Experimental Investigation of the Mechanical Behavior of Corroded Q345 and Q420 Structural Steels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Test Specimens
2.2. Test Procedure
3. Experimental Results
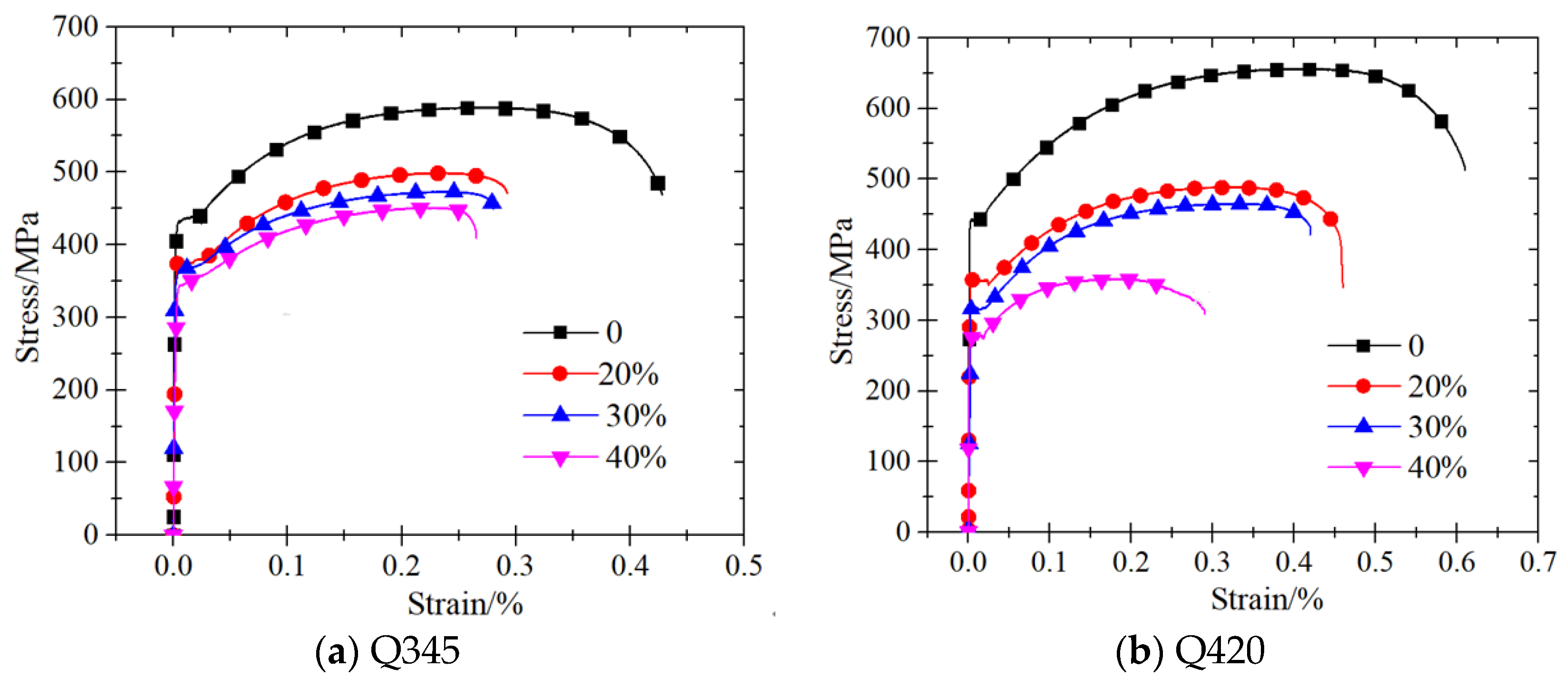
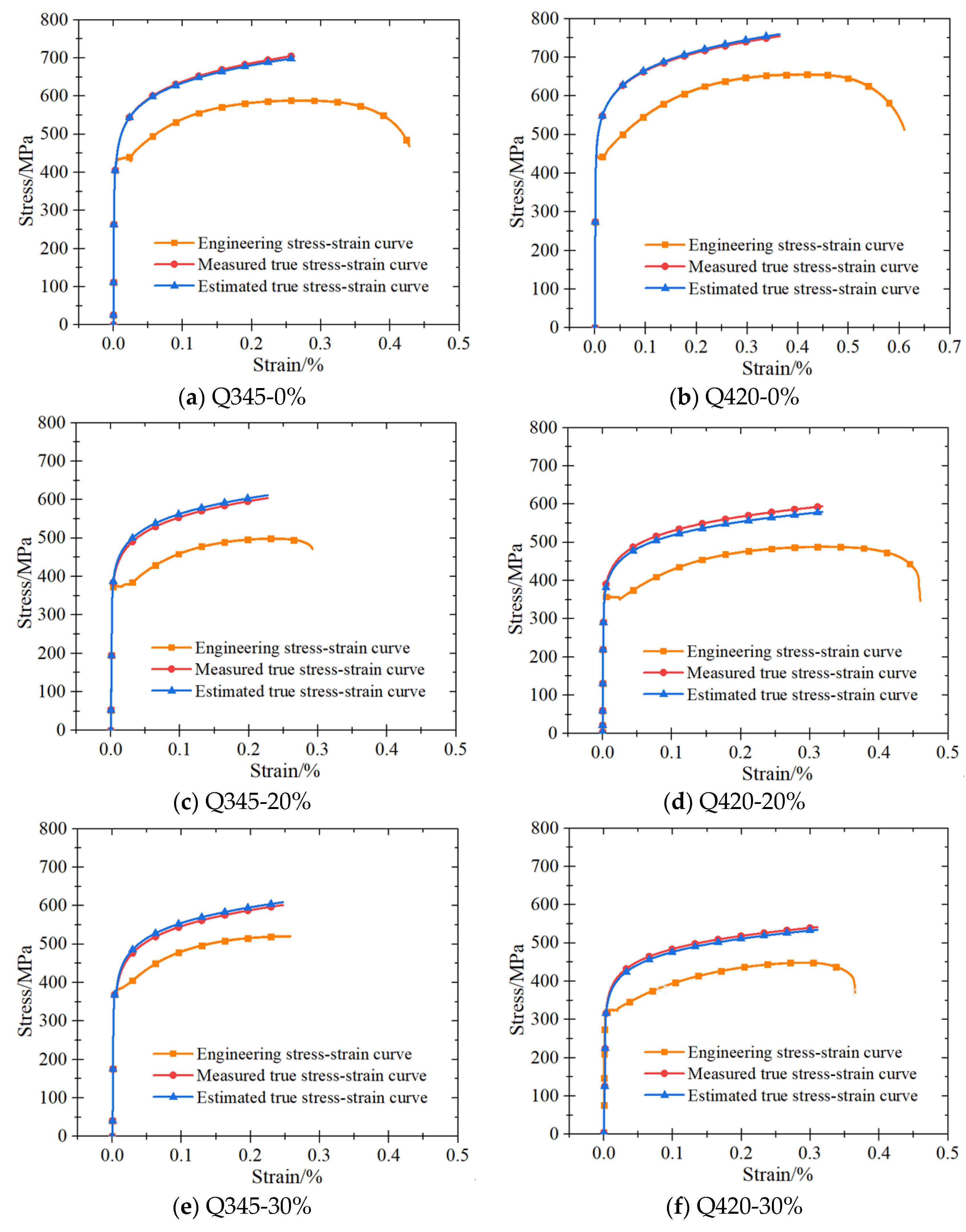
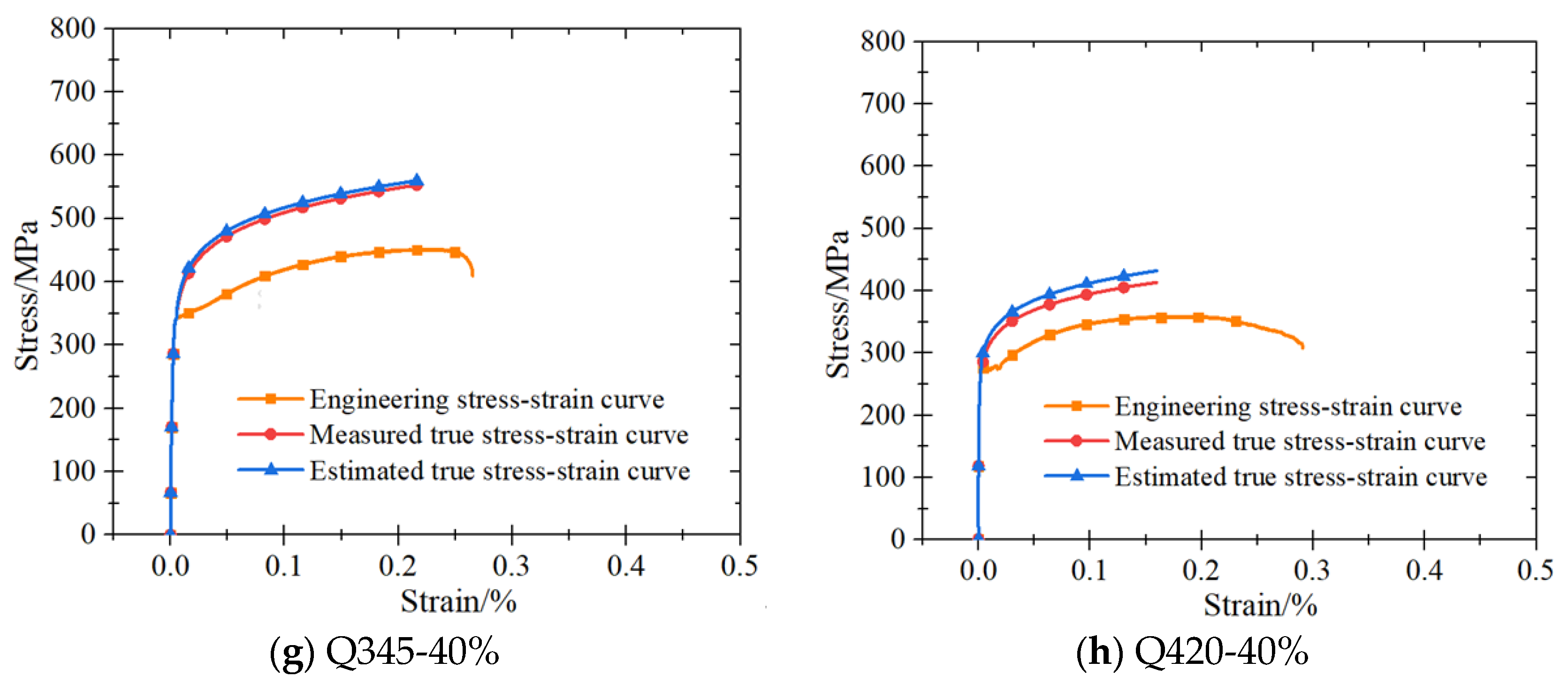
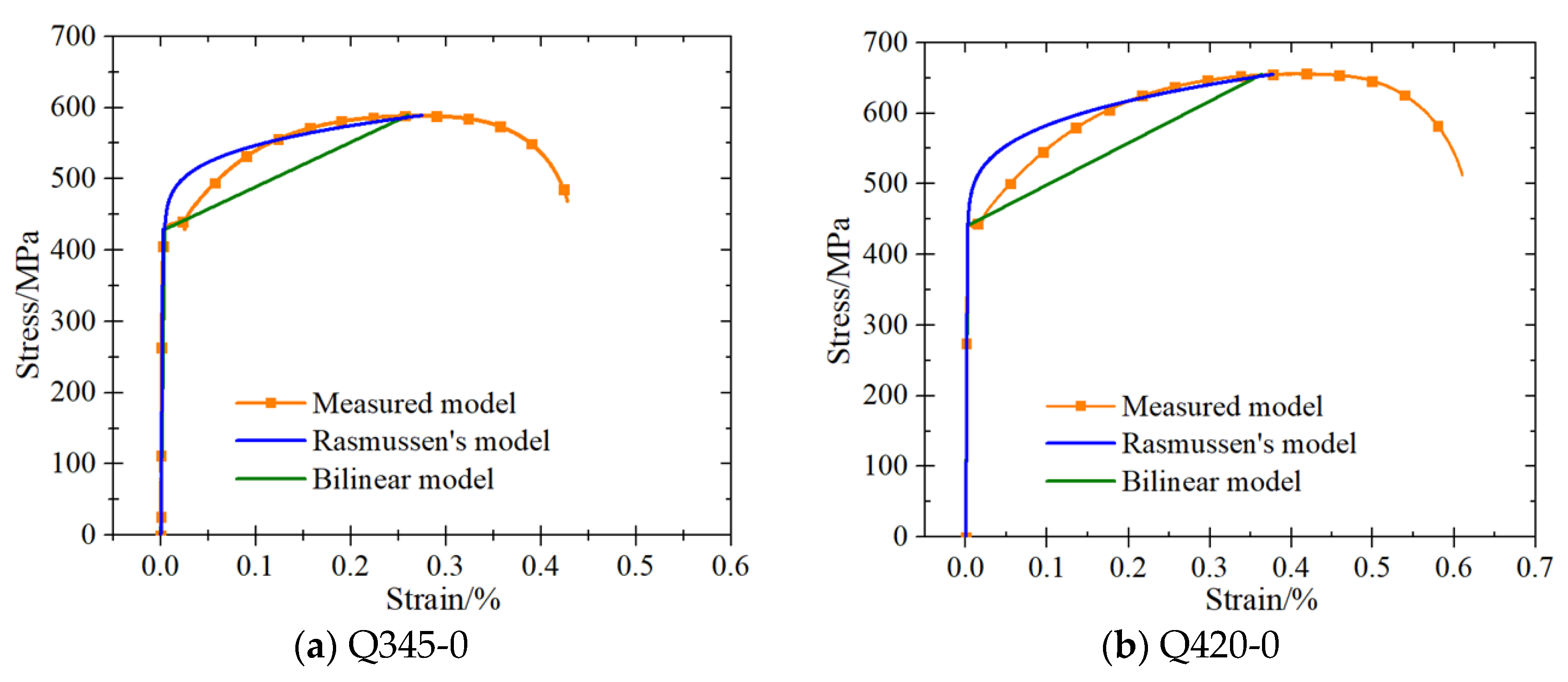
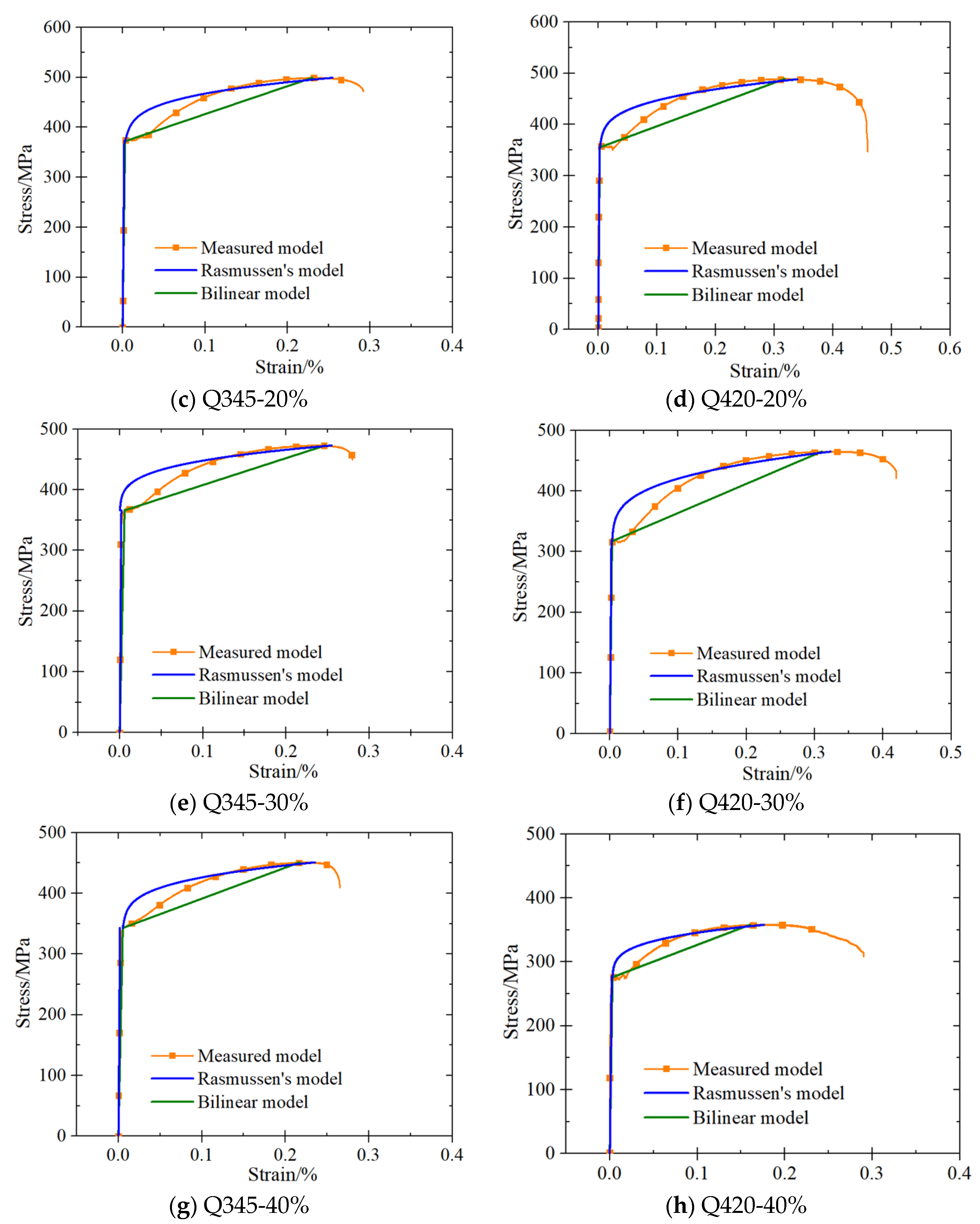
3.1. Stress–Strain Curves
3.2. Key Materials Properties
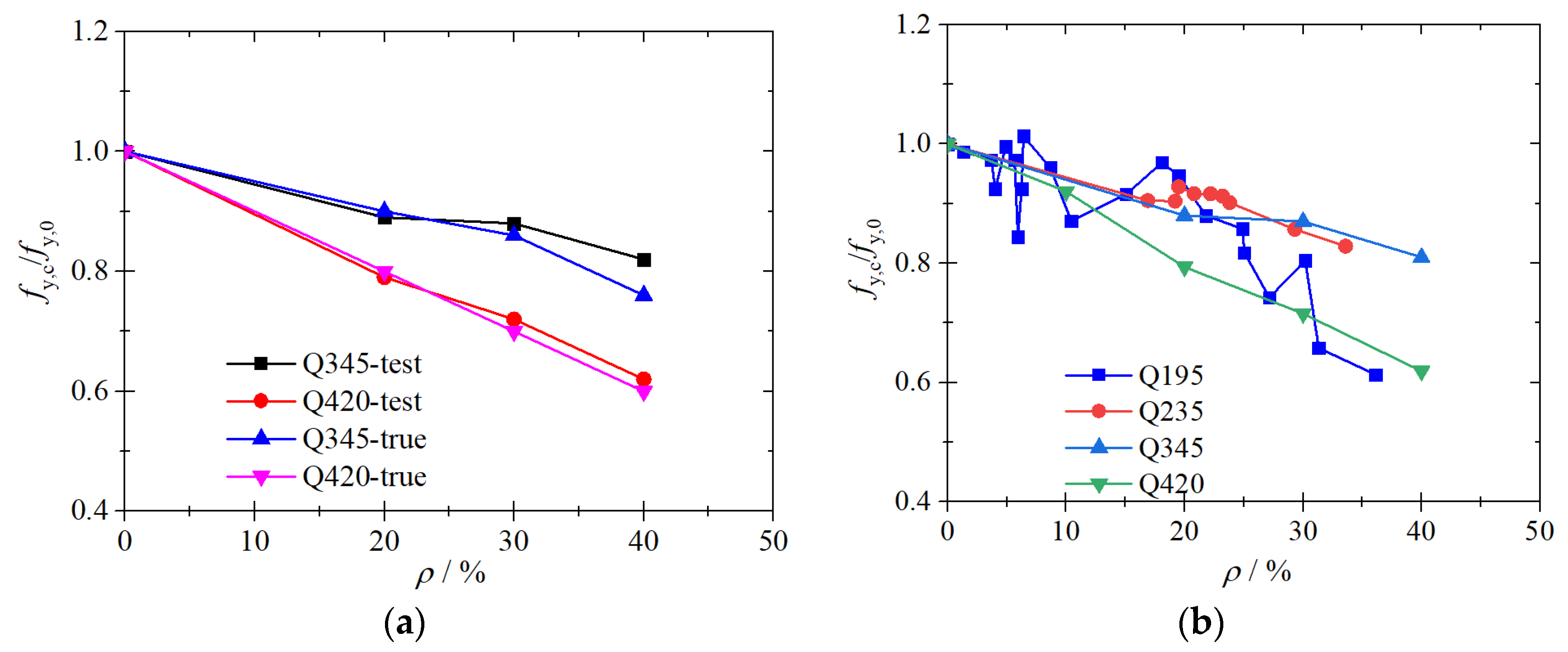
3.2.1. Yield Strength
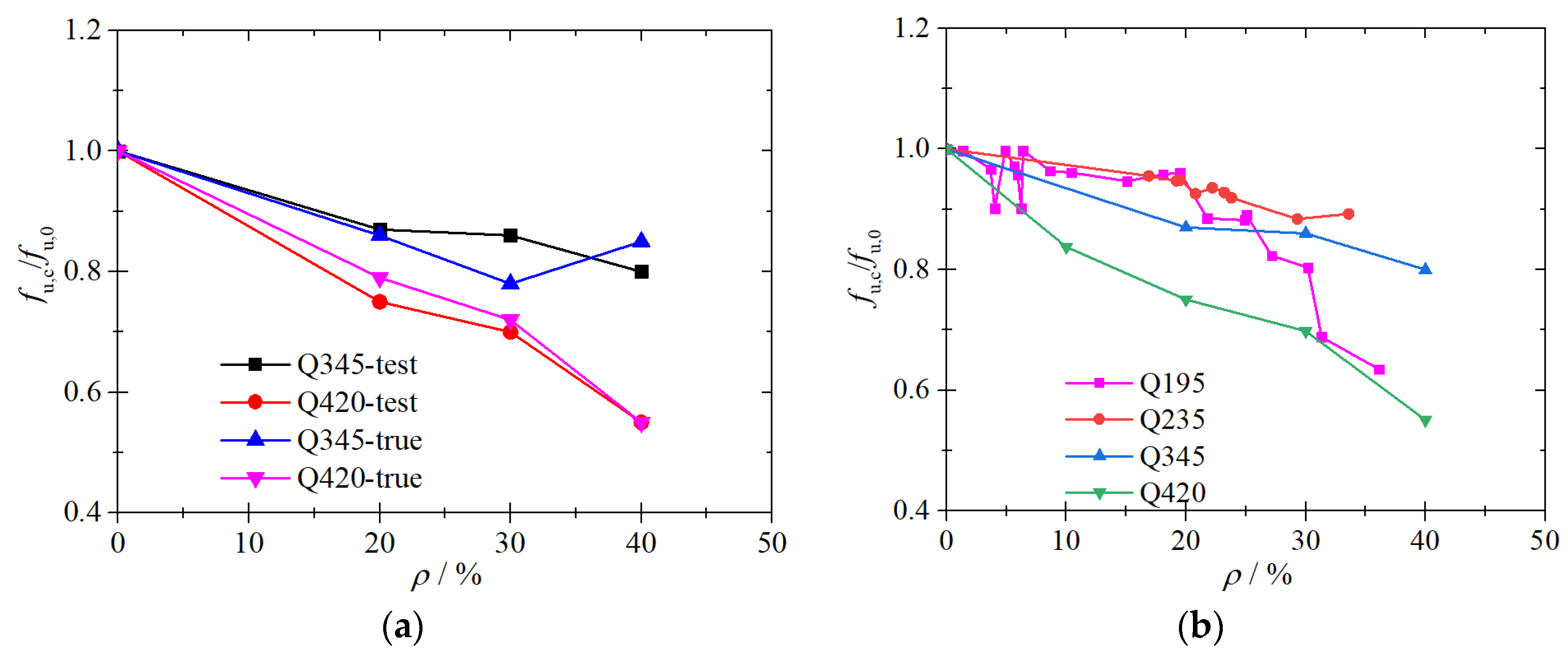
3.2.2. Ultimate Strength
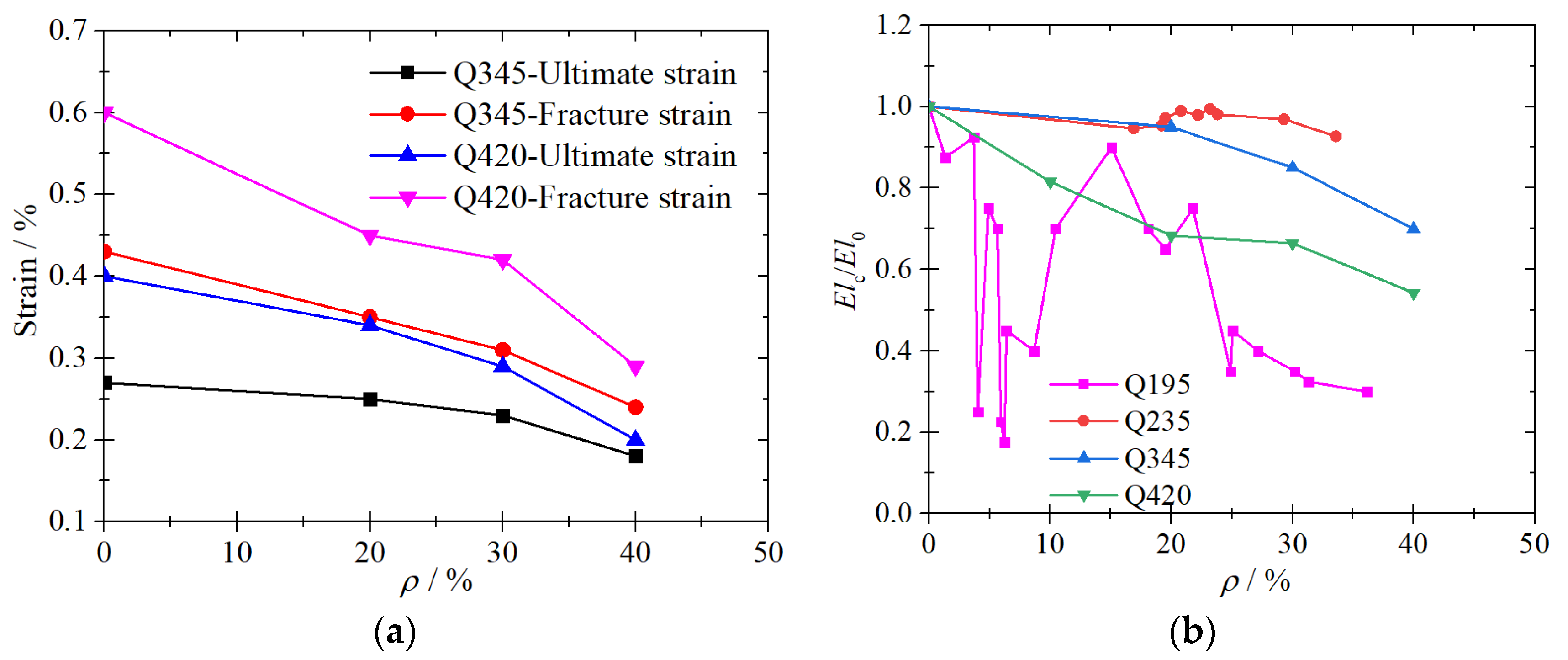
3.2.3. Ductility
3.3. Failure Modes
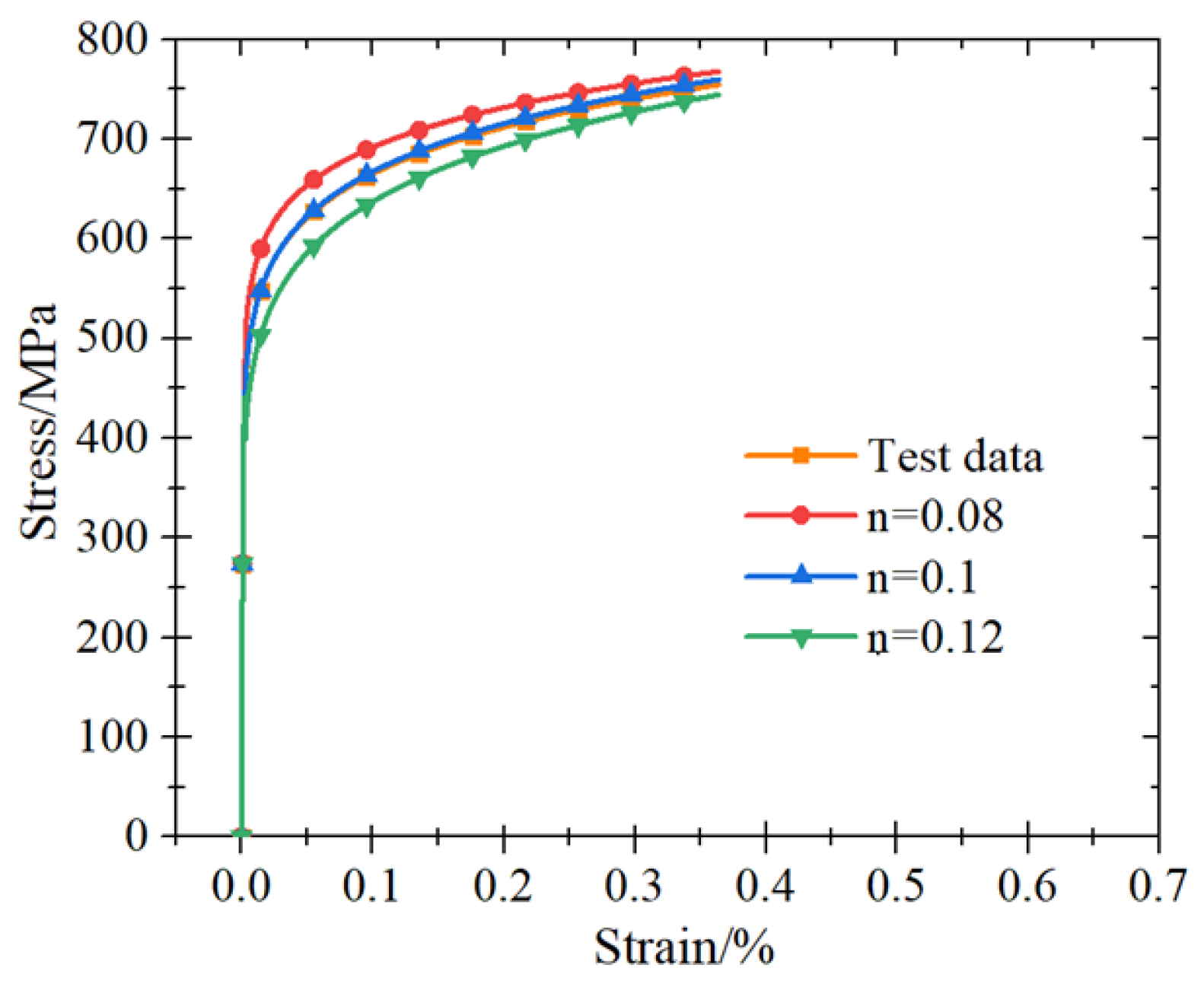
4. Constitutive Model
5. Prediction Equation
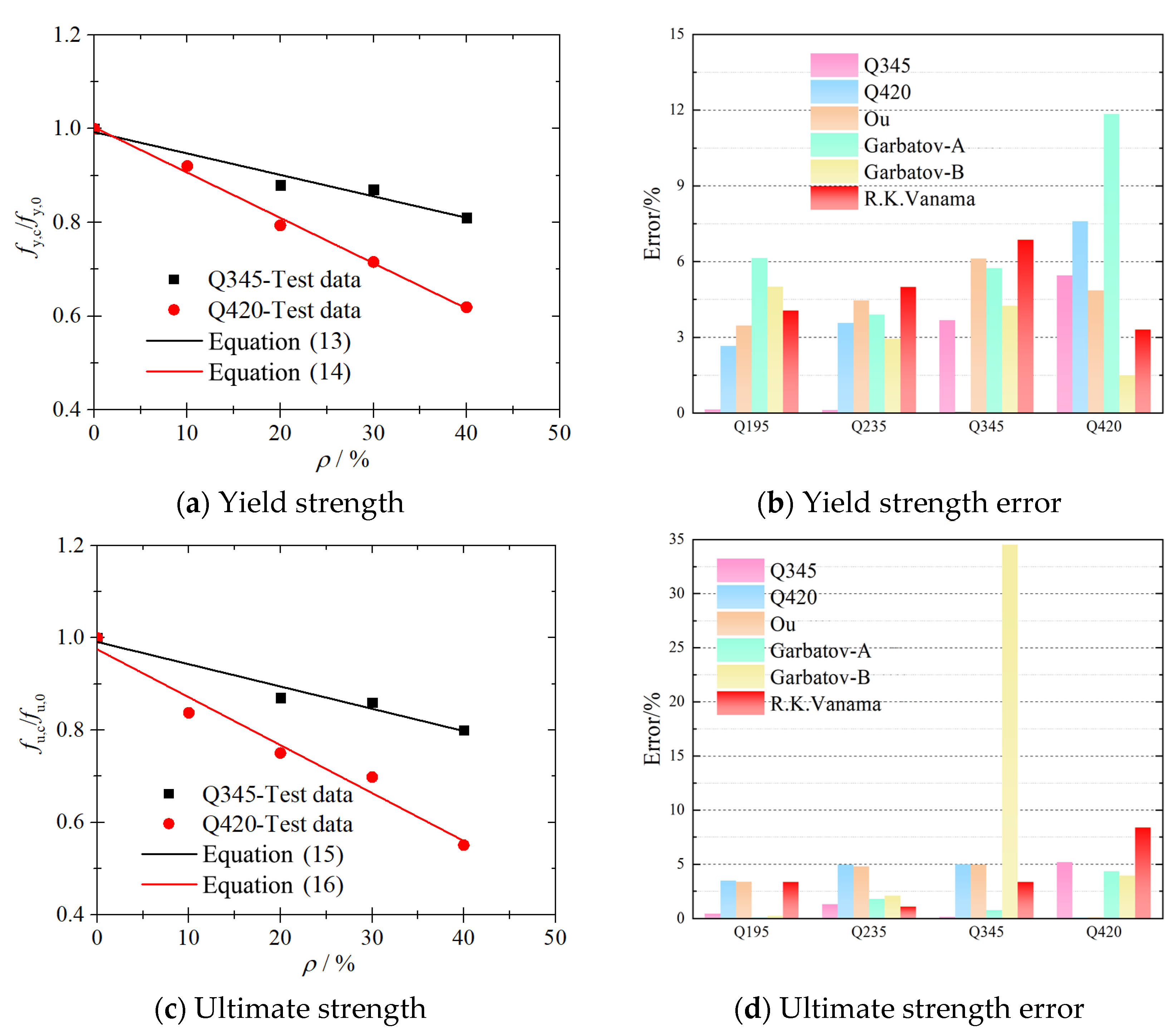
5.1. Yield Strength
- ▪
- Q345
- Q420
5.2. Ultimate Strength
- ▪
- Q345
- ▪
- Q420
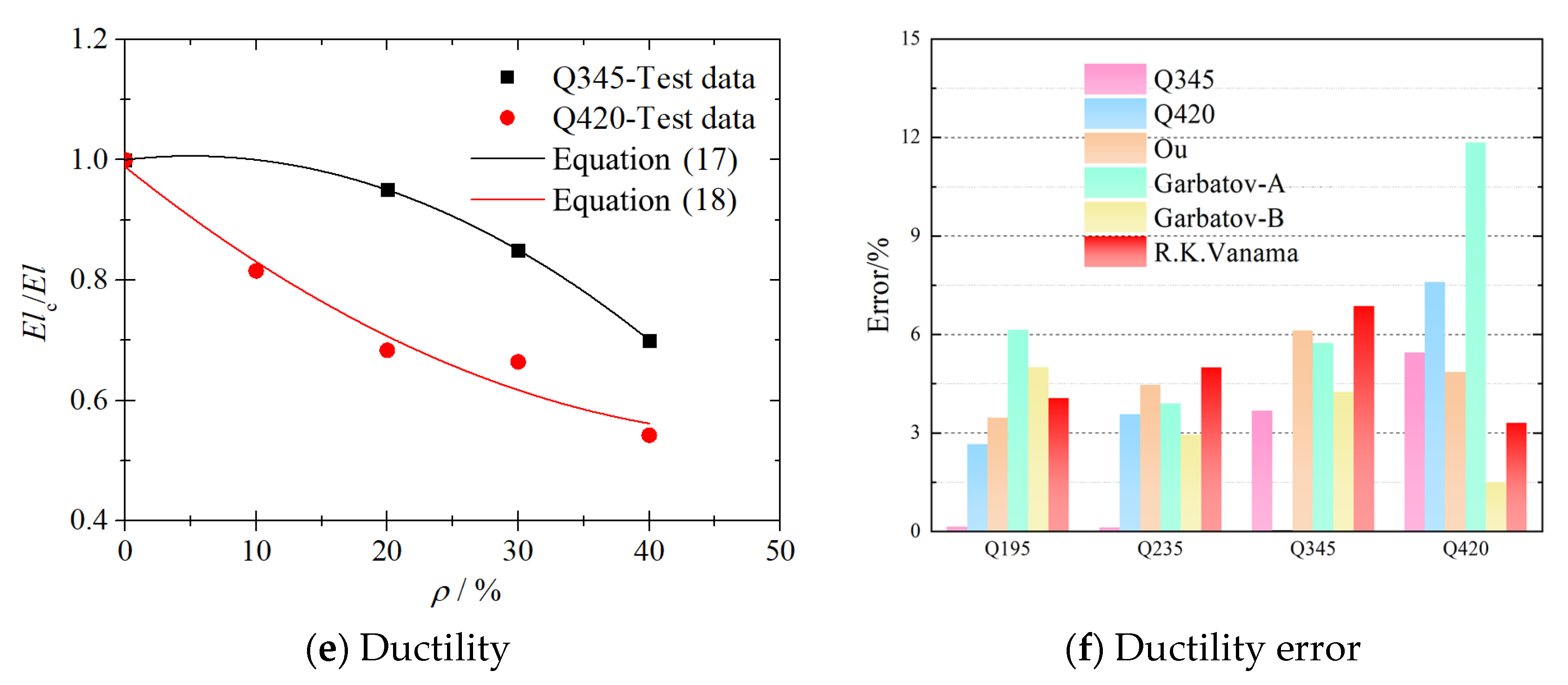
5.3. Ductility
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baddoo, N.R. Stainless steel in construction: A review of research, applications, challenges and opportunities. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2008, 64, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.; Szyniszewski, S.; Hajjar, J.; Schafer, B.; Arwade, S. Steel foam for structures: A review of applications, manufacturing and material properties. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2012, 71, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, R.; Song, G. Effects of pre-fatigue damage on mechanical properties of Q690 high-strength steel. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 252, 118845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariappan, K.; Shankar, V.; Sandhya, R.; Bhaduri, A.; Laha, K. Comparative assessment of remnant tensile properties of modified 9Cr-1Mo steel under prior low cycle fatigue and creep-fatigue interaction loading. Int. J. Fatigue 2017, 103, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Jia, B.; Wang, J. Influence of artificial cooling methods on post-fire mechanical properties of Q355 structural steel. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 252, 119092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, R.; Song, G. Residual mechanical properties of Q460 and Q690 high-strength steels after fire-fighting foam cooling. Thin-Walled Struct. 2020, 156, 106983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudze, M.; Melchers, R. Operational based corrosion analysis in naval ships. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 3296–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Si, R.; Dai, Q.; You, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J. A critical review of corrosion development and rust removal techniques on the structural/environmental performance of corroded steel bridges. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 126–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidaparti, R.M.; Rao, A.S. Analysis of pits induced stresses due to metal corrosion. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 1932–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchers, R.E. Extreme value statistics and long-term marine pitting corrosion of steel. Probabilistic Eng. Mech. 2008, 23, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbatov, Y.; Soares, C.G.; Parunov, J. Fatigue strength experiments of corroded small scale steel specimens. Int. J. Fatigue 2013, 59, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NSBA. Corrosion Protection of Steel Bridges, Steel Bridge Design Handbook; National Steel Bridge Alliance: Chicago, IL, USA, 2006; Chapter 23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xian, L.; Liu, H. Tensile strength of Q345 steel with random pitting corrosion based on numerical analysis. Thin-Walled Struct. 2019, 148, 106579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, T.; Matsushita, H.; Yamamoto, N. Effect of pitting corrosion on strength of web plates subjected to patch loading. Thin-Walled Struct. 2006, 44, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, J.; Lee, J.; Ko, M. Ultimate shear strength of plate elements with pit corrosion wastage. Thin-Walled Struct. 