Finite Element Analysis for Restraint Intensity and Welding Residual Stress of the Lehigh Specimen Made of Ti80 Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
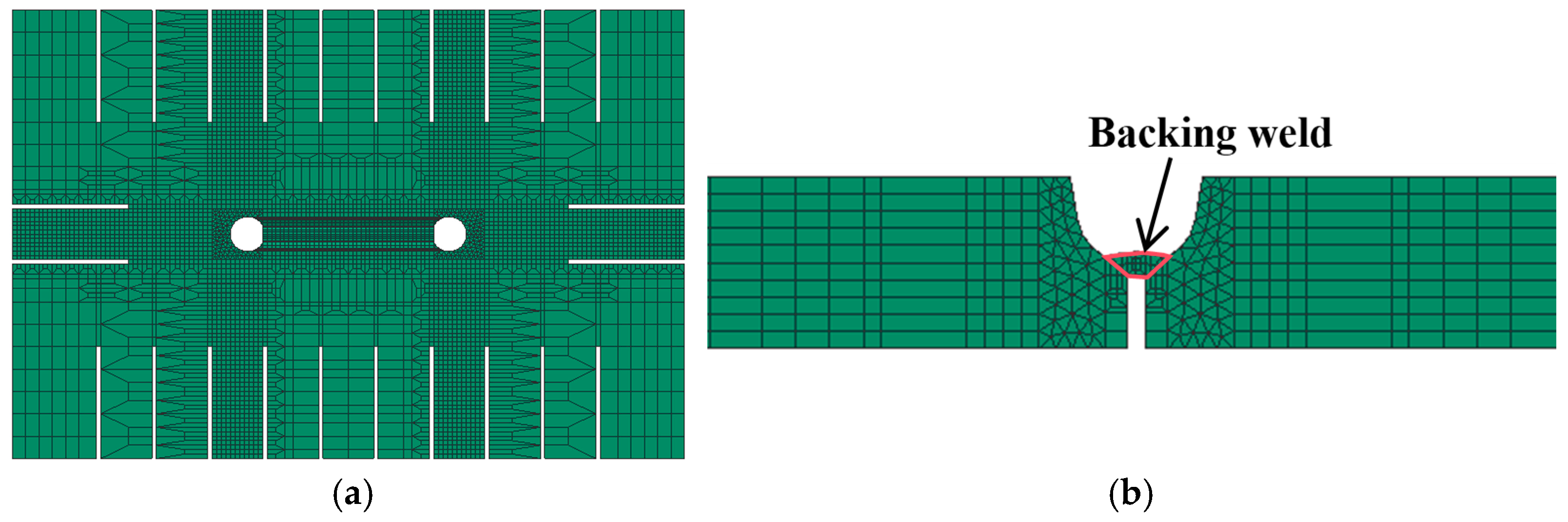
2. FE Simulation and Verification
2.1. Fundamental Principles
