Mitigating the Transaction Costs of Project Subcontracting Management: The Heterogeneous Effect of Behavior Control and Outcome Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Organizational Arrangement of Subcontracting
2.2. Transaction Costs of Subcontracting
2.3. Management Control
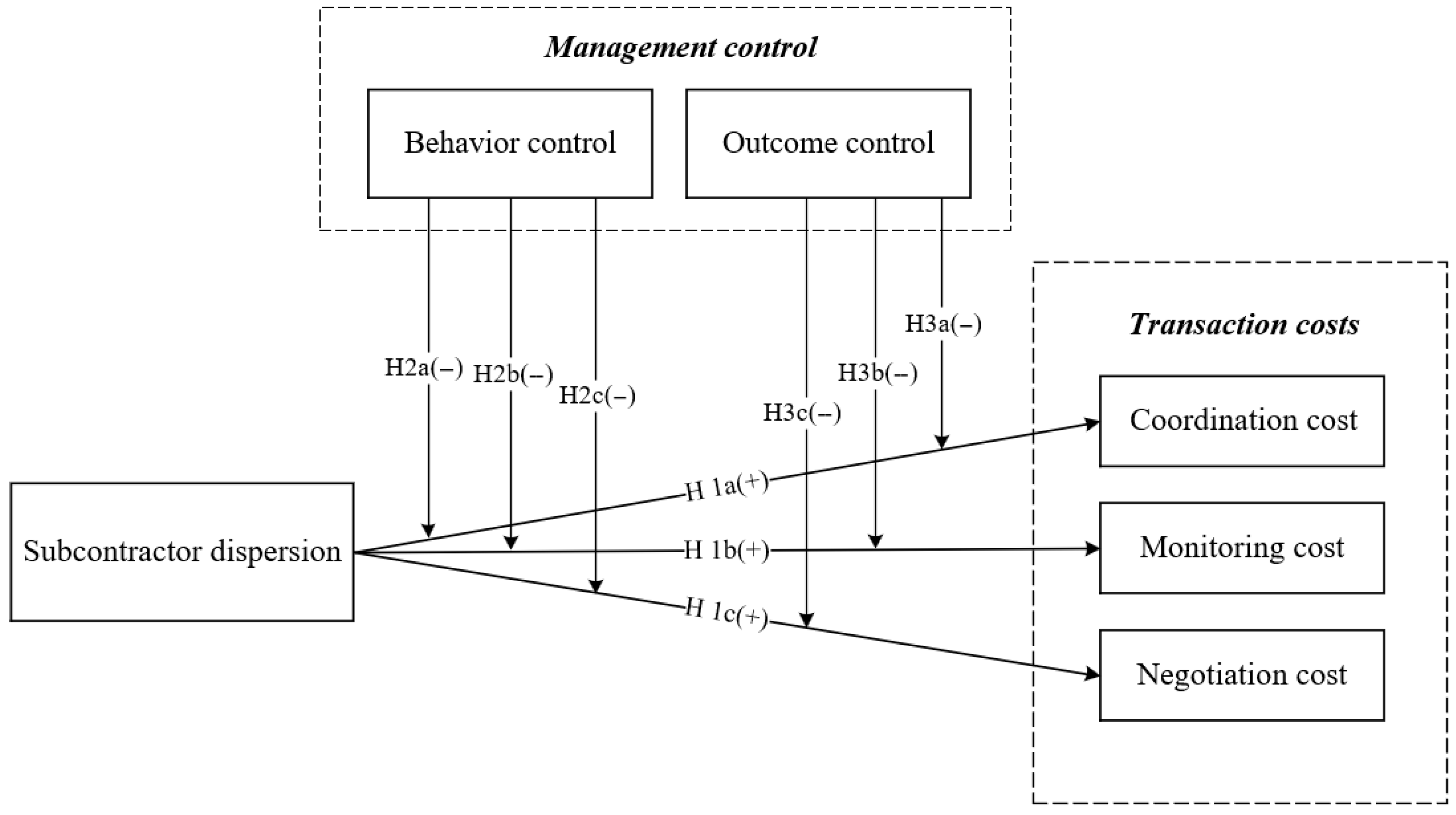
3. Development of Hypotheses
3.1. Transaction Cost Implications of Multi-Subcontractor Dispersion
3.2. Moderation Effect of Behavior Control
3.3. Moderation Effect of Outcome Control
4. Method
4.1. Sample Identification and Data Collection
4.2. Measures
4.3. Analytical Method
4.4. Construct Validity and Reliability
5. Results
5.1. Structural Model Validity Testing
5.2. Hypothesis Analysis
6. Discussion
6.1. The Direct Effect
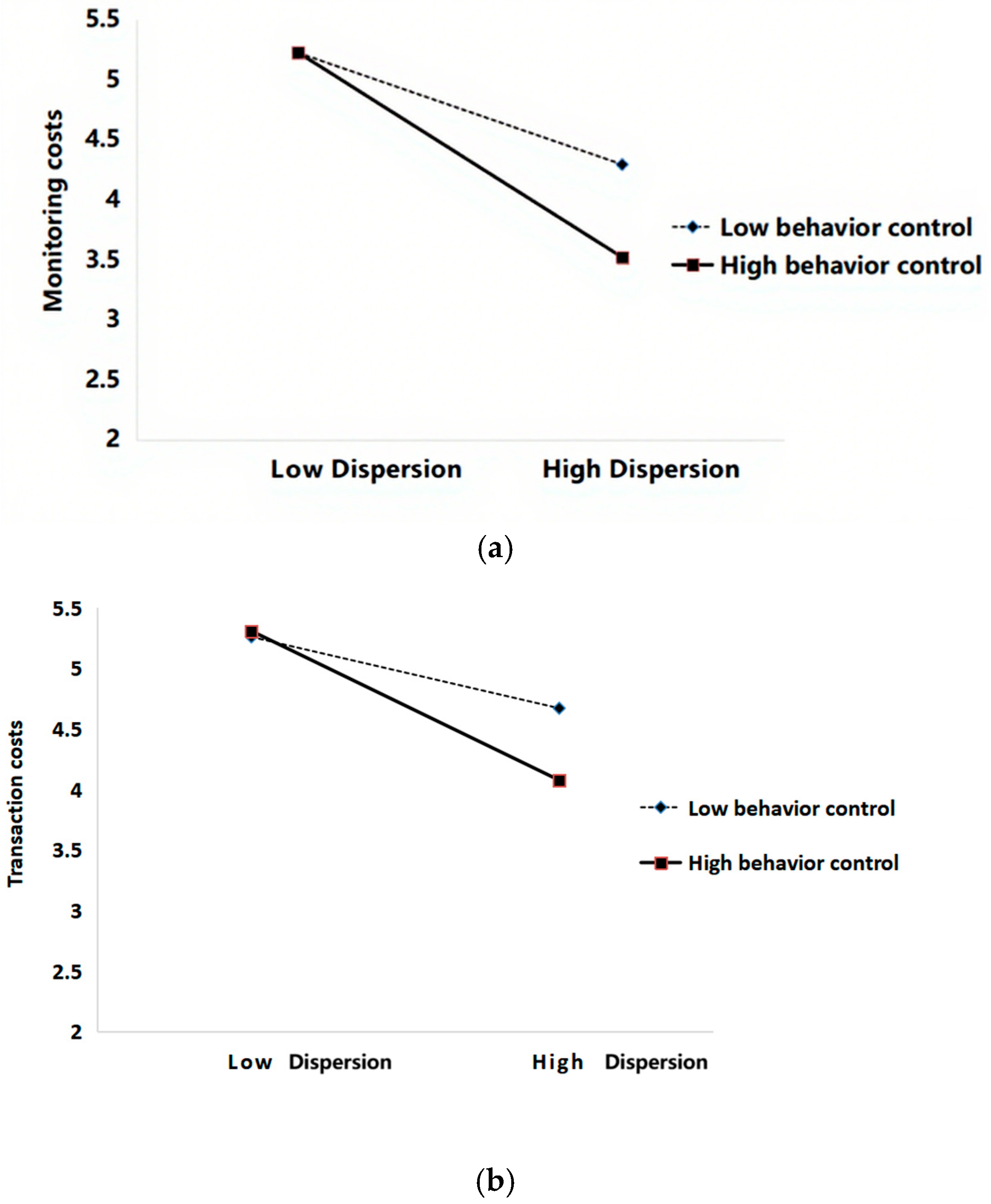
6.2. The Moderating Effect
7. Conclusions and Implications
7.1. Theoretical Implications
7.2. Managerial Implications
7.3. Limitations and Directions for Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AVE | Average variance extracted |
| CR | Composite reliability |
| ENR | Engineering News-Record |
| GOF | Goodness-of-Fit |
| KMO | Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin |
| PLS | Partial Least Squares |
| SFL | Standardized factor loading |
| TCE | Transaction cost economics |
References
- Hui, P.P.; Davis-Blake, A.; Broschak, J.P. Managing Interdependence: The Effects of Outsourcing Structure on the Performance of Complex Projects*. Decis. Sci. 2008, 39, 5–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hua, Y.; Fu, Y. Impacts of Risk Allocation on Conflict Negotiation Costs in Construction Projects: Does Managerial Control Matter? Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2020, 38, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Chen, Y.; Hua, Y.; Tang, Y. Understanding Subcontracting Organizational Arrangements for Construction Projects in China: Integrating Capabilities and Uncertainty. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2023, 30, 2381–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Arditi, D.; Meng, F. Effects of the General Contractor’s Governance Capabilities and Project Goals on the Organizational Arrangement of Subcontracting. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manage. 2023, 70, 1724–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handley, S.M.; Benton, W.C. The Influence of Task- and Location-Specific Complexity on the Control and Coordination Costs in Global Outsourcing Relationships. J. Oper. Manag. 