Harnessing Industrial Waste for Sustainable Arsenic in a Mine Leachate Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
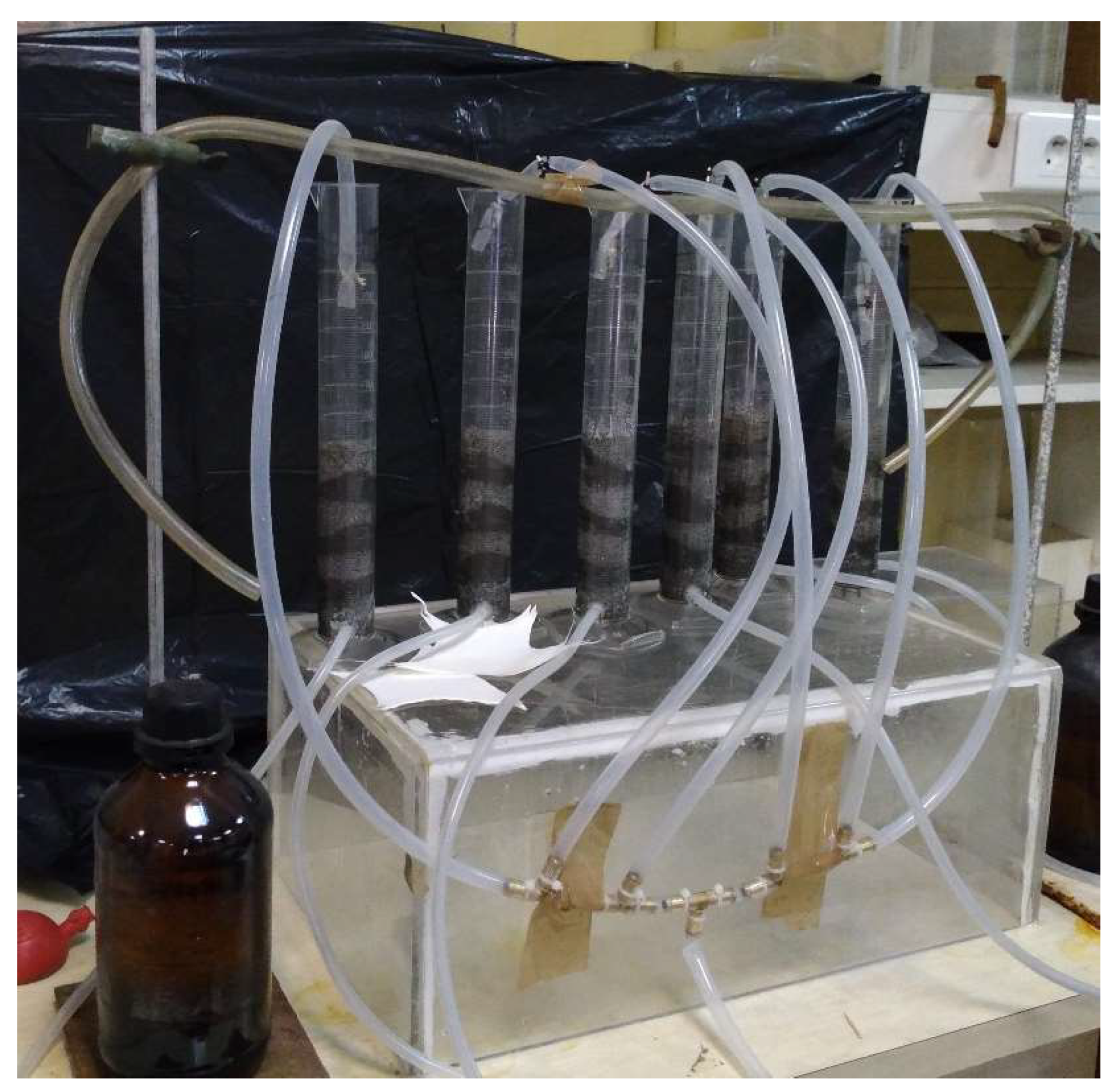
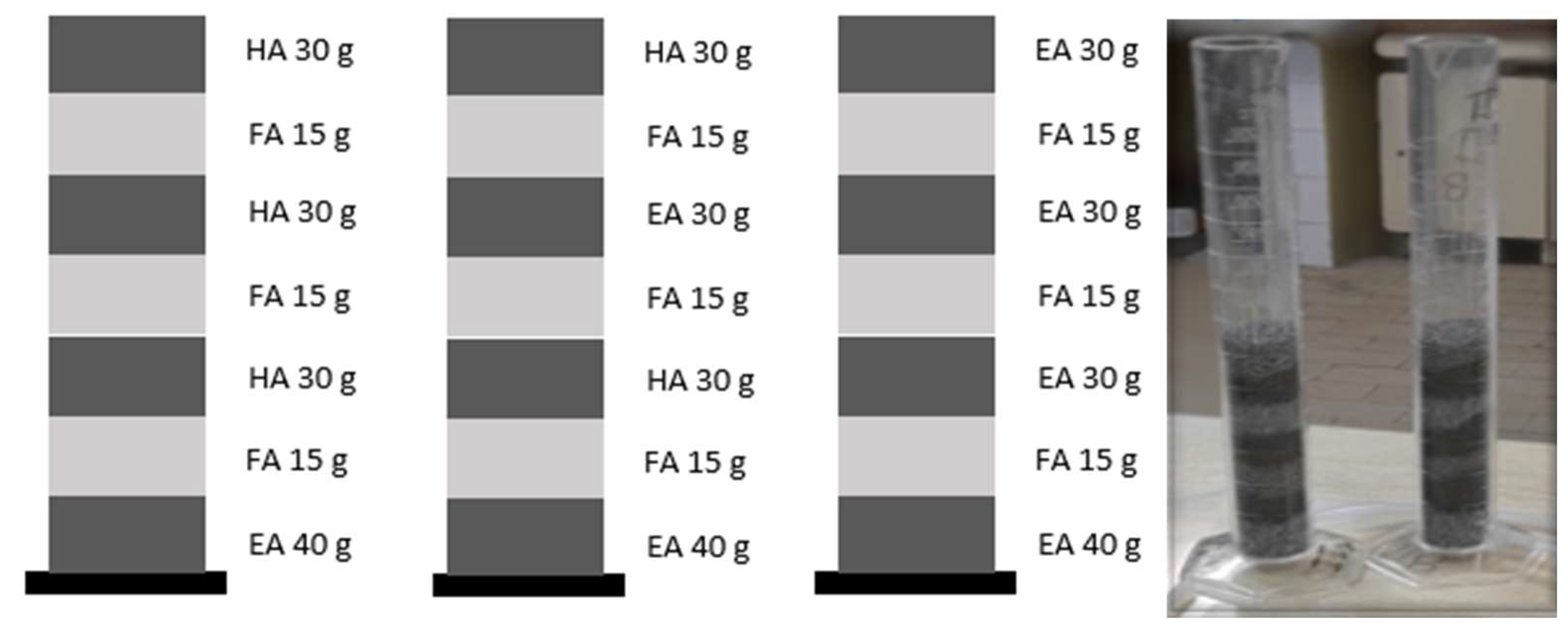
2.2.1. Columns
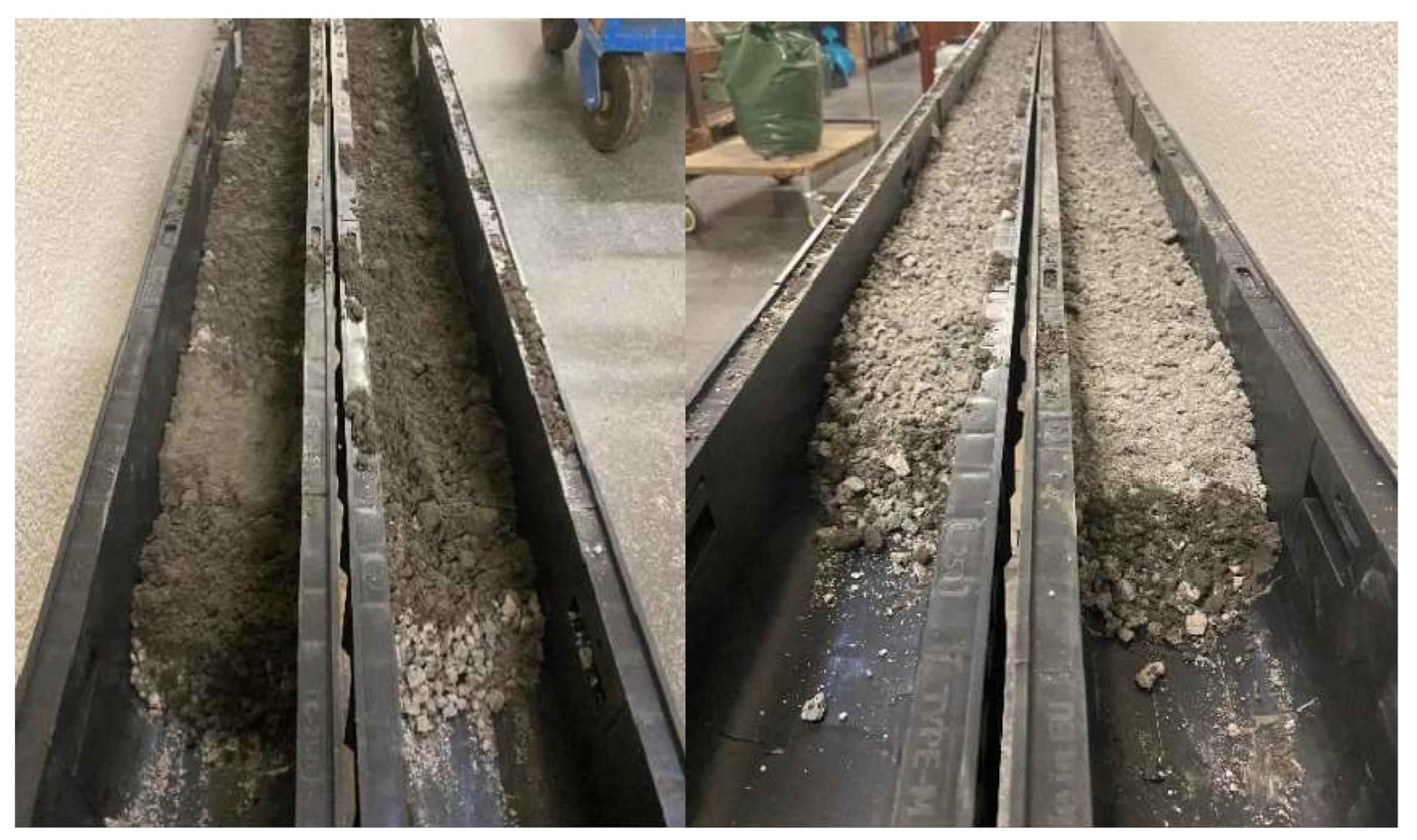
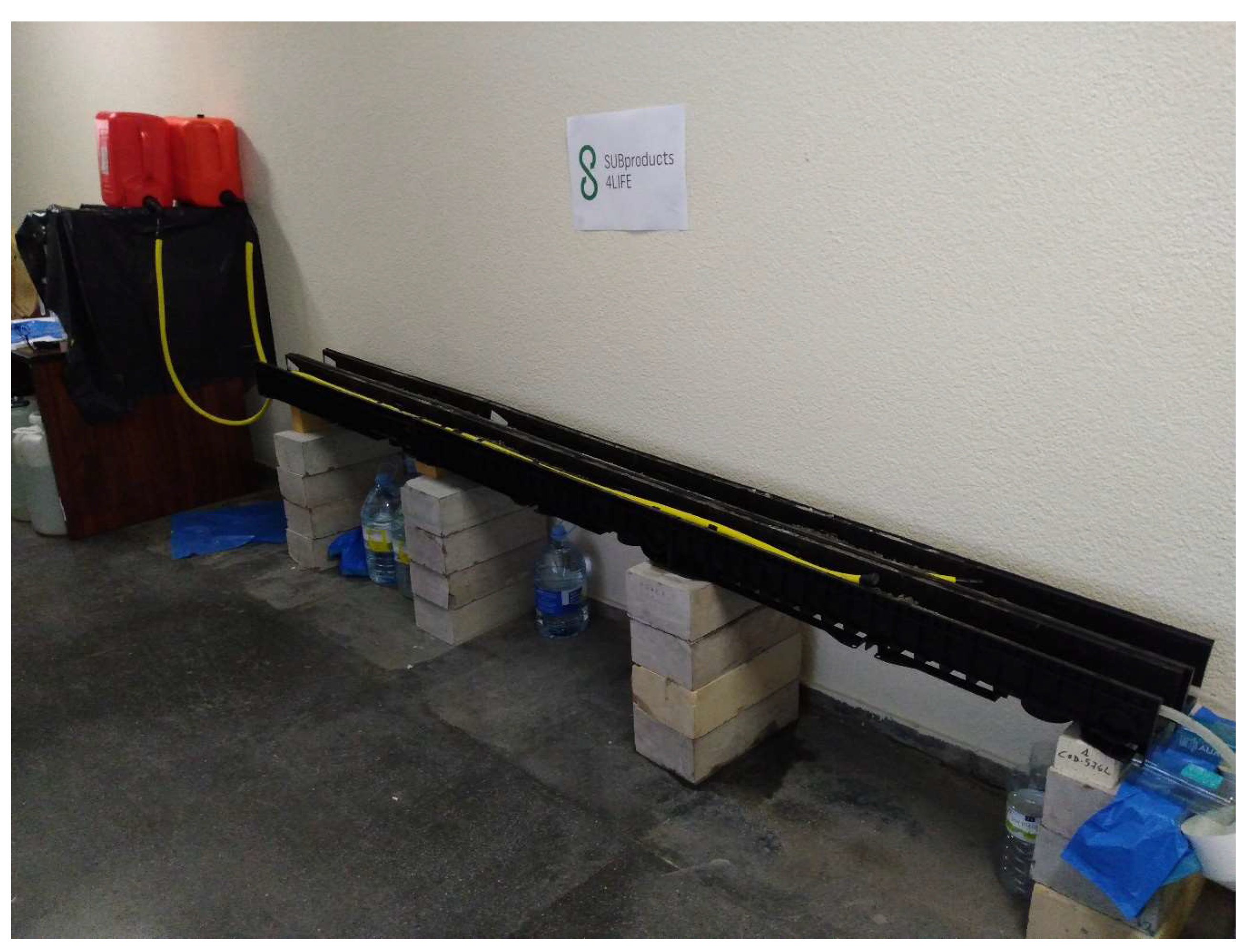
2.2.2. Microchannels
3. Results and Discussions
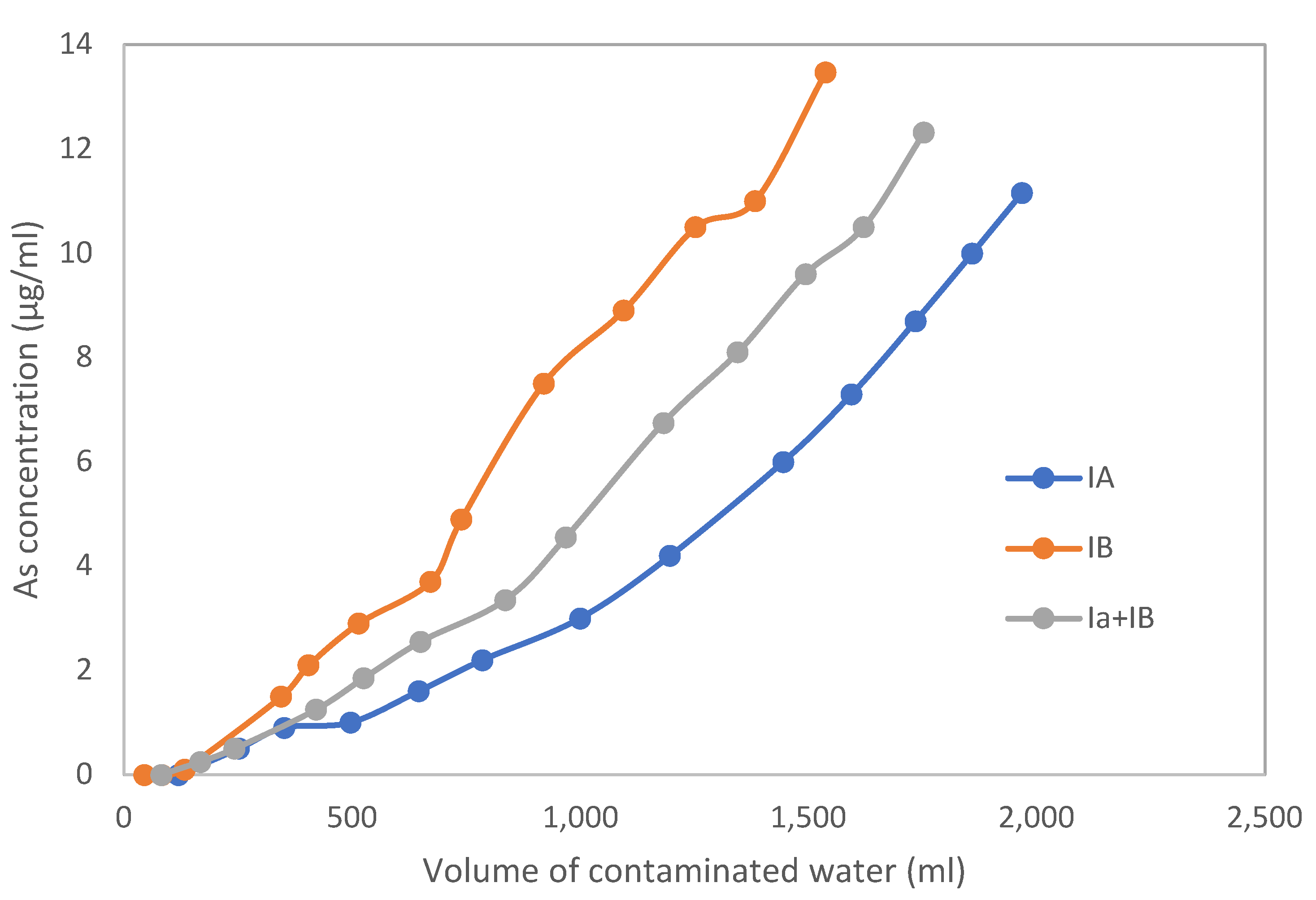
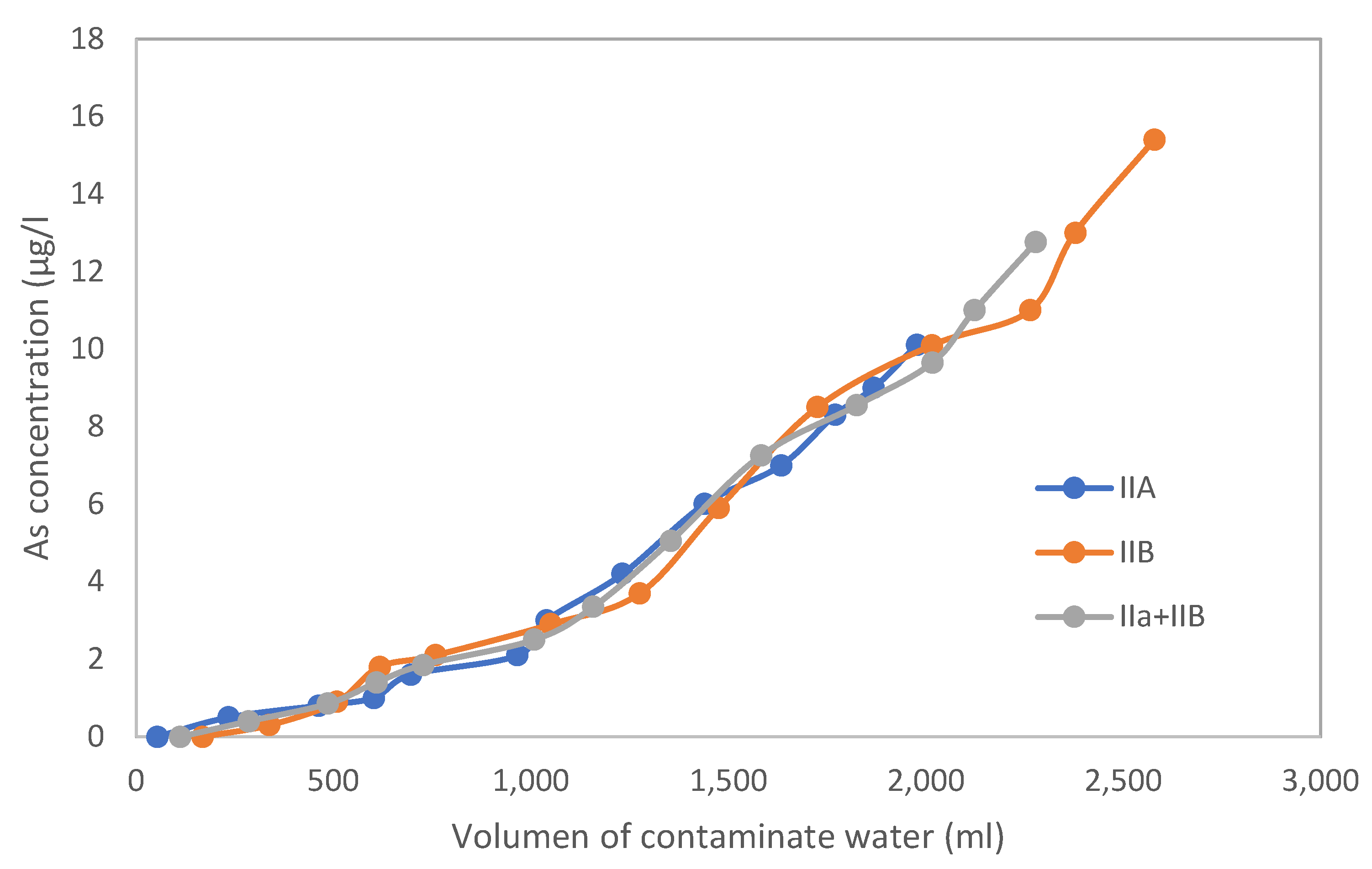
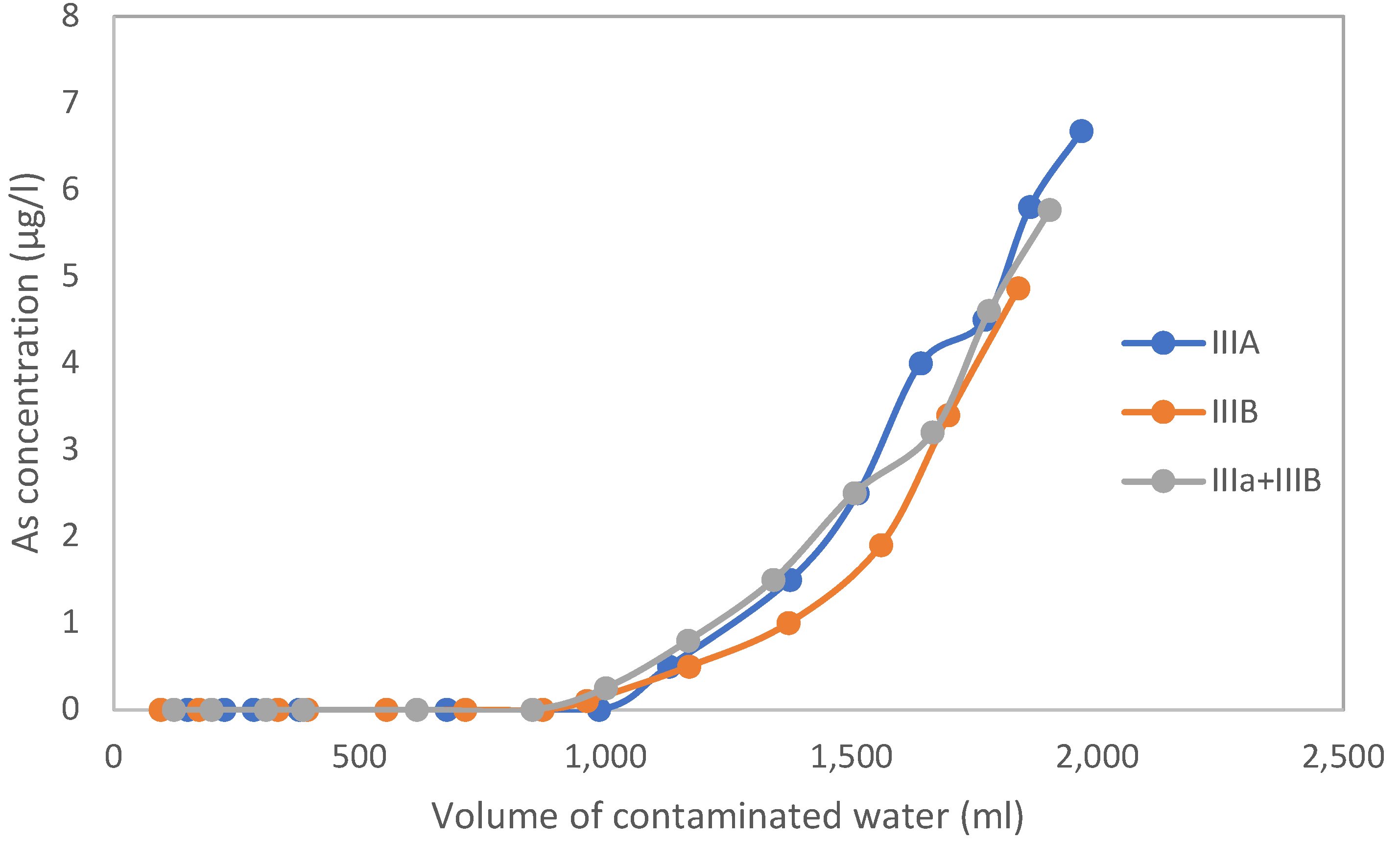
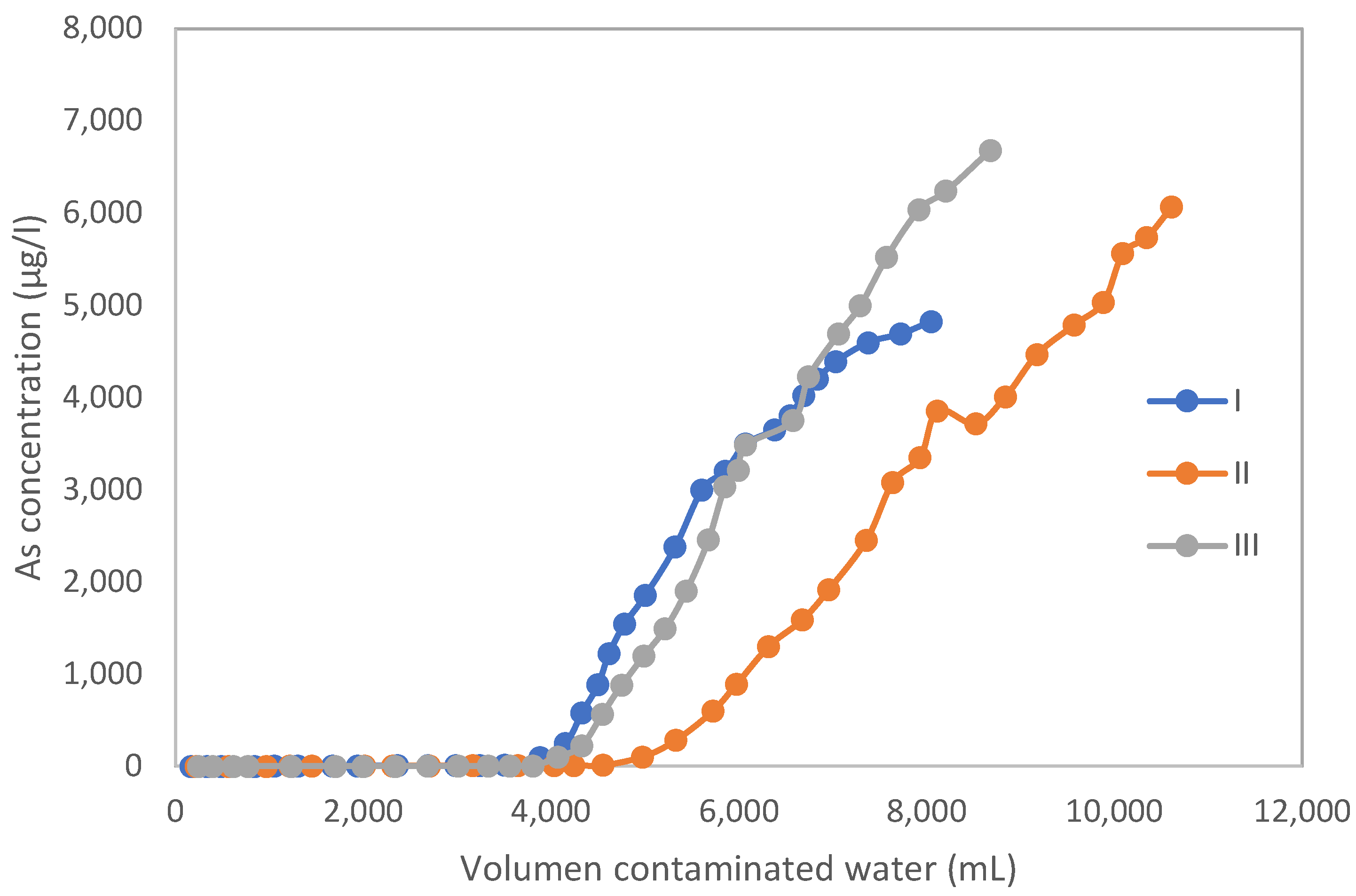
3.1. Test Columns
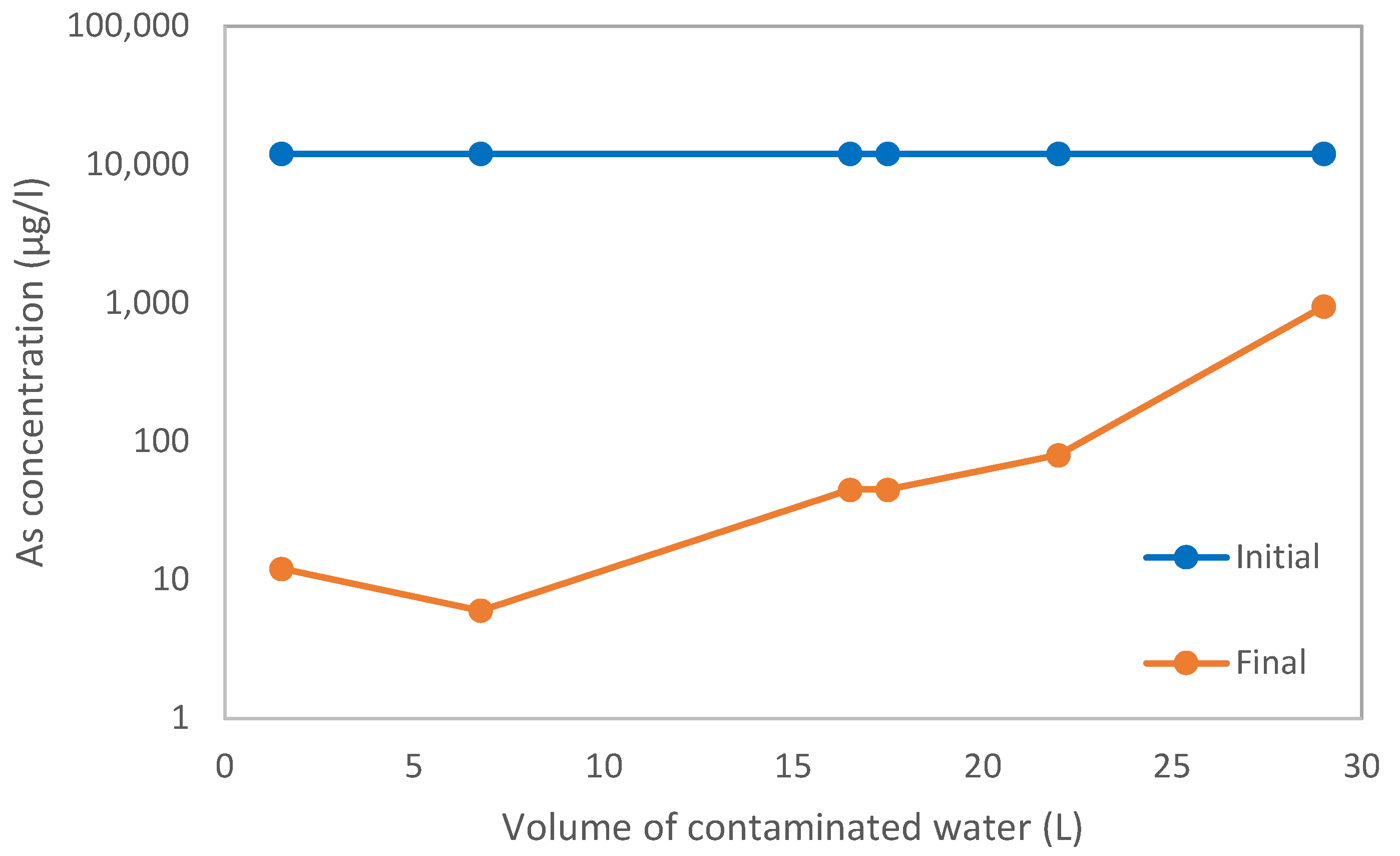
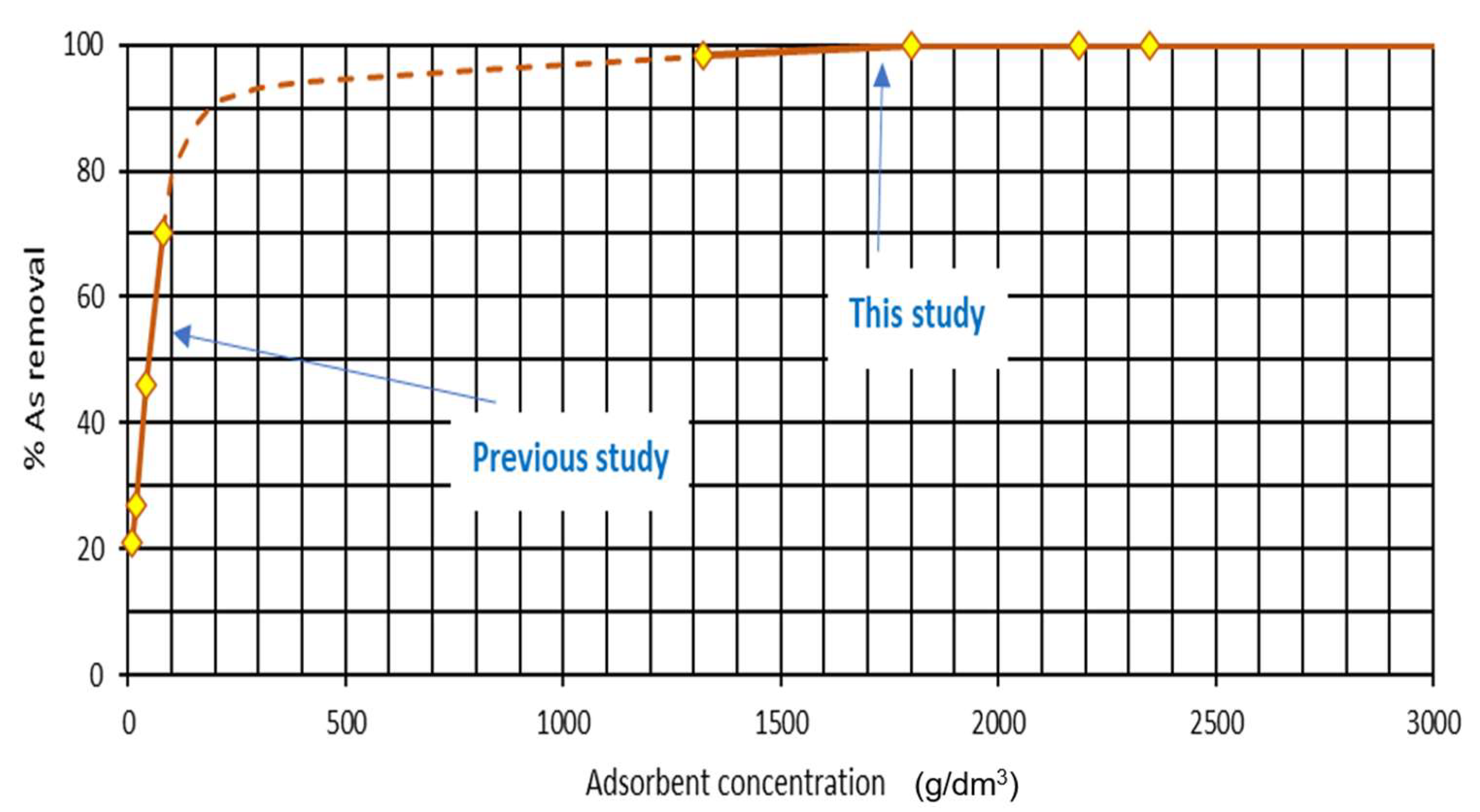
3.2. Microchannels
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kedar, H.N.; Patel, S.; Shirol, S.S. Bulk utilization of steel slag–fly ash composite: A sustainable alternative for use as road construction materials. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2023, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Mehdizadeh, H.; Ling, T. Environmental, economic and engineering performances of aqueous carbonated steel slag powders as alternative material in cement pastes: Influence of particle size. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Singh, S.; Parihar, P.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M. Arsenic contamination, consequences and remediation techniques: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 112, 247–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Huang, L.; Xue, S.; Huang, Y.; Hartley, W.; Cui, M.; Wong, M. Arsenic sorption by red mud-modified biochar produced from rice straw. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 18168–18178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieuwerts, J.; Mighanetara, K.; Braungardt, C.; Rollinson, G.; Pirrie, D.; Azizi, F. Geochemistry and mineralogy of arsenic in mine wastes and stream sediments in a historic metal mining area in the UK. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, M.; Drahota, P.; Machovič, V.; Böhmová, V.; Mihaljevič, M. Arsenic mineralogy and mobility in the arsenic-rich historical mine waste dump. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 536, 713–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haffert, L.; Craw, D. Mineralogical controls on environmental mobility of arsenic from historic mine processing residues, New Zealand. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 1467–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, N.M.A.; Othman, M.H.D.; Tai, Z.S.; Amhamed, A.O.A.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Puteh, M.H.; Sokri, M.N.M. Recent progress, bottlenecks, improvement strategies and the way forward of membrane distillation technology for arsenic removal from