1. Introduction
Box-shaped hollow thin-walled piers are widely employed in bridge engineering due to their high strength-to-weight ratio. However, under peripheral compressive loads (e.g., hydrostatic and ice pressure), their inner walls exhibit significant susceptibility to flexural cracking, potentially leading to structural leakage and durability degradation [
1,
2]. This vulnerability is particularly critical in water-submerged environments, such as reservoir impoundment zones, where existing piers may experience unforeseen loading regimes. The renovation of the Ulahada Water Control Project (Zhangjiakou, Hebei) exemplifies this challenge: submerged piers along the Zhangjiakou–Chengde Expressway now face combined hydrostatic pressure and seasonal ice thrust.
For the reinforcement of box-shaped hollow thin-walled piers, the most common solutions include external steel jacketing, external reinforced concrete jacketing, and internal concrete infilling. While these methods offer construction convenience and widespread application, their reinforcement effectiveness is often limited, material consumption is substantial, and they struggle to adequately address structural issues arising from peripheral loads. Pavese et al. [
3] and Lignola et al. [
4] investigated the application of fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) composites in the seismic retrofitting of hollow piers, paving the way for the utilization of novel materials in this field. Building on engineering precedents, Epackachi et al. [
5], Choi et al. [
6], and Nie et al. [
7] demonstrated the versatility and superior performance of steel plate reinforcement applied to bridge piers across diverse projects. Notably, the high-strength tensile properties exhibited by steel plates in these practical applications are well-aligned with the predominantly circumferential tensile stresses generated in thin-walled piers under combined ice–water pressure. This synergy offers a viable solution pathway for the specific challenge addressed in this study. Furthermore, Adriano Reggia et al. [
8] proposed a method involving an external jacket of high-performance fiber-reinforced concrete (HPFRC) encasing the hollow pier. This technique aims to enhance the pier’s load-bearing capacity and ductility, thereby improving its resistance to both traffic loads and seismic loads. Their experimental verification demonstrates the superiority of composite reinforcement schemes for hollow-pier strengthening projects.
However, current strengthening strategies for box piers primarily target seismic retrofitting [
9,
10], axial load enhancement [
8,
11], or damage repair [
12,
13], with limited focus on peripheral pressure-induced failure. Notably, ice pressure—characterized by high local intensity [
14,
15,
16]—demands specialized solutions. While fiber-reinforced polymers (FRPs) and steel jacketing have been studied for seismic contexts, their efficacy against distributed circumferential bending remains underexplored. To address this gap, we propose a steel plate-bonded composite strengthening system tailored for localized flexural resistance. This method leverages the high tensile strength of externally bonded steel plates to counteract hoop stresses in pier walls, mitigating crack propagation under hydrostatic–ice loading.
Based on the mechanical characteristics of piers under hydrostatic and ice pressure, we establish a mechanical model of the strengthened system. Through the structural mechanics theory, we analyze the load-bearing mechanisms of individual components and establish a mechanical model of the strengthened structure, deriving theoretical formulas for stress responses. Within this framework, allowable stress and displacement limits are defined. Concurrently, practical constructability considerations inform the adjustability ranges of key strengthening parameters.
Due to the strong coupling and highly nonlinear nature of steel plate-reinforcement design involving multiple parameters, such as thickness, height, and hoop spacing, traditional methods struggle to achieve efficient optimization. This paper proposes the introduction of a genetic optimization algorithm to address this challenge. We formulate a cost-minimization objective function and develop a genetic algorithm (GA)-based optimizer for key parameters (plate thickness, bonding length, adhesive stiffness). The program determines the optimal design solution through iterative computation. Finally, finite element (FE) models of the optimized structure are established. Comparative analysis with the original structure’s FFE results validates the design rationality through computational verification. FE models of optimized designs are benchmarked against unreinforced piers, evaluating stress redistribution, displacement compliance, and validating the design rationality. And the core methodological innovation of this study lies in proposing and implementing the integration of composite reinforcement theory models with advanced intelligent optimization algorithms, thereby establishing a holistic framework to systematically address these complex reinforcement design challenges.
2. Strengthening Design
The proposed composite strengthening system for box-shaped concrete bridge piers, utilizing externally bonded steel plates, is illustrated in
Figure 1. The internal structure in the figure is the original concrete box pier. The geometric parameters of strengthening materials shown are provisional rather than final, as optimal values will be determined through subsequent design optimization.
Implementation procedure:
① Cast concrete infill blocks at pier nodal zones;
② Install circumferential steel plates supported by these blocks;
③ Inject waterproof polymeric foam into the gap between steel plates and the existing structure.
Polymer-modified concrete (PMC) is employed for bonding at both [
11,
17,
18]:
(a) Concrete infill block-to-existing concrete interface;
(b) Steel plate-to-infill block interfaces.
The core innovation lies in modifying load transfer paths by leveraging steel’s superior tensile properties and elastic modulus differentials between materials, within the pier cross-section. The original rigid-frame system (subjected to combined compression-flexure) transforms into a compression–truss mechanism carrying purely compressive loads. The externally bonded steel plates function as a suspended-cable system, transferring peripheral pressures to nodal zones.
Considering the hydrostatic pressure acting perpendicular to contact surfaces, the steel plate profile adopts an arcuate configuration based on the principle of optimal arch axis [
19,
20]. This design capitalizes on three key advantages: steel’s high tensile strength, concrete’s compressive performance, and structural efficiency of truss systems. Three parties collectively address failure modes induced by peripheral ice–water pressure.
Additionally, this configuration induces biaxial-to-triaxial compressive stress states in the original pier, implicitly enhancing its load-bearing capacity for sustained and live loads [
21,
22].
3. Theoretical Mechanical Analysis of the Strengthening Scheme
3.1. Development of Mechanical Model
The adopted strengthening system transfers peripheral ice–water pressure loads to externally bonded steel plates, which subsequently transmit forces to nodal zones of the box-shaped pier via concrete infill blocks. This mechanism transforms the original flexure-dominant rigid-frame system into a compression-governed truss system, significantly enhancing peripheral load resistance.
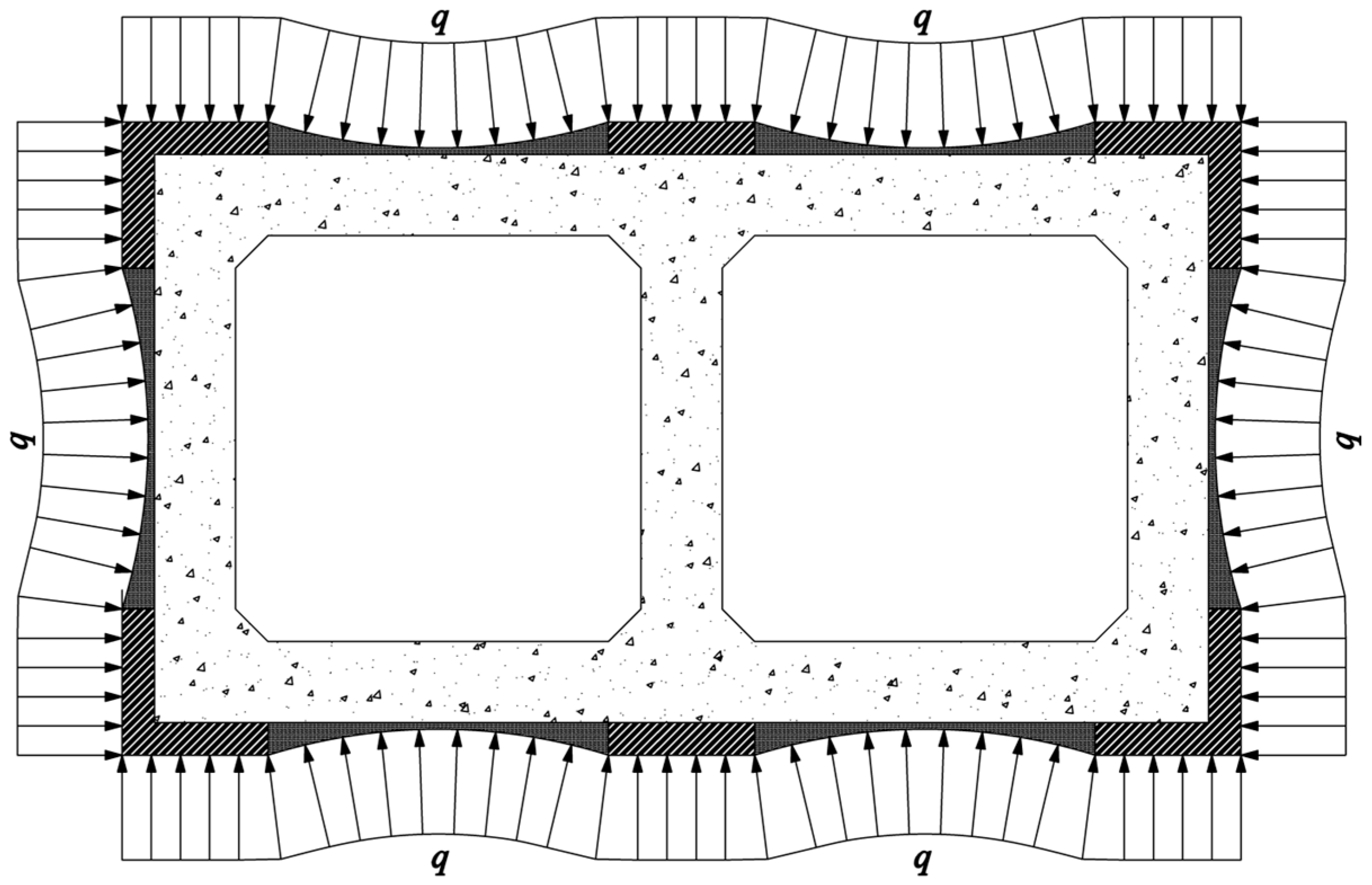
Figure 2 illustrates the global force distribution of the strengthened pier, assuming symmetric uniform pressure loading of 1.5 MPa.
The strengthened structure comprises two interactive components: inner original concrete structure and external steel plate system.