2004, 42, 1161–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Xia, J. Effect of simulated pitting corrosion on the tensile properties of steel. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 131, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.-T.; Dao, D.K.; Jeong, Y.-S.; Huh, J.; Ahn, J.-H. Effect of corrosion on the tension behavior of painted structural steel members. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2017, 133, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbatov, Y.; Soares, C.G.; Parunov, J.; Kodvanj, J. Tensile strength assessment of corroded small scale specimens. Corros. Sci. 2014, 85, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbatov, Y.; Parunov, J.; Kodvanj, J.; Saad-Eldeen, S.; Soares, C.G. Experimental assessment of tensile strength of corroded steel specimens subjected to sandblast and sandpaper cleaning. Mar. Struct. 2016, 49, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.-C.; Susanto, Y.T.T.; Roh, H. Tensile behavior of naturally and artificially corroded steel bars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 103, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, S.; Li, R. Comparative investigation of the effect of corrosion on the mechanical properties of different parts of thin-walled steel. Thin-Walled Struct. 2020, 146, 106450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, H.; Li, A. Predicting the residual strength and deformability of corroded steel plate based on the corrosion morphology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 152, 777–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Han, Q.; Xu, K.; Du, X. Corrosion influences on monotonic properties of ultra-high-strength reinforcing steels. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 198, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanama, R.K.; Ramakrishnan, B. Improved degradation relations for the tensile properties of naturally and artificially corroded steel rebars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 249, 118706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 1591-2018, eqv. ICS 77.140.01; High