2013, 31, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Yao, H. Watch Out for the Hidden Costs of Subcontracting in Construction Projects: The Impacts of Subcontractor Dispersion. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2023, 149, 04023113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, O.E. The Economic Institutions of Capitalism. Firms, Markets, Relational Contracting; The Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Das, T.K.; Teng, B.-S. Trust, Control, and Risk in Strategic Alliances: An Integrated Framework. Organ. Stud. 2001, 22, 251–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinal, L.B.; Kreutzer, M.; Miller, C.C. An Aspirational View of Organizational Control Research: Re-Invigorating Empirical Work to Better Meet the Challenges of 21st Century Organizations. Acad. Manag. Ann. 2017, 11, 559–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ning, Y.; Rowlinson, S. Interaction of Interorganizational and Intraorganizational Controls in Shaping Professionals’ Behaviors in Outsourced Architectural and Engineering Design Consulting Projects. J. Manag. Eng. 2021, 37, 05021006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heide, J.B.; Wathne, K.H.; Rokkan, A.I. Interfirm Monitoring, Social Contracts, and Relationship Outcomes. J. Mark. Res. 2007, 44, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stouthuysen, K.; Slabbinck, H.; Roodhooft, F. Controls, Service Type and Perceived Supplier Performance in Interfirm Service Exchanges. J. Oper. Manag. 2012, 30, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hätönen, J.; Eriksson, T. 30+ Years of Research and Practice of Outsourcing—Exploring the Past and Anticipating the Future. J. Int. Manag. 2009, 15, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espino-Rodríguez, T.F.; Padrón-Robaina, V. A Review of Outsourcing from the Resource-Based View of the Firm. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2006, 8, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.; Caerteling, J. Subcontractor Procurement in Construction: The Interplay of Price and Trust. Supply Chain. Manag. Int. J. 2010, 15, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.T.; Tang, Z.; Palaneeswaran, E. Factors Contributing to the Success of Equipment-Intensive Subcontractors in Construction. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2009, 27, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasianjahromi, H.; Sepehri, M.; Abbasi, O. A Decision-Making Framework for Subcontractor Selection in Construction Projects. Eng. Manag. J. 2018, 30, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yung, K.L.; Ip, W.H. A Heuristic Genetic Algorithm for Subcontractor Selection in a Global Manufacturing Environment. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C (Appl. Rev.) 2001, 31, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yao, H. Influence of Prior Ties on Trust in Contract Enforcement in the Construction Industry: Moderating Role of the Shadow of the Future. J. Manag. Eng. 2018, 34, 04017064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manu, E.; Ankrah, N.; Chinyio, E.; Proverbs, D. Trust Influencing Factors in Main Contractor and Subcontractor Relationships during Projects. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2015, 33, 1495–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.P. Subcontracting and Competitive Bidding on Incomplete Procurement Contracts. RAND J. Econ. 2014, 45, 705–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Gao, W. Model and Simulation of Benefit Distribution of Collaborative Cooperation in the Supply Chain of General Contracting Projects. Buildings 2023, 13, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, L. Influence Factors on General Contractor Capability in the Context of Transforming China. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, e8874579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Hammad, A.W.A.; Waller, S.T.; Haddad, A.N. Modelling Supplier Selection and Material Purchasing for the Construction Supply Chain in a Fuzzy Scenario-Based Environment. Autom. Constr. 2023, 150, 104847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarziján, J.; Brahm, F. Subcontracting in Project-Based Firms: Do You Follow the Same Pattern across Your Different Projects? Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2014, 32, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Chen, Y.; Fu, Y.; Meng, C. Influencing Factors of Outsourcing in Construction Projects: A Holistic Perspective. Int. J. Manag. Proj. Bus. 2022, 15, 396–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drews, F. Designing Meta-Organisations: An Empirical Study of Boundary Setting in Large Infrastructure Projects; The University of Manchester: Manchester, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, D. Relaxation of Some Restrictions on Subcontracting for Construction Projects in China. Available online: https://www.mondaq.com/china/corporate-and-company-law/25449/relaxation-of-some-restrictions-on-subcontracting-for-construction-projects-in-china (accessed on 28 August 2025).
