Spatio-Temporal Patterns and Sentiment Analysis of Ting, Tai, Lou, and Ge Ancient Chinese Architecture Buildings
Abstract
1. Introduction
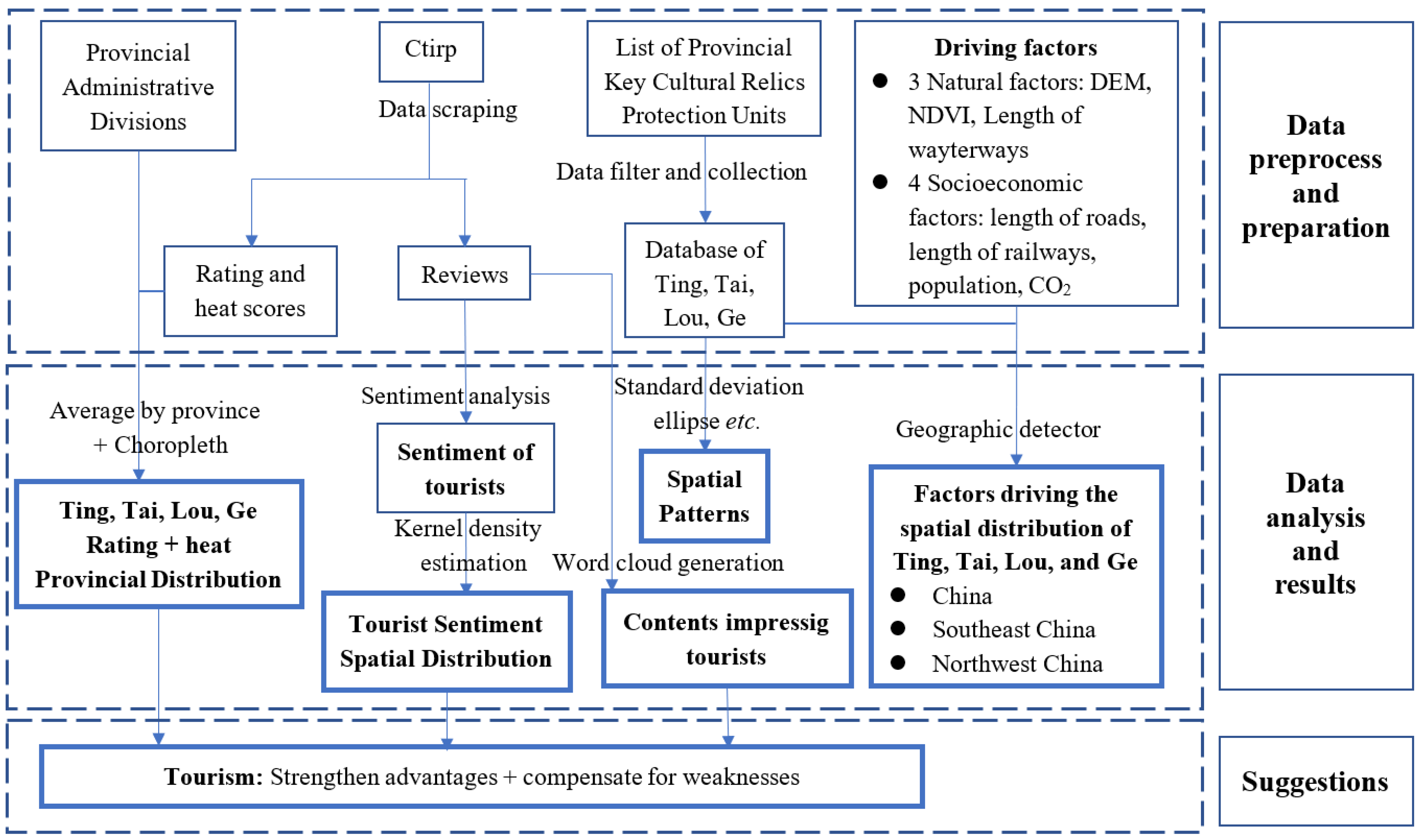
2. Data Sources
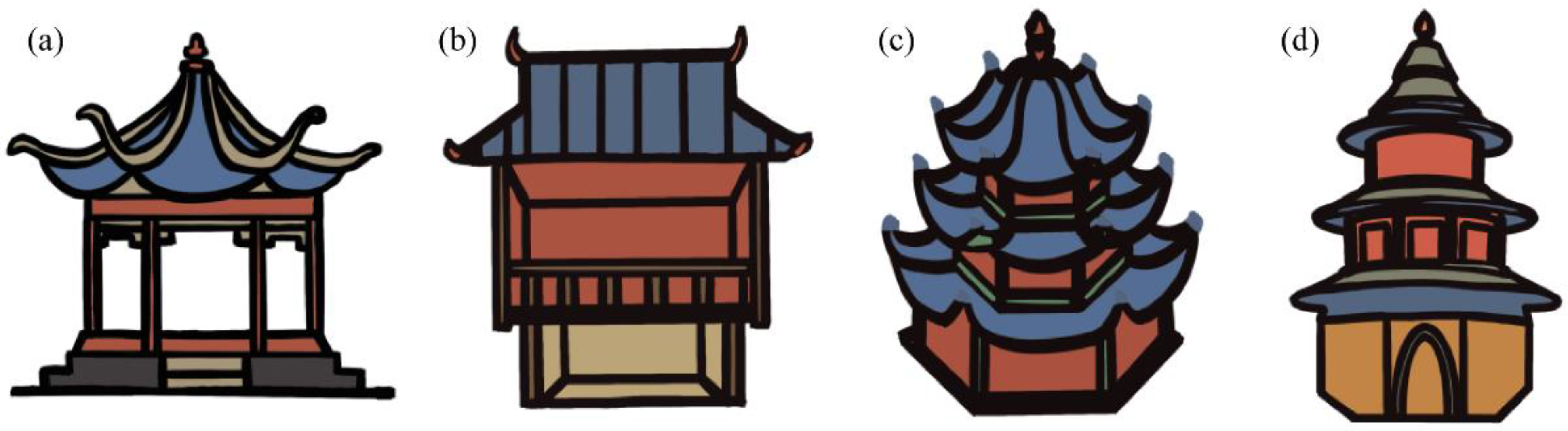
2.1. Ting, Tai, Lou, and Ge Building Information
2.2. Analysis of Factors Driving the Spatial Distribution of Buildings
3. Methods
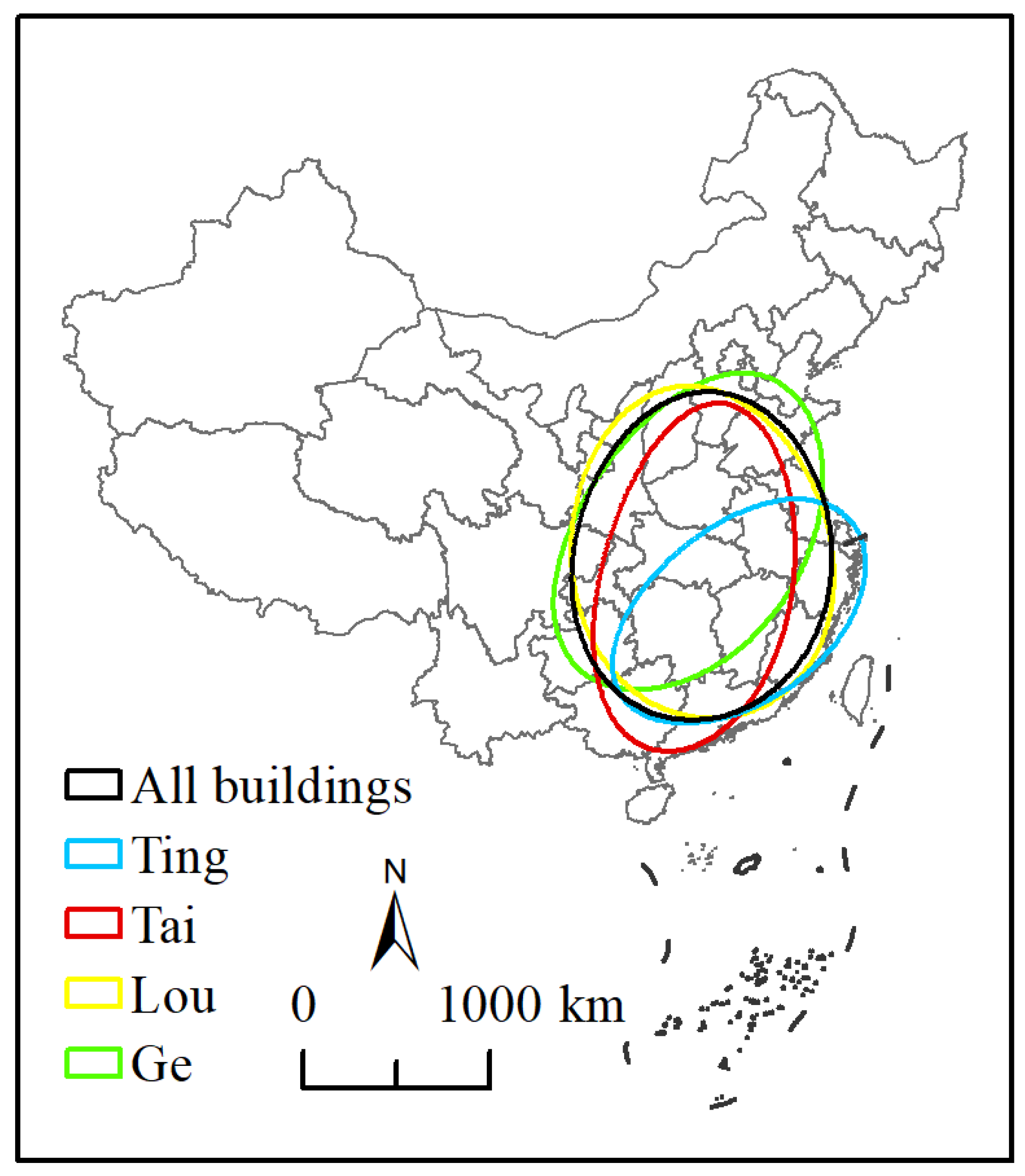
3.1. Standard Deviation Ellipse
3.2. Geographic Detector
3.3. Kernel Density Estimation
3.4. Sentiment Analysis and Word Cloud Generation
4. Results and Discussion
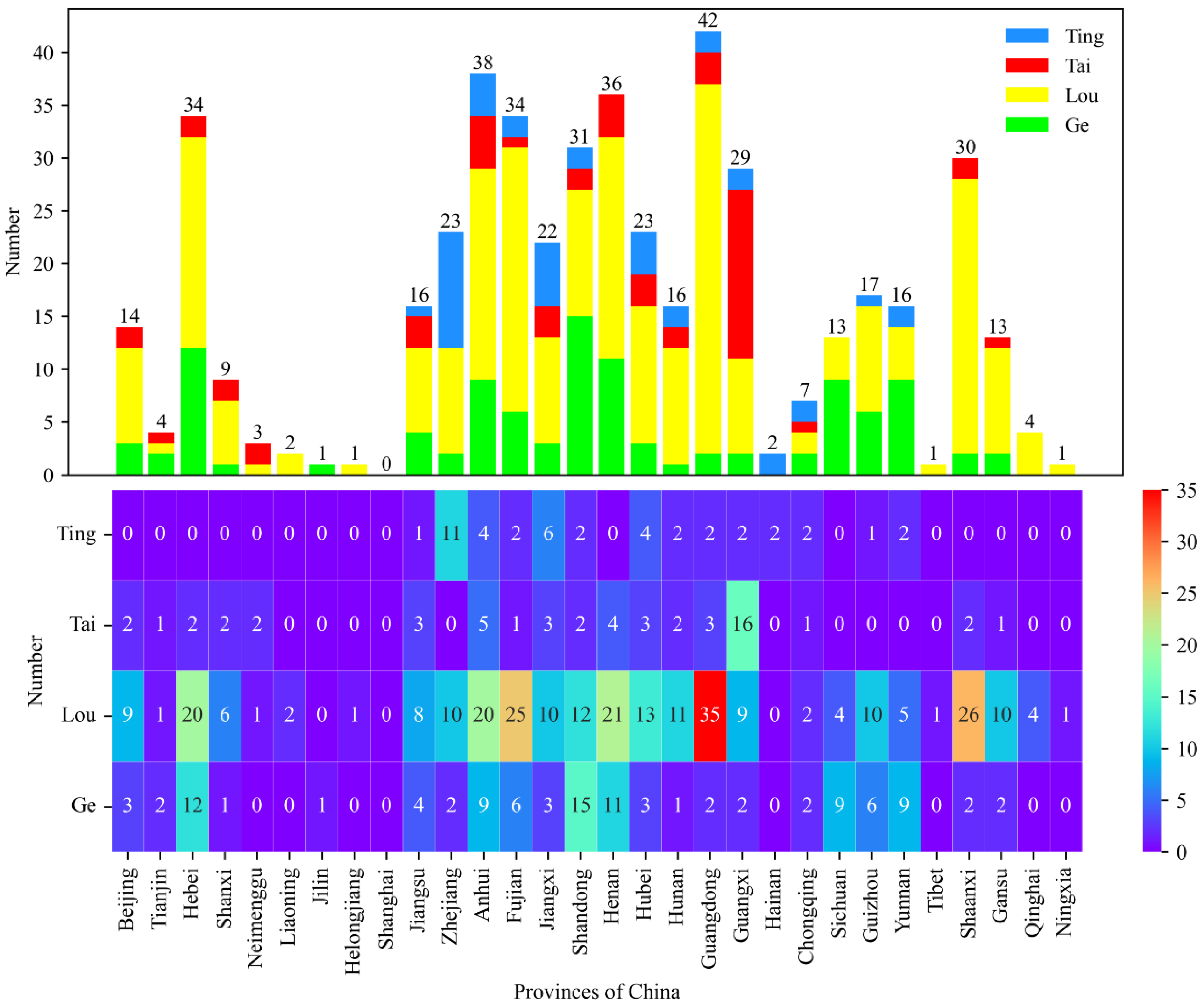
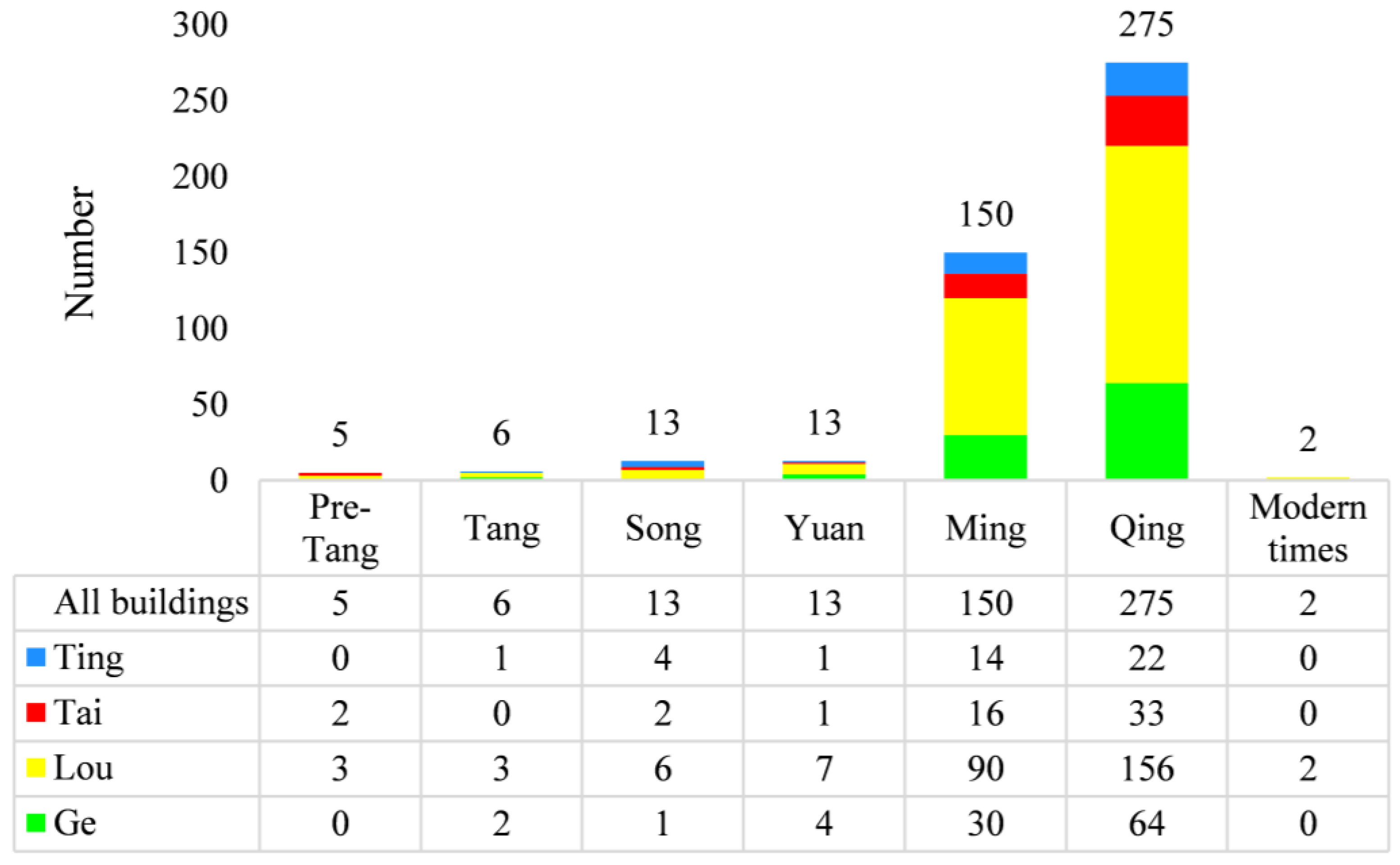
4.1. General Building Characteristics
4.2. Spatio-Temporal Patterns
4.3. Driving Factors
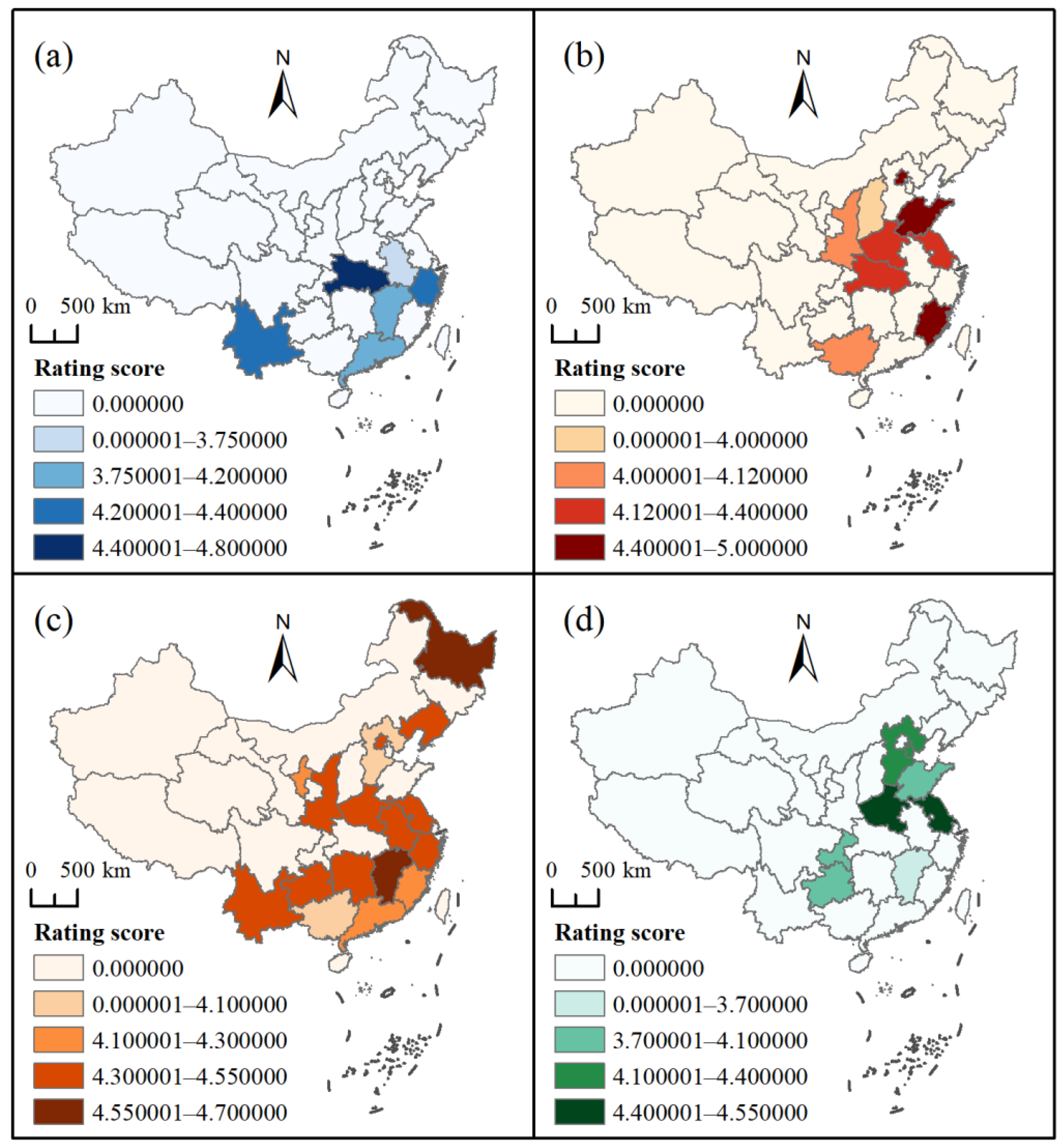