Strength Low Alloy Structural Steels. General Administration of Quality Supervision, and Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Joun, M.; Eom, J.G.; Lee, M.C. A new method for acquiring true stress–strain curves over a large range of strains using a tensile test and finite element method. Mech. Mater. 2008, 40, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaya, M.; Kawakubo, M. A procedure for determining the true stress–strain curve over a large range of strains using digital image correlation and finite element analysis. Mech. Mater. 2011, 43, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Wang, L.; Chang, Y.; Yan, J. Identification of post-necking stress–strain curve for sheet metals by inverse method. Mech. Mater. 2016, 92, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmmad, M.; Sumi, Y. Strength and deformability of corroded steel plates under quasi-static tensile load. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2010, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheider, I.; Brocks, W.; Cornec, A. Procedure for the Determination of True Stress-Strain Curves From Tensile Tests With Rectangular Cross-Section Specimens. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 2004, 126, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaya, M.; Kawakubo, M. True stress–strain curves of cold worked stainless steel over a large range of strains. J. Nucl. Mater. 2014, 451, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaya, M.; Kitsunai, Y.; Koshiishi, M. True stress–strain curve acquisition for irradiated stainless steel including the range exceeding necking strain. J. Nucl. Mater. 2015, 465, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jitsukawa, S.; Abe, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Okubo, N. Development of Models for Irradiation-induced Changes to Microstructure and Stress–Strain Relations of Austenitic Steels. ASTM STP 2012, 1547, 288–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaya, M. Stress–strain curve estimation procedures for stainless steels based on yield and ultimate strengths. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2014, 127, 194–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dundu, M. Evolution of stress–strain models of stainless steel in structural engineering applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 165, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, K.J. Full-range stress–strain curves for stainless steel alloys. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2003, 59, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ENV 1993-1-4; Design of Steel Structures—Part 1.4: General Rules—Supplementary Rules for Stainless Steels. British standards institution: Brussels, Belgium, 2006.
- GB/T 228.1-2010, eqv. ISO 6892-1: 2009; MOD Metallic Materials- Tensile Testing- Part 1: Method of Test at Room Temperature. General Administration of Quality Supervision, and Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2010.
- Hollomon, J. Tensile deformation. Trans. AIME. 1945, 162, 268–290. [Google Scholar]
- Cottrell, A.H.; Bilby, B.A. Dislocation Theory of Yielding and Strain Ageing of Iron. Proc. Phys. Soc. Sect. A 1949, 62, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Guo, X.; Li, J.; Mao, J.; Lu, W. The gradual disappearance of yield plateau in Zr–Sn–Nb–Fe–Mo alloy by the trace addition of Cr and V. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 760, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Yang, Y.; He, Z.; Wang, Y. Experimental study on generalized constitutive model of hull structural plate with multi-parameter pitting corrosion. Ocean Eng. 2018, 170, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
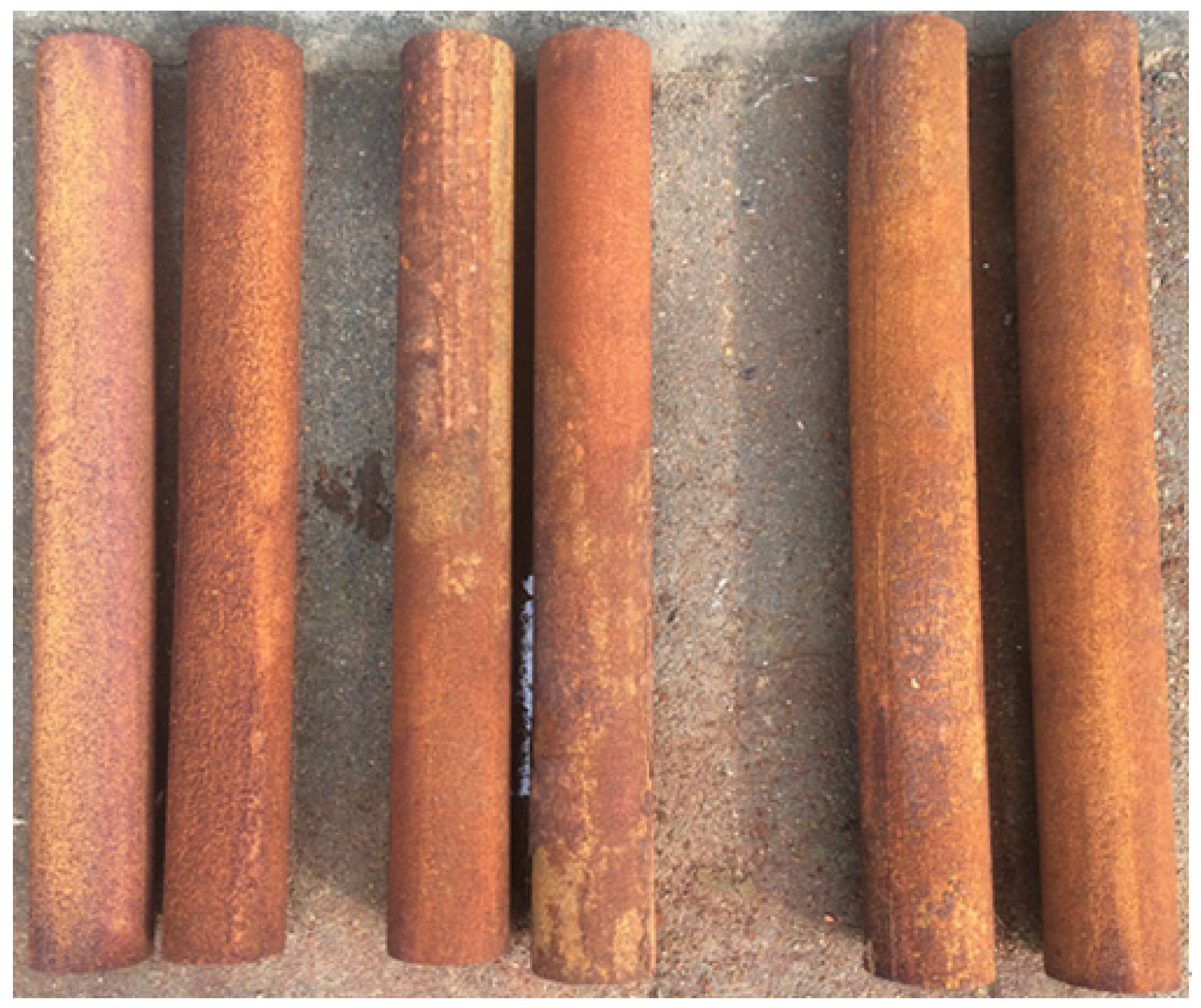
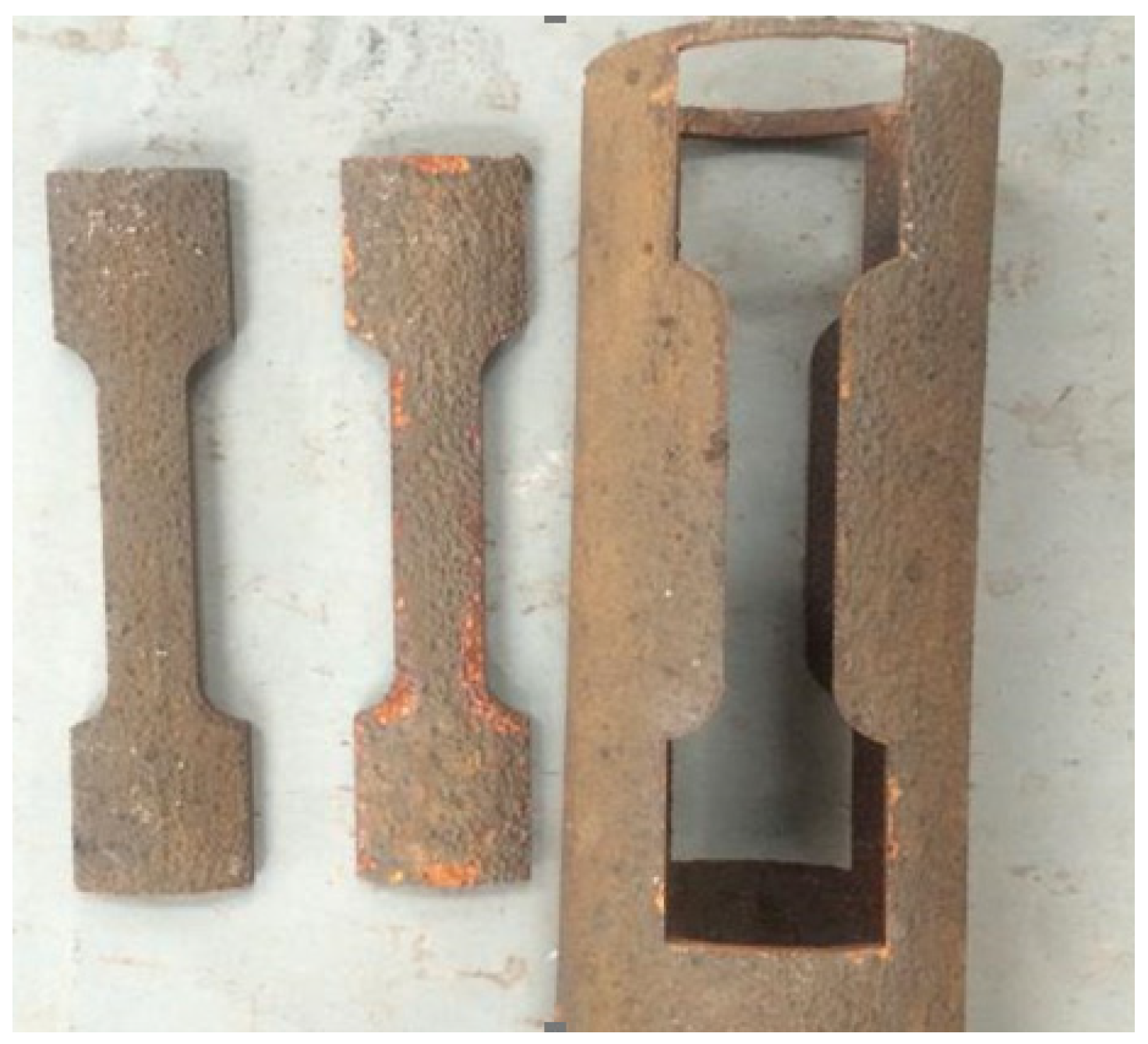
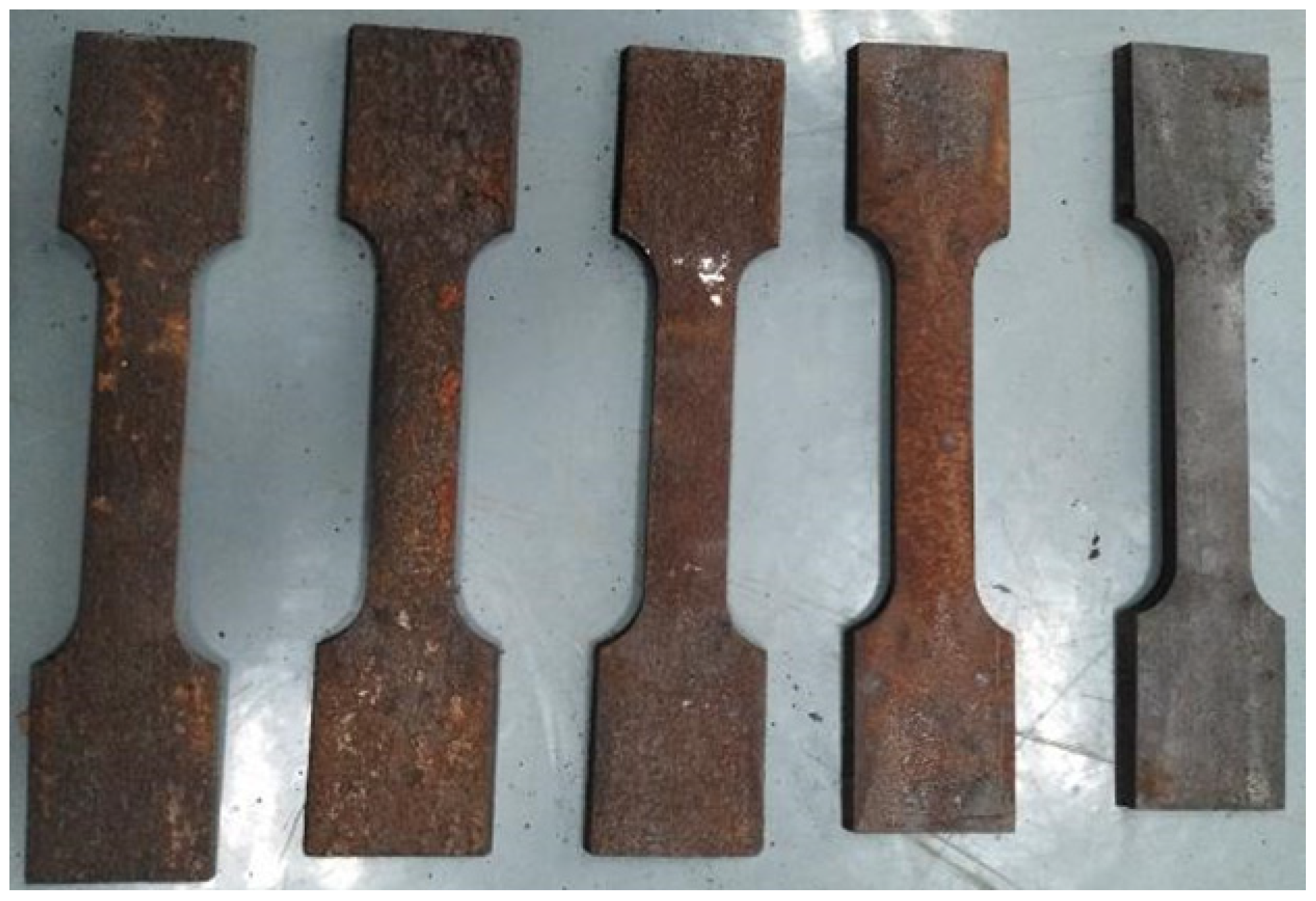
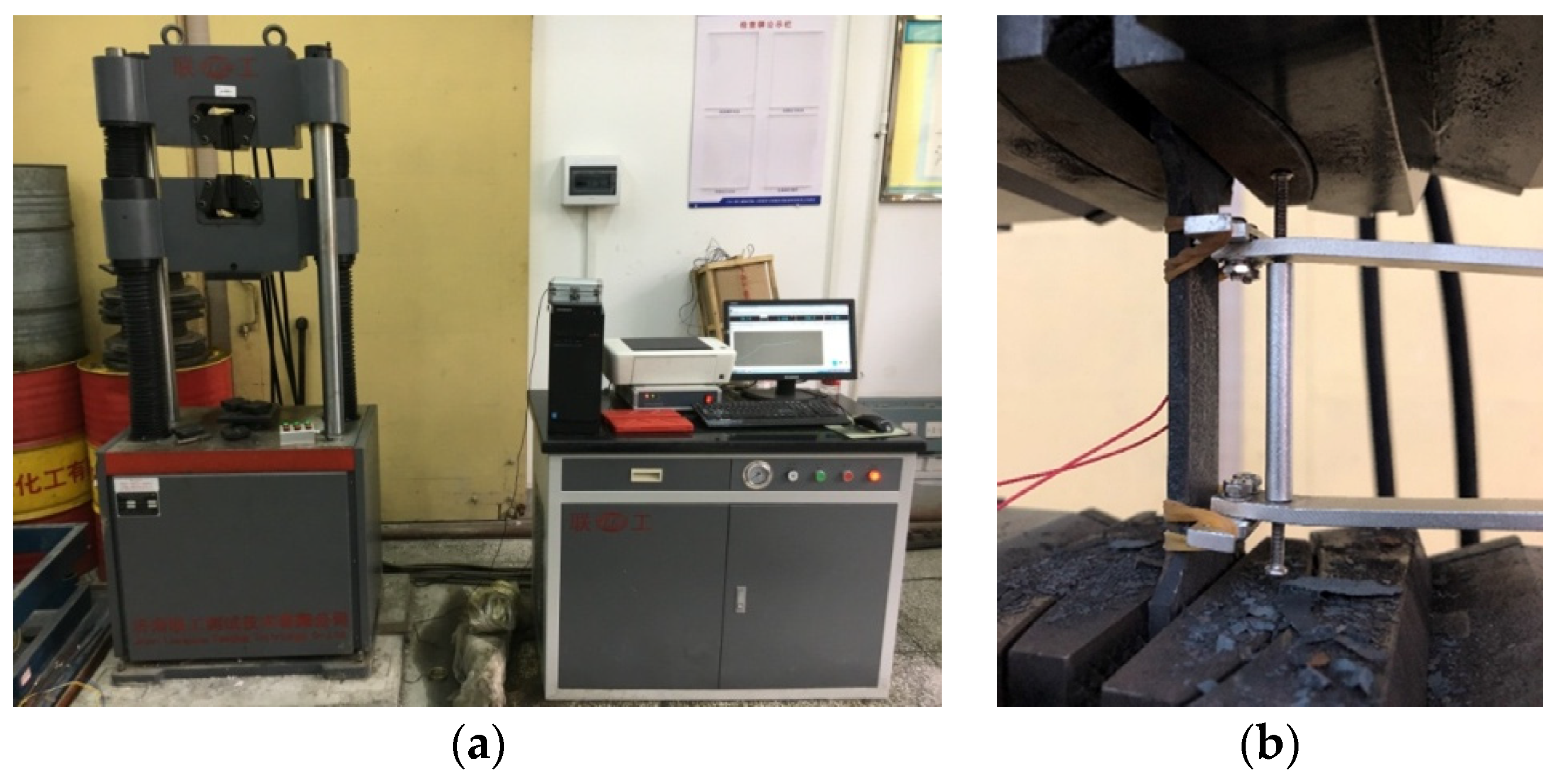

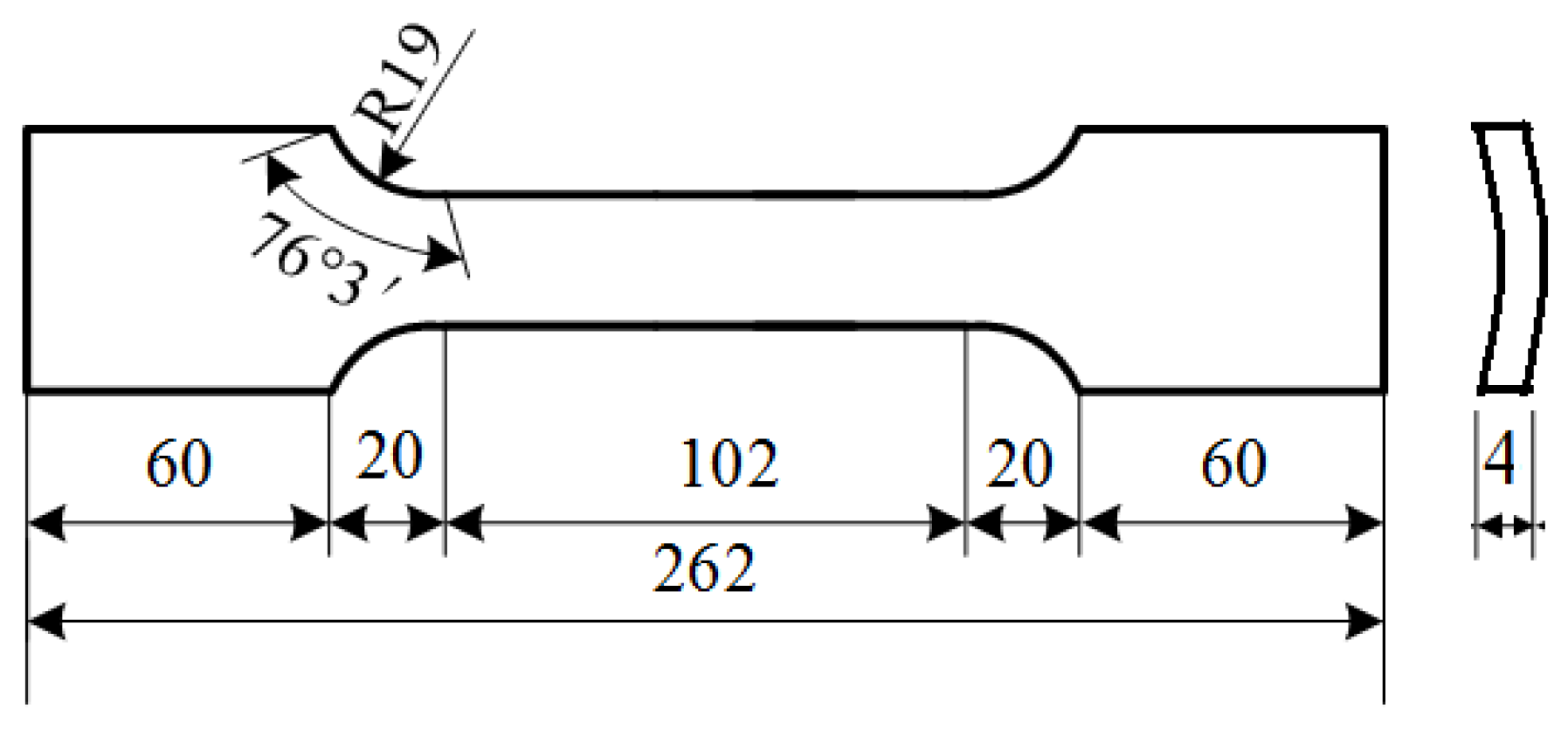



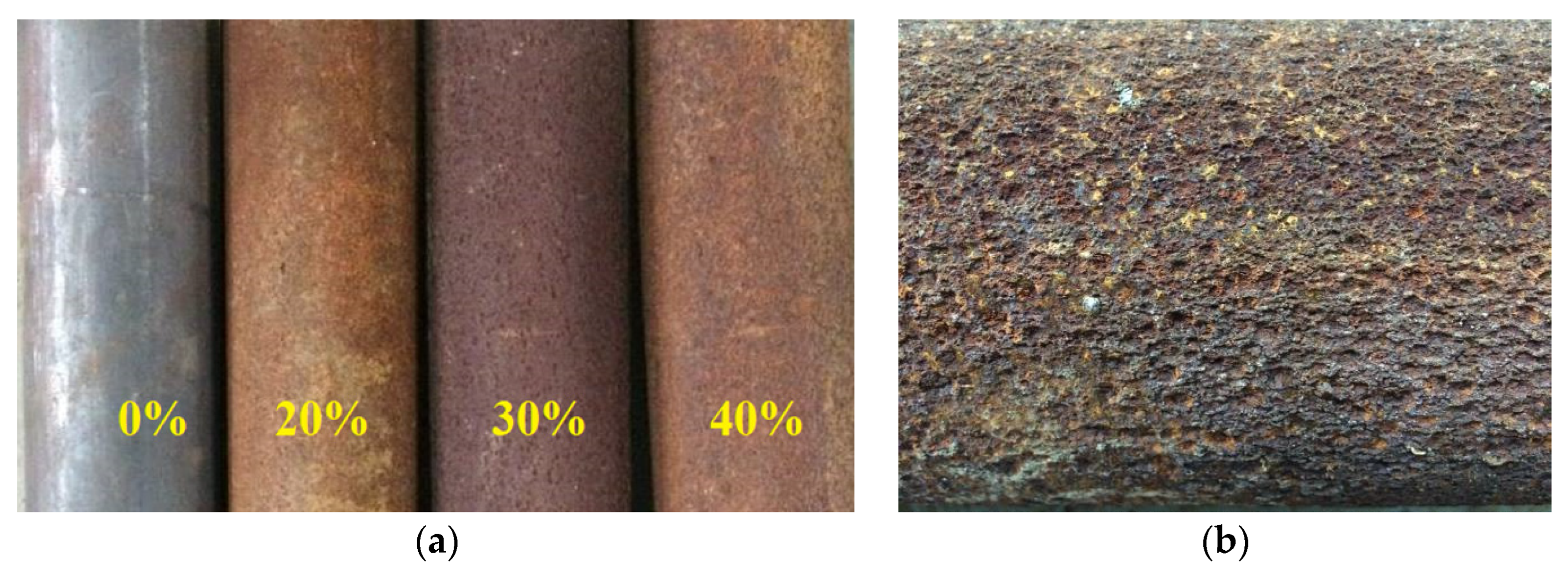
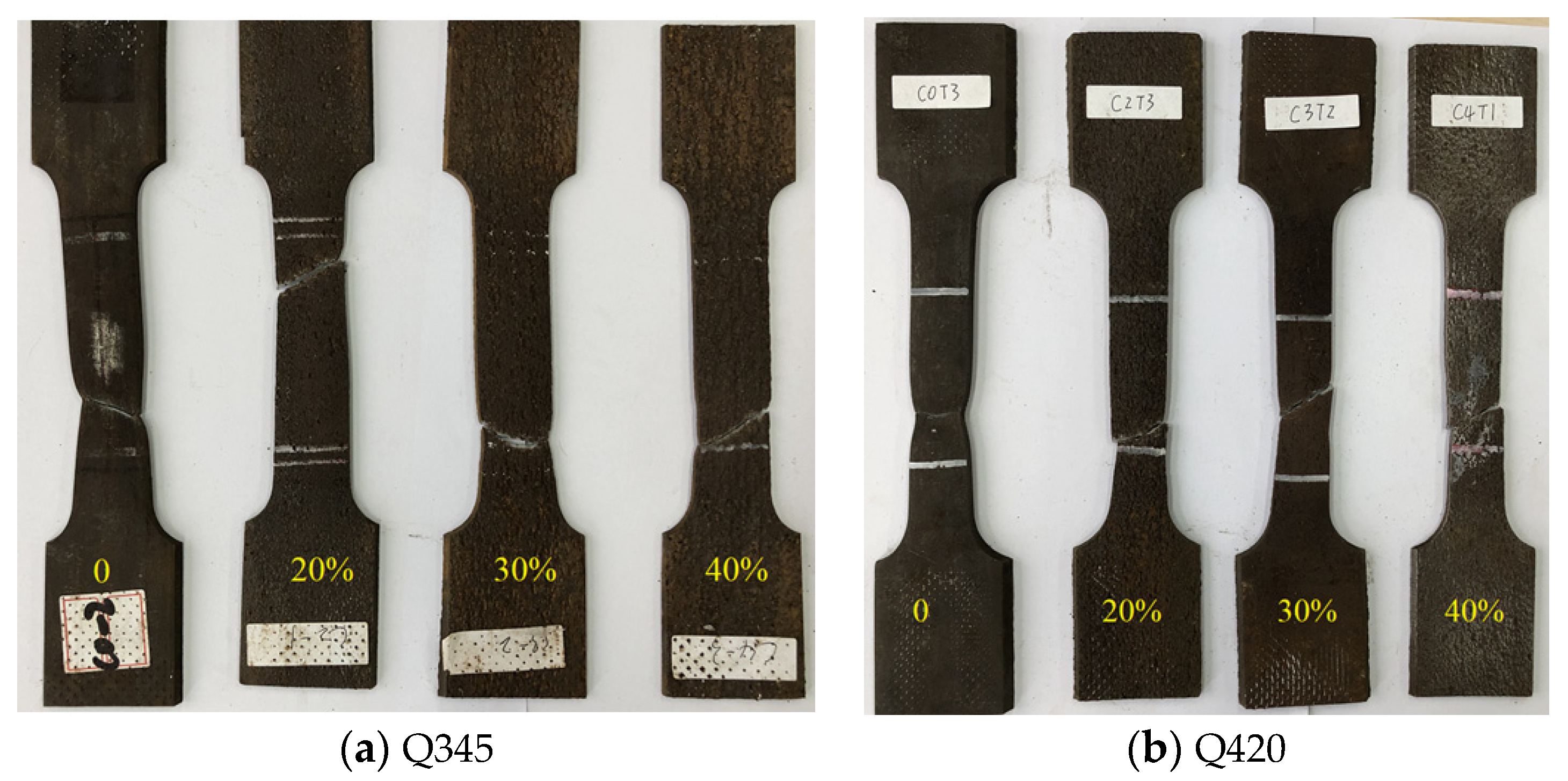
| Chemical Composition | C | Si | Mn | S | Ni | Cr | Cu | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q345 | 0.14 | 0.55 | 1.40 | - | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.01 |
