Intelligent ESG Evaluation for Construction Enterprises in China: An LLM-Based Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
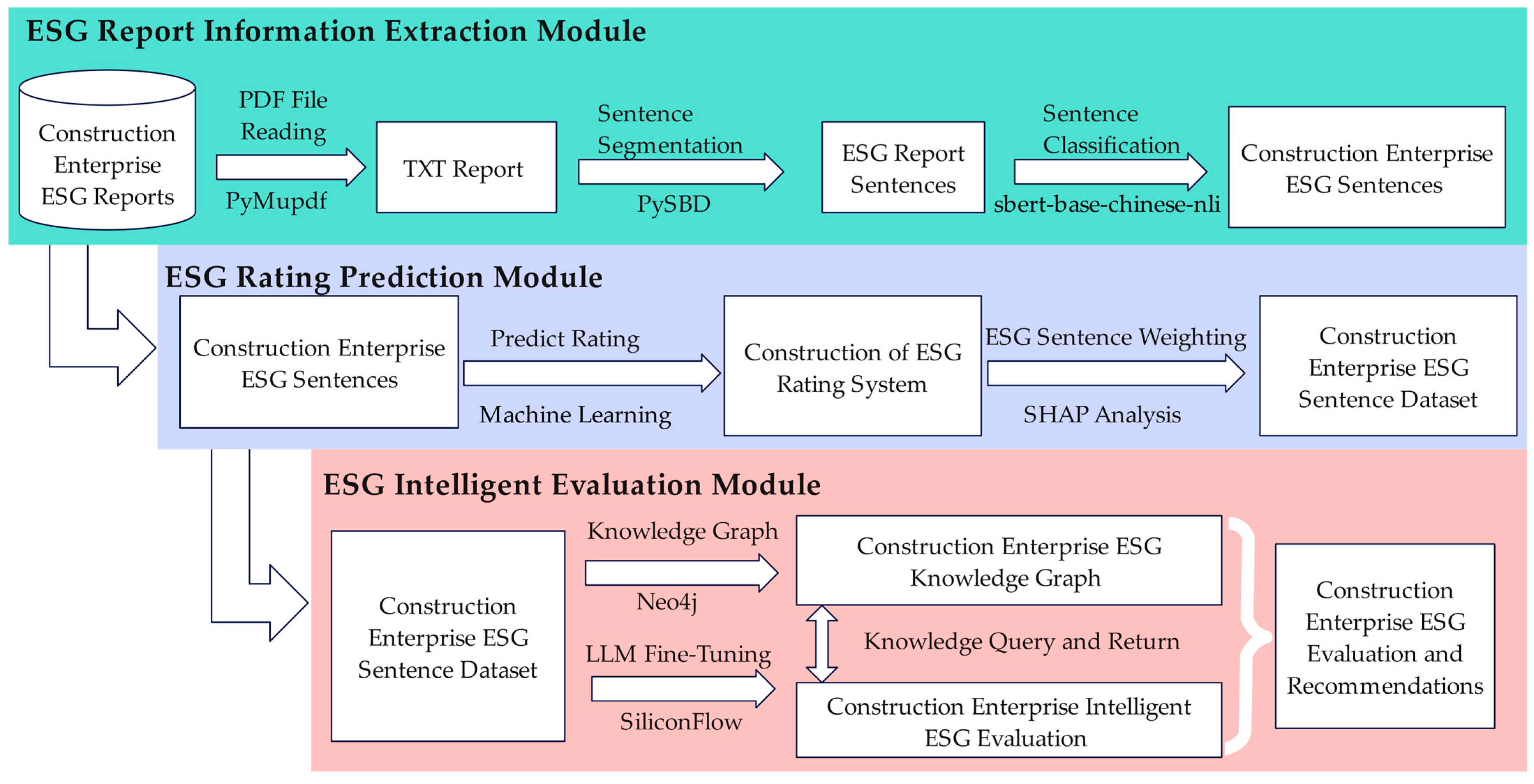
2. LLM-Based Intelligent ESG Evaluation Model
2.1. ESG Report Information Extraction Module
2.2. ESG Rating Prediction Module
- Random Forest Regression—This approach employs an ensemble of 200 decision trees trained with bootstrap sampling. By constructing trees on random subsets of both data and features, the model captures complex, non-linear relationships inherent in ESG disclosures while exhibiting robustness to overfitting [45]. The Random Forest prediction can be expressed in Equation (3):where is the Random Forest prediction function, is the number of trees, and represents the prediction of the decision tree.
- XGBoost Regression—This gradient boosting framework iteratively builds 200 regression trees, where each successive tree is trained to correct