Green Land Use Efficiency and Influencing Factors of Resource-Based Cities in the Yellow River Basin under Carbon Emission Constraints
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
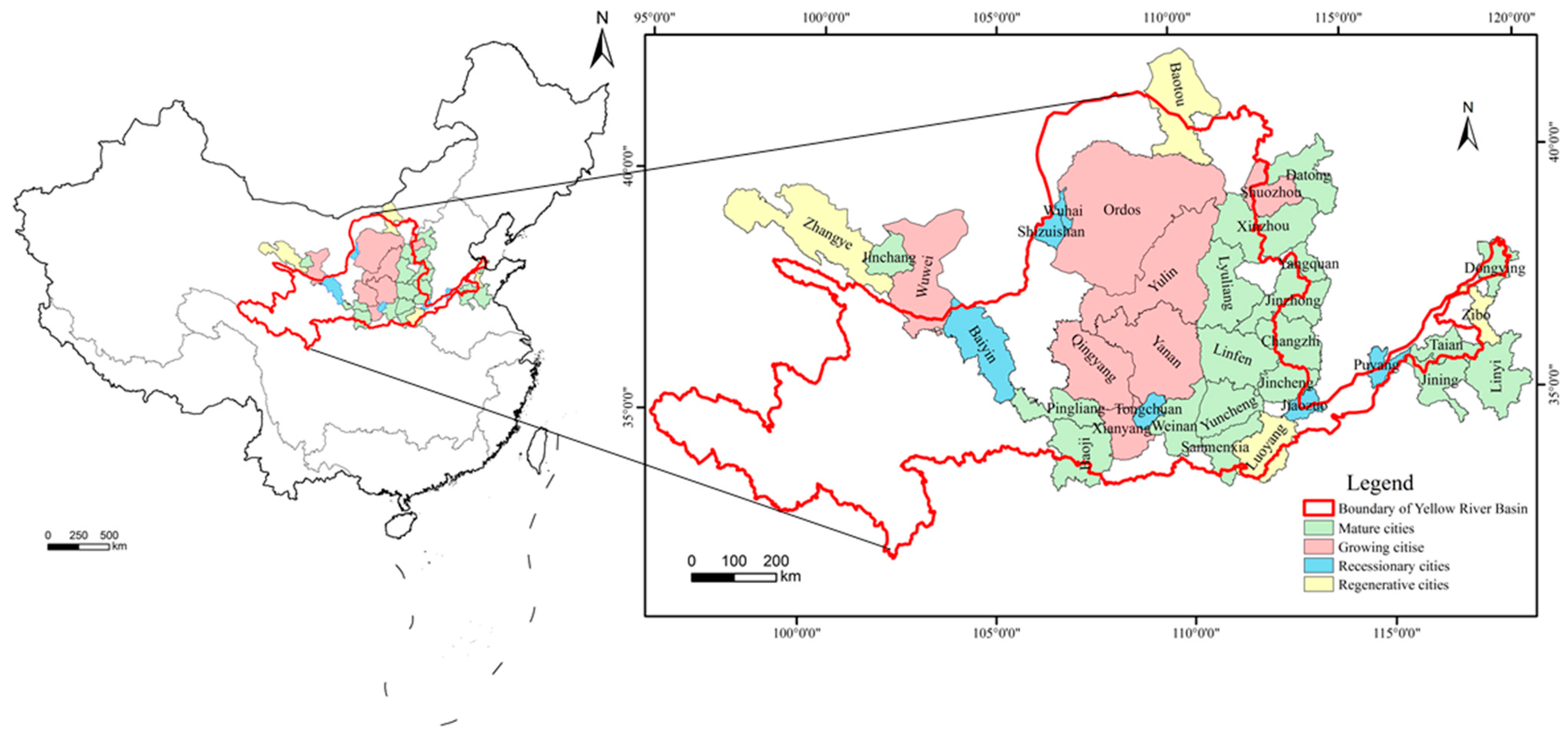
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Super-Efficiency SBM Model Considering Undesirable Output
2.3.2. Nonparametric Kernel Density Estimation
2.3.3. Tobit Regression Model
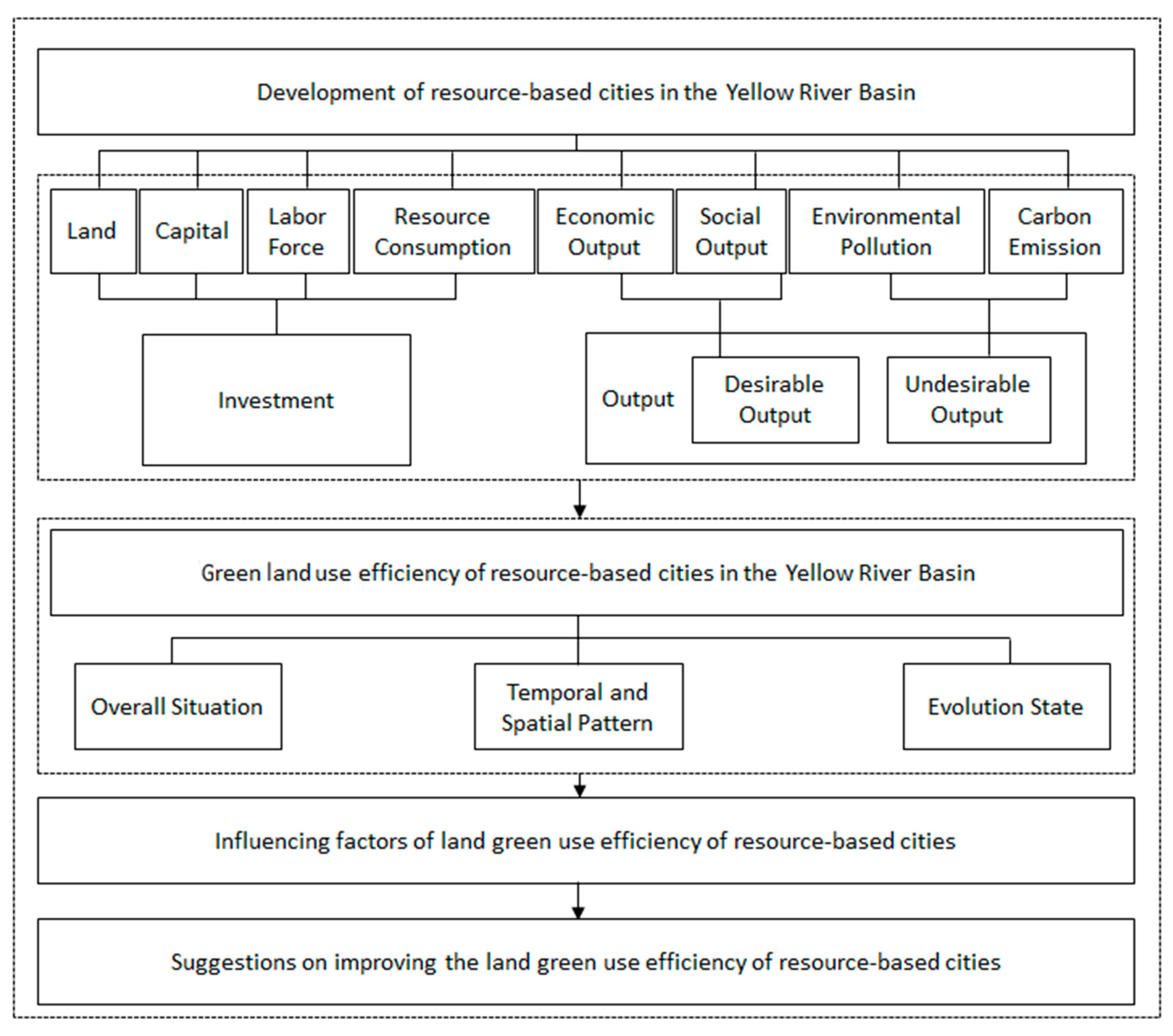
2.4. Index Determination and Data Processing
2.4.1. Evaluation of GLUE in Resource-Based Cities
2.4.2. Influencing Factors of GLUE in Resource-Based Cities
3. GLUE in Resource-Based Cities in the YRB
3.1. Comprehensive Study of GLUE
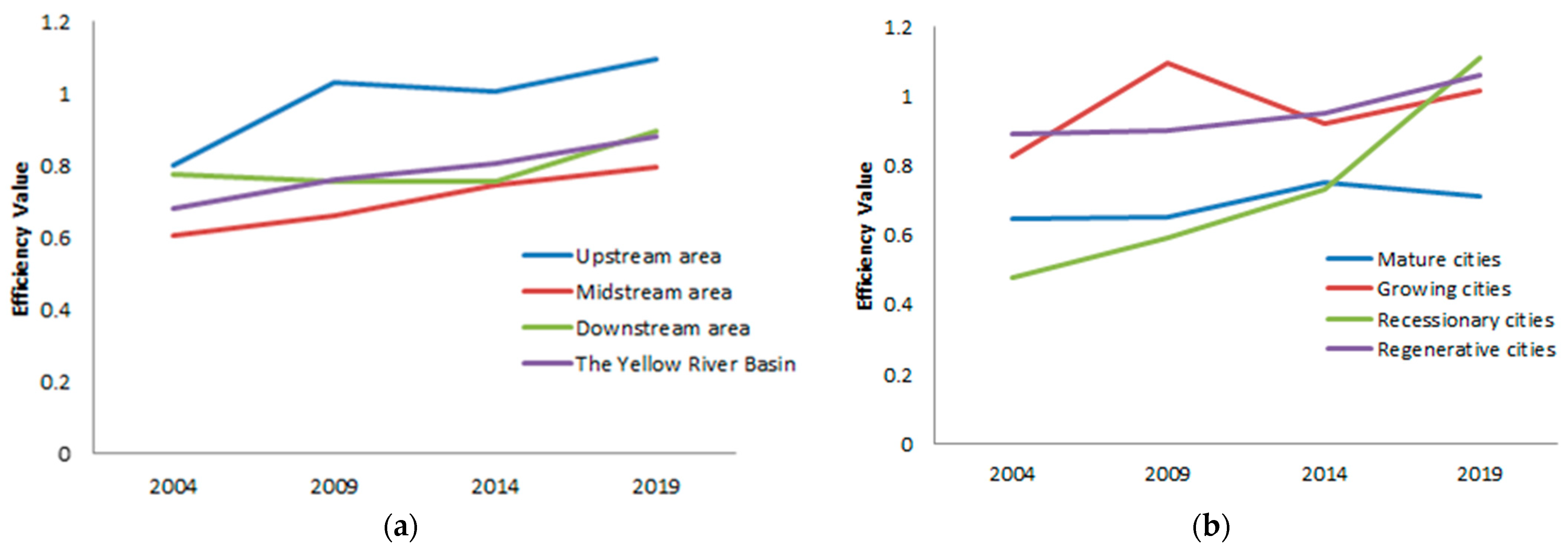
3.1.1. Characteristics of GLUE of Each Area
3.1.2. Characteristics of GLUE of Each Type
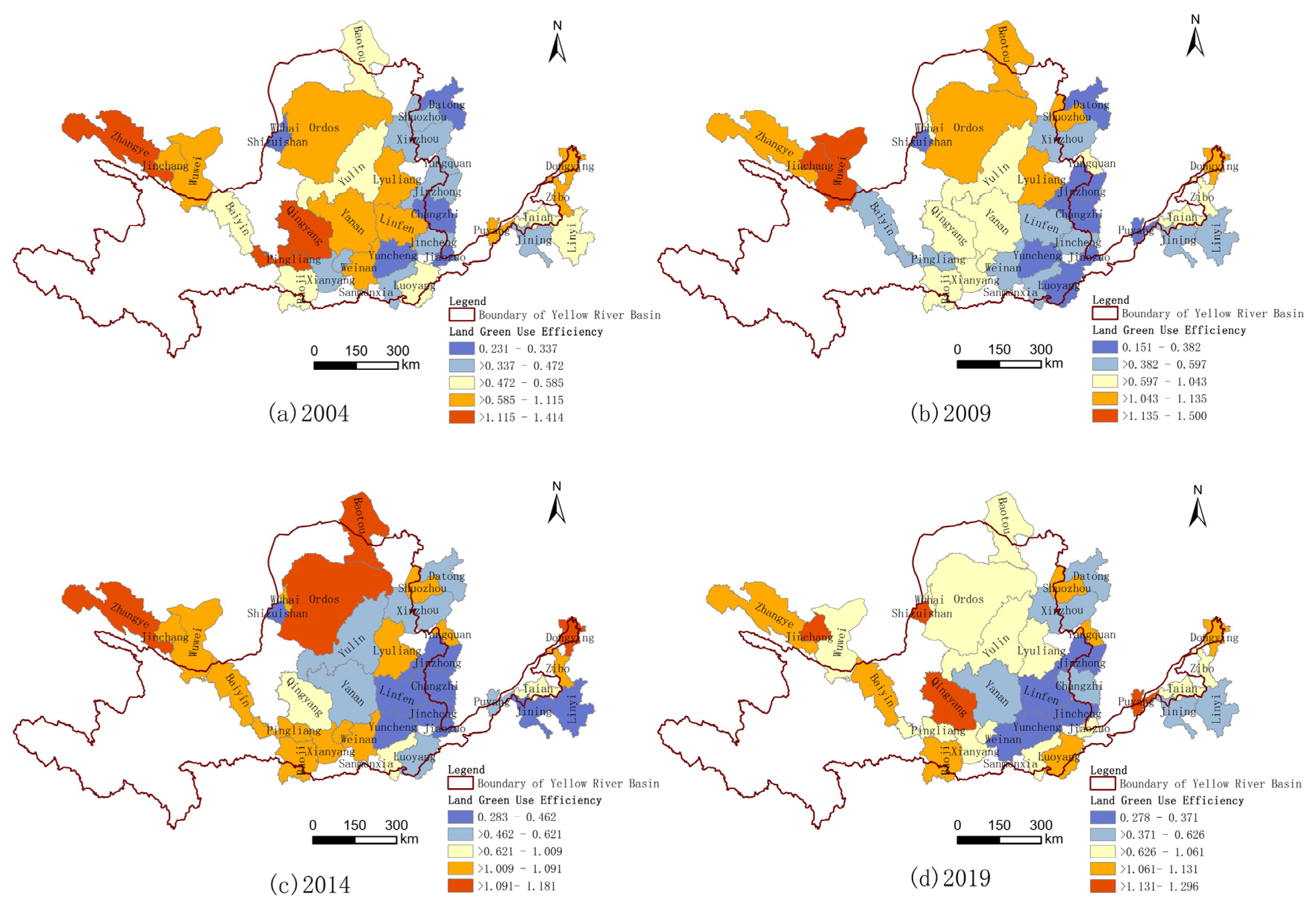
3.2. Spatial and Temporal Pattern of GLUE
3.3. Evolution Characteristics of GLUE
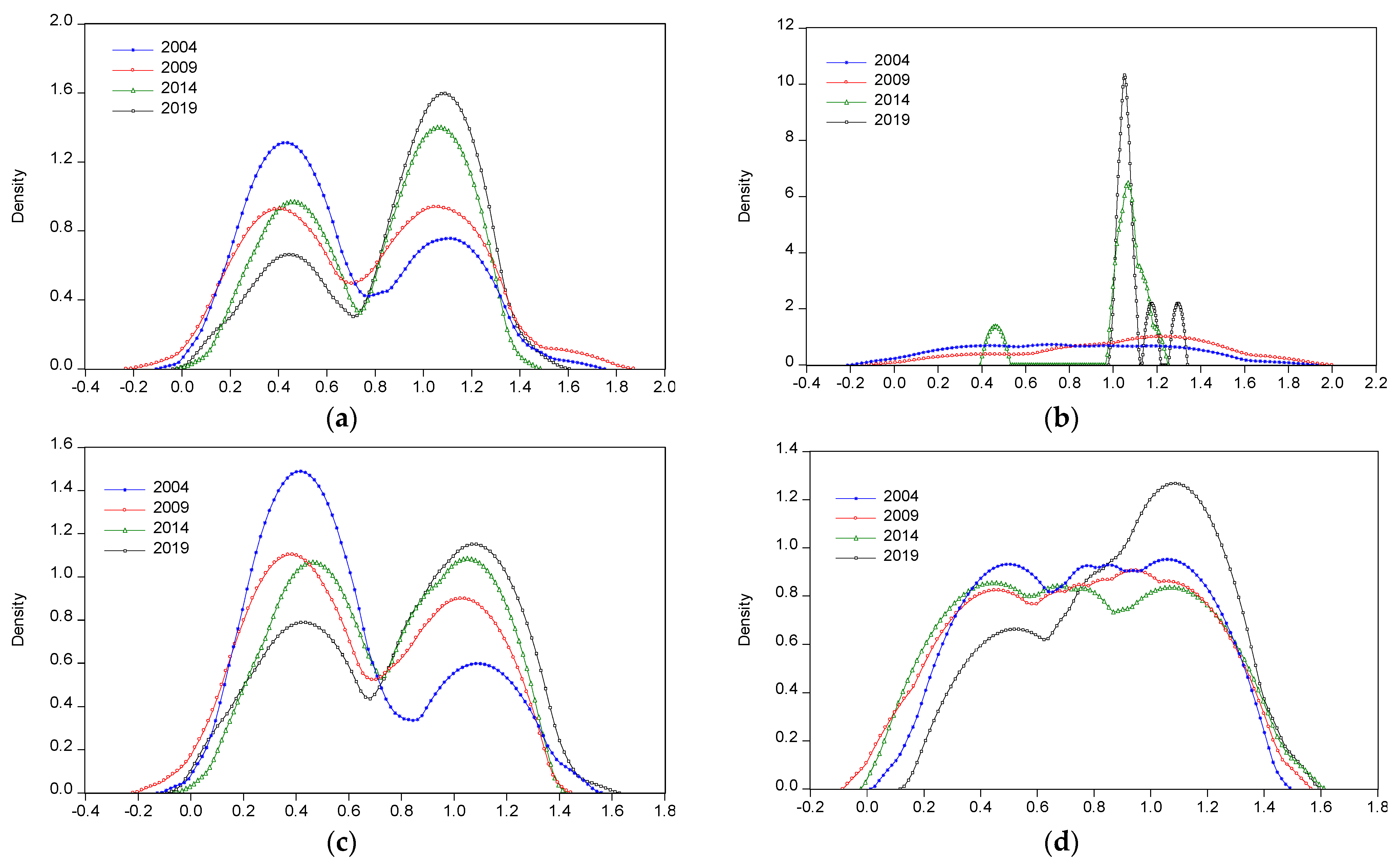
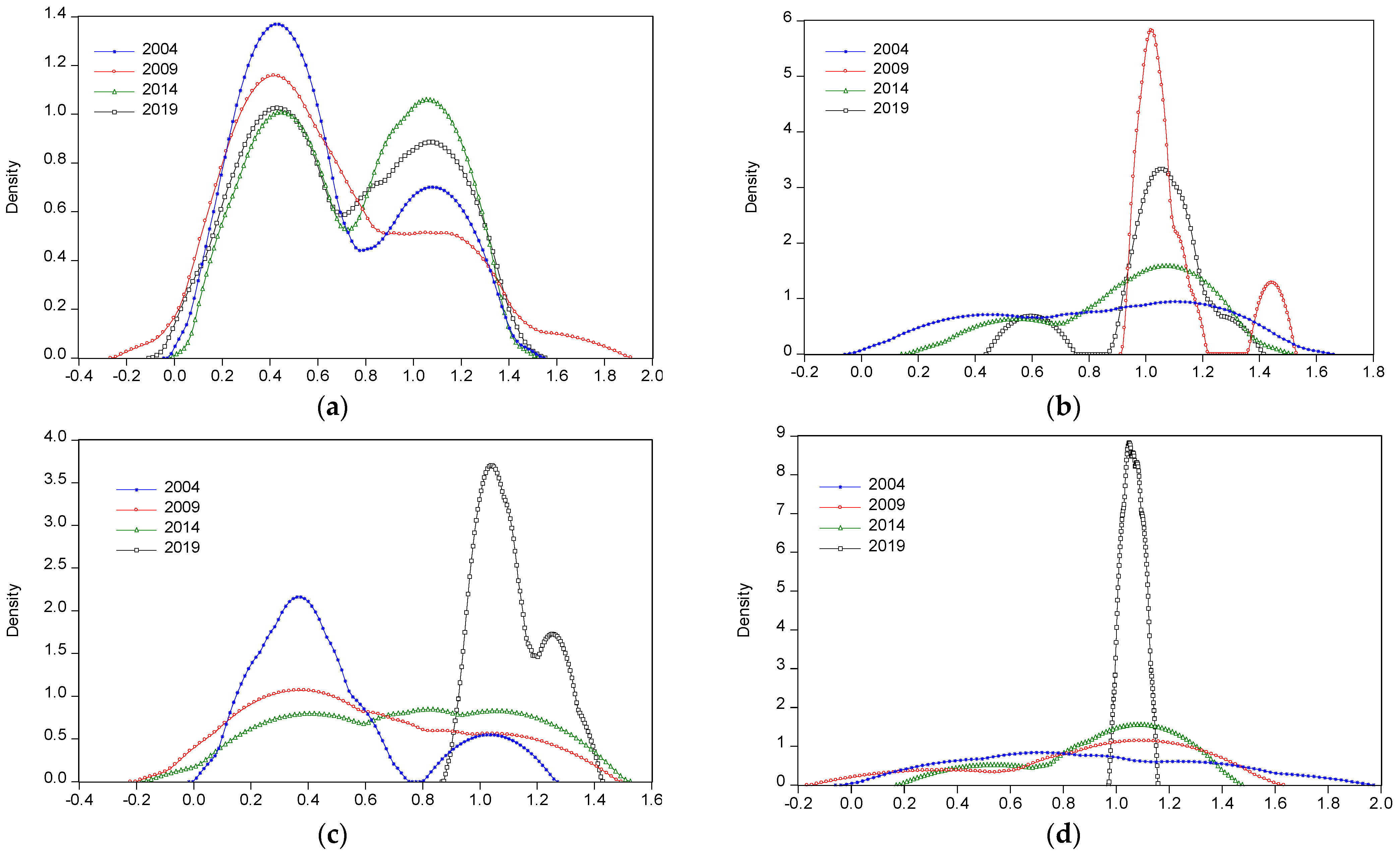
3.3.1. Time Series Evolution of Each Area
3.3.2. Time Series Evolution of Various Types
4. Analysis of Influencing Factors of GLUE in Resource-Based Cities
5. Discussion
5.1. GLUE with Carbon Emissions Included in Undesirable Output
5.2. GLUE Considering Carbon Emissions and Influencing Factors
5.3. Suggestions for Improving the GLUE
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marshall, J.D. Urban land area and population growth: A new scaling relationship for metropolitan expansion. Urban Stud. 2007, 18, 11–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, I.R.; Kaloop, M.R. Monitoring urban growth and land use change detection with GIS and remote sensing techniques in Daqahlia governorate Egypt. Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 2015, 4, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Lu, X.; Wang, M.; Jiang, B.; Chen, D.; Ge, K. Assessing the threshold effects of road infrastructure construction on farmland use transition: An empirical study in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Zhou, S.; Yan, X. A review of the recent researches on China’s urbanization and global environmental change. Prog. Geogr. 