Abstract
Compared with vanadium extraction by sodium roasting followed by water leaching, the calcification roasting–sulfuric acid leaching method is considered a promising approach for the comprehensive utilization of vanadium titanomagnetite, as it avoids the introduction of alkali metals. However, during vanadium extraction by sulfuric acid heap leaching, the diffusion of leaching reagents and leaching products was hindered by the deposition of leaching solid products. To address this issue, this study systematically investigated the leaching kinetics and the mechanisms underlying the deposition of leaching solid products. The results indicated that vanadium leaching was governed by a combination of liquid film diffusion and internal diffusion through solid-phase products during days 0–2, and by internal diffusion alone from day 2 to day 9. The primary solid products formed during leaching were calcium sulfate and silica gel. Calcium sulfate precipitated and grew within the pore via two-dimensional nucleation, while silicates formed silica gel through dehydration. By optimizing the sulfuric acid leaching conditions—specifically, maintaining an H+ concentration of 2 mol/L, a leaching temperature of 40 °C, and a liquid-to-solid ratio of 5:1—the formation of calcium sulfate and silica gel was effectively suppressed. Under these conditions, the vanadium leaching efficiency reached 75.82%.
1. Introduction
Vanadium is a silver–gray metal known for its high hardness, corrosion resistance, and elevated melting point [1]. According to statistics, more than 90% of vanadium is consumed in the steel industry, where it serves as an alloying element that markedly enhances the strength, toughness, and heat resistance of steel [2]. Beyond metallurgy, vanadium and its oxides play crucial roles in the chemical industry, particularly as catalysts in sulfuric acid production and petroleum refining [3]. Additionally, vanadium is gaining importance in the new energy sector, notably in all-vanadium redox flow batteries for energy storage [4], and is also utilized in aerospace applications and superconducting materials due to its unique physical properties.
Vanadium titanomagnetite (VTM) is a crucial raw material for vanadium extraction [5,6], with approximately 88% of vanadium products in China derived from this source [7]. Given the low vanadium content in VTM, the prevailing industrial approach involves enriching vanadium via the blast furnace–converter process to produce vanadium-rich steel slag, from which vanadium is subsequently extracted [8]. Current research primarily focuses on developing efficient and environmentally friendly methods for recovering vanadium from this slag [9,10,11]. However, significant vanadium losses occur during the ironmaking and steelmaking stages, as partly vanadium transitions from VTM to the slag phase [12,13], thereby reducing the overall utilization efficiency of vanadium from VTM [14].
Many studies have focused on the direct vanadium extraction method to improve vanadium recovery efficiency by reducing the traditional blast furnace–converter smelting process. Currently, direct extraction from VTM mainly involves several approaches: sodium roasting followed by water leaching [15], calcification roasting followed by acid leaching, additive-free roasting followed by alkali leaching [16], and additive-free roasting followed by acid leaching [17]. Sodium roasting followed by water leaching has been widely employed to extract vanadium from both VTM and vanadium-rich steel slag [18]. In this process, highly alkaline sodium salts react with vanadium oxides in VTM to form soluble sodium vanadate, enabling selective vanadium extraction through subsequent water leaching. To enhance the sodium roasting process, the sodium salt dosage during roasting typically ranges from 50 wt% to 80 wt%. However, excessive sodium addition adversely affects the downstream utilization of other elements in leached slag, requiring the removal of sodium prior to ironmaking. This additional step complicates the process and hinders the economical and efficient utilization of leached slag [19]. In addition, although the additive-free roasting-alkaline leaching method avoids the introduction of large quantities of sodium salts, it suffers from a low vanadium conversion rate during the roasting stage. This results in poor selectivity during the subsequent alkaline leaching process, with a vanadium leaching efficiency of only 59.1% [16]. Consequently, this method currently cannot serve as an effective alternative to the widely adopted roasting with the sodium–water leaching process.
The calcification roasting–sulfuric acid leaching process is considered one of the most promising alternatives to roasting with sodium–water leaching for vanadium extraction from VTM. By using a calcific agent instead of sodium salts during roasting, this method effectively avoids the adverse impact of sodium on the utilization of leached slag [20]. Moreover, the sulfuric acid leaching step offers high selectivity for vanadium extraction, further enhancing its potential as a cleaner and more efficient approach. Current research has focused on the selection of calcific agents [21,22], the enhancement of vanadium oxidation during the roasting process [14], and the optimization of the sulfuric acid leaching process [23]. Previous studies have shown that promoting vanadium oxidation by precisely controlling the preheating temperature and duration during calcification roasting can significantly improve vanadium leaching efficiency. Under optimized heap leaching conditions (a sulfuric acid concentration of 3.5 mol/L, liquid-to-solid ratio of 3:1, leaching temperature of 90 °C, and leaching duration of 100 h), a vanadium leaching efficiency of 72.89% was achieved. However, substantial formation of calcium sulfate has been observed in leached pellet, which interferes with leaching kinetics and mass transfer, thereby limiting vanadium recovery efficiency [21,23]. Therefore, a systematic study on the formation characteristic of solid products during the sulfuric acid leaching of calcification roasted pellets is urgently needed.
