Computational Simulation of the Correlations in a Port–Hinterland System from a Tourism Spatial Optimization Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data Sources
2.1.1. Mohan Port
2.1.2. Yunnan’s Economic Hinterland
2.1.3. Data Sources
2.2. Research Methodology
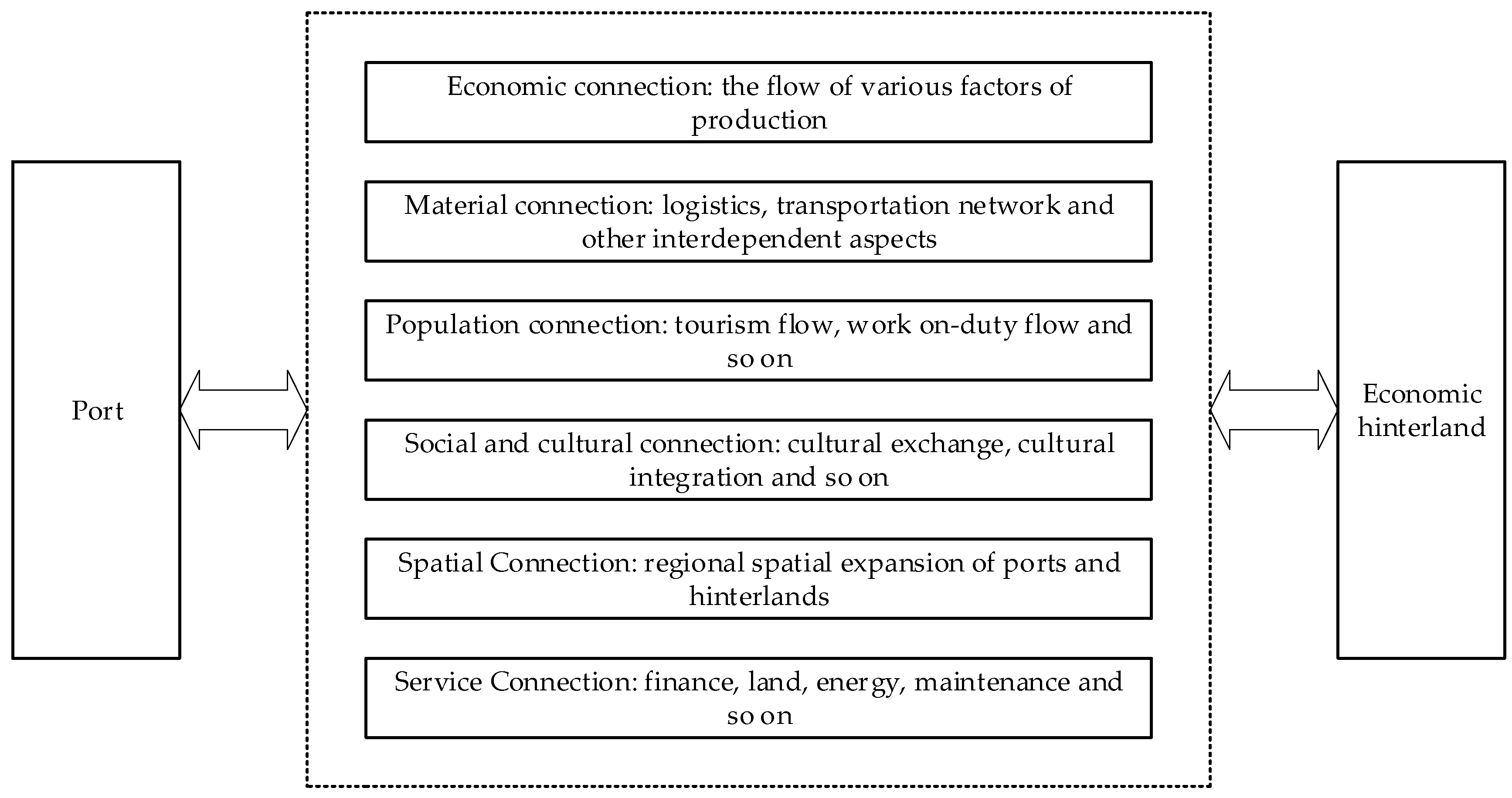
2.2.1. Indicator System Construction
2.2.2. Computer Simulation of Gray Correlation
3. Results
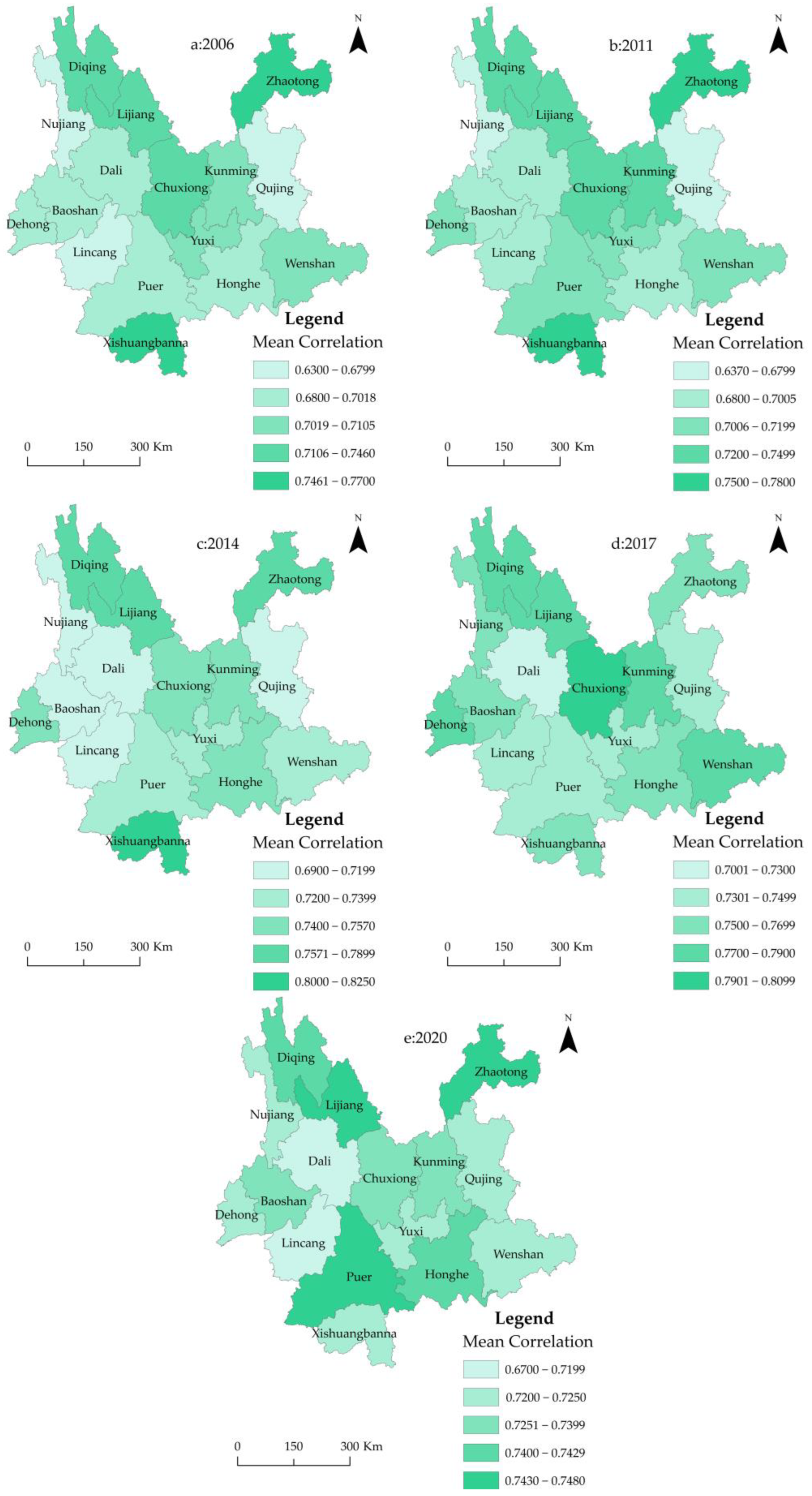
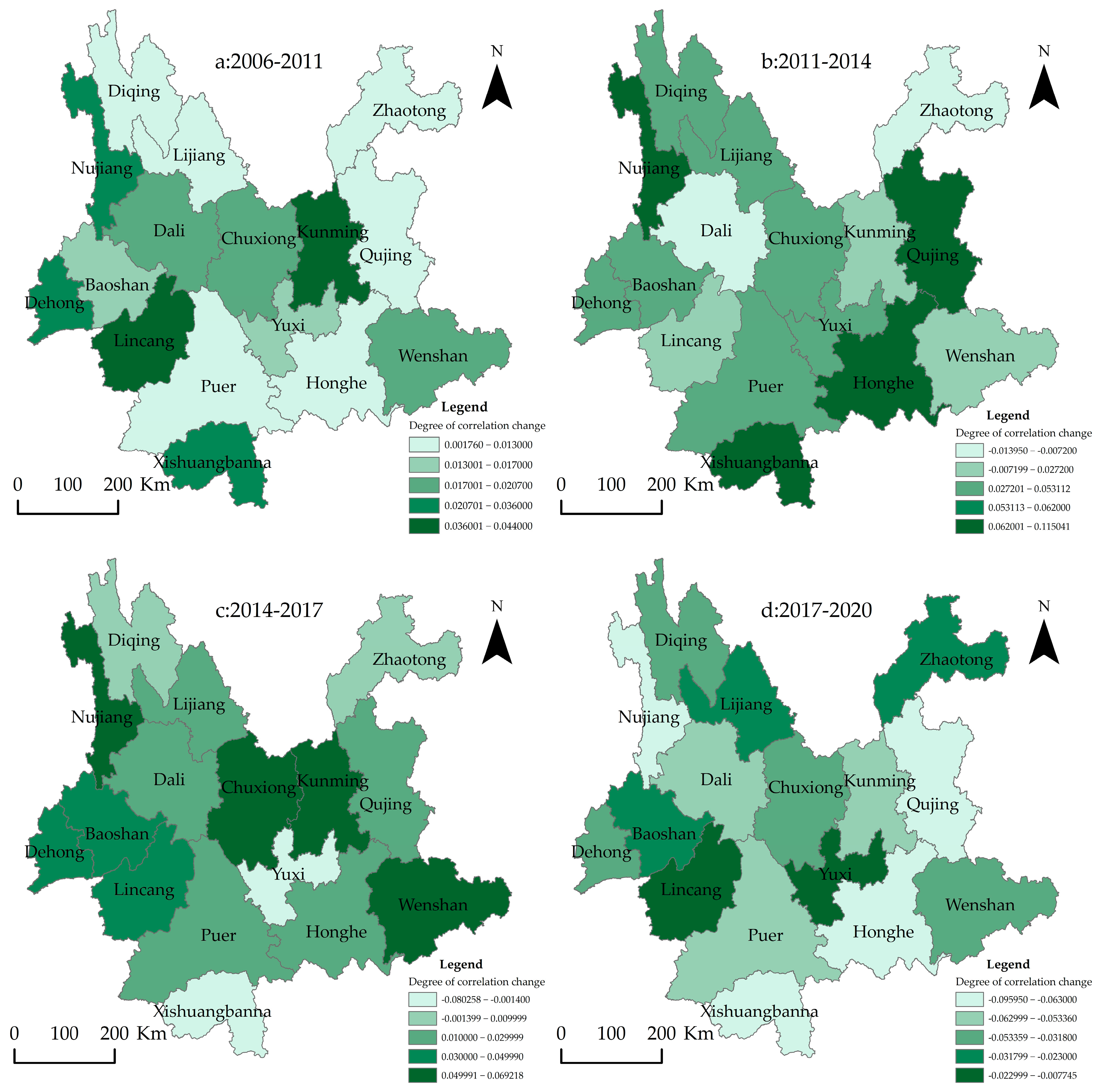
3.1. Spatial Evolution Analysis of Correlation Properties Based on Computer Simulation
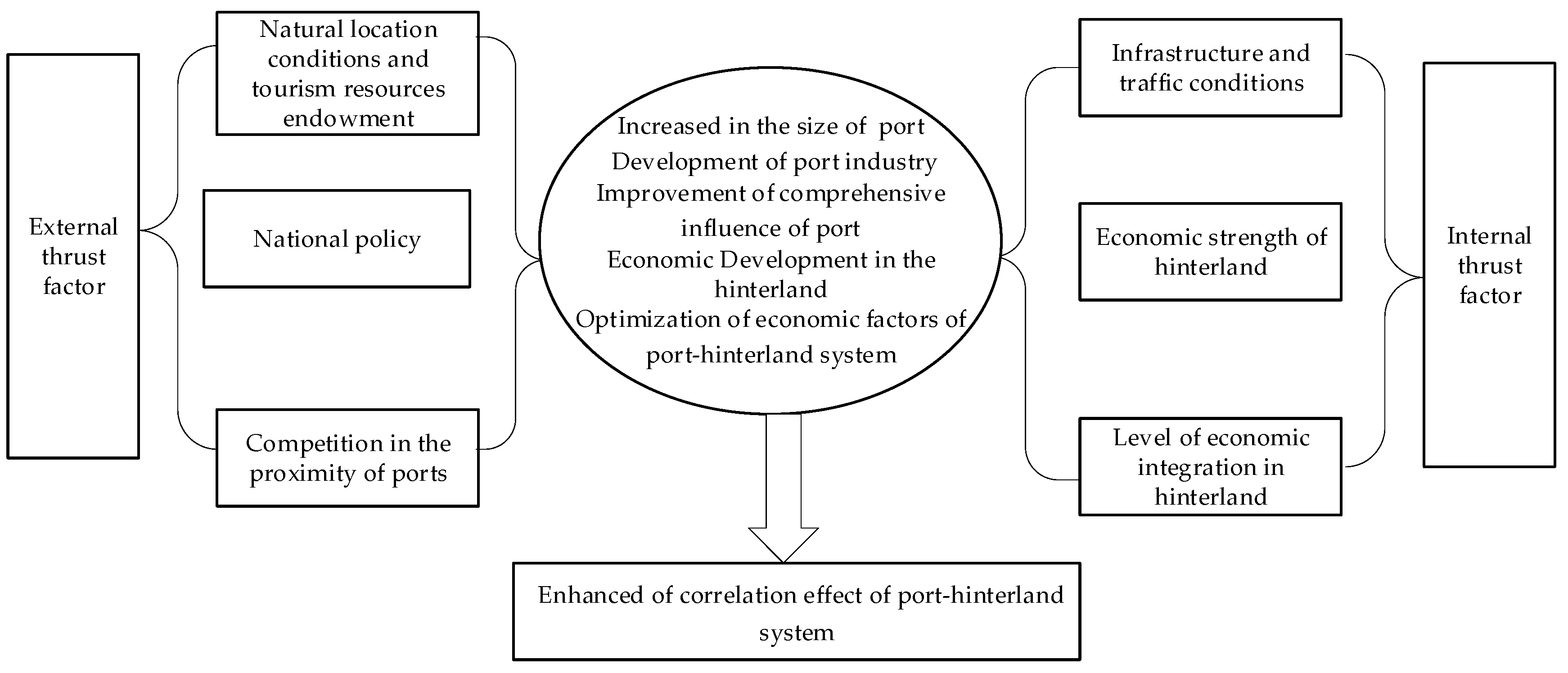
3.2. Driving Mechanism Analysis of the Correlation Development from the Perspective of Tourism Spatial Optimization
- (1)
- Natural conditions of the location and tourism resources endowments
- (2)
- Infrastructure and traffic conditions
- (3)
- Economic strength and integration level of the hinterland
- (4)
- Policy orientation
- (5)
- Competition from neighboring ports
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, C.; Huang, L.; Zhang, S.-B. Public space optimization strategy of “Sharing Farm” tourist rural in Hainan. Guangdong Land Arch. 2018, 40, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Bland, J. Space-planning by ant colony optimisation. Int. J. Comput. Appl. Technol. 1999, 12, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubogu, A.; Ariyo, J.; Mamman, M. Port-hinterland trucking constraints in Nigeria. J. Transp. Geogr. 2011, 19, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.-J.; Chu, Y.-L. Optimization for Hub-and-Spoke Port Logistics Network of Dynamic Hinterland. Phys. Procedia 2012, 33, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Song, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wuzhati, Y.; Song, T.; Niu, F.; Han, M. Progress in research on the Belt and Road Initiative. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 620–636. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z. Study on the Correlation measure of Harbor-Hinterland: Taking Qingdao Port-Shandong Economic Region as an Example. Master’s Thesis, Liaoning Normal University, Dalian, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Xu, C.; Zhou, W. The space-time evolutionary mechanism of port group hinterland under the “dual circulation” new development pattern-Taking the port group of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao greater bay area as the case. China Bus. Mark. 2022, 36, 20–32. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigue, J.-P.; Notteboom, T. The terminalization of supply chains: Reassessing the role of terminals in port/hinterland logistical relationships. Marit. Policy Manag. 2009, 36, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, C.; Parola, F.; Gattorna, E. Measuring the quality of port hinterland accessibility: The Ligurian case. Transp. Policy 2011, 18, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.M.P.; Salvador, R.; Dias, J.C.Q.; Soares, C.G. Assessment of port economic impacts on regional economy with a case study on the Port of Lisbon. Marit. Policy Manag. 2018, 45, 684–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, P.H.; Thill, J.-C. Sea-land interdependence and delimitation of port hinterland-foreland structures in the international transportation system. J. Transp. Geogr. 2022, 99, 103297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sdoukopoulos, E.; Boile, M. Strengthening the Collaborative Environment in Port-Hinterland Corridor Management Initiatives: A Value System Approach. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Liu, N. Improving the Resilience of Port–Hinterland Container Logistics Transportation Systems: A Bi-Level Programming Approach. Sustainability 2021, 14, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmund, C. River Port and Deep-Sea Port Developments in Nigeria: Implications for West African Gateways and Hinterland Markets. Am. J. Ind. Bus. Manag. 2022, 12, 531–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notteboom, T.E.; Rodrigue, J.-P. Regionalização Portuária: Rumo a uma Nova Fase no Desenvolvimento Portuário. Marit. Policy Manag. 2014, 4, 123–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Han, Z. Review and prospect of the research on spatial connection between port and city. Prog Geogr. 2010, 29, 1490–1498. [Google Scholar]
- Gurzhiy, A.; Kalyazina, S.; Maydanova, S.; Marchenko, R. Port and City Integration: Transportation Aspect. Transp. Res. Procedia 2021, 54, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X. Study on Spatial Function and Linkage Development Mechanism of Dalian Port and Northeast Hinterland System. Ph.D. Thesis, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Song, H.; Jeong, S. Prioritizing environmental justice in the port hinterland policy: Case of Busan New Port. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2021, 41, 100672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y. Research on the Comprehensive Strength of Coastal Ports and Spatial Evolution of Hinterland. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, P.; Wang, Z.; Wang, P.; Yin, H.; Wang, J.; Dawson, K.A.; Indekeu, J.O.; Stanley, H.E.; Tsallis, C. Dynamic evolution of shipping network based on hypergraph. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2022, 598, 127247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Liu, B.; Li, Z. Study on the correlation measure of harbor-hinterland and its driving forces: Taking Lianyungang port-Huaihai economic region as an example. Geogr. Res. 2009, 28, 716–725. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Li, W. Mobility and re-spatialization: A study on the urbanization process of Mohan port in China-Laos borders. J. Guangxi Univ. Natl. Philos. Soc. Sci. Technol. Ed. 2019, 41, 118–127. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B. Yunnan border crossings and the hinterland logistics system construction and urban spatial structure Yunnan border crossings and the hinterland logistics system construction and urban spatial structure optimization. J. Honghe Univ. 2015, 13, 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X. Research on location degree of border ports and spatial connection of “port-hinterland” in Heilongjiang Province. China Ste. Foc. 2022, 5, 125–128. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T.; Wang, L. Research on the correlation effect of Qingdao port-city based on grey correlation model. J. Qingdao Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2019, 32, 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Study on the Level, Function and Spatial Structure of China’s Port System. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Qin, B. Analyzation on the advantages and disadvantages of China and North Korea border port development. Guizhou Ethn. Stud. 2022, 43, 134–141. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, S.; Wang, H. A preliminary study on socioeconomic integration in the Yangtze River delta. China Soft Sci. 2004, 5, 123–129. [Google Scholar]

| Evaluation Object | Indicator Variables | Indicator Content |
|---|---|---|
| Hinterland | X1 | GDP per capita |
| X2 | Hinterland fixed asset investment | |
| X3 | Ratio of the output value of the tertiary and secondary industries | |
| X4 | Foreign exchange earnings from tourism | |
