Abstract
The incentive mechanism functions as a core safeguard to ensure the efficient execution of consortium-based Public–Private Partnership (PPP) projects and the realization of value-added outcomes. The heterogeneity of consortium members, their reciprocal preferences, and the collaborative dynamics of the team collectively contribute to the formation of project alliances characterized by resource synergy, complementary advantages, and risk sharing. However, these same factors also contribute to the multi-layered structure of principal–agent relationships and the inherent complexity of incentive pathways and mechanisms in consortium-based PPP settings. Drawing upon the team collaboration effect and reciprocal preferences among consortium members, this study incorporated the member heterogeneity and developed three incentive models for such projects, such as the Dual-Performance (DP) mode, the Total-Performance (TP) mode, and the Individual-Performance (IP) mode. This study examined the conditions under which these incentive modes were established, the relationship between incentive intensity and optimal effort levels of consortium members, and the influence of reciprocal preferences on incentive effectiveness. Further, the selection criteria and appropriate application scenarios for each of the three incentive models were analyzed according to a comparative analysis, thereby putting forward effective suggestions for improving the effort levels of private investors in consortium-based PPP projects. The study results indicate that team synergy effects play an imperative role in improving the optimal effort levels under all three modes, whereas reciprocity preferences exhibit a negative relationship with effort in the DP and TP modes. When reciprocity remains within a moderate range, the DP mode achieves highest aggregate effort levels, whereas the IP mode induces positive incentive effects only under extreme reciprocity conditions. Thus, the application of dual incentive coefficients can enhance operational adaptability and allocative efficiency and governments should establish a multidimensional collaborative incentive for consortium-based PPP projects to strengthen effectiveness and project quality. This comprehensive evaluation provides crucial insights for policymakers, emphasizing the strategic selection of incentive mechanisms to enhance the sustainability and effectiveness of consortium-based PPP Projects.
1. Introduction
Public–Private Partnership (PPP) projects represent a collaborative framework in which governments attract private capital through market-based mechanisms to deliver public services. This model not only alleviates fiscal pressure but also improves operational efficiency by leveraging the professional management expertise of private sectors [1]. Globally, the Public–Private Partnership (PPP) model has driven a transformative shift in the provision of infrastructure and public services from a government-led approach to a collaborative governance model in which public authorities and private sector actors jointly deliver services [2]. This transition, exemplified by the long-term evolution of PPP practices in countries such as the United Kingdom and France, has gradually evolved into a procurement and governance framework for infrastructure and public services that is oriented toward achieving sustainable development goals [3]. The World Bank’s Private Participation in Infrastructure (PPI) database indicates that over the past three decades, PPP projects have demonstrated a trend of rapid growth amid fluctuations, both in terms of project numbers and total investment volume. As of December 2023, the cumulative global implementation of PPP projects has reached a total investment value of USD 2220.085 billion, spanning key sectors including energy, information and communication technology (ICT), municipal solid waste management, transport, and water and sewerage. These projects have emerged as an innovative model for delivering infrastructure and public services on a global scale.
Given their substantial investment demands, prolonged implementation timelines, and intricate construction and operational requirements, PPP projects require significant financial capacity, technical knowledge, and risk management capabilities from their private partners [4]. To address these complexities, private entities often form consortiums to consolidate resources and distribute risk. The adoption of consortium-based structures involving multiple private sector entities for the implementation of PPP projects represents a highly prevalent and institutionalized practice, widely observed across both developed and developing countries, as well as across multiple infrastructure sectors including energy, transport, water and sanitation, ICT, and municipal solid waste management [5]. According to data from the World Bank’s PPI database, in large or complex PPP projects, the participation of consortia typically exceeds 90%, and in many countries, it approaches or reaches 100%. Notable examples include the London Underground PPP projects, the Channel Tunnel (Eurotunnel), Sydney Metro Northwest, and the Brisbane Cross River Rail project, all of which were awarded to and implemented by consortia comprising construction firms, service operators, and financial institutions. The consortium model not only enables the effective integration of specialized expertise and resources among participating parties, but also enhances project feasibility, sustainability, and delivery efficiency through mechanisms of risk-sharing and benefit-allocation [6]. As such, it has emerged as one of the core organizational forms driving innovation in the provision of infrastructure and public services on a global scale.
As an important type of PPP model, Consortium-based PPP projects exhibit unique characteristics in terms of principal–agent relationships and the behavioral patterns of involved parties. In such arrangements, the government no longer interacts with a single private sector, but rather with a consortium formed through consortium agreements among multiple enterprises [1]. Each member of the consortium has its own interests, social preferences, and behavioral patterns. The consortium operates as a collaborative team to implement the PPP project, and its interactions with the government demonstrate distinct traits compared to those involving a single private sector entity. First, the presence of multiple entities leads to a two-tiered structure of information asymmetry and goal incongruence, both between the government and the consortium as a whole, and within the consortium itself [7]. This dual asymmetry in information and objectives further increases agency costs, necessitating well-designed incentive mechanisms to align the diverse interests of all parties, mitigate the negative effects of information asymmetry, and thereby reduce agency costs in PPP implementation [8]. Second, as the consortium functions as a collective team in delivering the PPP project, the heterogeneity among members and team collaboration results in complex internal coordination. To address this, robust incentive mechanisms considering team collaboration are required to facilitate shared benefits and jointly binding responsibilities within the consortium, optimize resource allocation, minimize internal frictions, and ultimately lower transaction costs [9]. Third, consortium-based PPP projects are typically associated with a wide range of risks, reciprocity serves not only as the underlying psychological rationale that enables project collaboration among consortium members, but also as the core bond that sustains multi-member coordination. This necessitates refined incentive mechanisms considering reciprocity capable of addressing the intricacies of risk sharing, thereby ensuring smooth project implementation.
Existing research on incentive mechanisms for consortium-based PPP projects often simplifies the consortium as a single homogeneous entity, paying insufficient attention to team collaboration effects and reciprocal preferences among consortium members. Consequently, such studies tend to overlook the unique complexity of the incentive subject and its distinctive requirements for incentive mechanisms. To fill the research gap, this study attempts to construct a scientific and bounded incentive mechanism based on the heterogeneity of consortium members, taking into account team collaboration effects and reciprocal preferences among members. By doing so, it explores effective incentive pathways for the consortium with the aim of promoting the successful implementation and sustainable development of consortium-based PPP projects.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Theoretical Basis
Consortium-based PPP projects are fundamentally a form of public–private governance structure, in which the government, acting as the representative of public interest, serves as the principal, while the consortium functions as the agent [10]. This relationship establishes a principal–agent relationship between the two parties, which is characterized by information asymmetry and misaligned objectives, giving rise to classic principal–agent problems [11]. Within the traditional principal–agent framework, since the consortium and its members may conceal actions or information such as reducing effort levels or shifting risks, the government needs to employ well-designed incentive mechanisms (e.g., performance-based payments, availability payments, reward-and-penalty clauses, etc.) to guide the behavior of the consortium and align its objectives with the public interest [12]. However, classical principal–agent models typically assume that the agent is a fully rational economic actor, thereby overlooking the agent’s inherent social preferences and collaborative motivations.