the residual errors of the ensemble. XGBoost incorporates L1 and L2 regularization terms to effectively control model complexity and prevent overfitting [46]. The prediction process can be formulated using Equation (4):where denotes the final XGBoost prediction, is the number of f boosting iterations (trees), and is the output of the regression tree.
2.3. Intelligent ESG Evaluation Module
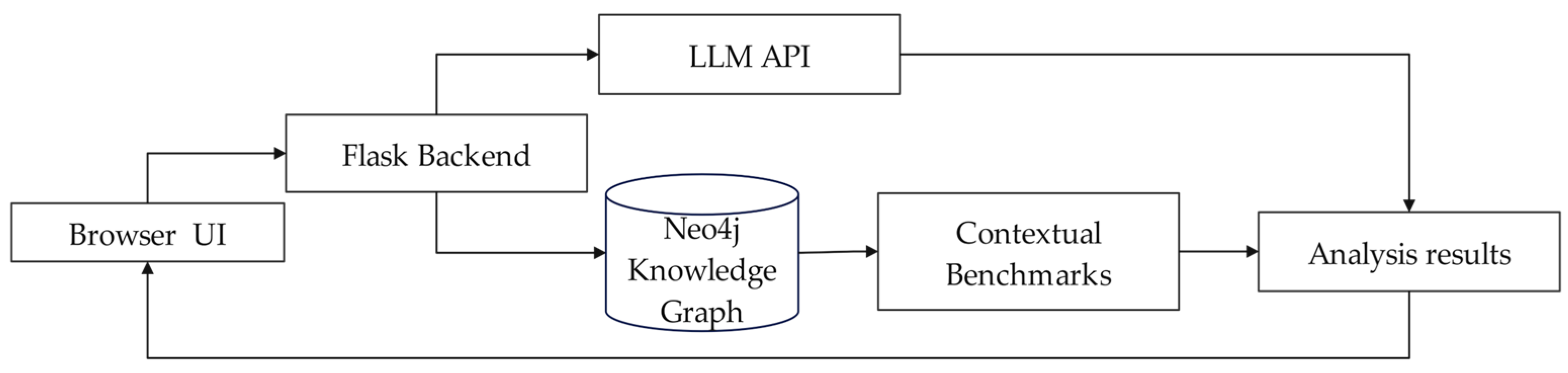
3. Data-Based Prototype
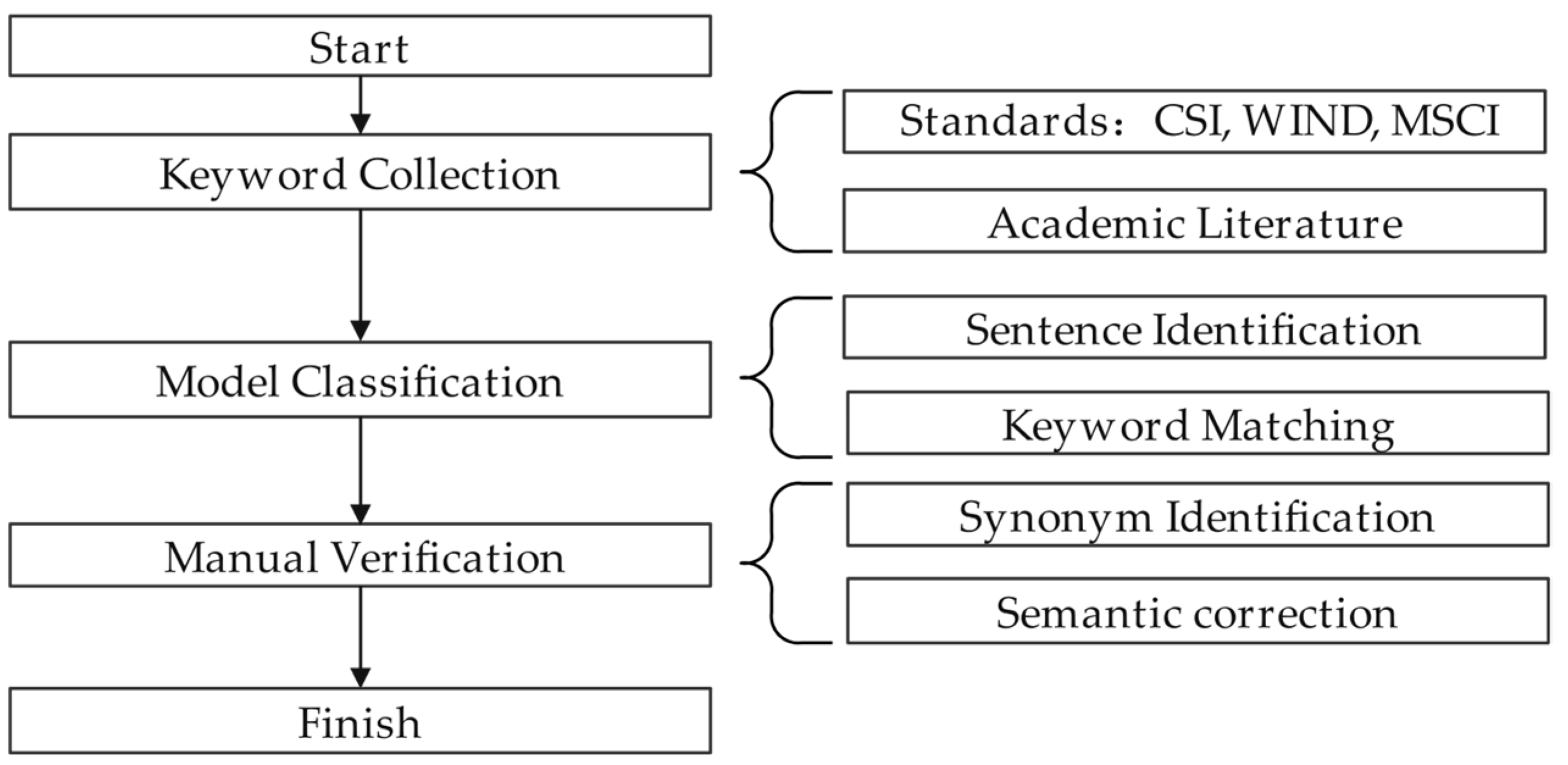
3.1. Data Collection and Processing
3.2. Prototype Building and Verification
3.2.1. ESG Knowledge Graph Construction
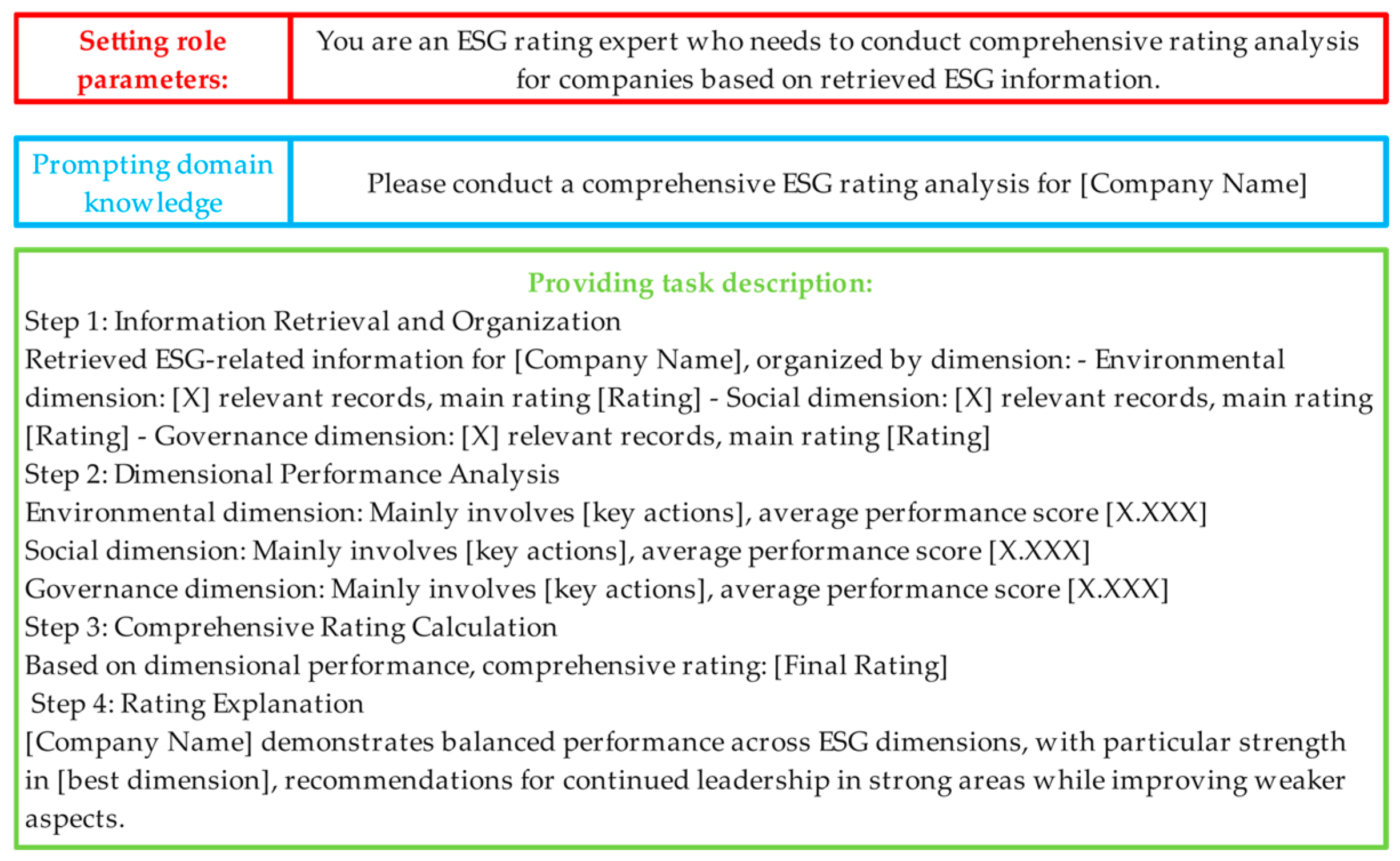
3.2.2. LLM Fine-Tuning
- Single-sentence analysis samples: These samples perform a six-step analysis for individual ESG statements, including sentence classification, key indicator identification, weight assessment, industry benchmarking, score calculation, and reasoning explanation.