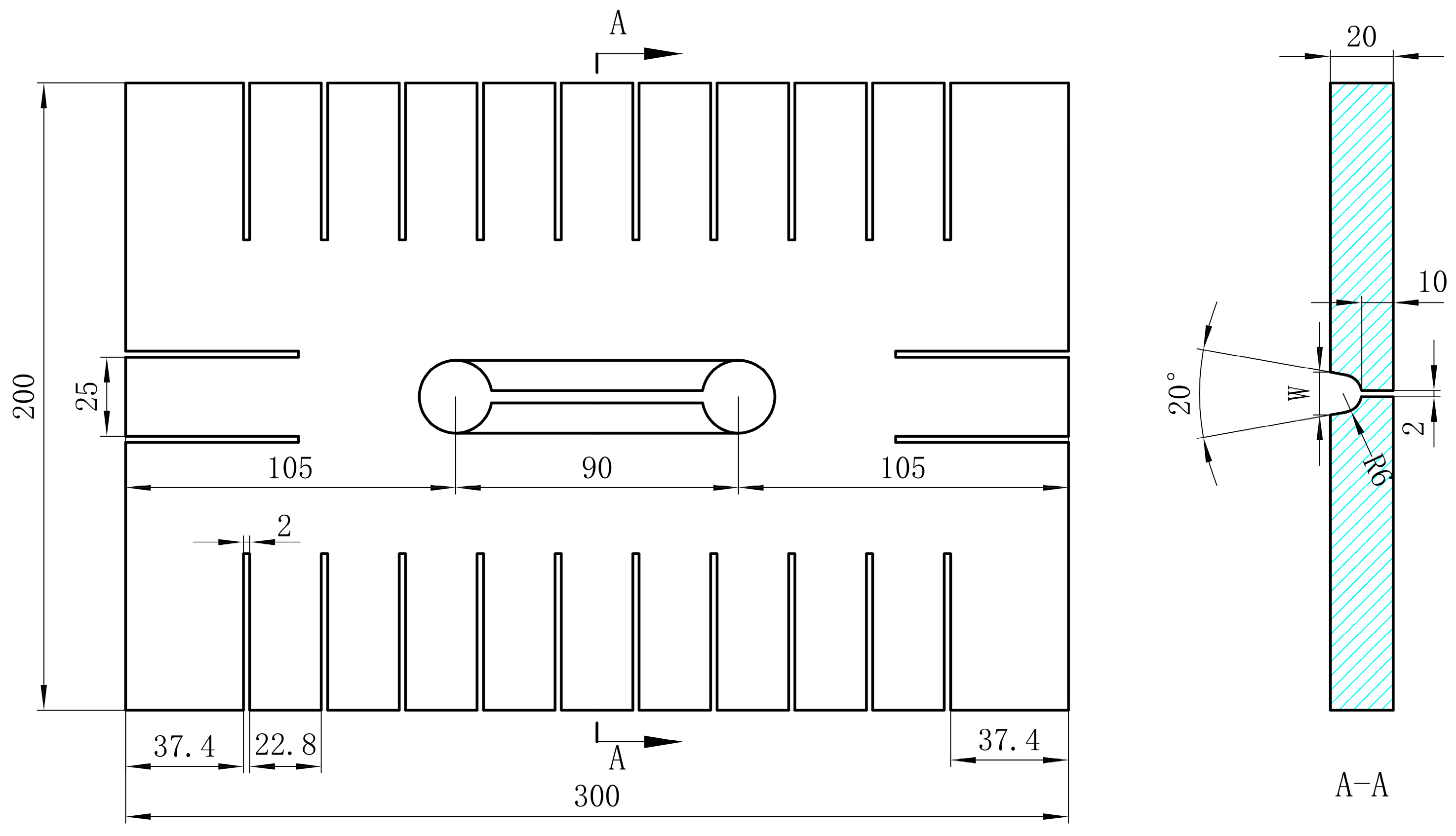
2.2. Dimensions
2.3. Thermal and Mechanical Parameters
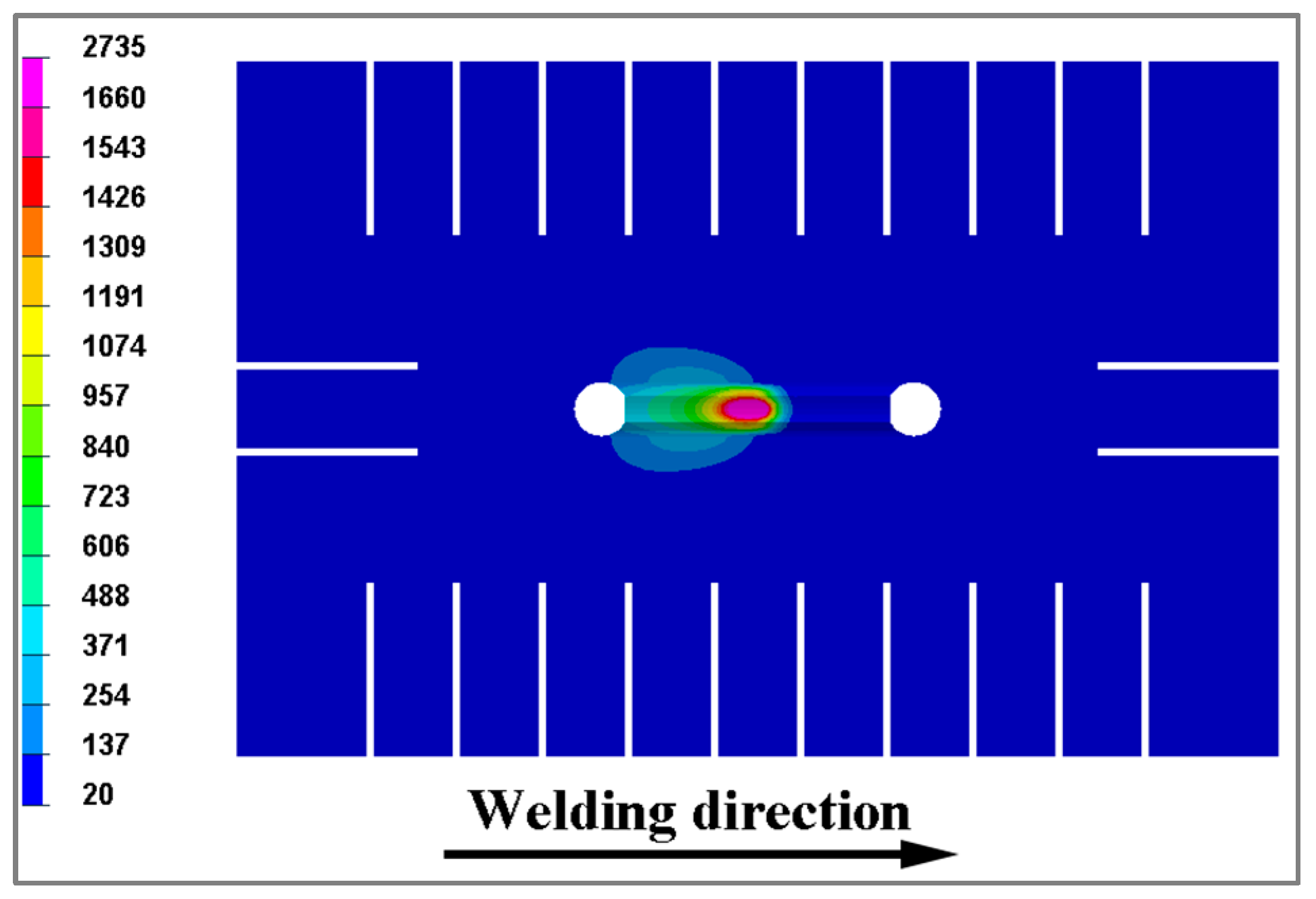
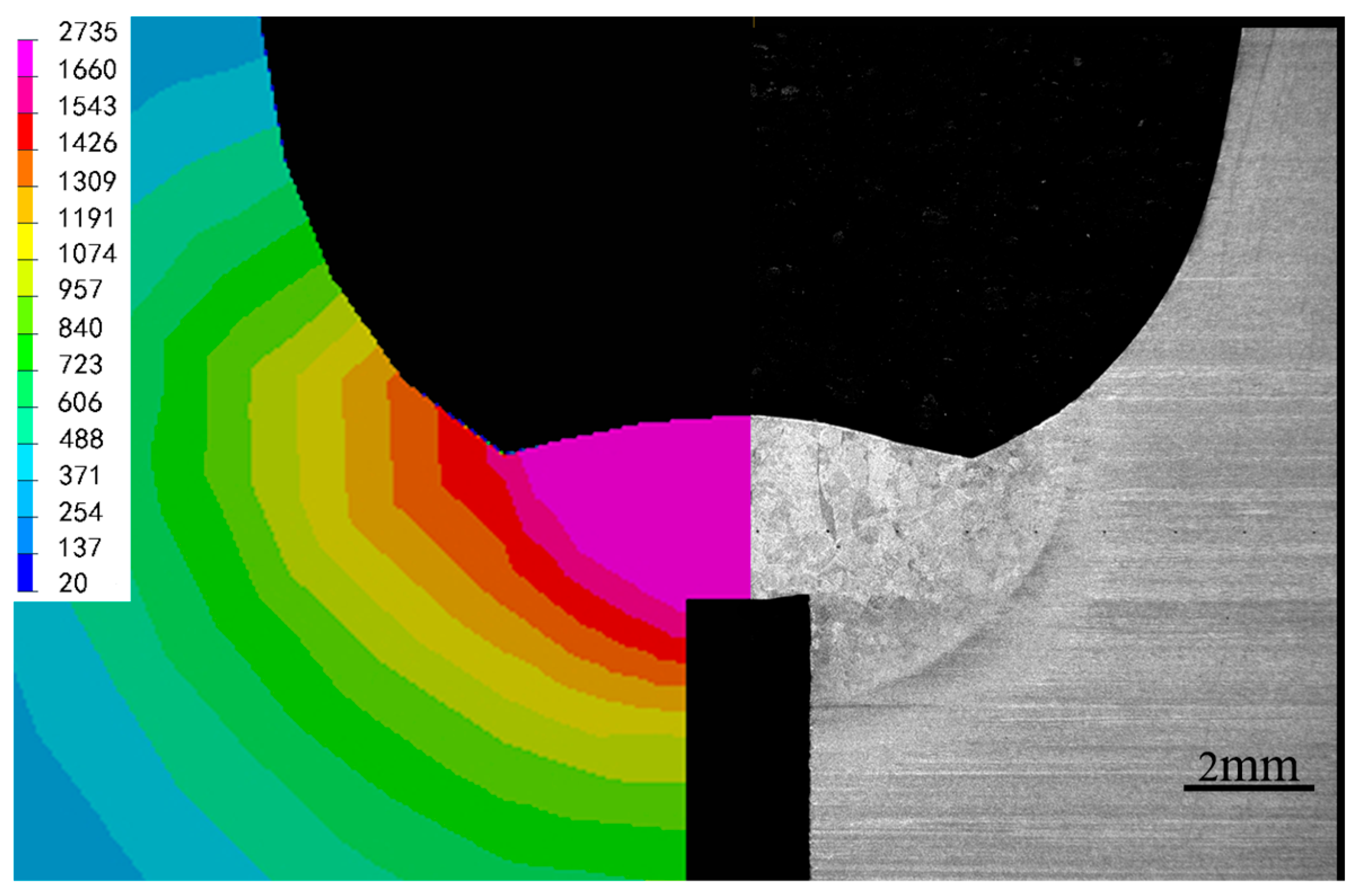
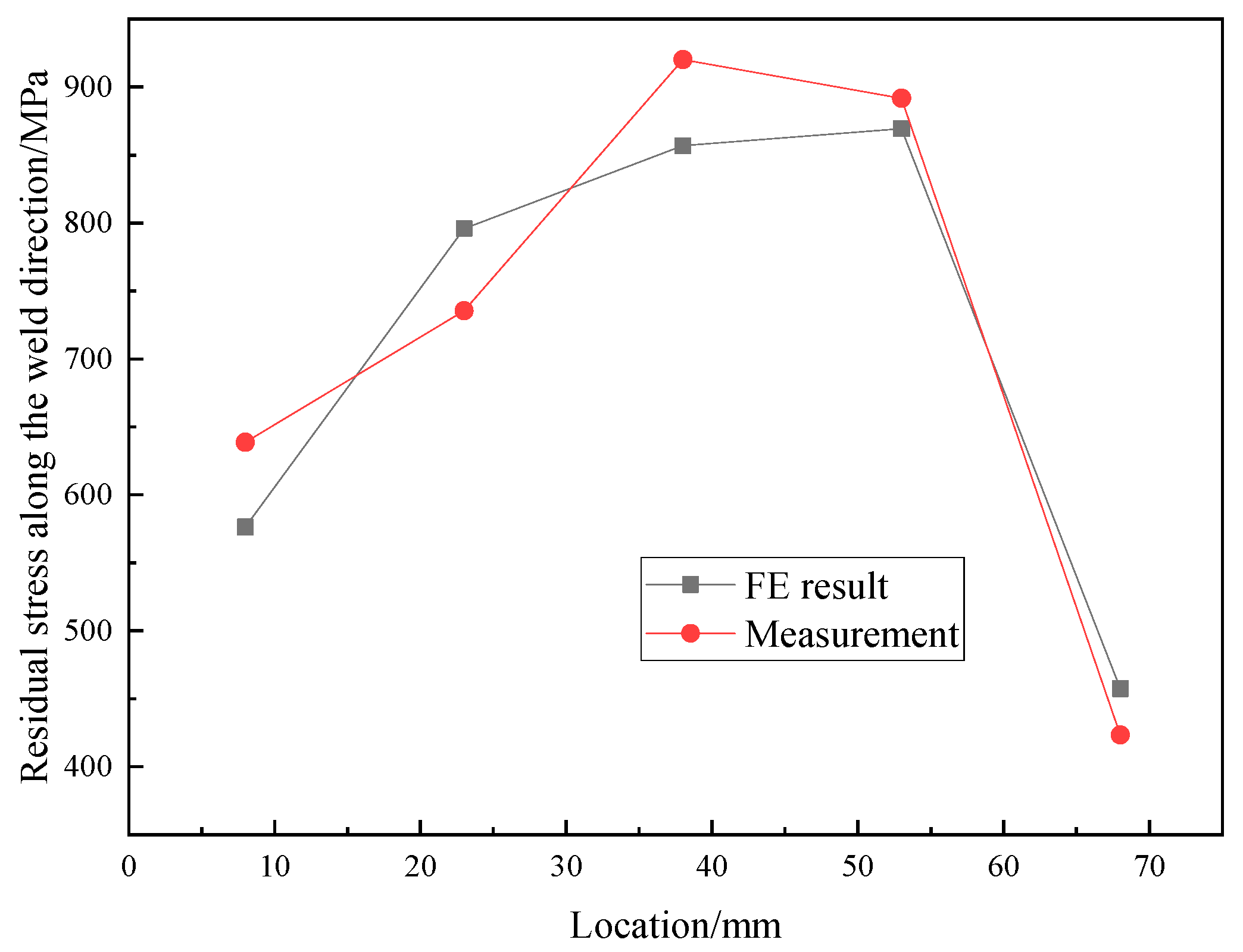
2.4. Experimental Validations
