Influence of Tempering Time on the Behavior of Large Carbides’ Coarsening in AISI H13 Steel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
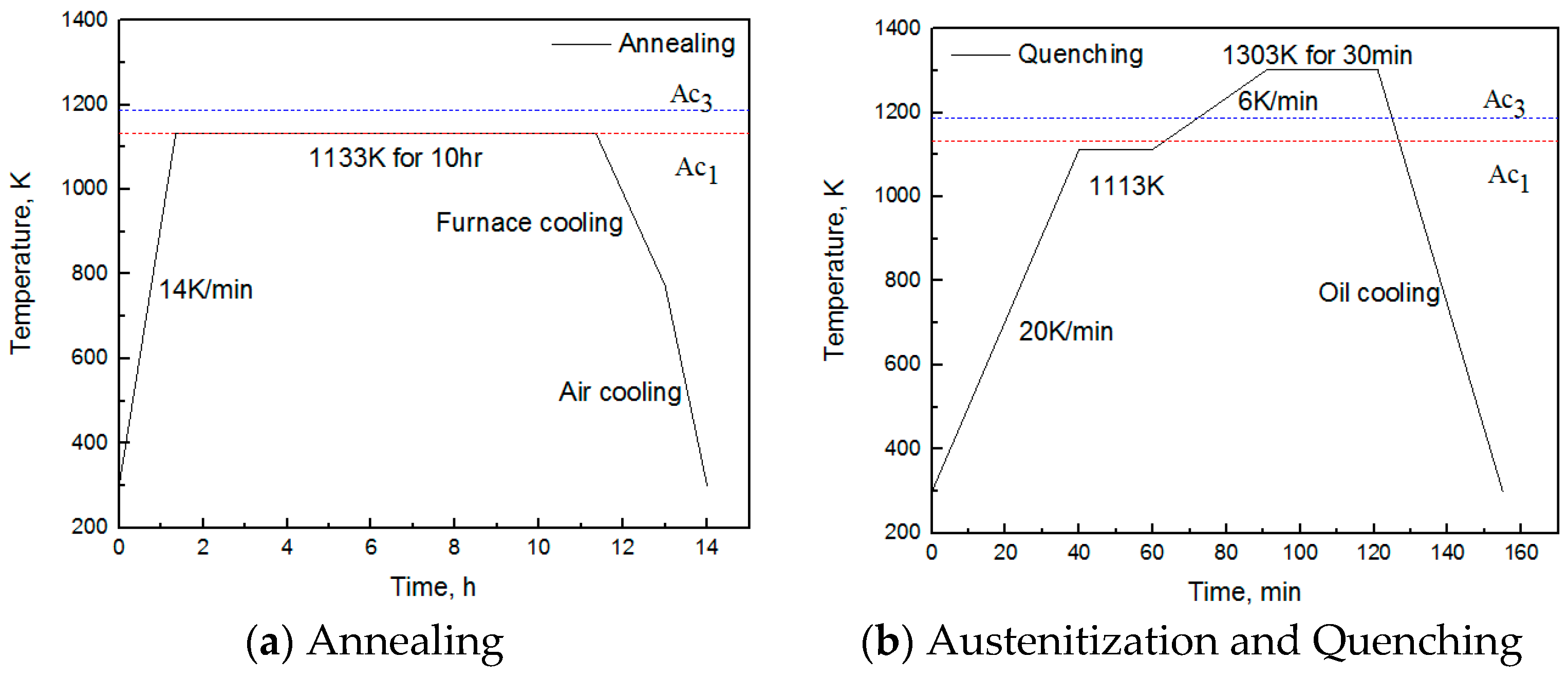
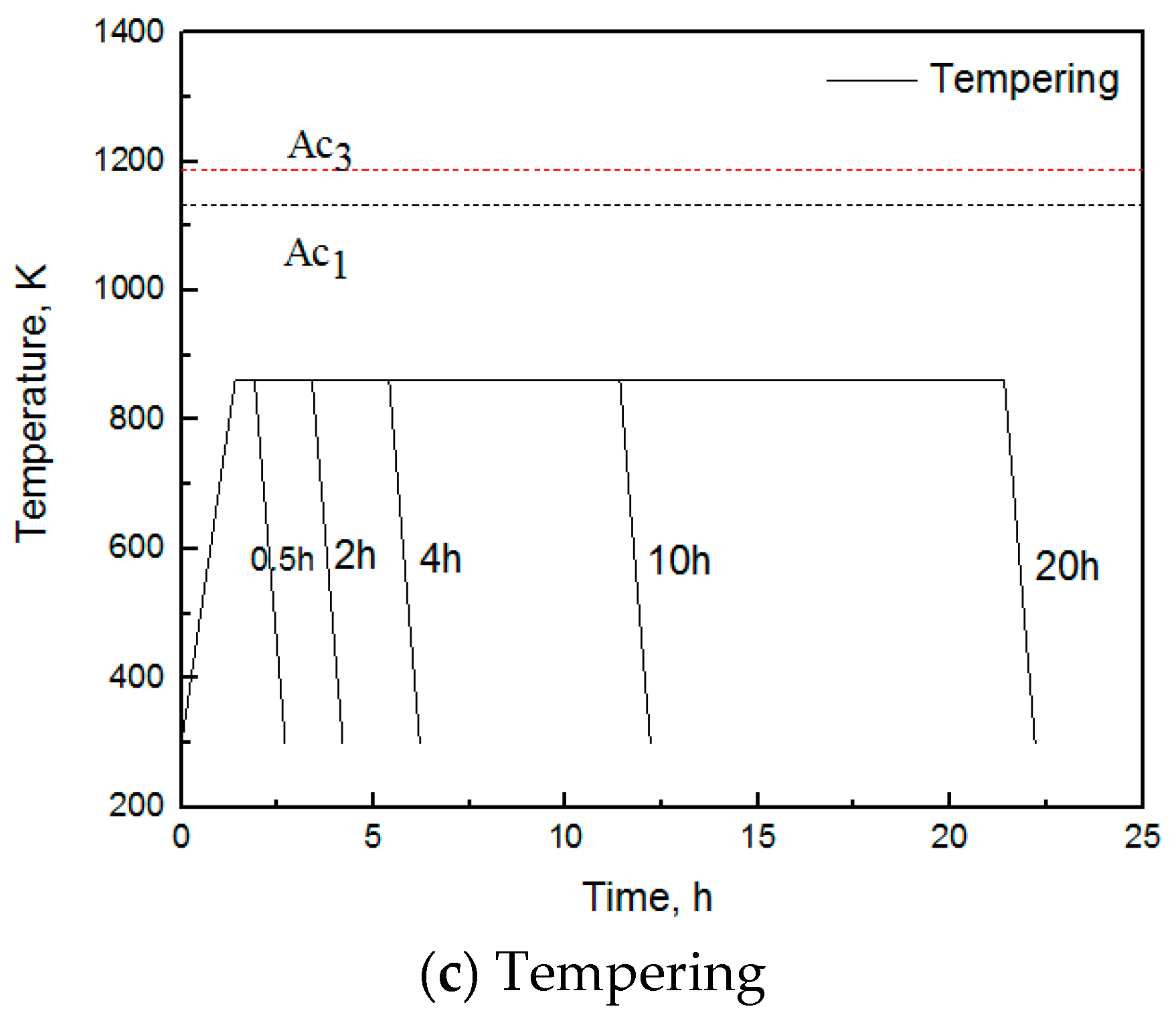
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
3. Experimental Results
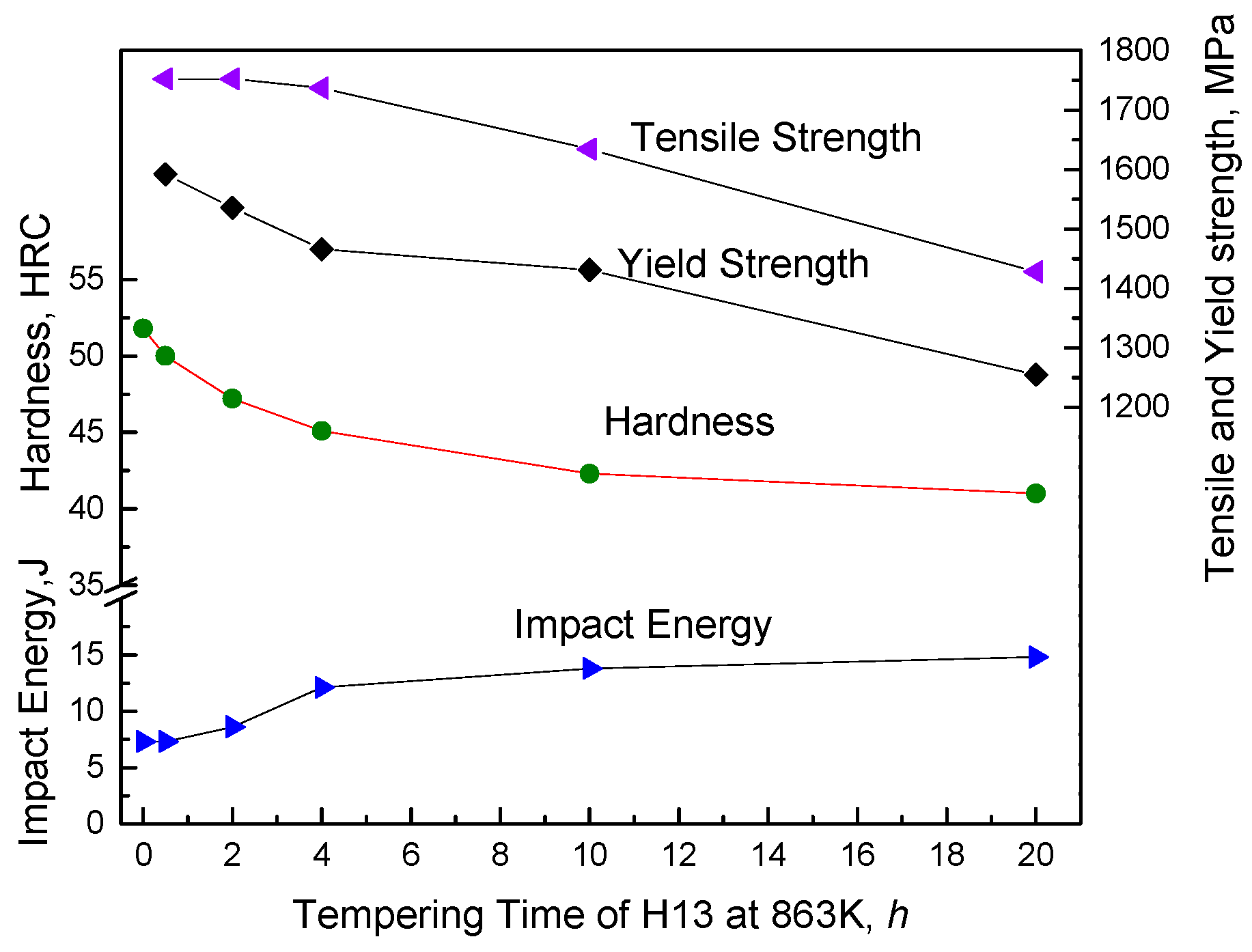
3.1. Mechanical Properties of H13
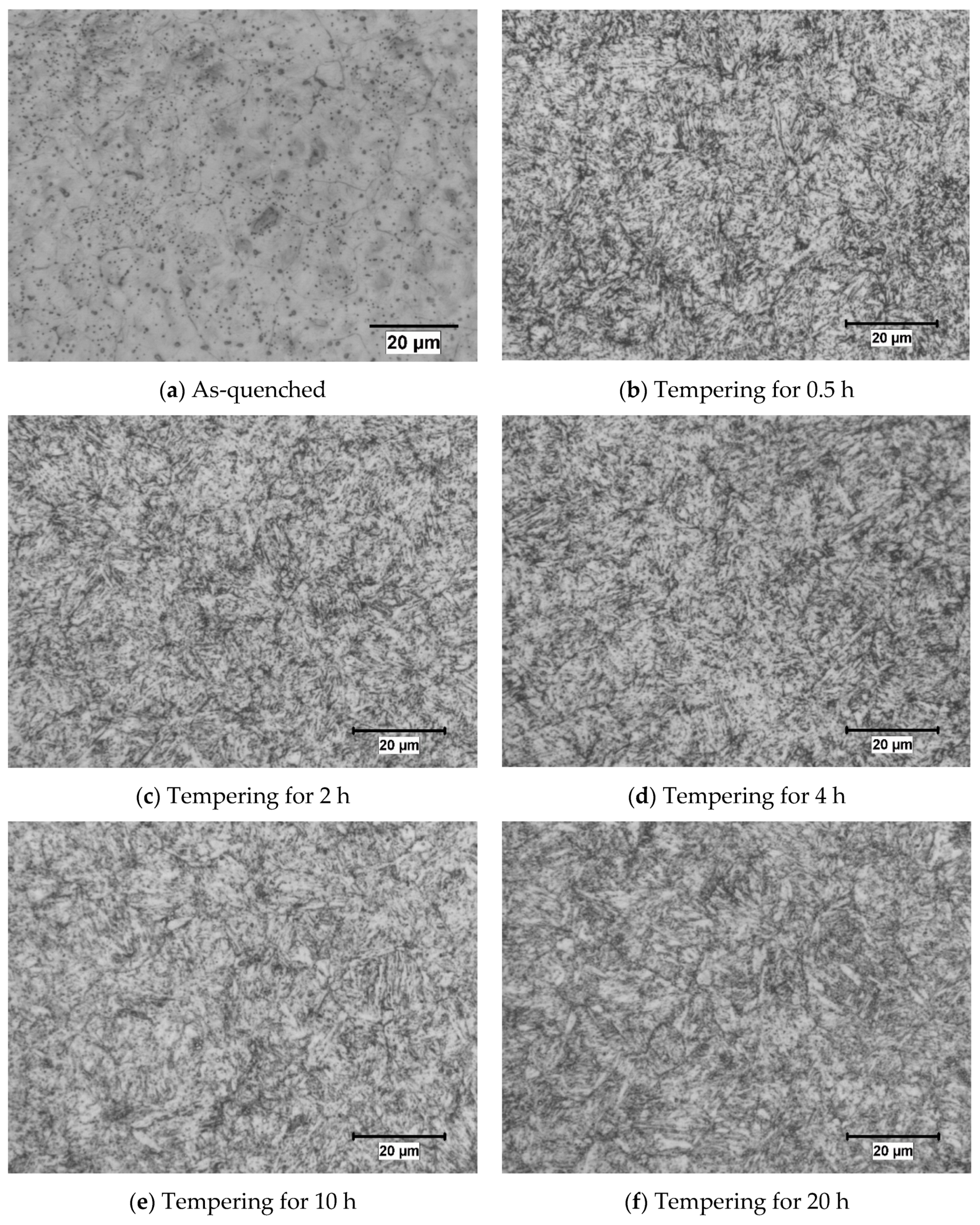
3.2. Microstructure
3.3. Effect of Precipitates on Mechanical Properties
3.3.1. Types, Size and Volume Fraction of Large Carbides in H13 after 863 K Tempering
3.3.2. Calculation of Precipitation Strengthening
4. Calculation of Thermodynamic and Coarsening Kinetics of Precipitates in H13
5. Verification of Ostwald Ripening Model
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Y.G.; Liang, Y.H.; Zhou, W.; Qin, Q.D.; Jiang, Q.C. Effect of current pulse on the thermal fatigue behavior of cast hot work die steel. ISIJ Int. 2005, 45, 410–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, M.; Belzunce, F.J. The effect of deep cryogenic treatments on the mechanical properties of an AISI H13 steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 624, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fu, P.; Liu, H.; Sun, C.; Gao, J.; Li, D. Carbides Evolution and Tensile Property of 4Cr5MoSiV1 Die Steel with Rare Earth Addition. Metals 2017, 7, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirandish, S.; Noorian, A. Effect of niobium on microstructure of cast AISI H13 hot work tool steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2008, 15, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Yu, L.C.; Huo, J.H. Mechanism of improvement on strength and toughness of H13 die steel by nitrogen. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 640, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Park, G.; Jung, J.G.; Kim, B.H.; Lee, Y.K. The effects of annealing temperature and cooling rate on carbide precipitation behavior in H13 hot-work tool steel. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 627, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, Z.H.; Xie, J.X. Improving strength and ductility of H13 die steel by pre-tempering treatment and its mechanism. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 752, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.X.; Wang, F.M.; Li, C.R.; Li, Y.L.; Cheng, J. Microstructural evolution, coarsening behavior of precipitates and mechanical properties of boron bearing steel 25CrMoNbB during tempering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 712, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, A.; Hattestrand, M. Coarsening of precipitates in an advanced creep resistant 9% chromium steel—Quantitative microscopy and simulations. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 333, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hald, J.; Korcakova, L. Precipitate stability in creep resistant ferritic steels-experimental investigations and modelling. ISIJ Int. 2003, 43, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, T.; Selvi, S.P.; Parameswaran, P.; Laha, K. Influence of thermal ageing on microstructure and tensile properties of P92 steel. High Temp. Mater. Process. 2018, 37, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.; Rojas, D.; Carrasco, C.; Kaysser-Pyzalla, A.R. Investigations on coarsening of MX and M23C6 precipitates in 12% Cr creep resistant steels assisted by computational thermodynamics. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 5976–5983. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.; Liu, G.Q.; Hu, B.F; Wang, J.S.; Ma, W.B. Coarsening behavior for M23C6 carbide in 12%Cr-reduced activation ferrite/martensite steel: Experimental study combined with DICTRA simulation. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 5410–5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.Z.; Zhang, Y.N.; Zhang, H.L.; Li, H.J.; Qu, F.; Han, J.; Cheng, L.; Wu, B.T.; Lu, Y.; Ma, Y. Precipitates and Particles Coarsening of 9Cr-1.7W-0.4Mo-Co Ferritic Heat-Resistant Steel after Isothermal Aging. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.Q.; Lu, L.; He, Y.L.; Li, L.; Lu, X.G. Coarsening of M23C6 Precipitates in an Fe-Cr-C Ternary Alloy. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2012, 19, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.Y.; Bai, P.C.; Yang, J.C. Cracking the initiation mechanism of high Cu-bearing nitrogen-alloyed austenitic stainless steel in the process of hot deformation. Metals 2018, 8, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, A.G.; Mao, W.W.; Chen, X.C.; Guo, H.J.; Guo, J. Precipitation behavior of carbides in H13 hot work die steel and its strengthening during tempering. Metals 2017, 7, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.W.; Min, Y.A.; Wu, X.C. Study on carbides and their evolution in H13 hot work steel. Trans. Mater. Heat Treat. 2009, 30, 122–126. [Google Scholar]
- Delagnes, D.; Lamesle, P.; Mathon, M.H.; Mebarki, N.; Levaillant, C. Influence of silicon content on the precipitation of secondary carbides and fatigue properties of a 5%Cr tempered martensitic steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 394, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Ning, A.; Guo, H. Nanoscale precipitates and comprehensive strengthening mechanism in AISI H13 steel. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2016, 23, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.B.; Li, L.; Wu, X.C.; Zhang, M. Coarsening behavior of M23C6 carbides after ageing or thermal fatigue in AISI H13 steel with niobium. Int. J. Fatigue 2006, 28, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totten, G.E. Steel Heat Treatment: Metallurgy and Technologies; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Michaud, P.; Delagnes, D.; Lamesle, P.; Mathon, M.H.; Levaillant, C. The effect of the addition of alloying elements on carbide precipitation and mechanical properties in 5% chromium martensitic steels. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 4877–4889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, A.G.; Guo, H.J.; Chen, X.C.; Wang, M.B. Precipitation behaviors and strengthening of carbides in H13 steel during annealing. Mater. Trans. 2015, 56, 581–586. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.X.; Wang, F.M.; Li, C.R.; He, Y.T. Dissolution and precipitation behaviors of boron bearing phase and their effects on hardenability and toughness of 25CrMoNbB steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 701, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.Q.; Oin, Y.C. Metal Science and Heat Treatment; Machinery Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, G.H.; Han, L.Z.; Li, C.W.; Luo, X.M.; Gu, J.F. Characteristic of retained austenite decomposition during tempering and its effect on impact toughness in SA508 gr.3 steel. J. Nucl. Mater. 2017, 483, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittemeher, E.J.; Cheng, L.; van der Schaaf, P.J.; Brakman, C.M.; Korevaar, B.M. Analysis of nonisothermal transformation kinetics; tempering of iron-carbon and iron-nitrogen martensites. Metall. Trans. A 1988, 19, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lifshitz, I.M.; Slyozov, V.V. The kinetics of precipitation from supersaturated solid solutions. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1961, 19, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C. Theory of precipitate change by redissolution. Z. Elektrochem. 1961, 65, 581–591. [Google Scholar]