This study systematically investigates the vanadium dissolution leaching kinetics during sulfuric acid leaching. The key factors limiting vanadium leaching efficiency were identified, and the growth mechanisms of calcium sulfate and silica gel were elucidated. Based on these insights, targeted inhibition strategies were proposed to suppress the formation of these solid products, thereby enhancing the efficiency of the leaching process. These findings provide a technical foundation for minimizing solid product formation and improving vanadium leaching efficiency in sulfuric acid leaching.
2. Methodology
2.1. Raw Materials
The roasted calcification VTM pellets used for sulfuric acid leaching were prepared in our previous study. The chemical composition of these pellets is presented in Table 1. According to the X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis shown in Figure 1, the primary phases present in the roasted calcification pellets are Fe(Ti)2O3 and Fe2TiO5. Other components, including vanadium-bearing phases, are present in low concentrations, and no distinct characteristic peaks associated with them were observed in the XRD patterns.

Table 1.
Chemical compositions of the roasted calcification VTM pellets (wt%).

Figure 1.
The XRD patterns of roasted calcification pellets.
The microstructure and elemental distributions at both the shell and core of the roasted calcification pellets are shown in Figure 2a,b. The microstructural analysis revealed that the pellets were thoroughly oxidized, exhibited a uniform structure, and contained abundant inter-particle pore features that are favorable for vanadium extraction via sulfuric acid leaching. Elemental mapping further indicated a strong spatial correlation between vanadium and titanium, as well as between calcium, magnesium, and silicon. These observations suggested that vanadium in the roasted calcification pellets was primarily associated with plate titanite and silicate phases.
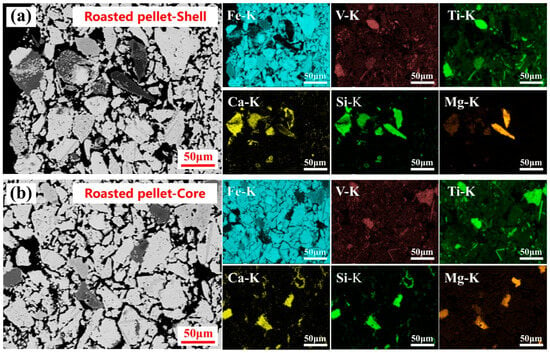
Figure 2.
Microstructure and elemental distribution of the roasted calcification pellet shell (a) and core (b).
2.2. Sulfuric Acid Leaching
The sulfuric acid leaching experiments were conducted under varying conditions, including different acid concentrations (0.5–2.5 mol/L H+/0.25–1.25 mol/L H2SO4), leaching temperatures (25–60 °C), and liquid-to-solid ratios (1:1–5:1), with a fixed leaching time of 24 days. During the leaching process, the concentrations of H+ and vanadium in the leachate were monitored. Additional sulfuric acid was added as necessary to maintain a consistent H+ concentration. Upon completion of leaching, the leachate and solid residues were separated via vacuum filtration. The concentrations of vanadium, silicon, and calcium in the leachate were measured using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) to evaluate the leaching efficiencies of vanadium, silicon, and calcium. Finally, the leached pellets were examined using scanning electron microscopy coupled with energy-dispersive spectroscopy (SEM-EDS) to investigate the aggregation behavior of calcium sulfate and silica sol.
2.3. Analysis and Characterization
The leaching efficiency of vanadium, calcium, and silicon (R) was defined by the following formula:
where C is the content of vanadium, calcium, and silicon in the leachate (g/L), V is the volume of leachate (L), m is the mass of roasted VTM pellets before sulfuric acid leaching (g), and ε is the element mass content of vanadium, calcium, and silicon in the roasted VTM pellets (wt%).
The chemical composition of the roasted VTM calcification pellets was determined by chemical titration tests for characterization. The content of vanadium, silicon, and calcium in leachate was measured by an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP-MS, TCP-5100-VDV, Agilent Technologies, Malaysia). The various phases presented in samples and sulfuric acid leached pellets were identified by powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD, Rigaku D/Max, Shimadzu Manufacturing, Kyoto, Japan) using CuKα radiation (λ = 1.5418 Å). The operated voltage and anode current were 35 kV and 20 mA, respectively. The microstructure of the roasted calcification pellet and leached pellets were examined employing the SEM. Additionally, the samples underwent SEM/EDS analysis utilizing a scanning electron microscope (VEGA3 LMH; TRSCAN, JSM-7900F, Nippon Electronics Corporation, Japan) outfitted with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (Oxford, Octane X, EDAX, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of the Vanadium Leaching Kinetic Behavior
The sulfuric acid leaching results at different temperatures over a 9-day period are presented in Figure 3. It was evident that increasing the leaching temperature from 25 °C to 40 °C enhanced vanadium leaching efficiency during the leaching process. Furthermore, the leaching behavior over the 0–9-day period can be divided into two distinct stages based on changes in the vanadium leaching rate. In the first stage (0–2 days), vanadium leaching efficiency increased rapidly, reaching approximately 45% within two days. In the second stage (2–9 days), the vanadium leaching rate declined significantly, and the leaching efficiency increased more slowly, ultimately reaching about 60–65% by day 9.