| X5 | Total passenger traffic in the hinterland | |
| X6 | Total freight volume in the hinterland | |
| X7 | Road network density | |
| X8 | Urbanization rate | |
| X9 | Number of overseas visitors | |
| X10 | Tourism resource endowment | |
| X11 | Total retail sales of consumer goods | |
| X12 | Share of tertiary sector in GDP | |
| Port | X13 | Foreign trade throughput at ports |
| X14 | Cargo throughput at ports | |
| X15 | Total tourism revenue at ports |
| Hinterland | Mean Correlation Degree | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
| Yunnan | 0.7103 | 0.7211 | 0.7319 | 0.7135 | 0.7528 | 0.7657 | 0.7844 | 0.7736 | 0.7416 | 0.7365 | 0.7278 |
| Kunming | 0.7021 | 0.7326 | 0.7354 | 0.7495 | 0.7487 | 0.7771 | 0.7635 | 0.7898 | 0.7622 | 0.7210 | 0.7315 |
| Qujing | 0.6312 | 0.6388 | 0.6428 | 0.6899 | 0.7124 | 0.7225 | 0.7148 | 0.7326 | 0.7451 | 0.7302 | 0.7219 |
| Yuxi | 0.7089 | 0.7189 | 0.7195 | 0.7258 | 0.7396 | 0.7500 | 0.7724 | 0.7385 | 0.7436 | 0.7521 | 0.7215 |
| Zhaotong | 0.7652 | 0.7742 | 0.7852 | 0.7769 | 0.7634 | 0.7882 | 0.7963 | 0.7650 | 0.7552 | 0.7464 | 0.7457 |
| Baoshan | 0.6868 | 0.6964 | 0.7076 | 0.7125 | 0.7169 | 0.7245 | 0.7354 | 0.7522 | 0.7624 | 0.7210 | 0.7314 |
| Lijiang | 0.7458 | 0.7487 | 0.7568 | 0.7635 | 0.7695 | 0.7705 | 0.7932 | 0.7852 | 0.7661 | 0.7604 | 0.7433 |
| Pu’er | 0.7001 | 0.7012 | 0.7125 | 0.7258 | 0.7364 | 0.7452 | 0.7551 | 0.7487 | 0.7620 | 0.7375 | 0.7431 |
| Lincang | 0.6734 | 0.6979 | 0.6994 | 0.7122 | 0.7029 | 0.7189 | 0.7255 | 0.7366 | 0.7251 | 0.7167 | 0.7088 |
| Dehong | 0.7016 | 0.7173 | 0.7253 | 0.7353 | 0.7496 | 0.7851 | 0.8034 | 0.7722 | 0.7666 | 0.7521 | 0.7230 |
| Nujiang | 0.6523 | 0.6754 | 0.6899 | 0.6941 | 0.7195 | 0.7436 | 0.7324 | 0.7558 | 0.7651 | 0.7409 | 0.7218 |