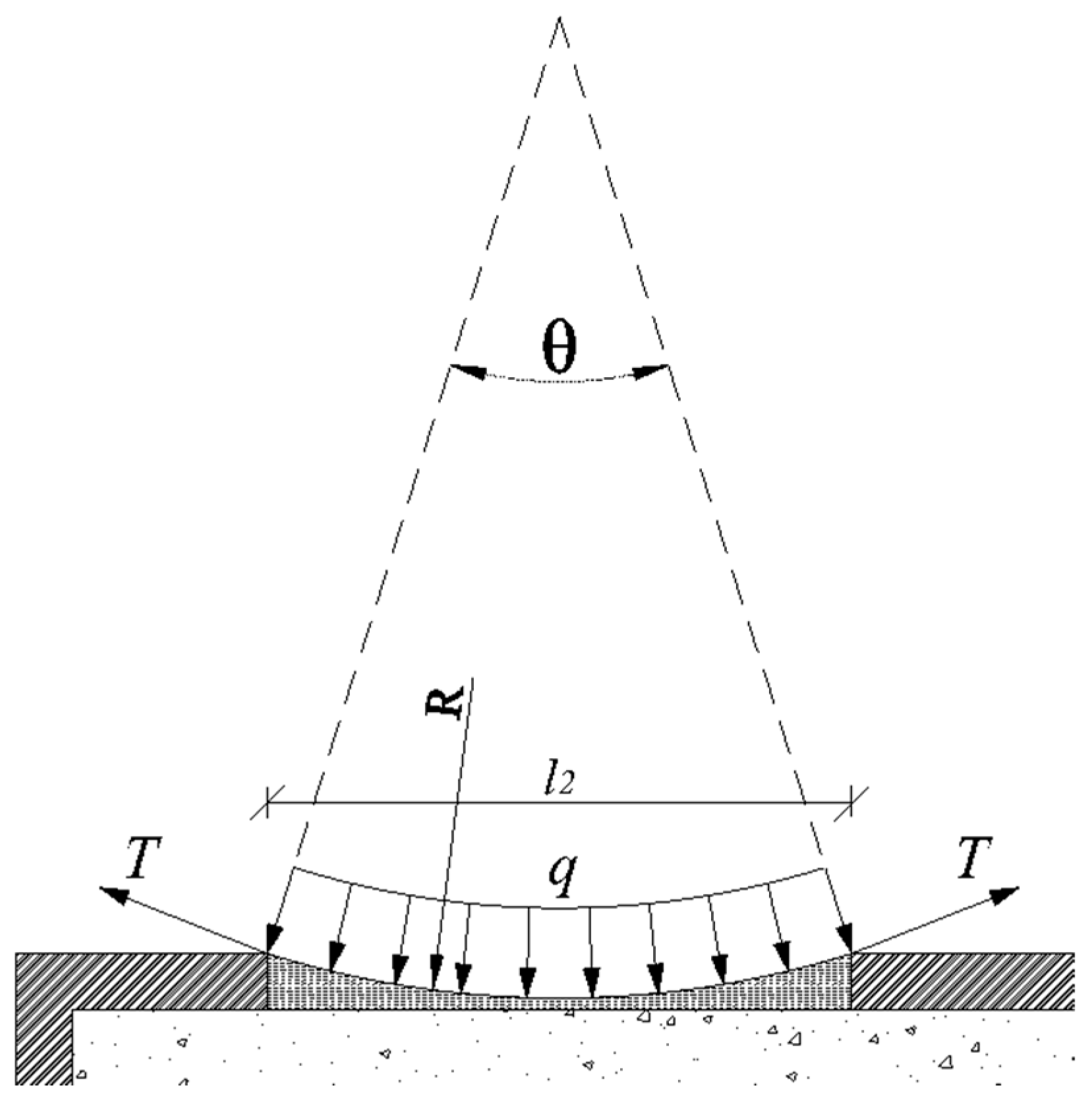
Steel plate analysis: The circumferential steel plate functions as a suspended-cable main girder supported on infill blocks, subjected to uniformly distributed loads normal to its axis. Considering only axial tension effects and invoking the principle of optimal arch axis under uniform radial loading, the plate adopts an arcuate profile with span
l2 and angular span
θ (
Figure 3).
Original concrete structure analysis: Modeled as a moment-resisting frame, the concrete box structure sustains three primary force actions (
Figure 4):
① Direct compressive loads transmitted through nodal infill blocks;
② Support reactions at steel plate endpoints;
③ Shear forces induced by steel plate tension via infill blocks.
Figure 4.
Simplified force diagram of original concrete structure.
Figure 4.
Simplified force diagram of original concrete structure.
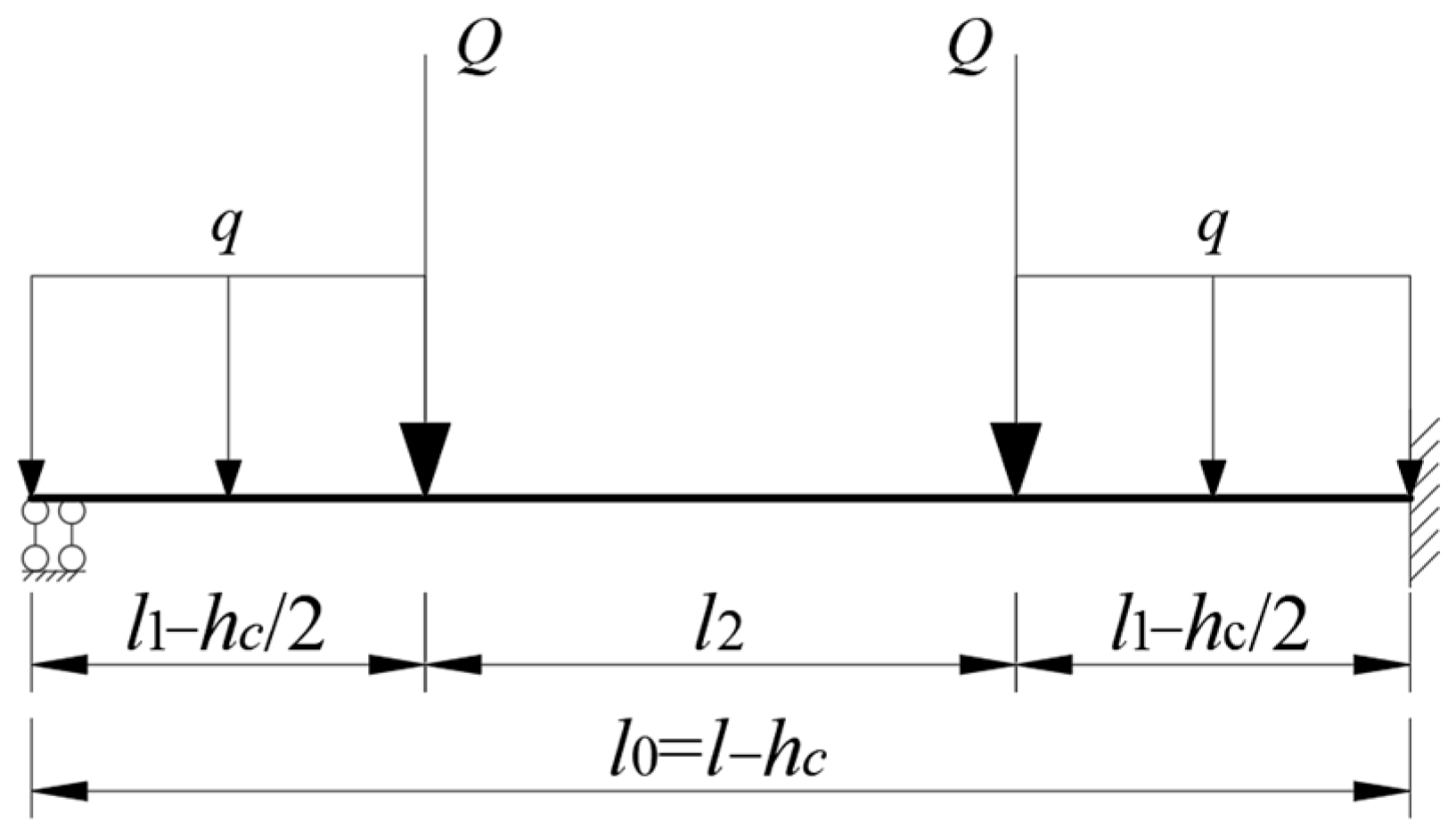
Leveraging structural symmetry and symmetric loading conditions, the six nodal zones of the box pier are approximated as rotationally fixed (
θ = 0) while permitting axial displacement. Accounting solely for bending effects in pier walls, the mechanical system further simplifies to the schematic shown in
Figure 5.
3.2. Structural Mechanics Derivation
3.2.1. Steel Plate Analysis
The steel plate is subjected to a uniform radial load, q, and a counterpressure, q1(s) (a function of arc coordinate s), from the foam material. Given the negligible elastic modulus of the foam material, q1(s) is disregarded. Thus, the net radial force is approximated as q.
The tensile force in the steel plate is:
Assumption: Minor deformation-induced load variations are neglected.
The support reaction at concrete nodes is derived as:
3.2.2. Concrete Beam-Bending Analysis
The pier wall is modeled as a beam with one end fully fixed and the other end rotationally constrained, subjected to symmetric loading comprising a uniform distributed load, q, and a concentrated loads, Q. Based on the principle of linear superposition, the structure is decomposed into scenarios subjected separately to a symmetric uniform distributed load, q, and symmetric concentrated loads, Q. The internal force effects induced by these two load cases are then superimposed. The force method, as shown in Equation (3), is employed to solve for the internal force effects in the beam under each load condition.
Applying linear superposition theory:
Based on structural analysis, the maximum bending moment (indicating the most critical section) occurs at the mid-span section of the beam. The mid-span bending moment is given by:
The peak tensile stress of the structure—the tensile stress to which the bottom edge of the concrete at the mid-span cross-section is subjected—is as follows:
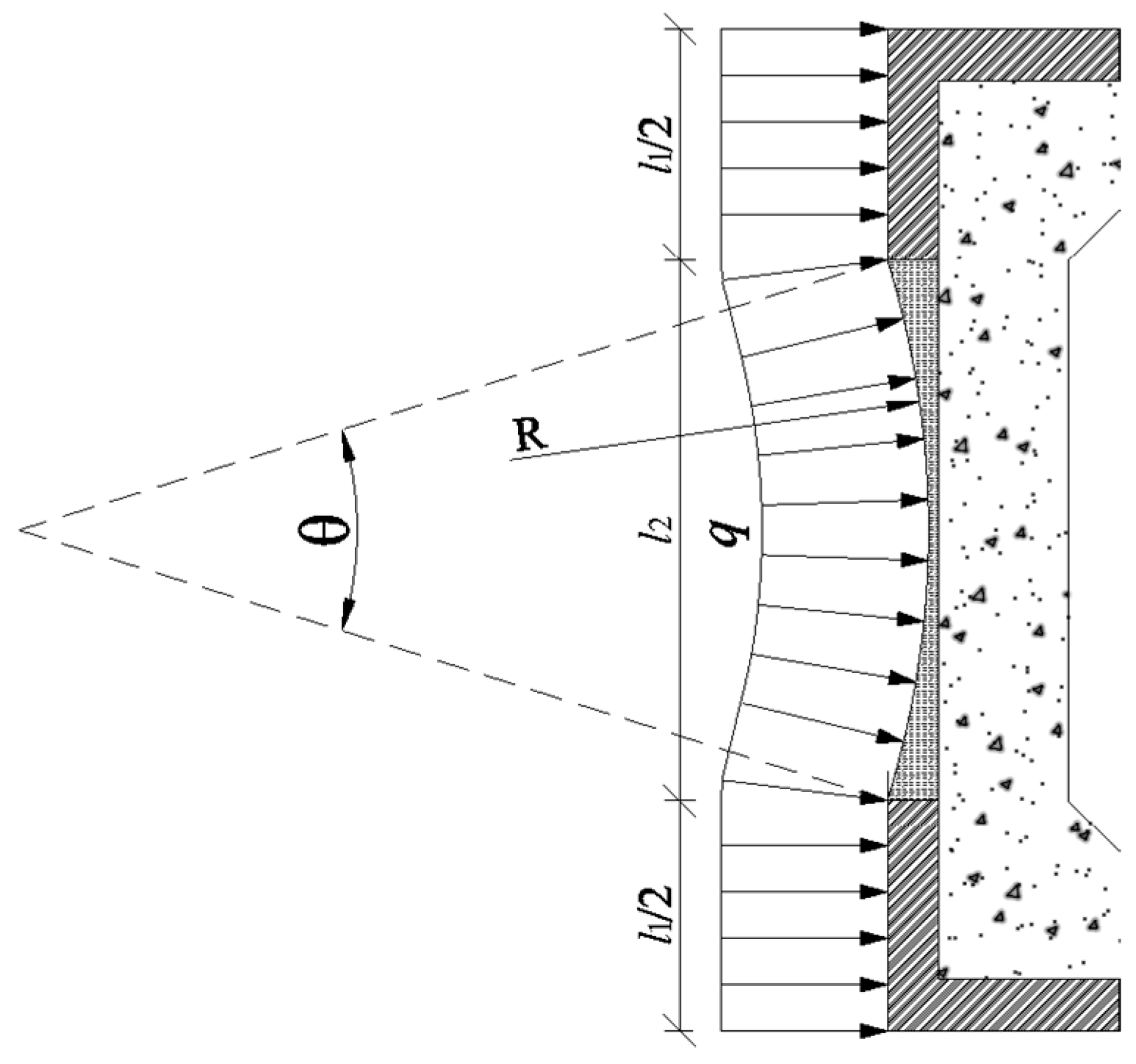
3.2.3. Concrete-Beam Axial Compression Analysis
Eripheral ice pressure induces beneficial compressive stresses superimposed on bending effects. Axial forces originate from direct transverse pressure on cross-girders and tensile action from plate deflection. As shown in
Figure 6, the cross-girder is subjected to forces from both straight and curved plate segments.