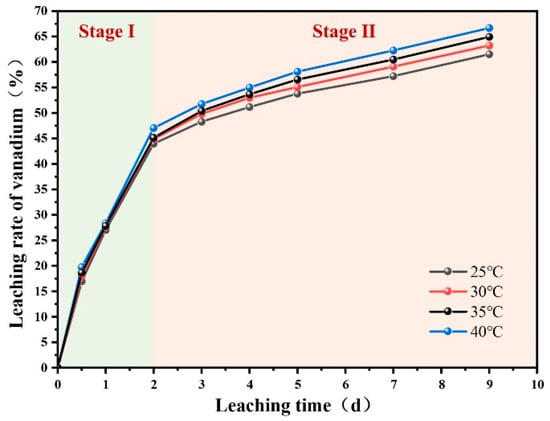
Figure 3.
Effect of leaching temperature on vanadium leaching rate.
Compared to the roasted pellets, the mass loss during the leaching process was minimal, and the pellet volume remained largely unchanged throughout sulfuric acid leaching. Moreover, sulfuric acid was replenished in a timely manner to maintain a constant H+ concentration as the reaction progressed. Therefore, the leaching of roasted calcification pellets can be reasonably approximated as a homogeneous reaction with constant particle size and constant acid concentration. Under these conditions, the unreacted shrinking core model applies [24] with different kinetic equations corresponding to different rate-controlling steps to the following:
Liquid film diffusion control:
kt = 1 − (1 − δ)2/3
Surface chemical reaction control:
kt = 1 − (1 − δ)1/3
Internal diffusion of solid phase product control:
kt = 1 + 2(1 − δ) − 3(1 − δ)2/3
Liquid film diffusion and internal diffusion of solid phase product control:
where t is the leaching time, δ is the vanadium leaching efficiency, and k is the apparent reaction rate constant.
kt = 2 + 2(1 − δ) − 4(1 − δ)2/3
The leaching experimental data in stage Ⅰ and stage Ⅱ at different leaching temperature were fitted into the above four kinetic equations, respectively, and the calculated correlation coefficients R2 are shown in Figure 4a,b to judge the controlling factors of the vanadium leaching efficiency during sulfuric acid leaching.
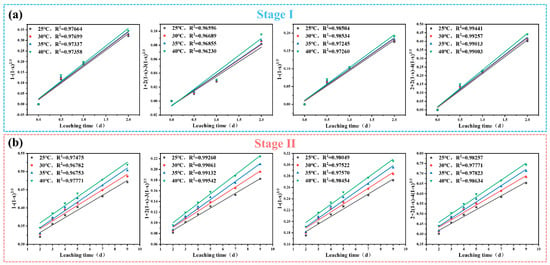
Figure 4.
Plot of 1 − (1 − x)2/3, 1 + 2(1 − x) − 3(1 − x)2/3, 1 − (1 − x)1/3, and 2 + 2(1 − x) − 4(1 − x)2/3 versus leaching time at (a) stage Ⅰ (0–2d) and (b) stage Ⅱ (2–9d).
As shown in Figure 4a, a clear linear relationship was observed between 2 + 2(1 − δ) − 4(1 − δ)2/3 and leaching time (t) during stage Ⅰ. The corresponding R2 values at different leaching temperatures were 0.9944 (25 °C), 0.9925 (30 °C), 0.9901 (35 °C), and 0.9900 (40 °C). Additionally, the correlation coefficients obtained using Equation (7) were significantly higher than those from Equations (4)–(6), indicating that vanadium leaching efficiency in stage Ⅰ (0–2 days) was controlled by a combination of liquid film diffusion and internal diffusion of solid phase products. Similarly, in the stage Ⅱ (2–9 days), there also existed strong linear relationships between 1 + 2(1 − δ) − 3(1 − δ)2/3 and leaching time (t), as shown in Figure 4b. The R2 values for stage Ⅱ at different leaching temperatures were 0.9926 (25 °C), 0.9906 (30 °C), 0.9913 (35 °C), and 0.9954 (40 °C). In this case, the correlation coefficients of vanadium leaching efficiency calculated by Equation (6) were significantly higher than those of Equations (4), (5) and (7). Therefore, internal diffusion control of solid phase products was the dominant rate-controlling mechanism during stage II.
In addition, the apparent reaction rate constant k1 for stage Ⅰ was 0.2141 at 40 °C, which was significantly higher than the apparent reaction rate constant k2 for stage Ⅱ, calculated at 0.0179 under the same conditions. These kinetic results indicated that a substantial amount of vanadium was rapidly dissolved by sulfuric acid during stage I. However, in stage II, the vanadium leaching rate declined markedly due to the increasing resistance from internal diffusion of solid phase products.
The apparent reaction rate constants k at temperatures of 25 °C, 30 °C, 35 °C, and 40 °C at different stages were plotted against 1000/T and fitted, as shown in Figure 5a,b. The correlation coefficients R2 exceeded 0.99, indicating a strong linear relationship between lnk and 1000/T, consistent with the Arrhenius equation. Based on the slope of the fitted lines, the apparent activation energy Ea for vanadium sulfuric acid leaching was calculated to be 4.22 kJ/mol for stage I and 13.93 kJ/mol for stage II. In the conventional unreacted shrinking core model for liquid–solid reactions, the apparent activation energy for external diffusion is typically in the range of 0–8 kJ/mol [25,26], while that for internal diffusion control of solid phase product control ranges from 8 to 30 kJ/mol [27,28]. The apparent activation energy determined in this study falls within these ranges, indicating consistency with previously reported values.
