An Investigation of the Mechanical Properties of Basalt Fibre-Reinforced Graphite Tailings Cement Mortar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experimental Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and Mixing Proportions
2.2. Specimen Casting and Curing Conditions
2.3. Experimental Methods
2.3.1. Macro Performance Testing
Workability Properties Test
Water Absorption and Surface Moisture Content
Mechanical Properties Test
2.3.2. Macro Performance Testing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Macro Comprehensive Performance Analysis on BFR-GTCM
3.1.1. Workability Performance of BFR-GTCM
3.1.2. Water Absorption and Surface Water Content of BFR-GTCM
3.1.3. The Changes in Flexural Strength of BFR-GTCM
3.1.4. Compressive Strength of BFR-GTCM
3.1.5. Elastic Modulus of BFR-GTCM
3.2. Reinforcement Mechanism Analysis of BFR-GTCM
3.2.1. Micro-Morphological Analysis of BFR-GTCM
3.2.2. The Hydration Products of BFR-GTCM
3.2.3. Analysis of Functional Group Changes in BFR-GTCM
3.2.4. The Pore Structure Distribution of BFR-GTCM
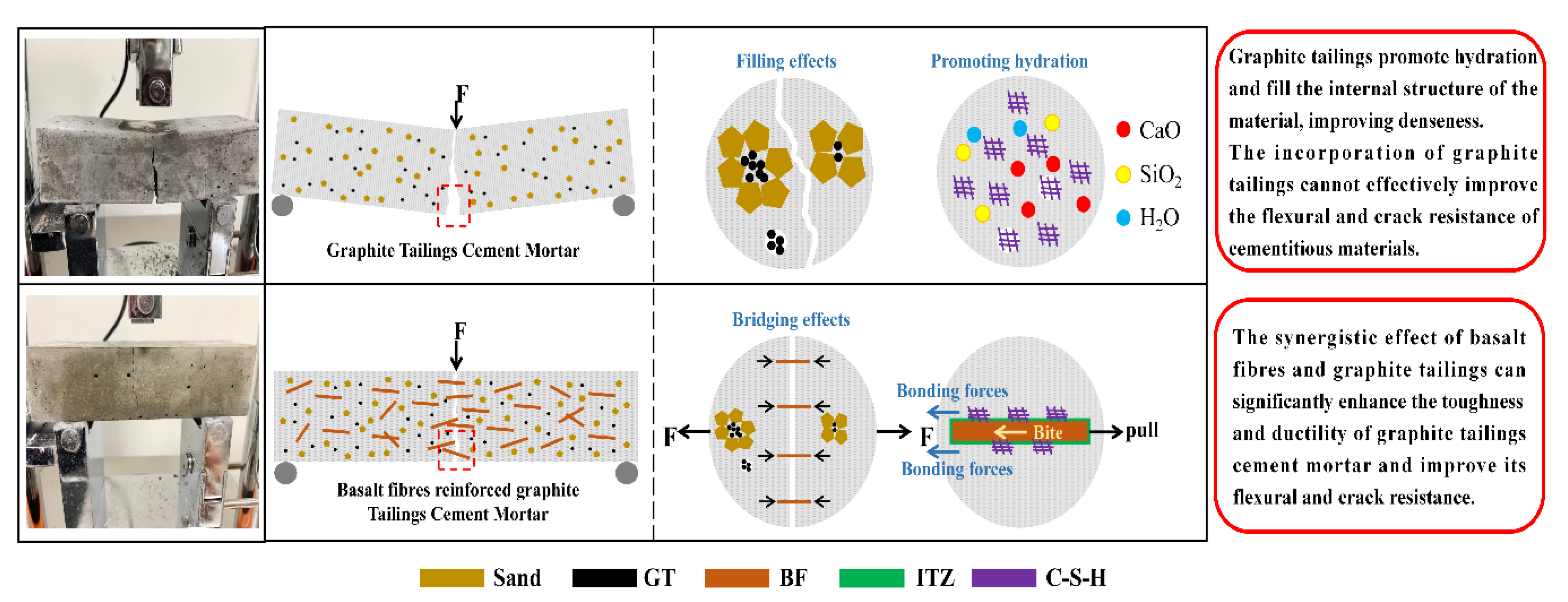
3.3. The Synergistic Enhancement Mechanism of BF and GT to BFR-GTCM
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.H. Preparation of Foam Concrete from Graphite Tailing. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 356–360, 1994–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-R.; Li, B.; Liu, H.-B.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Qin, X. Degradation characteristics of graphite tailings cement mortar subjected to freeze-thaw cycles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 234, 117422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathirvel, P.; Kwon, S.-J.; Lee, H.-S.; Karthick, S.; Saraswathy, V. Graphite ore tailings as partial replacement of sand in concrete. Discussion by Ben Li, Hongbo Liu, Jing Xue, Zhongrui Wang, Weiguo Shen. ACI Mater. J. 2019, 3, 133–135. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Xue, J.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Lv, X.; Zhang, J. Effect of graphite tailings as substitute sand on mechanical properties of concrete. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2022, 26, 2635–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, K.; Lan, Z.; Zhang, D. Mechanical and Electrical Characteristics of Graphite Tailing Concrete. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 9297628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, B.; Xue, J.; Zhang, J. Mechanical and Electroconductivity Properties of Graphite Tailings Concrete. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020, 9385097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xue, J.; Liu, H.; Shen, W. Comment on the paper of P. Kathirvel et al. [ACI Materials Journal, 115 (2018) 481–492]. ACI Mater. J. 2019, 115, 133–136. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, L.H.; Lee, T.W. Experimental study on mechanical properties and deformation behavior of concrete with recycled aggregates and steel fiber. J. Korea Concr. Inst. 2016, 28, 357–363. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, B.; Xu, G. Preparation of autoclaved aerated concrete by using graphite tailings as an alternative silica source. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 267, 121792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, R.B.; Mirza, O.; Kang, W.H. Mechanical properties of steel fiber reinforced recycled aggregate concrete. Struct. Concr. 