Force from the straight plate segment:
Force from the curved plate segment:
The net tensile stress at the critical section (mid-span bottom fiber) becomes:
3.3. Derivation of Steel Plate Deformation
To minimize reinforcement material consumption and reduce the scale of the strengthening works, the concrete pads should be designed with minimal thickness while satisfying the required sagging height of the steel plate. Under peripheral loading, relative displacements occur throughout the structure [
23]. The relative deformation between the curved steel plate segment and the inner concrete beam directly influences the magnitude of plate sagging. Furthermore, the deflection of the curved steel plate segment exhibits significant sensitivity to external loads. Consequently, it is necessary to calculate the sagging magnitude of the curved steel plate segment under applied structural loads. The downward deflection of the steel plate is primarily induced by the following factors:
(1) Variation in Support Height: The compressive deformation of the concrete pads under load reduces the support height. However, given that the pads utilize C50 concrete with a high elastic modulus and possess a geometric thickness significantly smaller than the overall model dimensions, the compressive deformation of the concrete pads under pressure loading can be considered negligible.
(2) Reduction in Steel Plate Span: Axial compression of the beam leads to a reduction in the span of the steel plate, resulting in downward deflection. Following deformation, the structure remains subjected to a uniformly distributed load perpendicular to its surface. Neglecting the bending resistance contribution of the steel plate, the deformed configuration of the structure can still be idealized as an arc segment. The span of the deformed steel plate is expressed as:
(3) Elongation of Steel Plate Arc Length: Under external loading, the steel plate experiences tensile elongation. The increase in the arc length of the steel plate contributes to an increase in deflection. The arc length of the deformed steel plate is given by:
In summary, the relative deformation between the steel plate and the concrete beam at the mid-span position is:
where the relationship between the radii of the steel plate before and after deformation is:
4. Optimization Based on a Genetic Algorithm
4.1. Optimization Problem
Considering the complexity and specificity of the optimization problem, coupled with the highly nonlinear nature of the objective function and the presence of multiple constraints, this study proposes a genetic algorithm (GA)-based optimization tool for the composite reinforcement scheme of immersed box-type bridge piers [
24,
25,
26]. This tool addresses the structural parameter setting problem for the reinforcement scheme. The design variables, objective function, and constraints are defined as follows:
(1) Design Variables: Based on the preliminary design of the reinforcement scheme and practical engineering considerations, the following mutually independent adjustable design parameters are established:
(a) Span of the curved steel plate segment (l2);
(b) Thickness of the steel plate (hs);
(c) Thickness of the concrete bedding layer (h);
(d) Rotation angle of the steel plate (θ).
These parameters allow for the adjustment of the concrete pad and steel plate thicknesses, as well as the steel plate span and its rotation angle.
(2) Objective Function: The reinforcement structure design prioritizes project economy, forming the basis for the objective function. The unit cost of materials is presented in
Table 1. The formulated objective function is given by Equation (13).
(3) Constraint Conditions: The optimization process for this reinforcement scheme primarily considers stress constraints and displacement constraints. Under peripheral loading, cracking must be prevented in the concrete of the box-shaped hollow thin-walled pier’s inner wall. Consequently, the tensile stress (
σ) at the inner wall mid-span must be less than the design tensile strength of C40 concrete (
ftd = 1.65 MPa). The tensile stress in the steel plate (
σs) under external loading must not exceed its strength limit, i.e., it must be less than the design tensile strength of the steel (
fd = 270 MPa). Furthermore, significant downward deflection occurs in the steel plate. To prevent excessive deformation causing direct contact with the concrete structure—which could lead to stress concentration in the plate and cracking in the concrete—the steel plate deformation must be constrained. Additionally, a safety clearance of 2 cm is incorporated to account for construction tolerances and unforeseen adverse factors. This ensures that the minimum clearance between the deformed steel plate and the outer concrete wall remains greater than 2 cm. The constraint equations for the relevant design parameters are given by Equations (14)–(16):
4.2. Genetic Algorithm
4.2.1. Encoding Scheme
This study employs a real-number encoding scheme to directly represent the physical meaning of the design variables. Each chromosome comprises four genes:
l2,
hs,
h, and
θ [
27,
28]. Real-number encoding eliminates the decoding error inherent in binary encoding, preserves the physical precision of the design variables, perfectly aligns with the continuous nature of engineering parameters, and enhances the algorithm’s search efficiency within continuous search spaces [
29].
4.2.2. Population Initialization
The initial population is generated using a uniform sampling strategy. The No Free Lunch (NFL) theorem indicates that uniform sampling is the optimal strategy for covering the entire search space in the absence of prior knowledge [
30,
31]. For complex engineering problems potentially harboring multiple local optima, uniform sampling helps avoid entrapment by engineering intuition biases. From a computational efficiency perspective, uniform sampling exhibits a time complexity of O(n), offers high computational efficiency, imposes no additional storage requirements, and is independent of historical data or spatial partitioning structures. It also possesses excellent parallelization characteristics: each sample is generated independently, making it suitable for GPU acceleration. Consequently, initial individuals are randomly generated within the defined variable domains using the uniform sampling method. The design variable domains are set as follows:
(a) Net span of the steel plate: l2 ∈ [100, 2500] (mm);
(b) Thickness of the reinforcing steel plate: hs ∈ [10, 500] (mm);
(c) Height of the concrete pad: h ∈ [10, 500] (mm);
(d) Rotation angle of the steel plate: θ ∈ [0.1, π] (rad).
4.2.3. Crossover Operator
The Simulated Binary Crossover (SBX) operator is employed to simulate the recombination process of biological chromosomes [
32,
33]. The direct use of binary crossover would disrupt the structure of the continuous search space; therefore, SBX is utilized to precisely control the distribution of offspring [
34,
35]. The SBX operator enables controlled exploration via the distribution index
η. A larger
η results in offspring positioned farther from the parents, while a smaller
η yields offspring closer to the parents. The offspring generation formula is given by Equation (17):
where
u is a uniform random number
u ∈ [0, 1]. When
u ≤ 0.5,
. If
η → 0,
β exhibits significant variability, resulting in offspring distributed at diverse locations (strong exploration). If
η → ∞,
β ≈ 1, resulting in offspring close to the parents (weak exploration). When
u > 0.5,
, generating offspring outside the parental range and exploring new regions.
4.2.4. Mutation Operator
The polynomial mutation (PM) operator implements intelligent perturbation to simulate biological gene mutation [
36,
37,
38]. PM controls the mutation strength via the distribution index,
η, allowing adaptive adjustment of the mutation step size based on an individual’s position within the search space. The mutation formula is given by Equation (18):
where
represent the relative distances of the individual
x to the lower bound and upper bound, respectively, and
u is a uniform random number
u ∈ [0, 1]. The PM operator dynamically senses the individual’s position through
δ1 and
δ2. When an individual is near a boundary, the mutation amplitude decreases to prevent exceeding the feasible domain and generating invalid mutations. When an individual is far from boundaries, the mutation amplitude increases, enhancing global exploration capability. The distribution index,
ηm, governs the mutation strength: a larger
ηm results in smaller mutation amplitudes, facilitating local fine-tuning, while a smaller
ηm produces larger mutation amplitudes, suitable for global exploration.
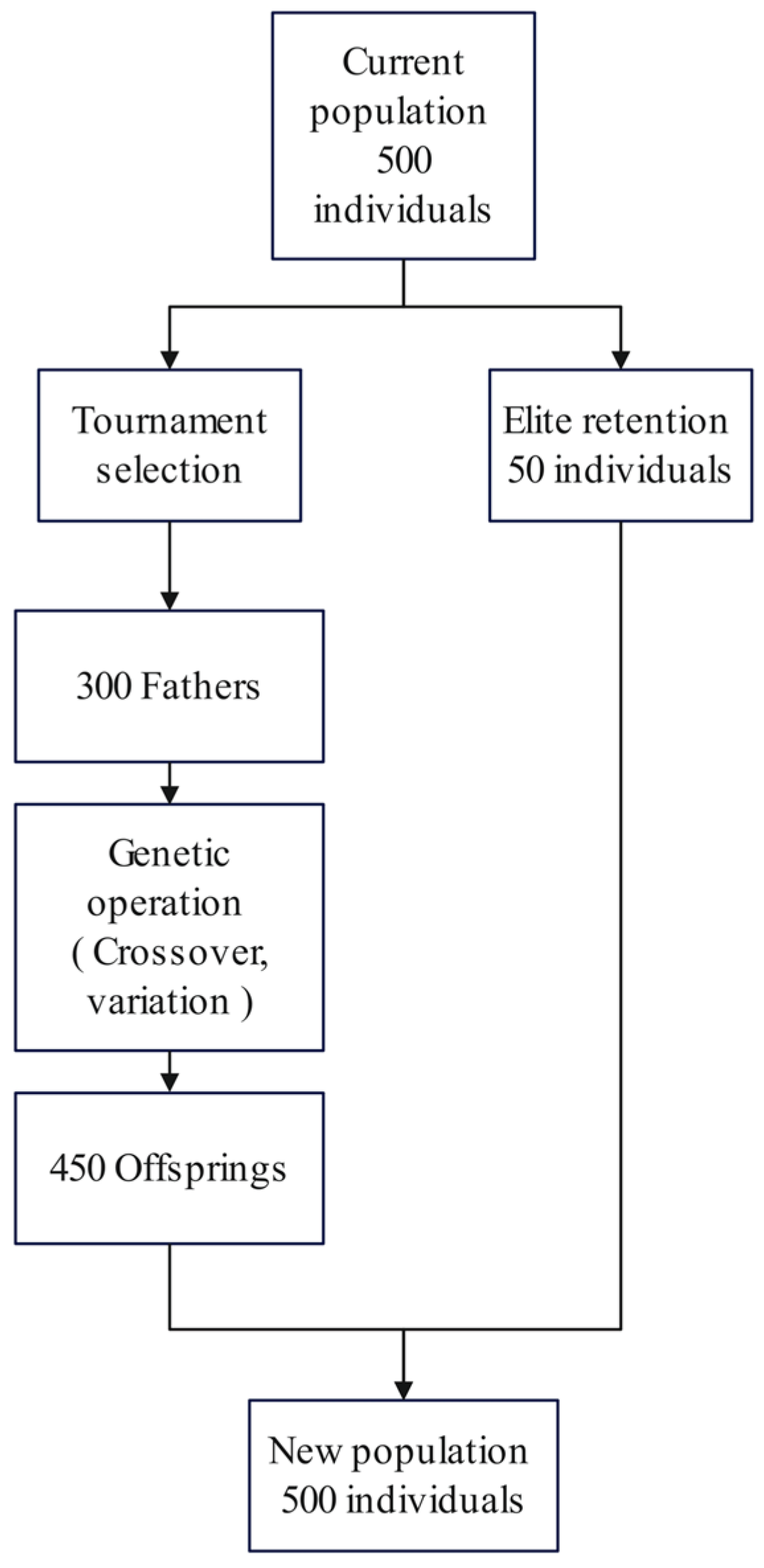
4.2.5. Selection Mechanism and Elite Preservation
Selection mechanisms and elite preservation strategies constitute the core components enabling genetic algorithms to realize the evolutionary principle of “survival of the fittest.” Collectively, they determine the direction and efficiency of population evolution. For the engineering optimization problem addressed in this study, these mechanisms were meticulously tailored to ensure algorithmic efficiency and robustness within complex constrained environments.