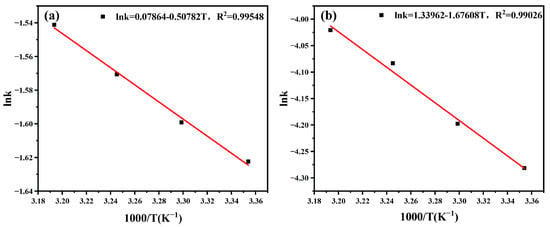
Figure 5.
Arrhenius plot for the leaching process controlled by liquid film diffusion and internal diffusion of solid phase product control at stage Ⅰ (a) and internal diffusion of solid phase product control at stage Ⅱ (b).
The leaching kinetics of sulfuric acid extraction from calcification-roasted vanadium titanomagnetite pellets were investigated by Wang [23] and Zheng [14] et al. Their experimental results, fitted using the classical unreacted shrinking core model, indicated that the vanadium leaching process in the later stages of sulfuric acid treatment is controlled by internal diffusion control of solid phase products. The apparent activation energy of the leaching process was calculated using the Arrhenius equation to be 25.88 kJ/mol. In their study, Wang et al. employed a cyclic sulfuric acid leaching approach, which led to the continuous enrichment of vanadium in the leaching solution. This accumulation was found to hinder the further dissolution of vanadium, potentially explaining the higher apparent activation energy observed compared to that obtained in the present study.
Therefore, as the leaching time increased, the vanadium leaching rate gradually increased, accompanied by a rise in the energy required for vanadium extraction from roasted calcification pellets via sulfuric acid leaching. The observed kinetic behavior suggests that the reduction in leaching efficiency and the increase in apparent activation energy was primarily attributed to diffusion resistance caused by the accumulation of solid reaction products. Calcium sulfate and silica gel are the main solid products formed in the sulfuric acid leaching process, and the generation principle of these two solid products will be revealed in depth later.
3.2. Calcium Sulfate Crystal Growth Mechanism
Previous studies have shown that the formation of solid calcium sulfate during the roasted-calcification-pellet sulfuric acid leaching hindered the diffusion of reactants and leaching products. In this section, the crystallization behavior and growth mechanism of calcium sulfate were further investigated to elucidate its role in limiting vanadium leaching efficiency. These insights aimed to provide a foundation for developing strategies to enhance vanadium recovery in subsequent work.
The microstructure and elemental distributions of the leached pellets after one day of sulfuric acid leaching are shown in Figure 6. As observed in Figure 6a, significant acid decomposition of the silicate phase occurred at the pellet shell, indicating that sulfuric acid preferentially reacted with silicate phases in the roasted calcification pellets. In contrast, titano-hematite and plate titanite remained largely intact, showing minimal acid decomposition. Additionally, no sulfur-containing phases were detected at the leached pellet shell. In the leached pellet center, however, a clear accumulation of sulfur-containing phases was observed, with a strong spatial correlation between sulfur and calcium elements. These results suggested that calcium sulfate preferentially precipitated in the center of the leached pellets, while its formation was limited at the shell during the first day of sulfuric acid leaching.
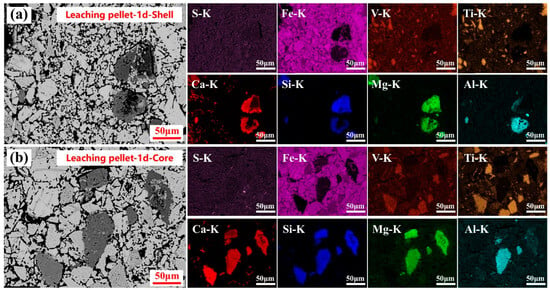
Figure 6.
Microstructure and elemental distribution of the leached pellets shell (a) and core (b) after one day of sulfuric acid leaching.
As the sulfuric acid leaching time was extended to 5 days, the large-sized silicate particles at both the shell and centers of the leached pellets underwent further acid decomposition. The inter-particle pores were noticeably enlarged, creating additional space for calcium sulfate crystallization. However, even after 5 days, no significant aggregation of sulfur-containing phases was observed at the leached pellet shell. In contrast, compared to the pellets leached for 1 day, a substantial amount of calcium sulfate in the leached pellet centers continued to crystallize and grow, accumulating within the enlarged inter-particle pores, as shown in Figure 7b. The results indicated that calcium sulfate preferentially crystallized in the center of the leached pellet during the 5-day sulfuric acid leaching process.
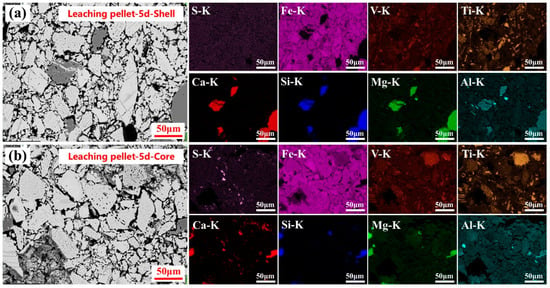
Figure 7.
Microstructure and elemental distribution of the leached pellets shell (a) and core (b) after 5 days of sulfuric acid leaching.