2010, 29, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wang, Q.; Bai, Z.; Shi, Z. Transition of “Production-Living-Ecological” space and its carbon storage effect under the vision of carbon neutralization: A case study of Guizhou Province. China Land Sci. 2021, 35, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Wang, X. Research on coupling degree and coupling path between China’s carbon emission efficiency and industrial structure upgrade. J. Nat. Resour. 2019, 34, 2305–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Liu, X. Urban land use efficiency under resource-based economic transformation—A case study of Shanxi Province. Land 2021, 10, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Lu, X.; Wang, P.; Qin, J.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, A. Land development and utilization for carbon neutralization. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 2995–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Jiang, S.; Liu, B.; Wang, Z.; Shao, Q. Statistical analysis of the relationship between carbon emissions and temperature rise with the spatially heterogenous distribution of carbon dioxide concentration. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 934–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xie, Z.; Wang, Z. The spatiotemporal pattern evolution and influencing factors of CO2 emissions at the county level of China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2021, 76, 3103–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Ye, X.; Jiang, H. Spatial econometric analysis of carbon emission intensity and its driving factors from energy consumption in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2013, 68, 1418–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wu, C. Research on obstacles and countermeasures of industrial transformation in resource-based Cities. Econ. Theory Bus. Manag. 2001, 21, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Li, Z.; Li, B.; Xue, M. The Problems and strategies on economic transformation of resource-based cities in China. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2007, 99, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Liu, L.; Yang, L.; Ge, L. Environmental regulation and employment in resource-based cities in China: The threshold effect of industrial structure transformation. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 828188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Long, R.; Sun, Q.; Jiang, S.; Liu, B. Has the sustainable development planning policy promoted the green transformation in China’s resource-based cities? Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 180, 106181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Mao, J.; Wang, D. Exploring the dilemma and influencing factors of ecological transformation of resource-based cities in China: Perspective on a tripartite evolutionary game. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, D.; Bu, X.; Xu, Z.; Li, G.; Wu, D. Comprehensive evaluation and impact mechanism of high-quality development of China’s resource-based cities. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2021, 76, 2489–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, F.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, Y. Using net primary productivity to characterize the spatio-temporal dynamics of ecological footprint for a resource-based city, Panzhihua in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Huang, J.; Zhao, Y. Coupling coordination analysis of ecosystem services and urban development of resource-based cities: A case study of Tangshan City. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yan, T.; Ren, Q. Does Innovative Development Drive Green Economic Growth in Resource-Based Cities? Evidence from China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 9, 745498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xu, C. Increasing urban ecological resilience based on ecological security pattern: A case study in a resource-based city. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 175, 106486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Wang, D.; Qi, Y.; Shao, S.; Zhou, Y.; Shan, Y. The governance-production nexus of eco-efficiency in Chinese resource-based cities: A two-stage network DEA approach. Energy Econ. 2021, 101, 105408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yeung, G.; Zhu, D.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, L. Efficiency of urban land use in China’s resource-based cities, 2000–2018. Land Use Policy 2022, 115, 106009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Dong, G. The efficiencies and their changes of China’s resources-based cities employing DEA and Malmquist index models. Geogr. Res. 2010, 29, 2155–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chen, W.; Ning, S.; Liu, E.; Zhao, M. Exploring the industrial land use efficiency of china’s resource-based cities. Cities 2019, 93, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wan, K.; Wang, D. Factors influencing green transformation efficiency in China’s mineral resource-based cities: Method analysis based on IPAT-E and PLS-SEM. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 330, 129783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dewan, H. Efficiency differences among China’s resource-based cities and their determinants. Resour. Policy 2017, 51, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, C. Theoretical discussion on the connotation of green transformation of resource-based cities. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2009, 19, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, H.; Ahmad, M.; Xue, C. Analysis of influencing factors of carbon emissions in resource-based cities in the Yellow River basin under carbon neutrality target. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 29, 23847–23860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Tu, J. The spatio-temporal evolution and driving factors of eco-efficiency of resource-based cities in the Yellow River Basin. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.; Rhodes, E. Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1978, 2, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D. Energy efficiency and the economists: The case for a policy based on economic principles. Annu. Rev. Energy Environ. 1995, 20, 495–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Guan, X.; Lu, S.; Zhou, M.; Deng, Y. Input-output efficiency of urban agglomerations in China: An application of Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA). Urban Stud. 2013, 50, 2766–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, G.; Tian, Z. Built-up land efficiency in urban China: Insights from the General Land Use Plan (2006–2020). Habitat Int. 2016, 51, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, T.; Ramankutty, N.; Baldos, U. Global market integration increases likelihood that a future African Green Revolution could increase crop land use and CO2 emissions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13799–13804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, S.S.; Mahmood, R.; Niyogi, D.; Lei, M.; Foster, S.A.; Hubbard, K.G.; Douglas, E.; Sr, R.P. Impacts of the agricultural Green Revolution–induced land use changes on air temperatures in India. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D21108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mojca, N.; Milan, K.; Klemen, E. Urban heat islands in relation to green land use in European cities. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 37, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liyanage, W.; Gamage, N.; Kumara, G.; Xulong, L. An assessment of the contribution of an analog forest as a sustainable land-use ecosystem for the development of rural green economy in sri lanka. J. Trop. For. Environ. 2013, 3, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Yang, X.; Chen, Z. Measurement and temporal-spatial evolution characteristics of urban land green use efficiency in China. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2020, 30, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Li, X.; Ma, J. Impacts of land finance on green land use efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic Belt: A spatial econometrics analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, F.; Wang, M.; Cao, N. The spatial-temporal differentiation of green land use in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei urban agglomeration. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2018, 16, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Ling, H. Study on Green Utilization Efficiency of Urban Land in Yangtze River Delta. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, B.X.; Li, J.; Kuang, B. Evolution characteristics and influencing factors of urban land use efficiency difference under the concept of green development. Econ. Geogr. 2018, 38, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of super-efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 143, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, K.; Zou, S.; Ke, S.; Chen, D. Does urban agglomeration promote urban land green use efficiency? Take the Yangtze River Economic Zone of China as an example. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Hu, B.; Kuang, B.; Zhou, M. Regional differences and dynamic evolution of urban land green use efficiency within the Yangtze River Delta, China. Land Use Policy 2021, 106, 105449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Yong, Y.; Yuan, C. Measurement of urban land green use efficiency and its spatial differentiation characteristics: An empirical study based on 284 cities. China Land Sci. 2019, 33, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, N.; Lu, X.; Kuang, B. Regional differences and influencing factors of green and low-carbon utilization of cultivated land under the carbon neutrality target in China. China Land Sci. 2021, 35, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Yao, S. Convergence and differentiation characteristics on agro-ecological efficiency in China from a spatial perspective. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2019, 29, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Sun, F.; Zhang, W. Spatio-temporal change and influencing factors of environmental regulation in China’s coastal urban agglomerations. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2019, 39, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X. Research on Temporal-Spatial Pattern and Spillover Effects of Urban. Land Green Use Efficiency in China under the Background of New and Old Kinetic Energy Conversion; Central China Normal University: Wuhan, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheather, S.J. Density estimation. Stat. Sci. 2004, 19, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Guo, Q.; Qin, M. Temporal-spatial evolution and influencing factors of land green use efficiency of resource-based cities in the Yellow River Basin, China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Mao, D.; Jiang, Z.; Li, K. Research on factors decomposition and decoupling effects of land use carbon emissions in Chang-Zhu-Tan Urban Agglomeration. Ecol. Econ. 2019, 35, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Yu, X.; Zhou, L. Carbon emission efficiency growth of land use structure and its spatial correlation: A case study of Nanjing city. Geogr. Res. 2018, 37, 2177–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Xia, C.; Li, Y.; Tong, J.; Shi, Z. Relationships between carbon emission, urban growth, and urban forms of urban agglomeration in the Yangtze River Delta. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 6302–6313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, J.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, W. Dynamic Changes and Influencing Factors of Urban Construction Land Use Efficiency Under Carbon Emission Constraint in Fujian Province. China Land Sci. 2020, 34, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paustian, K.; Ravindranath, N.H.; Amstel, A.V. 