The selection mechanism emulates the natural process of “selective elimination,” with its primary objective being the screening of high-quality individuals from the current population for reproduction. This study employs a hybridized selection strategy.
i. Tournament selection
The tournament selection algorithm is widely adopted in genetic algorithms and evolutionary computation for selecting high-quality individuals. Through its localized deterministic comparison mechanism, it mitigates excessive stochastic interference and prevents dominance by super-individuals [
39,
40,
41]. This approach demonstrates significant advantages over roulette wheel selection in terms of convergence speed, solution stability, computational efficiency, and parameter controllability [
42,
43].
ii. Constrained dominance principle
In engineering optimization, feasibility requirements take precedence over objective values [
44,
45]. A tiered selection criterion enforces hierarchical prioritization wherein (1) feasible solutions strictly dominate infeasible solutions; (2) individuals exhibiting smaller aggregate constraint violations are prioritized; and (3) superior objective function values are subsequently considered. The operational logic of this selection mechanism is formally delineated in
Figure 7.
Elite preservation is a critical mechanism in evolutionary algorithms that prevents the loss of high-performing individuals during genetic operations and maintains superior genetic material within the population, effectively serving as a memory unit of the evolutionary process. This study designs an adaptive elite pool management strategy comprising three core components—elite identification, dynamic preservation ratio adjustment, and elite injection—to ensure effective elite retention.
i. Elite Identification Mechanism
The identification of elite individuals adheres to a tiered sorting principle to address the common coexistence of feasible and infeasible solutions in constrained optimization problems [
46]. The specific procedure executes as follows: the current population is rigorously partitioned into feasible and infeasible solution sets; the feasible set is sorted in ascending order by objective function value (where lower values receive higher rank); concurrently, the infeasible set is sorted in ascending order by aggregate constraint violation (with lower violation indicating greater proximity to the feasible domain boundary and higher evolutionary potential). Following preset elite preservation ratios, selection prioritizes top-ranked individuals from the sorted feasible set; should feasible elites prove insufficient to satisfy the preservation quota, the best-performing individuals from the leading portion of the sorted infeasible set are supplemented. This mechanism thus guarantees retention of promising boundary solutions under scarce feasible solutions.
ii. Elite Injection Mechanism
Identified elite individuals are granted privileged direct entry into the subsequent generation, exempt from participation in ensuing genetic operations (selection, crossover, mutation). During new population construction, all elite members are initially injected into the nascent population; the remaining vacancies are then populated by offspring generated through genetic operations until the preset population size is attained. This mechanism thereby ensures lossless preservation of the most superior genetic material across generational transitions.
4.2.6. Constraint-Handling Mechanism
Constraint handling constitutes a fundamental challenge for genetic algorithms in engineering optimization, particularly under the complex nonlinear constraints investigated in this study. The discrimination between feasible and infeasible solutions serves as a foundational premise for algorithmic design in constrained optimization. This research strictly adheres to the Feasibility Precedence Principle: feasible solutions maintain absolute priority throughout the evolutionary process. This principle is implemented through the fitness evaluation function as follows: for individuals satisfying all constraints, their original objective function value directly defines fitness to ensure performance-based selection within the feasible domain; conversely, for those violating any constraint, a penalization mechanism assigns fitness as the summation of a sufficiently large constant and their aggregate constraint violation magnitude. This dual approach guarantees both the absolute precedence of feasible solutions and differentiation among infeasible individuals based on violation severity.
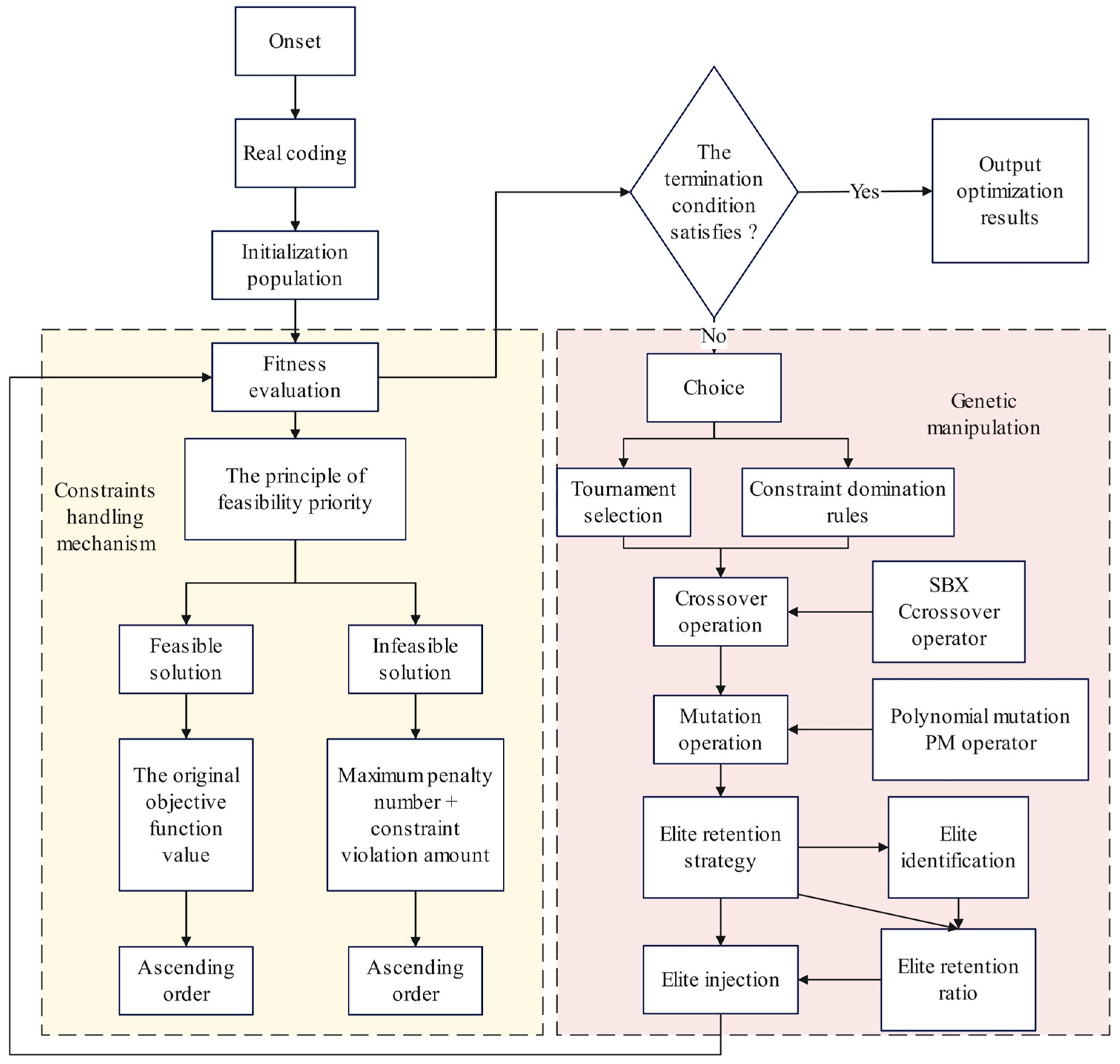
4.3. Optimization Workflow
Upon genetic algorithm initialization, the process commences with a setup phase: a predefined real-valued encoding scheme constructs the solution space while randomly generating an initial population as the first-generation candidate solution set. The algorithm subsequently progresses to the evaluation and constraint-handling phase, computing the raw objective function value for each individual. Here, the Feasibility Precedence Principle is rigorously enforced: solutions satisfying all constraints retain their original objective values, whereas infeasible solutions undergo computation of aggregate constraint violation with fitness recorded as “violation magnitude + sufficiently large penalty constant” through penalization. This mechanism ensures infeasible solutions exhibit significantly inferior fitness relative to feasible counterparts, thereby actively guiding the search toward the feasible domain.
Post-evaluation, the algorithm sorts the population in ascending order of fitness values, positioning superior individuals (lower fitness) at higher ranks. Termination conditions are subsequently verified: if satisfied, the current optimal solution is output as the final optimization result; if unmet, the process proceeds to the genetic evolution phase. During selection operations, parent individuals are screened through tournament rules and the constrained dominance principle, ensuring feasible solutions consistently dominate infeasible counterparts. Among infeasible solutions, those exhibiting smaller aggregate constraint violations are prioritized; among feasible solutions, individuals with superior objective function values are selected.
Following parental selection, evolutionary operations are executed to generate offspring: the crossover operation employs the Simulated Binary Crossover (SBX) operator, which emulates binary string crossover to recombine real-coded parental chromosomes while preserving population diversity and inheriting advantageous genetic traits; concurrently, the mutation operation applies polynomial mutation to impart minimal stochastic perturbations to offspring solutions, facilitating escape from local optima and exploration of novel regions within the solution space.
Following evolutionary operations, the elite preservation strategy is implemented: elite individuals (e.g., top 10% by fitness rank) are identified from the current generation and directly retained in the subsequent population via the elite injection mechanism, displacing inferior offspring. This fixed-ratio strategy ensures historical optima remain immune to disruptive evolutionary operations, thereby effectively balancing convergence rate with global exploration capability.
Finally, the newly generated population—comprising offspring from crossover/mutation operations and preserved elite individuals—serves as the initial population for the subsequent generation. This initiates the iterative re-execution of the full cycle, evaluation → sorting → selection → evolution → elite preservation, until termination criteria are satisfied. Through the synergistic integration of constraint handling mechanisms, evolutionary operators, and elite strategies, the process asymptotically converges toward the optimal feasible solution. The comprehensive workflow of this genetic algorithm optimization framework is delineated in
Figure 8.
