A Novel Method for Named Entity Recognition in Long-Text Safety Accident Reports of Prefabricated Construction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
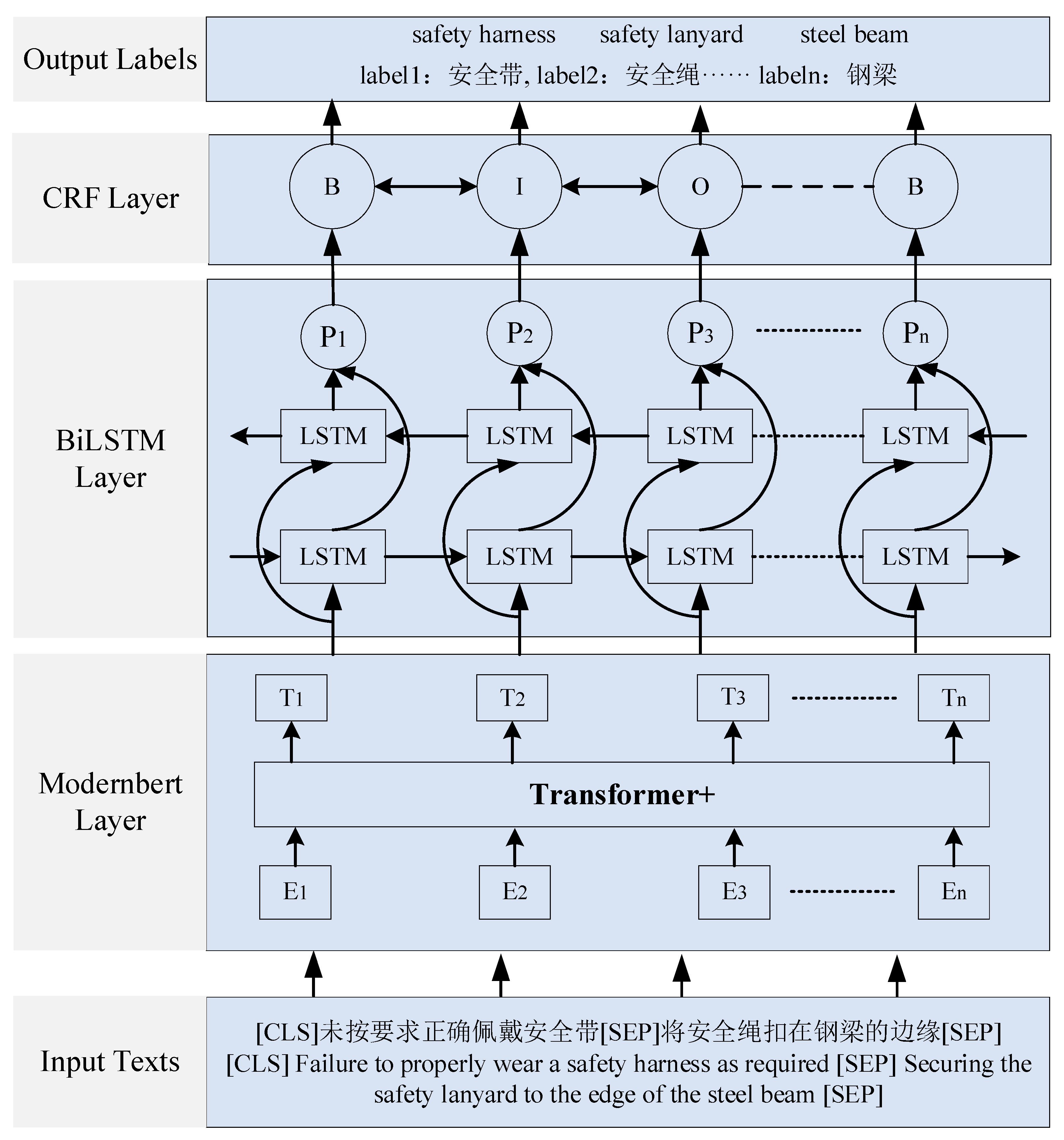
3. Methodology
3.1. ModernBERT
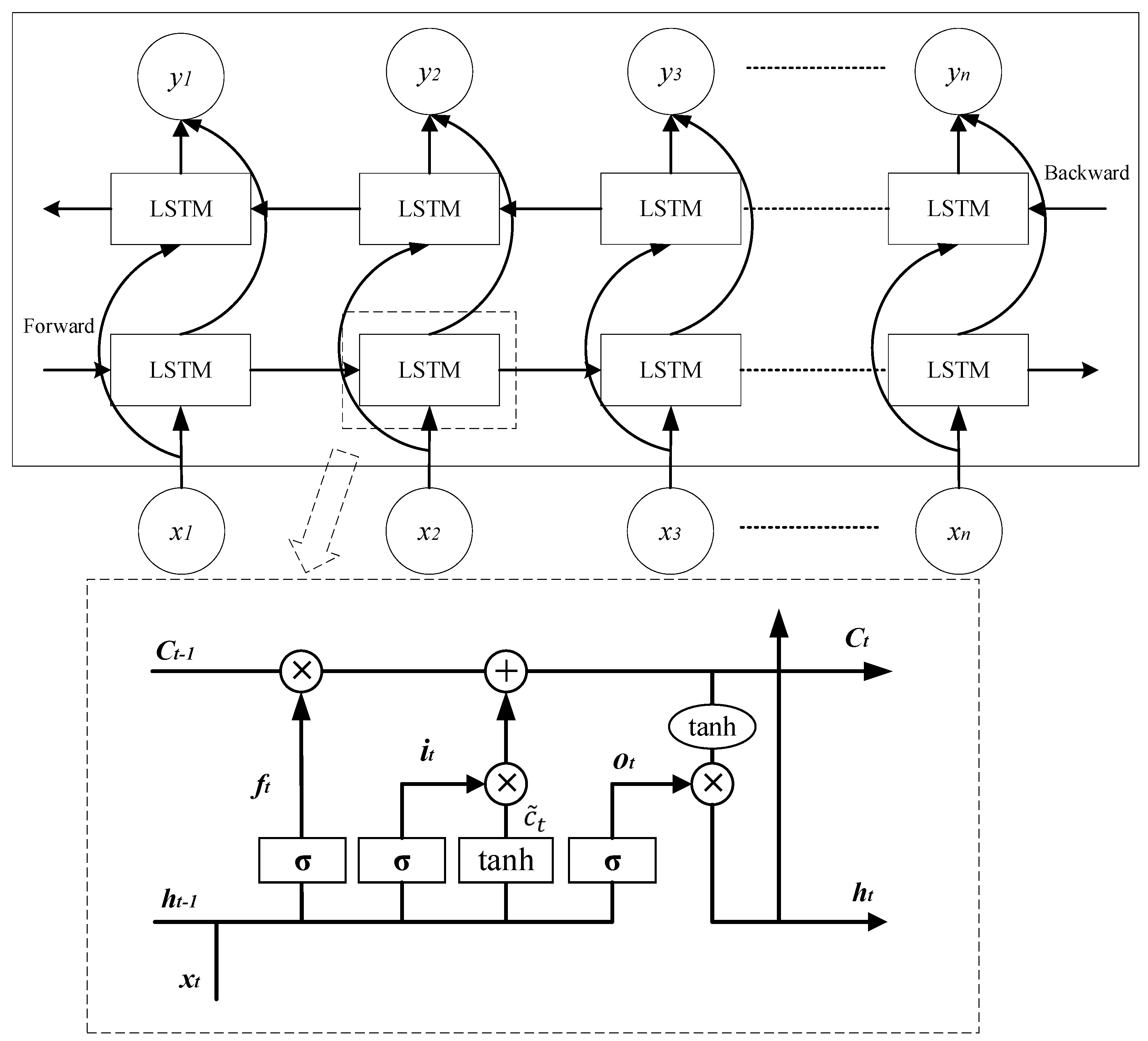
3.2. BiLSTM
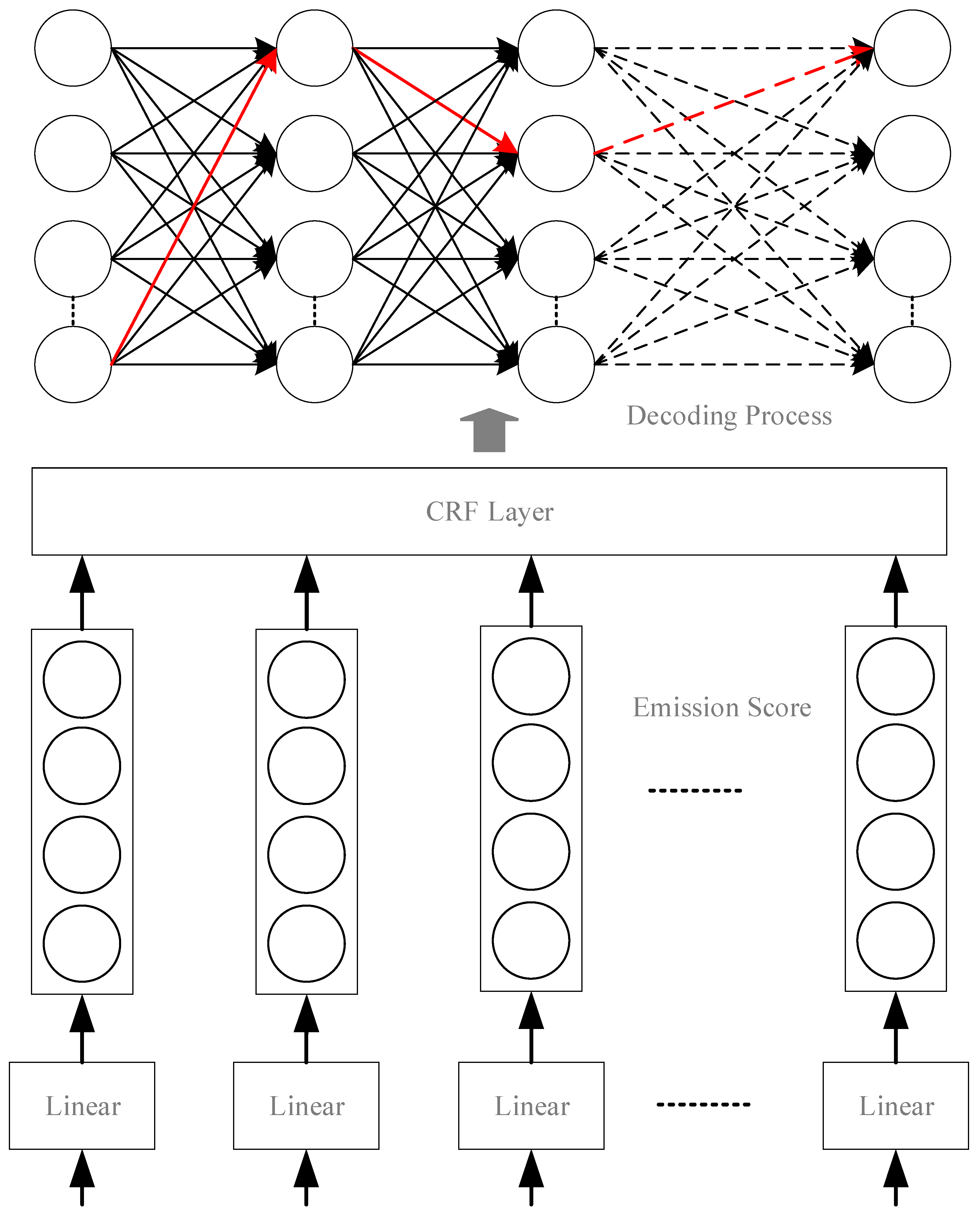
3.3. CRF
3.4. Evaluation Metrics for NER
4. Experiments and Results
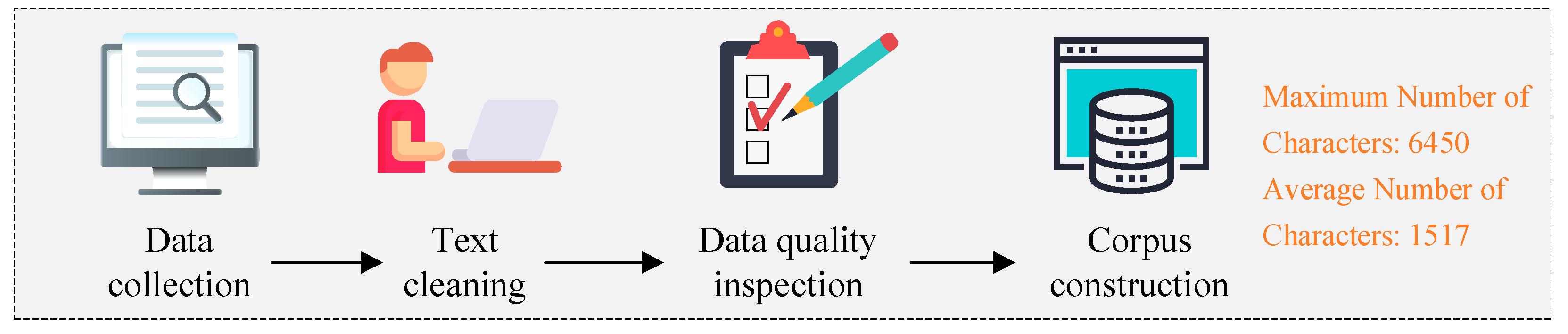
4.1. Data Collection and Processing
4.2. Entity Type Definition and Annotation
4.3. Experimental Setup
4.4. NER Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Model Performance Analysis
5.2. Knowledge Contributions
5.3. Limitations and Future Work
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Meng, X.; Liu, X.; Feng, Y. Assessing the air pollution abatement effect of prefabricated buildings in China. Environ. Res. 2023, 239, 117290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miracco, G.; Nicoletti, F.; Ferraro, V.; Muzzupappa, M.; Mattanò, V.M.; Alberti, F. Achieving nZEB goal through prefabricated buildings: Case study in Italy. Energy Build. 2025, 329, 115301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Hao, J.L.; Gong, G.; Ma, W.; Zuo, J.; Di Sarno, L. Decarbonizing prefabricated building waste: Scenario simulation of policies in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 458, 142529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modular Building Institute MBI. 2024 Annual Modular Construction Reports. 2024. Available online: https://www.modular.org/industry-analysis/ (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, D.; Guo, F. Study of Occupational Safety Risks in Prefabricated Building Hoisting Construction Based on HFACS-PH and SEM. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, G.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.S.; Park, M.; Hyun, H. Analysis of safety risk factors of modular construction to identify accident trends. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2022, 21, 1040–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, H.; Cheung, C.M.; Yunusa-Kaltungo, A.; Manu, P. A systematic review of occupational safety and health in modular integrated construction. Saf. Sci. 2025, 189, 106897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Musa, S.N.; Onn, C.C.; Ramesh, S.; Liang, L.; Wang, W.; Ma, K. The role and contribution of green buildings on sustainable development goals. Build. Environ. 