2019, 20, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimipour, A.; Ghalehnovi, M.; De Brito, J. Mechanical and durability properties of steel fibre-reinforced rubberised concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 257, 119463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, J.Y.; Sung, C.Y. Engineering properties of carbon fiber and glass fiber reinforced recycled polymer concrete. J. Korean Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 58, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Safiuddin, M.; Yakhlaf, M.; Soudki, K.A. Key mechanical properties and microstructure of carbon fibre reinforced self-consolidating concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 164, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathish, T.; Palanikumar, B.; Karthick, S. Comparative study on addition of carbon fiber in concrete with partial replacement of demolished concrete waste in structural concrete. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 33, 2585–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, B.; Yaman, İ.Ö. Fatigue performance of PVA fibre reinforced cementitious composite overlays. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2021, 22, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, Z.P.; Mo, K.H.; Tan, C.G.; Yeo, S.H. Mechanical characteristics and flexural behaviour of fibre-reinforced cementitious composite containing PVA and basalt fibres. Sādhanā 2019, 44, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodnarova, L.; Hoško, M. Effects of type of PVA fibres on the properties of fibre-cement composites. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: Melville, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 2210, p. 020021. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Yao, J.; Lin, X.Y.; Li, H.D.; Lam, J.Y.K.; Leung, C.K.Y.; Sham, I.M.L.; Shih, K.M. Tensile performance of sustainable strain-hardening cementitious composites with hybrid PVA and recycled PET fibers. Cement Concr. Res. 2018, 107, 10–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.C.; Zhang, J.H.; Chen, G.; Chen, G.M.; Xie, Z.H. Fracture behaviors of a new steel fiber reinforced recycled aggregate concrete with crumb rubber. Construct. Build. Mater. 2014, 53, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.M.; Yang, H.; Lin, C.; Chen, J.F.; He, Y.H.; Zhang, H.Z. Fracture behavior of steel fibre reinforced recycled aggregate concrete after exposure to elevated temperatures. Construct. Build. Mater. 2016, 128, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; He, H.; Senetakis, K. Behavior of carbon fiber-reinforced recycled concrete aggregate. Geosynth. Int. 2017, 24, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, S.R.; Prabhakara, H.M.; Bramer, E.A.; Dierkes, W.; Akkerman, R.; Brem, G. A critical review on recycling of end-of-life carbon fibre/glass fibre reinforced composites waste using pyrolysis towards a circular economy. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 136, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkan, Ş.; Demir, F. The hybrid effects of PVA fiber and basalt fiber on mechanical performance of cost effective hybrid cementitious composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 263, 120564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, V.; Scalici, T.; Di Bella, G.; Valenza, A. A review on basalt fiber and its composites. Compos. B Eng. 2015, 74, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, V.; Tolmare, N.S.; Brik, V.B. Performance Evaluation of 3-D Basalt Fibre Reinforced Concrete&Basalt Rod Reinforced Concrete; IDEA Program Final Report Contract No. NCHRP-45; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ayub, T.; Shafiq, N.; Nuruddin, M.F. Effect of chopped basalt fibers on the mechanical properties and microstructure of high performance fiber reinforced concrete. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2014, 587686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, G.; Cui, J. Corrosion behavior and mechanism of basalt fibers in sodiumhydroxide solution. Materials 2018, 11, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhao, Y. Experimental research on the mechanical behavior of chopped basalt fiber reinforced concrete. Ind. Construct. 2007, 137, 10–881. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, D.P.; Thaumaturgo, C. Fracture toughness of geopolymer concretes reinforced with basalt fibers. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2005, 27, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Qiu, X.; Cheng, L.; Wang, Y. Experimental research on the fundamental mechanical properties of presoaked basalt fiber concrete. In Advances in FRP Composites in Civil Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Kabay, N. Abrasion resistance and fracture energy of concretes with basalt fiber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 50, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- High, C.; Seliem, H.M.; El-Safty, A.; Rizkalla, S.H. Use of basalt fibers for concrete structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 96, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surul, O.; Bilir, T.; Gholampour, A.; Sutcu, M.; Ozbakkaloglu, T.; Gencel, O. Recycle of ground granulated blast furnace slag and fly ash on eco-friendly brick production. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2020, 26, 1738–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesina, A. Performance of cementitious composites reinforced with chopped basalt fibres—An overview. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 266, 120970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrociocchi, G.; Albe, M.; Tirillo, J.; Sarasini, F.; Valente, M.; Santarelli, M.L. Basalt fibers as a sustainable reinforcement for cement based mortars: Preliminary study, materials characterization VII 109. WIT Trans. Eng. Sci. 2015, 90, 109–120. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ding, Y.; Xu, P. Mechanical properties and microstructure of basalt fiber-reinforced recycled concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Jia, B.; Huang, H.; Mou, Y. Experimental study on basic mechanical properties of basalt fiber reinforced concrete. Materials 2020, 13, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Huang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Chen, D. Effect of polypropylene and basalt fiber on the behavior of mortars for repair applications. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 5927609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, G. Experimental research on basalt fiber reinforced cementitious composites. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 253–255, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 17671–1999; Cement Mortar Strength Test Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999.
- JGJ/T70–2009; Standard for Basic Performance Test Methods of Building Mortar. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009.
- GB/T2419–2005; Method for Determining Fluidity of Cement Mortar. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005.
