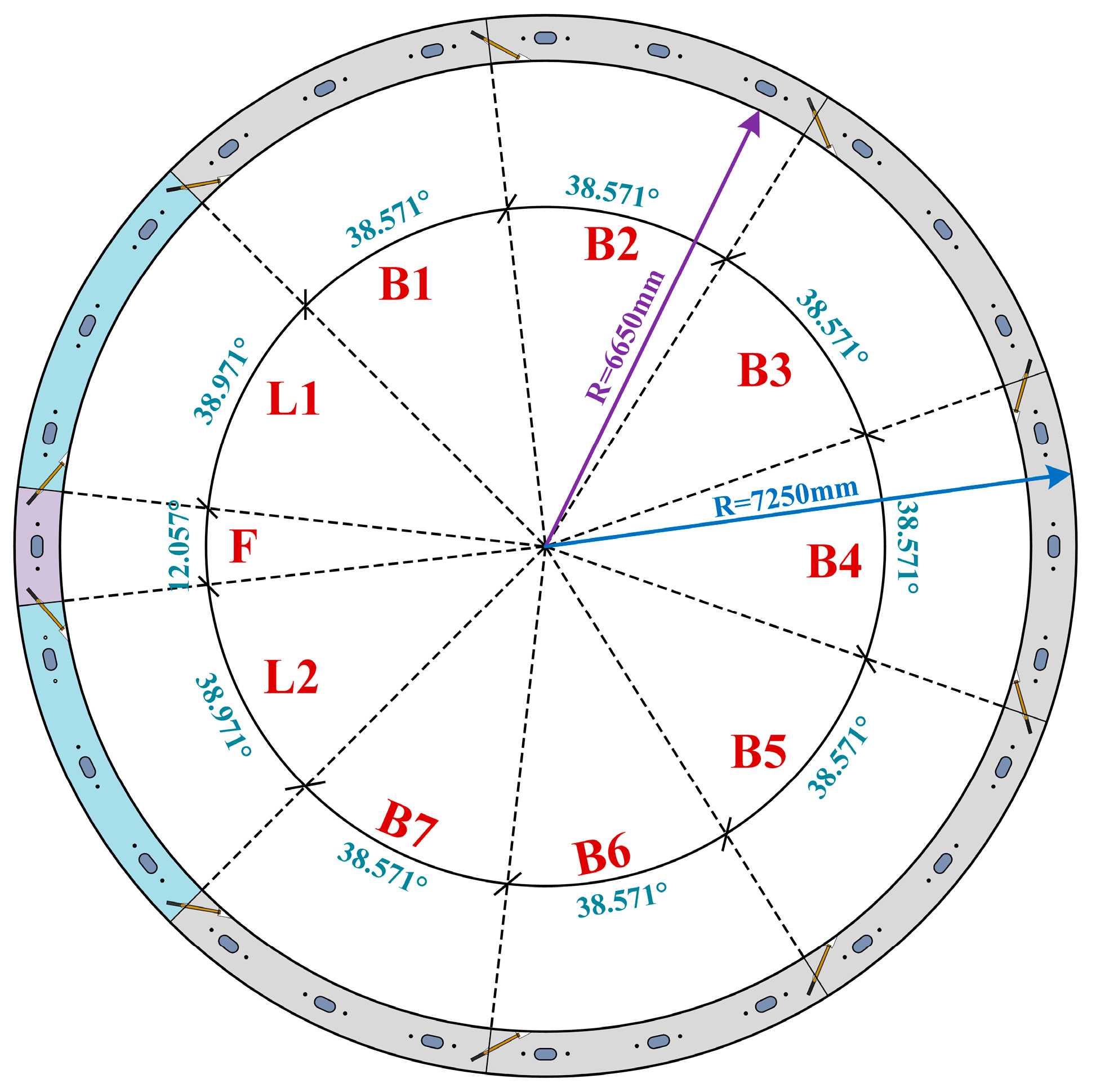
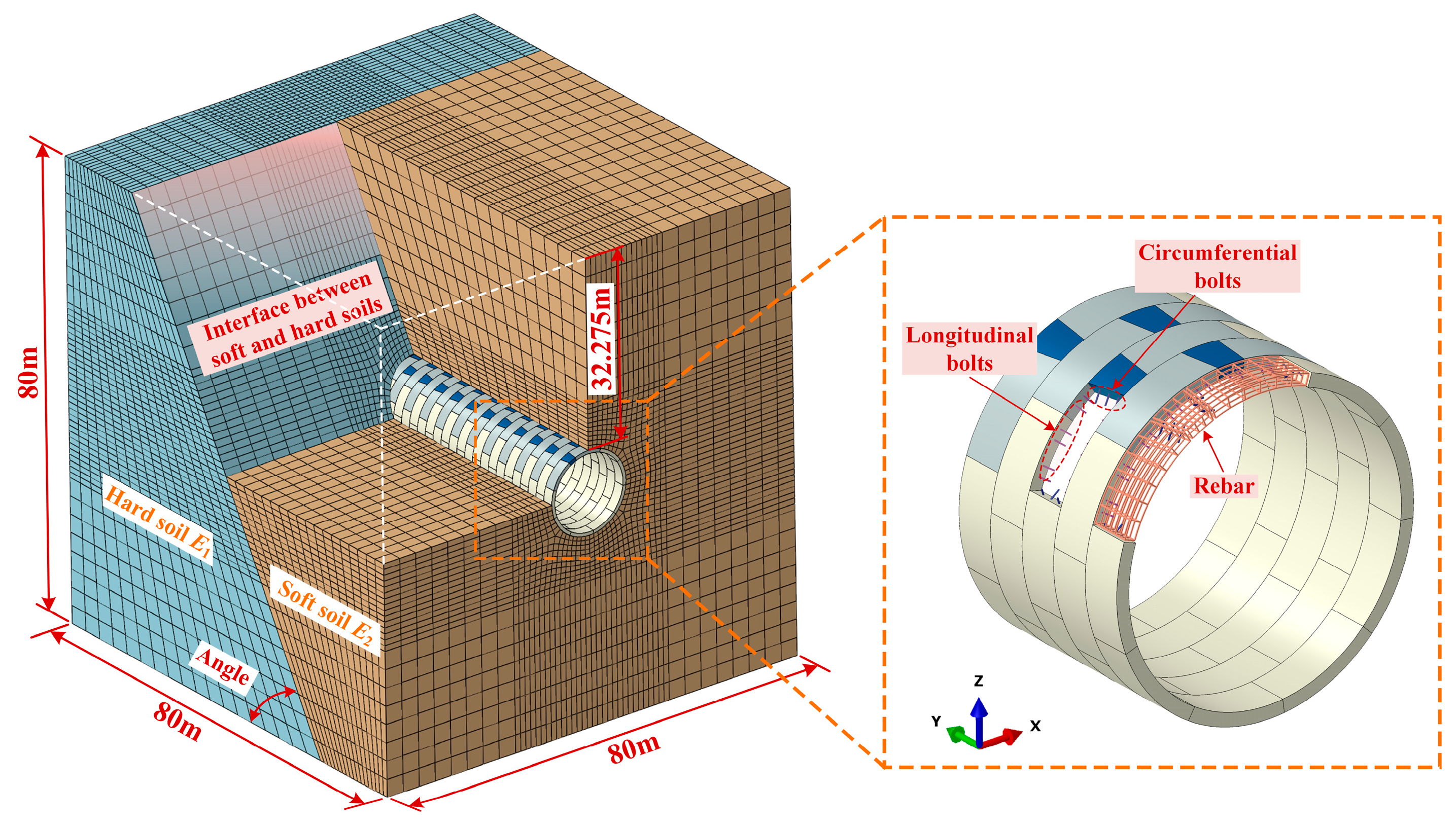
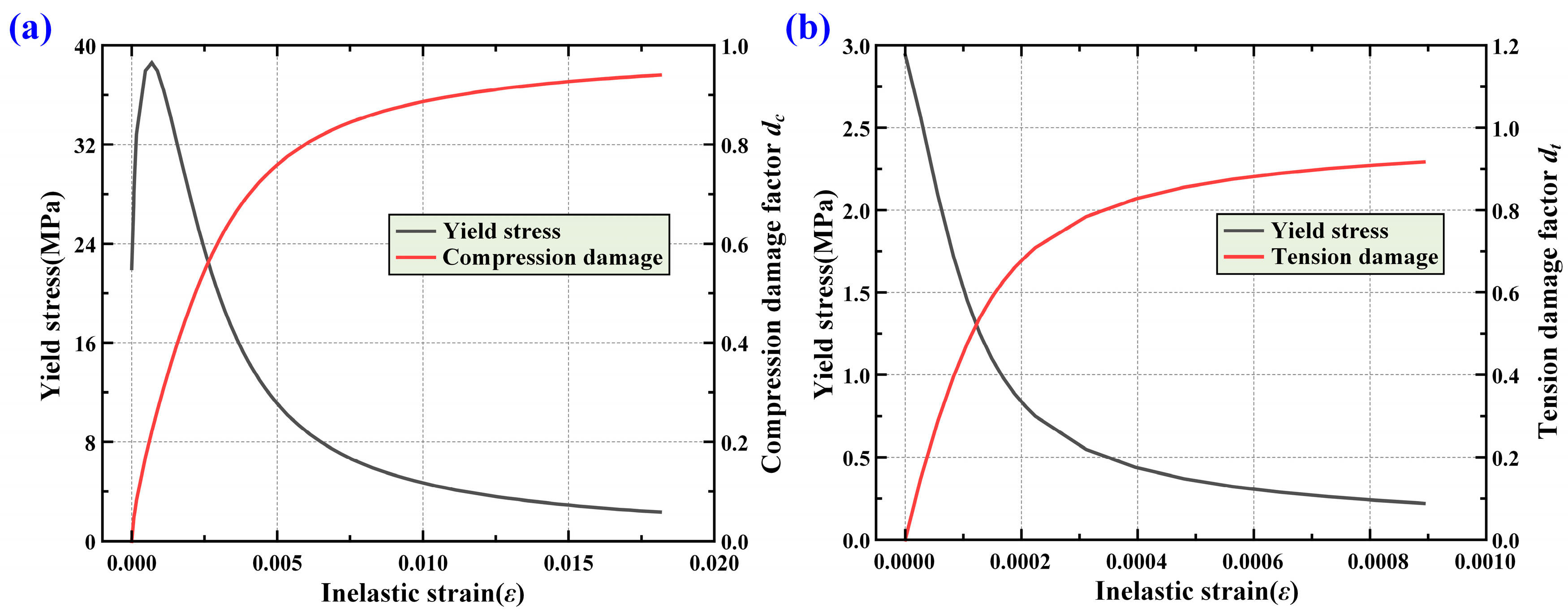
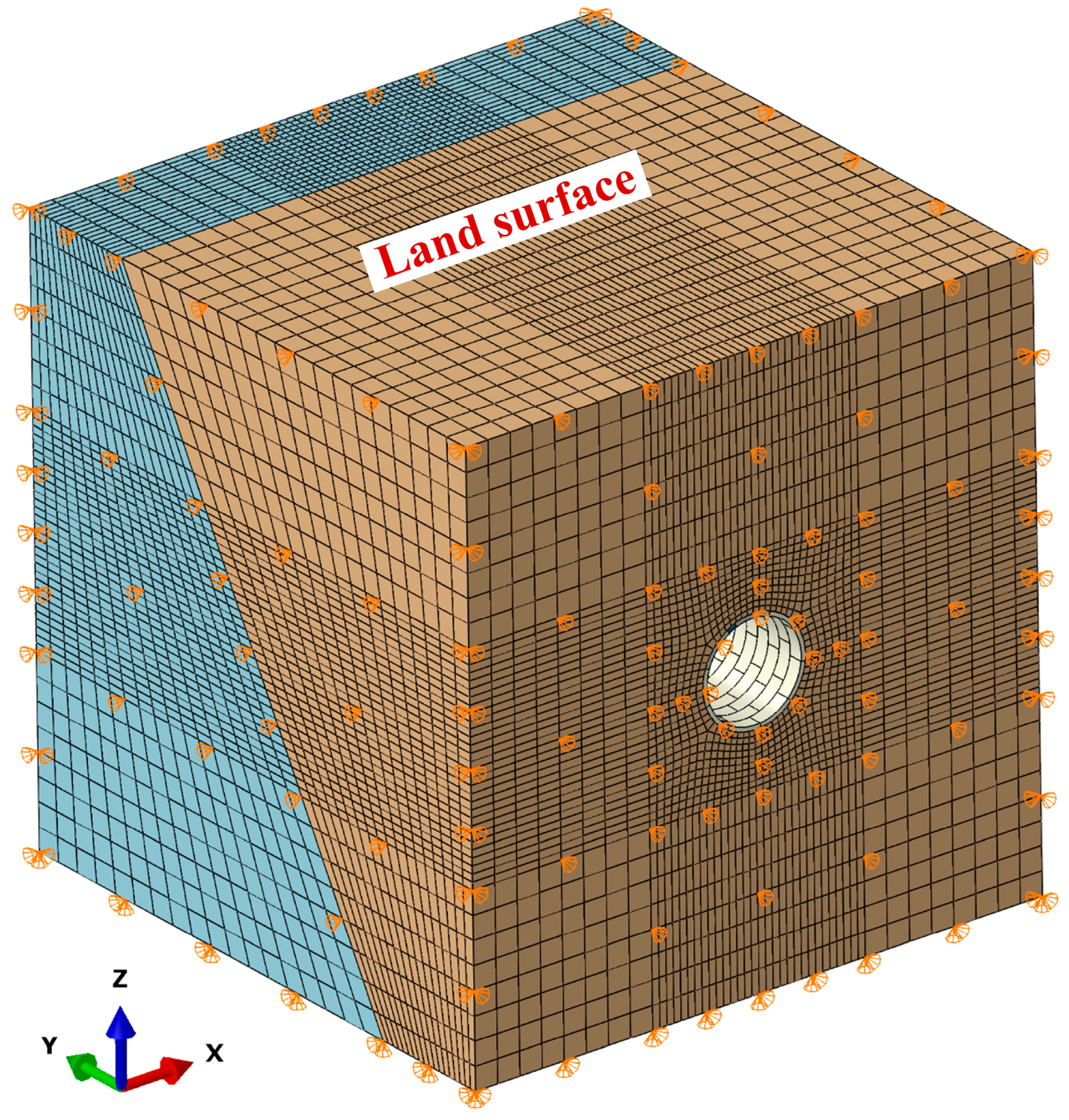



| Parameters | Ψ (°) | ξ | σb0/σc0 | Kc | μ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C60 | 38 | 0.1 | 1.16 | 2/3 | 1 × 10−4 |
| Items | Density (kg·m−3) | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Poisson’s Ratio | Friction Angle (°) | Cohesion (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soft soil | 1910 | 0.04 | 0.3 | 20.8 | 0.0192 |
| Hard soil | 2150 | 0.16 | 0.3 | 22 | 0.075 |
