Sustainable Utilization of Modified Electrolytic Manganese Residue as a Cement Retarder: Workability, Mechanical Properties, Hydration Mechanisms, Leaching Toxicity, and Environmental Benefits
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Used Materials
2.2. Preparation of Modified EMR and Modified EMR-Cement Mortar
2.3. Mix Design for Modified EMR-Cement Mortar
2.4. Leaching Toxicity of Modified EMR-Cement Mortar
2.5. Analysis and Characterization Methods
3. Results
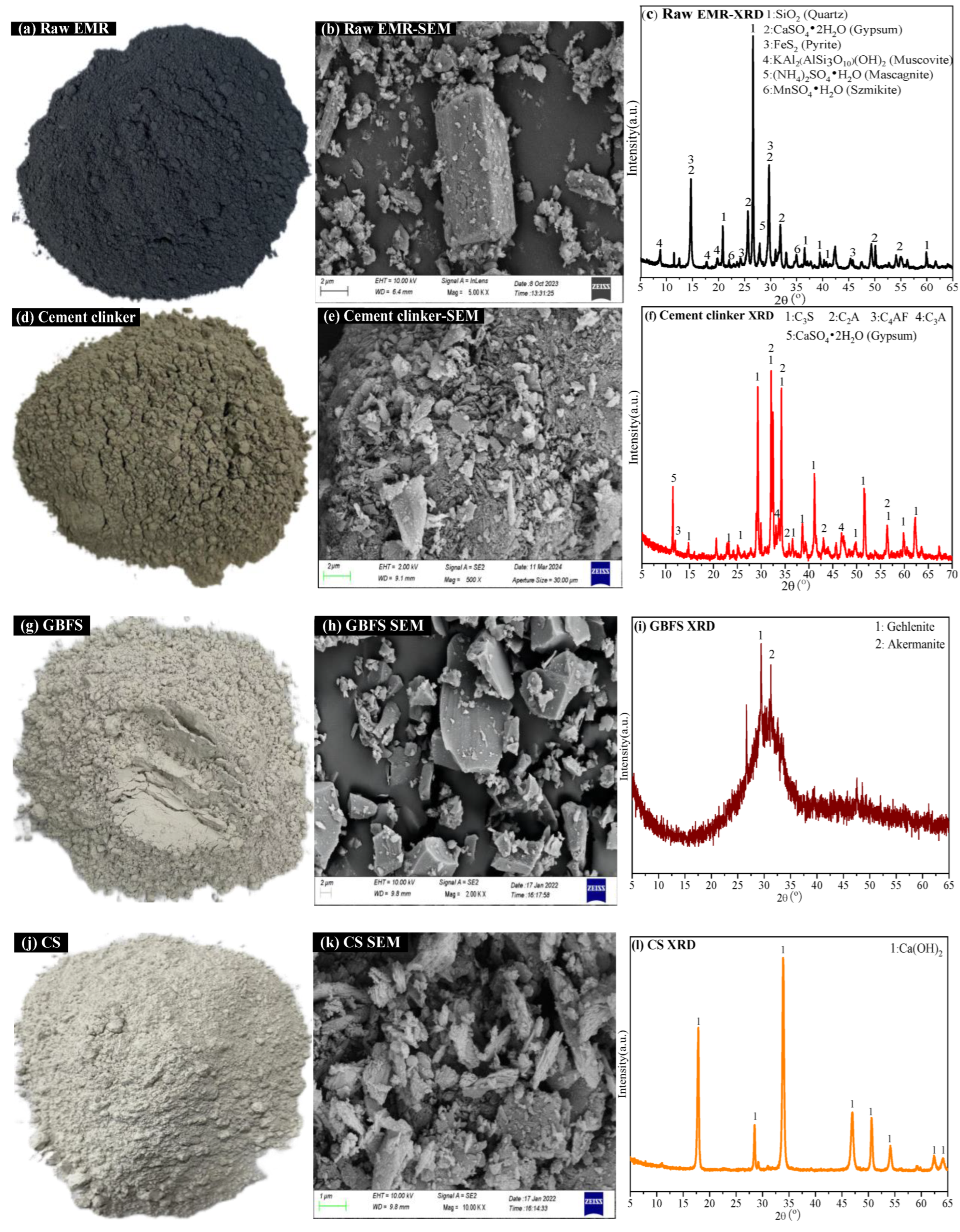
3.1. Leaching Toxicity and XPS Analysis of Modified EMR
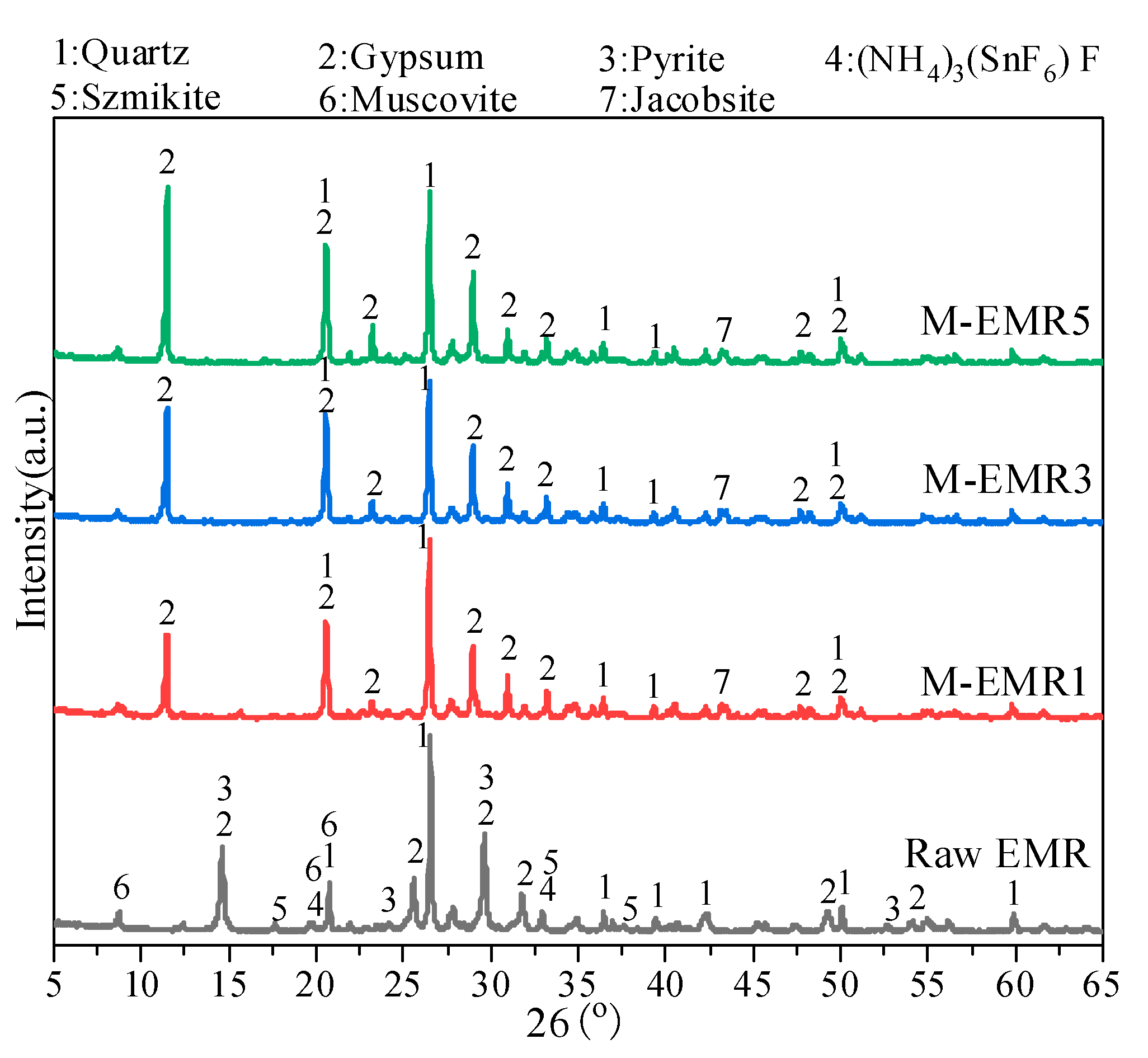
3.2. XRD and SEM-EDS Analysis of Modified EMR
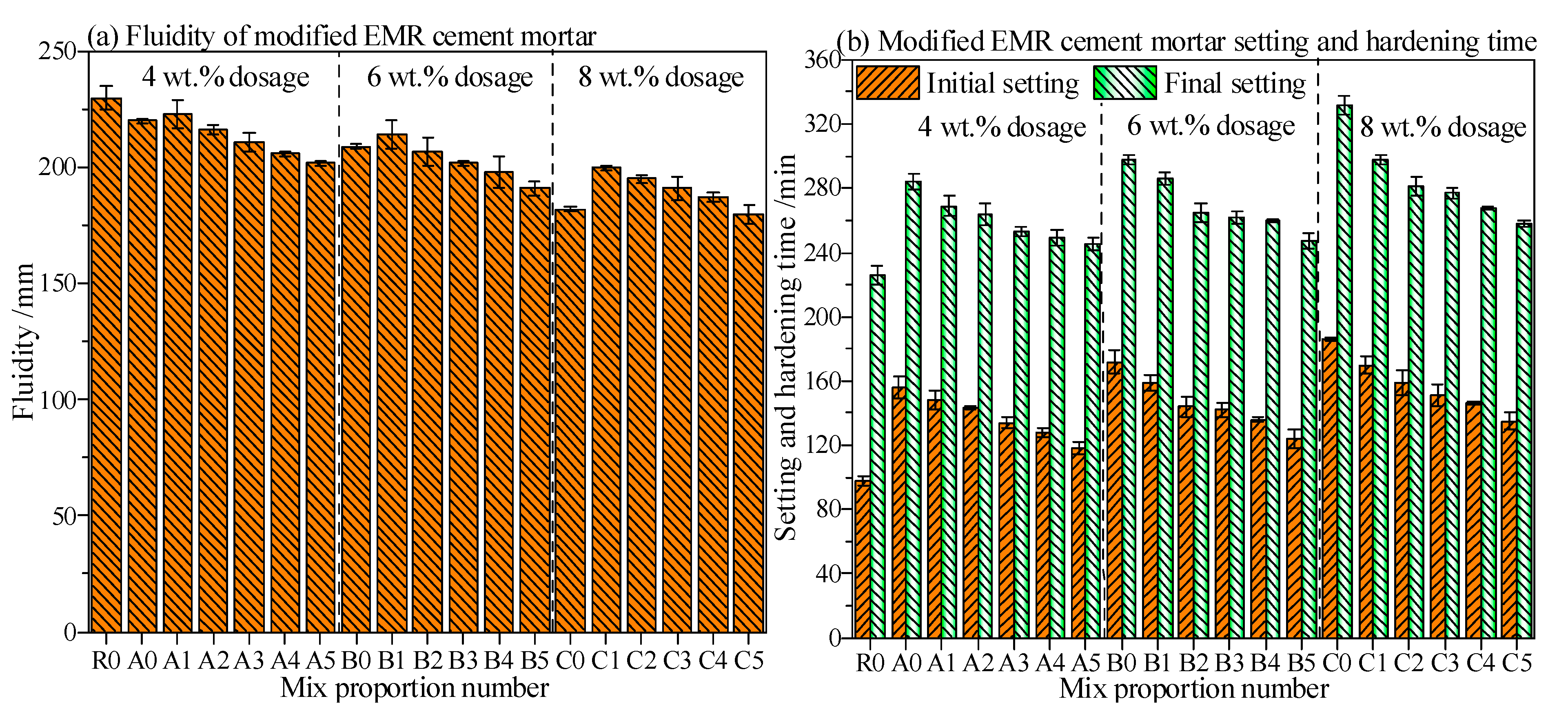
3.3. Fluidity and Setting Time of Modified EMR-Cement Mortar
3.4. Compressive Strength of Modified EMR-Cement Mortar
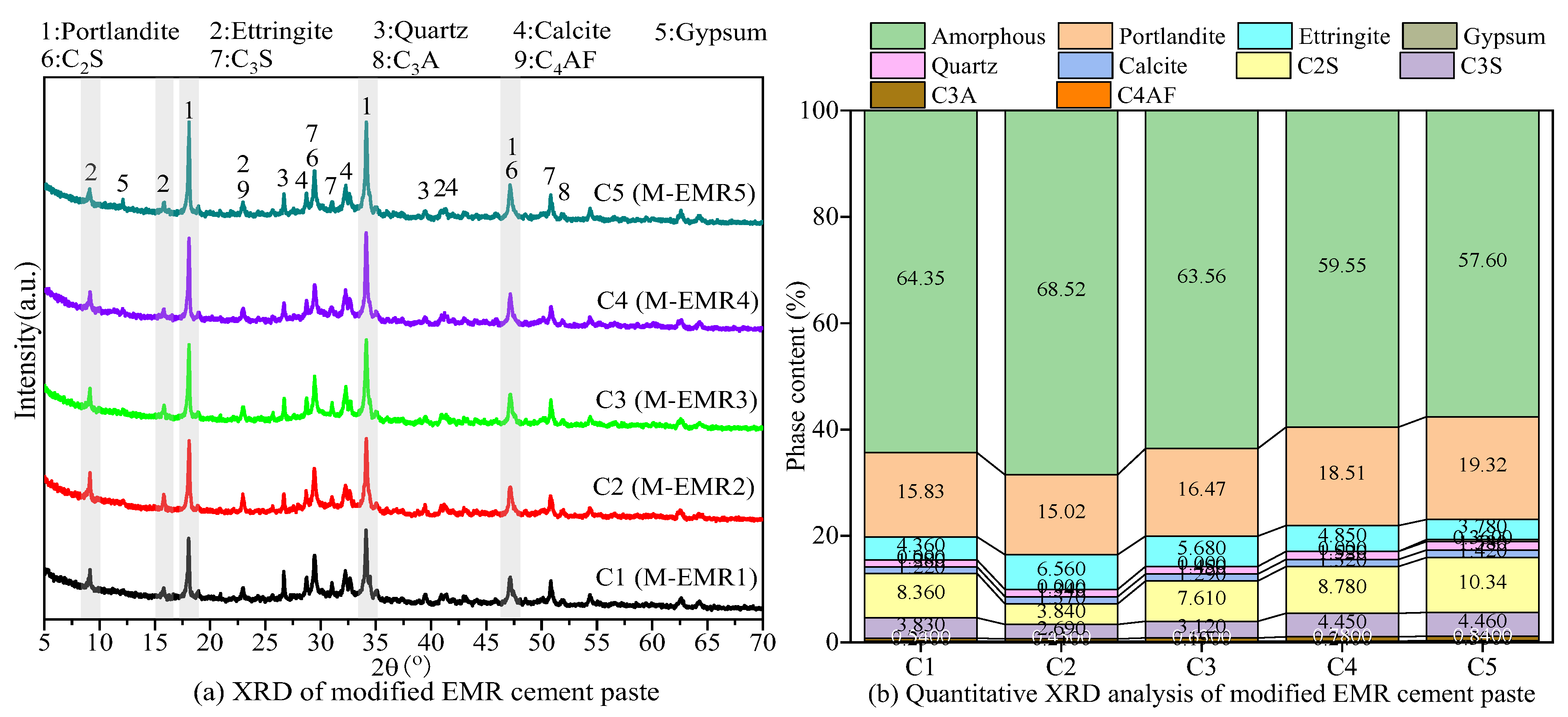
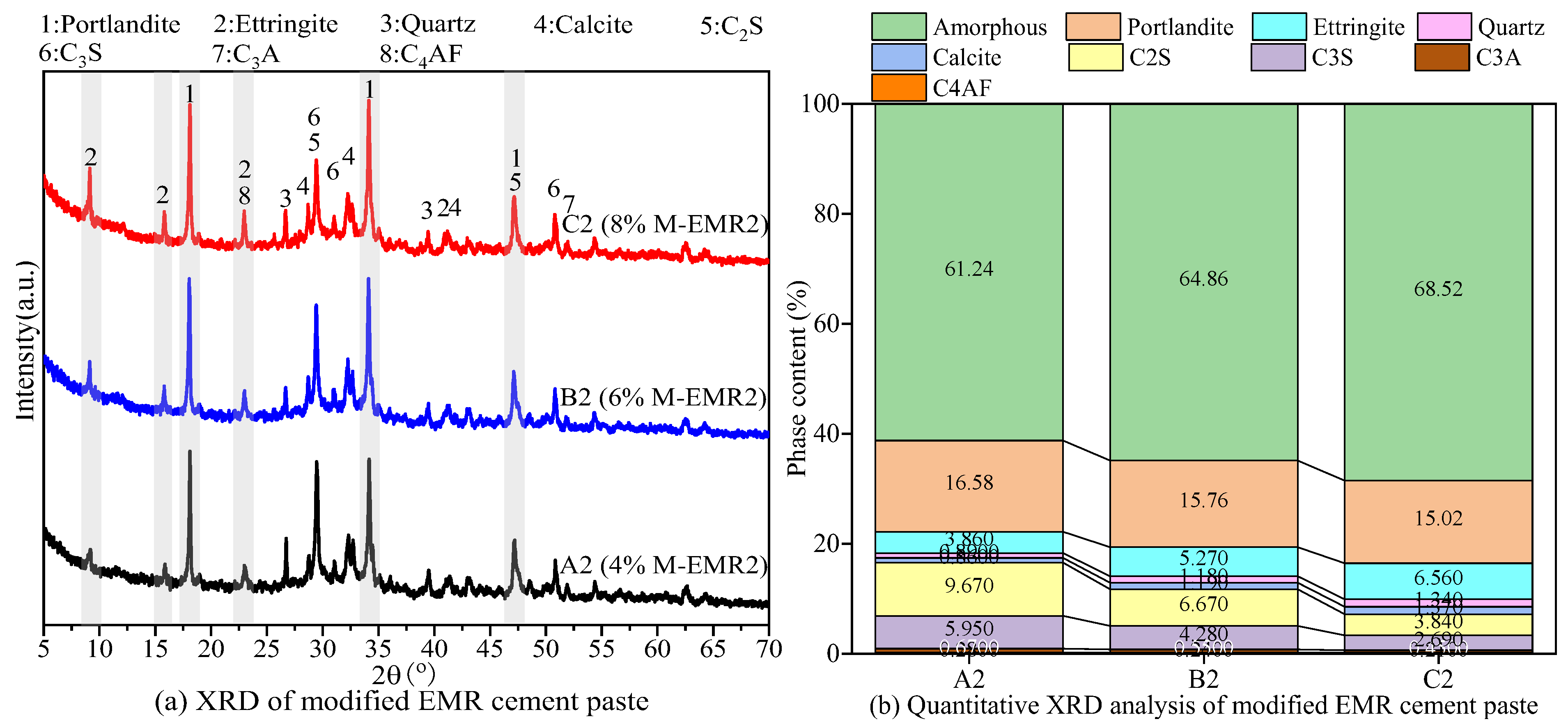
3.5. XRD Analysis of Modified EMR-Cement Paste
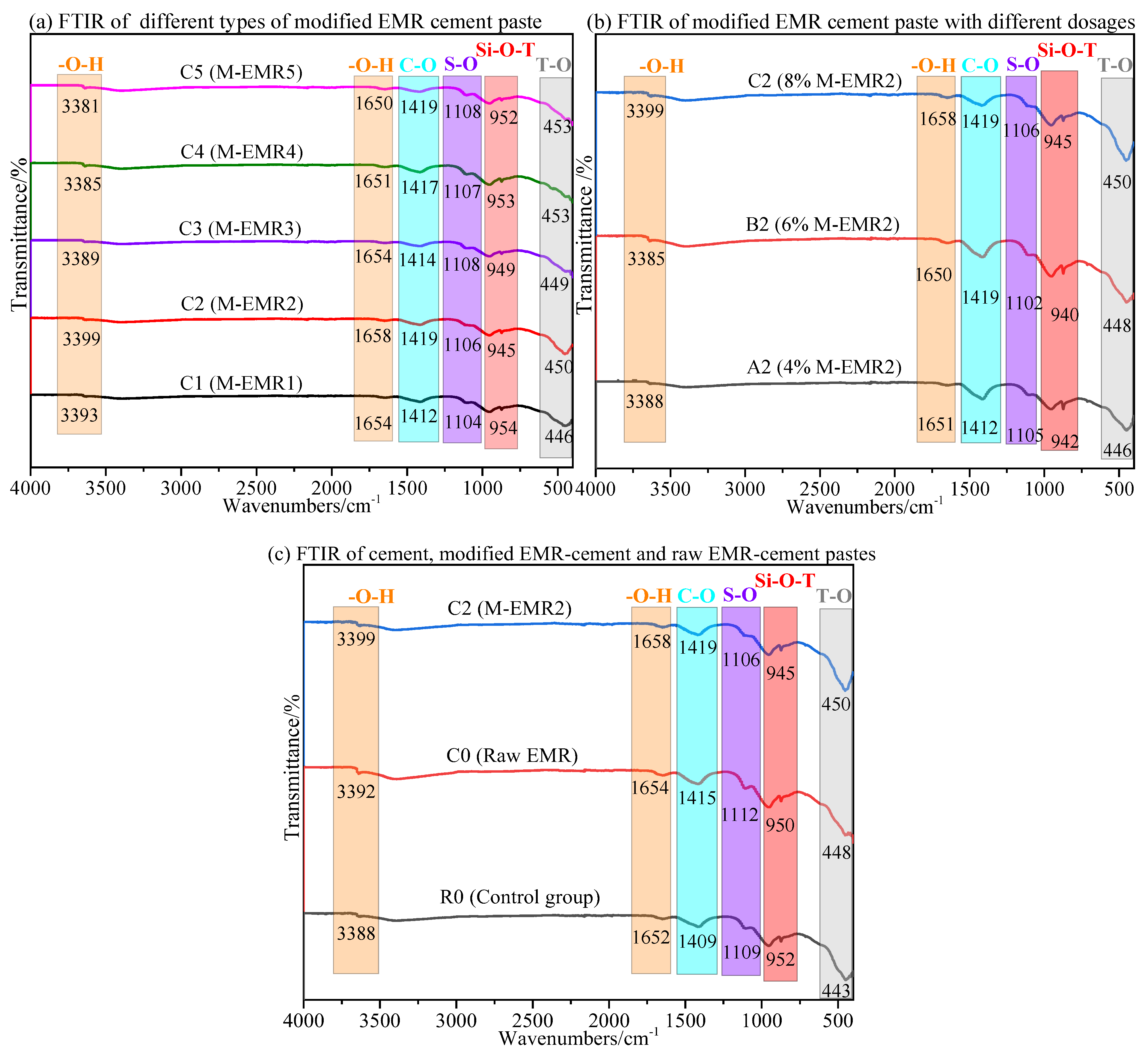
3.6. FTIR Analysis of Modified EMR-Cement Paste
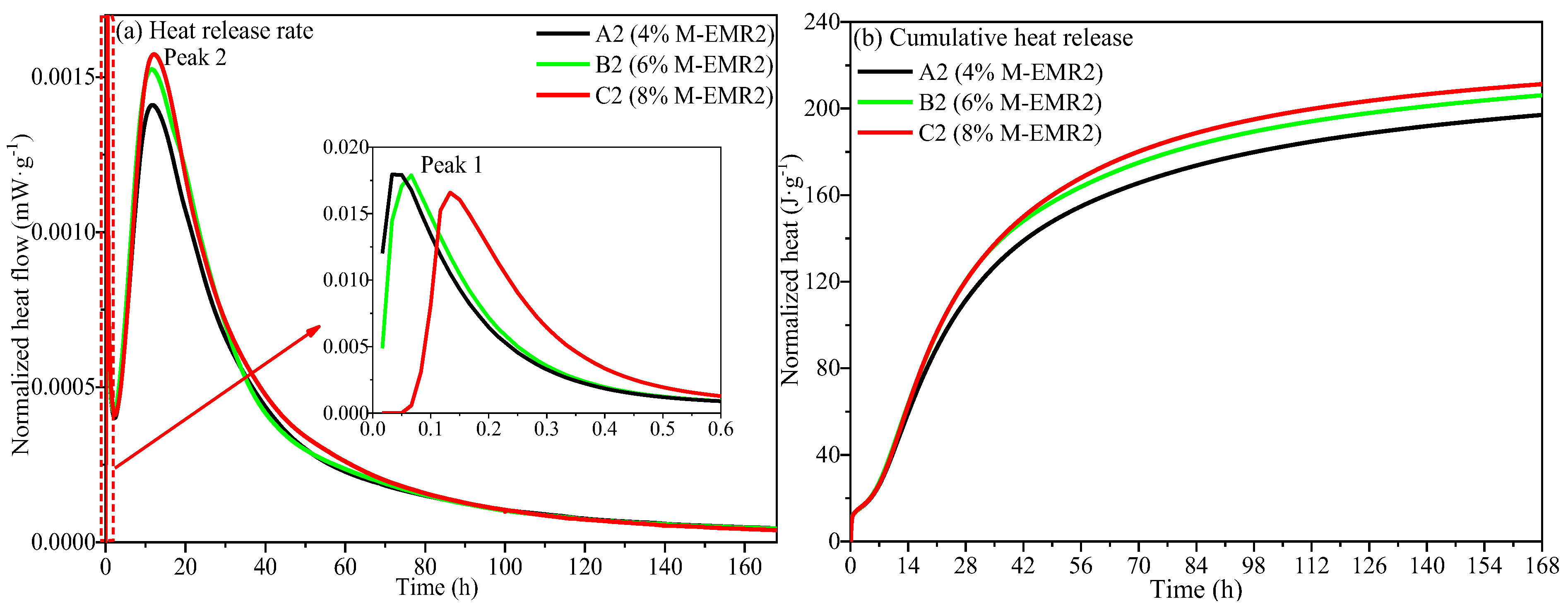
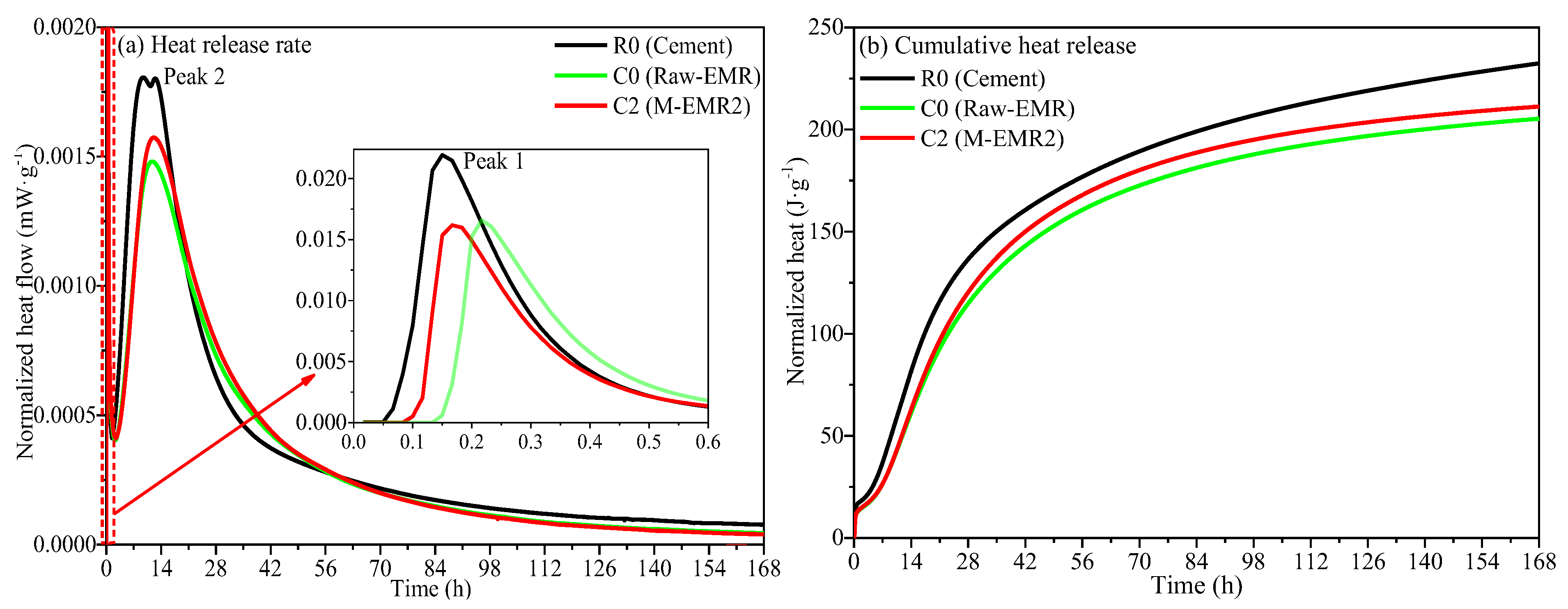
3.7. Hydration Heat of Analysis of Modified EMR-Cement Paste
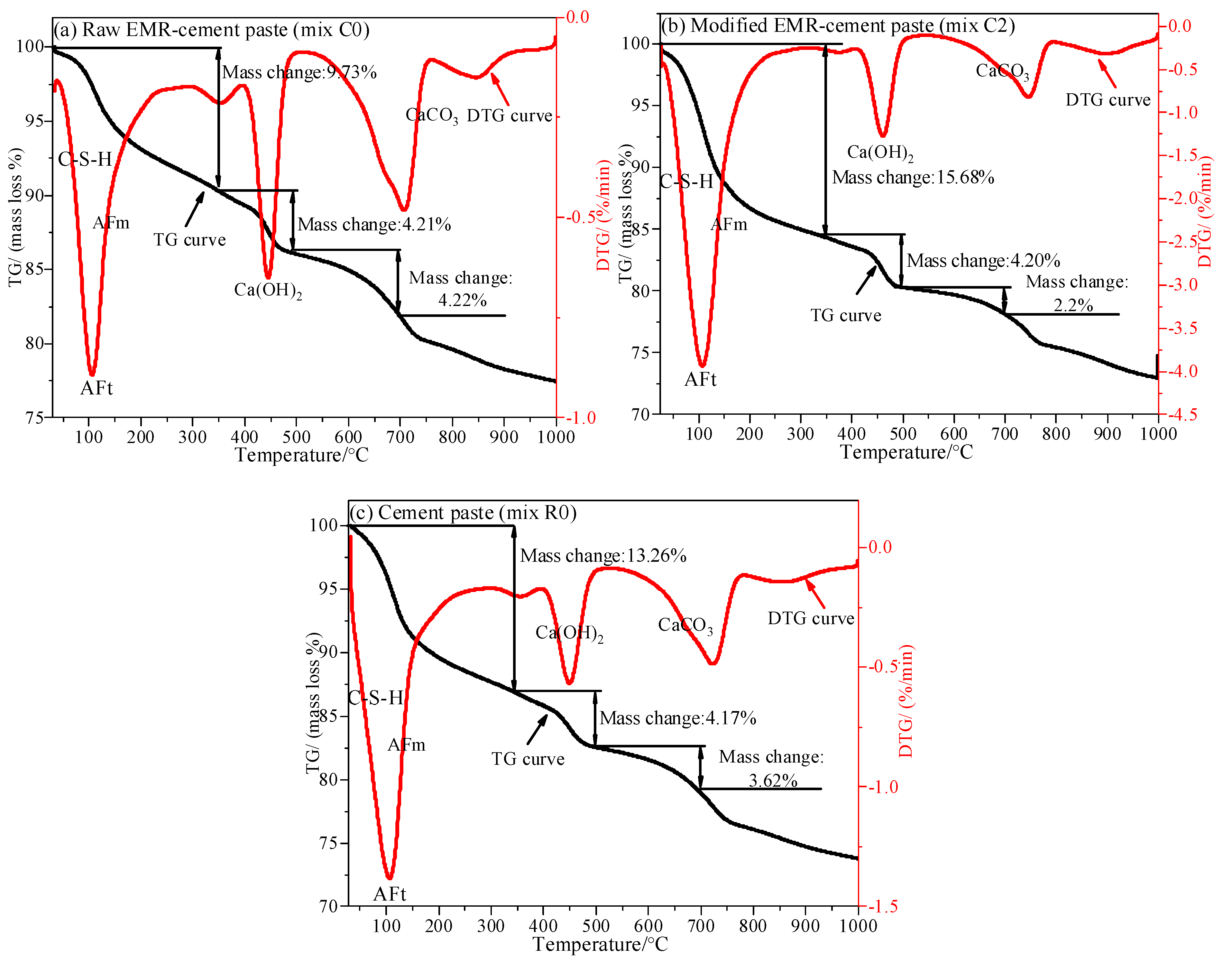
3.8. TG-DTG Analysis of Modified EMR-Cement Paste
3.9. SEM-EDS Analysis of Modified EMR-Cement Paste
3.10. Leaching Toxicity and Solidification Mechanism of Modified EMR-Cement Mortar
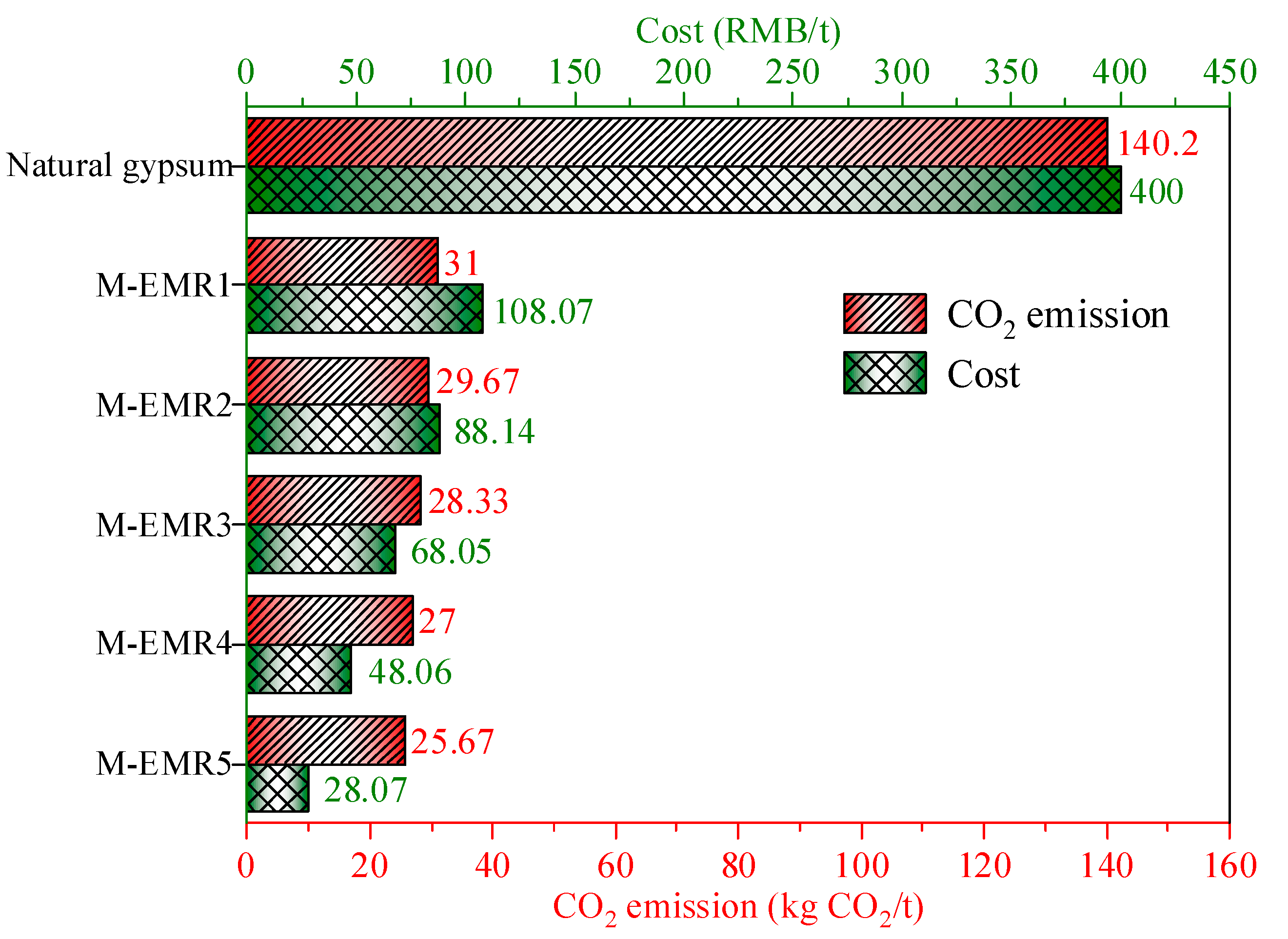
3.11. Carbon Emissions and Cost Analysis of Modified EMR-Cement Mortar
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, T.; Xue, S.; Zhuang, S.; Zhou, X.; Hou, H.; Huang, B.T.; Lan, J. Activated Electrolytic Manganese Residue-Based Environmental Materials for Mine Remediation: Performance and Mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 482, 136560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, M.; Wang, B.; Chen, M.; Wu, P.; Zhang, X. Remediation of Antimony and Arsenic in Co-Contaminated Soil by Electrolytic Manganese Residue–Biochar Composite: Effects, Mechanisms, and Microbial Response. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 366, 125371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Ma, X.; Li, C.; Xue, J.; Wang, S. Highly Efficient CO2 Mineralization: Mechanisms and Feasibility of Utilizing Electrolytic Manganese Residue as a Feedstock and Implementing Ammonia Recycling. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, K.; Shang, S.; Ran, J.; Xia, H.; Luo, Z.; Dong, R. Exploration of the Effects of Electrolytic Manganese Residue on the Environmental, Economic, and Engineering Performance of Magnesium Oxychloride Cement: A Possible Utilization Method of Electrolytic Manganese Residue. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, L.; Zhu, M.; Pu, S. Recycling engineering sediment waste as sustainable subgrade material using ground granulated blast-furnace slag, electrolytic manganese residue and cement. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 37, 103969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Shu, J.; Wang, R.; Chen, M.; Wang, R.; Gao, Y.; Wang, N. A Critical Review on Approaches for Electrolytic Manganese Residue Treatment and Disposal Technology: Reduction, Pretreatment, and Reuse. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Li, L.; Chen, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, M. Modification of Phosphogypsum Using Circulating Fluidized Bed Fly Ash and Carbide Slag for Use as Cement Retarder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 338, 127630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Gan, G.; Dong, R.; Chen, H.; Tan, Y.; Zhou, M. Utilization of Solidified Phosphogypsum as Portland Cement Retarder. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2012, 14, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, J.; Li, C.; Lu, W.; Rong, T.; Huang, P.; Hu, T. Study on Retarders for Desulfurized Building Gypsum. New Build. Mater. 2017, 44, 143–145. [Google Scholar]
- Altun, İ.A.; Sert, Y. Utilization of Weathered Phosphogypsum as Set Retarder in Portland Cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, M. Hydration behavior of clinker with dry flue gas desulfurization byproduct and desulfurization gypsum. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 44, 663–667. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; He, Z.; Pei, S.; Han, J.; Zou, M.; Qin, M.; Yu, Z. Hydration Characteristics and Pollutant Solidification Mechanism of Full Solid Waste Electrolytic Manganese Residue Super Sulfate Cement. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 84, 108563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Q.; Xue, J. Reuse of Hazardous Electrolytic Manganese Residue: Detailed Leaching Characterization and Novel Application as a Cementitious Material. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 154, 104645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, B.; Mukiza, E. Investigation on Sulfate Activation of Electrolytic Manganese Residue on Early Activity of Blast Furnace Slag in Cement-Based Cementitious Material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 229, 116831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Long, G.; Dong, R.; Li, Y. Analysis of Strength, Microstructure and Carbon Emission of Mortar Mixed with Electrolytic Manganese Residue. J. Railw. Sci. Eng. 2023, 20, 1382–1391. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Long, Y. Experimental Study on Electrolytic Manganese Residue as a Cement Retarder. Fujian Build. Mater. 