Seawater-Neutralized Bauxite Residue–Polyester Composites as Insulating Construction Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
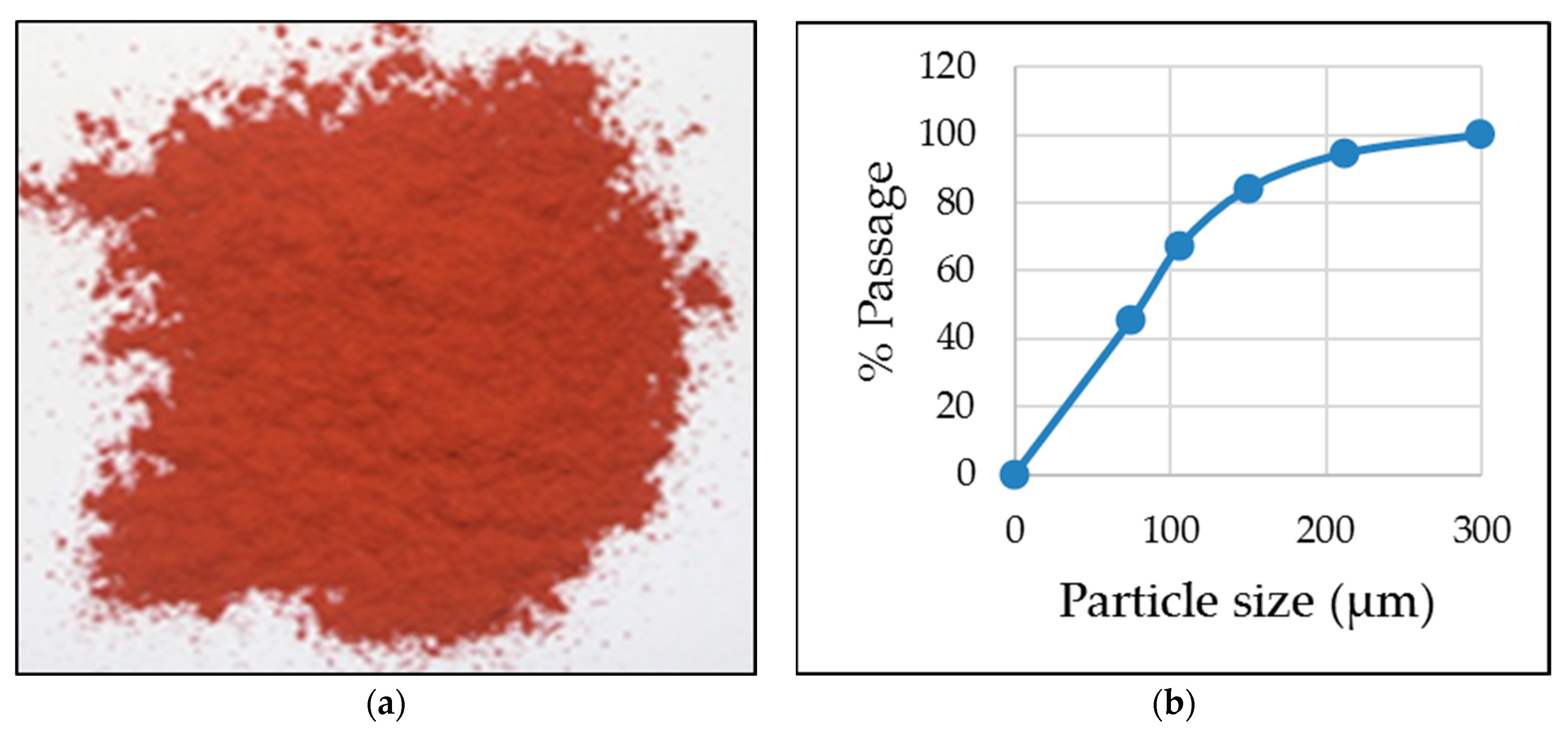
2.1. Material
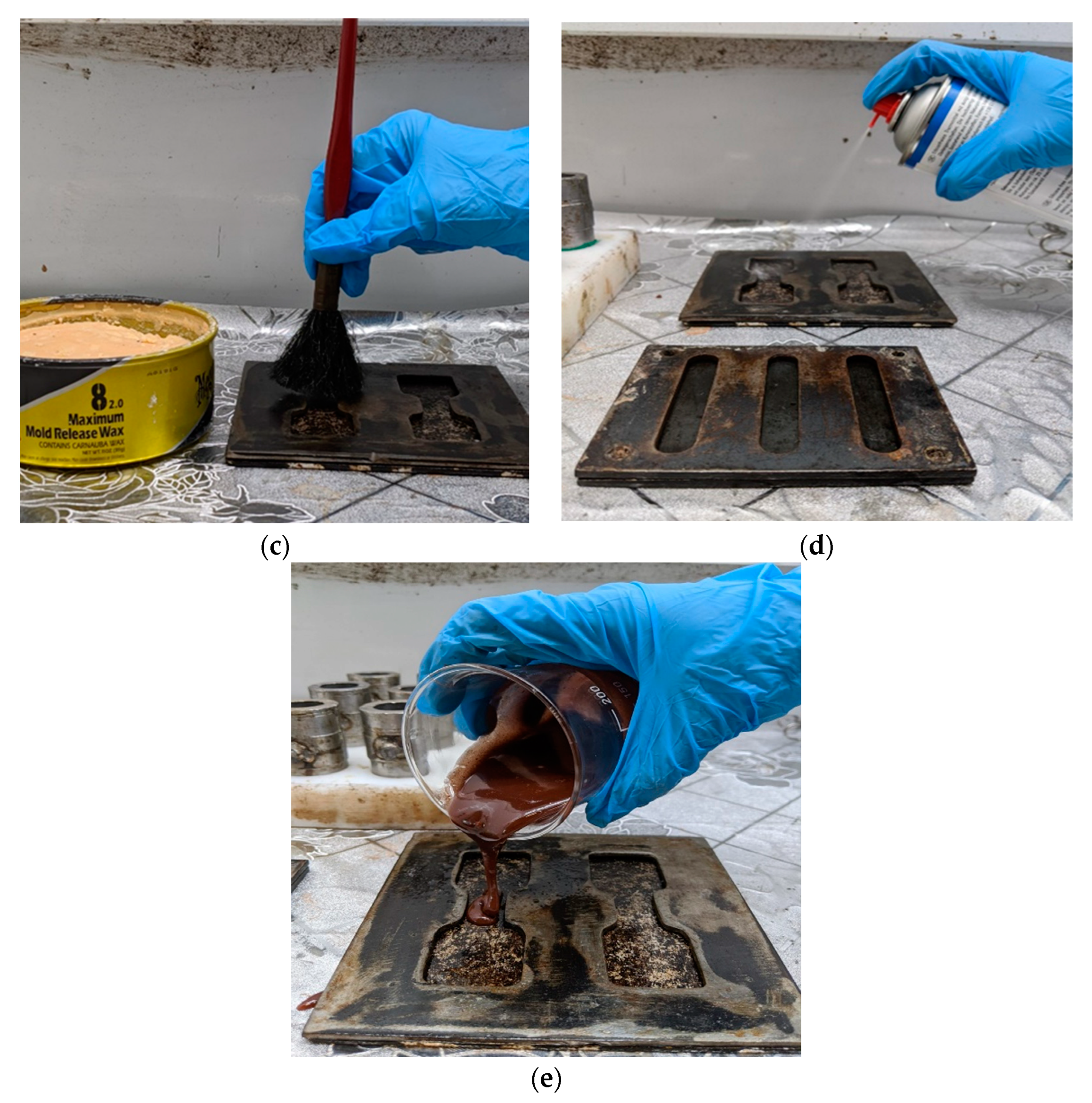
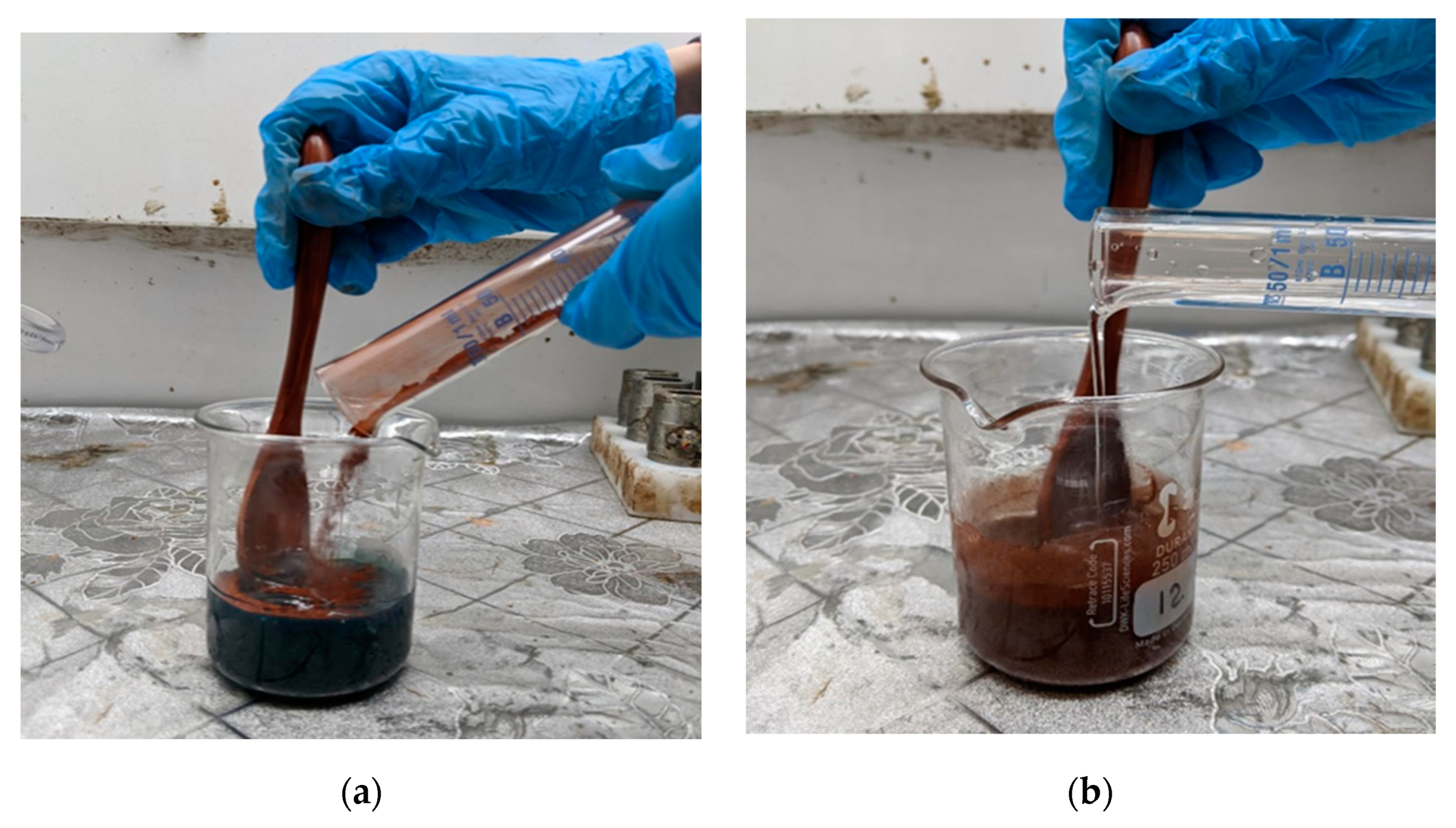
2.2. Composite Fabrication
2.3. Mechanical Testing
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
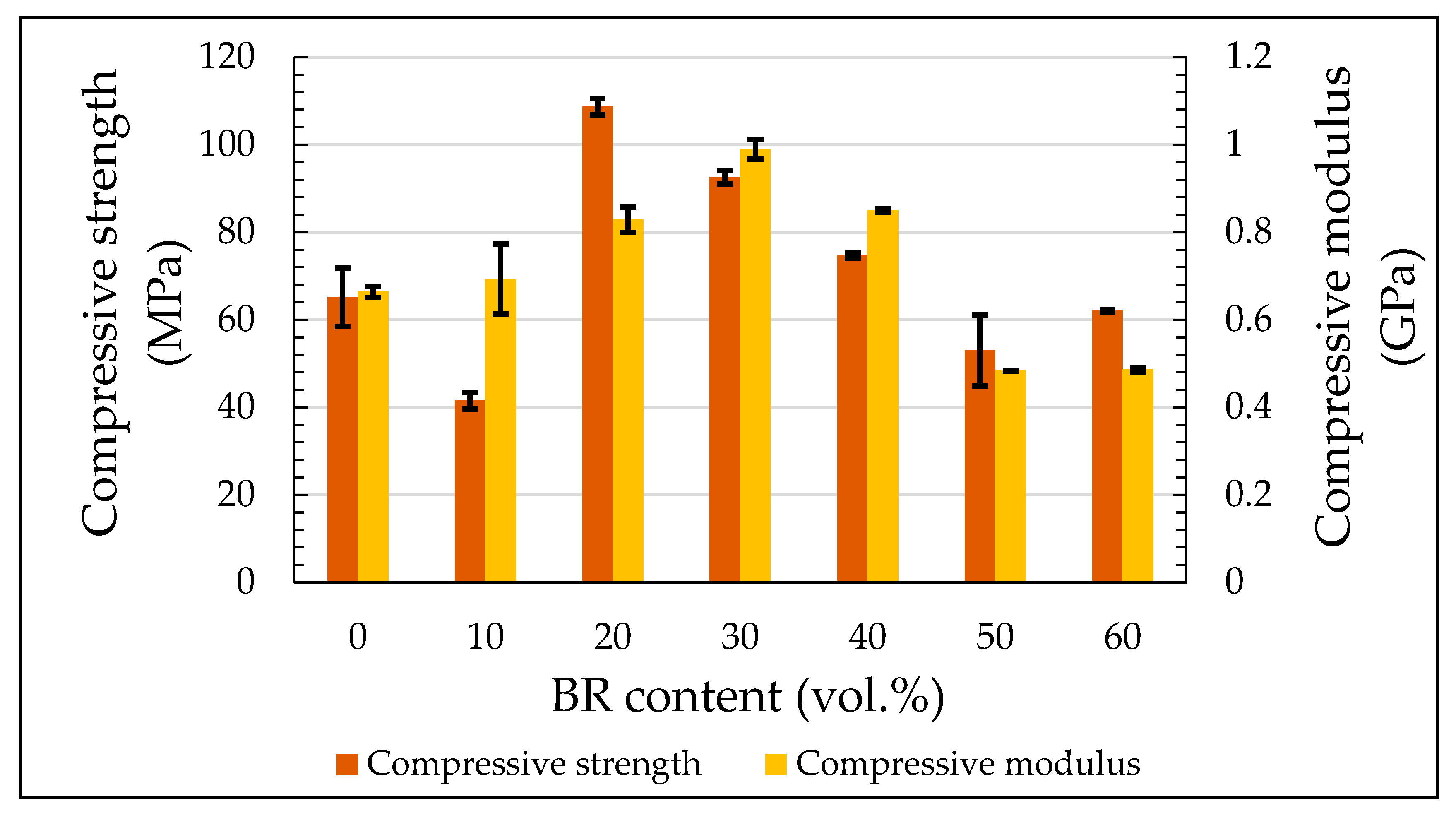
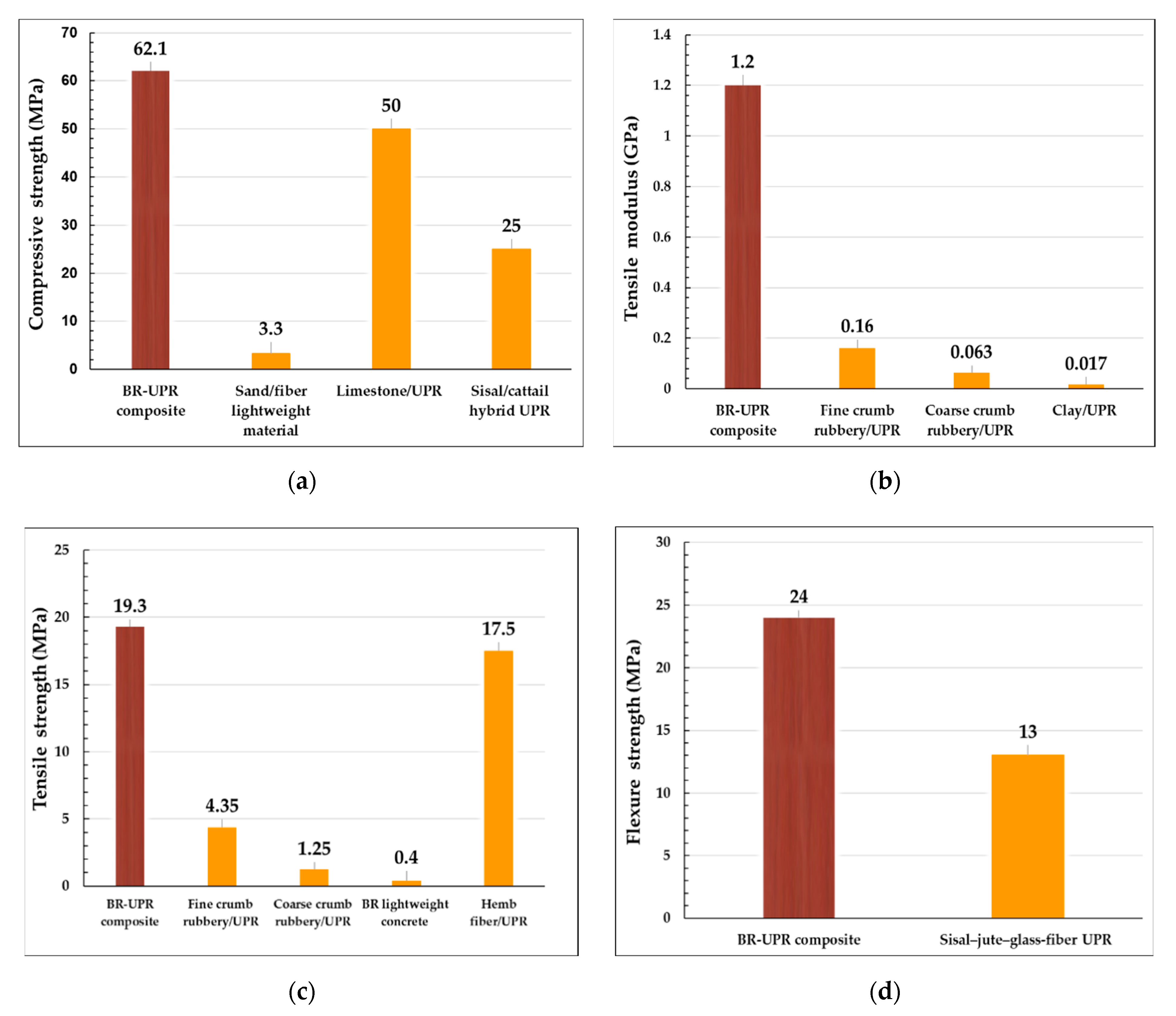
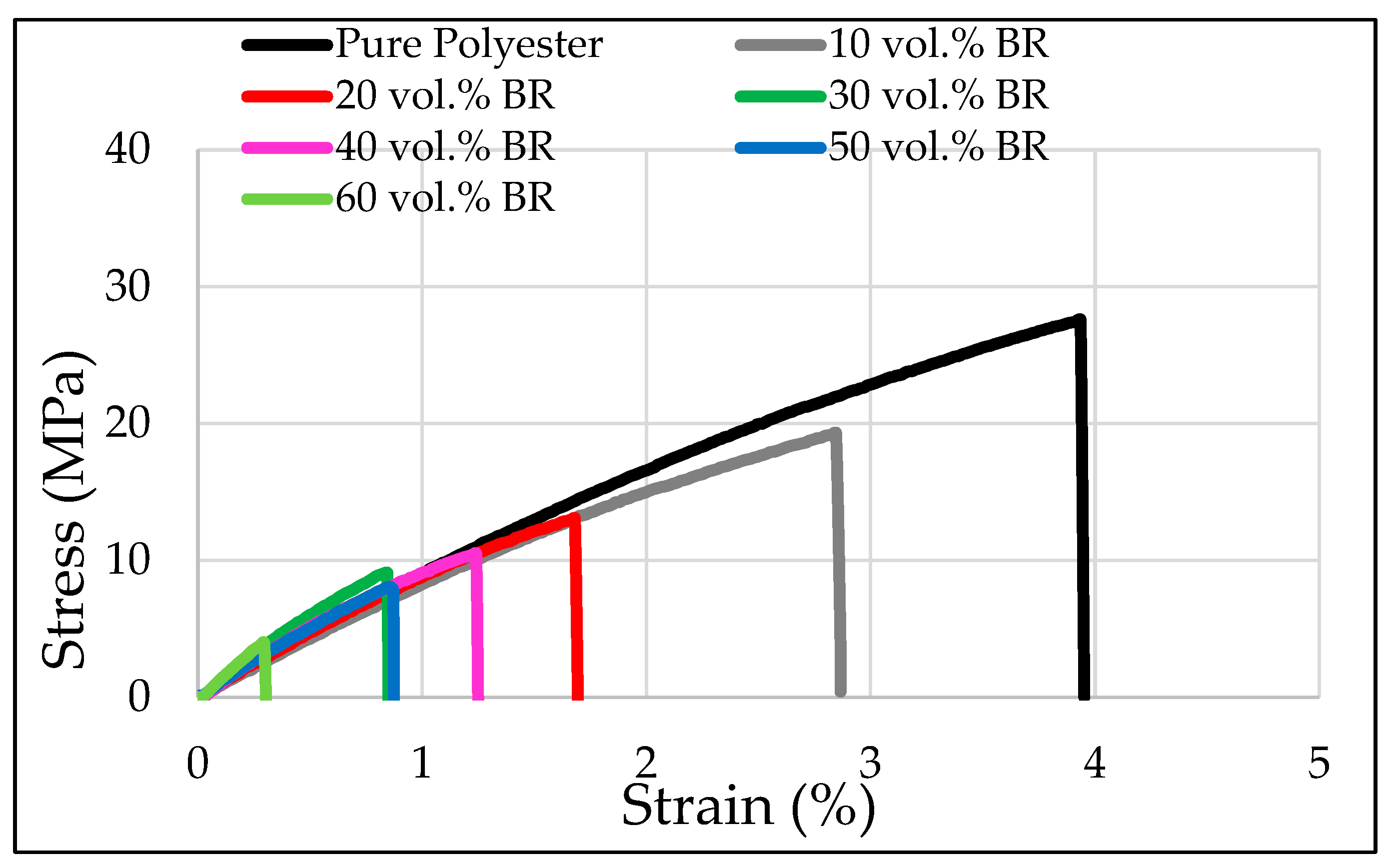
3.1. Compression Properties
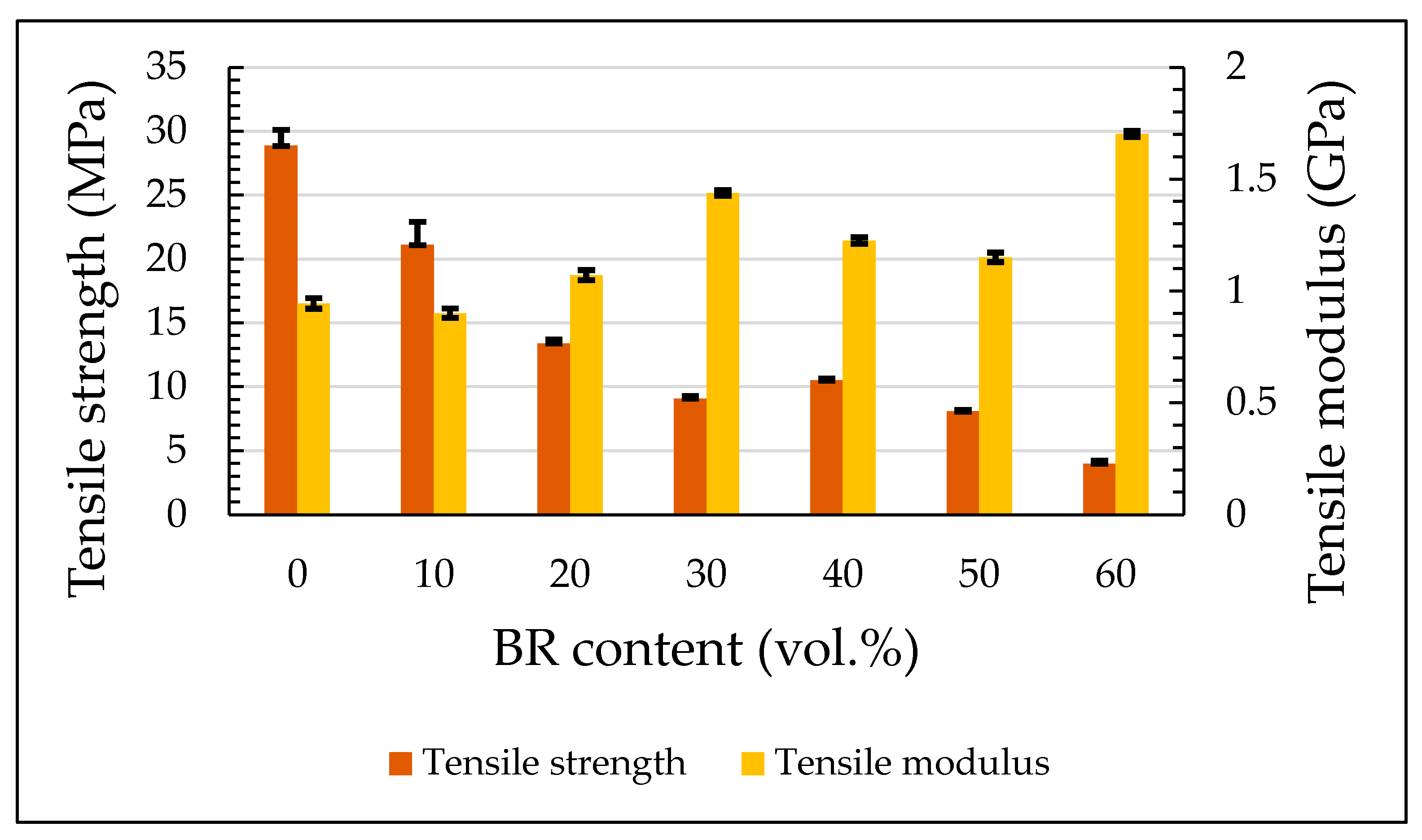
3.2. Tensile Properties
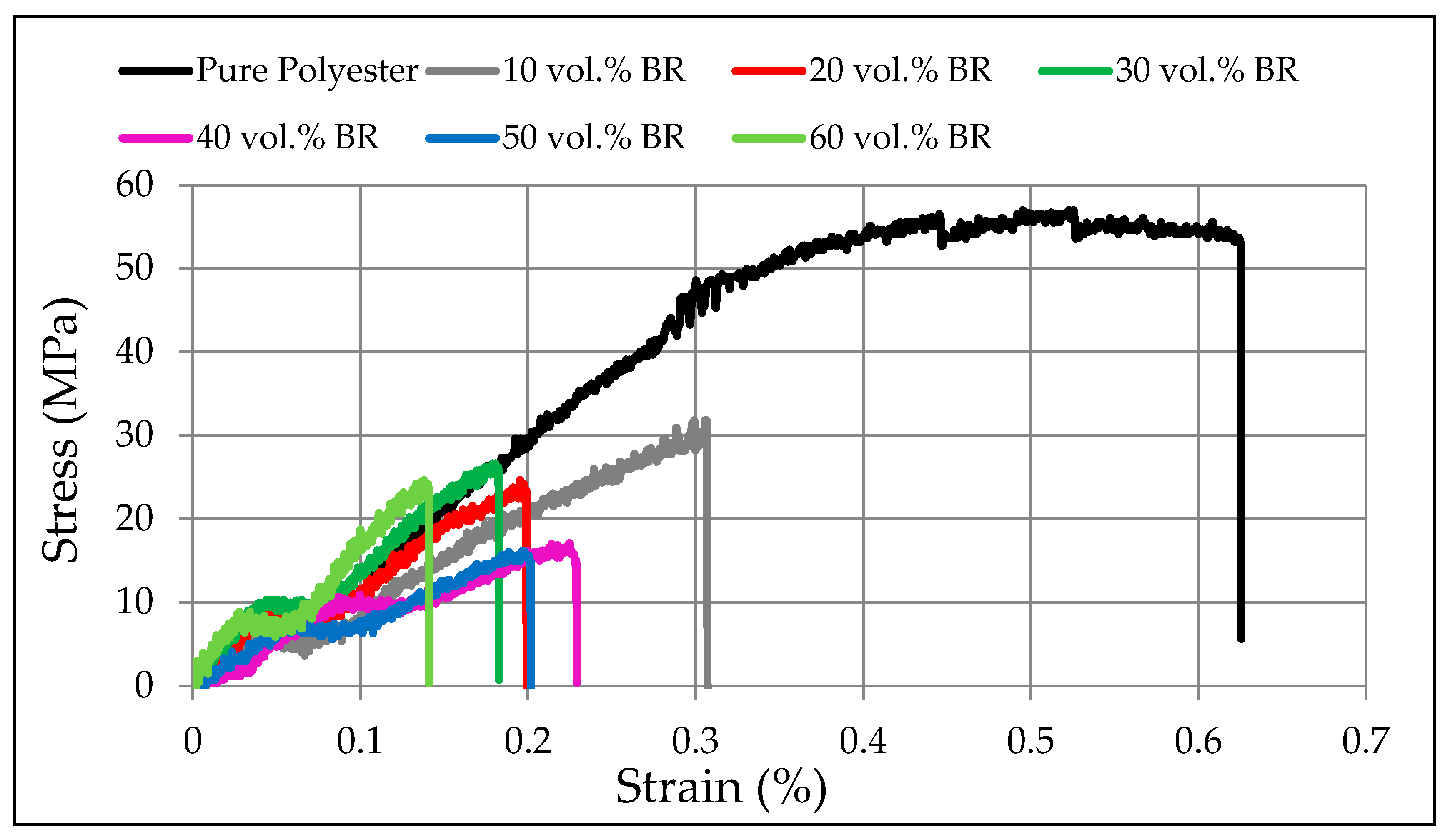
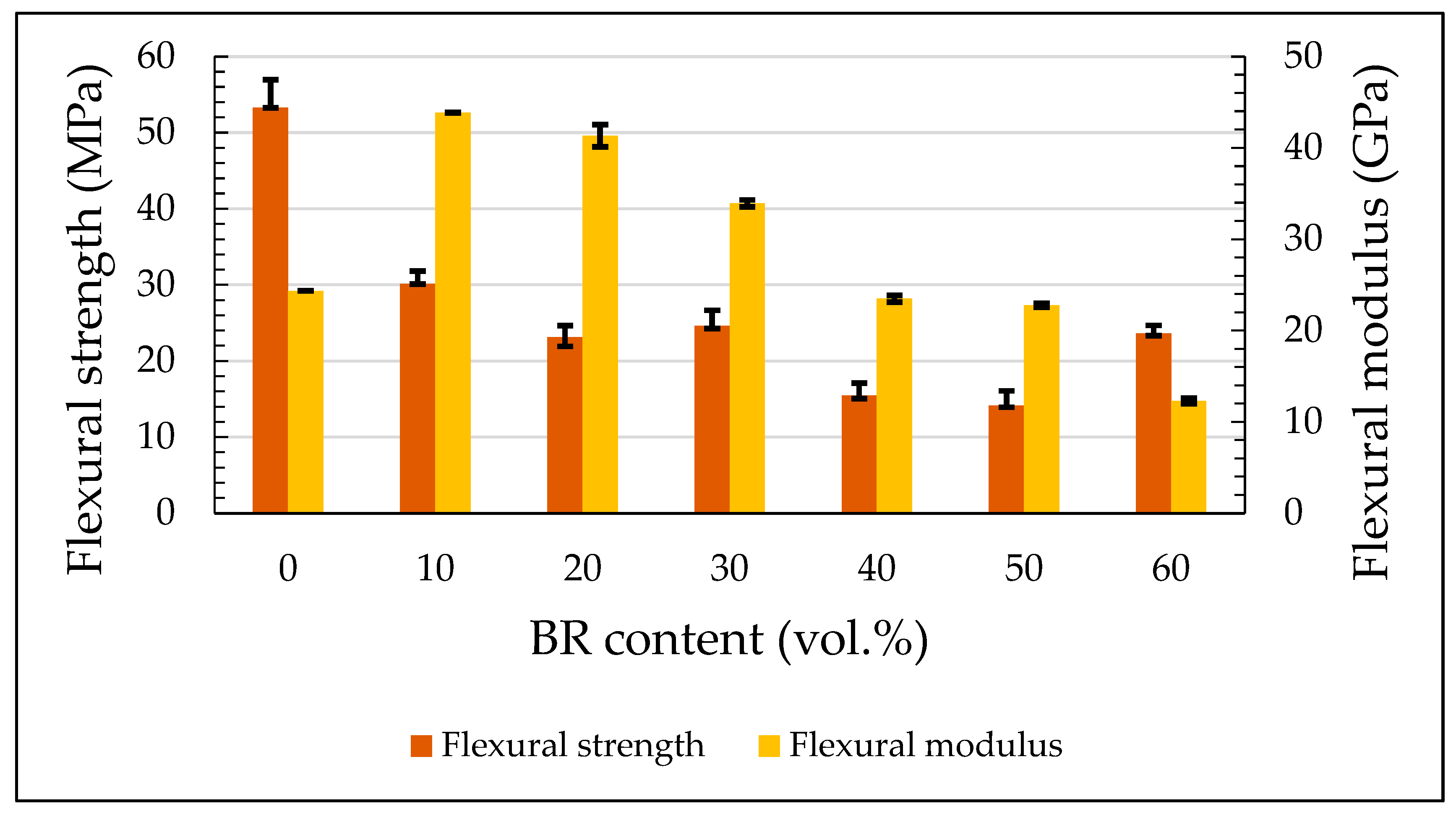
3.3. Flexural Properties
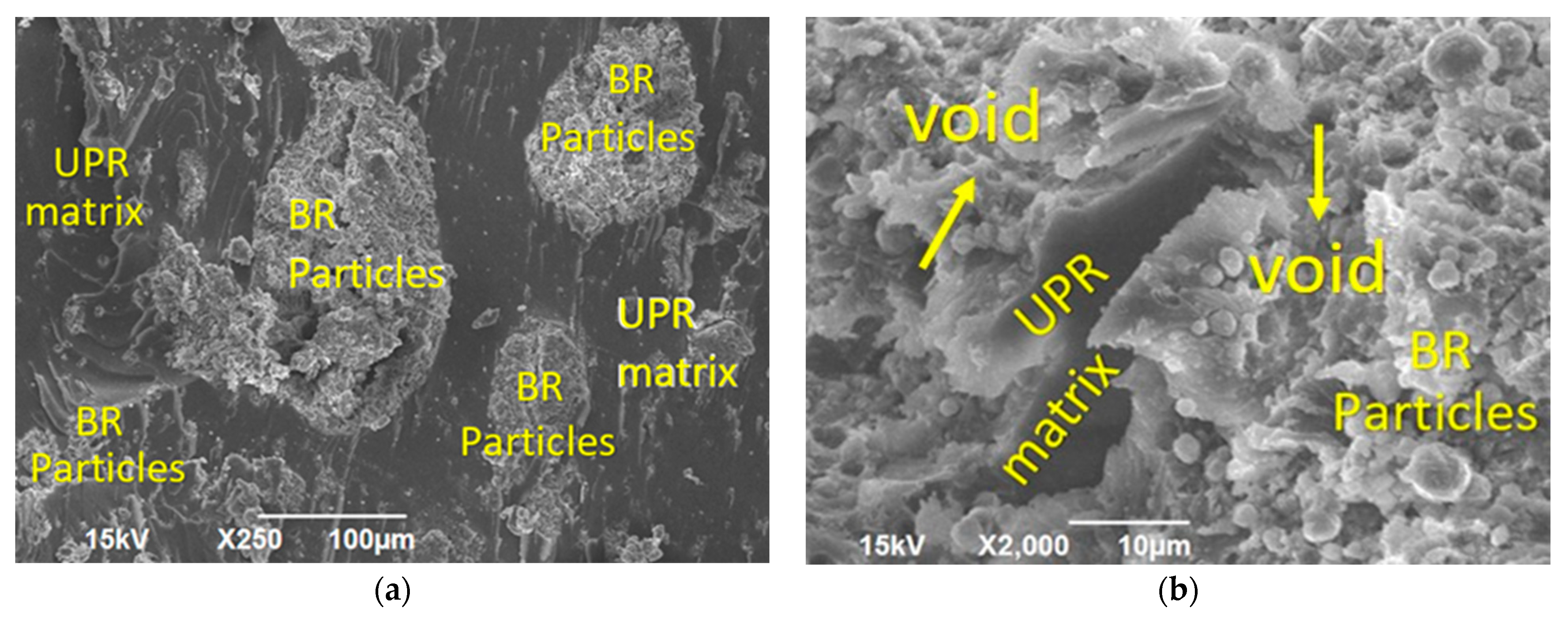
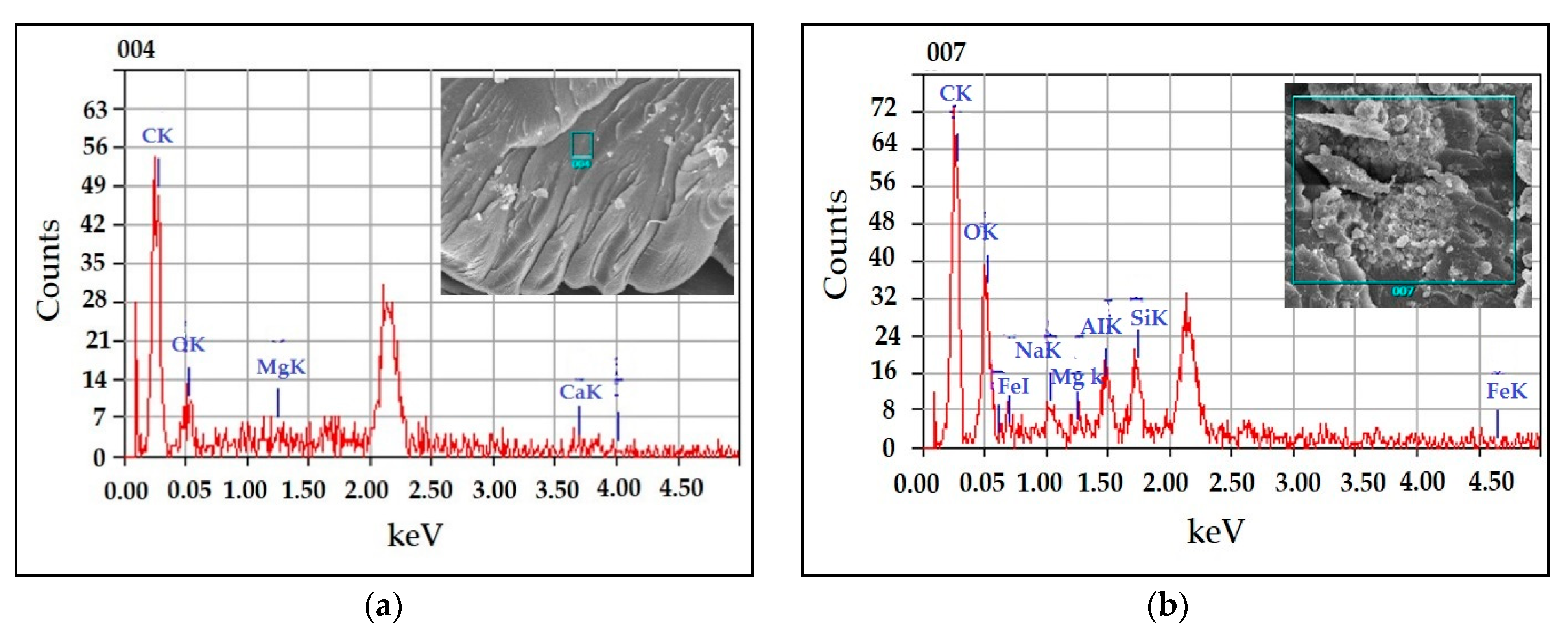
3.4. EDX Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsakiridis, P.E.; Agatzini-Leonardou, S.; Oustadakis, P. Red mud addition in the raw meal for the production of Portland cement clinker. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 116, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodoo-Arhin, D.; Konadu, D.S.; Annan, E.; Buabeng, F.P.; Yaya, A.; Agyei-Tuffour, B. Fabrication and characterisation of Ghanaian bauxite red mud-clay composite bricks for construction applications. Am. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 3, 110–119. [Google Scholar]
- Power, G.; Gräfe, M.; Klauber, C. Bauxite residue issues: I. Current management, disposal and storage practices. