Effect of Niobium Addition on the High-Temperature Oxidation Behavior of 22Cr25NiWCoCu Stainless Steel in Air
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment and Method
2.1. Materials and Sample Preparation
2.2. High-Temperature Oxidation Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure Analysis of As-Reannealed Specimens
3.2. High-Temperature Oxidation Behavior
3.3. Analysis of Oxide Surface Morphology
3.4. Analysis of Oxide Layers at Cross-Section
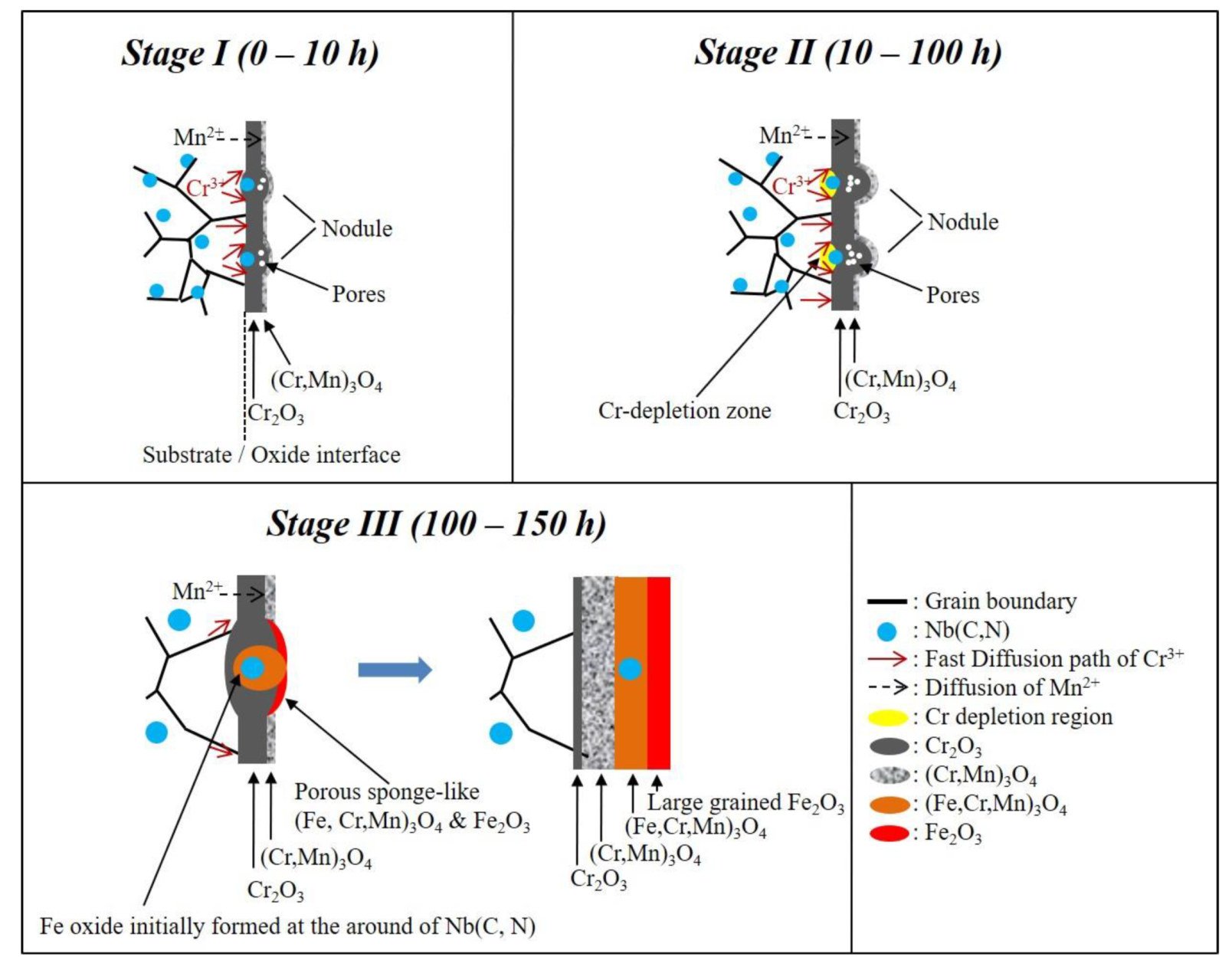
3.5. Effect of Nb Addition on Oxidation Behavior
3.6. Effect of Precipitates on the Oxidation Behavior
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Energy Agency. Global Energy & CO2 Status Report–The latest trends in energy and emissions in 2017. Available online: https://www.iea.org/publications/freepublications/publication/GECO2017.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2018).