- Comprehensive analysis samples: These samples simulate RAG scenarios by conducting a multi-dimensional comprehensive ESG rating analysis for companies, encompassing information retrieval and organization, dimensional performance analysis, comprehensive rating calculation, and rating justification.
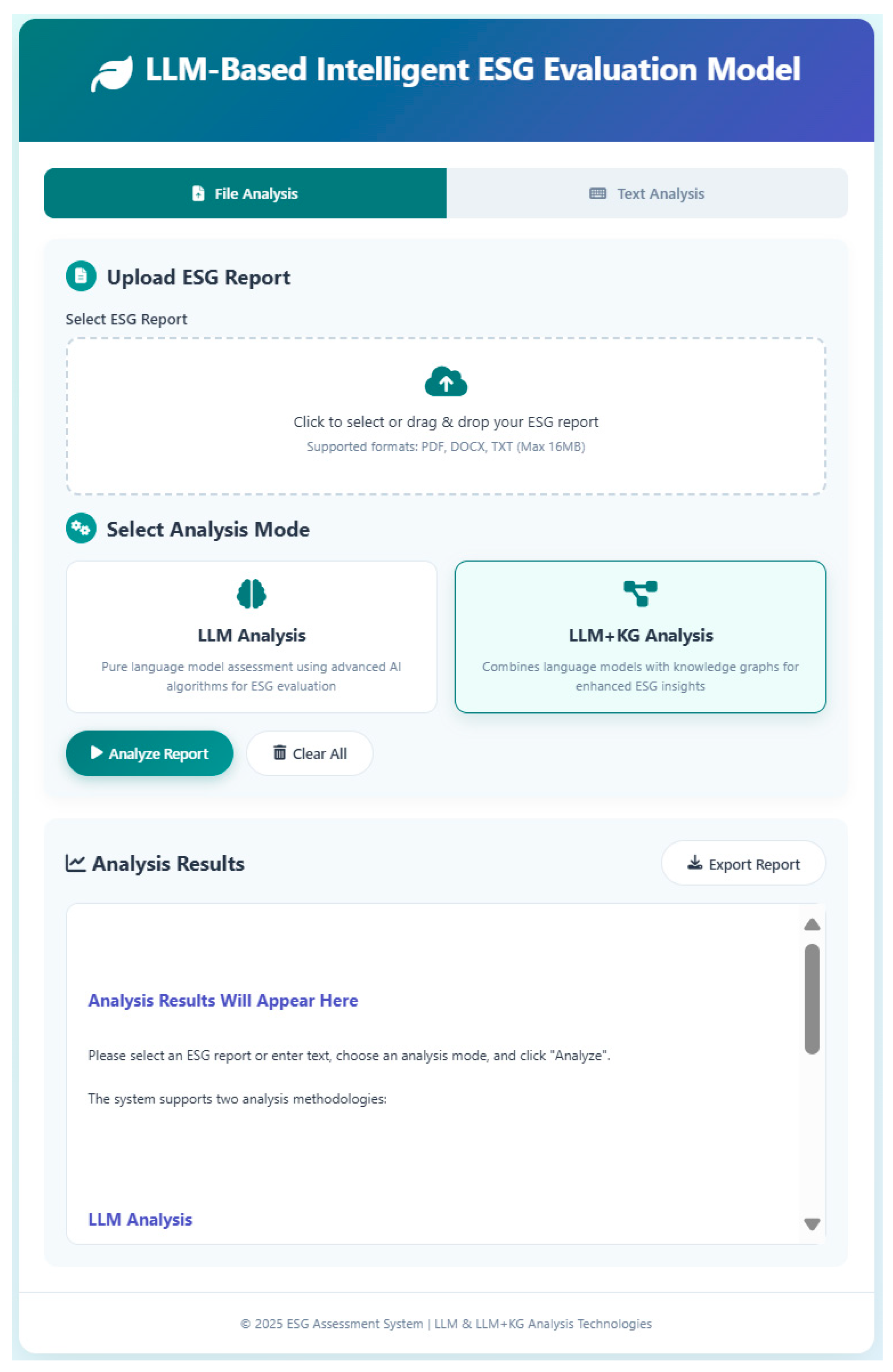
3.2.3. Prototype Verification
4. Results
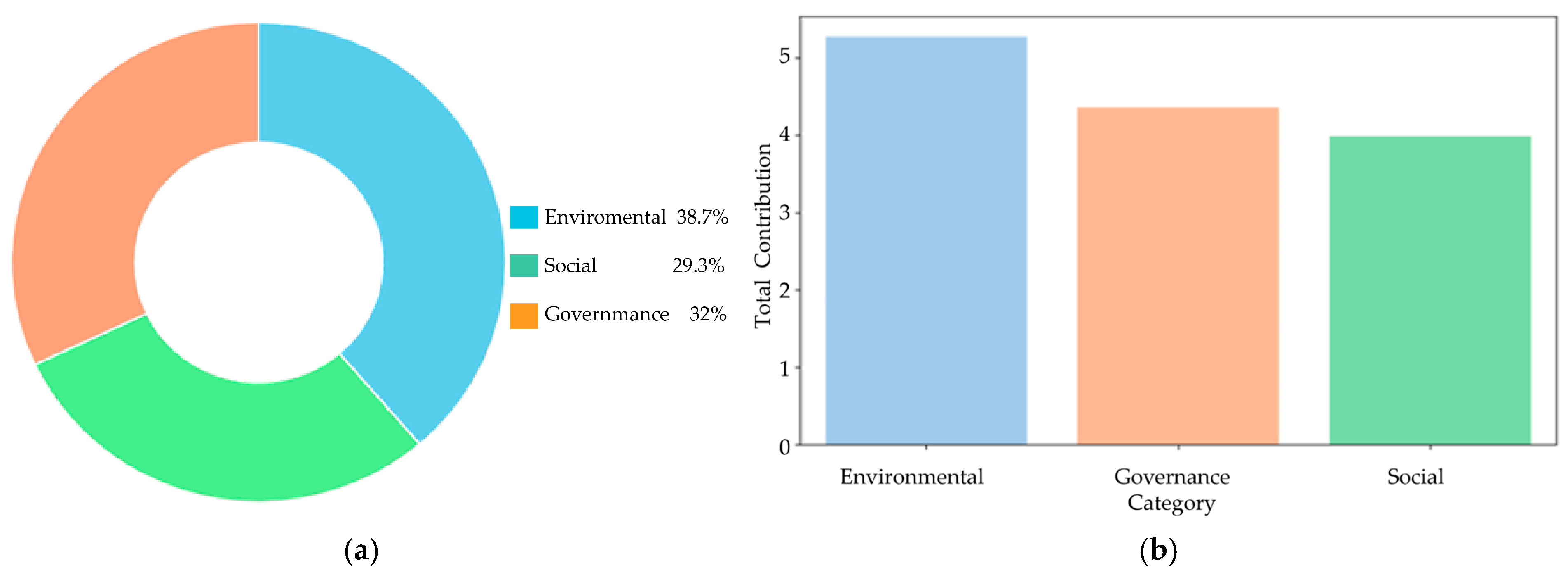
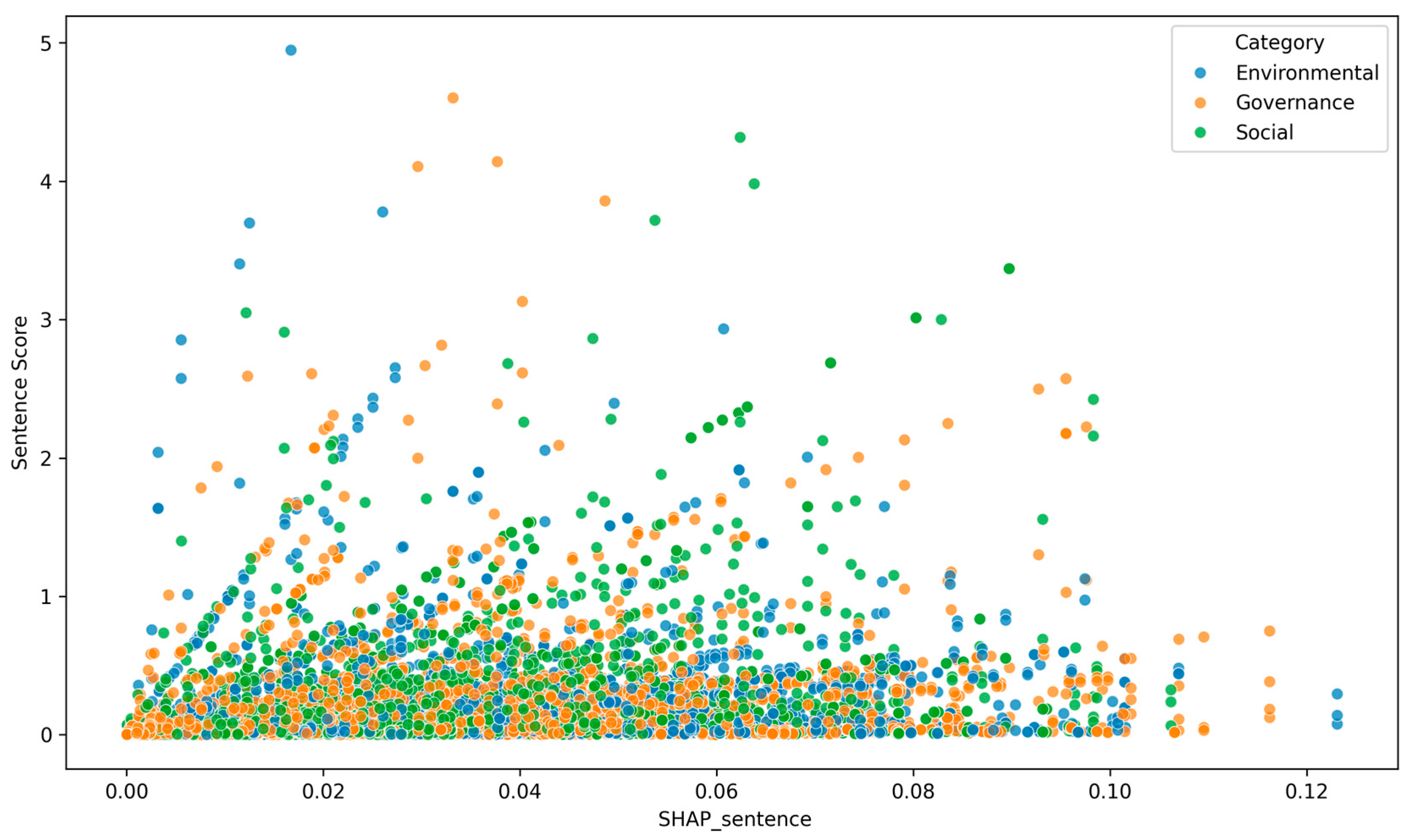
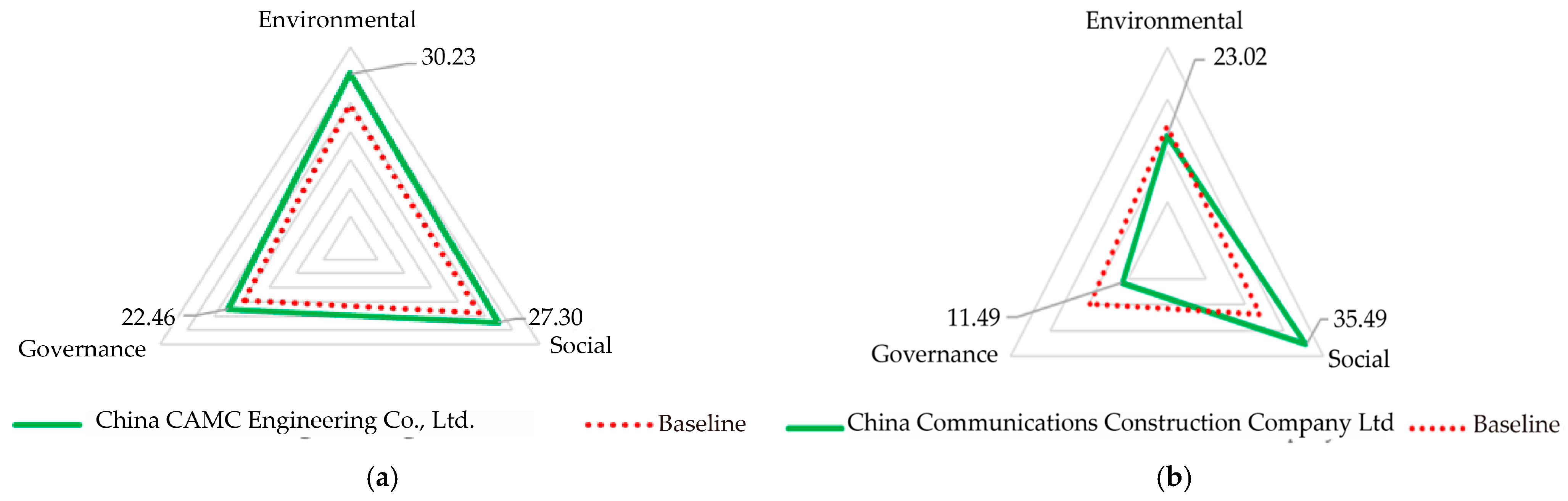
4.1. ESG Rating Prediction Results and SHAP Analysis
4.2. ESG Rating LLM Evaluation Results
5. Discussion
5.1. NLP-Based ESG Rating Framework
5.2. Reasoning Ability of the LLM-Based Intelligent ESG Evaluation Model
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ESG | Environmental, Social, and Governance |
| LLM | Large Language Model |
| XGBoost | Extreme Gradient Boosting |
| SHAP | SHapley Additive exPlanation |
| CoT | Chain-of-Thought |
| NLP | Natural Language Processing |
| RAG | Retrieval-Augmented Generation |
| LoRA | Low-Rank Adaptation |
| KG | Knowledge Graph |
| API | Application Programming Interface |
References
- Global ESG Assets Predicted to Hit $40 Trillion by 2030, Despite Challenging Environment, Forecasts Bloomberg Intelligence. 2025. Available online: https://www.bloomberg.com/company/press/global-esg-assets-predicted-to-hit-40-trillion-by-2030-despite-challenging-environment-forecasts-bloomberg-intelligence (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Eccles, R.G.; Kastrapeli, M.D.; Potter, S.J. How to Integrate ESG into Investment Decision-Making: Results of a Global Survey of Institutional Investors. J. Appl. Corp. Financ. 2017, 29, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Duuren, E.; Plantinga, A.; Scholtens, B. ESG Integration and the Investment Management Process: Fundamental Investing Reinvented. J. Bus. Ethics 2016, 138, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Managi, S. Disclosure or action: Evaluating ESG behavior towards financial performance. Financ. Res. Lett. 2022, 44, 102108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S. Enterprise Value Assessment Based on ESG Evaluation. Front. Bus. Econ. Manag. 2022, 4, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Yu, C.; Zhang, G. How does green manufacturing enhance corporate ESG performance?—Empirical evidence from machine learning and text analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Song, Y.; Gao, P. Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance and financial outcomes: Analyzing the impact of ESG on financial performance. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, R.R.R.; Martins, V.W.B.; Macedo, A.N. Validation of Challenges for Implementing ESG in the Construction Industry Considering the Context of an Emerging Economy Country. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewumi, A.S.; Opoku, A.; Dangana, Z. Sustainability assessment frameworks for delivering Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) targets: A case of Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method (BREEAM) UK New Construction. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2024, 31, 3779–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Building Materials and the Climate: Constructing a New Future. 2023. Available online: https://www.unep.org/resources/report/building-materials-and-climate-constructing-new-future (accessed on 21 July 2025).
- Construction Fatalities Hit Highest Number in More Than a Decade. 2024. Available online: https://www.newsweek.com/construction-fatalities-hit-highest-number-over-decade-2004244 (accessed on 21 July 2025).
- Construction Worker Deaths on the Rise, HSE Confirms. 2024. Available online: https://www.constructionnews.co.uk/health-and-safety/construction-worker-deaths-reach-four-year-high-hse-reveals-21-11-2024/ (accessed on 21 July 2025).