- Seher, R.J.; James, H.M.; Maniar, G.N. Stereology and Quantitative Metallography, West Conshohocken; Pellissier, G.E., Purdy, S.M., Eds.; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1972; pp. 119–137. [Google Scholar]
- Kneissl, A.C.; Garcia, C.I.; Deardo, A.J. HSLA Steels: Processing, Properties, and Applications; Geoffrey, T., Zhang, S., Eds.; The Minerals, Metals and Materials Society: San Diego, CA, USA, 1992; pp. 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- Leslie, W.C. Iron and its dilute substitutional solid solution. Metall. Trans. 1972, 3, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rade, L.; Westergren, B. Beta Mathematics Handbook, Studentlitteratur; Lund University Press: Lund, Sweden, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.D.; Van-Tyne, C.J.; Vigil, C.J.; Hackenberg, R.E. Induction hardening 5150 steel: Effects of initial microstructure and heating rate. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2011, 20, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhan, G. Rate-controlling parameters in the coarsening kinetics of cementite in Fe-0.6C steels during tempering. Scr. Mater. 2010, 63, 273–276. [Google Scholar]
- Bjorklund, S.; Donaghey, L.F; Hillert, M. The effect of alloying elements on the rate of Ostwald ripening of cementite in steel. Acta Metall. 1972, 20, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.W.; Doherty, R.D.; Cantor, B. Stability of Microstructure in Metallic System, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Philippe, T.; Voorhees, P.W. Ostwald ripening in multicomponent alloys. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 4237–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umantsev, A.; Olson, G.B. Ostwald ripening in multicomponent alloys. Scr. Metall. Mater. 1993, 29, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faranak, N.; Johann, H.A.; Philippe, B. Modeling of cementite coarsening during tempering of low-alloyed-medium carbon steel. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 6198–6218. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, Q.L. Secondary Phases in Steels; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Tsumura, T.; Okada, Y.; Ohtani, H. Effect of microalloying elements on the hardenability and the properties after tempering at high temperature in boron treated Cr-Mo-Nb steels. ISIJ Int. 1986, 72, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar]

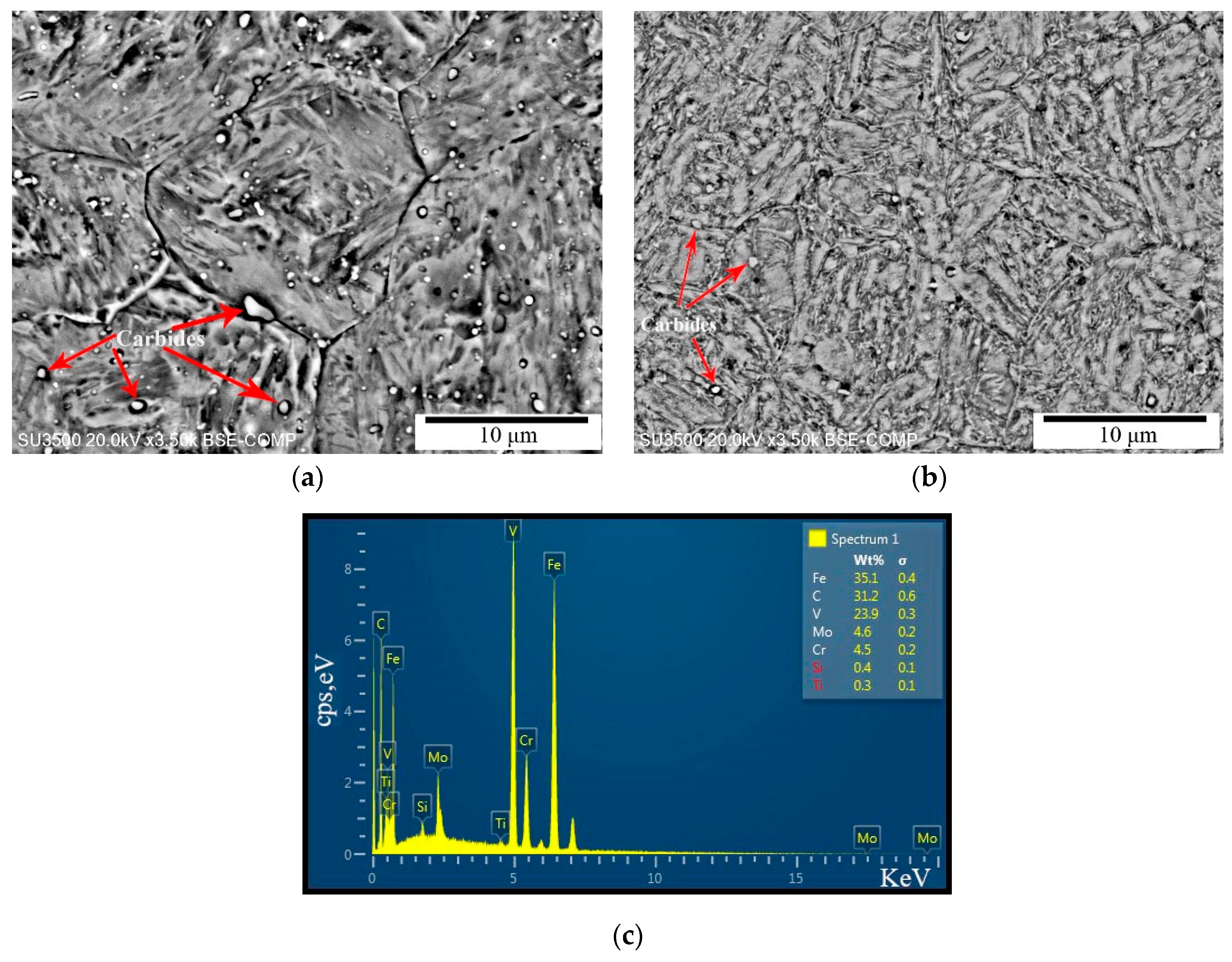
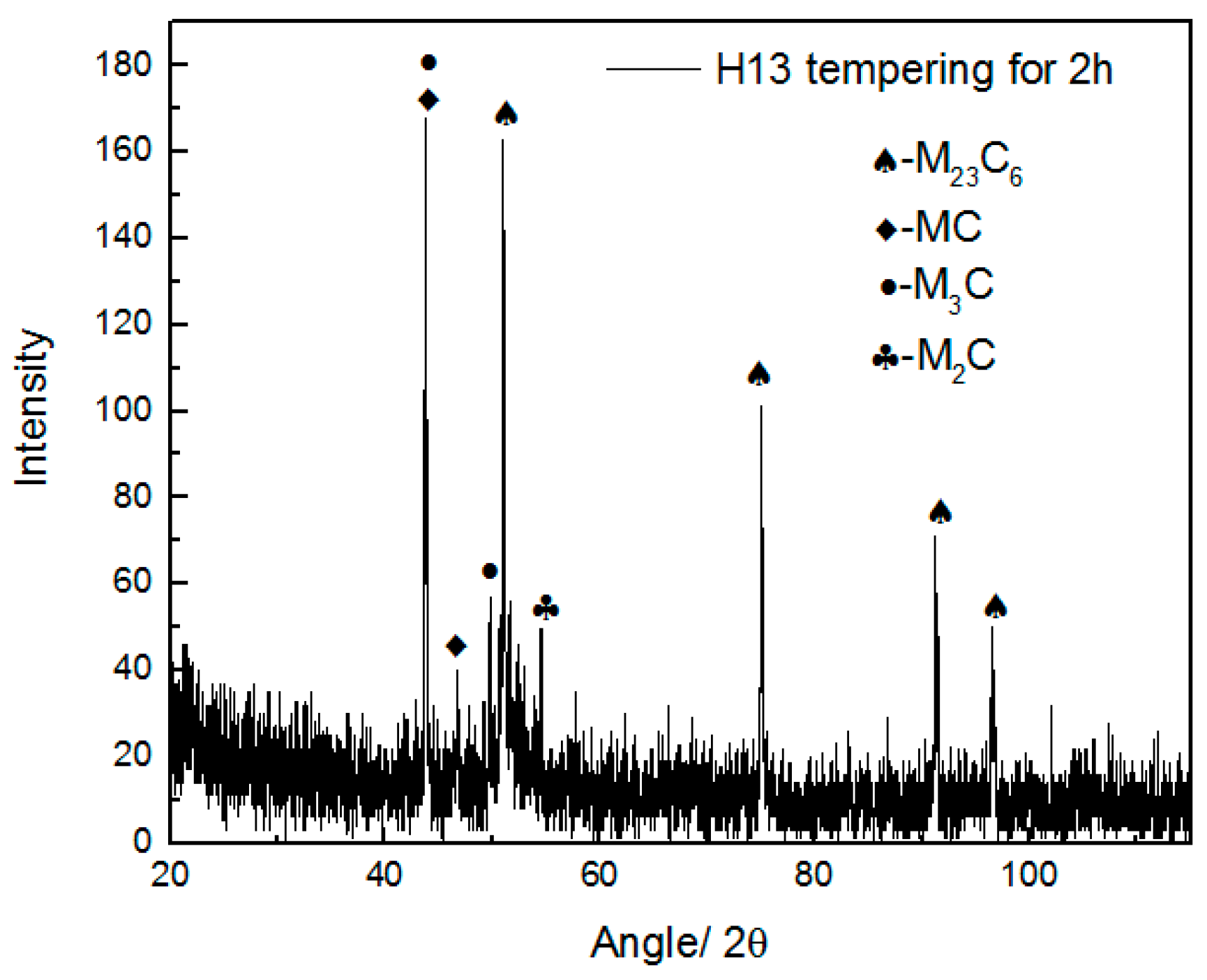
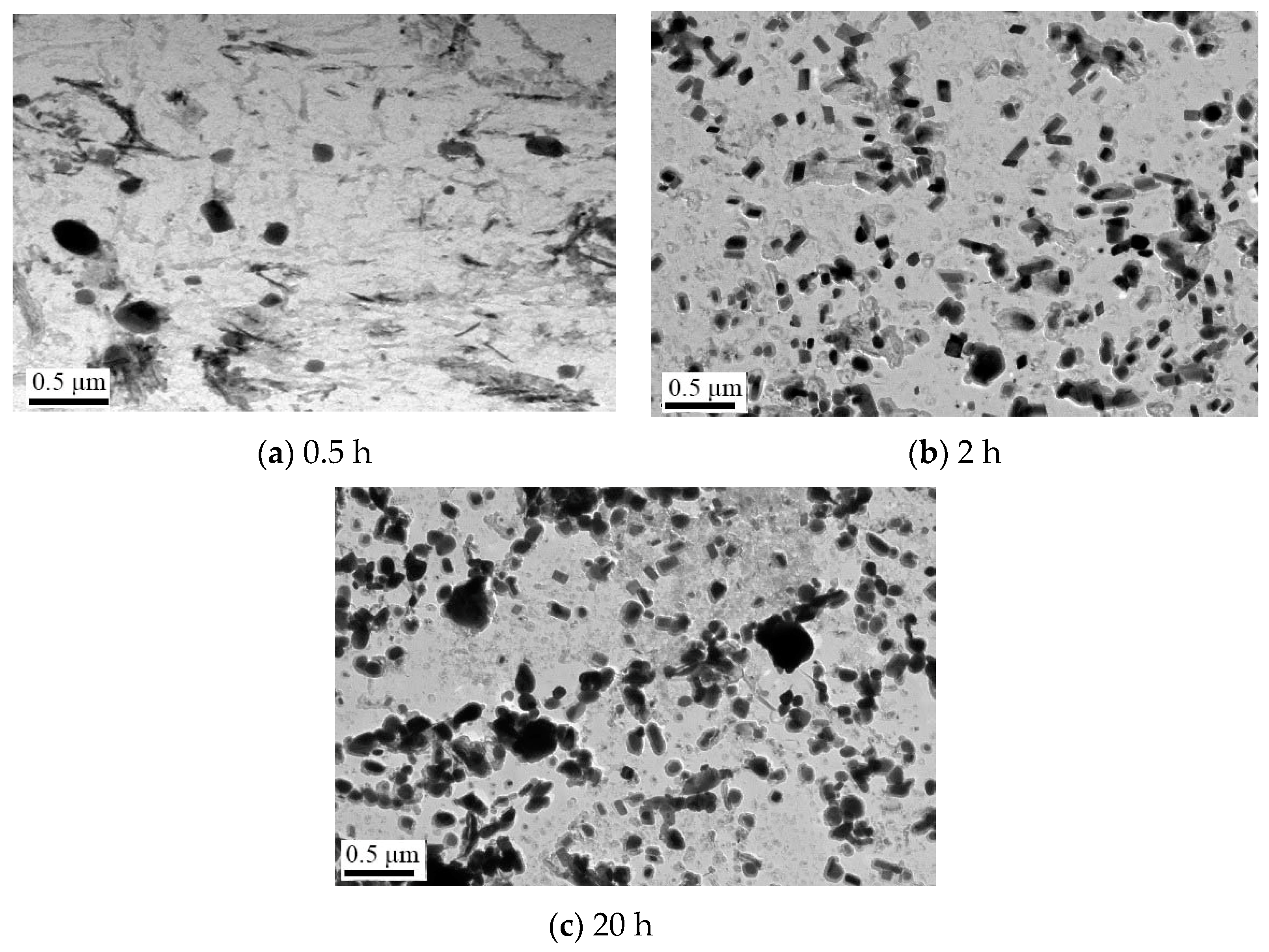
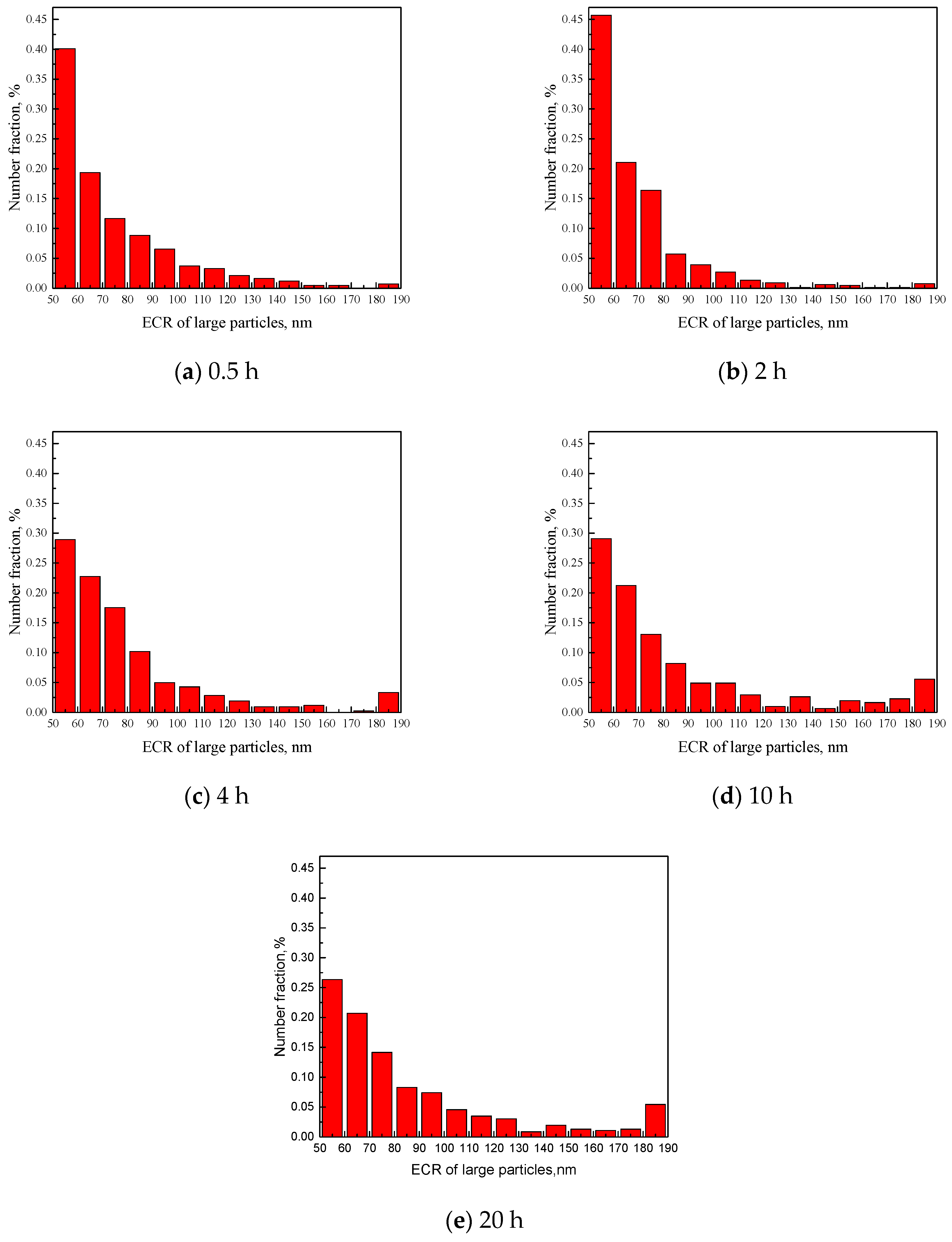
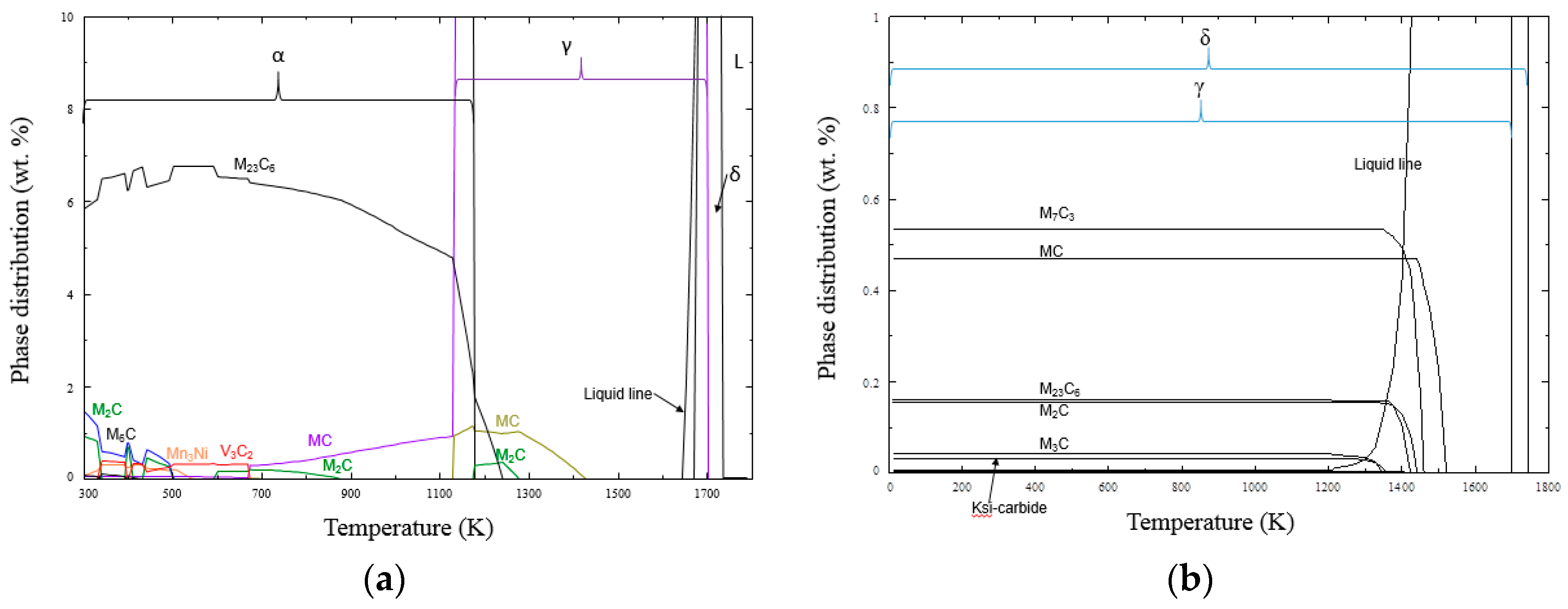
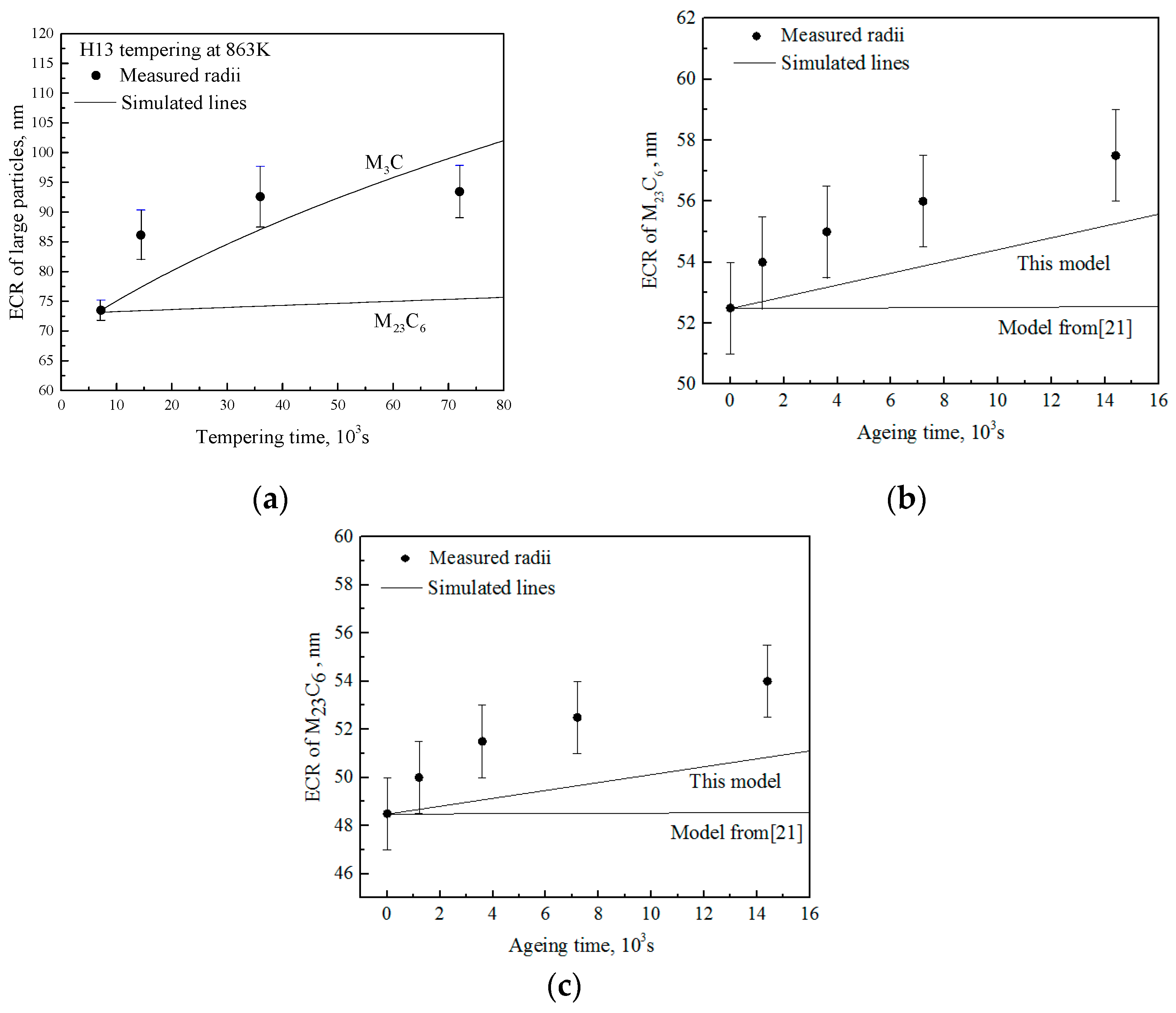
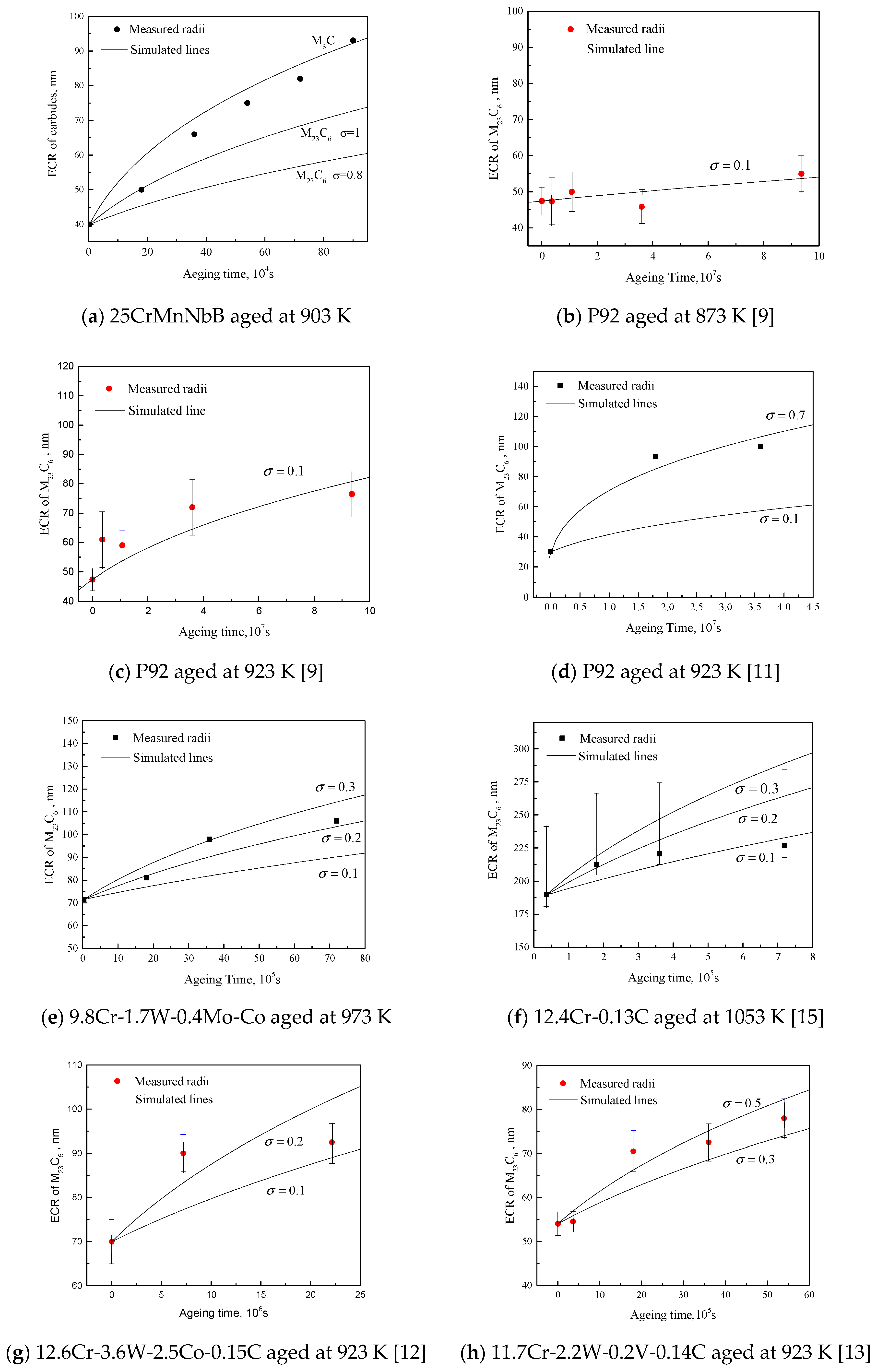
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Cu | Mo | V | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.39 | 0.98 | 0.38 | 0.0011 | 0.0006 | 5.09 | 0.083 | 0.054 | 1.39 | 0.9 | 0.047 |
| Radius Range (nm) | 0.5 h | 2 h | 4 h | 10 h | 20 h | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Average Radius (nm) | Number | Average Radius (nm) | Number | Average Radius (nm) | Number | Average Radius (nm) | Number | Average Radius (nm) | |
| 55–65 | 172 | 59.5 | 304 | 59.6 | 122 | 60.1 | 89 | 59.8 | 121 | 59.7 |
| 65–75 | 83 | 69.2 | 140 | 69.7 | 96 | 70.1 | 65 | 69.8 | 95 | 69.8 |
| 75–85 | 50 | 79.1 | 109 | 79.1 | 74 | 79.8 | 40 | 79.6 | 65 | 79.8 |
| 85–95 | 38 | 89.1 | 38 | 89.8 | 43 | 90.2 | 25 | 90.3 | 38 | 89.8 |
| 95–105 | 28 | 99.6 | 26 | 99.2 | 21 | 99.5 | 15 | 99.8 | 34 | 99.4 |
| 105–115 | 16 | 109.3 | 18 | 109.5 | 18 | 109.4 | 15 | 109.2 | 21 | 109.8 |
| 115–125 | 14 | 119.6 | 9 | 118.4 | 12 | 119.5 | 9 | 120.7 | 16 | 120.4 |
| 125–135 | 9 | 130.6 | 6 | 129.4 | 8 | 130.0 | 3 | 128.9 | 14 | 130.5 |