2012, 9, 12–14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Zeng, R.; Tao, C. Experimental Study on Using Electrolytic Manganese Slag as a Cement Retarder Instead of Industrial Gypsum. Cem. Eng. 2024, 2, 10–19. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Qiao, H.; Feng, Q.; Chen, K.; Li, Y.; Xue, C.; Zhang, Y. Review of New Methods for Resource Utilisation of Electrolytic Manganese Residue and Its Application in Building Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 401, 132901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Jin, H.; Xie, H.; Wang, D. Progress in Comprehensive Utilization of Electrolytic Manganese Residue: A Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 48837–48853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.; Chen, M.; Wu, H.; Li, B.; Wang, B.; Li, B.; Liu, Z. An Innovative Method for Synergistic Stabilization/Solidification of Mn2+, NH4+-N, PO43− and F− in Electrolytic Manganese Residue and Phosphogypsum. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 376, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Long, G.; Bai, M.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, J.L. A New Perspective on Belite-Ye’elimite-Ferrite Cement Manufactured from Electrolytic Manganese Residue: Production, Properties, and Environmental Analysis. Cem. Concr. Res. 2023, 163, 107019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.; Cardoso, T.; Degen, M.; Silvestro, L.; Rodríguez, E.; Kirchheim, A.P. Influence of Retarder Admixtures on the Hydration, Rheology, and Compressive Strength of White Portland Cements under Different Temperatures. Cement 2023, 11, 100057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.; Liu, R.; Liu, Z.; Chen, H.; Du, J.; Tao, C. Solidification/Stabilization of Electrolytic Manganese Residue Using Phosphate Resource and Low-Grade MgO/CaO. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 317, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, D.; Luo, Z.; Zeng, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Cao, W.; Chen, M. Electrolytic Manganese Residue Disposal Based on Basic Burning Raw Material: Heavy Metals Solidification/Stabilization and Long-Term Stability. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 153774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Long, G.; Bai, M.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J.L.; Zhou, X. Application of Electrolytic Manganese Residues in Cement Products through Pozzolanic Activity Motivation and Calcination. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 338, 130629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Zhu, H.; Luo, T.; Wang, H.; Hou, H. Pure Water Leaching Soluble Manganese from Electrolytic Manganese Residue: Leaching Kinetics Model Analysis and Characterization. