Influence of Shot Peening Treatment in Erosion Wear Behavior of High Chromium White Cast Iron
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material, Specimens, Treatments, Experimental Procedures, and Results
2.1. Material and Specimens
2.2. Treatments
2.2.1. Heat Treatments
2.2.2. Shot Peening Treatment
2.3. Optical Microscopy Analysis
2.4. Phase Analysis by X-Ray Diffraction and SEM Observation
2.5. Hardness Measurement
2.6. Roughness Measurement
2.7. Erosion Tests
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rundman, K.B.; Lacoviello, F. Cast Irons, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R. Applied Welding Engineering; Processes; Codes and Standards; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara, Y.; Sasaguri, N.; Shimizu, K.; Yu, S.K. Solidification and abrasion wear of white cast irons alloyed with 20% carbide forming elements. Wear 2001, 250, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, T.A.; Dogan, Ö.N. Erosive wear and impact damage of high-chromium white cast irons. Wear 1999, 225–229, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çetinkaya, C. An investigation of the wear behaviours of white cast irons under different compositions. Mater. Des. 2006, 27, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Hao, Q.; Zuo, X.; Chen, N.; Rong, Y. High hardness and toughness of white cast iron: The proposal of a novel process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 618, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karantzalis, A.E.; Lekatou, A.; Mavros, H. Microstructural Modifications of As-Cast High-Chromium White Iron by Heat Treatment. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2009, 18, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrett, C.P.; Sare, I.R. The effect of heat treatment on the abrasion resistance of alloy white irons. Wear 1997, 203–204, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiengmoon, A.; Chairuangsri, T.; Brown, A.; Brydson, R.; Edmonds, D.V.; Pearce, J.T.H. Microstructural and crystallographical study of carbides in 30wt.%Cr cast irons. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 4143–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.H.; Chung, R.; Pang, C.J.; Li, D.Y.; Hinckley, B.; Dolman, K. Microstructure of high (45 wt.%) chromium cast irons and their resistances to wear and corrosion. Wear 2011, 271, 1426–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, G.; Gundlach, R.; Röhrig, K. Abrasion-Resistant Cast Iron Handbook; American Foundry Society: Schaumburg, IL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gundlach, R. High-alloy white irons. In ASM Handbook Volume 15: Casting, formerly 9th ed.; Metals Handbook; ASM International: Geauga County, OH, USA, 1988; pp. 395–448. [Google Scholar]