- GB/T 16594–2008; General Rules for Measurement of Length in Micron Scale by SEM. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- GB/T 30904–2014; Inorganic Chemicals for Industrial Use: Crystal Form Analysis on X-ray Diffraction Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- ISO 19618–2017; Measurement Method for Normal Spectral Emissivity Using Blackbody Reference with an FTIR Spectrometer. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- GB/T 21650–2008; Pore Size Distribution and Porosity of Solid Materials by Mercury Porosimetry and Gas adsorption. Part 1: Mercury Porosimetry. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- Martys, N.S.; Ferraris, C.F. Capillary transport in mortars and concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 1997, 27, 747–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C. Water sorptivity of mortars and concretes: A review. Mag. Concr. Res. 1989, 41, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, Z. Combined Effects of Graphite Tailings and Curing Conditions on the Early-Age Performances of Cement Mortar. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 5965328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, T.; Mercury, L.; Poulet, F.; D’Hendecourt, L. Diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy as a tool to characterise water in adsorption/confinement situations. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 304, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Kirkpatrick, R.J.; Poe, B.; McMillan, P.F.; Cong, X. Structure of calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H): Near-, Mid-, and Far-infrared spectroscopy. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1999, 82, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
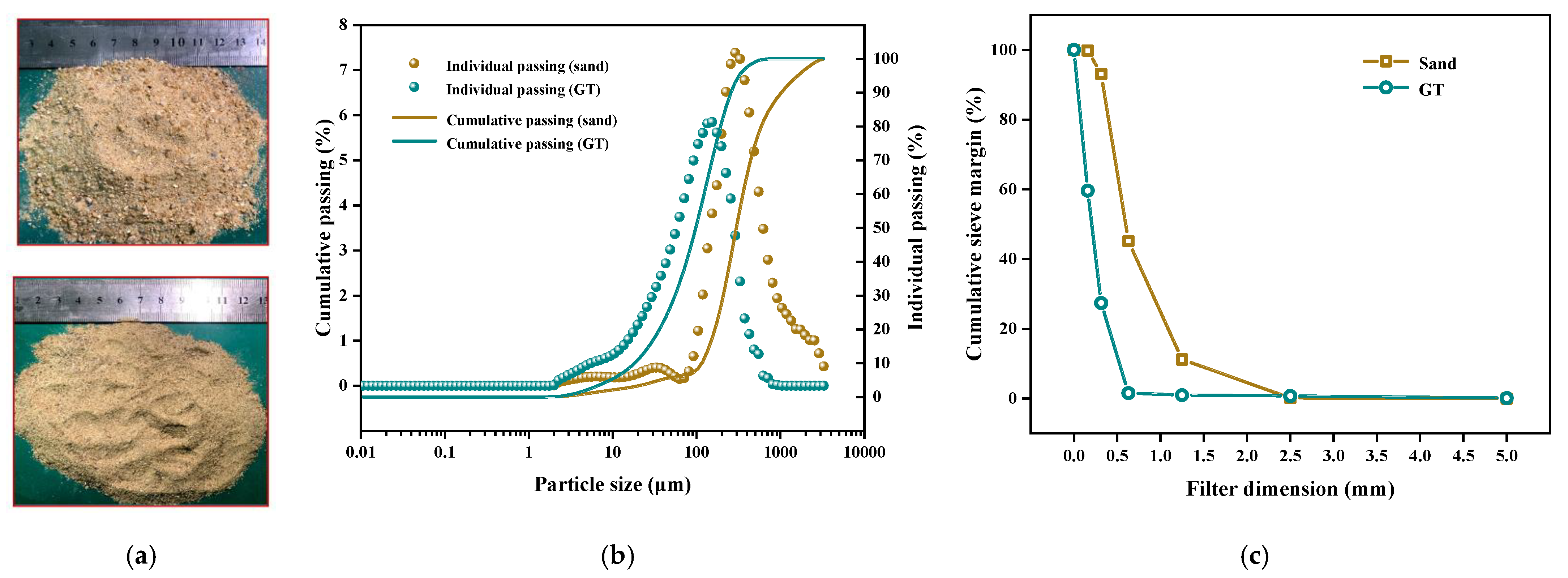
















| Flexural Strength (MPa) | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Fineness | Setting Time (min) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 days | 28 days | 3 days | 28 days | 1.2 | Initial setting | Final setting |
| 4.2 | 7.1 | 19.4 | 43.6 | 173 | 268 | |
| Materials | Chemical Compositions | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | SO3 | Loss | ||
| 59.65 | 22.47 | 5.80 | 4.32 | 3.24 | 2.08 | 2.44 | |||
| GT | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | SO3 | V2O5 | K2O | Loss |
| 15.55 | 62.50 | 10.21 | 5.07 | 2.33 | 0.54 | 0.42 | 2.26 | 1.12 | |
| Sand | SiO2 | Loss | |||||||
| 99.88 | 0.12 | ||||||||
| Physical Properties | Fine Aggregate | |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Natural stand | Graphite tailings |
| Size (mm) | 0.17–5 | 0.2–0.4 |
| Apparent density (kg/m3) | 2620 | 2855 |
| Bulk density (kg/m3) | 1630 | 1540 |
| 24-h water absorption (%) | 16.80 | 37.10 |
| Fineness modulus | 2.49 | 0.90 |
| pH value | 7.00 | 10.30 |
| Fibre | Length (mm) | Diameter (μm) | Density (g/cm3) | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BF | 12 | 17 | 2.9 | 100 | 3300 | 3.1 |