| 135–145 | 7 | 141.5 | 1 | 139.6 | 4 | 138.8 | 8 | 140.1 | 4 | 138.0 |
| 145–155 | 5 | 151.7 | 4 | 151.0 | 4 | 149.4 | 2 | 149.3 | 9 | 149.4 |
| 155–165 | 2 | 157.9 | 3 | 160.1 | 5 | 163.3 | 6 | 158.9 | 6 | 161.6 |
| 165–175 | 2 | 168.2 | 1 | 170.2 | 0 | 0.0 | 5 | 169.5 | 5 | 170.2 |
| 175–185 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 179.3 | 1 | 183.4 | 7 | 179.9 | 6 | 182.5 |
| 185–355 | 3 | 229.3 | 5 | 198.3 | 14 | 273.9 | 17 | 231.9 | 25 | 247.8 |
| Tempering | Measured Number of Large Particles (55–355 nm) | Average ECR of Large Particles (nm) | Volume of Large Particles (%) | Strengthening of Large Particles (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 h | 429 | 78.8 ± 2.4 | 2.74 | 255.8 |
| 2 h | 665 | 73.5 ± 1.7 | 4.22 | 265.3 |
| 4 h | 422 | 86.2 ± 4.2 | 4.98 | 262.9 |
| 10 h | 306 | 92.6 ± 5.1 | 4.19 | 243.7 |
| 20 h | 459 | 93.5 ± 4.4 | 4.87 | 239.5 |
| M23C6 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | 863 | 0.0494 | 0.5076 | 5.47 × 10−15 | 973 | 0.0459 | 0.4540 | 2.85 × 10−13 |
| Mn | 863 | 0.0030 | 2.6 × 10−6 | 1.69 × 10−14 | 973 | 0.0028 | 7.7 × 10−6 | 5.41 × 10−13 |
| V | 863 | 0.0074 | 1.4 × 10−6 | 1.01 × 10−14 | 973 | 0.0077 | 8.9 × 10−6 | 4.52 × 10−13 |
| Mo | 863 | 0.0057 | 0.1033 | 1.79 × 10−14 | 973 | 0.0043 | 0.1026 | 6.60 × 10−13 |
| m | 0.38 | 1.39 | ||||||
| M3C | T | T | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | 863 | 0.0494 | 0.0560 | 5.47 × 10−15 | 973 | 0.0512 | 0.0646 | 2.85 × 10−13 |
| Mn | 863 | 0.0030 | 0.0257 | 1.69 × 10−14 | 973 | 0.0027 | 0.0280 | 5.41 × 10−13 |
| V | 863 | 0.0074 | 0.0044 | 1.01 × 10−14 | 973 | 0.0085 | 0.0310 | 4.52 × 10−13 |
| Mo | 863 | 0.0057 | 0.0251 | 1.79 × 10−14 | 973 | 0.0064 | 0.0160 | 6.60 × 10−13 |
| m | 2.09 | 5.89 | ||||||
| Precipitates | T | Steel | Experimental Data in Literatures | Prediction of the Model in This Work (Formula (4)) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M23C6 | 863 K | H13(this work) | - | - | 0.38 | 0.5 |