As a complex agent formed by multiple entities under contractual arrangements, a consortium exhibits multi-agent characteristics and cooperative complexity, which significantly complicates the principal–agent problems in consortium-based PPP projects. On the one hand, a consortium is a team formed by multiple individuals pursuing a common objective. The performance of the project depends not only on the individual efforts of each member, but also more critically on the quality of collaboration and synergistic effects among members [13]. However, due to prevalent issues such as free-riding behavior and coordination costs during collaboration, individual members may tend to focus solely on their own tasks while neglecting the overall objectives, thereby leading to consortium-wide performance that falls short of expectations. As a result, incentive mechanisms need to effectively identify and reinforce team collaboration behaviors by employing arrangements such as bundled incentives, risk-sharing, and benefit-sharing, so as to enhance members’ willingness to contribute to the collective goal [14]. On the other hand, in consortium-based PPP projects, collaborative relationships among members are often not fully governed by formal contracts, particularly when dealing with complex task allocations, risk-sharing arrangements, and long-term cooperation. In such contexts, reciprocity preferences emerge as a critical informal mechanism that sustains cooperative behavior. Specifically, when a member perceives that others are making efforts toward the collective goal, they are more likely to reciprocate with cooperative actions; conversely, they may reduce their own effort or even engage in opportunistic behavior [15]. This reciprocity-driven behavioral logic cannot be fully captured by the material incentives embedded in traditional principal–agent models, yet it has significant implications for the operational efficiency and long-term stability of the consortium [16]. Traditional incentive mechanism designs often rely on the assumption of the rational economic agent, focusing primarily on either a single actor or the overall output, while overlooking the profound influence of members’ reciprocity preferences and team collaboration effects on behavior and performance.
Building upon the core logic of principal–agent theory, this study extends its application to the consortium context by emphasizing that a consortium is not merely a single agent entity, but also an internal structure characterized by multi-agent collaboration and incentive differentiation. Consequently, an effective incentive mechanism must not only address the incentive compatibility between the government and the consortium but also take into account collaborative incentives and reciprocal behaviors among the consortium’s internal members. This theoretical perspective provides the institutional logic foundation for subsequently designing a hybrid incentive model that balances government objectives with the behavioral characteristics of the consortium.
2.2. Studies on Incentive Mechanisms for PPP Projects
Previous research has primarily focused on developing effective incentive mechanisms for PPP projects. The effectiveness of incentive mechanisms is influenced by multiple factors. Previous studies have primarily examined this issue from four perspectives, (1) project governance and the design of overall incentive frameworks, (2) incentive motivation and revenue distribution mechanisms, (3) performance-based incentives and risk-sharing models, and (4) the social preferences of private capital, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Main Literature Sources Identifying Key Factors to Construct incentive mechanisms for PPP projects.
Sabry argued that good governance and robust institutional frameworks are essential for creating an environment in which incentive mechanisms in PPPs such as performance-based payments, accountability structures, and risk-sharing arrangements can function effectively, thereby aligning private sector behavior with public objectives and improving overall project performance [17]. Liu et al. integrated speculation models into the principal–agent theory to examine the relationship among incentive intensity, profit distribution ratios, and social productivity, concluding that effective incentives could mitigate speculative behaviors among private partners [20]. Hwang and Kim analyzed the incentive effects of demand risk transfer in Korean waste treatment PPPs, demonstrating that excessive shifting of demand risk to the private sector distorts investment and operational incentives, ultimately reducing government cost efficiency, and underscoring the importance of balanced risk allocation to align private sector efforts with public cost-containment goals through appropriate incentive structures [23]. Wang et al. proposed an incentive mechanism model that incorporated the dual information asymmetries, capability endowments, and effort levels, while also considering private partners’ fairness preferences to optimize the government incentives [24]. Liu et al. further applied a dynamic evolutionary game model to analyze the decision-making behavior between governments and private entities, offering insights into incentive mechanism designs [25]. Maurya and Srivastava revealed that static contractual incentives alone are insufficient to curb private sector opportunism in PPPs and demonstrated how public actors adapt governance mechanisms such as dynamically optimizing incentive mixes, strengthening oversight, and fostering relational governance to continuously refine incentive structures, thereby effectively mitigating opportunistic behaviors and enhancing collaborative performance [18]. Wang et al. investigated incentive strategies for addressing opportunistic behavior in highway PPP projects, providing theoretical support for formulating optimal minimum revenue guarantee schemes for governments [19]. Warsen et al. explored how professionals involved in PPPs from Canada, the Netherlands, and Denmark perceive the governance of PPPs, highlighting that the effectiveness of incentive mechanisms, including performance-based payments and risk-sharing arrangements, is crucially influenced by professionals’ perceptions of governance structures, trust levels, and accountability mechanisms [22]. Jiang et al. applied evolutionary game theory to analyze a PPP cooperation scheme for promoting renewable hydrogen production and hydrogen energy vehicles in China, demonstrating that incentive mechanisms such as subsidies, risk sharing, and performance rewards significantly influence the evolutionary stability of cooperation by shaping private sector strategies and trust-building dynamics [21]. Sun et al. employed rank-dependent expected utility theory to investigate the operation supervision of PPP projects, demonstrating that incentive mechanisms particularly performance-based oversight rewards and accountability penalties are significantly shaped by the emotional states of stakeholders, which in turn affect their decision-making strategies and the overall effectiveness of supervision [28].