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas. Inventories; International Panel on Climate Change: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Study on Green Utilization Efficiency of Industrial Land and Its Influencing Factors in China; Qingdao University: Qingdao, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L. Theortical Study on the Transformation of Resources-Based Cities in China; Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Bai, Z. Evolution of Land Use Pattern and Management Countermeasures in Typical Mine-Agriculture-City Complex Area; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
| Indicator Type | Considerations | Specific Indicators | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Land Input | Area of urban construction land in municipal districts | km2 |
| Capital Input | Investment in fixed assets in municipal districts | 104 yuan | |
| Labor Input | Employees in secondary and tertiary industries in municipal districts | person | |
| Resource Consumption | Total urban water supply | 104 m3 | |
| Total electricity consumption in municipal districts | 104 kWh | ||
| Desirable Output | Economic Output | GDP in municipal districts | 104 yuan |
| Social Output | Average wage of on-the-job employees in municipal districts | yuan | |
| Undesirable Output | Environmental Pollution | Industrial sulfur dioxide emissions | t |
| Industrial smoke and dust emission | t | ||
| Industrial wastewater discharge | 104 t | ||
| Carbon Emission | Carbon emission of energy consumption and household | t |
| Types of Energy | Conversion Coefficient of Standard Coal | Coefficient of Carbon Emission (kg/kgce) | Types of Energy | Conversion Coefficient of Standard Coal | Coefficient of Carbon Emission (kg/kgce) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coal | 0.714,3 | 0.755,9 | Diesel Oil | 1.457,1 | 0.592,1 |
| Coke | 0.971,4 | 0.855,0 | Fuel Oil | 1.428,6 | 0.618,5 |
| Crude Oil | 1.428,6 | 0.585,7 | Liquefied petroleum Gas | 1.714,3 | 0.504,2 |
| Gasoline | 1.471,4 | 0.553,8 | Natural Gas | 1.214,3 | 0.448,3 |
| Kerosene | 1.471,4 | 0.571,4 | Electric Power | 0.122,9 | 0.733,0 |
| Variable Name | Influencing Factors | Specific Indicators | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peop | Population Growth | Natural population growth rate | % |
| Econ | Economic Development | Per capita GDP | yuan/person |
| Indu | Industrial Structure | Proportion of output value of tertiary industry and secondary industry | % |