| Q420 | 0.17 | 0.25 | 1.40 | 0.007 | 0.20 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 0.031 |
| Mass Loss | Q345 | Q420 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | At | Ac | (Ac − At)/At × 100 | n | At | Ac | (Ac − At)/At × 100 | |
| 0% | 0.094 | 812.35 | 800.94 | −1.40 | 0.068 | 832.72 | 840.85 | 0.98 |
| 20% | 0.111 | 705.05 | 709.62 | 0.65 | 0.098 | 647.72 | 666.36 | 2.88 |
| 30% | 0.095 | 697.06 | 701.45 | 0.63 | 0.137 | 606.86 | 601.18 | −0.94 |
| 40% | 0.115 | 649.23 | 653.30 | 0.63 | 0.097 | 493.93 | 519.00 | 5.08 |
| Mass Loss Rate | Specimen | Yield Strength fy/MPa | Ultimate Strength fu/MPa | Elastic Modulus E/GPa | Ductility El/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q345 | Q420 | Q345 | Q420 | Q345 | Q420 | Q345 | Q420 | ||
| C0-1 | 429.13 | 441.16 | 589.31 | 655.81 | 206.21 | 209.24 | 28.5 | 34.23 | |
| 0 | C0-2 | 432.42 | 444.75 | 569.93 | 652.32 | 203.27 | 200.10 | 29.2 | 36.62 |
| C0-3 | 416.69 | 453.4 | 573.44 | 644.58 | 200.33 | 211.20 | 27.8 | 30.47 | |
| Mean value | 426.08 | 446.43 | 577.56 | 650.9 | 203.27 | 206.85 | 28 | 33.77 | |
| C20-1 | 372.79 | 355.62 | 499.04 | 488.83 | 200.25 | 207.43 | 27.5 | 22.75 | |
| 20% | C20-2 | 374.36 | 348.06 | 497.58 | 488.4 | 209.62 | 205.12 | 25.8 | 24.36 |
| C20-3 | 385.77 | 359.32 | 516.48 | 488.25 | 210.47 | 204.67 | 26.7 | 22.13 | |
| Mean value | 377.64 | 354.33 | 504.36 | 488.49 | 206.78 | 205.74 | 26.67 | 23.08 | |
| C30-1 | 379.66 | 317.78 | 521.29 | 465.33 | 200.77 | 205.78 | 26.8 | 20.26 | |
| 30% | C30-2 | 366.59 | 321.58 | 473.07 | 448.99 | 205.62 | 203.84 | 23.3 | 24.83 |
| C30-3 | 373.83 | 318.85 | 491.23 | 449.06 | 204.45 | 205.44 | 21.7 | 22.19 | |
| Mean value | 373.36 | 319.40 | 495.19 | 454.46 | 203.61 | 205.02 | 23.9 | 22.43 | |
| C40-1 | 343.54 | 276.15 | 451.12 | 358.68 | 203.75 | 202.86 | 20.6 | 22.11 | |
| 40% | C40-2 | 343.22 | 278.01 | 457.58 | 356.91 | 207.08 | 204.74 | 19.8 | 16.35 |
| C40-3 | 356.45 | 275.02 | 474.03 | 359.99 | 210.42 | 208.43 | 18.8 | 16.48 | |
| Mean value | 347.74 | 276.4 | 460.91 | 358.53 | 207.08 | 205.34 | 19.7 | 18.31 | |