Consortium-based PPP projects generally involve heterogeneous participants, including construction firms, design agencies, operating entities, and financial institutions (e.g., banks, securities firms, trusts, and funds). Collaborative arrangements among multiple private sector actors introduce unique challenges to incentive mechanism design that differ significantly from single-entity PPPs. Grimsey and Lewis highlighted that consortium-based PPPs often suffer from incentive misalignment and divergent objectives among members, leading to coordination failures and suboptimal effort levels [29]. On the one hand, consortium members capitalize on their specialized expertise to execute specific project components, with successful delivery contingent on the collective fulfillment of the assigned tasks. This heterogeneity implies variations in members’ capability endowments and access to private information. On the other hand, the systemic nature of PPP project outputs entails strong organizational, technical, and strategic interdependencies, requiring consistent cooperation among members. Thus, project performance depends not only on individual production efforts but also on inter-member collaboration and cooperative engagement. Reciprocity preferences grounded in the cooperative behavior of social agents represent a fundamental mechanism for governing relationships and serve as a key synergistic pathway for designing incentive schemes in consortium settings [30]. Existing studies on control rights allocation and incentive mechanism design have increasingly highlighted the role of reciprocity preferences. For instance, Zhao et al. proposed a control rights allocation model incorporating reciprocity preferences to examine their influence on rights distribution [27], whereas Rolstadas and Schiefloe explored how risk preferences and reciprocity could jointly affect the incentive effects of control rights allocation [26].
Accordingly, the design of incentive mechanisms for consortium members should address both individual production incentives and collaborative contributions to joint output. However, most current models assume homogeneity among private actors and treat them as identical and independent entities in terms of production, revenue allocation, and control rights. This assumption neglects the internal incentive disparities arising from heterogeneity and fails to account for the motivational role of collaborative efforts and reciprocity preferences. As a result, incentive schemes often remain suboptimal, undermining the overall effectiveness of PPP incentive structures [31]. To bridge this gap, this study constructed an incentive model tailored to consortium-based PPP projects that integrated member heterogeneity, reciprocity preferences, and collaborative dynamics. The model investigated the conditions for incentive viability, explored the relationships between incentive intensity and optimal effort levels of consortium members, and examined the mechanisms by which reciprocity preferences could influence incentive effectiveness. This framework can refine the design of incentive mechanisms for consortium-based PPP projects.
3. Materials and Methodology
This chapter employs a theoretical modeling approach based on principal–agent theory, incorporating reciprocity preferences and collaborative behavior among consortium members. The research design aims to develop an incentive mechanism model that aligns individual efforts with collective outcomes in consortium-based PPP projects. The analysis will proceed in three steps: (1) constructing the multi-agent incentive model with reciprocity parameters and synergistic efficiency of the consortium, (2) solving for equilibrium effort levels under different incentive schemes, and (3) conducting comparative statics to examine how collaboration and reciprocity affect optimal contract design.
3.1. Model Assumptions
Consider a consortium of N (N ≥ 2) heterogeneous private entities that jointly participate in a PPP project. Each entity is denoted as i or j. The consortium functions as a project team characterized by interdependence and collaborative synergy. Drawing from team production theory, the effort of member i is conceptualized as a twofold input: a production effort (self-directed input toward individual tasks, where ) and a collaborative effort (altruistic input toward assisting member j, where , ). The two effort components, and , are assumed to be mutually independent. When , the interaction between members i and j reflects strategic independence, indicating no reciprocal dependence on effort contributions. Accordingly, the performance output of member i is specified as follows:
where εi denotes an independent and identically distributed random shock affecting the output of member i, satisfying . Hence, the aggregate performance of the consortium functioning as a collaborative team in the PPP project is formalized as follows:
where quantifies the synergistic efficiency of the consortium, defined as the ratio of collective PPP project output to the sum of individual member outputs [27]. This effect is principally determined by the intensity of knowledge sharing and the level of team coordination and is statistically independent of .
Within the PPP consortium, member i incurs binary effort costs , comprising production and collaborative components. Both components exhibit strictly increasing marginal costs, with . For theoretical tractability, each member is assumed to exhibit separable marginal cost functions () for both effort types. Consequently, the total effort cost function for member i is represented as follows:
In consortium-based PPP projects, private sector participants serve dual roles as implementers of project-specific tasks and equity investors [32] (e.g., construction firms often act as primary contractors while simultaneously assuming investor responsibilities). Consequently, the compensation structure for member i comprises two components: (1) a deterministic fixed component , which includes the contractual payments derived from task execution or expected returns on financial investment and remains unaffected by effort levels [33], and (2) a variable, performance-based component representing the allocated share of aggregate project output as determined by the incentive mechanism. Owing to inherent information asymmetries between governmental entities and the consortium, as well as among consortium members, governments are limited to monitoring observable performance metrics of individual members i as proxies for actual effort. To enhance incentive effectiveness, the performance-based component is further decomposed into two parts: revenue linked to individual output characterized by a marginal return coefficient and revenue linked to the total consortium output characterized by a marginal return coefficient . Accordingly, the compensation function is formalized as , , and , where (,) ≠ (0,0). Based on this formulation, three incentive regimes are defined: DP Mode () for dual-performance-based compensation, TP Mode () for total-performance-based compensation, and IP Mode () for individual-performance-based compensation.
3.2. Model Specification and Solution
Building on the assumptions presented in Section 2.1, we sequentially construct and solve three incentive-theoretic models (DP, TP, and IP) to investigate effective revenue allocation mechanisms.
3.2.1. Incentive Model Contingent Under Dual-Performance Metrics: Aggregate Consortium Output and Agent-Specific Contribution (DP Mode)
(1) Model Specification and Equilibrium Derivation
Under the DP mode, the benefits derived by consortium member i from a PPP project are given by , where and . Accordingly, the net profit of member i is expressed as
Assuming that the consortium member is risk-averse with a risk preference coefficient and seeks to maximize the expected utility, the certainty-equivalent payoff is given by
Moving beyond the zero-sum nature of traditional project contracts, the evaluation criterion for PPP project implementation centers on the Value for Money principle [34]. The government’s objective in adopting PPPs is to enhance the project value. This enhancement is defined as the expected difference between the total performance output of the project and the incentive expenditures incurred. Thus, the expected value enhancement can be expressed as
The incentive model for maximizing value enhancement in consortium PPP projects is formulated as
where conditions IR and IC denote the participation constraint and incentive compatibility constraint, respectively; and represents the consortium member’s reservation utility. The government determines the contractual parameters and , whereas the consortium member determines its dual effort inputs. Given that the Hessian matrix , constitutes a strictly concave function of and . Solving and can obtain
The analysis indicates that the production effort of a consortium member is jointly influenced by both incentive coefficients and , whereas the cooperative effort depends solely on the total output share coefficient . Considering the public welfare orientation of consortium-based PPP projects, where private sector returns must not exceed reservation utility, the participation constraint binds at the optimum: . Substituting the consortium member’s optimal strategy can provide the value enhancement objective, as follows:
Under reciprocal preferences, a linear dependence exists between and , satisfying , where quantifies the reciprocal preference intensity of member i. Substituting into the incentive model can obtain
Given that the Hessian matrix of CM is negative, CM is strictly concave regarding both and . Setting the partial derivatives of CM to zero, the optimal conditions can be derived from the corresponding first-order conditions:
The equilibrium values of the individual performance-based reward coefficient and the aggregate output-based reward coefficient are jointly determined by solving this system of first-order conditions:
where denotes the risk cost factor of consortium member i, determined by its risk aversion coefficient, output uncertainty, and effort cost coefficient. It quantifies the magnitude of risk cost borne by the member i. The equilibrium productive and collaborative efforts are obtained as follows:
(2) Equilibrium Analysis
Based on equilibrium solutions, the influencing factors and mechanism pathways of DP-mode incentives are derived as follows:
Theorem 1.