water: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 52, 103504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, Z.; Karim, A.; Karam, A.; Khalloufi, S. Adsorption of Heavy Metals: Mechanisms, Kinetics, and Applications of Various Adsorbents in Wastewater Remediation—A Review. Waste 2023, 1, 775–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsiah-Gyambibi, R.; Sokama-Neuyam, Y.A.; Boakye, P.; Ampomah, W.; Aggrey, W.N.; Wang, S. Valorization of coal fly ash (CFA): A multi-industry review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 12807–12822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgül, S.T.; Yıldıran, İ.; Erdem, T.; Ateş, N.; Bekaroğlu, Ş.Ş. A systematic study on adsorptive removal of arsenic using low-cost adsorbents with or without the presence of NOM. Int. J. Energy Stud. 2023, 8, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhou, W.; Lyu, X.; Liu, X.; Su, H.; Li, C.; Wang, H. Comprehensive utilization of steel slag: A review. Powder Technol. 2023, 422, 118449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.S.; Chon, C.; Moon, H.; Kim, K. Arsenic removal using steel manufacturing byproducts as permeable reactive materials in mine tailing containment systems. Water Res. 2003, 37, 2478–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, C.; Rhee, S.; Oh, M.; Park, J. Removal characteristics of As(III) and As(V) from acidic aqueous solution by steel making slag. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 213–214, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaja, A.; Delsing, A.; Van Der Laan, S.; Brouwers, H.; Yu, Q. Effects of carbonation on the retention of heavy metals in chemically activated BOF slag pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 148, 106534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meer, I.; Nazir, R. Removal techniques for heavy metals from fly ash. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2018, 20, 703–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aigbe, U.O.; Ukhurebor, K.E.; Onyancha, R.B.; Osibote, O.A.; Darmokoesoemo, H.; Kusuma, H.S. Fly ash-based adsorbent for adsorption of heavy metals and dyes from aqueous solution: A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 2751–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alinnor, I. Adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution by fly ash. Fuel 2006, 86, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Terdkiatburana, T.; Tadé, M. Single and co-adsorption of heavy metals and humic acid on fly ash. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 58, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xie, X.; Sun, S.; Wang, Y. Arsenic transformation and redistribution in groundwater is induced by the complex geochemical cycling of iron and sulfur. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 894, 164941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.; Kuo, S. Removal efficiency of arsenic in water using desulfurization slag. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2023, 55, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, J.; Fernández, B. Industrial waste materials as adsorbents for the removal of As and other toxic elements from an abandoned mine spoil heap leachate: A case study in Asturias. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 384, 121446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeno, K. Atlas of Eh-pH Diagrams. Intercomparison of Thermodynamic Databases. Geological Survey of Japan Open File Report No.419; National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology Research Center for Deep Geological Environments: Tokyo, Japan, 2005; pp. 30–31.