| Cult | Cultural Development | Proportion of people with a college degree or above | % |
| Hosp | Medical Conditions | Hospital beds per 10,000 people | bed |
| Educ | Education Investment | Proportion of education expenditure | % |
| Scie | Science and Technology Investment | Proportion of science and technology expenditure | % |
| Envi | Environmental Management | Comprehensive utilization rate of industrial solid waste | % |
| Variable Name | 2004 | 2009 | 2014 | 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peop | −0.307 (0.283) | 0.225 (0.240) | −0.854 *** (0.253) | −0.687 *** (0.205) |
| Econ | 0.918 * (0.551) | 1.054 *** (0.292) | 0.410 ** (0.178) | 0.514 ** (0.260) |
| Indu | −0.185 (0.287) | −0.230 (0.235) | −0.066 (0.163) | −0.171 (0.259) |
| Cult | −0.338 (0.277) | 0.059 (0.216) | −0.288 * (0.169) | −0.399 * (0.231) |
| Hosp | −0.437 * (0.248) | −0.958 *** (0.363) | 0.075 (0.212) | 0.328 (0.248) |
| Educ | 0.595 ** (0.302) | −0.312 (0.262) | −0.159 (0.213) | 0.225 (0.272) |
| Scie | −0.401 (0.606) | −0.252 (0.265) | −0.122 (0.157) | −0.098 (0.169) |
| Envi | 0.286 (0.215) | 0.007 (0.200) | 0.283 (0.187) | 0.106 (0.147) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, M.; Wang, Q.; Bai, Z.; Shi, Z.; Meng, P.; Hao, M. Green Land Use Efficiency and Influencing Factors of Resource-Based Cities in the Yellow River Basin under Carbon Emission Constraints. Buildings 2022, 12, 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12050551
Chen M, Wang Q, Bai Z, Shi Z, Meng P, Hao M. Green Land Use Efficiency and Influencing Factors of Resource-Based Cities in the Yellow River Basin under Carbon Emission Constraints. Buildings. 2022; 12(5):551. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12050551
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Meijing, Qingri Wang, Zhongke Bai, Zeyu Shi, Peng Meng, and Miao Hao. 2022. "Green Land Use Efficiency and Influencing Factors of Resource-Based Cities in the Yellow River Basin under Carbon Emission Constraints" Buildings 12, no. 5: 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12050551
APA StyleChen, M., Wang, Q., Bai, Z., Shi, Z., Meng, P., & Hao, M. (2022). Green Land Use Efficiency and Influencing Factors of Resource-Based Cities in the Yellow River Basin under Carbon Emission Constraints. Buildings, 12(5), 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12050551