The incentive mechanism is implementable if and only if both boundary conditions and are simultaneously satisfied.
Proof of Theorem 1.
The incentive mechanism holds if
and , where
always holds. Additionally,
is obtained via
and
while
is determined by . □
To implement performance incentives based on individual and total outputs, the exceedance of a critical threshold by reciprocal preference coefficients is required, whereas collaborative effects should remain within sustainable bounds. A lack of sufficient reciprocity among consortium members can render individual-output incentives ineffective while excessively amplifying those for collective output, thereby invalidating the mechanism. Under conditions of low reciprocity, governments exhibit a greater preference for total-output incentive frameworks. Excessive collaborative effects between members necessitate prohibitively high implementation costs, which substantially diminishes the government’s motivation for incentive deployment.
Theorem 2.
When the incentive mechanism holds,
,
,
and
uniformly exhibit positive correlations with
. In contrast,
is uncorrelated with
,
demonstrates a positive correlation with
, and
,
, and
present consistent negative correlations with
. In particular, under the boundary condition of
,
holds, which implies that the collaborative efforts between i and j achieve strict equivalence with those between j and i.
Proof of Theorem 2.
Given
,
, and
,
,
, and
all exhibit positive correlations with
. Given
, as
and
,
demonstrates positive correlations with
. Given , is uncorrelated with . From , demonstrates a positive correlation with . Under the joint conditions of , , and , , , and exhibit negative correlations with . □
As collaborative effects within the consortium intensify, members simultaneously elevate their productive effort and collaborative contribution, which significantly increases the total output of the PPP project. Correspondingly, the unit incentive intensity linked to individual output is enhanced by the government. Although the amplification of collaboration does not increase the incentive intensity for collective output, members still receive augmented performance incentives because of elevated total output. For governments, the incremental value generated through intensified collaboration outweighs additional performance payments to the consortium, thereby yielding increased deterministic benefits.
Under the conditions of high reciprocal preference, optimal incentive effects are achieved by governments primarily through the incentivization of individual output among members. In contrast, the equilibrium productive effort and collaborative contribution of consortium members decrease as reciprocal preference strengthens. Once incentive mechanisms are established, greater reciprocal preference enables members to attain identical incentive returns with reduced effort provision. Within the bounded rationality framework, economic equilibrium incorporating reciprocal preferences facilitates Pareto-superior outcomes through the maximization of both individual and collective welfare. Mutual reciprocal preferences among members not only mitigate opportunistic behavior through the enhancement of goodwill but also amplify complementarities in capabilities and resources, thereby accelerating resource integration efficiency and securing maximal mutual gains.
3.2.2. Total Performance-Based Incentive Mechanism
(1) Model Formulation and Solution
Under the TP mode, the revenue of consortium member i consists of two components, including contractual revenue for the specialized entity undertaking PPP project implementation tasks and distributive returns proportional to the project’s total output for an investor [15]. Thus, the material payoff of consortium member i is expressed as follows:
The certainty equivalent income of consortium member i is expressed as follows:
The value increment of a consortium-based PPP project is defined as the difference between the project’s aggregate performance output and incentive costs. Its expectation is determined as
The incentive model for maximizing the PPP project’s value increment is formalized as
The Hessian matrix of is negative. Consequently, the objective function is strictly concave with respect to and . A globally optimal solution can be obtained by solving the system of first-order conditions, given by and .
Under the TP mode, the optimal productive effort and collaborative effort of consortium member i are identical, both exhibiting a linear dependence on the incentive intensity coefficient. Given the public good attributes of PPP projects and their alignment with social welfare objectives, the return to private investors should not exceed their reservation utility. As a result, the participation constraint binds at the optimal point . Substituting into CM yields the value-increment objective function:
Under reciprocal preferences, variables and demonstrate a linear relationship defined by , where represents the degree of reciprocity for the consortium member i [34]. Incorporating this relationship into the incentive model yields
where , indicating the strict concavity of CM. Solving the simultaneous first-order conditions yields , thereby providing explicit equilibrium expressions, as follows:
(2) Analysis of Model Results
Based on the analytical solution of the model, this study investigated the determinants and functional mechanisms of incentive structures under the TP mode.
Theorem 3.
TP mode is feasible if and only if .
Proof of Theorem 3.
Let the incentive compatibility constraint be defined as , where the boundary condition universally holds. Given , can be obtained. □
Subthreshold reciprocal preferences lead to hyperinflation of total output-based incentive intensity, thereby triggering the institutional breakdown of the mechanism. Within the subthreshold reciprocity regime, the government is forced to continuously escalate the incentive intensity for project-specific outputs, while the resulting convex cost escalation gradually erodes the implementation momentum.
Theorem 4.
When the incentive mechanism holds,
,
, and
exhibit positive correlations with
, whereas
is uncorrelated with
. Moreover,
demonstrates a positive correlation with
, whereas
,
, and
present negative correlations with
. Specifically,
contributes to
, and the cooperative effort of i toward j equals that from j to i.
Proof of Theorem 4.
From and , both and exhibit positive correlations with . Given , where , implies that is positively correlated with . From , is uncorrelated with . Furthermore, based on , , and , , , and exhibit negative correlations with . □
As collaborative synergy within the team intensifies, consortium members concurrently escalate both productive and collaborative efforts, thereby significantly amplifying the total output of PPP projects. While enhanced synergy does not increase the unit incentive intensity linked to aggregate consortium output, the resulting expansion in output nonetheless enhances members’ incentive earnings. For governments, the incremental value of PPP projects generated through intensified synergy exceeds the corresponding performance-based remuneration paid to the consortium, resulting in increased non-contingent fiscal payoffs.