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 108, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, T.; Pontikes, Y. Geopolymers, inorganic polymers, alkali-activated materials and hybrid binders from bauxite residue (red mud)–Putting things in perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikbin, I.M.; Aliaghazadeh, M.; Charkhtab, S.H.; Fathollahpour, A. Environmental impacts and mechanical properties of lightweight concrete containing bauxite residue (red mud). J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 2683–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, H.; Sahoo, P.; Sahoo, A. Characterization of Red Mud treated under high temperature fluidization. Powder Technol. 2015, 269, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, H.; Han, H.; Qiao, P. Synthesis of LDHs using red mud and bittern and its influence on the flame retardant properties of EVA/LDHs composites. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2020, 28, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneshwaran, S.; Uthayakumar, M.; Arumugaprabu, V. Development and sustainability of industrial waste-based red mud hybrid composites. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 230, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfroi, E.P.; Cheriaf, M.; Rocha, J.C. Microstructure, mineralogy and environmental evaluation of cementitious composites produced with red mud waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 67, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, B.; Freire, L.; Nóvoa, X.R.; Pérez, M.C. Chloride and CO2 transport in cement paste containing red mud. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2015, 62, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brentner, L.B.; Eckelman, M.J.; Zimmerman, J.B. Combinatorial life cycle assessment to inform process design of industrial production of algal biodiesel. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7060–7067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyce, P.J.; Hertel, T.; Goronovski, A.; Tkaczyk, A.H.; Pontikes, Y.; Björklund, A. Identifying hotspots of environmental impact in the development of novel inorganic polymer paving blocks from bauxite residue. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 138, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabu, V.A.; Johnson, R.D.J.; Amuthakkannan, P.; Manikandan, V. Usage of industrial wastes as particulate composite for environment management: Hardness, tensile and impact studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1289–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, S.; Rajakarunakaran, S.; Pandian, R.S. Modeling and optimization of sliding specific wear and coefficient of friction of aluminum based red mud metal matrix composite using taguchi method and response surface methodology. Mater. Phys. Mech. 2012, 15, 150–166. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.-X.; Poon, C.-S. Utilization of red mud derived from bauxite in self-compacting concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, N.; Yang, J.; Liang, S.; Hu, Y.; Hu, J.; Xiao, B.; Huang, Q. Synthesis and strength optimization of one-part geopolymer based on red mud. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 111, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthayakumar, M.; Manikandan, V.; Rajini, N.; Jeyaraj, P. Influence of redmud on the mechanical, damping and chemical resistance properties of banana/polyester hybrid composites. Mater. Des. 2014, 64, 270–279. [Google Scholar]
- Fedroff, D.; Ahmad, S.; Savas, B.Z. Mechanical properties of concrete with ground waste tire rubber. Transp. Res. Rec. 1996, 1532, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganeshan, P.; Raja, K. Improvement on the Mechanical Properties of Madar Fiber Reinforced Polyester Composites. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Technol./Vol. VII/Issue II/April–June 2016, 261, 264. [Google Scholar]
- Saradava, B.J.; Rachchh, N.V.; Misra, R.K.; Roychowdhary, D.G. Mechanical characterization of coir fiber reinforced polymer composite using red mud as filler. J. Inf. Knowl. Res. Mech. Eng. 2013, 2, 472–476. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Jdayil, B.; Adi, M.; Al Ghaferi, F.; Al Yahyaee, S.; Al Jabri, M. Physical and thermal insulation properties of the composites based on seawater-neutralised bauxite residue. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 123723. [Google Scholar]
- Alavudeen, A.; Rajini, N.; Karthikeyan, S.; Thiruchitrambalam, M.; Venkateshwaren, N. Mechanical properties of banana/kenaf fiber-reinforced hybrid polyester composites: Effect of woven fabric and random orientation. Mater. Des. (1980–2015) 2015, 66, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makki, M.S.I.; Abdelaal, M.Y.; Bellucci, S.; Abdel Salam, M. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes/unsaturated polyester composites: Mechanical and thermal properties study. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 2014, 22, 820–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, S.K.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Bang, S.S. Remediation of concrete using micro-organisms. ACI Mater. J. Am. Concr. Inst. 2001, 98, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Topcu, I.B. The properties of rubberized concretes. Cem. Concr. Res. 1995, 25, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedari, J.; Suttisonk, B.; Pratinthong, N.; Hirunlabh, J. New lightweight composite construction materials with low thermal conductivity. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2001, 23, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benazzouk, A.; Douzane, O.; Mezreb, K.; Laidoudi, B.; Quéneudec, M. Thermal conductivity of cement composites containing rubber waste particles: Experimental study and modelling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MolaAbasi, H.; Saberian, M.; Li, J. Prediction of compressive and tensile strengths of zeolite-cemented sand using porosity and composition. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 202, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbeche, S.M.; Wambua, P.M.; Githinji, D.N. Mechanical Properties of Sisal/Cattail Hybrid-Reinforced Polyester Composites. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Jdayil, B.; Mourad, A.-H.; Hittini, W.; Hassan, M.; Hameedi, S. Traditional, state-of-the-art and renewable thermal building insulation materials: An overview. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 214, 709–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Jdayil, B.; Mourad, A.-H.I.; Hussain, A. Investigation on the mechanical behavior of polyester-scrap tire composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 127, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-R.; Park, H.-M.; Lim, H.; Kang, T.; Li, X.; Cho, W.-J.; Ha, C.-S. Microstructure, tensile properties, and biodegradability of aliphatic polyester/clay nanocomposites. Polymer 2002, 43, 2495–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Yuan, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Zheng, J. Investigation of the fatigue modulus decay in cement stabilized base material by considering the difference between compressive and tensile modulus. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 223, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okonkwo, E.G.; Anabaraonye, C.N.; Daniel-Mkpume, C.C.; Egoigwe, S.V.; Okeke, P.E.; Whyte, F.G.; Okoani, A.O. Mechanical and thermomechanical properties of clay-Bambara nut shell polyester bio-composite. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, A.M. State of the art in thermal insulation materials and aims for future developments. Energy Build. 2005, 37, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, A.C.C.; Rohen, L.A.; Mantovani, D.P.; Carvalho, J.P.R.G.; Vieira, C.M.F.; Lopes, F.P.D.; Simonassi, N.T.; da Luz, F.S.; Monteiro, S.N. Comparative mechanical properties between biocomposites of Epoxy and polyester matrices reinforced by hemp fiber. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohama, Y.; Ramachandran, V.S. Polymer-modified mortars and concretes. In Concrete Admixtures Handbook; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 558–656. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L. Study of the Possibilities of Using Red Mud as an Additive in Concrete and Grout Mortar; Citeseer: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zainudin, E.S.; Sapuan, S.M.; Abdan, K.; Mohamad, M.T.M. Mechanical properties of compression molded banana pseudo-stem filled unplasticized polyvinyl chloride (UPVC) composites. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2008, 48, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, S.M.D.; Goncalves, A.R.; Del’Arco, A.P., Jr. Mechanical behavior and microstructural analysis of sugarcane bagasse fibers reinforced polypropylene composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.; Sudhakara, D.; Vinod, B. Investigation on industrial waste eco-friendly natural fiber-reinforced polymer composites. J. Bio-Tribo-Corros. 