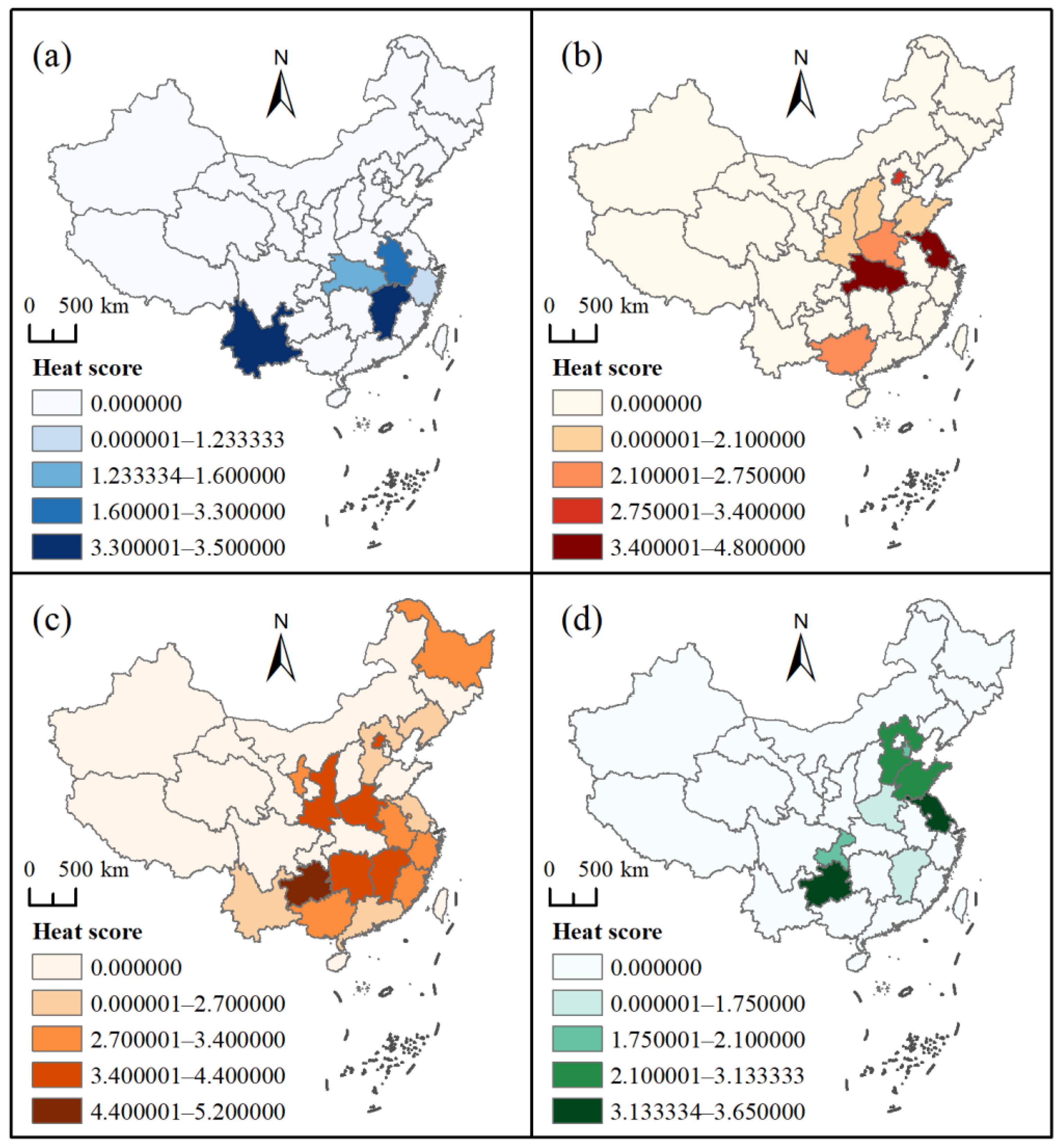
4.4. Rating and Heat Scores
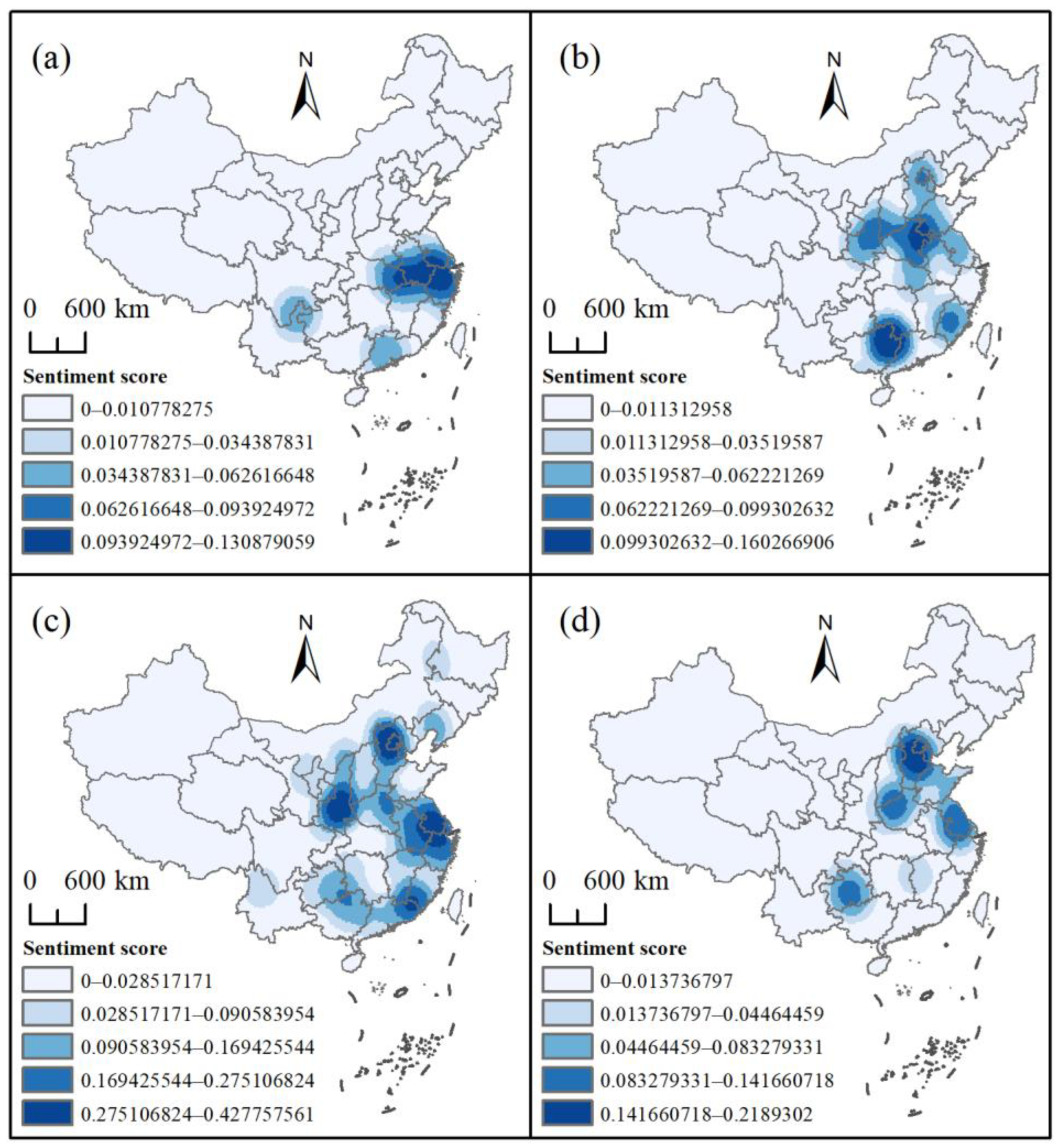
4.5. Sentiment Analysis
4.5.1. Kernel Density Results
4.5.2. Word Cloud Results
| Type | Site | Word (Frequency) |
|---|---|---|
| Historical story | Ting | Yu Zhou (周瑜, 43), Three Kingdoms period (三国, 16); Yanshui Ting (烟水亭, 81), Dianjiang Terrace (点将台, 30), Juyi Bai (白居易, 12), Xiu Ouyang (欧阳修, frequency = 51), Northern Song Dynasty (北宋, 15), famous essay (醉翁亭记, 32), Zuiweng Ting (醉翁亭, 94), Zuiweng Ting (醉翁亭), Chuzhou (滁州, 36), Liangya Mountain (琅琊山, 45) |
| Tai | Boya Yu (俞伯牙, 43; 伯牙, 55), Zhong Ziqi (钟子期, 41; 子期, 25), a kindred spirit with Boya Yu through music (知音, 82), ‘High mountains and flowing water’ (高山流水, 62), Guqin Tai (古琴台, 89; 伯牙台, 3), Song Dynasty (北宋, 33), Huanghe Lou (黄鹤楼, 29), Qingchuan Ge (晴川阁, 27) | |