After extending the sulfuric acid leaching time to 24 days, the microstructures and elemental distributions at the shell and centers of the leached pellets are shown in Figure 8. The sulfuric acid leaching process completely disrupted the dense pore structure of the roasted calcification pellets, and the microcrystalline bonding between titano-hematite particles was dissolved. A large portion of the silicate phases were leached into the solution, forming visible voids or black holes in the leached pellet microstructure. Notably, in the leached pellet center, the correlation between calcium and silicon elements decreased significantly, while the correlation between calcium and sulfur elements increased markedly. This indicated that sulfuric acid leaching dissolved silicate phases and simultaneously promoted the formation of bar-shaped calcium sulfate crystals around the resulting pores. Additionally, similar to the leaching results after 1 day and 5 days, the calcium sulfate content was substantially higher in the leached pellet center compared to the shell.
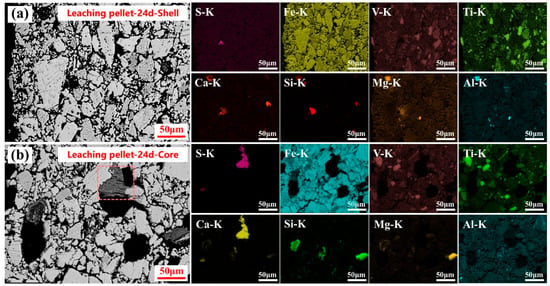
Figure 8.
Microstructure and elemental distribution of the leached pellet shell (a) and core (b) after 24 days of sulfuric acid leaching.
The XRD patterns of the leached pellets after 1, 5, and 24 days of sulfuric acid leaching are shown in Figure 9. The main phases identified in the leached samples were Fe(Ti)2O3 and Fe2TiO5. These results indicated that the sulfuric acid leaching process exhibited good selectivity for vanadium, while iron-bearing phases such as hematite and titanite displayed poor solubility. Additionally, after 24 days of sulfuric acid leaching, characteristic peaks corresponding to calcium sulfate began to appear. This phase formed through the acid dissolution of calcium-containing silicate minerals in the calcification roasted pellets, followed by the reaction of released calcium with sulfate ions. The results suggested that the formation and growth of calcium sulfate were promoted with prolonged leaching time. These XRD findings were consistent with the observed microstructure and elemental distribution of the leached pellets.
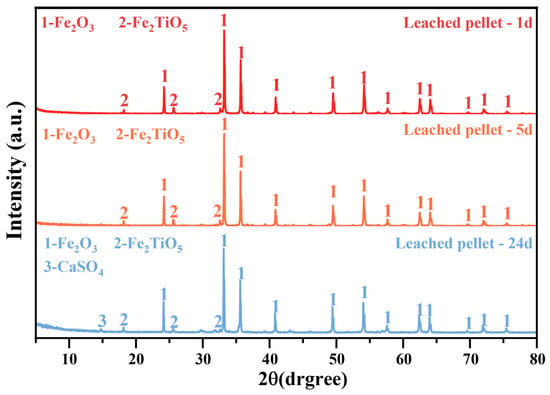
Figure 9.
The XRD patterns of leached pellet after sulfuric acid leaching for 1 day, 5 days, and 24 days.
Calcium sulfate crystals commonly grow through three kinetic mechanisms: spiral growth, two-dimensional nucleation growth, and adhesion growth. Spiral growth typically occurs at low supersaturation levels, two-dimensional nucleation growth is favored as supersaturation increases, and adhesion growth dominates at high supersaturation levels. These growth modes produce distinct crystal morphologies: generally, spiral growth yields needle-like calcium sulfate crystals, two-dimensional nucleation results in rod-like calcium sulfate crystals, and adhesion growth produces lamellar calcium sulfate crystals. Based on the observed microstructure, the calcium sulfate crystals in the center of the leached pellets predominantly exhibited rod-like morphology, indicating a two-dimensional nucleation growth mechanism. Furthermore, these rod-shaped crystals appeared to be stacked within inter-particle pores formed during sulfuric acid leaching process, without attachment to other particle surfaces, suggesting that their formation occurred via spontaneous two-dimensional nucleation and growth within the pore spaces.
The proposed mechanism of calcium sulfate crystal growth during the sulfuric acid leaching of the VTM-roasted calcification pellet process is illustrated in Figure 10. In the initial stage of leaching, sulfuric acid diffuses into the pellet and initiates the acid hydrolysis of calcium silicate (CaSiO3), resulting in increased concentrations of calcium and sulfate ions in the leachate. As sulfuric acid leaching progresses, the ionic product of calcium and sulfate ions eventually exceeds the solubility product of calcium sulfate, leading to its nucleation and crystallization. With rising supersaturation, calcium sulfate molecules begin to accumulate in two dimensions on the crystal nuclei, forming rod-like crystals through a two-dimensional nucleation growth manner. Thus, the crystallization behavior of calcium sulfate is strongly influenced by the relationship between the ionic product and the solubility product. At the pellet shell, efficient mass transfer of reactants and leaching products reduces the local ionic product of calcium and sulfate ions, resulting in low supersaturation and the formation of only minor amounts of needle-like calcium sulfate crystals. In contrast, mass transfer to the pellet center is hindered due to limited pore connectivity and longer diffusion paths. This leads to localized accumulation of calcium ions and elevated supersaturation, promoting more extensive crystallization and nucleation. Consequently, calcium sulfate preferentially forms and aggregates into rod-shaped crystals within the central pores of the leached pellet.