2020, 185, 107091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Zhong, B.; Wang, Y.; Shen, L. Identification of accident-injury type and bodypart factors from construction accident reports: A graph-based deep learning framework. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2022, 54, 101752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, H.; Hallowell, M.R.; Tixier, A.J.P. Automatically learning construction injury precursors from text. Autom. Constr. 2020, 118, 103145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.Y.; Kusoemo, D.; Gosno, R.A. Text mining-based construction site accident classification using hybrid supervised machine learning. Autom. Constr. 2020, 118, 103265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Guo, S.; Dong, Y.; Niu, H.; Zhang, P. Cause analysis of construction collapse accidents using association rule mining. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2023, 30, 4120–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wei, L.; Luan, H. Deep learning for named entity recognition in extracting critical information from struck-by accidents in construction. Autom. Constr. 2025, 173, 106106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, K.; Lee, G.; Yang, S.; Jeong, H.D. Named entity recognition of building construction defect information from text with linguistic noise. Autom. Constr. 2022, 143, 104543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Goodfellow, S.D. Domain-specific language models pre-trained on construction management systems corpora. Autom. Constr. 2024, 160, 105316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, G.; You, X. HBert: A Long Text Processing Method Based on BERT and Hierarchical Attention Mechanisms. Int. J. Semant. Web Inf. Syst. 2023, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golizadeh, H.; Hon, C.K.H.; Drogemuller, R.; Reza Hosseini, M. Digital engineering potential in addressing causes of construction accidents. Autom. Constr. 2018, 95, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurmu, A.T. Hybrid Model for Assessing the Influence of Safety Management Practices on Labor Productivity in Multistory Building Projects. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2021, 147, 04021139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, U.; Sagoo, A.; Benachir, M. Safety Management System (SMS) framework development—Mitigating the critical safety factors affecting Health and Safety performance in construction projects. Saf. Sci. 2021, 143, 105402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.; Jung, W.; Han, S.H. A critical review of text-based research in construction: Data source, analysis method, and implications. Autom. Constr. 2021, 132, 103915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricketts, J.; Barry, D.; Guo, W.; Pelham, J. A Scoping Literature Review of Natural Language Processing Application to Safety Occurrence Reports. Safety 2023, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Ma, L.; Wang, L.; Deng, Y.; Ni, G. Extracting Domain Knowledge Elements of Construction Safety Management: Rule-Based Approach Using Chinese Natural Language Processing. J. Manag. Eng. 2021, 37, 04021001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, T.; Tsai, C.Y.; Lu, Y.; Yao, L. Evolution and emerging trends of named entity recognition: Bibliometric analysis from 2000 to 2023. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Fleyeh, H.; Wang, X.; Lu, M. Construction site accident analysis using text mining and natural language processing techniques. Autom. Constr. 2019, 99, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Gupta, V.; Kumar, M. Recent Named Entity Recognition and Classification techniques: A systematic review. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2018, 29, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, A.; Han, J.; Li, C. A Survey on Deep Learning for Named Entity Recognition. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2022, 34, 50–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Chi, S.; Im, S.B. Automated detection of contractual risk clauses from construction specifications using bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (BERT). Autom. Constr. 2022, 142, 104465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Luo, H.; Fang, W.; Love, P.E.D. A contrastive learning framework for safety information extraction in construction. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2023, 58, 102194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wen, C.; Yuan, Q.; Chen, Q.; Cao, Y. Construction and application of knowledge graph for construction accidents based on deep learning. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2023, 32, 1097–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Chen, S.; Yang, C.; Li, Z.; Luo, L.; Ren, Z. Revealing the coupled evolution process of construction risks in mega hydropower engineering through textual semantics. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2024, 62, 102713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishehgarkhaneh, M.B.; Moehler, R.C.; Fang, Y.; Hijazi, A.A.; Aboutorab, H. Transformer-Based Named Entity Recognition in Construction Supply Chain Risk Management in Australia. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 41829–41851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, F.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Xu, G.; Wang, J. A Novel Named Entity Recognition Algorithm for Hot Strip Rolling Based on BERT-Imseq2seq-CRF Model. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, S.; Cui, D.; Xu, H.; Luo, H. Information Integration of Regulation Texts and Tables for Automated Construction Safety Knowledge Mapping. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2024, 150, 04024034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, B. A rationale-augmented NLP framework to identify unilateral contractual change risk for construction projects. Comput. Ind. 2023, 149, 103940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltagy, I.; Peters, M.E.; Cohan, A. Longformer: The Long-Document Transformer. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.05150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaheer, M.; Guruganesh, G.; Dubey, A.; Ainslie, J.; Alberti, C.; Ontanon, S.; Pham, P.; Ravula, A.; Wang, Q.; Yang, L.; et al. Big Bird: Transformers for Longer Sequences. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2007.14062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wehbe, R.M.; Ahmad, F.S.; Wang, H.; Luo, Y. A comparative study of pretrained language models for long clinical text. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2023, 30, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Hu, Y.; Gu, J.; Han, X. Integrating deep learning and multi-attention for joint extraction of entities and relationships in engineering consulting texts. Autom. Constr. 2024, 168, 105739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morteza, A.; Chou, R.A. Distributed Matrix Multiplication: Download Rate, Randomness and Privacy Trade-Offs. In Proceedings of the 2024 60th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing, Urbana, IL, USA, 24–27 September 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Warner, B.; Chaffin, A.; Clavié, B.; Weller, O.; Hallström, O.; Taghadouini, S.; Gallagher, A.; Biswas, R.; Ladhak, F.; Aarsen, T.; et al. Smarter, Better, Faster, Longer: A Modern Bidirectional Encoder for Fast, Memory Efficient, and Long Context Finetuning and Inference. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.13663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, A.; Fernández, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Bidirectional LSTM Networks for Improved Phoneme Classification and Recognition. In Artificial Neural Networks: Formal Models and Their Applications—ICANN 2005; Duch, W., Kacprzyk, J., Oja, E., Zadrozny, S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 799–804. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Du, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Xie, C.; Li, H.; Li, X. UD_BBC: Named entity recognition in social network combined BERT-BiLSTM-CRF with active learning. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 116, 105460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafferty, J.D.; McCallum, A.; Pereira, F.C.N. Conditional Random Fields: Probabilistic Models for Segmenting and Labeling Sequence Data. In Proceedings of the Eighteenth International Conference on Machine Learning, San Francisco, CA, USA, 28 June–1 July 2001; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.: Burlington, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 282–289. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Long, D.; Yang, C.; Xu, H. Knowledge Graph Improved Dynamic Risk Analysis Method for Behavior-Based Safety Management on a Construction Site. J. Manag. Eng. 2023, 39, 04023023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Yin, Y.; Jiao, L.; Zhang, Y. A data-driven and knowledge graph-based analysis of the risk hazard coupling mechanism in subway construction accidents. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2024, 250, 110254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Ren, G.; Li, H. Knowledge Management in Construction Health and Safety Based on Ontology Modeling. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.H.W.; Goh, Y.M. Ontology for design of active fall protection systems. Autom. Constr. 2017, 82, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Zhong, B.; Luo, H.; Li, H.; Wu, H. Ontology for safety risk identification in metro construction. Comput. Ind. 2019, 109, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Liang, Y.; Guo, C.; Meng, B.; Zhou, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, B. Entity recognition in the field of coal mine construction safety based on a pre-training language model. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2023, 32, 2590–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Li, X. YEDDA: A Lightweight Collaborative Text Span Annotation Tool. In Proceedings of ACL 2018, System Demonstrations; Liu, F., Solorio, T., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Melbourne, Australia, 2018; pp. 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer, H.; Idrissi-Yaghir, A.; Bewersdorff, J.; Frihat, S.; Friedrich, C.M.; Zesch, T. Medication event extraction in clinical notes: Contribution of the WisPerMed team to the n2c2 2022 challenge. J. Biomed. Inform. 2023, 143, 104400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, S.; Kitada, S.; Iyatomi, H. Majority or Minority: Data Imbalance Learning Method for Named Entity Recognition. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 9902–9909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hu, C.; Zhang, R.; Chen, J.; Guo, X. Zero-Shot Cross-Lingual Named Entity Recognition via Progressive Multi-Teacher Distillation. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2024, 32, 4617–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Related Work | Methodology | F1 Score | Research Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| [27] | BERT | 93.4% | Identification of Contractual Risk Clauses in Construction Specifications |