| 873 K | P92 [9] | 0.079 | 0.1-0.5 | 0.081 | 0.1 | |
| P92 [10] | 0.11 | 0.1 | 0.081 | 0.1 | ||
| P91 [10] | 0.31 | 1.0 | 0.28 | 1.0 | ||
| 903 K | 25CrMoNbB [8] | 0.88 | - | 0.59 | 1 | |
| 923 K | P92 [9] | 0.17 | 0.1-0.3 | 0.17 | 0.1 | |
| P92 [10] | 0.24 | 0.1 | 0.17 | 0.1 | ||
| P91 [10] | 0.63 | 0.8 | 0.48 | 0.8 | ||
| P92 [11] | 0.32 | - | 0.32 | 0.7 | ||
| 12.6Cr-3.6W-2.5Co-0.15C [12] | 0.27 | 0.3 | 0.32 | 0.2 | ||
| 11.7Cr-2.2W-0.2V-0.14C [13] | 0.40 | 0.5 | 0.42 | 0.5 | ||
| 973 K | H13 [21] | 1.54 | 0.5 | 1.40 | 0.5 | |
| H13Nb [21] | 1.52 | 0.5 | 1.24 | 0.5 | ||
| 9.8Cr-1.7W-0.4Mo-Co [14] | 0.38 | - | 0.37 | 0.1 | ||
| 1053 K | 12.4Cr-0.13C [15] | 2.07 | 0.1–0.3 | 2.04 | 0.1 | |
| M3C | 863 K | H13(this work) | - | - | 2.09 | 0.45 [42] |
| 973 K | H13 [21] | - | - | 5.89 | 0.38 [42] | |
| 903 K | 25CrMoNbB [8] | - | - | 0.93 | 0.43 [42] | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ning, A.; Yue, S.; Gao, R.; Li, L.; Guo, H. Influence of Tempering Time on the Behavior of Large Carbides’ Coarsening in AISI H13 Steel. Metals 2019, 9, 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9121283
Ning A, Yue S, Gao R, Li L, Guo H. Influence of Tempering Time on the Behavior of Large Carbides’ Coarsening in AISI H13 Steel. Metals. 2019; 9(12):1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9121283
Chicago/Turabian StyleNing, Angang, Stephen Yue, Rui Gao, Lingxia Li, and Hanjie Guo. 2019. "Influence of Tempering Time on the Behavior of Large Carbides’ Coarsening in AISI H13 Steel" Metals 9, no. 12: 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9121283
APA StyleNing, A., Yue, S., Gao, R., Li, L., & Guo, H. (2019). Influence of Tempering Time on the Behavior of Large Carbides’ Coarsening in AISI H13 Steel. Metals, 9(12), 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9121283