| Sample Number | Cement (kg/m3) | Sand (kg/m3) | Graphite Tailings (kg/m3) | Water (kg/m3) | Fiber Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BFGT000 | 772.14 | 1158.21 | 0 | 308.86 | 0 |
| BFGT100 | 772.14 | 1158.21 | 0 | 308.86 | 0.1 |
| BFGT200 | 772.14 | 1158.21 | 0 | 308.86 | 0.2 |
| BFGT300 | 772.14 | 1158.21 | 0 | 308.86 | 0.3 |
| BFGT010 | 772.14 | 1042.39 | 126.21 | 308.86 | 0 |
| BFGT110 | 772.14 | 1042.39 | 126.21 | 308.86 | 0.1 |
| BFGT210 | 772.14 | 1042.39 | 126.21 | 308.86 | 0.2 |
| BFGT310 | 772.14 | 1042.39 | 126.21 | 308.86 | 0.3 |
| BFGT020 | 772.14 | 926.57 | 310.09 | 308.86 | 0 |
| BFGT120 | 772.14 | 926.57 | 310.09 | 308.86 | 0.1 |
| BFGT220 | 772.14 | 926.57 | 310.09 | 308.86 | 0.2 |
| BFGT320 | 772.14 | 926.57 | 310.09 | 308.86 | 0.3 |
| BFGT030 | 772.14 | 810.75 | 378.63 | 308.86 | 0 |
| BFGT130 | 772.14 | 810.75 | 378.63 | 308.86 | 0.1 |
| BFGT230 | 772.14 | 810.75 | 378.63 | 308.86 | 0.2 |
| BFGT330 | 772.14 | 810.75 | 378.63 | 308.86 | 0.3 |
| BFGT040 | 772.14 | 694.93 | 463.28 | 308.86 | 0 |
| BFGT140 | 772.14 | 694.93 | 463.28 | 308.86 | 0.1 |
| BFGT240 | 772.14 | 694.93 | 463.28 | 308.86 | 0.2 |
| BFGT340 | 772.14 | 694.93 | 463.28 | 308.86 | 0.3 |
| BFGT050 | 772.14 | 579.11 | 579.11 | 308.86 | 0 |
| BFGT150 | 772.14 | 579.11 | 579.11 | 308.86 | 0.1 |
| BFGT250 | 772.14 | 579.11 | 579.11 | 308.86 | 0.2 |
| BFGT350 | 772.14 | 579.11 | 579.11 | 308.86 | 0.3 |
| Specimen | Porosity (%) | Total Intruded Volume (mL/g) | Total Surface Area (m2/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BFGT000 | 13.277 | 0.0363 | 3.3622 |
| BFGT020 | 13.003 | 0.0399 | 4.0772 |
| BFGT120 | 15.860 | 0.0449 | 3.0707 |
| BFGT220 | 16.985 | 0.0430 | 4.6107 |
| BFGT320 | 12.960 | 0.0395 | 2.6285 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Li, B.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, W.-x. An Investigation of the Mechanical Properties of Basalt Fibre-Reinforced Graphite Tailings Cement Mortar. Buildings 2022, 12, 2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12122106
Zhang C, Li B, Yu Y, Zhang Y, Xu H, Wang W-x. An Investigation of the Mechanical Properties of Basalt Fibre-Reinforced Graphite Tailings Cement Mortar. Buildings. 2022; 12(12):2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12122106
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chen, Ben Li, Ying Yu, Yu Zhang, Hu Xu, and Wen-xue Wang. 2022. "An Investigation of the Mechanical Properties of Basalt Fibre-Reinforced Graphite Tailings Cement Mortar" Buildings 12, no. 12: 2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12122106
APA StyleZhang, C., Li, B., Yu, Y., Zhang, Y., Xu, H., & Wang, W.-x. (2022). An Investigation of the Mechanical Properties of Basalt Fibre-Reinforced Graphite Tailings Cement Mortar. Buildings, 12(12), 2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12122106