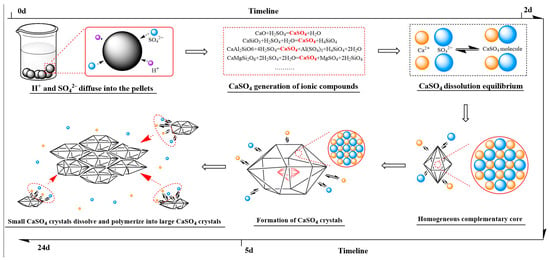
Figure 10.
The calcium sulfate crystal growth mechanism during sulfuric acid leaching process.
3.3. Silica Sol Agglomeration Mechanism
The E-pH diagram for silicic acid is shown in Figure 11b. The pH of the solution has a significant effect on the fugacity state of silicic acid. Under the condition of pH <10, the main existent form of silica acid is H4SiO4, which is transformed only when the pH is biased to strongly alkaline conditions. Since the sulfuric acid leaching system is acidic, the silicon was leached and existed in the solution mainly in the H4SiO4 state. The transformation of H4SiO4 from a molecule to a solid involves sol and gel stages. Silicic acid molecules can undergo free Brownian motion in the leaching solution, and simple silicic acid molecules polymerize with each other to form silica sols in the process of free motion. That is, two H4SiO4 molecules in contact with each other after the occurrence of the combination of a H4SiO4 in the H4SiO4 in the H+ and another H4SiO4 in the OH− were broken in their hydrogen bonding connection. While the two silicate molecules combined with each other to form a new structure, these H4SiO4 molecules in combination with each other to form a small-scale colloid are called silica sol. During the prolonged roasted pellet leaching process, the silica sols grow further and combine with each other to form a silicate gel. These silicate gels render the leaching solution immobile. As shown in Figure 11a, the residual silica gel content in the leached pellets gradually increased with the extension of sulfuric acid leaching time.
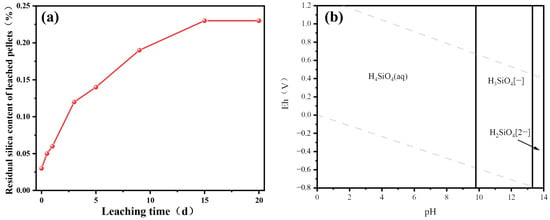
Figure 11.
Alkali leaching results of sulfuric acid-leached pellets (a) and E-pH of silicic acid (b).
The sulfuric acid leached pellets were alkaline-leached subsequently with sodium hydroxide to further demonstrate the formation of silica sol during sulfuric acid leaching. The microstructure and elemental distribution of the alkali leached pellets are shown in Figure 12. After alkaline leaching, the main physical phase of the leached pellets did not change; they were still dominated by titanium hematite and plate titanium with a strong correlation between iron and titanium elements. It was noteworthy that there was a strong correlation between sodium and silicon elements in the alkali leached pellets, and that the associated sodium-containing particles were located on the surface of titanium hematite particles. The EDS analysis shown in Figure 12b further proved that the gray particles on the surface of titanium hematite particles were sodium silicoaluminate. The acid leaching process of roasted calcification pellets generated silicic acid, which accumulated and grew during the long leaching process and adhered to the surface of vanadium-containing particles, hindering the reaction between vanadium-containing phases and sulfuric acid, thus reducing the vanadium leaching efficiency.
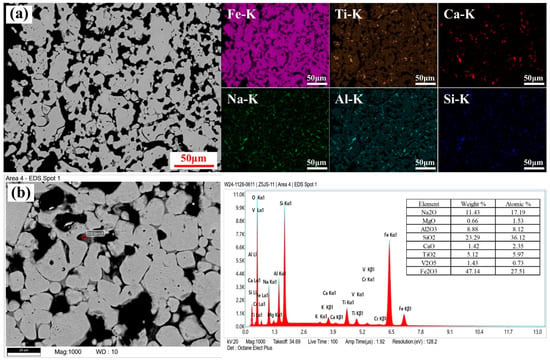
Figure 12.
Microstructure (b) and elemental distribution (a) of the alkali leached pellets.
3.4. Sulfuric Acid Leaching Process Enhancement
Research on the growth mechanism of calcium sulfate crystals has demonstrated that the formation of calcium sulfate during sulfuric acid leaching can be inhibited by either reducing the ionic product of calcium and sulfate ions or by increasing the solubility of calcium sulfate. In parallel, investigations into the agglomeration mechanism of silica sol have revealed that its formation can be suppressed by increasing the pH of the leaching solution or by reducing the silicon content in the roasted calcification pellets. Based on these findings, the sulfuric acid leaching process was optimized in this study to mitigate the formation of calcium sulfate and silica sol, thereby enhancing the vanadium leaching efficiency from the roasted calcification of VTM pellets.
The effect of H+ concentrate on vanadium, calcium, and silicon leaching rates is presented in Figure 13a–c. As the H+ concentration increased, the vanadium leaching rate initially rose and then leveled off. The increase in H+ concentration introduced more sulfate ions and decreased the pH in the leaching system, which facilitated the formation of calcium sulfate and silica gel. In addition, H+ ions served as essential reactants in the vanadium leaching reaction; their beneficial effect was most pronounced when the concentration was below 2.0 mol/L. Beyond this threshold, specifically at 2.5 mol/L, the process became increasingly limited by internal diffusion of solid phase products, thereby restricting further improvement in vanadium leaching efficiency.