4.4. Genetic Algorithm Parameter Optimization
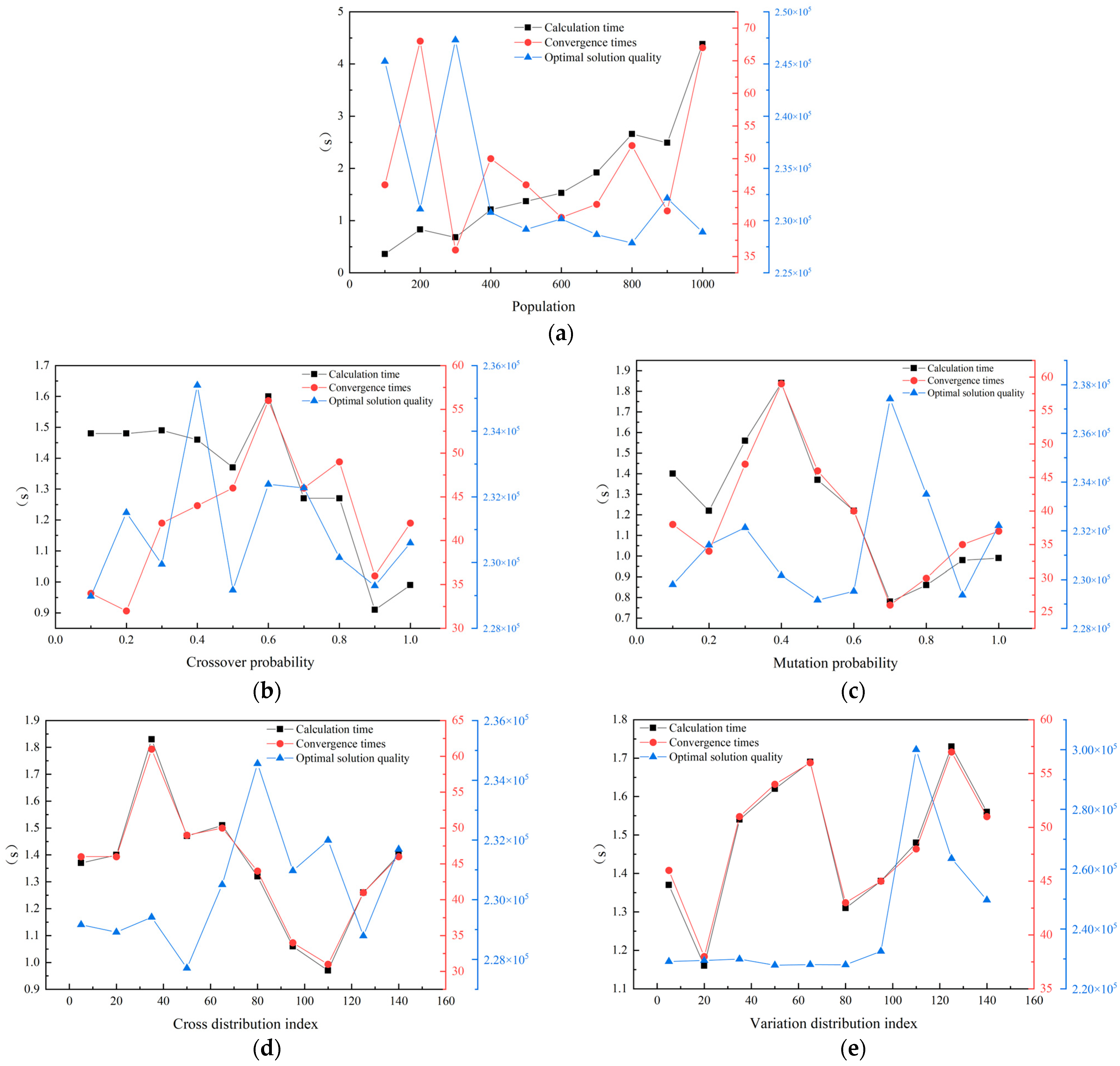
The performance of genetic algorithms (GAs) is highly dependent on parameter configuration. Inappropriate parameter settings can lead to premature convergence, low search efficiency, or wastage of computational resources. To ensure the robustness of the algorithm in engineering optimization, this study systematically optimized key parameters through sensitivity analysis.
A controlled variable method was employed to independently test core parameters, evaluating their impact patterns on algorithm performance. Convergence was defined as the condition where the improvement rate remained below 0.1% for 10 consecutive generations. The optimization effectiveness under different parameter settings was assessed using the following metrics: computational time, convergence generation, and solution quality (represented by the optimal objective function value obtained). The core parameters considered were:
- (1)
Population Size: Tested range: [100, 1000] in increments of 100.
- (2)
Crossover Probability: Tested range: [0.1, 1.0] in increments of 0.1.
- (3)
Mutation Probability: Tested range: [0.1, 1.0] in increments of 0.1.
- (4)
Crossover Distribution Index: Tested range: [5, 140] in increments of 15.
- (5)
Mutation Distribution Index: Tested range: [5, 140] in increments of 15.
The baseline parameter set for the algorithm was configured as follows: Population Size = 500, Crossover Probability = 50%, Mutation Probability = 50%, Crossover Distribution Index = 5, and Mutation Distribution Index = 5. The results of the sensitivity analysis for each parameter are presented below.
As shown in
Figure 9a, computational time increases approximately linearly with population size, exhibiting accelerated growth beyond 900 individuals. Convergence generation remains within the range of 36–52 generations across most population sizes, but experiences significant delays (exceeding 67 generations) at sizes of 200 and 1000, indicating convergence difficulty. A population size of 600 achieves higher solution quality (optimal objective value) at a lower computational cost.
Figure 9b reveals that computational time gradually decreases with increasing crossover probability. Convergence generation initially rises with crossover probability, peaks at 0.6, and subsequently declines. Solution quality shows no significant correlation with crossover probability. Notably, a crossover probability of 0.9 yields favorable levels across all three metrics: computational time, convergence generation, and solution quality. Analysis of
Figure 9c indicates that computational time and convergence generation manifest a strong correlation under the influence of mutation probability, both peaking around 0.4 (highest computational cost) and reaching a trough at 0.7 (lowest computational cost), albeit with compromised solution quality at the latter. Considering all three evaluation metrics, a mutation probability of 0.9 is optimal.
Figure 9d demonstrates that computational time and convergence generation also exhibit high consistency in response to the crossover distribution index, attaining lower values at a moderate index of approximately 110. Solution quality is enhanced at an index of 50, where the associated computational cost remains acceptable. Finally,
Figure 9e shows computational time and convergence generation maintain their correlated behavior under variation in the mutation distribution index, reaching minima at an index of 20. Solution quality remains relatively stable (below 2.3 × 10
5) and largely unaffected by the mutation distribution index for values up to 80.
Based on the above analysis, the genetic algorithm parameters were thus determined to be a population size of 600, a crossover probability of 0.90, a mutation probability of 0.90, a crossover distribution index of 50, and a mutation distribution index of 20. Genetic optimization was subsequently performed based on this parameter configuration.
4.5. Optimization Results
Following the execution of the genetic algorithm, the following numerical optimal solution was obtained:
- (1)
Optimal Solution: [l2, hs, h, θ] = [2411.982, 429.069, 11.031, 1.308].
- (2)
Optimal Objective Value: 227,415.94.
- (3)
Constraint Violation: [−0.36933417, −0.07143207, −0.14365926].
5. Structural Finite Element Simulation
5.1. Planar Model Development
This study focuses on the in-plane failure of a box-section concrete pier under peripheral loading. Consequently, the problem was simplified to a plane stress condition. A planar finite element model was developed using ABAQUS to analyze the stress and deformation responses of the retrofitted structure under external loads. This analysis serves to validate the genetic algorithm optimization results and assess the effectiveness of the retrofit. The planar model specifications are as follows.
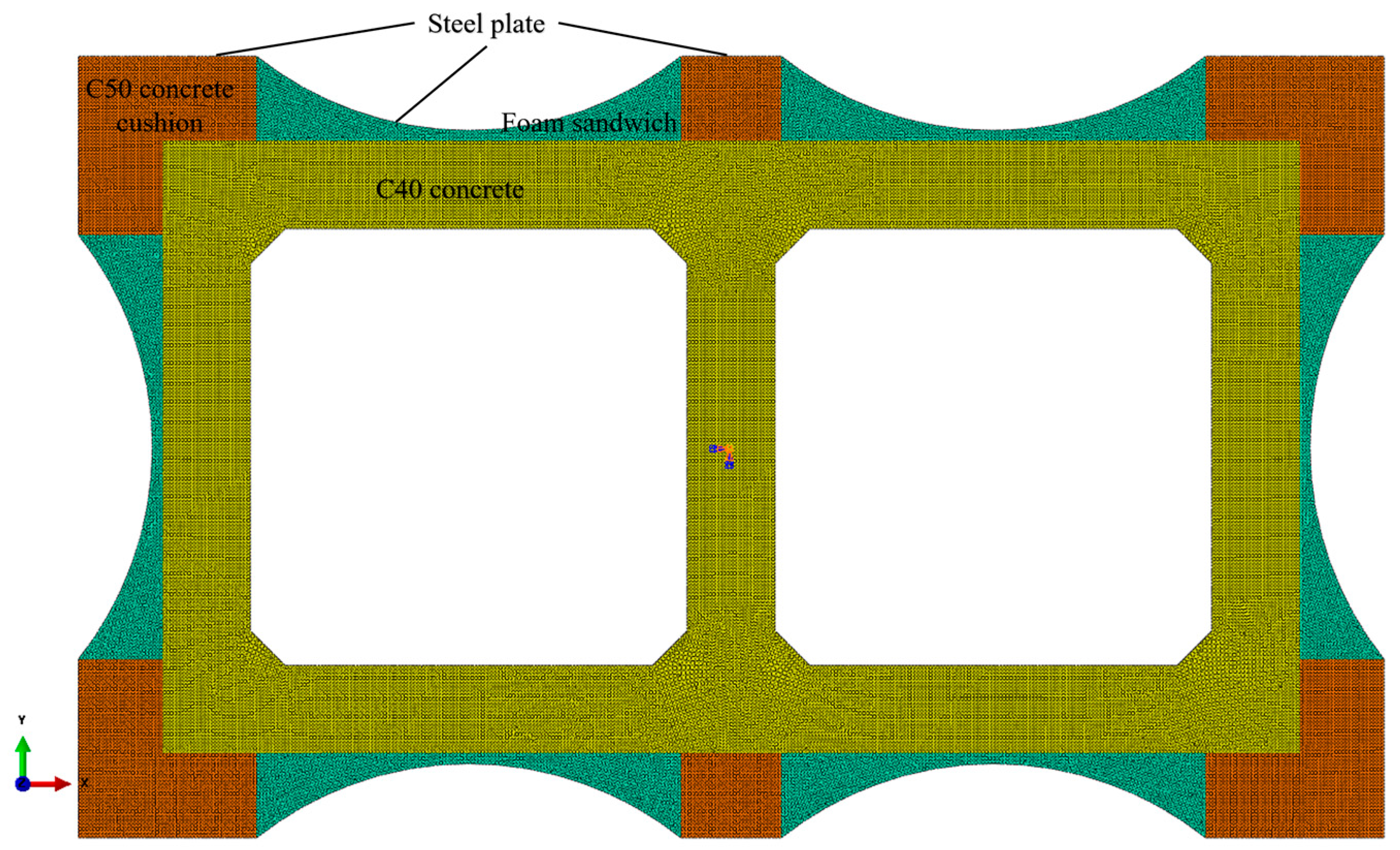
5.1.1. Geometry and Meshing
The planar finite element model was constructed based on the numerically optimal solution obtained from the genetic algorithm optimization. Key geometric parameters include arc steel plate span = 2412 mm, external steel plate thickness = 11 mm, C50 concrete block height = 429 mm, and arc steel plate curvature = 1.308 rad. The original C40 concrete, C50 concrete blocks, and infill foam were modeled using shell elements with a unit thickness of 1 mm. The external steel plates were modeled using beam elements with a cross-section height of 11 mm and a thickness of 1 mm. A global mesh size of 20 mm was applied to all components. The established planar model is depicted in
Figure 10.
5.1.2. Material Constitutive Definition
Considering that the retrofitted pier is expected to remain in an elastic state without failure or plastic deformation under peripheral pressure loading, material nonlinearity was neglected in the finite element analysis. The linear elastic constitutive parameters for each material are listed in
Table 2.