| Loading Condition | E1 (MPa) | E2 (MPa) | Additional Load (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 40 | 160 | 0.1 |
| 2 | 40 | 160 | 0.2 |
| 3 | 40 | 160 | 0.3 |
| 4 | 40 | 160 | 0.4 |
| Cases | Longitudinal Force (MPa) | Bolt Diameter (mm) | Bolt Inclination Angle (°) | Bolt Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1/2/3 | 30 | 31.2147 | 56 |
| 2 | 1 | 30/36/42/48 | 31.2147 | 56 |
| 3 | 1 | 30 | 20/31.2147/40/50 | 56 |
| 4 | 1 | 30 | 31.2147 | 14/28/42/56 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, X.; Zeng, Q.; Peng, X.; Ran, Q.; Xie, Y.; Wu, B.; Wu, L. Study of Factors Influencing the Longitudinal Mechanical Performance of Shield Tunnels Traversing Soft–Hard Heterogeneous Soils. Buildings 2025, 15, 3417. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183417
Xue X, Zeng Q, Peng X, Ran Q, Xie Y, Wu B, Wu L. Study of Factors Influencing the Longitudinal Mechanical Performance of Shield Tunnels Traversing Soft–Hard Heterogeneous Soils. Buildings. 2025; 15(18):3417. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183417
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Xiaojie, Qingcheng Zeng, Xushu Peng, Qihang Ran, Yi Xie, Bohan Wu, and Luxiang Wu. 2025. "Study of Factors Influencing the Longitudinal Mechanical Performance of Shield Tunnels Traversing Soft–Hard Heterogeneous Soils" Buildings 15, no. 18: 3417. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183417
APA StyleXue, X., Zeng, Q., Peng, X., Ran, Q., Xie, Y., Wu, B., & Wu, L. (2025). Study of Factors Influencing the Longitudinal Mechanical Performance of Shield Tunnels Traversing Soft–Hard Heterogeneous Soils. Buildings, 15(18), 3417. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183417