An elevated orientation toward reciprocity within the consortium reduces the unit incentive intensity associated with total output. Both equilibrium productive effort and collaborative effort decline as the reciprocity orientation strengthens. Under a fixed incentive mechanism, equivalent incentive returns are achieved by members with reduced effort inputs, as greater reciprocity orientation improves effort efficiency, indicating that reciprocity escalation directly enhances the premium on effort efficiency.
3.2.3. Mechanism Based on Individual-Performance of Consortium Members
(1) Model Formulation and Solution
Under the IP mode, the revenue of a consortium member consists of proceeds from the PPP project implementation contract and performance-based remuneration linked to individual output. Specifically, member i enhances economic gains by improving individual performance output [35]. Accordingly, pecuniary returns accruing to member i from consortium participation are formalized as follows:
Assuming that consortium member i is risk-averse with the risk aversion coefficient , the certainty equivalent income of member i is expressed as
The expected value increment of the consortium PPP project is given by
The incentive model maximizing the PPP project value increment is formulated as
The Hessian matrix of is negative definite. Consequently, constitutes a strictly concave function with respect to and . As both and , we can obtain
The production effort of consortium member i exhibits a positive correlation with the incentive coefficient , whereas the cooperative effort is zero. Given the public welfare and social benefit attributes of the consortium PPP project, the net revenue of member i should not exceed its reservation utility [1]. Consequently, the participation constraint binds at the optimum, that is, . Substituting this into the CM expression yields the objective formulation for the value increment of the consortium PPP project:
Under reciprocal preferences, a linear relationship exists between and , satisfying . Given and , then . Substituting this into the incentive model yields
Within the CM function, because , the specified condition confirms that CM is a concave function. From the first-order condition , is obtained. Consequently, the equilibrium production effort and cooperative effort are defined as
(2) Analysis of Model Results
This section investigates the influencing factors and operational mechanisms of the incentive scheme based on the individual outputs of the consortium members, as derived from the model solutions.
Theorem 5.
The incentive mechanism is feasible only if the condition
holds. Under this condition,
,
, and
all exhibit strictly positive correlations with
.
Proof of Theorem 5.
The incentive mechanism is feasible if and only if . As , the condition is satisfied. From the partial derivatives , , and , it follows that , , and each exhibit strictly positive correlations with . □
For governments to adopt performance-based incentives centered on the individual output of consortium members, the degree of collaborative synergy must be controlled. Excessively high collaboration can result in the prohibitively high implementation costs for governments, thereby weakening their willingness to enforce such incentive mechanisms.
4. Comparative Analysis of Three Incentive Modes
4.1. Optimal Effort Levels of Consortium Members
Building on the assumption in Section 3.1 that the marginal productivities of self-interested and prosocial efforts are identical, a member’s output level is determined by their aggregate effort level (i.e., the sum of self-interested and prosocial components). Accordingly, this section comparatively examines the optimal aggregate effort levels of consortium members under the three incentive modes.
Theorem 6.
(1) When
, the IP mode serves as the sole effective incentive mechanism. (2) When
, both the TP and IP modes demonstrate operational viability, with the relationship
holding. (3) When
, DP, TP, and IP modes are all feasible, and
. (4) When
, DP, TP, and IP continue to constitute feasible incentive frameworks, and the inequality
holds.
Proof of Theorem 6.
Comparing the optimal effort levels of consortium members under the TP and IP modes, that is, , and using to represent the derived expression, it can be shown that . Given this, the viability condition for DP is , as previously concluded. According to theorem 1, TP remains operational when . Theorem 5 further confirms that IP’s effectiveness is not constrained by , and is verified via difference analysis. □
(1) According to Theorem 1 and 3, when , neither TP nor DP remains viable, such that IP emerges as the sole effective incentive mechanism.
(2) When , both DP and IP remain operational, whereas TP fails to be viable. Hence, . Given , then > 0, and .
(3) According to Theorem 1, 3, and 5, when , all three incentive modes remain operational. As , . The application of the difference method to compare the optimal effort levels under the DP and TP modes contributes to .
Given , then , can be obtained. Synthesizing the preceding proof steps can lead to .
(4) When , all three incentive modes remain operational. With , can be obtained. By employing the difference method to compare the optimal effort levels under the DP and IP modes, it is derived that . As , can be obtained with . Synthesizing Proof (3), can be derived.
The optimal effort levels under all three mechanisms increase monotonically with the intensity of reciprocal preferences. Under extreme levels of preference intensity, individual output-based incentives enhance effort primarily by intensifying self-interested behavior, thereby increasing consortium output without relying on altruistic contributions. In contrast, at moderate levels of preference intensity, hybrid incentives simultaneously strengthen both self-interested and altruistic components of effort, promoting output growth through their synergistic interaction.
4.2. Comparative Analysis of Consortium Members’ Optimal Incentive Coefficients
Theorem 7.
Under scenarios where all three incentive mechanisms (IP/DP/TP) are applicable,
and
.
Proof of Theorem 7.
Because and
, then , and . Given the conditions of and , can be obtained. □
Under the TP mode, the government primarily realizes effective incentives by adjusting the incentive coefficient associated with the consortium’s total output. In this mode, the incentive intensity based on the total output is significantly higher than that in the DP mode. In contrast, under the IP mode, incentive implementation focuses on coefficients linked to individual members’ outputs. In this context, the intensity of incentives targeting individual outputs surpasses that of the DP mode. The DP mode adopts a dual-channel framework that simultaneously incorporates both consortium-level and individual-level outputs into the incentive allocation. Consequently, the overall incentive intensity across both channels is consistently lower than the corresponding intensity levels under the TP and IP modes. Therefore, the DP mode enhances the flexibility and efficiency of incentive design and demonstrates strong practical applicability in real-world settings.
4.3. Numerical Analysis
The existence boundaries of the three incentive modes, the optimal effort levels of consortium members, and the government’s optimal incentive coefficients are closely associated with reciprocity preferences and team synergy effects. The numerical analysis further investigates the key influencing factors and evolutionary dynamics of member effort levels. According to the assumptions in Section 3.1, the number of consortium members is set to , the team collaboration coefficient is fixed, the absolute risk aversion coefficient is , the marginal cost is , and the variance is 2.
(1) Impact of Consortium Members’ Reciprocity Preferences on Optimal Effort Levels
Member effort consists of production and collaboration efforts, with the total effort defined as their sum. Under DP, TP, and IP modes, the optimal levels of production effort, collaboration effort, and total effort are illustrated in Figure 1, Figure 2, and Figure 3, respectively.