5.1.3. Boundary Conditions and Loading
The retrofitted pier cross-section retains its symmetry. Under external loading, the pier compresses inwards from all sides while the center position remains stationary. Therefore, a fixed constraint was applied at the central node, as illustrated in
Figure 10. Given the symmetry of both the model and the applied loads, the structure is deemed stable without distortional deformation under this boundary condition, confirming its validity. The load was applied as a beam load to the elements representing the steel plates, with a magnitude of 1.5 N/mm directed along the beam normal direction. Geometric nonlinearity was considered during the analysis.
5.2. Planar Model Results and Analysis
5.2.1. Concrete Stress
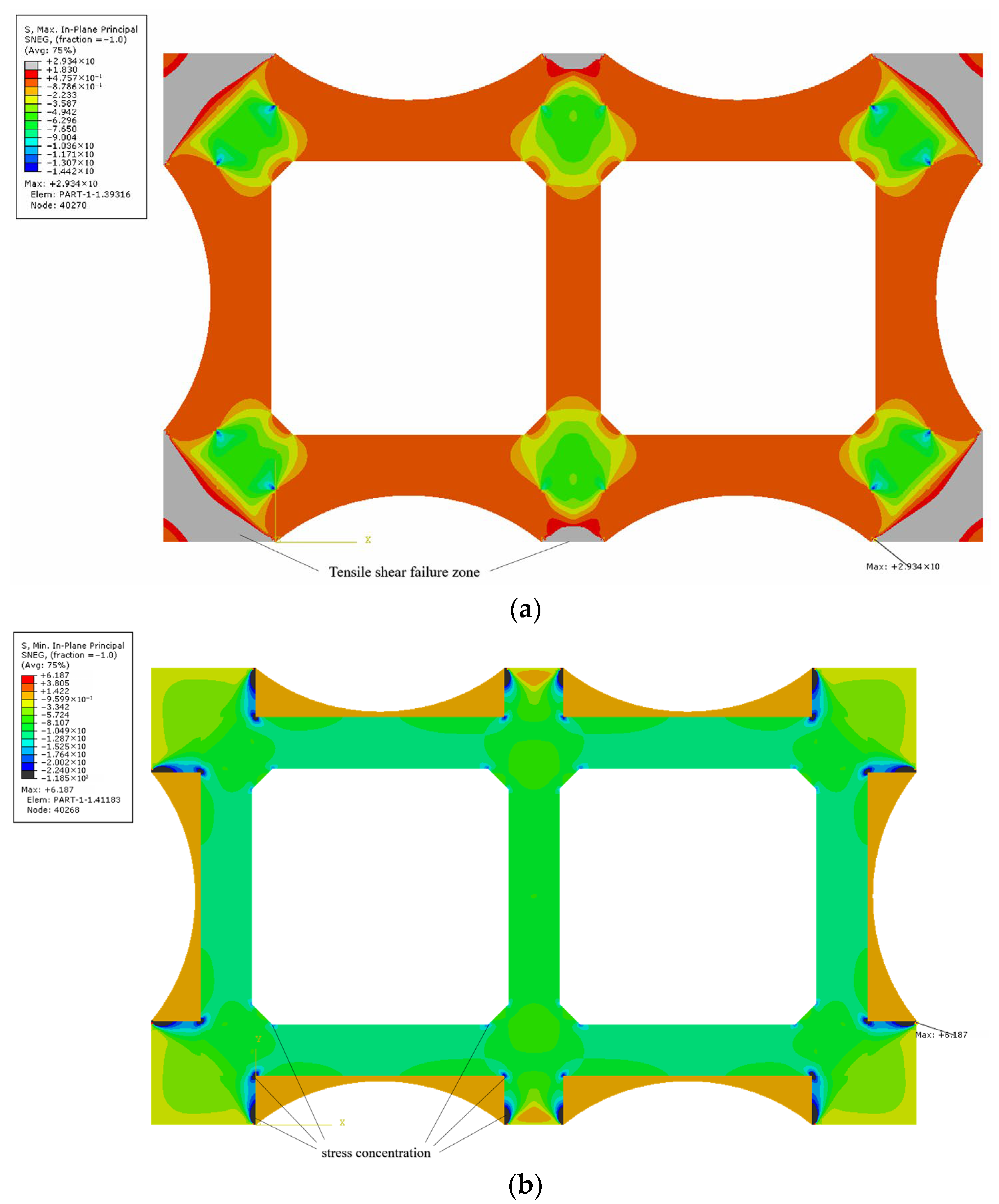
Under the action of perimeter pressure loading, the in-plane principal stress contour plot of the concrete structure is shown in
Figure 11. Considering the material properties of concrete, the principal tensile stress limit is set at 1.83 MPa, and the principal compressive stress limit at 22.4 MPa.
Analysis of the concrete stress contours reveals that under this perimeter loading condition, the Grade C50 concrete bearing block will experience extensive tensile failure, whereas the original Grade C40 concrete structure remains intact. This occurs because the mid-span segment of the curved steel plate deflects downward under compression, generating significant horizontal tension forces. These forces are subsequently transmitted to the surface of the supporting bearing block in the form of shear, inducing compression-shear failure in the concrete at the support points. To address this issue, localized prestressing can be applied.
Furthermore, it is observed that concrete principal compressive stresses exceeding the specified limit occur only in the corner regions. This localized overstress is attributed to stress concentration. In practical engineering applications, this phenomenon can be effectively mitigated by incorporating chamfers at these corners to eliminate stress concentration effects. Numerical simulation predictions indicate that under the corresponding load conditions, the compressive stress is lower than the concrete tensile design strength,
ftd, indicating compliance with the failure criteria defined in the Chinese standard [
47].
5.2.2. Steel Stress
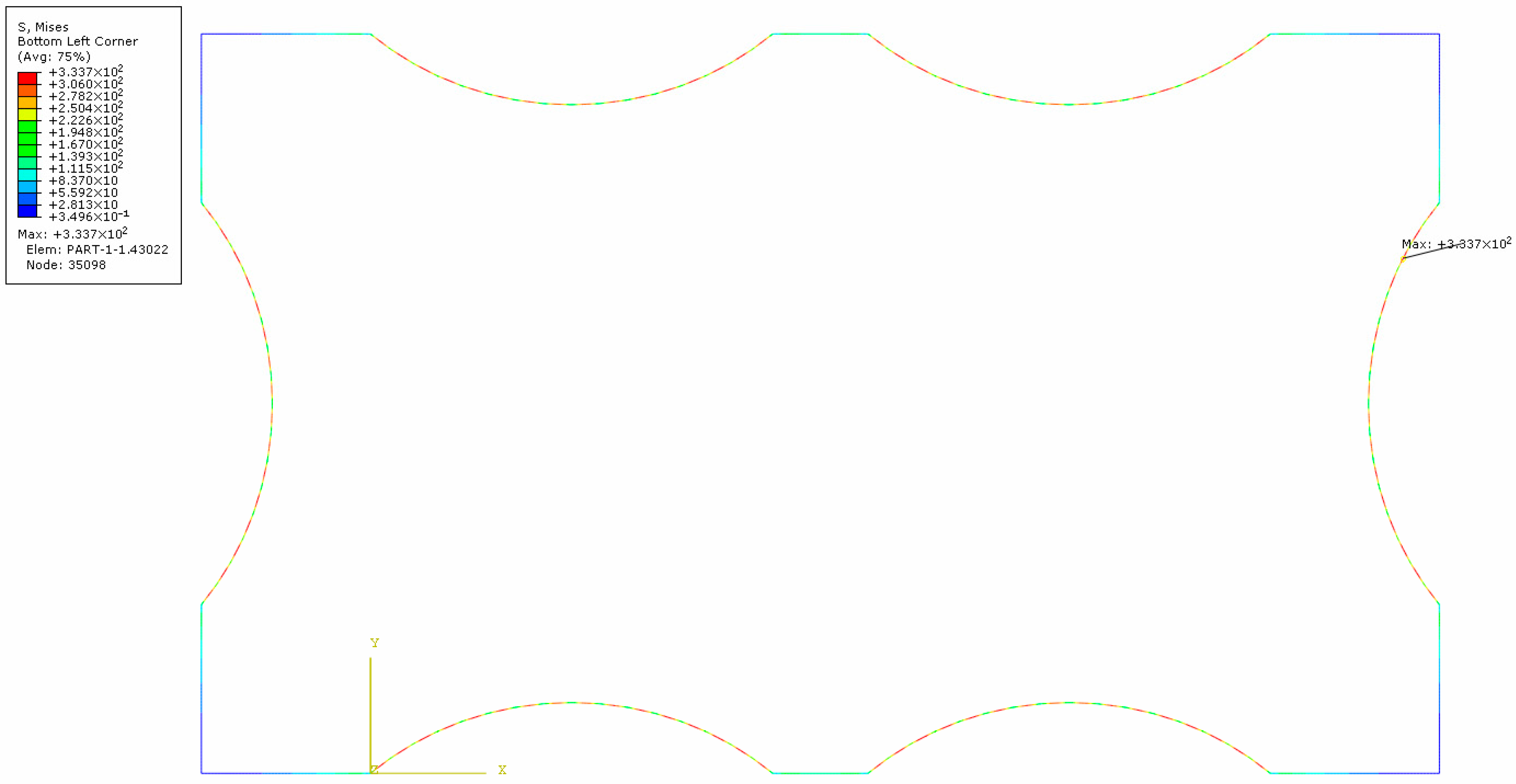
The von Mises stress contour of the steel plate is presented in
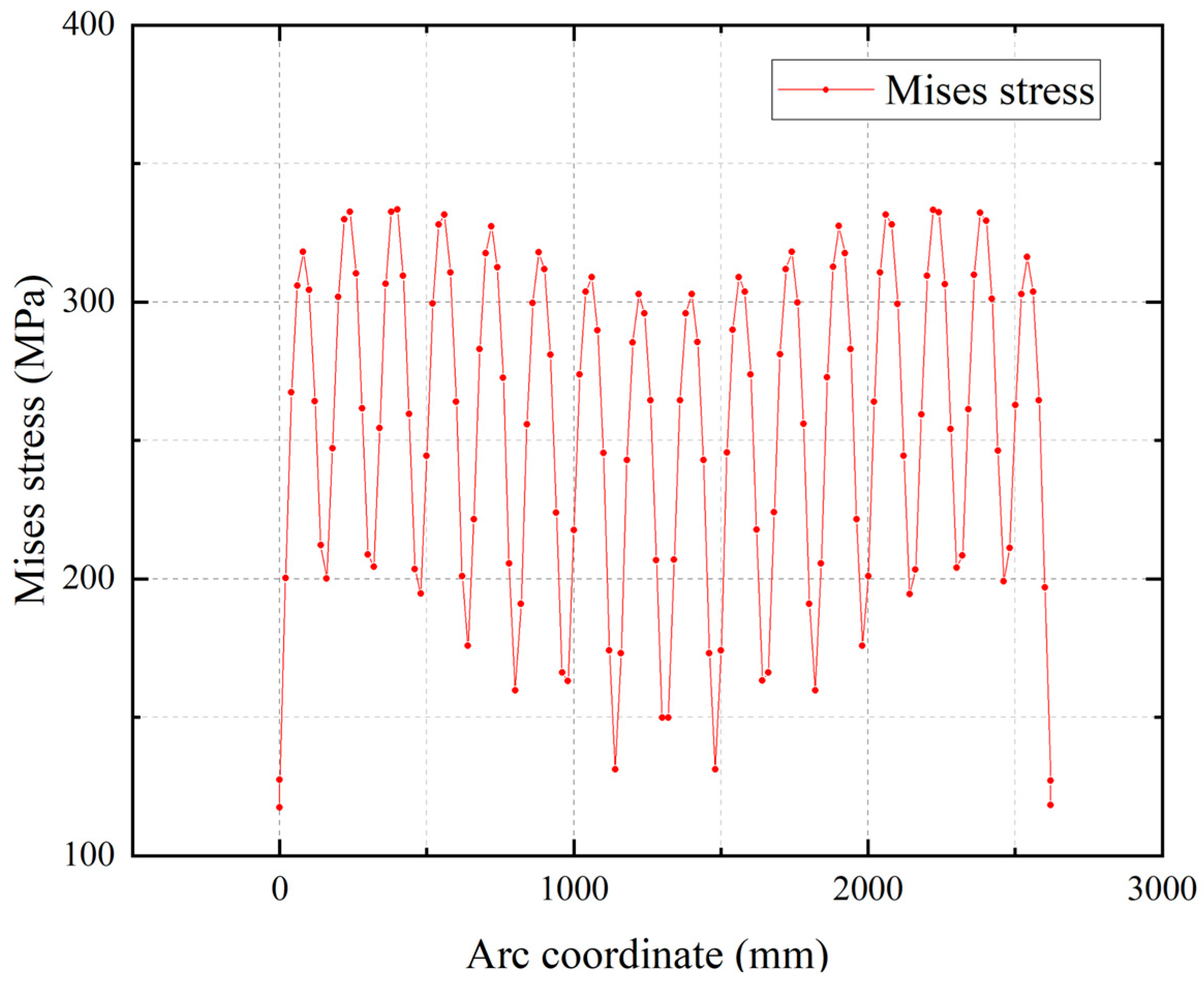
Figure 12. Notably, significantly higher stresses occur in the arc segment, while stresses at support locations remain lower due to composite action with the concrete. The von Mises stress distribution along the arc path is plotted in
Figure 13. The stress along the arc exhibits a quasi-periodic distribution pattern, featuring a peak value of 333 MPa and a trough value of 50 MPa. In reality, tensile stress in the steel plate should be approximately uniform along the arc path; the observed distribution is attributed to discretization-induced inaccuracies in the finite element simulation, with actual stresses expected to approximate the average nodal stress. Crucially, the average von Mises stress in the arc segment remains substantially below the material yield strength, confirming that the retrofitted steel structure operates well within the safe range.