| Lou | none | |
| Ge | none | |
| Tourism | Ting | scenic spot (景点, 42; 景区, 46), scenery (景色, 26), admission ticket (门票, 18), cost-effectiveness (性价比, 8) |
| Tai | scenic spot (景点, 68;景区, 44), park (公园, 47), admission ticket (门票, 55), cost-effectiveness (性价比, 14) | |
| Lou | scenic spot (景点, 195; 景区, 158), scenery (景色, f = 141), landmarks (地标, 40; 地标性建筑, 30; 地标建筑, 27), tourist (游客, 72), admission ticket (门票, 80), free (免费, 72), cost-effectiveness (性价比, 70), visit (参观, 83) | |
| Ge | scenic spot (景点, 54; 景区, 18), scenery (景色, 33), landmark (地标, 19), admission ticket (门票, 26), free (免费, 39), and cost-effectiveness (性价比, 10) | |
| Culture | Ting | history (历史, 39), culture (文化, 15), building (建筑, 14) |
| Tai | astronomy (天文, 63), instrument (仪器, 81), ancient observatories (古观象台, 57), place (地方, 81), history (历史, 76), building (建筑, 57), story (故事, f = 36), culture (文化, f = 35) | |
| Lou | history (历史, 405), building (建筑, 368), gate tower(城楼, 253), place (地方, 237), ancient city (古城, 171), historic building (古建筑, 99), Key Cultural Relics Protection Units (重点文物保护单位, 46) | |
| Ge | building (建筑, 202), place (地方, 84), history (历史, 83), historic building (古建筑, 30), ancient city (古城, 29), historic site (古迹, 19), Cultural Relics Protection Unit (重点文物保护单位, 17; 文物保护单位, 16), culture (文化, 20) | |
| Cities/ provinces | Ting | Jiujiang city (九江, 51; 九江市, 21), Chuzhou (滁州, 36, 滁州市, 8), Wenzhou (温州, 6), Anhui Province (安徽省, 7), regions south of the Yangtze River (江南, 11) |