| Diqing | 0.7365 | 0.7456 | 0.7521 | 0.7553 | 0.7852 | 0.7689 | 0.8012 | 0.7899 | 0.7852 | 0.7456 | 0.7401 |
| Dali | 0.6855 | 0.6986 | 0.7222 | 0.7421 | 0.6936 | 0.7522 | 0.6853 | 0.7011 | 0.7469 | 0.6855 | 0.6784 |
| Chuxiong | 0.7129 | 0.7253 | 0.7125 | 0.7555 | 0.7542 | 0.7662 | 0.7881 | 0.8025 | 0.7634 | 0.7885 | 0.7255 |
| Honghe | 0.6950 | 0.7001 | 0.7214 | 0.7103 | 0.7544 | 0.7667 | 0.7992 | 0.7666 | 0.7587 | 0.7910 | 0.7422 |
| Wenshan | 0.7028 | 0.7173 | 0.7151 | 0.7421 | 0.7368 | 0.7355 | 0.7589 | 0.7877 | 0.7544 | 0.7663 | 0.7237 |
| Xishuangbanna | 0.7567 | 0.7724 | 0.7949 | 0.8063 | 0.8211 | 0.8344 | 0.8010 | 0.7552 | 0.7646 | 0.7421 | 0.7224 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.; Gao, D.; Luo, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, J. Computational Simulation of the Correlations in a Port–Hinterland System from a Tourism Spatial Optimization Perspective. Buildings 2023, 13, 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13030832
Wang R, Gao D, Luo H, Chen Y, Liu H, Chen J. Computational Simulation of the Correlations in a Port–Hinterland System from a Tourism Spatial Optimization Perspective. Buildings. 2023; 13(3):832. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13030832
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Rui, Dashuai Gao, Huasong Luo, Yong Chen, Hang Liu, and Jingjing Chen. 2023. "Computational Simulation of the Correlations in a Port–Hinterland System from a Tourism Spatial Optimization Perspective" Buildings 13, no. 3: 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13030832
APA StyleWang, R., Gao, D., Luo, H., Chen, Y., Liu, H., & Chen, J. (2023). Computational Simulation of the Correlations in a Port–Hinterland System from a Tourism Spatial Optimization Perspective. Buildings, 13(3), 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13030832