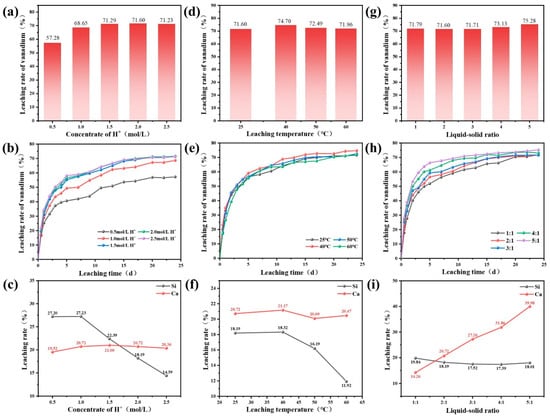
Figure 13.
Effect of H+ concentrate (a–c), leaching temperature (d–f), and liquid–solid ratio (g–i) on vanadium, calcium, and silicon leaching rate.
As shown in Figure 13d–f, leaching temperature has a significant influence on vanadium leaching behavior. With the increase of leaching temperature, the vanadium leaching efficiency initially increased, reaching a peak of 74.70% at 40 °C, and then began to decline. This trend correlated with the solubility characteristic of calcium sulfate, which reaches its maximum solubility at approximately 40 °C. Consequently, calcium leaching efficiency also showed a similar trend, peaking at 21.17% at 40 °C due to the enhanced dissolution of calcium sulfate. Additionally, elevated leaching temperatures accelerated the Brownian motion of silicate molecules in the leachate, thereby facilitating the agglomeration of silica sol, which in turn reduced silicon leaching efficiency. The formation of calcium sulfate and silica sol was detrimental to vanadium leaching efficiency as it contributes to internal diffusion of solid phase product resistance. Therefore, a leaching temperature of 40 °C was determined to be optimal for maximizing vanadium leaching efficiency.
The effect of liquid–solid ratio on vanadium, calcium, and silicon leaching efficiencies is presented in Figure 13g–i. The vanadium leaching efficiency increased progressively with the rise in the liquid–solid ratio. Notably, when the ratio reached 5:1, the vanadium leaching efficiency attained a maximum of 75.28%. Regarding calcium and silicon leaching behaviors, increasing the liquid–solid ratio resulted in a dilution of calcium ion concentration in the leachate, which enhanced the dissolution of calcium sulfate. Moreover, a higher liquid–solid ratio improved the fluidity of the leaching solution, avoiding the agglomeration of silica sol, thereby mitigating the adverse effects of silica sol formation on mass transfer processes. These combined effects contributed to a marked improvement in vanadium leaching efficiency.
4. Conclusions
This study systematically investigates the vanadium leaching kinetics during the sulfuric acid leaching of roasted calcification pellets. The key factors limiting vanadium leaching efficiency were identified, and the growth mechanisms of calcium sulfate and silica gel were elucidated. The following conclusions can be drawn.
- (1)
- The vanadium leaching was controlled by liquid film diffusion and internal diffusion of solid phase products during stage I (0–2 days), and by internal diffusion of solid phase products during stage II (2–9 days). The apparent activation energy Ea for vanadium sulfuric acid leaching was calculated to be 4.22 kJ/mol for stage I and 13.93 kJ/mol for stage II.
- (2)
- Calcium sulfate and silica gel are the main solid products formed in the sulfuric acid leaching process. Calcium sulfate preferentially aggregates into rod-shaped crystals within the center of the leached pellet compared to the shell, and the formation occurred via spontaneous two-dimensional nucleation within the pore spaces. While silicic acid molecules polymerize with each other to form silica sols, the silica sols further grow and combine to form a silicate gel.
- (3)
- Under the H+ concentration of 2 mol/L, a leaching temperature of 40 °C, and a liquid–solid ratio of 5:1, the sulfuric acid leaching process was optimized to mitigate the formation of calcium sulfate and silica sol; thereby, the vanadium leaching efficiency reached 75.28%.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.C. (Shuzhong Chen) and Y.G.; methodology, J.C., B.H., and F.C.; software, S.W. and L.Y.; validation, J.C., B.H., and Y.G.; formal analysis, Y.Z., S.C. (Shuzhong Chen), S.C. (Shiyuan Cui), and J.L.; investigation, S.C. (Shiyuan Cui), J.L., and L.Y.; resources, S.C. (Shiyuan Cui); writing—original draft, Y.Z.; writing—review and editing, J.C., S.C. (Shuzhong Chen), Y.G., and G.Q.; visualization, S.W., F.C., J.L., and L.Y.; supervision, Y.G. and G.Q.; project administration, S.W., F.C., and G.Q.; funding acquisition, J.C., Y.Z., B.H., and G.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University [2022ZZTS0118].
