Effects of Different Carbonation Treatment Methods for Recycled Concrete Aggregate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Recycled Concrete Aggregate (RCA)
2.2. Cement
2.3. Chemical Agent
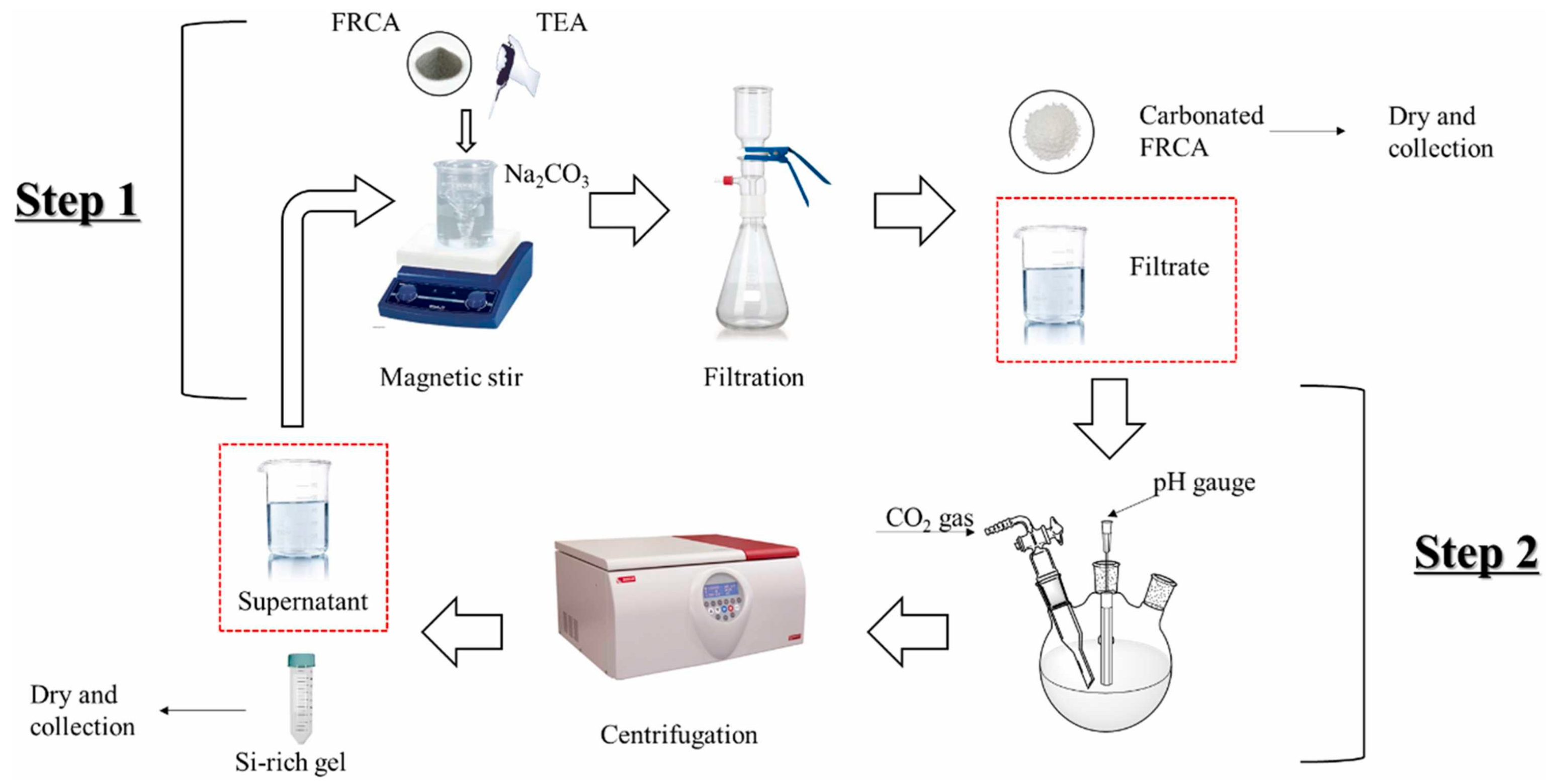
2.4. Treatment Method for RCA and FRCA
3. Testing Methods
3.1. Density and Water Absorption
3.2. Measurement of CO2 Uptake
3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.4. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
3.5. Compressive Strength
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Water Absorption and Density
4.2. Compressive Strength