| Mass Loss Rate | Specimen | Yield Strength | Ultimate Strength | Elastic Modulus | Ductility | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q345 | Q420 | Q345 | Q420 | Q345 | Q420 | Q345 | Q420 | ||
| C0-1 | 1.01 | 0.99 | 1.02 | 1.01 | 1.01 | 1.01 | 1.02 | 1.01 | |
| 0 | C0-2 | 1.01 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 1.04 | 1.08 |
| C0-3 | 0.98 | 1.02 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.02 | 0.99 | 0.90 | |
| Mean value | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| C20-1 | 0.87 | 0.80 | 0.86 | 0.75 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.67 | |
| 20% | C20-2 | 0.88 | 0.78 | 0.86 | 0.75 | 1.03 | 0.99 | 0.92 | 0.72 |
| C20-3 | 0.91 | 0.80 | 0.89 | 0.75 | 1.04 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.66 | |
| Mean value | 0.89 | 0.79 | 0.87 | 0.75 | 1.02 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.68 | |
| C30-1 | 0.89 | 0.71 | 0.90 | 0.71 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 0.60 | |
| 30% | C30-2 | 0.86 | 0.72 | 0.82 | 0.69 | 1.01 | 0.99 | 0.83 | 0.74 |
| C30-3 | 0.88 | 0.71 | 0.85 | 0.69 | 1.01 | 0.99 | 0.78 | 0.66 | |
| Mean value | 0.88 | 0.72 | 0.86 | 0.70 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.85 | 0.66 | |
| C40-1 | 0.81 | 0.62 | 0.78 | 0.55 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.74 | 0.65 | |
| 40% | C40-2 | 0.81 | 0.62 | 0.79 | 0.55 | 1.02 | 0.99 | 0.71 | 0.48 |
| C40-3 | 0.84 | 0.62 | 0.82 | 0.55 | 1.04 | 1.01 | 0.67 | 0.49 | |
| Mean value | 0.82 | 0.62 | 0.80 | 0.55 | 1.02 | 0.99 | 0.70 | 0.54 | |
| Mass Loss | Yield Strength fy/MPa | Ultimate Strength fu/MPa | Residual Yield Strength Factor | Residual Ultimate Strength Factor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q345 | Q420 | Q345 | Q420 | Q345 | Q420 | Q345 | Q420 | |
| 0% | 431.20 | 479.24 | 705.60 | 754.75 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 20% | 388.20 | 385.33 | 604.15 | 594.21 | 0.90 | 0.80 | 0.86 | 0.79 |
| 30% | 372.45 | 335.45 | 553.07 | 541.38 | 0.86 | 0.70 | 0.78 | 0.72 |
| 40% | 328.45 | 287.13 | 601.80 | 413.28 | 0.76 | 0.60 | 0.85 | 0.55 |