5.2.3. Structural Deformation
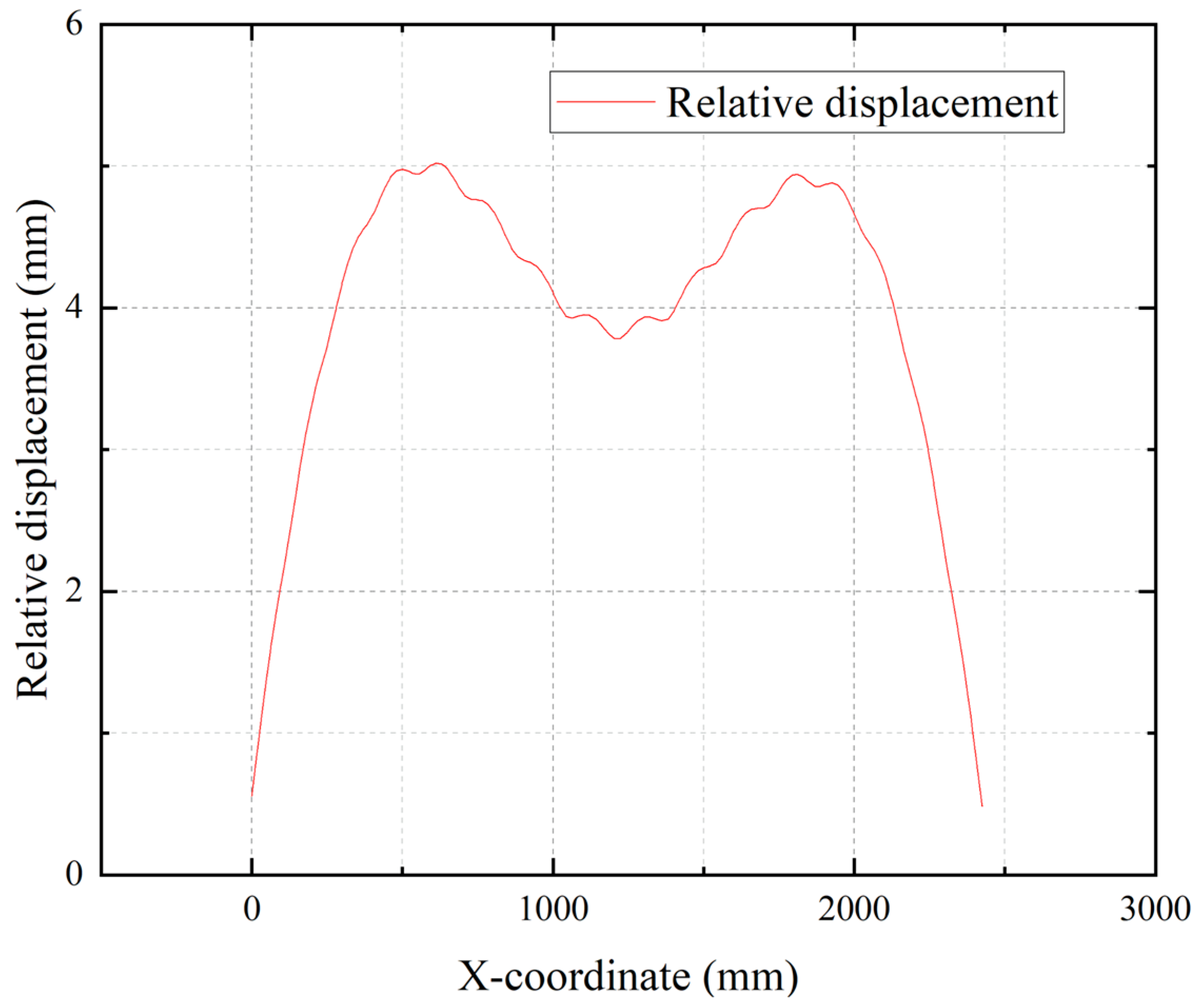
The differential deflection between the steel plate and the concrete beam along the beam axis is plotted in
Figure 14. As depicted, the maximum relative deformation occurs in the quarter-span region, with a magnitude of 5 mm. This deformation remains within acceptable limits and poses no threat to structural safety. Critically, the observed relative deformation is non-negligible, thereby validating the necessity of accounting for steel plate deformation during structural optimization analysis.
6. Discussion
The composite strengthening system proposed in this study demonstrates significant efficacy in mitigating flexural cracking in box-shaped hollow piers subjected to peripheral ice–water pressure. The integration of externally bonded steel plates with concrete infill blocks fundamentally alters the structural load path, transforming the original bending-dominated behavior into a compression–truss mechanism with suspended-cable action. This mechanistic shift aligns with the principles of structural efficiency articulated by Schlaich et al. [
48] for load-path optimization, while extending their application to submerged infrastructure.
6.1. Key Findings and Implications
Crack suppression mechanism: The 2D finite element analysis confirms that stress redistribution through the steel plate system reduces principal tensile stresses in the original C40 concrete below the design tensile strength, effectively preventing flexural cracking. This validates the theoretical premise that the compression–truss mechanism alleviates bending moments in pier walls, which is consistent with the mechanism proposed by Van den et al. [
49,
50]. Meanwhile, it verifies the high efficiency of Crisafulli et al.’s truss structure to resist lateral force [
51].
Infill block vulnerability: Contrary to theoretical predictions, localized tensile failure observed in C50 cushion (
Figure 11a) reveals an unanticipated shear-transfer mechanism. The downward deflection of steel plates generates significant horizontal shear at block interfaces, inducing tension–shear failure. This necessitates future refinement through localized prestressing or steel-fiber reinforcement.
Material synergy: The 333 MPa peak von Mises stress in steel plates (
Figure 12) remains below Q345 yield strength, confirming the effective utilization of steel’s tensile capacity. According to the research of Lam et al. [
52,
53], the stress concentration at corners (
Figure 11b) is resolvable through chamfering, demonstrating the system’s robustness when combined with constructability adjustments.
Algorithmic efficiency: The genetic algorithm optimization reduced strengthening costs while satisfying all constraints. The optimal solution highlights the method’s economic viability, particularly through steel plate thickness minimization (11 mm) and controlled infill height (429 mm).
6.2. Comparative Context
Unlike conventional pier strengthening (e.g., CFRP wrapping or steel jacketing [
4,
12]), which primarily enhances axial capacity [
54], this system specifically addresses peripheral pressure through load-path modification. This is consistent with the view proposed by Bassandeh et al. [
55]. on shell reinforcement of structures based on the load-path theory. The suspended-cable behavior resembles cable-stayed principles [
56], but applied internally to redistribute hydrostatic loads. This approach outperforms grout-infilled methods [
57,
58] by reducing concrete usage while eliminating cracking risks in original structures.
6.3. Limitations and Future Work
The 2D model simplification neglects 3D effects at pier corners and longitudinal joints. In reality, intersecting walls generate localized stress concentrations where bending moments from adjacent planes interact. The corner stresses may exceed 2D predictions due to out-of-plane constraint effects. This could exacerbate concrete crushing in nodal zones but may be mitigated through targeted corner chamfering or localized reinforcement. The assumption of uniform pressure along the pier height ignores potential ice-load variations due to water-level fluctuations or nonuniform ice thickness. Such variations would induce longitudinal bending, transferring stresses between strengthened segments. Field measurements suggest ice pressure may vary by ±30% vertically, potentially causing stress amplification up to 20% in critical sections when combined with global pier flexure.
Foam material behavior was idealized and viscoelastic effects under long-term loading require investigation. Foam viscoelasticity threatens the integrity of the adhesive layer through three pathways: time-dependent stress redistribution, low-temperature embrittlement, and fatigue accumulation. Moreover, dynamic ice impact loads were not considered in the current research. While these effects do not invalidate the core findings—given the model’s conservative material assumptions and safety margins in optimized parameters—they highlight opportunities for refinement. Future 3D-coupled fluid–structure–ice models will quantify these interactions more rigorously.
Crucially, while the Ulahada Water Control Project renovation provided the engineering context for this study, the current validation relies solely on theoretical derivation and numerical simulation; field data or experimental validation were not incorporated in this phase.
To address this gap and further substantiate the practical applicability and robustness of the proposed composite strengthening design, future research should:
(1) Develop 3D fluid–structure interaction models incorporating ice fracture dynamics.
(2) Validate the system through scaled laboratory testing under cryogenic conditions. Constructing geometrically scaled models (e.g., 1:5 or 1:10) of a representative pier segment. Simulating the peripheral loading regime using hydraulic actuators configured to apply controlled uniform pressure against the model’s outer surface. Employing advanced measurement techniques such as Digital Image Correlation (DIC) for non-contact, full-field mapping of surface strains and displacements on both the concrete and steel components. Progressively increasing the load beyond service levels to induce failure would reveal the ultimate load capacity, failure mechanisms (e.g., block crushing, plate yielding, bond failure), and validate the safety margins inherent in the design.
(3) Conduct prototype field monitoring of the actual bridge piers modified using this system in the Ulahada project. Embed strain gauges in critical sections of the original piers, pads, and external steel plates to continuously monitor stress levels under fluctuating hydrostatic pressure and seasonal ice loads. Installing displacement sensors to measure relative movement between the steel plates and concrete pier walls. Installing pressure sensors on the underwater pier surfaces to record the actual magnitude, distribution, and time history of ice pressures encountered. Assessing the durability of polymer adhesive bonding, the stability of foam fillers, and the overall system performance under cyclic environmental stresses through long-term monitoring over multiple freeze–thaw cycles.