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Ma, B.; An, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C. Improvement of Manganese Electrolytic Process and Secondary Resources Recovery of Manganese: A Review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 186, 895–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhan, J.; Liu, G.; Zheng, M.; Jin, R.; Yang, L.; Wang, P. Evaluation of Dioxins and Dioxin-Like Compounds from a Cement Plant Using Carbide Slag from Chlor-Alkali Industry as the Major Raw Material. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 330, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, B.; Li, T.; Wang, W. Toughness Study of Polyacrylamide-Modified Slag/Fly Ash-Based Alkali-Activated Cementitious Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 450, 138622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Shu, J.; Zeng, X.; Wei, Y.; Chen, M.; Tan, D.; Liang, Q. Synergistic Solidification/Stabilization of Electrolytic Manganese Residue and Carbide Slag. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 152175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; He, Z.; Chen, K.; Wang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Yu, Z.; Xiao, H. Study of Microscopic Properties and Heavy Metal Solidification Mechanism of Electrolytic Manganese Residue-Based Cementitious Materials. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 105056–105071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Tang, B.; Wang, Y. Preparation of Road Base Material by Utilizing Electrolytic Manganese Residue Based on Si–Al Structure: Mechanical Properties and Mn²⁺ Stabilization/Solidification Characterization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 122188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T 17671-2021; Cement Mortar Strength Test Method (ISO Method). Standard Press of China: Beijing, China, 2021. (In Chinese)
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Tang, B.; Wang, Y.; Mukiza, E. Synergic Effects of Electrolytic Manganese Residue–Red Mud–Carbide Slag on the Road Base Strength and Durability Properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 220, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 175-2020; Portland Cement. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2020. (In Chinese)
- HJ/T 299-2007; Sulphuric Acid and Nitric Acid Method for Total Digestion of Solid Waste. Standard Press of China: Beijing, China, 2007. (In Chinese)
- HJ 535-2009; Water Quality—Determination of Ammonia Nitrogen—Nessler’s Reagent Spectrophotometry. Standard Press of China: Beijing, China, 2009. (In Chinese)
- GB 8978-1996; Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard. Standard Press of China: Beijing, China, 1996. (In Chinese)