- González-Díaz, M.; Arruñada, B.; Fernández, A. Causes of Subcontracting: Evidence from Panel Data on Construction Firms. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 2000, 42, 167–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridge, A.J.; Tisdell, C. The Determinants of the Vertical Boundaries of the Construction Firm. Constr. Manag. Econ. 2004, 22, 807–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, N.; Pietroforte, R. Subcontracting Practices in USA Homebuilding—An Empirical Verification of Eccles’s Findings 20 Years Later. Eur. J. Purch. Supply Manag. 2002, 8, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellotti Da Fonseca, F.; Vanalle, R.M.; Camarotto, J.A. Identification of Ex-Ante and Ex-Post Transaction Costs in Industrial Construction Engineering Projects. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2018, 24, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinian, S.M.; Tavakoli, M. Markets, Hierarchies, or Hybrids as Alternative Governance Structures in Construction Contracts: Transaction Cost Economics Analysis. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2023, 149, 04022149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.B.; Rothwell, G.S. Transaction Costs, Regulation, and Subcontracting at Nuclear Power Plants. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 1998, 36, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, O.H.; Baekkeskov, E.; Potoski, M.; Brown, T.L. Measuring and Managing Ex Ante Transaction Costs in Public Sector Contracting. Public Adm. Rev. 2019, 79, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, O.E. Comparative Economic Organization: The Analysis of Discrete Structural Alternatives. Adm. Sci. Q. 1991, 36, 269–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Seo, J.; Park, M.; Ryu, H.; Kwon, S. Transaction-Cost-Based Selection of Appropriate General Contractor-Subcontractor Relationship Type. J. Constr. Eng. Manage. 2009, 135, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Arditi, D.; Wang, Z. Transaction-Related Issues and Construction Project Performance. Constr. Manag. Econ. 2012, 30, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemons, E.K.; Reddi, S.P.; Row, M.C. The Impact of Information Technology on the Organization of Economic Activity: The “Move to the Middle” Hypothesis. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 1993, 10, 9–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, V.; Malhotra, M.K. Transaction Cost Framework in Operations and Supply Chain Management Research: Theory and Measurement. J. Oper. Manag. 2003, 21, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeh, M.; Tookey, J.E.; Rotimi, J.O.B. Estimating Transaction Costs in the New Zealand Construction Procurement: A Structural Equation Modelling Methodology. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2015, 22, 242–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, G.; Xie, Y.M. Impact of Transaction Attributes on Transaction Costs in Project Alliances: Disaggregated Analysis. J. Manag. Eng. 2015, 31, 04014054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Zhang, L.; Pan, J. Identification and Analyses of Hidden Transaction Costs in Project Dispute Resolutions. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2015, 33, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havenvid, M.I.; Håkansson, H.; Linné, Å. Managing Renewal in Fragmented Business Networks. IMP J. 2016, 10, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhao, X.; Zuo, J. (Dis)Trust, Control, and Project Success: From a Chinese Project Owner’s Perspective. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallenburg, C.M.; Schäffler, T. The Interplay of Relational Governance and Formal Control in Horizontal Alliances: A Social Contract Perspective. J. Supply Chain Manag. 2014, 50, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhardt, K.M. Agency Theory: An Assessment and Review. AMR 1989, 14, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badenfelt, U. I Trust You, I Trust You Not: A Longitudinal Study of Control Mechanisms in Incentive Contracts. Constr. Manag. Econ. 2010, 28, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuuli, M.M.; Rowlinson, S.; Koh, T.Y. Control Modes and Mechanisms in Construction Project Teams: Drivers and Consequences. Constr. Manag. Econ. 2010, 28, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, W.G. A Conceptual Framework for the Design of Organizational Control Mechanisms. Manag. Sci. 1979, 25, 833–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwana, A. Systems Development Ambidexterity: Explaining the Complementary and Substitutive Roles of Formal and Informal Controls. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2010, 27, 87–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Jayaraman, V. Managing Business Process Outsourcing. Organ. Dyn. 2010, 39, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahm, F.; Tarziján, J. Transactional Hazards, Institutional Change, and Capabilities: Integrating the Theories of the Firm: Integrating Theories of Firm Boundaries. Strat. Mgmt. J. 2014, 35, 224–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, M.; Aulakh, P.S. Locus of Uncertainty and the Relationship Between Contractual and Relational Governance in Cross-Border Interfirm Relationships. J. Manag. 2017, 43, 771–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, N.; Zafar, M.S.; Bashir, S. The Combined Effects of Managerial Control, Resource Commitment, and Top Management Support on the Successful Delivery of Information Systems Projects. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2017, 35, 1459–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, V.; Antia, K.D.; Frazier, G.L. Contracts, Extracontractual Incentives, and Ex Post Behavior in Franchise Channel Relationships. J. Mark. Res. 2012, 49, 260–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, B.; Leicht, R.; Molenaar, K.; Messner, J. Impact of Team Integration and Group Cohesion on Project Delivery Performance. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2017, 143, 04016088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Jin, M. Revisiting the Relationship Between Contract Governance and Contractors’ Opportunistic Behavior in Construction Projects. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manage. 2019, 69, 2517–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlstrom, R.; Nygaard, A. An Empirical Investigation of Ex Post Transaction Costs in Franchised Distribution Channels. J. Mark. Res. 1999, 36, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, L.F.; Brush, T.H. Untangling Safeguard and Production Coordination Effects in Long-Term Buyer-Supplier Relationships. AMJ 2008, 51, 785–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ning, Y. Combining Formal Controls and Trust to Improve Dwelling Fit-out Project Performance: A Configurational Analysis. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2017, 35, 1238–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzels, M.; Odekerken-Schröder, G.; van Oppen, C. Using PLS Path Modeling for Assessing Hierarchical Construct Models: Guidelines and Empirical Illustration. MIS Q. 2009, 33, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error: Algebra and Statistics. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.F. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis: A Regression-Based Approach; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Buvik, A. Hybrid Governance and Governance Performance in Industrial Purchasing Relationships. Scand. J. Manag. 2002, 18, 567–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magelssen, C.; Sanchez, F.; Damanpour, F. Learning from Outsourcing: The Effects of Outsourcing Strategy on Organizational Efficiency. Acad. Manag. Proc. 2015, 2015, 17468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, G.; Beranek, P.; Martz, B.; Jiang, J. The Relationship of Control and Learning to Project Performance. Cybern. Syst. 2006, 37, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-Y.; Zuo, J.; Zillante, G.; Wang, X.-W. Critical Success Factors for BOT Electric Power Projects in China: Thermal Power versus Wind Power. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.; Shan, M.; Le, Y. Investigating the Impact of Governmental Governance on Megaproject Performance: Evidence from China. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2020, 26, 449–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T. Corporate Governance Mechanisms and Earnings Management in Transitional Countries—Evidence from Chinese Listed Firms. Ph.D. Thesis, Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane, Australia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
| Characteristic | Category | Frequency | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Project type | Liner engineering | 87 | 31.6 |
| Housing | 37 | 13.4 | |
| Port and waterway | 45 | 16.3 | |
| Energy development | 82 | 29.8 | |
| Industrial engineering | 24 | 8.7 | |
| Work experience (years) | <3 | 29 | 10.5 |
| 3–5 | 47 | 17 | |
| 6–8 | 56 | 20.3 | |
| 9–11 | 41 | 14.9 | |
| >11 | 102 | 37 | |
| Size | Less than 30 million RMB | 15 | 5.4 |
| 30–100 million RMB | 33 | 12 | |
| 100 million–1 billion RMB | 157 | 57 | |
| 1–3 billion RMB | 29 | 10.5 | |
| More than 3 billion RMB | 41 | 14.9 | |
| Job position | Project manager | 34 | 12.3 |
| Contract and business manager | 143 | 52 | |