| Tai | Wuhan (武汉, 56; 武汉市, 23), Gaoyou (高邮, 49), Beijing (北京, 44; 北京市, 17), Kaifeng (开封, 23), Hubei (湖北省, 17), Hanyang district (汉阳区, 15; 汉阳, 14) | |
| Lou | Beijing (北京, 112; 北京市, 7), Ningbo (宁波, 77; 宁波市, 25), Xi’an (西安, 73), Guiyang (贵阳, 66), Liuzhou (柳州, 48), the Old Town of Phoenix (凤凰古城, 43), Xuhuan District (宣化, f = 139), Jinhua (金华, 25), Shunde (顺德, f = 24) | |
| Ge | Yangzhou (扬州, 113; 扬州市, 21), Qingdao (青岛, 83), Baoding (保定, 66; 保定市, 20), Guiyang (贵阳, 52) |

5. Conclusions and Future Work
- (1)
- The ratio of Ting, Tai, Lou, and Ge buildings in Southeast China to that in Northwest China was approximately the same as that of the population (94:6).
- (2)
- Geographic detector analysis revealed that six of the seven natural and socioeconomic factors (topography, waterways, roads, railways, population, and CO2 emissions) had a significant influence on the spatial heterogeneity of these cultural heritage sites in China, with socioeconomic factors, particularly population, having a greater influence on building spatial distributions. All seven factors (including the NDVI) were significant in Southeast China, whereas all factors were non-significant in Northwest China, which may be explained by the small number of buildings in the latter region.
- (3)
- The average rating and heat scores for Ting, Tai, Lou, and Ge buildings reflected an imbalance between service quality and popularity. The service quality was acceptable whereas the popularity should be improved.