- Fu, Y.; Qiao, H.; Feng, Q.; Chen, K.; Li, Y.; Jia, Z.; Xue, C. Impact of Desulphurized Electrolytic Manganese Residue-Assisted Cementitious Materials on Silicate Cement Hydration and Environmental Safety Assessment. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 94, 109906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; He, Z.; Tang, J.; Yang, R.; Pei, S.; Xia, Y.; Yu, J. Study on the Microscopic Characteristics and Hydration Mechanism of Thermo-Alkali Activated Electrolytic Manganese Residue Geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 438, 137279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, N. Treating Electrolytic Manganese Residue with Alkaline Additives for Stabilizing Manganese and Removing Ammonia. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 30, 2037–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Hou, D.; Duan, N.; Zhou, C.; Wang, J.; Dan, Z. Immobilization of High Concentrations of Soluble Mn(II) from Electrolytic Manganese Solid Waste Using Inorganic Chemicals. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 7782–7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Feng, Z.; Pu, S.; Zeng, C.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, C. Mechanical Properties and Environmental Characteristics of the Synergistic Preparation of Cementitious Materials Using Electrolytic Manganese Residue, Steel Slag, and Blast Furnace Slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Chen, M.; Liu, H.; Wang, J. Preparation of Activated Electrolytic Manganese Residue–Slag–Cement Ternary Blended Cementitious Material: Hydration Characteristics and Carbon Reduction Potential. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 425, 135990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zunino, F.; Yang, L.; Wang, F.; Scrivener, K. Understanding the Negative Effects of Alkalis on Long-Term Strength of Portland Cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2023, 174, 107348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Qiao, H.; Feng, Q.; Chen, K.; Li, Y.; Jia, Z. Self-Stabilisation of High-Temperature Calcined Electrolytic Manganese Residue in Mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 386, 131460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Tang, B.; Wang, Y.; Mukiza, E. Preparation and Characterization of Cement Treated Road Base Material Utilizing Electrolytic Manganese Residue. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 980–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shui, Z.; Sun, T.; Li, H.; Chi, H.; Ouyang, G. Effect of MgO and Superfine Slag Modification on the Carbonation Resistance of Phosphogypsum-Based Cementitious Materials: Based on Hydration Enhancement and Phase Evolution Regulation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 415, 134914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratap, B.; Mondal, S.; Rao, B.H. Mechanical and Durability Assessment of Phosphogypsum–Bauxite Residue–Fly Ash-Based Alkali-Activated Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cretescu, I.; Harja, M.; Teodosiu, C.; Isopescu, D.N.; Chok, M.F.; Sluser, B.M.; Salleh, M.A.M. Synthesis and Characterisation of a Binder Cement Replacement Based on Alkali Activation of Fly Ash Waste. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 119, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Qian, J.; Huang, Y.; Yang, D. Synthesis of Belite Sulfoaluminate–Ternesite Cements with Phosphogypsum. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2015, 63, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y. Synergistic Use of Industrial Solid Wastes to Prepare Belite-Rich Sulphoaluminate Cement and Its Feasibility Use in Repairing Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 264, 120201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, M.; Yilmaz, E.; Kasap, T.; Guner, N.U. Strength and Microstructure Evolution in Cemented Mine Backfill with Low and High pH Pyritic Tailings: Effect of Mineral Admixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 328, 127109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gougar, M.L.D.; Scheetz, B.E.; Roy, D.M. Ettringite and C–S–H Portland Cement Phases for Waste Ion Immobilization: A Review. Waste Manag. 1996, 16, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Liu, R.; Jing, D.; Lu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, Z. Study on the Alkali–Sulfur Co-Activation and Mechanical Properties of Low-Carbon Cementitious Composite Materials Based on Electrolytic Manganese Residue, Carbide Slag, and Granulated Blast-Furnace Slag. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Lang, L.; Nie, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Ping, W.; Li, J. Utilization of Ground Granulated Blast-Furnace Slag and Electrolytic Manganese Residue as a Low-Carbon Cementitious Material. J. Sustain. Cem.-Based Mater. 2024, 13, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Long, G.; Bai, M.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, J.L. Feasibility of Low-Carbon Electrolytic Manganese Residue-Based Supplementary Cementitious Materials. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 883, 163672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fořt, J.; Černý, R.J. Carbon Footprint Analysis of Calcined Gypsum Production in the Czech Republic. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 177, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, H.L.; Doh, J.H.; Liu, J.; Lu, L.; Song, H.; Park, D. Comprehensive Assessment of Geopolymer Concrete Mechanical and Environmental Performance with Glass Cullet Fine Aggregates. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 76, 107094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fořt, J.; Mildner, M.; Černý, R. Consequences of Omitting Some Important Factors in the Environmental Analyses of Commercial Sodium Silicate/Sodium Hydroxide Use for Alkaline Activation in the Light of Comparison with Cement-Based Composites. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 928, 172324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Compound | SiO2 | SO3 | CaO | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | Na2O | K2O | MnO | P2O5 | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMR | 38.55 | 27.32 | 9.34 | 7.78 | 6.58 | 2.34 | 0.78 | 3.01 | 3.11 | — | 1.2 |
| Cement | 19.88 | 3.47 | 65.66 | 5.22 | 2.75 | 0.49 | — | — | — | — | 1.59 |
| GBFS | 32.49 | 1.62 | 35.28 | 19.22 | 0.52 | 8.76 | 0.61 | 0.40 | 0.19 | — | 1.1 |
| CS | 5.23 | 0.97 | 87.33 | 0.67 | 1.89 | 0.86 | 0.21 | — | — | — | 2.84 |
| Number | EMR Dosage (g) | CS Dosage (g) | GBFS Dosage (g) | Water (g) (Water Solid Ratio = 0.5) | CS:GBFS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M-EMR1 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0:10 |
| M-EMR2 | 100 | 25 | 75 | 100 | 2.5:7.5 |
| M-EMR3 | 100 | 50 | 50 | 100 | 5:5 |
| M-EMR4 | 100 | 75 | 25 | 100 | 7.5:2.5 |
| M-EMR5 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 10:0 |
| Number | Standard Cement Dosage (g) | Raw EMR Dosage (g) | M-EMR1 Dosage (g) | M-EMR2 Dosage (g) | M-EMR3 Dosage (g) | M-EMR4 Dosage (g) | M-EMR5 Dosage (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R0 | 450 | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| A0 | 450 | 18 (4 wt.%) | / | / | / | / | / |
| A1 | 450 | / | 18 (4 wt.%) | / | / | / | / |
| A2 | 450 | / | / | 18 (4 wt.%) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| A3 | 450 | / | / | / | 18 (4 wt.%) | / | / |
| A4 | 450 | / | / | / | / | 18 (4 wt.%) | 0 |
| A5 | 450 | / | / | / | / | / | 18 (4 wt.%) |
| B0 | 450 | 27 (6 wt.%) | / | / | / | / | / |
| B1 | 450 | / | 27 (6 wt.%) | / | / | / | / |
| B2 | 450 | / | / | 27 (6 wt.%) | / | / | / |
| B3 | 450 | / | / | / | 27 (6 wt.%) | / | / |
| B4 | 450 | / | / | / | / | 27 (6 wt.%) | / |
| B5 | 450 | / | / | / | / | / | 27 (6 wt.%) |
| C0 | 450 | 36 (8 wt.%) | / | / | / | / | / |
| C1 | 450 | / | 36 (8 wt.%) | / | / | / | / |
| C2 | 450 | / | / | 36 (8 wt.%) | / | / | / |
| C3 | 450 | / | / | / | 36 (8 wt.%) | / | / |
| C4 | 450 | / | / | / | / | 36 (8 wt.%) | / |
| C5 | 450 | / | / | / | / | / | 36 (8 wt.%) |
| Phase | Space Group | Lattice Parameter | ICSD | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | α | β | γ | |||
| Alite | R3m | 33.108 | 7.036 | 18.521 | – | 94.137 | – | 94,742 |