7. Conclusions
This study establishes a comprehensive framework for optimizing composite strengthening of submerged box piers under peripheral ice–water pressure. The principal conclusions are:
Mechanism innovation: The integration of arced steel plates (functioning as suspended cables) and nodal concrete blocks successfully transforms bending-dominated rigid-frame behavior into a hybrid compression–truss system. This eliminates tensile cracking in original pier walls while maintaining stresses below material limits.
Optimization efficacy: The genetic algorithm parameterization framework achieves a cost reduction relative to preliminary designs. Key optimized parameters—steel plate span (2412 mm), thickness (11 mm), block height (429 mm), and curvature (1.308 rad)—demonstrate the critical balance between material economy and structural performance.
Validation rigor: Finite element analyses confirm that peak steel stresses (333 MPa) remain within the elastic range (<345 MPa yield); original C40 concrete tensile stresses are suppressed below design strength; and maximum relative deformation (5 mm) satisfies the safety clearance.
Practical significance: The system provides a constructible, cost-effective solution for retrofitting existing piers in reservoir impoundment scenarios.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.L.; methodology, X.L.; software, X.L.; validation, J.M. and H.S.; investigation, Y.Y.; resources, Y.Y.; data curation, Y.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, X.L.; writing—review and editing, H.S.; project administration, H.S.; funding acquisition, H.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 52078164; the National Key Research and Development Program (SQ2022YFC3800080) and its affiliated project (2022YFC3801104). And The APC was funded by Harbin Institute of Technology.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Correction Statement
This article has been republished with a minor correction to the Data Availability Statement. This change does not affect the scientific content of the article.
References
- Zhou, L.Y.; Liu, Z. Investigation of the buckling behaviour of thin-walled hollow concrete piers. Struct. Concr. 2016, 17, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Bairán, J.-M.; Li, W. Influence of wall thickness on the seismic performance of thin-walled precast UHPC hollow piers. Thin-Walled Struct. 2025, 212, 113205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavese, A.; Bolognini, D.; Peloso, S. FRP seismic retrofit of RC square hollow section bridge piers. J. Earthq. Eng. 2004, 8, 225–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lignola, G.; Prota, A.; Manfredi, G.; Cosenza, E. Experimental performance of RC hollow columns confined with CFRP. J. Compos. Constr. 2007, 11, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epackachi, S.; Nguyen, N.H.; Kurt, E.G.; Whittaker, A.S.; Varma, A.H. In-plane seismic behavior of rectangular steel-plate composite wall piers. J. Struct. Eng. 2015, 141, 04014176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.; Rhee, I.; Park, J.; Cho, B.-S. Seismic retrofit of plain concrete piers of railroad bridges using composite of FRP-steel plates. Compos. Part B Eng. 2011, 42, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Wang, J.; Gou, S.; Zhu, Y.; Fan, J. Technological development and engineering applications of novel steel-concrete composite structures. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 2019, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reggia, A.; Morbi, A.; Plizzari, G.A. Experimental study of a reinforced concrete bridge pier strengthened with HPFRC jacketing. Eng. Struct. 2020, 210, 110355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantelides, C.P.; Duffin, J.B.; Reaveley, L.D. Seismic strengthening of reinforced-concrete multicolumn bridge piers. Earthq. Spectra 2007, 23, 635–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadatmanesh, H.; Ehsani, M.R.; Jin, L. Seismic strengthening of circular bridge pier models with fiber composites. ACI Struct. J. 1996, 93, 639–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Sun, H.; Jia, M.; Peng, B.; Li, X.; Yuan, H.; Liu, G. Experimental study and theoretical prediction of axial compression behavior in PMC-reinforced CFST columns with void defects. Eng. Struct. 2024, 313, 118258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Dai, J.; Huang, S.; Huang, Y. Rapid repair of seismic damaged short RC piers with CFRP composite strengthening method. Structures 2025, 71, 108201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Yan, Q.; Li, L.; Li, S. Field test and probabilistic vulnerability assessment of a reinforced concrete bridge pier subjected to blast loads. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023, 143, 106802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltaos, S.; Burrell, B.C.; Miller, L.; Sullivan, D. Hydraulic interaction between ice and bridges. In Proceedings of the 12th Workshop on the Hydraulics of Ice Covered Rivers, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 19–20 June 2003; CGU-HS Committee on River Ice Processes and the Environment: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Watts, F.J.; Podolny, W. Ice Loads on Bridge Piers; Federal Highway Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.; Lei, J.; Li, C.; Yu, H.; Shan, S. Compressive strength of floating ice and calculation of ice force on bridge piers during ice collision. In Proceedings of the Cold Regions Engineering 2009: Cold Regions Impacts on Research, Design, and Construction, Duluth, MN, USA, 31 August–2 September 2009; pp. 609–617. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, E.; Sugita, J. Composite mechanism of polymer modified cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 1995, 25, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardon, J.B. Polymer-modified concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 1997, 9, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, Y.-j.; Zhang, G.-j. Discussion on Reasonable Arch Axis of Long-Span Arch Bridges. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Arch Bridges, Fuzhou, China, 25–27 October 2023; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 258–266. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.-J.; Liu, Y.-J.; Liu, J. Analytical solution and calculation method of reasonable arch axis of through arch bridge. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2022, 22, 217–230. [Google Scholar]
- Selby, R.G. Three-Dimensional Constitutive Relations for Reinforced Concrete; Department of Civil Engineering, University of Toronto: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H.; Liang, L. Uniaxial compressive properties of ecological concrete: Experimental and three-dimensional (3D) mesoscopic investigation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 278, 121034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivlin, R. Large elastic deformations. In Collected Papers of RS Rivlin: Volume I and II; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 318–351. [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher, K.; Sambridge, M. Genetic algorithms: A powerful tool for large-scale nonlinear optimization problems. Comput. Geosci. 1994, 20, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Sethares, W.A. Nonlinear parameter estimation via the genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1994, 42, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdoğmuş, P.; Ekiz, S. Nonlinear regression using particle swarm optimization and genetic algorithm. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2016, 153, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, D.E. Real-coded genetic algorithms, virtual alphabets and blocking. Complex Syst. 1990, 5, 139–167. [Google Scholar]
- Eshelman, L.J.; Schaffer, J.D. Real-coded genetic algorithms and interval-schemata. In Foundations of Genetic Algorithms; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; Volume 2, pp. 187–202. [Google Scholar]
- Tezuka, M.; Munetomo, M.; Akama, K. Linkage identification by nonlinearity check for real-coded genetic algorithms. In Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 June 2004; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 222–233. [Google Scholar]
- Marguet, A. Uniform sampling in a structured branching population. Bernoulli 2019, 25, 2649–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Gupta, R.; Roy, S.; Meel, K.S. Knowledge Compilation meets Uniform Sampling. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Logic for Programming, Artificial Intelligence and Reasoning (LPAR-22), Awassa, Ethiopia, 17–21 November 2018; pp. 620–636. [Google Scholar]
- Chacón, J.; Segura, C. Analysis and enhancement of simulated binary crossover. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 8–13 July 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Deb, K.; Sindhya, K.; Okabe, T. Self-adaptive simulated binary crossover for real-parameter optimization. In Proceedings of the 9th Annual Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation, London, UK, 7–11 July 2007; pp. 1187–1194. [Google Scholar]
- Bandaru, S.; Tulshyan, R.; Deb, K. Modified SBX and adaptive mutation for real world single objective optimization. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Congress of Evolutionary Computation (CEC), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–8 June 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 1335–1342. [Google Scholar]
- Deb, K.; Beyer, H.-G. Self-adaptive genetic algorithms with simulated binary crossover. Evol. Comput. 2001, 9, 197–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep, K.; Thakur, M. A new mutation operator for real coded genetic algorithms. Appl. Math. Comput. 2007, 193, 211–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäck, T.; Fogel, D.B.; Michalewicz, Z. Mutation operators. In Evolutionary Computation 1; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 275–293. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.M.; Sultan, A.B.M.; Sulaiman, M.N.; Mustapha, A.; Leong, K.Y. Crossover and mutation operators of genetic algorithms. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Comput. 2017, 7, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.L.; Goldberg, D.E. Genetic algorithms, tournament selection, and the effects of noise. Complex Syst. 1995, 9, 193–212. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Soh, C.K. Structural optimization by genetic algorithms with tournament selection. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 1997, 11, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Pandey, H.M.; Mehrotra, D. Comparative review of selection techniques in genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Futuristic Trends on Computational Analysis and Knowledge Management (ABLAZE), Greater Noida, India, 25–27 February 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 515–519. [Google Scholar]
- Filipović, V. Fine-grained tournament selection operator in genetic algorithms. Comput. Inform. 2003, 22, 143–161. [Google Scholar]
- Lavinas, Y.; Aranha, C.; Sakurai, T.; Ladeira, M. Experimental analysis of the tournament size on genetic algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Miyazaki, Japan, 7–10 October 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 3647–3653. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, P.; Tian, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y. A Constraint Priority Decision framework for constrained multi-objective optimization with complex feasible regions. Appl. Soft Comput. 2025, 172, 112873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinneck, J.W. Feasibility and Infeasibility in Optimization: Algorithms and Computational Methods; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dehuri, S.; Patnaik, S.; Ghosh, A.; Mall, R. Application of elitist multi-objective genetic algorithm for classification rule generation. Appl. Soft Comput. 2008, 8, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Communications Highway Planning and Design Institute Co., Ltd. Specifications for Design of Highway Reinforced Concrete and Prestressed Concrete Bridges and Culverts; China Communications Highway Planning and Design Institute Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2018; p. 261. [Google Scholar]
- Schlaich, J.; Schäfer, K.; Jennewein, M. Toward a consistent design of structural concrete. PCI J. 1987, 32, 74–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Hoogen, M. Beam or Truss Mechanism for Shear in Concrete. Master’s Thesis, University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.-J.; Xiong, J.; Yang, L.-H.; Yu, G.-C.; Yang, W.; Wu, L.-Z. Shear and bending performance of new type enhanced lattice truss structures. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2017, 134, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisafulli, F.J.; Carr, A.J.; Park, R. Analytical modelling of infilled frame structures: A general review. Bull. N. Z. Soc. Earthq. Eng. 2000, 33, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, E.S.-S.; Tse, K.-L.; Leung, S.-S.; Man-lung, I. Strengthening of reinforced concrete beam-column joints using chamfers. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2002, 14, 535–563. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, E.S.-S.; Li, B.; Xue, Z.-H.; Leung, K.-T.; Lam, J.Y.-K. Experimental studies on reinforced concrete interior beam-column joints strengthened by unsymmetrical chamfers. Eng. Struct. 2019, 191, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Lin, N.-J. Analytical model for predicting axial capacity and behavior of concrete encased steel composite stub columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2006, 62, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassandeh, A. An Application of Load Path Theory to the Design of Structures. Master’s Thesis, UNSW Sydney, Sydney, Australia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gimsing Niels, J.; Georgakis, C.T. Cable-Stayed, Cable Supported Bridges; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Abrams, D.; Smith, T.; Lynch, J.; Franklin, S. Effectiveness of rehabilitation on seismic behavior of masonry piers. J. Struct. Eng. 2007, 133, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikooravesh, M.; Soltani, M. Behavior of unreinforced masonry piers strengthened using centercore method; experimental investigation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 189, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).