- Schön, C.; Sinatora, A. Simulation of solidification paths in high chromium white cast irons for wear applications. Calphad 1998, 22, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pero, J.; Plaza, D.; Verdeja, J.; Asensio, J. Metallographic Characterization of Hypoeutectic Martensitic White Cast Irons: Fe-C-Cr System. Mater. Charact. 1999, 43, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertin, E.; Sinatora, A. Effect of carbide fraction and matrix microstructure on the wear of cast iron balls tested in a laboratory ball mill. Wear 2001, 250, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Jiang, Y.; Xiao, H.; Tan, J. Study on fragmentation and dissolution behavior of carbide in a hot-rolled hypereutectic high chromium cast iron. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 618, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Pariente, I.; Belzunce-Varela, F.J. Influencia de diversos tratamientos térmicos en la microestructura de una fundicion blanca con alto contenido en cromo. Rev. Metal. 2006, 42, 279–286. [Google Scholar]
- Dogan, O.N.; Hawk, J.A.; Laird, Y.G., II. Solidification structure and abrasion resistance of high chromium white irons. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1997, 28, 1315–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairhust, W.; Rohrig, K. Abrasion resistant high chromium cast irons. Foundry Trade J. 1974, 136, 685–698. [Google Scholar]
- Pero, J.A. Fundiciones Férreas; Ed. Dossat: Madrid, Spain, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Heino, V.; Kallio, M.; Valtonen, K.; Kuokkala, V.-T. The role of microstructure in high stress abrasion of white cast irons. Wear 2017, 388–389, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; San-Martín, D.; Rivera, P.E.J. Stability of retained austenite in martensitic high carbon steels. Part I: Thermal stability. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 711, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, W.; Gintalas, M.; Rivera, P.E.J. Stability of retained austenite in martensitic high carbon steels. Part II: Mechanical stability. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 711, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gasan, H.; Ertuk, F. Effects of a destabilization heat treatment on the microstructure and abrasive wear behavior of high chromium white cast iron investigated using different characterization techniques. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 4993–5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, L.; Barbosa, A.; Viana, F.; Baptista, A.M.; Dias, C.; Ribeiro, C.A. Abrasion wear behaviour of alloyed and chilled cast irons. Wear 2011, 270, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherifard, S.; Slawik, S.; Fernández, I.; Pauly, C.; Mücklich, F.; Guagliano, M. Nanoscale surface modification of AISI 316L stainless steel by severe shot peening. Mater. Des. 2016, 102, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guagliano, M.; Vergani, L. An approach for prediction of fatigue strength of shot peened components. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2004, 71, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, C.; Guagliano, M.; Vergani, L. Fatigue Crack Growth Behaviour of nitrided and Shot Peened Specimens. SID 2005, 1, 253–265. [Google Scholar]