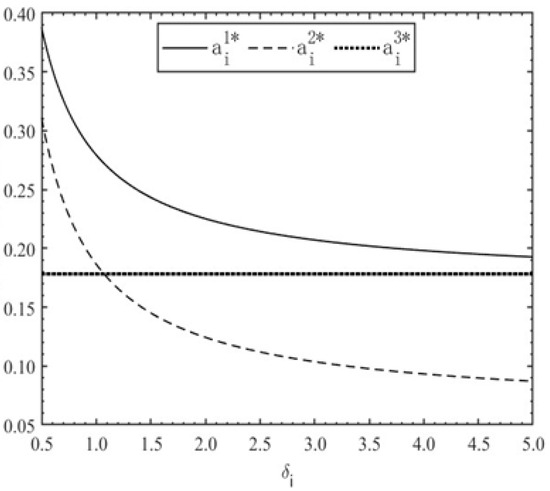
Figure 1.
Optimal production effort level of consortium members versus reciprocity preference level .
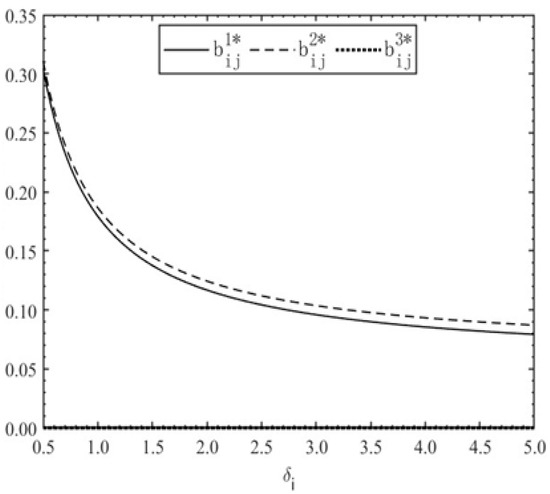
Figure 2.
Optimal cooperative effort level of consortium members versus reciprocity preference level .
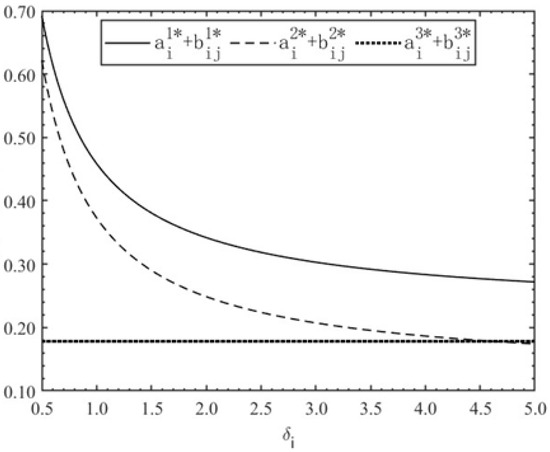
Figure 3.
Optimal total effort level of consortium members versus reciprocity preference level .
Figure 1 demonstrates that reciprocal preferences exert no impact on the optimal productive effort in the IP mode. Under the DP and TP modes, productive effort declines sharply as reciprocal preference increases and subsequently stabilizes. The DP mode consistently results in higher levels of productive effort than the TP mode, with the performance gap expanding in response to increased reciprocal preference. Figure 2 indicates that cooperative effort remains zero under the IP mode. For the DP and TP modes, the cooperative effort decreases as the reciprocal preference increases, whereas the TP mode maintains marginally higher levels than the DP mode. As shown in Figure 3, the total effort under the IP mode remains unaffected by variations in . In contrast, the DP and TP modes exhibit decreasing total effort with increasing , characterized by a rapid drop when < 1.5, followed by asymptotic convergence. Notably, the total effort under the IP mode surpasses that under the TP mode when > 4.8. Under the IP mode, because members’ compensation depends on individual outputs, efforts are exclusively directed towards self-interested output generation, with no engagement in cooperative activities. However, even with moderate levels of reciprocity, the productive effort under the IP mode remains lower than that under the DP mode. The IP mode yields the highest level of productive effort only when reciprocal preference becomes excessively high. Conversely, the DP mode balances both productive and cooperative efforts, as members indiscriminately allocate efforts to any action contributing to the overall PPP project output regardless of its typology. Nevertheless, excessive cooperative effort results in diminishing marginal returns, thereby impairing total project output. Comparatively, within a reasonable range of reciprocal preferences, the DP mode achieves a more effective combination of productive effort and aggregate effort intensity, thereby optimizing comprehensive project outcomes relative to other incentive structures.
(2) Impact of Consortium Members’ Reciprocal Preferences on Optimal Incentive Intensity
The incentive intensity coefficient and output level jointly determine the government’s incentive strength and associated cost allocations to consortium members. The optimal incentive intensity coefficients under the three governance modes are illustrated in Figure 4 and Figure 5.
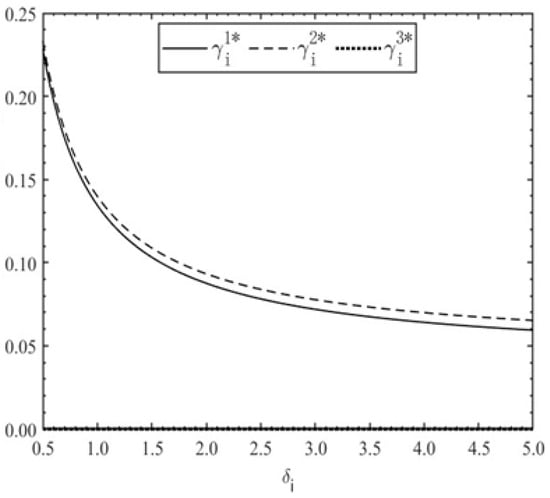
Figure 4.
Incentive coefficient based on total output versus reciprocity preference level .
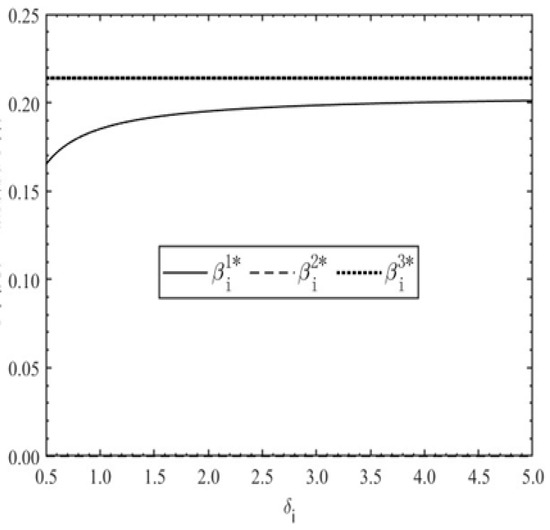
Figure 5.