- Dai, M.; Xia, L.; Song, S.; Peng, C.; Lopez-Valdivieso, A. Adsorption of As (V) inside the pores of Porous hematite in water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 307, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, A.; Sengupta, A.; Bhadu, M.K.; Pandey, A.; Mondal, A. Efficient Removal of Arsenic (V) from Water Using Steel-Making Slag. Water Environ. Res. 2014, 86, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.; Chaudhry, S.A. Iron oxide and its modified forms as an adsorbent for arsenic removal: A comprehensive recent advancement. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 111, 592–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluteau, M.C.; Becze, L.; Demopoulos, G.P. The dissolution of scorodite in gypsum-saturated waters: Evidence of Ca–Fe–AsO4 mineral formation and its impact on arsenic retention. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 97, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H. Comparison of adsorption in batch and fixed-bed columns: A critical review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 10409–10426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbosiuba, T.C.; Abdulkareem, A.S. Highly efficient multi-walled carbon nanotubes, synthesised and oxidised, for the adsorption of copper (II) and zinc (II) ions in a batch and fixed bed process. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 2848–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaartinen, T.; Laine-Ylijoki, J.; Ahoranta, S.; Neitola, R. Removal of arsenic from mine water using sorption techniques. Mine Water Environ. 2017, 36, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koua-Koffi, N.A.A.; Coulibaly, S.L.; Ouattara, P.J.-M.; Coulibaly, L. Adsorption of Arsenic by Laterite, Sandstone and Shale in a Fixed-Bed Column. J. Mater. Sci. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 45–60. Available online: https://www.scirp.org/jounal/msce (accessed on 28 July 2025). [CrossRef]
- Mojori, A.; Raznu, E.; Dermani, B.K.; Rezania, S.; Kasmuri, N.; Vakili, M.; Farraji, H. Adsorption methods for arsenic removal from water bodies: A critical evaluation of their effectiveness and limitations. Front. Water 2024, 6, 1301648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litynska, M.; Dontsova, T.; Krymets, G.; Gusak, A. Nanostructured Adsorbents for Arsenic Compounds’ Removal. In Proceedings of the NANO 2022, Palma de Mallorca, Spain, 4–8 July 2022; Springer Proceedings in Physics. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| FA | EA | HA | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 (wt %) | 56.5 | 34.2 | 13.8 |
| Fe2O3 (wt %) | 9.5 | 0.3 | 37.9 |
| MgO (wt %) | 0.9 | 5.7 | 1.1 |
| K2O (wt %) | 2.6 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| Al2O3 (wt %) | 23.9 | 12.8 | 2.1 |
| CaO (wt %) | 3.4 | 42 | 38.3 |
| SO3 (wt %) | 2.0 | 3.3 | 1.14 |
| TiO2(wt %) | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.5 |
| MnO (wt %) | - | 0.3 | 3.5 |
| Hg mg/Kg | 2 | 5.5 | 16.3 |
| As mg/Kg | 59 | 10.3 | 37.8 |
| Zn mg/Kg | 90 | 4 | 57.5 |
| Cu mg/Kg | 57 | 2.2 | 26 |
| Cr mg/Kg | 83.6 | 27 | 49 |
| Pb mg/Kg | 16 | 1 | 9 |
| Ni mg/Kg | 65.4 | 0.4 | 24 |
| Cd mg/Kg | 1.8 | - | 0.16 |
| pH | 10.9 | 11.3 | 11.0 |
| real density g/cm3 | 2.4 | 3.0 | 3.6 |
| Subproduct | FA | EA | HA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subproducts mass (kg) | 0.135 | 0.240 | 0.150 |
| As | As | As | |
| Initial concentration (mg/kg) | 59 | 10.3 | 37.8 |
| Final concentration (mg/kg) | 1229 | 250.3 | 489.6 |
| Concentration increase (mg/kg) | 1110 | 240 | 451.8 |
| Mass of As retained (mg) | 157.9 | 57.6 | 67.8 |
| As | |
|---|---|
| Volume of contaminated water (L) | 29.48 |
| Average initial concentration (µg/L) | 12,472 |
| Average final concentration (µg/L) | 147 |
| Concentration reduction (%) | 98.82 |
| Concentration reduction (µg/L) | 12,325 |
| As mass retention (mg) | 363.3 |
| Subproduct | FA | HA |
|---|---|---|
| Subproducts mass (kg) | 15.5 | 23.5 |
| As | As | |
| Initial concentration (mg/kg) | 59 | 1.05 |
| Final concentration (mg/kg) | 71.46 | 7.94 |
| Concentration increase (mg/kg) | 12.46 | 6.89 |
| Mass of As retained (mg)) | 193.13 | 161.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández, B.; Ayala, J.; Rodríguez, R. Harnessing Industrial Waste for Sustainable Arsenic in a Mine Leachate Treatment. Metals 2025, 15, 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080888
Fernández B, Ayala J, Rodríguez R. Harnessing Industrial Waste for Sustainable Arsenic in a Mine Leachate Treatment. Metals. 2025; 15(8):888. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080888
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández, Begoña, Julia Ayala, and Rafael Rodríguez. 2025. "Harnessing Industrial Waste for Sustainable Arsenic in a Mine Leachate Treatment" Metals 15, no. 8: 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080888
APA StyleFernández, B., Ayala, J., & Rodríguez, R. (2025). Harnessing Industrial Waste for Sustainable Arsenic in a Mine Leachate Treatment. Metals, 15(8), 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080888