3. Results and Discussion
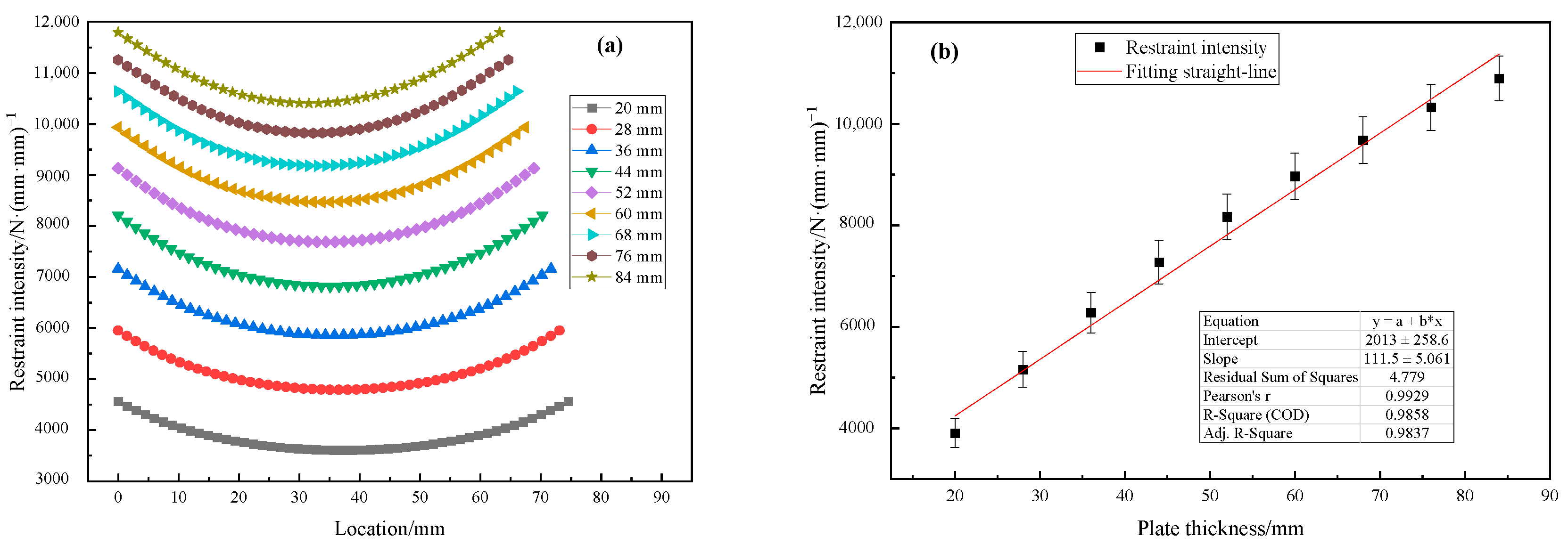
3.1. Effect of Plate Thickness on Restraint Intensity
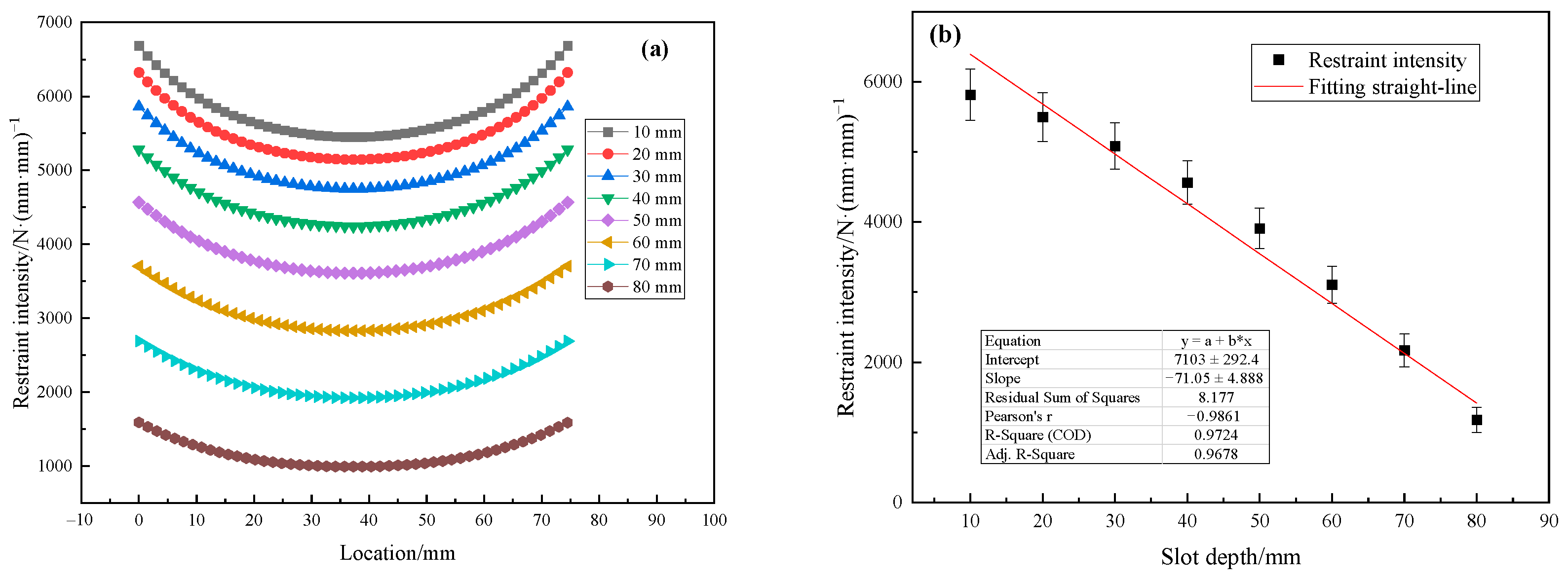
3.2. Effect of Slot Depth on Restraint Intensity
3.3. Linear Regression Analysis
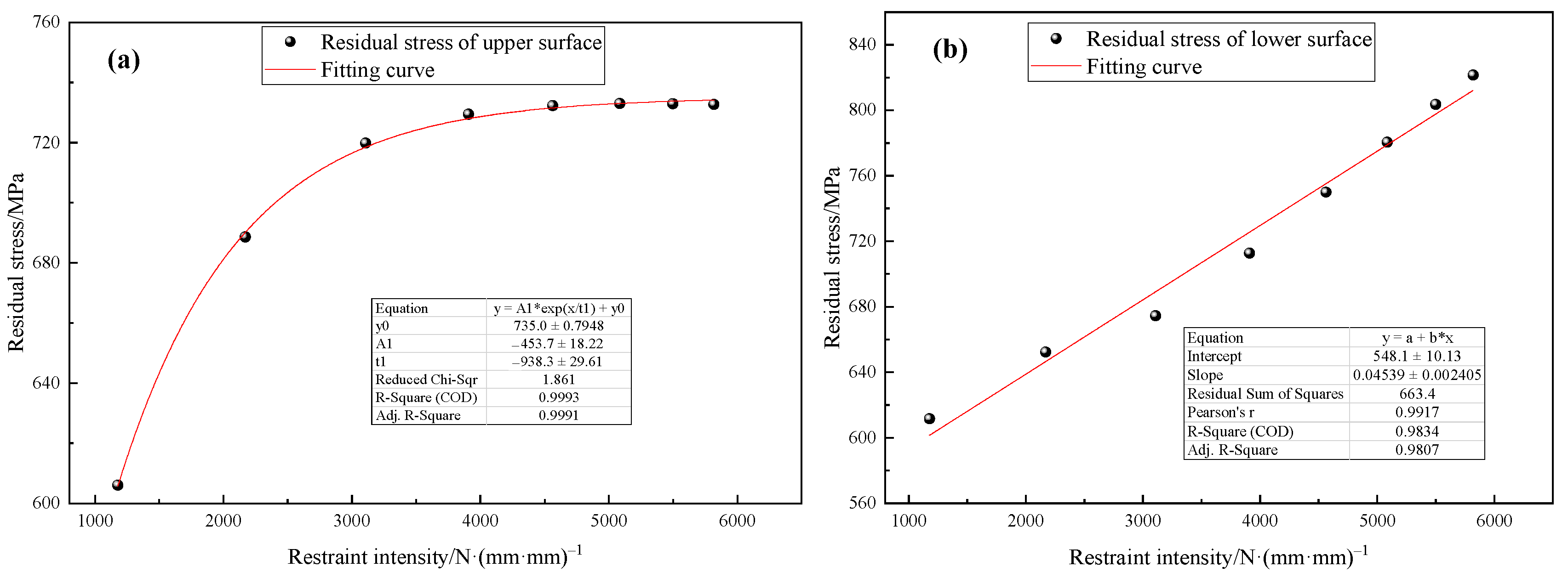