| Belite | P21/n | 5.512 | 6.758 | 9.314 | – | 94.58 | – | 81,096 |
| Tricalcium aluminate | Pa-3 | 15.26 | – | – | – | – | – | 1,841 |
| Gypsum | C2/c | 6.284 | 15.2 | 6.523 | – | 127.41 | – | 409,581 |
| Portlandite | P-3m | 3.592 | – | 4.906 | – | – | – | 202,220 |
| Ettringite | P3c | 11.229 | – | 21.478 | – | – | – | 155,395 |
| Zincite | P63mc | 3.253 | 3.253 | 5.207 | 90 | 90 | 120 | 9,004,179 |
| Number | Mn (mg/L) | NH3-N (mg/L) | pH Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw EMR | 1220 | 149 | 5.80 |
| M-EMR1 | 27.672 | 3.6224 | 10.66 |
| M-EMR2 | 0.0736 | 2.7861 | 11.43 |
| M-EMR3 | 0.0251 | 1.5654 | 12.25 |
| M-EMR4 | 0.0084 | 0.5831 | 12.78 |
| M-EMR5 | 0.0023 | 0.0871 | 13.14 |
| GB8978-1996 standard | 2 | 15 | / |
| Group | Leaching Concentration (mg/L) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | NH3-N | Hg | Pb | Cd | Cr | Cu | Zn | |
| Raw EMR | 1220 | 149 | 0.0012 | 0.0132 | 0.0732 | 0.0252 | 0.4640 | 1.700 |
| C1 | 0.0545 | 0.0862 | 0.0005 | 0.0014 | 0.0088 | N.D. | 0.1542 | 0.0932 |
| C2 | 0.0058 | 0.0056 | N.D. | 0.0002 | 0.0043 | N.D. | 0.0260 | 0.0256 |
| C3 | 0.0012 | 0.0013 | 0.0003 | 0.0018 | 0.0019 | N.D. | 0.0052 | 0.0075 |
| C4 | N.D. | N.D. | 0.0002 | 0.0011 | 0.0008 | N.D. | 0.0021 | 0.0053 |
| C5 | N.D. | N.D. | 0.0004 | N.D. | 0.0002 | N.D. | 0.0034 | 0.0021 |
| GB8978-1996 | 2 | 15 | 0.05 | 1 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, L.; Fořt, J.; Černý, R.; He, Z. Sustainable Utilization of Modified Electrolytic Manganese Residue as a Cement Retarder: Workability, Mechanical Properties, Hydration Mechanisms, Leaching Toxicity, and Environmental Benefits. Buildings 2025, 15, 1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15101586
Tang L, Fořt J, Černý R, He Z. Sustainable Utilization of Modified Electrolytic Manganese Residue as a Cement Retarder: Workability, Mechanical Properties, Hydration Mechanisms, Leaching Toxicity, and Environmental Benefits. Buildings. 2025; 15(10):1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15101586
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Liang, Jan Fořt, Robert Černý, and Zhaoyi He. 2025. "Sustainable Utilization of Modified Electrolytic Manganese Residue as a Cement Retarder: Workability, Mechanical Properties, Hydration Mechanisms, Leaching Toxicity, and Environmental Benefits" Buildings 15, no. 10: 1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15101586
APA StyleTang, L., Fořt, J., Černý, R., & He, Z. (2025). Sustainable Utilization of Modified Electrolytic Manganese Residue as a Cement Retarder: Workability, Mechanical Properties, Hydration Mechanisms, Leaching Toxicity, and Environmental Benefits. Buildings, 15(10), 1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15101586