- Aroonwilas, A.; Veawab, A. Integration of CO2 capture unit using single- and blended-amines into supercritical coal-fired power plants: Implications for emission and energy management. Int. J. Greenh. Gas. Control. 2007, 1, 43–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, G.C.; Wright, I.G.; Hodgkiess, T.; Whittle, D.P. A Comparison of the Oxidation of Fe-Cr, Ni-Cr and Co-Cr Alloys in Oxygen and Water Vapour. Mater. Corros. 1970, 21, 900–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birks, N.; Meier, G.H.; Pettit, F.S. Introduction to the high temperature oxidation of metals, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; ISBN 978-0-521-48042-0. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, G.; Nilsson, J.O.; Boström, M.; Högberg, J.; Forsberg, U. Advanced Heat Resistant Austenitic Stainless Steels. In Advanced Steels: The recent scenario in steel science and technology; Weng, Y., Dong, H., Gan, Y., Eds.; Springer-Verlag GmbH: Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 385–396. ISBN 978-3-319-19165-2. [Google Scholar]
- Intiso, L.; Johansson, L.G.; Canovic, S.; Bellini, S.; Svensson, J.E.; Halvarsson, M. Oxidation Behaviour of Sanicro 25 (42Fe22Cr25NiWCuNbN) in O2/H2O Mixture at 600 °C. Oxid. Met. 2012, 77, 209–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intiso, L.; Johansson, L.G.; Svensson, J.E.; Halvarsson, M. Oxidation of Sanicro 25 (42Fe22Cr25NiWCuNbN) in O2 and O2 + H2O Environments at 600—750 °C. Oxid. Met. 2015, 83, 367–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurek, J.; Yang, S.M.; Lin, D.Y.; Hüttel, T.; Singheiser, L.; Quadakkers, W.J. Microstructural stability and oxidation behavior of Sanicro 25 during long-term steam exposure in the temperature range 600–750 °C. Mater. Corros. 2015, 66, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowski, B.; Gil, A.; Czyrska-Filemonowicz, A. Microstructure and chemical composition of the oxide scale formed on the Sanicro 25 steel tubes after fireside corrosion. Corrosion Sci. 2016, 102, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowski, B.; Galanis, A.S.; Gil, A.; Czyrska-Filemonowicz, A. A novel approach to the characterization of thin oxide layers. Mater. Lett. 2016, 173, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, G.C.; Tempest, P.A.; Tyler, J.W.; Wild, R.K. Oxidation behavior of 20%Cr/25%Ni/Nb stabilized stainless steel in CO2 environments. Oxid. Met. 1984, 21, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, J.W. Characterization of the initial oxide formed on annealed and unannealed 20Cr-25Ni-Nb-stabilized steel in 50 torr CO2 at 973 K. Oxid. Met. 1985, 24, 149–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.Y.; Kuo, J.C.; Tsai, W.T.; Lin, D.Y.; Pan, Y.T. Effect of Niobium on Microstructure and Precipitation in As-annealed Sanicro 25 Steel. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobb, R.C.; Evans, H.E. A determination of the chromium concentration for ‘healing’ layer formation during the oxidation of chromium-depleted 20Cr-25Ni-Nb stainless steel. Corrosion Sci. 1984, 24, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledjeff, K.; Rahmel, A.; Schorr, M. Influence of Metal Grain Growth on the Oxidation Behavior of a 25Cr-20Ni Steel. Oxid. Met. 1981, 15, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trindade, V.B.; Krupp, U.; Hanjari, B.Z.; Yang, S.; Christ, H.J. Effect of alloy grain size on the high-temperature oxidation behavior of the austenitic steel TP 347. J. Mater. Res. 2005, 8, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, D.I.; Suwas, S.; Fleury, E.; Yi, K.W. Grain-Size Effects on the High-Temperature Oxidation of Modified 304 Austenitic Stainless Steel. Oxid. Met. 2013, 79, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Yan, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, F. Effect of grain refinement on the resistance of 304 stainless steel to breakaway oxidation in wet air. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 5079–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y. Oxidation behavior of TiC particle-reinforced 304 stainless steel. Corrosion Sci. 2010, 52, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Wang, W.; Zhu, S.L.; Wang, F.H. Oxidation Behavior of Super 304H Steel in Steam at 700–900 °C. J. Chin. Soc. Corros. Prot. 2014, 34, 218–224. [Google Scholar]
- Birosca, S.; Dingley, D.; Higginson, R.L. Microstructural and microtextural characterization of oxide scale on steel using electron backscatter diffraction. J. Microsc. 2003, 213, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, G.D.; Birosca, S.; Higginson, R.L. Phase determination and microstructure of oxide scales formed on steel at high temperature. J. Microsc. 2003, 217, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higginson, R.L.; Jepson, M.A.E.; West, G.D. Use of EBSD to Characterise high temperature oxides formed on low alloy and stainless steels. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2006, 22, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, D.I.; Shim, J.H.; Yi, K.W. Investigation into the high temperature oxidation of Cu-bearing austenitic stainless steel using simultaneous electron backscatter diffraction-energy dispersive spectroscopy analysis. Corrosion Sci. 2013, 77, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, E.W. On the role of dislocations in bulk diffusion. Acta Metallurgica 1957, 5, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeltzer, W.W.; Haering, R.R.; Kirkaldy, J.S. Oxidation of metals by short circuit and lattice diffusion of oxygen. Acta Metallurgica 1961, 9, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzig, C.; Mishin, Y. Grain Boundary Diffusion in Metals. In Diffusion in condensed matter: Methods, materials, models; Heitjans, P., Kärger, J., Eds.; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 336–366. ISBN 978-3-540-30970-3. [Google Scholar]
- Wind, R.K. High temperature oxidation of austenitic stainless steel in low oxygen pressure. Corrosion Sci. 1977, 17, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeguas, F.; Lee, L. Oxidation of Iron-aluminum alloys in the range 500–1000 °C. Corrosion 1966, 22, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewicz, P.; Wallwork, G.R. Observations of nodule growth during the oxidation of pure binary iron-aluminum alloys. Oxid. Met. 1983, 19, 165–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewicz, P.; Wallwork, G.R. The oxidation of high-purity iron-chromium-aluminum alloys at 800 °C. Oxid. Met. 1983, 20, 75–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, P.R.S.; Wallwork, G.R. High temperature oxidation of iron-manganese-aluminum based alloys. Oxid. Met. 1984, 21, 135–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pint, B.A.; Wright, I.G. Long-term high temperature oxidation behavior of ODS ferritics. J. Nucl. Mater. 2002, 307–311, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.G.; Hou, P.Y.; Gesmundo, F.; Niu, Y. Effect of surface roughness on the development of protective Al2O3 on Fe-10Al (at.%) alloys containing 0–10 at.% Cr. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 253, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, G.C.; Whittle, D.P. The mechanism of breakthrough of protective chromium oxide scales on Fe-Cr alloys. Corrosion Sci. 1967, 7, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, G.C. High-Temperature Oxidation of Alloys. Oxid. Met. 1970, 2, 11–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasco, A.L.; Young, D.J. The oxidation of Iron-Chromium-Manganese alloys at 900 °C. Oxid. Met. 1991, 36, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplan, D.; Sproule, G.I. Effect of oxide grain structure on the high-temperature oxidation of Cr. Oxid. Met. 1975, 9, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, H.V. A review of the role of short-circuit diffusion in the oxidation of nickel, chromium, and nickel-chromium alloys. Oxid. Met. 1985, 24, 117–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Specimen | Fe | Cr | Ni | W | Cu | Co | N | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Nb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-Nb | Bal. | 22.20 | 24.40 | 3.39 | 2.90 | 1.47 | 0.23 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 0.49 | 0.009 | 0.005 | 0 |
| 0.29-Nb | Bal. | 22.10 | 24.30 | 3.40 | 2.90 | 1.49 | 0.23 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 0.49 | 0.01 | 0.005 | 0.29 |
| 0.58-Nb | Bal. | 21.90 | 24.20 | 3.36 | 2.90 | 1.45 | 0.23 | 0.07 | 0.20 | 0.49 | 0.01 | 0.005 | 0.58 |
| 0.86-Nb | Bal. | 21.80 | 24.10 | 3.52 | 2.90 | 1.54 | 0.23 | 0.07 | 0.20 | 0.49 | 0.01 | 0.005 | 0.86 |
| Specimen | 0-Nb | 0.29-Nb | 0.58-Nb | 0.86-Nb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HV) | 214.3 ± 8.2 | 218.2 ± 8.4 | 214.6 ± 4.6 | 210.9 ± 7.4 |
| Specimen | Kpo | n | C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0-Nb | 0.08 | 1.86 | 0.54 |
| 0.29-Nb | 0.10 | 1.92 | 0.52 |
| 0.58-Nb | 0.44 | 3.70 | 0.27 |
| 0.86-Nb | 0.44 | 3.08 | 0.32 |
| Specimen. | Time (h) | Cr2O3 (%) | M3O4 (%) | Fe2O3 (%) | γ (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-Nb | 10 | 72.1 | 20.6 | 0 | 7.3 |
| 25 | 64.5 | 26.9 | 0 | 8.6 | |
| 50 | 66.4 | 32.0 | 0.1 | 1.5 | |
| 75 | 71.8 | 26.9 | 0.4 | 0.9 | |
| 100 | 67.8 | 28.0 | 0 | 4.2 | |
| 150 | 73.5 | 23.5 | 2.7 | 0.3 | |
| 0.29-Nb | 10 | 76.8 | 9.8 | 0 | 13.4 |
| 25 | 76.0 | 10.1 | 0 | 13.9 | |
| 50 | 76.3 | 19.5 | 3.4 | 0.8 | |
| 75 | 87.4 | 7.5 | 0 | 5.1 | |
| 100 | 86.7 | 9.6 | 2.7 | 1.0 | |
| 150 | 80.5 | 12.3 | 0.9 | 6.3 | |
| 0.58-Nb | 10 | 75.8 | 8.2 | 0 | 16.0 |
| 25 | 79.9 | 12.7 | 2.8 | 4.6 | |
| 50 | 82.6 | 17.3 | 0 | 0.1 | |
| 75 | 91.9 | 5.8 | 1.6 | 0.7 | |
| 100 | 90.3 | 6.5 | 2.4 | 0.8 | |
| 150 | 40.1 | 16.7 | 38.1 | 5.1 | |
| 0.86-Nb | 10 | 75.7 | 9.1 | 1.7 | 13.5 |
| 25 | 86.5 | 11.0 | 2.0 | 0.5 | |
| 50 | 83.6 | 14.4 | 0 | 2.0 | |
| 75 | 93.1 | 6.0 | 0.7 | 0.2 | |
| 100 | 81.7 | 8.2 | 9.4 | 0.7 | |
| 150 | 26.5 | 12.1 | 53.1 | 8.3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, S.-Y.; Tsai, W.-T.; Pan, Y.-T.; Kuo, J.-C.; Chen, H.-W.; Lin, D.-Y. Effect of Niobium Addition on the High-Temperature Oxidation Behavior of 22Cr25NiWCoCu Stainless Steel in Air. Metals 2019, 9, 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9090975
Huang S-Y, Tsai W-T, Pan Y-T, Kuo J-C, Chen H-W, Lin D-Y. Effect of Niobium Addition on the High-Temperature Oxidation Behavior of 22Cr25NiWCoCu Stainless Steel in Air. Metals. 2019; 9(9):975. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9090975
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Sheng-Yao, Wen-Ta Tsai, Yeong-Tsuen Pan, Jui-Chao Kuo, Hsien-Wei Chen, and Dong-Yih Lin. 2019. "Effect of Niobium Addition on the High-Temperature Oxidation Behavior of 22Cr25NiWCoCu Stainless Steel in Air" Metals 9, no. 9: 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9090975
APA StyleHuang, S.-Y., Tsai, W.-T., Pan, Y.-T., Kuo, J.-C., Chen, H.-W., & Lin, D.-Y. (2019). Effect of Niobium Addition on the High-Temperature Oxidation Behavior of 22Cr25NiWCoCu Stainless Steel in Air. Metals, 9(9), 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9090975