| Mass Loss | ɛy % | ɛu/% | ɛf/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q345 | Q420 | Q345 | Q420 | Q345 | Q420 | |
| 0 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.27 | 0.40 | 0.43 | 0.60 |
| 20% | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.25 | 0.34 | 0.35 | 0.45 |
| 30% | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.23 | 0.29 | 0.31 | 0.42 |
| 40% | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.24 | 0.29 |
| Mass Loss Rate | m | Ey | K | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q345 | Q420 | Q345 | Q420 | Q345 | Q420 | |
| 0 | 3.57 | 3.40 | 14.851 | 19.941 | 624.512 | 592.093 |
| 20% | 3.63 | 3.54 | 15.953 | 18.197 | 559.817 | 421.687 |
| 30% | 3.63 | 3.46 | 13.871 | 14.701 | 468.880 | 482.714 |
| 40% | 3.63 | 3.70 | 8.065 | 14.000 | 510.156 | 522.300 |
| Reference | Steel Type | Predictive Models |
|---|---|---|
| Garbatov 2014 [18] | S235: fy = 235 MPa, fu = 400 MPa | |
| Garbatov 2016 [19] | S235: fy = 235 MPa, fu = 400 MPa | |
| Ou 2016 [20] | A706: fy = 420 MPa, fu = 630 MPa | , |
| Vanama 2020 [24] | MS250: fy = 250 MPa, fu = 410 MPa MS350: fy = 250 MPa, fu = 410 MPa | , |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, N.; Zhang, C. Experimental Investigation of the Mechanical Behavior of Corroded Q345 and Q420 Structural Steels. Buildings 2023, 13, 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13020475
Zhao N, Zhang C. Experimental Investigation of the Mechanical Behavior of Corroded Q345 and Q420 Structural Steels. Buildings. 2023; 13(2):475. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13020475
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Nan, and Chuntao Zhang. 2023. "Experimental Investigation of the Mechanical Behavior of Corroded Q345 and Q420 Structural Steels" Buildings 13, no. 2: 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13020475
APA StyleZhao, N., & Zhang, C. (2023). Experimental Investigation of the Mechanical Behavior of Corroded Q345 and Q420 Structural Steels. Buildings, 13(2), 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13020475