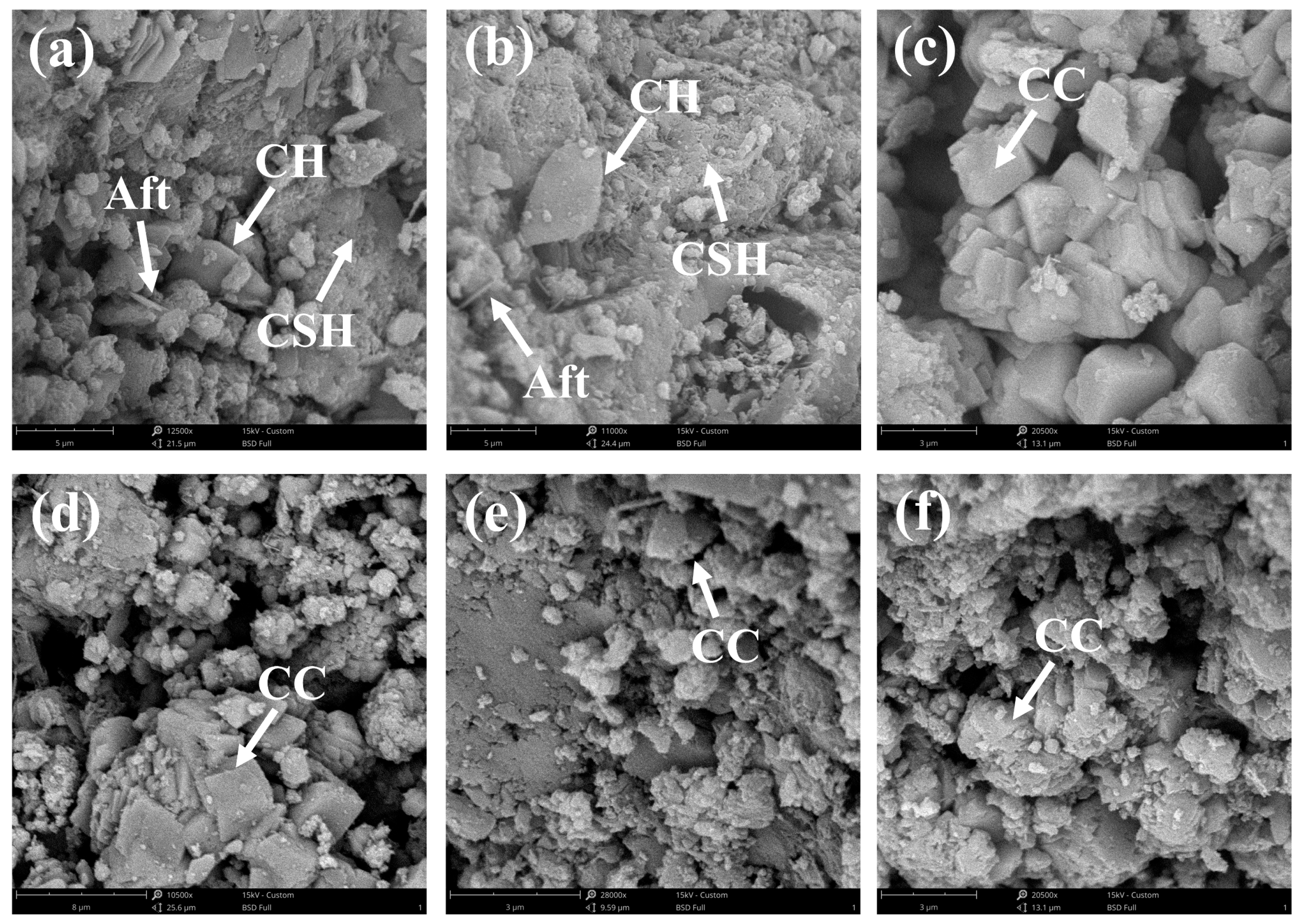
4.3. Microscopic Observation
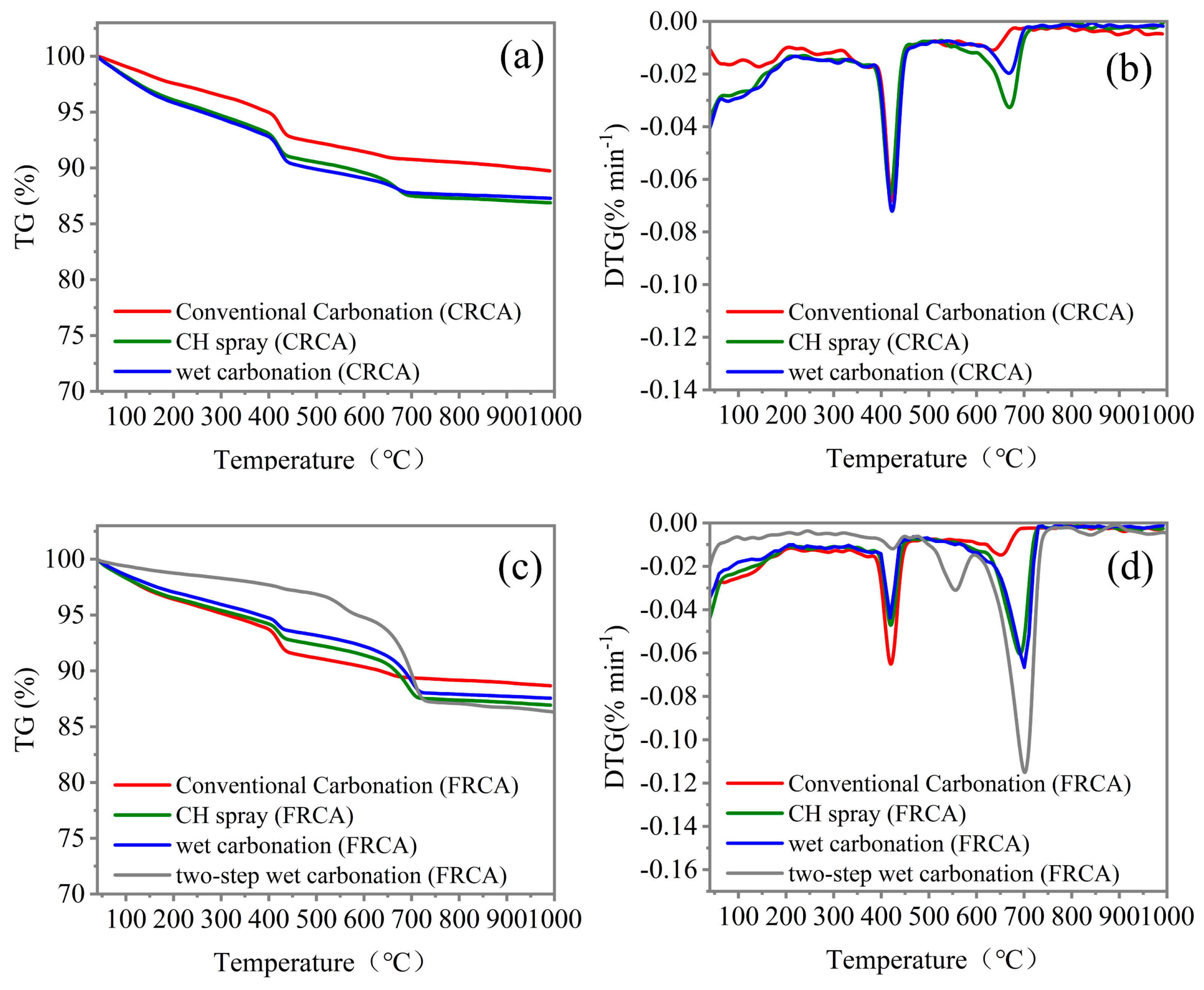
4.4. Hydration Profiles
4.5. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis
4.6. CO2 Uptake
5. Conclusions
- All carbonation methods significantly reduced the water absorption and improved the apparent density of both CRCA and FRCA. This was because carbonation products like calcite (CC) filled the pores and cracks near the surface of CRCA and FRCA particles, making the microstructure denser. In addition, FRCA exhibited particularly notable enhancements because of a higher level of adhered mortar content.
- After carbonation, the hydration products, including CH, C-S-H gel, and Aft, were largely carbonated, and the pores and cracks near the surface areas of the FRCA particles were filled by carbonation products, making the microstructure denser.
- Different carbonation treatments impacted the formation of CC in CRCA and FRCA. For CRCA, the pretreatment of CH spray provided more Ca2+ and resulted in the highest production of CC. For FRCA, liquid–solid wet carbonation was the most effective method for the generation of CC due to a high reaction efficiency.