- Zhang, H.; Xia, B.; Li, Q.; Wang, X. The effect of self-enhancement motivation and political skill on the relationship between workplace exclusion and ingratiation. Curr. Psychol. 2025, 44, 5399–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Tong, X.; Jia, X. Executives’ Legal Expertise and Corporate Innovation. Corp. Gov. Int. Rev. 2024, 32, 954–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Du, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Tong, G.; Zhou, R. Does ESG Disclosure Affect Corporate-Bond Credit Spreads? Evidence from China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilivogui, P.; Iqbal, M.A. Do ESG scores matter? An empirical analysis of corporate financial performance in BRICS economies. Environ. Res. Commun. 2025, 7, 065023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Chu, D.; Zheng, J.; Ye, T. Environmental, social and governance performance: Can it be a stock price stabilizer? J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyönyörová, L.; Martin, S.; Stašek, D. ESG ratings: Relevant information or misleading clue? Evidence from the S&P Global 1200. J. Sustain. Financ. Investig. 2023, 13, 1075–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.Y.; Zhang, J.H. Renovation in environmental, social and governance (ESG) research: The application of machine learning. Asian Rev. Account. 2024, 32, 554–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, C.; Tang, S.; Stubbs, W. On managing hypocrisy: The transparency of sustainability reports. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 114, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterji, A.K.; Durand, R.; Levine, D.I.; Touboul, S. Do ratings of firms converge? Implications for managers, investors and strategy researchers. Strateg. Manag. J. 2016, 37, 1597–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, F.; Kölbel, J.F.; Rigobon, R. Aggregate Confusion: The Divergence of ESG Ratings*. Rev. Financ. 2022, 26, 1315–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, J.H.; Jung, H.S. ESG-KIBERT: A new paradigm in ESG evaluation using NLP and industry-specific customization. Decis. Support Syst. 2025, 193, 114440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escrig-Olmedo, E.; Fernández-Izquierdo, M.Á.; Ferrero-Ferrero, I.; Rivera-Lirio, J.M.; Muñoz-Torres, M.J. Rating the Raters: Evaluating how ESG Rating Agencies Integrate Sustainability Principles. Sustainability 2019, 11, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, S.; You, X.; Xu, T. Sustainable Supplier Evaluation: From Current Criteria to Reconstruction Based on ESG Requirements. Sustainability 2024, 16, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cunha, Í.G.F.; Policarpo, R.V.S.; de Oliveira, P.C.S.; Abdala, E.C.; do Nascimento Rebelatto, D.A. A systematic review of ESG indicators and corporate performance: Proposal for a conceptual framework. Future Bus. J. 2025, 11, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Wu, Q.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Mardani, A. An integrated MCDM framework for evaluating the environmental, social, and governance (ESG) sustainable business performance. Ann. Oper. Res. 2024, 342, 987–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, C.; Kim, Y. Identifying ESG Trends of International Container Shipping Companies Using Semantic Network Analysis and Multiple Case Theory. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, W.; Tang, S.; Yin, J.; Li, X. The ESG index evaluation system for idol economy is constructed based on the two levels of companies and individuals and the correlation is verified. BCP Bus. Manag. 2022, 23, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Kim, J. Analyzing and Visualizing Text Information in Corporate Sustainability Reports Using Natural Language Processing Methods. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimanski, T.; Reding, A.; Reding, N.; Bingler, J.; Kraus, M.; Leippold, M. Bridging the gap in ESG measurement: Using NLP to quantify environmental, social, and governance communication. Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 61, 104979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischbach, J.; Adam, M.; Dzhagatspanyan, V.; Mendez, D.; Frattini, J.; Kosenkov, O.; Elahidoost, P. Automatic ESG Assessment of Companies by Mining and Evaluating Media Coverage Data: NLP Approach and Tool. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (BigData), Sorrento, Italy, 15–18 December 2023; pp. 2823–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Shen, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, S.; Huang, G.Q. Optimizing ESG reporting: Innovating with E-BERT models in nature language processing. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 265, 125931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, S.H.; Park, H.; Kim, J.H.; Jung, H.S. ESG2PreEM: Automated ESG grade assessment framework using pre-trained ensemble models. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronzini, M.; Nicolini, C.; Lepri, B.; Passerini, A.; Staiano, J. Glitter or gold? Deriving structured insights from sustainability reports via large language models. EPJ Data Sci. 2024, 13, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamura, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Managi, S. Evaluating the impact of report readability on ESG scores: A generative AI approach. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2025, 101, 104027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q. Generative AI-assisted evaluation of ESG practices and information delays in ESG ratings. Financ. Res. Lett. 2025, 74, 106757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Gu, Y.; Dai, J. Environmental, Social, and Governance Taxonomy Simplification: A Hybrid Text Mining Approach. J. Emerg. Technol. Account. 2023, 20, 305–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Satapathy, R.; Guo, D.; Li, B.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, C.A.; Filho, R.S.; Goh, R.S.M. Information Extraction: Unstructured to Structured for ESG Reports. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 9 December 2024; pp. 487–495. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Luo, X.; Lu, W.-Z. Public perceptions of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) based on social media data: Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 387, 135840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Ji, L. An interactive multi-task ESG classification method for Chinese financial texts. Appl. Intell. 2024, 55, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, P.; Berninger, M.; Kiesel, F. Environmental, social and governance reporting in annual reports: A textual analysis. Financ. Mark. Inst. Instrum. 2020, 29, 93–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatov, K. When ESG talks: ESG tone of 10-K reports and its significance to stock markets. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2023, 89, 102745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, D.E.; Yoon, Y. Using Machine Learning to Generate a Dictionary for Environmental Issues. In Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction, Proceedings of the 7th IFIP TC 5, TC 12, WG 8.4, WG 8.9, WG 12.9 International Cross-Domain Conference, CD-MAKE 2023, Benevento, Italy, 29 August–1 September 2023, Proceedings; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, V.; D’Ecclesia, R.; Levantesi, S. ESG score prediction through random forest algorithm. Comput. Manag. Sci. 2022, 19, 347–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.H.; Zein Alabdeen, Z.; Anupam, A. Firm-level climate change risk and adoption of ESG practices: A machine learning prediction. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2024, 30, 1741–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghallabi, F.; Souissi, B.; Du, A.M.; Ali, S. ESG stock markets and clean energy prices prediction: Insights from advanced machine learning. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2025, 97, 103889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, R.; Xu, S.; Xiao, Y.; Zhao, H. Intelligent Checking Method for Construction Schemes via Fusion of Knowledge Graph and Large Language Models. Buildings 2024, 14, 2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angioni, S.; Consoli, S.; Dessì, D.; Osborne, F.; Recupero, D.R.; Salatino, A. Exploring Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Discourse in News: An AI-Powered Investigation Through Knowledge Graph Analysis. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 77269–77283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, E.J.; Shen, Y.; Wallis, P.; Allen-Zhu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, W. Lora: Low-rank adaptation of large language models. ICLR 2022, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Huang, J.; Wu, M.; Luo, W.; Yu, R. Large language model based system with causal inference and Chain-of-Thoughts reasoning for traffic scene risk assessment. Knowl. Based Syst. 2025, 319, 113630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, M. ESG information extraction with cross-sectoral and multi-source adaptation based on domain-tuned language models. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 221, 119726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Wang, X.Z.; Schuurmans, D.; Bosma, M.; Ichter, B. Chain-of-Thought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 24824–24837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine-Tuning—SiliconFlow. 2025. Available online: https://docs.siliconflow.cn/en/userguide/guides/fine-tune (accessed on 21 July 2025).
- Lagasio, V. ESG-washing detection in corporate sustainability reports. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2024, 96, 103742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liang, C.; Wang, W.; Liu, X. Does environmental, social, and governance news coverage affect the cost of equity? A textual analysis of media coverage. Front. Public Health 2025, 13, 1509167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, J.H.; Jung, H.S. Deep-learning-based stock market prediction incorporating ESG sentiment and technical indicators. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajek, P.; Sahut, J.-M.; Myskova, R. Predicting corporate credit ratings using the content of ESG reports. Ann. Oper. Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmann, C.; Möllenhoff, S.; Lehner, S. On the Relationship Between Financial Distress and ESG Scores. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiriu, T.; Nozaki, M. A Text Mining Model to Evaluate Firms’ ESG Activities: An Application for Japanese Firms. Asia-Pac. Financ. Mark. 2020, 27, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Shi, M.; Chen, Z.; Deng, Z.; Lei, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Yang, S.; Tong, H.; Xiao, L.; Zhou, W. ESGReveal: An LLM-based approach for extracting structured data from ESG reports. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 489, 144572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, K.; Pyun, C.; Pham, H. Beyond Green Labels: Assessing Mutual Funds’ ESG Commitments through Large Language Models. Financ. Res. Lett. 2025, 74, 106713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

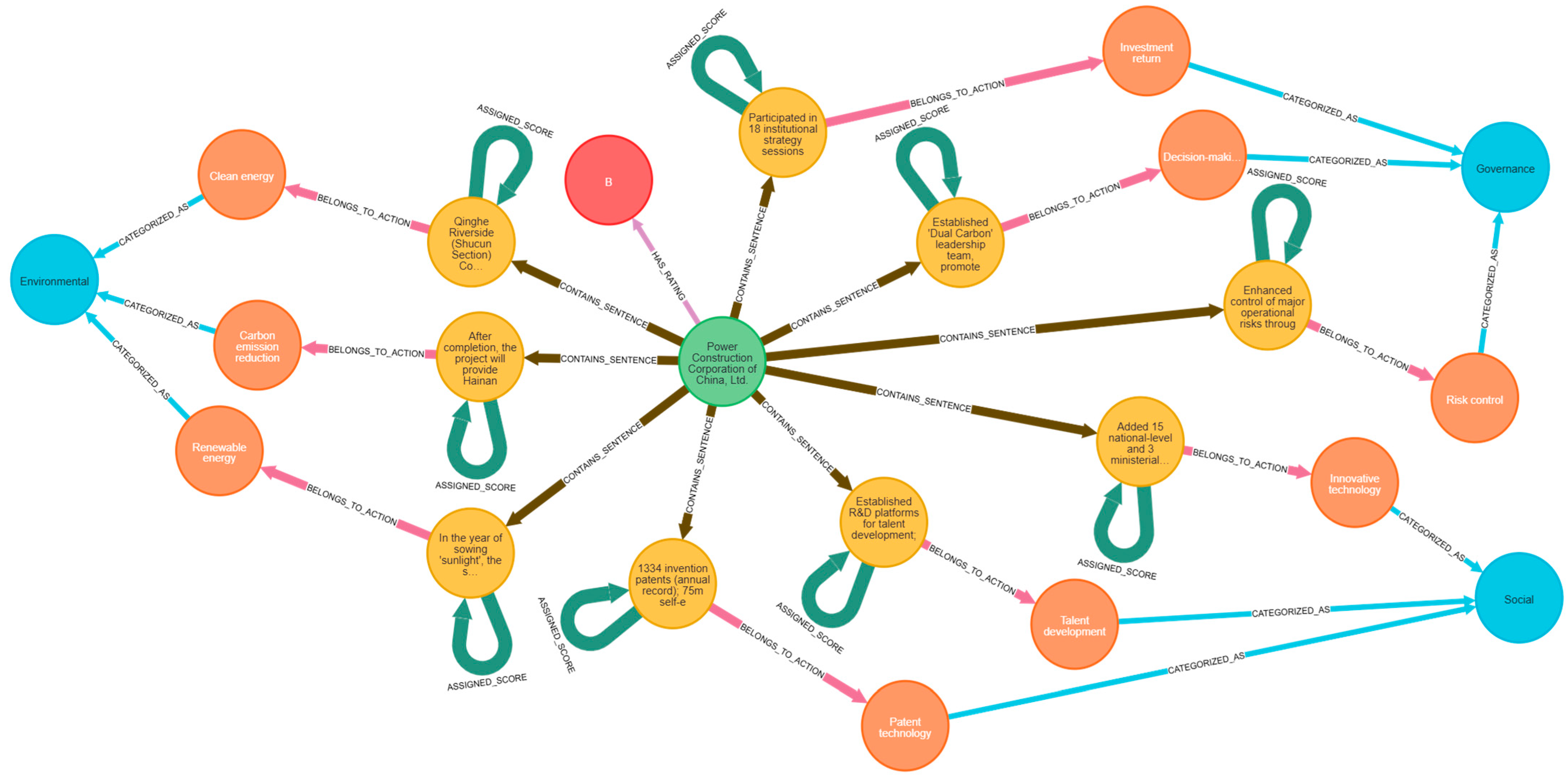



| Entity Type | Description | Examples/Details |
|---|---|---|
| Company | Construction companies in the dataset | 30 companies analyzed |
| ESG Rating | Classification system for ESG performance | A/B/C rating classifications |
| ESG Sentence | Textual content from company disclosures, includes the sentence score as an attribute | Raw text data from company reports |
| Action | Specific ESG activities and initiatives | Concrete ESG actions mentioned in disclosures |
| Category | ESG framework dimensions | Environmental, social, and governance |
| Calculated contribution values | SHAP analysis-derived scores |
| Relationship Type | Connection | Description |
|---|---|---|
| has_rating | Company → ESG Rating | Links companies to their ESG performance ratings |
| contains_sentence | Company → ESG Sentence | Associates companies with their disclosure sentences |
| belongs_to_action | ESG Sentence → Action | Maps sentences to specific ESG actions |
| assigned_score | ESG Sentence →ESG Sentence | Links sentences to their SHAP contribution scores |
| categorized_as | Action → Category | Classifies actions into ESG dimensions |
| Company (In Chinese) | Company | SinoSec ESG Rating 2024 | Wind ESG Rating 2024 | SynTao ESG Rating 2024 | Average ESG Rating 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 东华科技 | East China Engineering Science and Technology Co., Ltd. | B | BBB | B+ | B |
| 中国中冶 | China Metallurgical Group Corporation | BBB | A | B+ | A |