| Technician | 63 | 22.9 | |
| Others | 35 | 12.7 |
| Construct and Measure Items | SFL |
|---|---|
| Subcontractor dispersion (α = 0.811; AVE = 0.724; CR = 0.887) | |
| 0.862 |
| 0.860 |
| 0.831 |
| Coordination cost (α = 0.813; AVE = 0.650; CR = 0.881) | |
| 0.827 |
| 0.848 |
| 0.837 |
| 0.705 |
| Monitoring cost (α = 0.849; AVE = 0.685; CR = 0.896) | |
| 0.717 |
| 0.837 |
| 0.893 |
| 0.853 |
| Negotiation cost (α = 0.864; AVE = 0.643; CR = 0.899) | |
| 0.823 |
| 0.631 |
| 0.824 |
| 0.863 |
| 0.845 |
| Behavior control (α = 0.796; AVE = 0.624; CR = 0.869) | |
| 0.796 |
| 0.688 |
| 0.853 |
| 0.814 |
| Outcome control (α = 0.808; AVE = 0.648; CR = 0.880) | |
| 0.840 |
| 0.831 |
| 0.839 |
| 0.702 |
| Constructs | Means | SD | Construct Correlations | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD | CC | MC | NC | BC | OC | |||
| SD | 3.948 | 1.719 | 0.851 | |||||
| CC | 5.236 | 1.213 | 0.314 ** | 0.806 | ||||
| MC | 4.900 | 1.326 | 0.187 ** | 0.637 ** | 0.828 | |||
| NC | 4.342 | 1.340 | 0.204 ** | 0.532 ** | 0.582 ** | 0.802 | ||
| BC | 5.476 | 1.186 | 0.051 | 0.381 ** | 0.231 ** | 0.089 | 0.790 | |
| OC | 5.637 | 1.150 | 0.009 | 0.371 ** | 0.158 ** | 0.065 | 0.701 ** | 0.805 |
| Hypothesis | Path | Original Sample | t-Value | p-Value | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
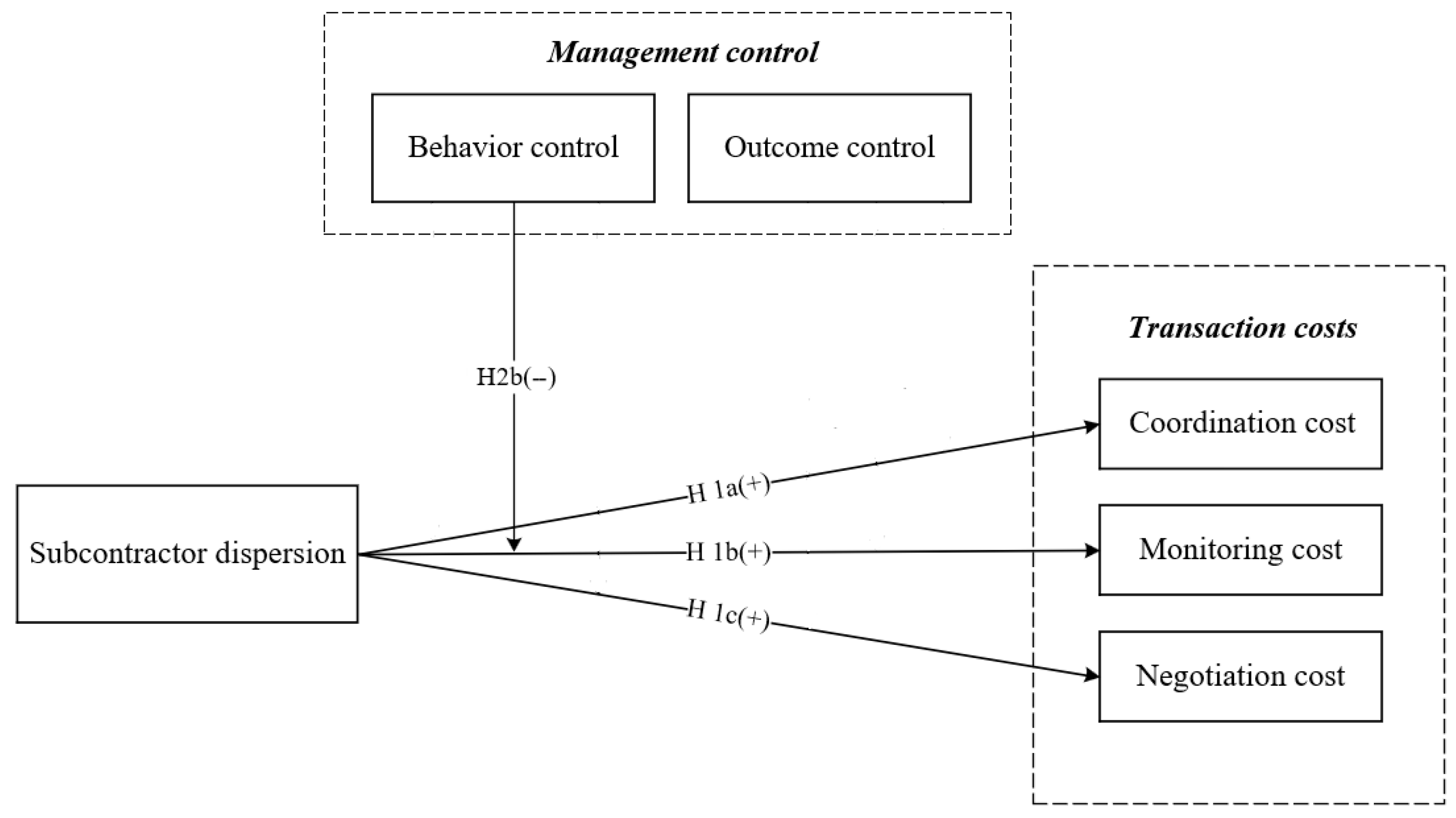
| H1a | SD→CC | 0.294 *** | 5.398 | 0.000 | S |
| H1b | SD→MC | 0.185 ** | 3.003 | 0.003 | S |
| H1c | SD→NC | 0.228 * | 2.325 | 0.020 | S |
| Hypothesis | Path | Original Sample | t-Value | p-Value | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD × BC→TC | −0.172 * | 2.012 | 0.044 | ||
| SD × OC→TC | 0.022 | 0.296 | 0.767 | ||
| H2a | SD × BC→CC | −0.060 | 0.676 | 0.499 | NS |
| H2b | SD × BC→MC | −0.179 * | 1.986 | 0.047 | S |
| H2c | SD × BC→NC | −0.173 | 1.625 | 0.104 | NS |
| H3a | SD × OC→CC | 0.018 | 0.203 | 0.839 | NS |
| H3b | SD × OC→MC | 0.036 | 0.418 | 0.676 | NS |
| H3c | SD × OC→NC | 0.010 | 0.136 | 0.892 | NS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hua, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Guo, W. Mitigating the Transaction Costs of Project Subcontracting Management: The Heterogeneous Effect of Behavior Control and Outcome Control. Buildings 2025, 15, 3300. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183300
Hua Y, Wang Y, Fu Y, Guo W. Mitigating the Transaction Costs of Project Subcontracting Management: The Heterogeneous Effect of Behavior Control and Outcome Control. Buildings. 2025; 15(18):3300. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183300
Chicago/Turabian StyleHua, Yuanyuan, Yuxin Wang, Yafan Fu, and Wenqian Guo. 2025. "Mitigating the Transaction Costs of Project Subcontracting Management: The Heterogeneous Effect of Behavior Control and Outcome Control" Buildings 15, no. 18: 3300. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183300
APA StyleHua, Y., Wang, Y., Fu, Y., & Guo, W. (2025). Mitigating the Transaction Costs of Project Subcontracting Management: The Heterogeneous Effect of Behavior Control and Outcome Control. Buildings, 15(18), 3300. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183300





