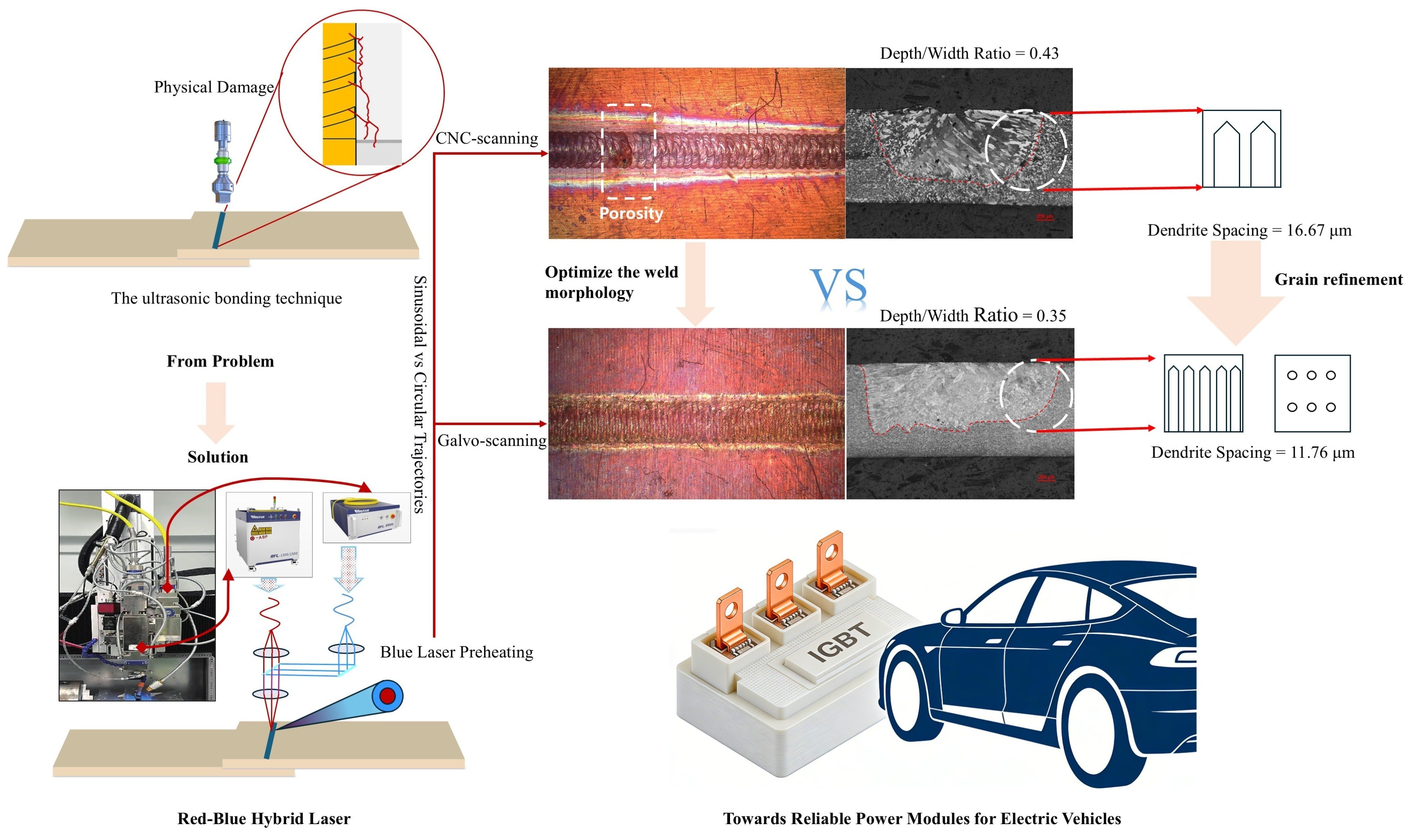
Fiber-Diode Hybrid Laser Welding of IGBT Copper Terminals
Abstract
Share and Cite
Yang, M.; Lv, Q.; Liu, S.; Fu, Q.; Wu, X.; Kang, Y.; Xing, X.; Deng, Z.; Yao, F.; Chen, S. Fiber-Diode Hybrid Laser Welding of IGBT Copper Terminals. Metals 2026, 16, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/met16020139
Yang M, Lv Q, Liu S, Fu Q, Wu X, Kang Y, Xing X, Deng Z, Yao F, Chen S. Fiber-Diode Hybrid Laser Welding of IGBT Copper Terminals. Metals. 2026; 16(2):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/met16020139
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Miaosen, Qiqi Lv, Shengxiang Liu, Qian Fu, Xiangkuan Wu, Yue Kang, Xiaolan Xing, Zhihao Deng, Fuxin Yao, and Simeng Chen. 2026. "Fiber-Diode Hybrid Laser Welding of IGBT Copper Terminals" Metals 16, no. 2: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/met16020139
APA StyleYang, M., Lv, Q., Liu, S., Fu, Q., Wu, X., Kang, Y., Xing, X., Deng, Z., Yao, F., & Chen, S. (2026). Fiber-Diode Hybrid Laser Welding of IGBT Copper Terminals. Metals, 16(2), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/met16020139