| 中国中铁 | China Railway Group Limited | B | A | B+ | B |
| 中国交建 | China Communications Construction Company Ltd. | BB | A | B+ | B |
| 中国化学 | China National Chemical Engineering Co., Ltd. | BB | BBB | B+ | B |
| 中国建筑 | China State Construction Engineering Corporation | BB | BBB | B+ | B |
| 中国核建 | China Nuclear Engineering & Construction Corporation Ltd. | CCC | BB | B | C |
| 中国海诚 | China Haisum Engineering Co., Ltd. | BB | BBB | B+ | B |
| 中国电建 | Power Construction Corporation of China, Ltd. | CCC | BBB | B+ | B |
| 中国能建 | China Energy Engineering Group Co., Ltd. | A | BBB | B+ | B |
| 中国铁建 | China Railway Construction Corporation Limited | B | BBB | B+ | B |
| 中工国际 | China CAMC Engineering Co., Ltd. | A | A | A− | A |
| 中材国际 | Sinoma International Engineering Co., Ltd. | A | AA | A− | A |
| 中船科技 | CSSC Steel Structure Engineering Co., Ltd. | BBB | BBB | A− | A |
| 中钢国际 | SINOSTEEL CORPORATION | BB | BBB | B+ | B |
| 中铝国际 | China Aluminum International Engineering Co., Ltd. | B | BBB | A− | B |
| 北方国际 | Norinco International Cooperation Ltd. | BBB | A | A− | A |
| 国机重装 | SINOMACH−HE Heavy Equipment Group Co., Ltd. | BBB | BBB | A− | A |
| 天健集团 | Shenzhen Tagen Group Co., Ltd. | CCC | BB | B | C |
| 宏润建设 | Hong Run Construction Group Co., Ltd. | CC | BB | B− | C |
| 山东路桥 | Shandong High-Speed Road & Bridge Co., Ltd. | CCC | BB | B | C |
| 普邦股份 | Pubang Landscape Architecture Co., Ltd. | B | B | B+ | C |
| 棕榈股份 | Palm Eco-Town Development Co., Ltd. | CC | BB | B+ | C |
| 汇绿生态 | Hui Lyu Ecological Technology Groups Co., Ltd. | B | BB | B | C |
| 浙江交科 | Zhejiang Communications Technology Co., Ltd. | BB | A | B+ | B |
| 浙江建投 | Zhejiang Construction Investment Group Co., Ltd. | BB | BBB | B+ | B |
| 浦东建设 | Shanghai Pudong Construction Co., ltd. | BB | A | A− | A |
| 空港股份 | Beijing Airport High-Tech Park Co., Ltd. | CC | B | B− | C |
| 苏文电能 | Suwen Electric Energy Technology Co., Ltd. | BBB | A | B+ | A |
| 龙建股份 | Longjian Road & Bridge Co., Ltd. | B | A | B+ | B |
| Company | Sentence | Category | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| East China Engineering Science and Technology | The company’s key green office initiatives include installing infrared sensors for switches, setting air conditioning temperatures to no lower than 26 °C in summer and no higher than 20 °C in winter, centrally turning off AC systems after work hours while keeping windows closed when AC operates, and powering off office appliances after hours and during holidays to reduce standby energy consumption. | Environment | Green office, Energy-saving, Low consumption |
| SINOMACH-HE Heavy Equipment | Upon completion, the project will actively contribute to promoting local infrastructure development, enhancing agricultural growth and the green economy, ensuring South Africa’s national energy security, while simultaneously creating substantial employment opportunities, driving economic development, and enhancing social well-being. | Social | Job creation, Public welfare, Sustainable development |
| China Metallurgical | MCC Group ensures timely information disclosure through shareholder meetings and roadshows, maintains transparent information sharing, improves investment returns, and strengthens company risk management and internal control systems. | Governance | Information transparency, Risk control |
| Algorithm | RMSE | R2 Score |
|---|---|---|
| Random Forest | 6.29 | 0.2875 |
| XGBoost | 5.10 | 0.5312 |
| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Rate | 0.0001 | Controls the step size for parameter updates during training |
| Number of Epochs | 5 | Number of complete passes through the training dataset |
| Batch Size | 16 | Number of samples processed simultaneously |
| LoRA Rank | 16 | Dimensionality of low-rank decomposition matrices |
| LoRA Alpha | 32 | Scaling factor that controls the magnitude of LoRA adaptations |
| LoRA Dropout | 0.1 | Regularization technique that randomly zeroes LoRA parameters during training |
| Max Tokens | 32,768 | Maximum sequence length the model can process |
| Company (In Chinese) | Company | Average ESG Rating 2024 | Prediction Score | Prediction ESG Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 东华科技 | East China Engineering Science and Technology Co., Ltd. | B | 69.99997711 | B |