Incentive coefficient based on individual member output versus reciprocity preference level .
Figure 4 illustrates that the optimal total-output-based incentive intensity coefficient is zero under the IP mode. Under both the DP and TP modes, this coefficient decreases monotonically as the reciprocal preference levels increase. Moreover, the coefficients under the TP mode remain consistently higher than those under the DP mode. Figure 5 indicates that the individual-output-based optimal incentive intensity coefficient is zero in the TP mode and remains uncorrelated with reciprocal preferences. However, under the IP mode, this coefficient is positively associated with the team collaboration factor, increasing asymptotically with rising reciprocal preference intensity and eventually converging to a stable value. These results suggest that excessive reciprocal preferences exert no significant influence on the DP mode. Notably, the DP mode exhibits uniformly lower incentive coefficients than the IP mode. When preferences remain moderate, the DP mode enables lower incentive costs while offering greater flexibility and adaptability in incentive design.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
5.1. Discussion
Team collaboration is both the fundamental motivation for members to form a consortium to implement PPP projects and the overarching objective of such collaboration. Mutual reciprocity among consortium members serves as a critical safeguard for the smooth operation of the consortium. Incorporating mutual reciprocity and cooperative behavior into the incentive mechanism design of consortium-based PPP projects transcends the conventional assumption of rational economic agents and better aligns with the behavioral characteristics of participants in project-based collaborative settings. This approach renders the incentive mechanism more consistent with the real-world context of consortium PPPs.
For consortium members, their optimal levels of productive effort and cooperative effort under different incentive schemes are positively correlated with the team collaboration coefficient. A higher level of team collaboration has an amplification effect on the overall output of the consortium, thereby incentivizing members to exert greater effort in pursuit of higher rewards. From the government’s perspective, the incentive coefficient for individual member outputs is positively associated with the strength of team collaboration effects, whereas the incentive coefficient for consortium-level output is independent of team collaboration. This is because the aggregate output of the consortium already embodies the benefits of team collaboration—that is, when the government adopts incentives based on total consortium output, it no longer needs to separately account for collaboration effects. However, excessively high team collaboration effects can lead to increased government incentive costs, thereby reducing the incentive intensity for individual outputs.
Reciprocity preferences play a decisive role in influencing the effectiveness of incentive mechanisms by affecting members’ cooperative effort levels. When reciprocity preferences are too low, the cooperative effort output of consortium members diminishes significantly, and their optimal behavior tends to focus primarily on productive effort. In such cases, incentive mechanisms that target consortium-level output become ineffective. Conversely, when reciprocity preferences are excessively high, all three incentive modes remain valid in theory, but the IP mode tends to yield the highest effort levels. This is because overly strong reciprocity may lead members to engage in excessively high levels of inefficient cooperative effort, which can ultimately reduce overall output. In such scenarios, incentives based on individual member outputs become more effective.
Nevertheless, in real-world engineering practice, consortium members typically exhibit moderate levels of reciprocity preferences. Under such conditions, the DP mode which incorporates both consortium-level output and individual outputs demonstrates superior incentive effectiveness and flexibility, making it the preferred option for governments when designing incentive mechanisms. For example, the Sydney Metro Northwest PPP project effectively stimulated collaborative effects and reciprocal preferences among consortium members by adopting a consortium-wide incentive approach, establishing risk-sharing and benefit-sharing mechanisms, and introducing long-term cooperation and reciprocity-oriented incentive arrangements. Similarly, the London Underground PPP projects, implemented by the Tube Lines and Metronet consortia, applied a dual-incentive mechanism that combined system-wide availability-based payments (i.e., aggregate output incentives) with individual performance evaluations for specific sub-tasks or subsystems (i.e., individual output incentives). This dual approach successfully facilitated project implementation.
5.2. Conclusions
Well-designed incentive mechanisms serve as essential safeguards for the effective implementation of consortium-based PPP projects [36]. The heterogeneity of consortium members, their reciprocity preferences, and the complexity of inter-member collaboration constitute the core logic and key determinants shaping the architecture of incentive systems. Based on consortium-level synergy and reciprocity orientation, this study formulates and solves three incentive models: dual-performance mechanism, total-performance mechanism, and individual-performance mechanism. The comparative analysis yielded the following major findings: (1) The optimal effort levels under all three mechanisms are positively correlated with team synergy effects. Reciprocity preferences exhibit a negative relationship with effort in the DP and TP modes, whereas no statistically significant effect is observed in the IP mode. (2) The IP mechanism induces positive incentive effects only under extreme reciprocity conditions (either excessively high or low). Under such scenarios, members tend to prioritize self-interested efforts, while altruistic efforts decline and revenue growth is driven by individual output maximization. (3) When reciprocity remains within a moderate range, the DP mechanism achieves higher aggregate effort levels than TP or IP mechanisms. The application of dual incentive coefficients enhances operational adaptability and allocative efficiency.
To strengthen incentive effectiveness and project quality, governments can establish a multidimensional collaborative incentive framework for consortium-based PPP projects. Simultaneously, the introduction of compensation schemes may support reciprocity-preference-driven incentive policies. However, owing to the long-term nature of PPP engagements, dynamic adjustments to incentive mechanisms are necessary. Governments should tailor these adjustments according to the implementation phase, collaboration level, and output performance of the consortium.