3.4. Effect of Restraint Intensity on Welding Residual Stress
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Restraint intensity in Lehigh specimens exhibits a strong positive linear correlation with plate thickness and a strong negative linear correlation with slot depth. A robust binary linear regression model effectively predicts restraint intensity across varied geometries with a mean prediction error of about 5.9%.
- (2)
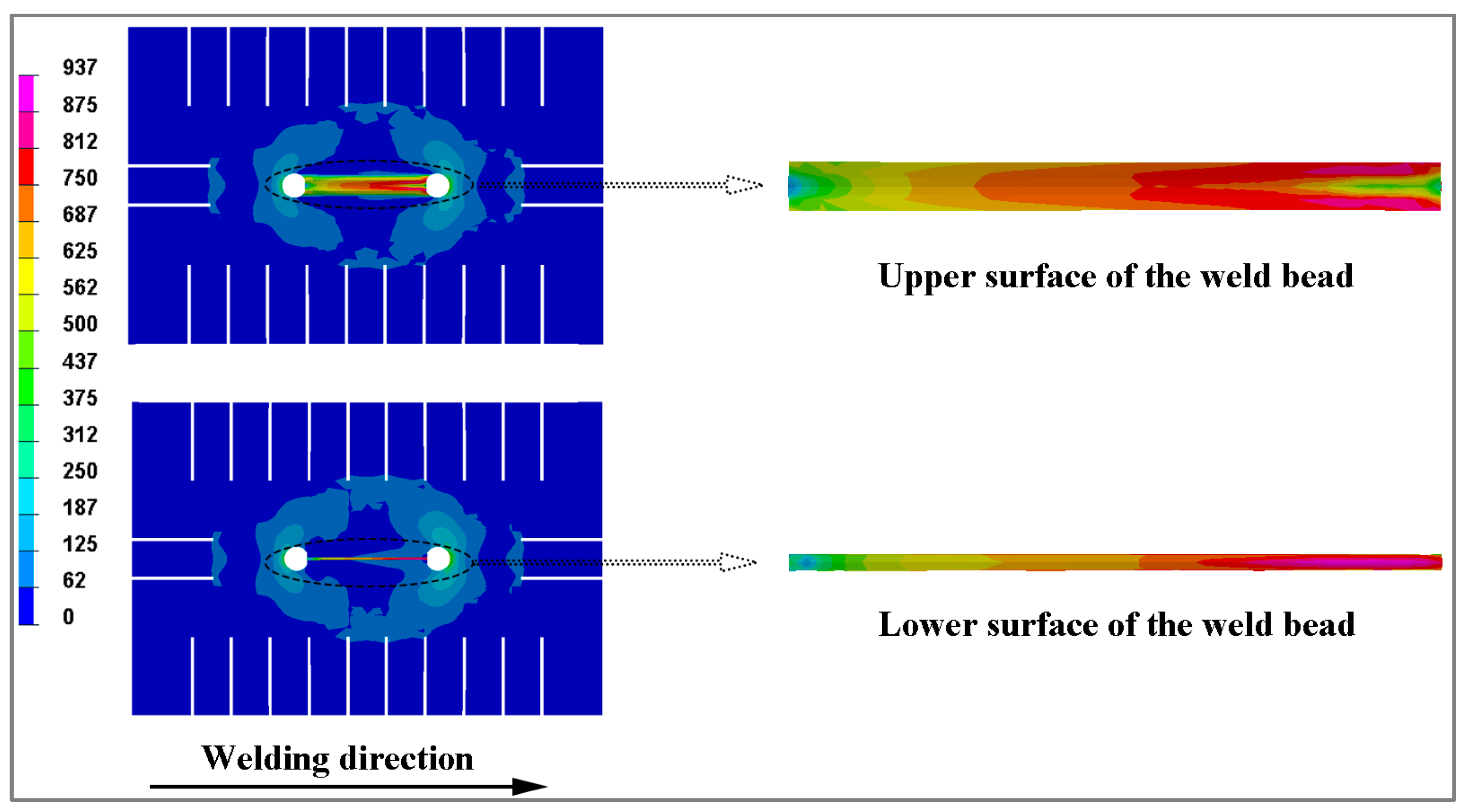
- Residual stresses of root pass display significant spatial heterogeneity; the upper surface stresses concentrate in the weld center, while the lower surface stresses peak near the weld termination zone. This asymmetry arises from differential constraint conditions across weld regions.