| [28] | CL-CasRel | 66.9% | NER in Safety Documents |
| [29] | BERT-BiLSTM-CRF | 88.26% | Identification of Construction Safety Knowledge Entities |
| [30] | BERT-GPLinker | 91.90% | Identification of Risk Factors in Large-Scale Hydropower Construction Projects |
| [13] | BERT-LSTM | 91% | Extraction of Key Information from Construction Accidents |
| [31] | RoBERTa | 85.80% | NER of Risks in the Construction Supply Chain |
| [32] | BERT-Imseq2seq-CRF | 91.47% | NER in Hot-Rolled Strip Rolling Process Texts |
| [14] | KoBERT | 91.0% | Information Extraction from Construction Defect Reports |
| [15] | RoBERTa | 95.6% | Extraction of Compliance Information in Construction Projects |
| [33] | BERT-BiLSTM-CRF | 85.65% | Extraction of Safety Specification Information in Construction |
| [34] | BERT-base-uncased | 87% | Identification of Risk Elements in Unilateral Contract Changes of Construction Projects |
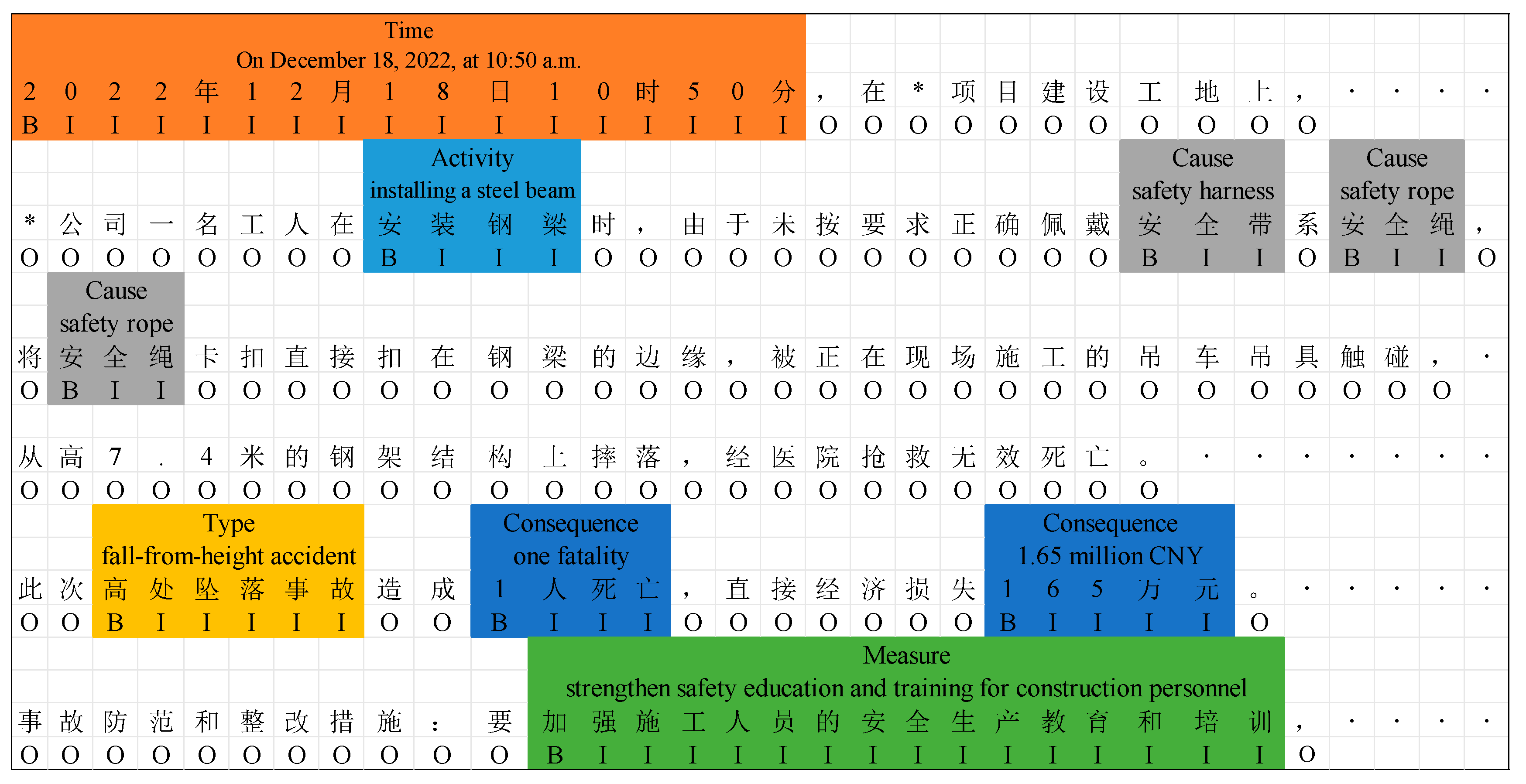
| Entity Category | Definition | Description | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accident Time | Time | The specific time point or time period when the accident occurred. | [44,45] |
| Construction Activity | Activity | The specific construction task being carried out at the time of the accident. | [44,46,47,48] |
| Accident Cause | Cause | The direct and indirect causes of the accident, such as unsafe worker behaviors, mechanical failures, and managerial deficiencies. | [13,29,44,45,46,47,48,49] |
| Accident Type | Type | The nature of the accident, including falls from height, struck-by-object incidents, collapses, etc. | [44,45,47] |
| Accident Consequence | Consequence | The impact of the accident, including casualties, injuries, and economic losses. | [13,29,44,45,46,48] |
| Preventive Measure | Measure | Recommended preventive actions or improvement strategies to avoid similar accidents. | [46,47,48] |
| Model | Precision | Recall | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| BERT | 0.6712 | 0.6753 | 0.6732 |
| BERT-BiLSTM-CRF | 0.7012 | 0.6825 | 0.6916 |
| ModernBERT-BiLSTM | 0.7381 | 0.6225 | 0.6656 |
| ModernBERT-BiLSTM-CRF | 0.6825 | 0.6643 | 0.6731 |