- Although the pretreatment of CH spray was effective for both CRCA and FRCA and exhibited the highest enhancement in CO2 uptake capacity for CRCA, the reduction in water absorption and improvement in density were inferior to those achieved by wet carbonation, as the reaction primarily concentrates on the quickly densified surface area.
- For FRCA, the two-step wet carbonation achieved a significantly high CO2 uptake of 9.2% compared with conventional carbonation, as the internal pores and cracks were filled instead of just surface accumulating, contributing to the creation of a denser matrix. Meanwhile, in terms of compressive strength, the two-step wet carbonation method had the best enhancement, which was almost close to the conditions of river sand.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Silva, R.V.; De Brito, J.; Dhir, R.K. Properties and Composition of Recycled Aggregates from Construction and Demolition Waste Suitable for Concrete Production. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 65, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Data from National Bureau of Statistics of China. 2023. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/ (accessed on 19 August 2025).
- United Nations Environment Programme. 2023 Global Status Report for Buildings and Construction: Beyond Foundations-Mainstreaming Sustainable Solutions to Cut Emissions from the Buildings Sector; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2024; ISBN 978-92-807-4131-5. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, R.V. Prediction of the Shrinkage Behavior of Recycled Aggregate Concrete: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 77, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, D.; Zhan, B.; Poon, C.S. Assessment of Mechanical Properties of Concrete Incorporating Carbonated Recycled Concrete Aggregates. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2016, 65, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Setién, J.; Polanco, J.A. Structural Recycled Aggregate Concrete Made with Precast Wastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 114, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthiban, K.; Saravana Raja Mohan, K. Influence of Recycled Concrete Aggregates on the Engineering and Durability Properties of Alkali Activated Slag Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 133, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, D.; De Brito, J.; Evangelista, L. Structural Concrete with Simultaneous Incorporation of Fine and Coarse Recycled Concrete Aggregates: Mechanical, Durability and Long-Term Properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 154, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.-C.; Huang, R.; Hwang, H.; Chao, S.-J. Properties of Concrete Incorporating Fine Recycled Aggregates from Crushed Concrete Wastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.; Lian, W.; Fang, X. Characterization of the Interfacial Transition Zone between Wet Carbonated Fine Recycled Aggregate and Fresh Cement Paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 458, 139702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Tan, Q.; Wang, D.; Zhang, F.; Lin, J. Dynamic Performance of Components Constructed from Recycled Concrete Incorporating Aggregates Modified by Accelerated Carbonation. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 95, 110273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Chong, L.; Xie, Z. Performance Enhancement of Recycled Concrete Aggregate—A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarnezhad, A.; Ong, K.C.G.; Zhang, M.H.; Tam, C.T.; Foo, T.W.J. Microwave-Assisted Beneficiation of Recycled Concrete Aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 3469–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Ma, H.; Pan, Y.; Ma, Z.; Duan, Z.; He, Z. Chloride Permeability and the Caused Steel Corrosion in the Concrete with Carbonated Recycled Aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 218, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Long, C.; Tam, V.W.; Poon, C.-S.; Duan, W.H. Effects of Nano-Particles on Failure Process and Microstructural Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 142, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Tng, D.Q.S.; Yang, E.-H. Surface Treatment of Recycled Concrete Aggregates through Microbial Carbonate Precipitation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 57, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Qian, X.; Chen, P.; Xu, Y.; Guo, J. An Environmentally Friendly Method to Improve the Quality of Recycled Concrete Aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 144, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.-C.; Poon, C.-S. Properties of Concrete Prepared with PVA-Impregnated Recycled Concrete Aggregates. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2010, 32, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, G.; Savva, P.; Petrou, M.F. Enhancing Mechanical and Durability Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 158, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zhan, B.; Poon, C.S. Enhancing the Accelerated Carbonation of Recycled Concrete Aggregates by Using Reclaimed Wastewater from Concrete Batching Plants. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 239, 117810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Zhou, Y.; Xing, F. Strategies to Improve the Life Cycle Net CO2 Benefit of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Engineering, 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, W.; Ye, S.; Ou Yong, R.; Tham, K.H.; Wang, C.; Tao, L.; Cheng, S. Techno-Economic Analysis of Mineralization and Utilization of CO2 in Recycled Concrete Aggregates. Processes 2025, 13, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zhan, B.; Poon, C.S. Enhancement of Recycled Aggregates and Concrete by Combined Treatment of Spraying Ca2+ Rich Wastewater and Flow-through Carbonation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 277, 122202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, S.; Kwan, W.H.; Ramli, M. Mechanical Strength and Durability Properties of Concrete Containing Treated Recycled Concrete Aggregates under Different Curing Conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 155, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuvo, A.K.; Sarker, P.K.; Shaikh, F.U.A. Efficacy of Various Accelerated Carbonation Techniques to Improve Recycled Concrete Aggregates: A Comprehensive Review. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 95, 110257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndiaye, S.; Condoret, J.-S.; Bourgeois, F.; Cassayre, L.; Camy, S. High-Pressure Carbonation of Mortar as a Model for Recycled Concrete Aggregates. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2023, 198, 105932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; He, P.; Drissi, S.; Zhang, J.; Hu, X.; Shi, C. Effect of Conditions on Wet Carbonation Products of Recycled Cement Paste Powder. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 144, 105307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Lu, N.; Ma, H.; Ma, Z.; Duan, Z. Carbonation Behavior of Recycled Concrete with CO2-Curing Recycled Aggregate under Various Environments. J. CO2 Util. 2020, 39, 101185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Unluer, C. Enhancement of the Wet Carbonation of Artificial Recycled Concrete Aggregates in Seawater. Cem. Concr. Res. 2024, 175, 107387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Xuan, D.; Zhan, B.; Li, W.; Poon, C.S. A Novel Upcycling Technique of Recycled Cement Paste Powder by a Two-Step Carbonation Process. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 290, 125192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Xuan, D.; Zhan, B.; Li, W.; Poon, C.S. Characterization and Optimization of a Two-Step Carbonation Process for Valorization of Recycled Cement Paste Fine Powder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 278, 122343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Xuan, D.; Shen, P.; Poon, C.S. Fast Enhancement of Recycled Fine Aggregates Properties by Wet Carbonation. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 313, 127867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BS EN 1097-6:2013; Tests for Mechanical and Physical Properties of Aggregates—Part 6: Etermination of Particle Density and Water Absorption. British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2013.
- Chung, F.H. Quantitative Interpretation of X-Ray Diffraction Patterns of Mixtures. I. Matrix-Flushing Method for Quantitative Multicomponent Analysis. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1974, 7, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y.; Fang, H.; Jing, Z.; Chen, P. Revisiting the Carbonation of Recycled Concrete Fine: A pH-Cycle Carbonation Method. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 77, 107438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Xian, X. A Review for Accelerated Carbonation Improvement of Recycled Concrete Coarse Aggregates and the Meta-Analysis of Environmental Benefit Assessment and Cost Analysis of Concrete so Produced. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 106, 112649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabsh, S.W.; Abdelfatah, A.S. Influence of Recycled Concrete Aggregates on Strength Properties of Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 1163–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shen, P.; Xuan, D.; Li, L.; Sojobi, A.; Zhan, B.; Poon, C.S. A Comparison of Liquid-Solid and Gas-Solid Accelerated Carbonation for Enhancement of Recycled Concrete Aggregate. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 118, 103988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, B.J.; Xuan, D.X.; Poon, C.S.; Scrivener, K.L. Characterization of Interfacial Transition Zone in Concrete Prepared with Carbonated Modeled Recycled Concrete Aggregates. Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 136, 106175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhan, B.J.; Lu, J.; Poon, C.S. Systematic Evaluation of the Effect of Replacing River Sand by Different Particle Size Ranges of Fine Recycled Concrete Aggregates (FRCA) in Cement Mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 209, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Lin, Q.; Lin, T.; Wang, D.; Wang, S. Effects of Pressurized Carbonation with Presoaking in Calcium Hydroxide Solution on the Fracture Behaviours of Recycled Coarse Aggregate Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 397, 132386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanapur, N.V.; Tripathi, B.; Pradhan, S.; Chandra, T. Synergistic Effect of Particle Packing Method, Aggregate Saturation Levels, and Paste Content in Improving the Performance of High Volume Fine Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 16901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Xuan, D.; Poon, C.S. Empirical Modelling of CO2 Uptake by Recycled Concrete Aggregates under Accelerated Carbonation Conditions. Mater. Struct. 2017, 50, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouet, E.; Poyet, S.; Le Bescop, P.; Torrenti, J.-M.; Bourbon, X. Carbonation of Hardened Cement Pastes: Influence of Temperature. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 115, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Gu, Z.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Xuan, D.; Zhang, S.; Poon, C.S. Preparation of Reactive Urchin-like Recycled Concrete Aggregate by Wet Carbonation: Towards Improving the Bonding Capability of the Interfacial Transition Zone in Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 143, 105235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesson, B.; Utgenannt, P. Microstructural Changes Caused by Carbonation of Cement Mortar. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Fan, M.; Yang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Yuan, L. A Comparison Study of Aggregate Carbonation and Concrete Carbonation for the Enhancement of Recycled Aggregate Pervious Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 371, 130797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leemann, A.; Moro, F. Carbonation of Concrete: The Role of CO2 Concentration, Relative Humidity and CO2 Buffer Capacity. Mater. Struct. 2016, 50, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Unit (kg/m3) | OPC | Water | Sand | 5–10 mm Aggregate | 10–20 mm Aggregate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 460 | 205 | 700 | 530 | 430 |
| Particle Size (mm) | 0.15–0.3 | 0.3–0.6 | 0.6–1.18 | 1.18–2.36 | 2.36–5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Passing (%) | 35.12 | 19.38 | 25.00 | 15.45 | 5.05 |
| CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | Na2O | SO3 | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 63.51 | 20.82 | 4.48 | 3.33 | 2.82 | 0.56 | 2.25 | 2.23 |
| Group | Type of Aggregate | Method of Carbonation Treatment | Particles of Aggregates (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| I-A | Raw aggregate | 5–10 | |
| I-B | Conventional carbonation for 3 h | ||
| I-C |
| ||
| I-D | Wet carbonation (10 min) | ||
| II-A | River sand | 0.15–5 | |
| II-B | Conventional carbonation for 3 h | ||
| II-C |
| ||
| II-D | Wet carbonation (10 min) | ||
| II-E | Two-step wet carbonation |
| Replacement Ratio | Cement | Water | River Sand | FRCA | Carbonated FRCA | Flowability (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 600 | 300 | 1800 | 0 | 185 ± 10 | |
| 25% | 600 | 300 | 1350 | 450 | ||
| 50% | 600 | 300 | 900 | 900 | ||
| 75% | 600 | 300 | 450 | 1350 | ||
| 100% | 600 | 300 | 0 | 1800 | ||
| 25% | 600 | 300 | 1350 | 450 | ||
| 50% | 600 | 300 | 900 | 900 | ||
| 75% | 600 | 300 | 450 | 1350 | ||
| 100% | 600 | 300 | 0 | 1800 |
| Size Range | Treatment Methods | Density (kg/m3) | Water Absorption (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5–10 mm | I-A | N/A | 2690.0 | 4.65 |
| I-B | Conventional carbonation for 3 h | 2796.7 | 3.92 | |
| I-C |
| 2741.7 | 4.15 | |
| I-D | Wet carbonation | 2772.0 | 3.64 | |
| 0.15–5 mm | II-A | N/A | 2749.14 | 12.37 |
| II-B | Conventional carbonation for 3 h | 2864.3 | 9.22 | |
| II-C |
| 2811.6 | 10.94 | |
| II-D | Wet carbonation | 2933.0 | 7.66 | |
| II-E | Two-step wet carbonation | 2820.9 | 7.68 |
| Conventional Carbonation | CH Spray | Wet Carbonation | Two-Step Wet Carbonation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC% | 7.3 | 8.9 | 11.1 | 16.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, W.; Wang, P.; Ye, N.; Shu, K.; Dai, R.; Ba, M.; Fang, X. Effects of Different Carbonation Treatment Methods for Recycled Concrete Aggregate. Buildings 2025, 15, 3054. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173054
Zhong W, Wang P, Ye N, Shu K, Dai R, Ba M, Fang X. Effects of Different Carbonation Treatment Methods for Recycled Concrete Aggregate. Buildings. 2025; 15(17):3054. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173054
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Weijun, Puyan Wang, Nan Ye, Kai Shu, Rongnan Dai, Mingfang Ba, and Xiaoliang Fang. 2025. "Effects of Different Carbonation Treatment Methods for Recycled Concrete Aggregate" Buildings 15, no. 17: 3054. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173054
APA StyleZhong, W., Wang, P., Ye, N., Shu, K., Dai, R., Ba, M., & Fang, X. (2025). Effects of Different Carbonation Treatment Methods for Recycled Concrete Aggregate. Buildings, 15(17), 3054. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15173054