- (4)
- Four main types of words were used with high frequency in the tourism reviews: historical stories, tourism, culture, and cities/provinces. Ting and Tai buildings showed similar word clouds, as did Lou and Ge buildings, with only the former including historical stories. Conversely, landmark was a high-frequency word only in the reviews of Lou and Ge buildings.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, W.; Chen, Y.; Cao, W.; Yu, R.; Rong, P.; Cheng, J. Spatial Pattern and Its Influencing Factors of National-Level Cultural Heritage in China. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buragohain, D.; Meng, Y.; Deng, C.; Li, Q.; Chaudhary, S. Digitalizing Cultural Heritage through Metaverse Applications: Challenges, Opportunities, and Strategies. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocchi, F. Diving Deeper into the Concept of ‘Cultural Heritage’ and Its Relationship with Epistemic Diversity. Soc. Epistemol. 2022, 36, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chi, L.; Zhang, T.; Ju, H. Spatial Pattern and Influencing Factors of Land Border Cultural Heritage in China. Herit. Sci. 2023, 11, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravagnuolo, A.; Angrisano, M.; Bosone, M.; Buglione, F.; De Toro, P.; Fusco Girard, L. Participatory Evaluation of Cultural Heritage Adaptive Reuse Interventions in the Circular Economy Perspective: A Case Study of Historic Buildings in Salerno (Italy). J. Urban Manag. 2024, 13, 107–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S. Cultivating National Identity with Traditional Culture: China’s Experiences and Paradoxes. Discourse Stud. Cult. Politics Educ. 2018, 39, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Cao, S.; Li, G.; Niu, Q.; Feng, Q. Conservation of Natural and Cultural Heritage in Dunhuang, China. Gondwana Res. 2014, 26, 1216–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Lourenço, P.B. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Visual Inspection for Cultural Heritage: State-of-the-Art Review. J. Cult. Herit. 2024, 66, 536–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, N.; Mishra, M.; Lourenço, P.B. Deep Learning-Based Automated Tile Defect Detection System for Portuguese Cultural Heritage Buildings. J. Cult. Herit. 2024, 68, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Garcia, B.; Guillen-Sanz, H.; Checa, D.; Bustillo, A. A Systematic Review of Virtual 3D Reconstructions of Cultural Heritage in Immersive Virtual Reality. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 89743–89793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X. Assessing Climate Risk Related to Precipitation on Cultural Heritage at the Provincial Level in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertacchini, E.; Frontuto, V. Economic Valuation of Industrial Heritage: A Choice Experiment on Shanghai Baosteel Industrial Site. J. Cult. Herit. 2024, 66, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, S. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Distribution of Cultural Heritage Sites along the Suzhou Canal of China. Herit. Sci. 2023, 11, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, F. Spatial–Temporal Distribution and Evolution of the Socialist Built Heritage in China, 1949–1978. Herit. Sci. 2023, 11, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, M.; Lu, L. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Toponymic Cultural Heritage in Jiangsu Province and Its Historical and Geographical Influencing Factors. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Wu, L. Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Intangible Cultural Heritage in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei. Herit. Sci. 2023, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Zoh, K.; Xie, Y. The Spatial Differentiation Mechanism of Intangible Cultural Heritage and Its Integration with Tourism Development Based on Explainable Machine Learning and Coupled Coordination Models: A Case Study of the Jiang-Zhe-Hu in China. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Qian, Y.; Li, Z.; Tong, T. Identifying Factors Influencing the Spatial Distribution of Minority Cultural Heritage in Southwest China. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, H.; Fan, Y.; Jin, H.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L. Integrated Study on the Conservation of Ecocultural Heritage in the Tiantai Mountain Area, China. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Mao, H. Study on the Spatiotemporal Distribution Patterns and Influencing Factors of Cultural Heritage: A Case Study of Fujian Province. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.; Huang, C.; Lin, F. Spatio-Temporal Evolution Characteristics of Cultural Heritage Sites and Their Relationship with Natural and Cultural Environment in the Northern Fujian, China. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Qin, X. Extended Interactive and Procedural Modeling Method for Ancient Chinese Architecture. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 5773–5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cui, Z.; Fan, T.; Ruan, S.; Wu, J. Spatial Distribution of Intangible Cultural Heritage Resources in China and Its Influencing Factors. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelinčić, D.A.; Mansfeld, Y. Applying Cultural Tourism in the Revitalisation and Enhancement of Cultural Heritage: An Integrative Approach. In Cultural Urban Heritage: Development, Learning and Landscape Strategies; Obad Šćitaroci, M., Bojanić Obad Šćitaroci, B., Mrđa, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 35–43. ISBN 978-3-030-10612-6. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, P.; He, J. The Impact of Cultural Heritage Rejuvenation Experience Quality on Visitors’ Destination Loyalty: A Serial Multiple Mediation Model. Nankai Bus. Rev. 2020, 23, 76–87. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Qiao, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L. Developing a Resilience Evaluation Index for Cultural Heritage Site: Case Study of Jiangwan Town in China. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2021, 26, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Chi, C.G.; Liu, Y. Authenticity, Involvement, and Image: Evaluating Tourist Experiences at Historic Districts. Tour. Manag. 2015, 50, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mgxekwa, B.B. Creating a Memorable Experience for Nelson Mandela Heritage Site Visitors. Afr. J. Hosp. Tour. Leis. 2017, 6, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, X.; Cao, R. Chinese Tourists’ Perceptions and Consumption of Cultural Heritage: A Generational Perspective. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2021, 26, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Bae, S.Y. Roles of Authenticity and Nostalgia in Cultural Heritage Tourists’ Travel Experience Sharing Behavior on Social Media. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2022, 27, 411–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Stepchenkova, S. Effect of Tourist Photographs on Attitudes towards Destination: Manifest and Latent Content. Tour. Manag. 2015, 49, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Liu, W.; Huang, Z.; Shi, C. Thematic Analysis of Reviews on the Air Quality of Tourist Destinations from a Sentiment Analysis Perspective. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2022, 42, 100969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; He, Z.; Wu, G.; Shi, C. Are All Tourism Review Information on the Platforms Equally Useful? J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2023, 57, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, T.; Zhang, Y. China Regional 250m Normalized Difference Vegetation Index Data Set (2000–2023); National Tibetan Plateau Data Center: Beijing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, N.I.; Lewis, T.; Embleton, B.J.J. Statistical Analysis of Spherical Data; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1987; ISBN 978-0-521-45699-9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X. Geographical Detectors-Based Health Risk Assessment and Its Application in the Neural Tube Defects Study of the Heshun Region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Haining, R.; Zhang, T.; Xu, C.; Hu, M.; Yin, Q.; Li, L.; Zhou, C.; Li, G.; Chen, H. Statistical Modeling of Spatially Stratified Heterogeneous Data. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2024, 114, 499–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-F.; Zhang, T.-L.; Fu, B.-J. A Measure of Spatial Stratified Heterogeneity. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Li, G.; Qi, W.; Sun, S.; Cui, X.; Ren, Y. Unbalanced Trend of Urban and Rural Development on the East and West Sides of Hu Huanyong Line and Micro-Breakthrough Strategy along the Bole-Taipei Line. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2023, 78, 443–455. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hannam, K.; Ryan, E. Time, Authenticity and Photographic Storytelling in The Museum of Innocence. J. Herit. Tour. 2019, 14, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, A.M.W.; Yeh, S.-S.; Zhou, Y.; Hung, C.-W.; Huan, T.-C. Exploring the Influence of Historical Storytelling on Cultural Heritage Tourists’ Value Co-Creation Using Tour Guide Interaction and Authentic Place as Mediators. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2024, 50, 101198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzerini, F. Intangible Cultural Heritage: The Living Culture of Peoples. Eur. J. Int. Law 2011, 22, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietro, L.D.; Mugion, R.G.; Mattia, G.; Renzi, M.F. Cultural Heritage and Consumer Behaviour: A Survey on Italian Cultural Visitors. J. Cult. Herit. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 5, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K. The Image of the City; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; London, UK, 1960; Volume 11, ISBN 0-262-62001-4. [Google Scholar]
- Son, A. The Measurement of Tourist Destination Image: Applying a Sketch Map Technique. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2005, 7, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ting | Tai | Lou | Ge | All | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 43 | 55 | 277 | 107 | 482 |
| With construction date | 42 | 54 | 267 | 101 | 464 |
| With reviews | 9 | 15 | 51 | 14 | 89 |
| Percent of buildings with reviews (%) | 20.93 | 27.27 | 18.41 | 13.08 | 18.46 |
| <100 reviews | 7 | 12 | 40 | 11 | 70 |
| ≥100 reviews | 2 | 3 | 11 | 3 | 19 |
| Percent of buildings with over 100 reviews (%) | 4.65 | 5.45 | 3.97 | 2.80 | 3.94 |
| Center X | Center Y | XStdDist | YStdDist | Rotation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All buildings | 113.44 | 30.94 | 7.17 | 8.04 | 32.53 |
| Ting | 115.36 | 28.11 | 7.69 | 4.35 | 65.15 |
| Tai | 113.02 | 29.93 | 5.29 | 8.61 | 21.99 |
| Lou | 113.39 | 31.13 | 7.36 | 8.02 | 164.40 |
| Ge | 113.01 | 32.12 | 9.19 | 5.84 | 51.14 |
| Factor | China | Southeast | Northwest | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q | p | q | p | q | p | ||
| Natural | DEM | 0.022 | 0.088 * | 0.049 | 0.011 ** | 0.053 | 0.475 |
| NDVI | 0.019 | 0.150 | 0.043 | 0.030 ** | 0.044 | 0.638 | |
| Waterway | 0.052 | 0.003 *** | 0.099 | 0.003 *** | 0.063 | 0.394 | |
| Socio | Road | 0.131 | 0.000 *** | 0.145 | 0.000 *** | 0.065 | 0.438 |
| economic | Railway | 0.108 | 0.012 ** | 0.100 | 0.060 * | 0.035 | 0.723 |
| Population | 0.156 | 0.000 *** | 0.104 | 0.007 *** | 0.104 | 0.202 | |
| CO2 | 0.051 | 0.010 *** | 0.049 | 0.036 ** | 0.033 | 0.754 | |
| Number of Provinces | Ting | Tai | Lou | Ge |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 14 | 18 | 27 | 22 |
| With review | 6 | 9 | 17 | 8 |
| With rating scores | 6 | 9 | 17 | 8 |
| With heat scores | 5 | 8 | 17 | 8 |
| Rating Score | Heat Score | |
|---|---|---|
| All | 4.35 | 3.00 |
| Ting | 4.23 | 2.35 |
| Tai | 4.32 | 2.76 |
| Lou | 4.40 | 3.25 |
| Ge | 4.27 | 2.71 |
| Ting | Tai | Lou | Ge | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | 7 | 12 | 48 | 11 | 78 |
| Negative | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 11 |
| Percent (%) | 77.78 | 80.00 | 94.12 | 78.57 | 87.64 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, J.; Wu, J.; Xiao, Z. Spatio-Temporal Patterns and Sentiment Analysis of Ting, Tai, Lou, and Ge Ancient Chinese Architecture Buildings. Buildings 2025, 15, 1652. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15101652
Xie J, Wu J, Xiao Z. Spatio-Temporal Patterns and Sentiment Analysis of Ting, Tai, Lou, and Ge Ancient Chinese Architecture Buildings. Buildings. 2025; 15(10):1652. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15101652
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Jinghan, Jinghang Wu, and Zhongyong Xiao. 2025. "Spatio-Temporal Patterns and Sentiment Analysis of Ting, Tai, Lou, and Ge Ancient Chinese Architecture Buildings" Buildings 15, no. 10: 1652. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15101652
APA StyleXie, J., Wu, J., & Xiao, Z. (2025). Spatio-Temporal Patterns and Sentiment Analysis of Ting, Tai, Lou, and Ge Ancient Chinese Architecture Buildings. Buildings, 15(10), 1652. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15101652