- Almen, J.O.; Black, P.H. Residual Stresses and Fatigue in Metals; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Bagherifard, S.; Fernández-Pariente, I.; Ghelichi, R.; Guagliano, M. Effect of severe shot peening on microstructure and fatigue strength of cast iron. Int. J. Fatigue 2014, 65, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pang, M. Fatigue life prediction of shot-peened steel. Int. J. Fatigue 2012, 43, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Real, E.; Rodríguez, C.; Belzunce, F.J.; Sanjurjo, P.; Canteli, A.F.; Fernández, I. Fatigue behaviour of duplex stainless steel reinforcing bars subjected to shot peening. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2009, 32, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherifard, S.; Fernández, I.; Ghelichi, R.; Guagliano, M. Fatigue behavior of notched steel specimens with nanocrystallized surface obtained by severe shot peening. Mater. Des. 2013, 45, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, I.; Guagliano, M. About the role of residual stresses and surface work hardening on fatigue ΔKth of a nitrided and shot peened low-alloy steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 3072–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhaede, M. Influence of surface treatments on surface layer properties; fatigue and corrosion fatigue performance of AA7075 T73. Mater. Des. 2012, 41, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, B.; Yazdi, M.R.; Azar, V. The wear and corrosion resistance of shot peened–nitrided 316L austeniticstainless steel. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 3287–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, J.; Bagherifard, S.; Guagliano, M.; Fernández, I. Influence of different shot peening treatments on surface state and fatigue behaviour of Al 6063 alloy. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2017, 185, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imurai, S.; Thanachayanont, C.; Pearce, J.T.H.; Chairuangsri, T. Microstructure and erosion-corrosion behaviour of as-cast high chromium white irons containing molybdenum in aqueous sulfuric-acid slurry. Arch. Metal. Mater. 2015, 60, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCusker, L.B.; von Dreele, R.B.; Cox, D.E.; Louërd, D.; Scardie, P. Rietveld refinement guidelines. J. Appl. Cryst. 1999, 32, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ASTM. E975-03 Standard Practice for X-Ray Determination of Retained Austenite in Steel with Near Random Crystallographic Orientation. ASTM Int. 2008, E975-13, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