| Model | Precision | Recall | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| BERT | 0.5912 | 0.5743 | 0.5827 |
| BERT-BiLSTM-CRF | 0.6023 | 0.5824 | 0.5922 |
| ModernBERT-BiLSTM | 0.7106 | 0.5756 | 0.6143 |
| ModernBERT-BiLSTM-CRF | 0.6855 | 0.5828 | 0.6234 |
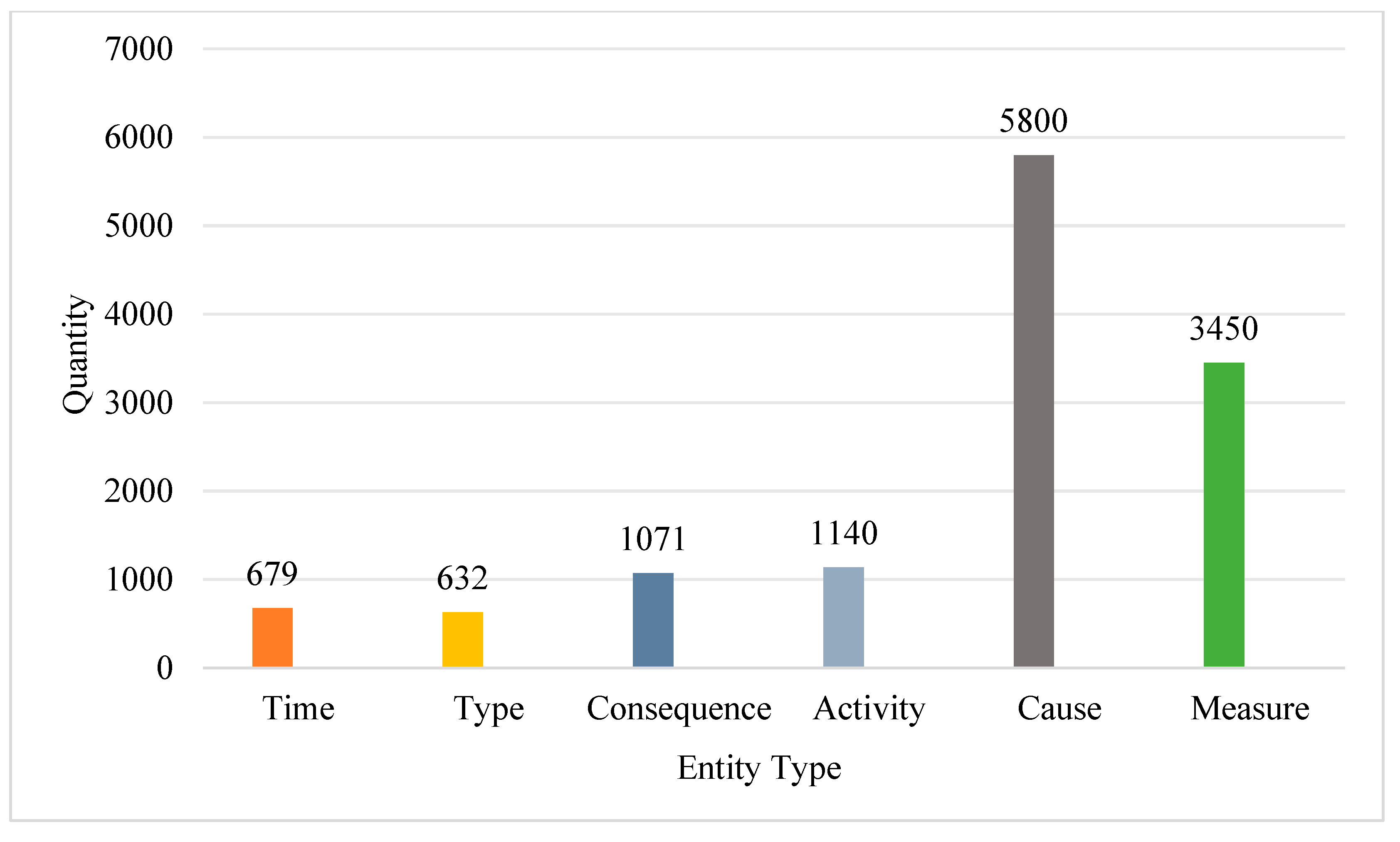
| Entity Category | Precision | Recall | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time | 0.98 | 0.65 | 0.78 |
| Activity | 0.49 | 0.26 | 0.34 |
| Cause | 0.58 | 0.33 | 0.43 |
| Type | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.92 |
| Consequence | 0.93 | 0.97 | 0.95 |
| Measure | 0.68 | 0.31 | 0.41 |
| No. | Related Work | Model | Data Scale | F1 Score | Text Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [36] | Clinical-Longformer | 1304 electronic medical records | Average 0.9055 | 4096 characters |
| Clinical-BigBird | Average 0.8945 | 4096 characters | |||
| 2 | [37] | Longformer-CASREL | 7 engineering consulting standards and specification documents | 0.6899 | 4096 characters |
| 3 | [49] | DeBERTa v3-Longformer | 1017 medical texts | 0.940 | 4096 characters |
| 4 | This method | ModernBERT-BiLSTM-CRF | 529 construction accident investigation reports | 0.6234 | 8192 characters |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Q.; Zhang, G.; Sun, Y. A Novel Method for Named Entity Recognition in Long-Text Safety Accident Reports of Prefabricated Construction. Buildings 2025, 15, 3063. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173063
Luo Q, Zhang G, Sun Y. A Novel Method for Named Entity Recognition in Long-Text Safety Accident Reports of Prefabricated Construction. Buildings. 2025; 15(17):3063. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173063
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Qianmai, Guozong Zhang, and Yuan Sun. 2025. "A Novel Method for Named Entity Recognition in Long-Text Safety Accident Reports of Prefabricated Construction" Buildings 15, no. 17: 3063. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173063
APA StyleLuo, Q., Zhang, G., & Sun, Y. (2025). A Novel Method for Named Entity Recognition in Long-Text Safety Accident Reports of Prefabricated Construction. Buildings, 15(17), 3063. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173063