2020, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristics. | UPR | BR–UPR Composite (20%) | BR–UPR Composite (40%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bulk density ρ (kg/m3) | 1200 | 1261 | 1484 |
| Thermal conductivity k ( | 0.098 | 0.082 | 0.096 |
| Thermal diffusivity, () | - | 0.272 | 0.161 |
| 24 h water retention @ 25 °C (wt.%) | 0.024 | 0.101 | 0.118 |
| Overall weight change (%) upon thermal load | 99.85 | 93.32 | 59.33 |
| BR-UPR Composite | BR Content (vol.%) | UPR Content (vol.%) |
|---|---|---|
| Pure polyester | 0 | 100 |
| 10 vol.% BR | 10 | 90 |
| 20 vol.% BR | 20 | 80 |
| 30 vol.% BR | 30 | 70 |
| 40 vol.% BR | 40 | 60 |
| 50 vol.% BR | 50 | 50 |
| 60 vol.% BR | 60 | 40 |
| Mechanical Property | BR Content (vol.%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | ||
| Compressive | σf 1 (MPa) | 65.2 ± 6.7 | 41.5 ± 1.9 | 108.7 ± 1.8 | 92.6 ± 1.5 | 74.7 ± 0.6 | 53.0 ± 8.1 | 62.1 ± 0.3 |
| E 2 (GPa) | 0.7 ± 0.01 | 0.7 ± 0.08 | 0.8 ± 0.03 | 1 ± 0.02 | 0.9 ± 0.004 | 0.5 ± 0.001 | 0.5 ± 0.005 | |
| Strain (%) | 40.8 ± 0.15 | 41.6 ± 0.4 | 51.2 ± 0.2 | 42.1 ± 0.08 | 34.4 ± 0.2 | 18.6 ± 0.4 | 18.8 ± 0.6 | |
| Tensile | σf (MPa) | 27.6 ± 1.3 | 19.3 ± 1.8 | 13.1 ± 0.3 | 9.1 ± 0.21 | 10.5 ± 0.13 | 8.1 ± 0.1 | 4 ± 0.23 |
| E (GPa) | 0.9 ± 0.02 | 0.9 ± 0.02 | 1.07 ± 0.02 | 1.4 ± 0.01 | 1.2 ± 0.01 | 1.2 ± 0.02 | 0.9 ± 0.01 | |
| Strain (%) | 4.4 ± 0.4 | 3.1 ± 0.3 | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 1.5 ± 0.3 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | |
| Flexure | σf (MPa) | 53.3 ± 3.7 | 30.1 ± 1.7 | 23.1 ± 1.5 | 24.6 ± 2.02 | 15.5 ± 1.7 | 14.1 ± 1.9 | 23.6 ± 1.04 |
| E (GPa) | 24.3 ± 0.03 | 43.9 ± 0.01 | 41.3 ± 1.2 | 33.9 ± 0.4 | 23.5 ± 0.4 | 22.8 ± 0.2 | 12.3 ± 0.3 | |
| Strain (%) | 0.6 ± 0.04 | 0.3 ± 0.02 | 0.2 ± 0.04 | 0.2 ± 0.03 | 0.2 ± 0.02 | 0.2 ± 0.04 | 0.1 ± 0.04 | |
| Element | Mass% | |
|---|---|---|
| UPR | BR–UPR Composite (40%) | |
| C K | 78.23 | 50.1 |
| O K | 18.25 | 28.28 |
| Mg K | 0.80 | 0.73 |
| Fe K | - | 10.82 |
| Al K | - | 4.02 |
| Si K | - | 4.02 |
| Na K | - | 2.03 |
| Ca K | 2.72 | - |
| Total | 100 | 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adi, M.; Abu-Jdayil, B.; Al Ghaferi, F.; Al Yahyaee, S.; Al Jabri, M. Seawater-Neutralized Bauxite Residue–Polyester Composites as Insulating Construction Materials. Buildings 2021, 11, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings11010020
Adi M, Abu-Jdayil B, Al Ghaferi F, Al Yahyaee S, Al Jabri M. Seawater-Neutralized Bauxite Residue–Polyester Composites as Insulating Construction Materials. Buildings. 2021; 11(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings11010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdi, Maissa, Basim Abu-Jdayil, Fatima Al Ghaferi, Sara Al Yahyaee, and Maryam Al Jabri. 2021. "Seawater-Neutralized Bauxite Residue–Polyester Composites as Insulating Construction Materials" Buildings 11, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings11010020
APA StyleAdi, M., Abu-Jdayil, B., Al Ghaferi, F., Al Yahyaee, S., & Al Jabri, M. (2021). Seawater-Neutralized Bauxite Residue–Polyester Composites as Insulating Construction Materials. Buildings, 11(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings11010020