- (3)
- Welding residual stress increases with higher restraint intensity. Residual stress on the upper weld surface follows an exponential growth trend, while the lower surface exhibits a linear increase. Predictions align with FE results with errors below 9%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, H.; Bai, X.; Li, Z. Electrochemical evaluation of stress corrosion cracking susceptibility of Ti-6Al-3Nb-2Zr-1Mo alloy welded joint in simulated deep-sea environment. Materials 2022, 15, 3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Y. Solidification microstructure and mechanical properties of laser additive manufactured near-α Ti-6Al-3Nb-2Zr-1Mo titanium alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2025, 34, 2208–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Xie, J.; Wang, J. Low-cycle and dwell fatigue properties for a near alpha titanium alloy Ti-6Al-3Nb-2Zr-1Mo. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 29, 2204–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Hirohata, M.; Chang, K. A streamlined FE method for deformation and residual stress prediction in butt welding using continuous heat input. Weld. World 2025, 69, 2471–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C. Effect of structural restraint caused by the stiffener on welding residual stress and deformation in thick-plate T-joints. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 21, 3397–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.R.; Zhu, K.K.; Pan, L. Investigation of the correlation between mechanical chip morphology and surface residual stress for Ti6Al4V alloy. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2020, 34, 3997–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toribio, J.; Kharin, V.; Ayaso, F.J. Failure analysis of a lifting platform for tree pruning. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2010, 17, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannengiesser, T.; Boellinghaus, T. Cold cracking tests—An overview of present technologies and applications. Weld. World 2013, 57, 3–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, J.; Sun, G. Modeling of welding residual stress in a dissimilar metal butt-welded joint between P92 ferritic steel and SUS304 austenitic stainless steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 4938–4954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, X. Guided wave-based crack detection in U-shaped flexural plate butt welds. Eng. Struct. 2024, 303, 117558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.L.; Vasileiou, A.N.; Pickering, E.J. Impact of weld restraint on the development of distortion and stress during the electron beam welding of a low-alloy steel subject to solid state phase transformation. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2021, 196, 106244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, X.; Liu, C.; Guo, X.; Xue, Z. Numerical simulation and experimental verification of the restraint intensity of pipeline girth welding joint. China Weld. 2016, 25, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Schroepfer, D.; Witte, J.; Kromm, A. Stresses in repair welding of high-strength steels—Part 1: Restraint and cold cracking risk. Weld. World 2024, 68, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chen, M. Calculation of the restraint intensity of VRC test assemblies. J. Southwest JiaoTong Univ. 1993, 2, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, W.; Zhang, W.; Chen, B. Relationship between restraint intensity and restraint stress in elasto-plastic range. Trans. China Weld. Inst. 1992, 13, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Qin, B.; Wang, L. Study on distribution of restraint intensity and restraint stress in slit weld specimen. Trans. China Weld. Inst. 1992, 13, 162–168. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Hensel, J.; Nitschke, P.T. Influence of Restraint Conditions on Welding Residual Stresses in H-Type Cracking Test Specimens. Materials 2019, 12, 2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurji, R.; Coniglio, N. Towards the establishment of weldability test standards for hydrogen-assisted cold cracking. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 77, 1581–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipooramirabad, H.; Paradowska, A.M.; Ghomashchi, R. Prediction of welding stresses in WIC test and its application in pipelines. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 1462–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeid, O.; Leslie, A.J.; Olabi, A.G. Influence of girth welding material on thermal and residual stress fields in welded lined pipes. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2022, 200, 104777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Zong, P.; Dong, J. The calculation method for welding restraint intensity of fillet weld in ring-stiffened cylinder. Trans. China Weld. Inst. 2013, 34, 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Chen, P. Finite element analysis of restraint intensities and welding residual stresses in the Ti80 T-joints. Metals 2023, 13, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Xu, J.; Xu, L. Finite element simulation of the restraint intensity of rigid butt-jointed cracking specimen and VRC specimen. Trans. China Weld. Inst. 2018, 39, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Y. Finite element analysis on restraint intensity of Ti80 alloy rigid restraint specimen. Chin. J. Rare Met. 2021, 45, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Schroepfer, D.; Kromm, A.; Kannengiesser, T. Engineering approach to assess residual stresses in welded components. Weld. World 2017, 61, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; An, G.; Ma, N. Effect of transverse restraint on welding residual stress in V-groove butt welding. Metals 2022, 12, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, T. Influence of restraint conditions on residual stress and distortion of 2219-T8 aluminum alloy TIG welded joints based on contour method. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 68, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čolić, K.; Kostić, S.M.; Sedmak, S. Structural Integrity and Life Assessment of Ti-6Al-4V Orthopaedic Implants. Metals 2025, 15, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Saadlaoui, Y.; Hamdi, H. An experimental and numerical case study of thermal and mechanical consequences induced by laser welding process. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 35, 102078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenneth, C.M. Recommended Values of Thermophysical Properties for Selected Commercial Alloys; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Abington, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]




| Al | Nb | Zr | Mo | Fe | C | N | O | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.24 | 2.86 | 1.94 | 0.95 | 0.023 | 0.009 | 0.0036 | 0.085 | Bal. |
| Temperature, °C | Density, g/cm3 | Thermal Conductivity, W/(m·K) | Specific Heat Capacity, J/(kg·K) | Coefficient of Thermal Expansion, 10−6/K | Young’s Modulus, GPa | Yield Strength, MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 4.51 | 6.95 | 547 | 9.1 | 116 | 814 |
| 100 | 4.48 | 7.47 | 562 | 9.1 | 112 | 800 |
| 200 | 4.46 | 8.71 | 583 | 9.2 | 107 | 700 |
| 300 | 4.44 | 10.04 | 607 | 9.3 | 102 | 625 |
| 400 | 4.42 | 11.32 | 628 | 9.5 | 96 | 550 |
| 500 | 4.40 | 12.53 | 650 | 9.7 | 90 | 470 |
| 600 | 4.38 | 14.10 | 674 | 10 | 85 | 385 |
| 700 | 4.36 | 15.54 | 693 | 10.5 | 81 | 310 |
| 800 | 4.34 | 17.71 | 713 | 11 | 75 | 225 |
| 900 | 4.32 | 20.15 | 735 | 11 | 72 | 184 |
| 1000 | 4.30 | 19.23 | 642 | 11 | 70 | 138 |
| 1100 | 4.28 | 20.88 | 658 | 11 | 68 | 65 |
| 1200 | 4.26 | 22.73 | 679 | 11 | 63 | 34 |
| 1300 | 4.25 | 23.62 | 695 | 11 | 55 | 12 |
| 20 | 4.51 | 6.95 | 547 | 9.1 | 116 | 814 |
| Specimen No. | Plate Thickness, mm | Slot Depth, mm | Predicted Value, N·(mm·mm)−1 | FE Simulation Value, N·(mm·mm)−1 | Error/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 45 | 32 | 9027.83 | 9818.67 | 8.05 |
| 2 | 72 | 18 | 14,234.62 | 16,131.56 | 11.76 |
| 3 | 33 | 65 | 4011.02 | 3868.72 | 3.68 |
| 4 | 80 | 42 | 12,936.38 | 12,715.93 | 1.73 |
| 5 | 26 | 77 | 1816.29 | 1774.15 | 2.37 |
| 6 | 59 | 11 | 13,114.50 | 14,500.02 | 9.56 |
| 7 | 20 | 53 | 3395.55 | 3686.31 | 7.89 |
| 8 | 64 | 29 | 12,000.31 | 13,289.02 | 9.70 |
| 9 | 37 | 56 | 5481.43 | 5585.09 | 1.86 |
| 10 | 51 | 47 | 8356.94 | 8604.38 | 2.88 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Song, G.; Wang, Q.; Chen, D.; Guo, X.; Dai, C.; Bu, W. Finite Element Analysis for Restraint Intensity and Welding Residual Stress of the Lehigh Specimen Made of Ti80 Alloy. Metals 2025, 15, 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15091019
Zhang L, Song G, Wang Q, Chen D, Guo X, Dai C, Bu W. Finite Element Analysis for Restraint Intensity and Welding Residual Stress of the Lehigh Specimen Made of Ti80 Alloy. Metals. 2025; 15(9):1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15091019
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Liang, Gang Song, Qi Wang, Dongjie Chen, Xiaolei Guo, Chang Dai, and Weixin Bu. 2025. "Finite Element Analysis for Restraint Intensity and Welding Residual Stress of the Lehigh Specimen Made of Ti80 Alloy" Metals 15, no. 9: 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15091019
APA StyleZhang, L., Song, G., Wang, Q., Chen, D., Guo, X., Dai, C., & Bu, W. (2025). Finite Element Analysis for Restraint Intensity and Welding Residual Stress of the Lehigh Specimen Made of Ti80 Alloy. Metals, 15(9), 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15091019