There are certain shortcomings associated with this study; therefore, there is a need to consider future research. Firstly, this study majorly focuses on constructing static incentive mechanisms for consortium-based PPP projects. However, owing to the long-term nature of PPP engagements, dynamic adjustments to incentive mechanisms are necessary, which can be continued in future studies. Secondly, in the implementation of consortium-based PPP projects, the accurate quantification of both consortium outputs and individual outputs serves as a critical foundation for the effective implementation of incentive mechanisms. The scientifical quantification standards and methods could be materialized in future studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.S. and Z.-Q.M.; methodology, Y.S.; software, F.Y.; validation, Y.S. and Z.-Q.M.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.S.; writing—review and editing, F.Y.; supervision, Z.-Q.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| PPP | Public–Private Partnership |
| DP | Dual-Performance |
| TP | Total-Performance |
| IP | Individual-Performance |
| PPI | Private Participation in Infrastructure |
| ICT | information and communication technology |
References
- Jayasena, N.S.; Chan, D.W.; Kumaraswamy, M.M.; Seidu, S.; Ekanayake, E.; Siu, F.M. Adoption of public-private partnership (PPP) in smart infrastructure development projects in developing nations: An explorative structural equation modelling analysis. Cities 2024, 152, 105232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppenjan, J.F.M.; Enserink, B. Public-Private partnerships in urban infrastructures: Reconciling private sector participation and sustainability. Public Adm. Rev. 2023, 69, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbany, S.; Yousefi, S.; Noorzai, E. Evaluating and optimizing performance of public-private partnership projects using copula Bayesian network. Eng. Constr. Arch. Manag. 2024, 31, 290–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batjargal, T.; Zhang, M. Review of key challenges in public-private partnership implementation. J. Infrastruct. Policy Dev. 2021, 5, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqar, A.; Khan, A.M.; Othman, I. Blockchain empowerment in construction supply chains: Enhancing efficiency and sustainability for an infrastructure development. J. Infrastruct. Intell. Resil. 2024, 3, 100065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomáš, P.; Kaššaj, M. Legal Easements as Enablers of Sustainable Land Use and Infrastructure Development in Smart Cities. Land 2025, 14, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessina, S. The Link Between Environmental Rights and the Rights of Nature: The Virtues of a Complexity-Based Approach. Jurid. Trib. Rev. Comp. Int. Law 2025, 15, 406–422. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Research on the Identification Model of Interest Conflict Influencing Factors in PPP Projects Construction of Smart City. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 12689–12698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, D.; Zhu, D.; Quayson, M.; Hossin, A.; Omoruyi, O.; Bediako, A.K. A multicriteria decision framework for governance of PPP projects towards sustainable development. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2023, 87, 101580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei-Kyei, R.; Chan, A.P.C. Review of studies on the Critical Success Factors for Public-Private Partnership (PPP) projects from 1990 to 2013. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2015, 33, 1335–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, Q.; Kabir, M.H.; Chaudhri, V. Managing Infrastructure Projects in Australia A Shift from a Contractual to a Collaborative Public Management Strategy. Adm. Soc. 2014, 46, 422–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, O. Incomplete contracts and public ownership: Remarks, and an application to public-private partnerships. Econ. J. 2003, 113, C69–C76. [Google Scholar]
- Rangel, T.; Vassallo, J.M.; Arenas, B. Effectiveness of safety-based incentives in Public Private Partnerships: Evidence from the case of Spain. Transp. Res. Part A 2012, 46, 1166–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, P.J.; Emanuel, L.; Pereira, R.H. Highway concessions and road safety: Evidence from Brazil. Res. Transp. Econ. 2021, 90, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladag, H.; Isik, Z. The Effect of Stakeholder-Associated Risks in Mega-Engineering Projects: A Case Study of a PPP Airport Project. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2020, 67, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez-Avila, C.; Hartmann, A.; Dewulf, G.; Henseler, J. Interplay of Relational and Contractual Governance in Public-Private Partnerships: The Mediating Role of Relational Norms, Trust and Partners’ Contribution. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2018, 36, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabry, M.I. Good Governance, Institutions and Performance of Public Private Partnerships. Int. J. Public Sect. Manag. 2015, 28, 566–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, D.; Srivastava, A.K. Managing partner opportunism in public-private partnerships: The dynamics of governance adaptation. Public Manag. Rev. 2019, 21, 1420–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J. Evaluation of the excess revenue sharing ratio in PPP projects using principalagent models. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2015, 33, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gao, R.; Cheah, C.Y.; Luo, J. Incentive mechanism for inhibiting investors’ opportunistic behavior in PPP projects. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2016, 34, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Liu, C.; Sun, Z. Promoting developments of hydrogen production from renewable energy and hydrogen energy vehicles in China analyzing a public-private partnership cooperation scheme based on evolutionary game theory. Energy 2023, 278, 127654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warsen, R.; Greve, C.; Klijn, E.H.; Koppenjan, J.F.M.; Siemiatycki, M. How do professionals perceive the governance of public-private partnerships? Evidence from Canada, the Netherlands and Denmark. Public Adm. 2020, 98, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.; Kim, H. Demand risk transfer and government’s cost efficiency: Focusing on Korean waste treatment PPP cases. Waste Manag. 2022, 137, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, H.O.; Liu, J. Incentive game of investor speculation in PPP highway projects based on the government minimum revenue guarantee. Transp. Res. Part A 2019, 125, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lei, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, J.; Xu, Z. Analyzing Factors Influencing Government Control Rights in PPP Projects from the Perspective of Investors. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2022, 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolstadas, A.; Schiefloe, P.M. Modelling project complexity. Int. J. Manag. Proj. Bus. 2017, 10, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y. Research on Driving factors of Government Dishonesty in PPP Projects Based on Grounded Theory. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 221, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ma, Z.Q.; Ding, Y. Rank-Dependent Expected Utility Game Analysis of Public-Private Partnership Project Operation Supervision Considering the Influence of Emotion. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2023, 27, 4572–4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimsey, D.; Lewis, M.K. Are Public Private Partnerships value for money? Evaluating alternative approaches and comparing academic and practitioner views. Account. Forum 2005, 29, 345–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervan, S.J.; Bove, L.L.; Johnson, L.W. Reciprocity as a key stabilizing norm of interpersonal marketing relationships: Scale development and validation. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2009, 38, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Jim, C.Y. A Performance Evaluation System for PPP Sewage Treatment Plants at the Operation-maintenance Stage. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2023, 27, 1423–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.P.; Levitt, R.; Tsui, C.-W.; Hsu, Y. Opportunism-Focused Transaction Cost Analysis of Public-Private Partnerships. J. Manag. Eng. 2015, 31, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, B.; Xiong, W.; Wu, G. Commercial investment in public-private partnerships: The impact of contract characteris-tics. Policy Politics 2018, 46, 589–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Love, P.E.; Liang, X.; Kong, T. Public-private partnerships and land value capture: A convergent framework to improve the procurement of urban rail transit infrastructure. Dev. Built Environ. 2024, 18, 100441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eze, E.C.; Ameyaw, E.E. Potential application areas and benefits of blockchain-enabled smart contracts adoption in infrastructure Public-private partnership (PPP) projects. Sustain. Futures 2025, 9, 100477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wang, H.; Shi, G. Collusion prevention mechanism in PPP highway projects: Optimal government subsidy, toll and penalty. Econ. Transp. 2025, 42, 100399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).