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Jianli Chen, Benliu He, Shuzhong Chen, Shiyuan Cui and Jing Liu were employed by the LB Group Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, J.; Yu, W.; Xiang, J.; Liu, W.; Zhong, D.; Xu, S.; Lv, X. Toward High-Purity Vanadium-Based Materials: Fundamentals, Purifications, and Perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 476, 143721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graedel, T.E.; Miatto, A. Vanadium: A U.S. Perspective on an Understudied Metal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 8933–8942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Jain, A.; Ichikawa, T.; Kojima, Y.; Dey, G.K. Development of Vanadium Based Hydrogen Storage Material: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wu, S.; Chen, F.; Xu, J. A Comparative Study of Iron-Vanadium and All-Vanadium Flow Battery for Large Scale Energy Storage. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zhu, D.; Pan, J.; Lu, S. Isothermal Reduction Kinetics and Microstructure Evolution of Various Vanadium Titanomagnetite Pellets in Direct Reduction. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 953, 170126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Jiang, W.; Dai, Z.; Yao, L.; Yang, L.; Zheng, J. Advancements and Challenges in Vanadium Extraction Processes from Vanadium Titano-Magnetite and Its Derivatives. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2025, 216, 108178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, C.; Han, X.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, L.; Wang, L.; He, Z. A Review on Vanadium Extraction Techniques from Major Vanadium-Containing Resources. Rare Met. 2024, 43, 4115–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Jiang, T.; Wen, J.; Yu, T.; Li, F. Review of Leaching, Separation and Recovery of Vanadium from Roasted Products of Vanadium Slag. Hydrometallurgy 2024, 226, 106313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Ye, L.; Du, J. Research Progress of Vanadium Extraction Processes from Vanadium Slag: A Review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 342, 127035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Yang, J. Vanadium Extraction from Steel Slag: Generation, Recycling and Management. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 343, 123126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, X.; Zhang, J.; Liang, Y.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G. Comparison and Evaluation of Vanadium Extraction from the Calcification Roasted Vanadium Slag with Carbonation Leaching and Sulfuric Acid Leaching. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 297, 121466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Sun, D.; Zhu, R.; Dong, K.; Bai, R. Effect of Side-Blowing Arrangement on Flow Field and Vanadium Extraction Rate in Converter Steelmaking Process. ISIJ Int. 2018, 58, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Tang, P. Optimization on Temperature Strategy of BOF Vanadium Extraction to Enhance Vanadium Yield with Minimum Carbon Loss. Metals 2021, 11, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, F.; Wang, S.; Guo, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, F.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L. Effect of Calcification Roasting Process on Vanadium Oxidation and Extraction from Vanadium Titanomagnetite Pellets via Sulfuric Acid Leaching: Mechanism and Enhancement. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 128859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Du, H.; Wang, S.; Chen, B.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, B.; Olayiwola, A.U. A Comparative Study of Extracting Vanadium from Vanadium Titano-Magnetite Ores: Calcium Salt Roasting vs. Sodium Salt Roasting. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2023, 44, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Y.; Gao, Q.; Shen, F. Transformation of Vanadium-Bearing Titanomagnetite Concentrate in Additive-Free Roasting and Alkaline-Pressure Leaching for Extracting Vanadium (V). Minerals 2019, 9, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ma, B.; Zhao, S.; Yao, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, B.; Gao, M.; Feng, G. Vanadium Extraction from Water-Cooled Vanadium Converter Slag via Salt-Free Roasting and Acid Leaching. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 172, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, G.; Xiao, R.; Luo, J.; Yi, L.; Rao, M. Extraction of Vanadium from Low-Vanadium Grade Magnetite Concentrate Pellets with Sodium Salt. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 5712–5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Qiao, S. Sodium Carbonate Roasting and Mild Acid Leaching of Vanadium Titanomagnetite Concentrates: Vanadium Extraction and Residue Sodium Decrease. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 185, 1132–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Che, X.; Cui, X.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, L. Selective Leaching of Vanadium from V-Ti Magnetite Concentrates by Pellet Calcification Roasting-H2SO4 Leaching Process. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2021, 31, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Han, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xie, K. Vanadium–Titanium Magnetite Concentrate, Calcium–Magnesium Composite Roasting and Sulfuric Acid Leaching for Vanadium Extraction from Pellets. Metals 2023, 13, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Peng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Xie, K. Study on the Properties of Vanadium Pellets Extracted from Vanadium Titanium Magnetite Concentrate by Calcium Roasting and Acid Leaching. Minerals 2023, 13, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Peng, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xie, K. Selective Sulfuric Acid Cyclic Leaching of Vanadium from the Calcification Roasting Pellets of Vanadium Titanomagnetite. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Guo, Y.; Chen, F.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Qiu, G. Fluoride Leaching of Titanium from Ti-Bearing Electric Furnace Slag in [NH4+]-[F−] Solution. Metals 2021, 11, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Jiang, T.; Xu, Y.; Wen, J.; Xue, X. Leaching Kinetics of Vanadium and Chromium During Sulfuric Acid Leaching With Microwave and Conventional Calcification-Roasted High Chromium Vanadium Slag. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2020, 41, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Guo, J.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Z.; Tao, C. Leaching kinetics of vanadium from calcification roasting converter vanadium slag in acidic medium. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5119–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Chen, J.; Luo, K.; Yan, F.; Zhang, W. The leaching model and leaching kinetics of lithium slag in alkaline solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 432, 136642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, N.; Chen, H.; Su, C.; Wang, H.; Dong, Y.; Wu, L. Kinetics Investigation of Phosphorus Leaching from Steelmaking Slag. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2023, 44, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).