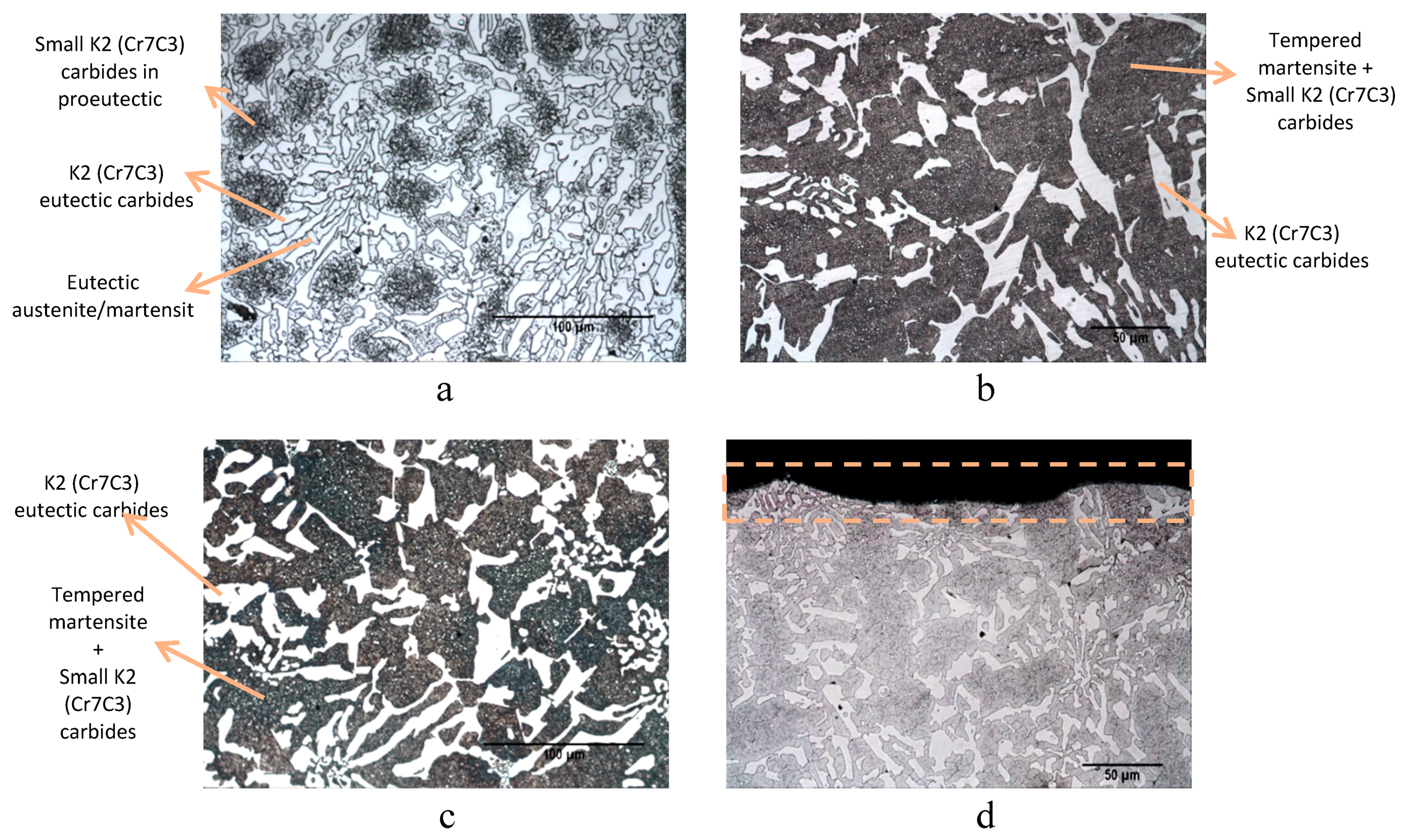



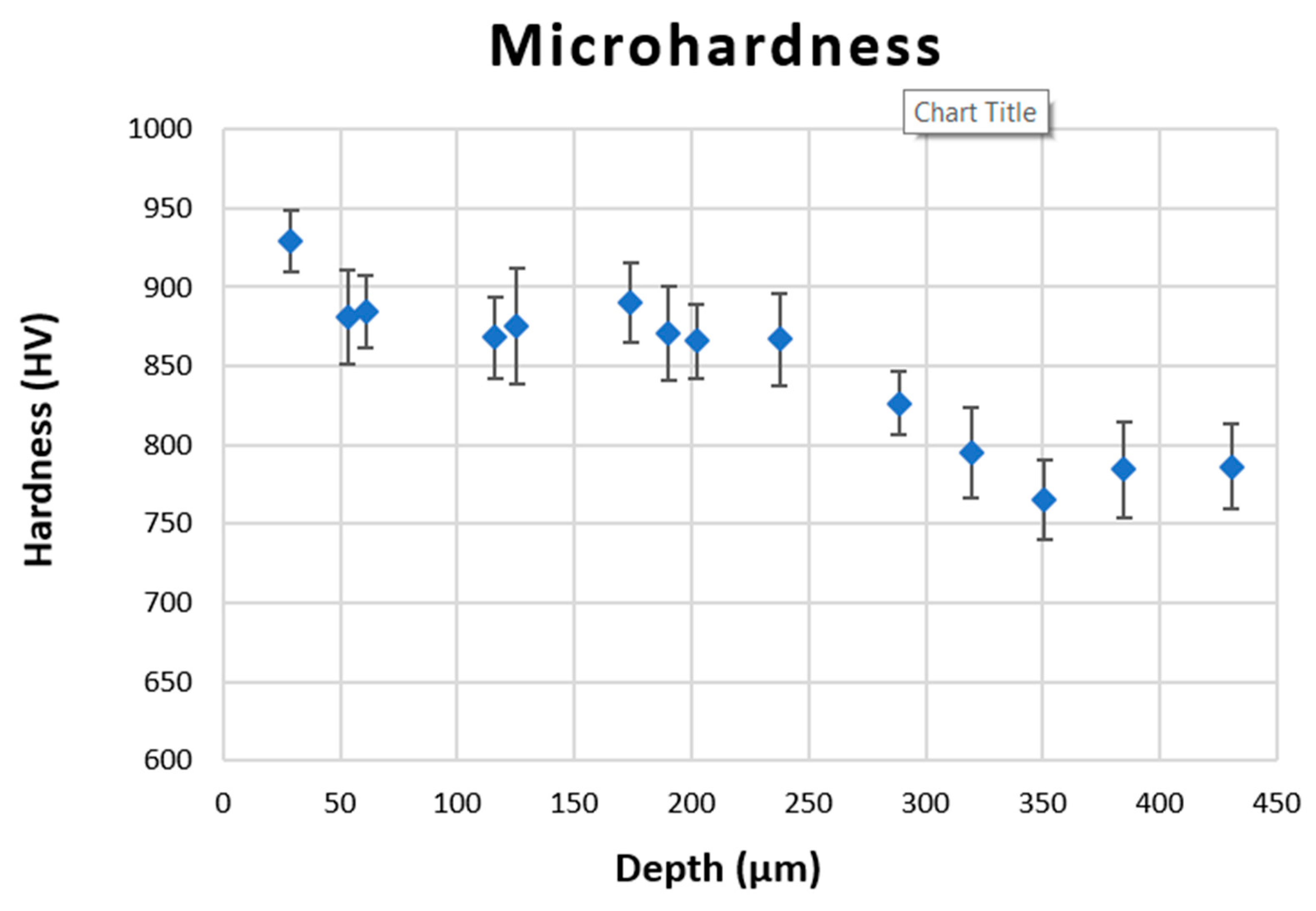

| 18%Cr-WCI | %C | %Si | %Mn | %Cr | %Mo |
| 3.01 | 1.17 | 0.82 | 18.2 | 2.05 |
| Treatment | Shot Diameter (mm) | Almen Intensity (0.0001 in.) | Time of Treatment (s) | Surface Coverage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional shot peening | 0.3 | 10A | 8 | 100 |
| Shots | Chemical Composition (%wt) | Diameter (mm) | Density (g/cm3) | Hardness (HV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zirshot Y300 | ZrO2 > 75% SiO2 < 25% | ~0.3 | 4.6 | 1000 |
| 18%Cr-WCI-Q | 18%Cr-WCI + Austenizing (1000 °C-6 h) + Air Quenching |
| 18%Cr-WCI-T | 18%Cr-WCI-Q + Tempering (500 °C-8 h) |
| 18%Cr-WCI-2T | 18%Cr-WCI-Q + Double tempering (500 °C-8 h) |
| 18%Cr-WCI-SP | 18%Cr-WCI-Q + SP (100% coverage) |
| Maximum Voltage (kV) | 30 | Maximum Intensity (mA) | 6.7 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radiation | Cr Kα. λ = 0.2291 nm | Carbides (%) | 0−Vc * |
| Filter | Vanadio | Colimator diameter (mm) | 5 |
| Austenite plane | (220) | Austenite diffraction angle (2θ°) | 130 |
| (200) | 80 | ||
| Ferrite plane | (211) | Ferrite diffraction angle (2θ°) | 156.4 |
| (200) | 106.1 |
| Series | HV |
|---|---|
| 18%Cr-WCI-Q | 783 ± 12 |
| 18%Cr-WCI-T | 575 ± 9 |
| 18%Cr-WCI-2T | 700 ± 39 |
| Sample | Roughnes Parameter | Average Values |
|---|---|---|
| 18%Cr-WCI-Q | Ra | 0.172 ± 0.087 |
| Rq | 0.273 ± 0.142 | |
| Rz | 1.272 ± 0.544 | |
| 18%Cr-WCI-T | Ra | 0.143 ± 0.091 |
| Rq | 0.172 ± 0.227 | |
| Rz | 0.970 ± 0.599 | |
| 18%Cr-WCI-2T | Ra | 0.121 ± 0.088 |
| Rq | 0.152 ± 0.121 | |
| Rz | 0.820 ± 0.629 | |
| 18%Cr-WCI-SP | Ra | 0.213 ± 0.025 |
| Rq | 0.116 ± 0.034 | |
| Rz | 0.662 ± 0.259 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González, J.; Peral, L.B.; Zafra, A.; Fernández-Pariente, I. Influence of Shot Peening Treatment in Erosion Wear Behavior of High Chromium White Cast Iron. Metals 2019, 9, 933. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9090933
González J, Peral LB, Zafra A, Fernández-Pariente I. Influence of Shot Peening Treatment in Erosion Wear Behavior of High Chromium White Cast Iron. Metals. 2019; 9(9):933. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9090933
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález, Juan, Luis Borja Peral, Alfredo Zafra, and Inés Fernández-Pariente. 2019. "Influence of Shot Peening Treatment in Erosion Wear Behavior of High Chromium White Cast Iron" Metals 9, no. 9: 933. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9090933
APA StyleGonzález, J., Peral, L. B., Zafra, A., & Fernández-Pariente, I. (2019). Influence of Shot Peening Treatment in Erosion Wear Behavior of High Chromium White Cast Iron. Metals, 9(9), 933. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9090933