| 中国中冶 | China Metallurgical Group Corporation | A | 72.61679077 | B |
| 中国中铁 | China Railway Group Limited | B | 69.99997711 | B |
| 中国交建 | China Communications Construction Company Ltd. | B | 70.00016022 | B |
| 中国化学 | China National Chemical Engineering Co., Ltd. | B | 70.01068878 | B |
| 中国建筑 | China State Construction Engineering Corporation | B | 70.00011444 | B |
| 中国核建 | China Nuclear Engineering & Construction Corporation Ltd. | C | 60.00028229 | C |
| 中国海诚 | China Haisum Engineering Co., Ltd. | B | 69.99997711 | B |
| 中国电建 | Power Construction Corporation of China, Ltd. | B | 70.00011444 | B |
| 中国能建 | China Energy Engineering Group Co., Ltd. | B | 69.99997711 | B |
| 中国铁建 | China Railway Construction Corporation Limited | B | 69.99997711 | B |
| 中工国际 | China CAMC Engineering Co., Ltd. | A | 79.99990845 | A |
| 中材国际 | Sinoma International Engineering Co., Ltd. | A | 79.9997406 | A |
| 中船科技 | CSSC Steel Structure Engineering Co., Ltd. | A | 79.99973297 | A |
| 中钢国际 | SINOSTEEL CORPORATION | B | 69.99997711 | B |
| 中铝国际 | China Aluminum International Engineering Co., Ltd. | B | 70.00011444 | B |
| 北方国际 | Norinco International Cooperation Ltd. | A | 77.22226715 | A |
| 国机重装 | SINOMACH-HE Heavy Equipment Group Co., Ltd. | A | 79.998703 | A |
| 天健集团 | Shenzhen Tagen Group Co., Ltd. | C | 60.00028229 | C |
| 宏润建设 | Hong Run Construction Group Co., Ltd. | C | 60.00028229 | C |
| 山东路桥 | Shandong High-Speed Road & Bridge Co., Ltd. | C | 70.16632843 | B |
| 普邦股份 | Pubang Landscape Architecture Co., Ltd. | C | 60.00028229 | C |
| 棕榈股份 | Palm Eco-Town Development Co., Ltd. | C | 60.00028229 | C |
| 汇绿生态 | Hui Lyu Ecological Technology Groups Co., Ltd. | C | 60.00028229 | C |
| 浙江交科 | Zhejiang Communications Technology Co., Ltd. | B | 70.00000000 | B |
| 浙江建投 | Zhejiang Construction Investment Group Co., Ltd. | B | 69.99983978 | B |
| 浦东建设 | Shanghai Pudong Construction Co., Ltd. | A | 79.99988556 | A |
| 空港股份 | Beijing Airport High-Tech Park Co., Ltd. | C | 60.00028229 | C |
| 苏文电能 | Suwen Electric Energy Technology Co., Ltd. | A | 77.21237946 | A |
| 龙建股份 | Longjian Road & Bridge Co., Ltd. | B | 69.99997711 | B |
| Company (In Chinese) | Company | Average ESG Rating 2025 | Baseline Evaluation | LLM Evaluation | LLM+KG Evaluation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evaluation Results | Accuracy | Evaluation Results | Accuracy | Evaluation Results | Accuracy | |||
| 中国中冶 | China Metallurgical Group Corporation | A | BBBBB CBBCB | 0% | ABBBB ACABA | 40% | BBBAA BAABA | 50% |
| 中国交建 | China Communications Construction Company Ltd. | A | BBABB ABBBB | 20% | CBBCB ABBAA | 30% | BBCAA BAAAB | 50% |
| 东华科技 | East China Engineering Science and Technology Co., Ltd. | B | CCBCB CBCCC | 30% | BBCBB CBABC | 60% | BABBB ABBBB | 80% |
| 中国建筑 | China State Construction Engineering Corporation | B | ABABA BABAB | 50% | BBBBC BCBBB | 80% | BBBBA BBBBB | 90% |
| 中国核建 | China Nuclear Engineering & Construction Corporation Ltd. | C | BBBBB BBBCB | 10% | BCCBC CBCBC | 60% | BCBBC CCCCA | 60% |
| 中钢国际 | SINOSTEEL CORPORATION | C | ABBBC ABCBC | 30% | BBCBC CBCCB | 50% | BACCC CCCAB | 60% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, B.; Ye, Z.; Chen, S. Intelligent ESG Evaluation for Construction Enterprises in China: An LLM-Based Model. Buildings 2025, 15, 2710. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15152710
Cai B, Ye Z, Chen S. Intelligent ESG Evaluation for Construction Enterprises in China: An LLM-Based Model. Buildings. 2025; 15(15):2710. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15152710
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Binqing, Zhukai Ye, and Shiwei Chen. 2025. "Intelligent ESG Evaluation for Construction Enterprises in China: An LLM-Based Model" Buildings 15, no. 15: 2710. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15152710
APA StyleCai, B., Ye, Z., & Chen, S. (2025). Intelligent ESG Evaluation for Construction Enterprises in China: An LLM-Based Model. Buildings, 15(15), 2710. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15152710








