Study on Incremental Sheet Forming Performance of AA2024 Aluminum Alloy Based on Adaptive Fuzzy PID Temperature Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
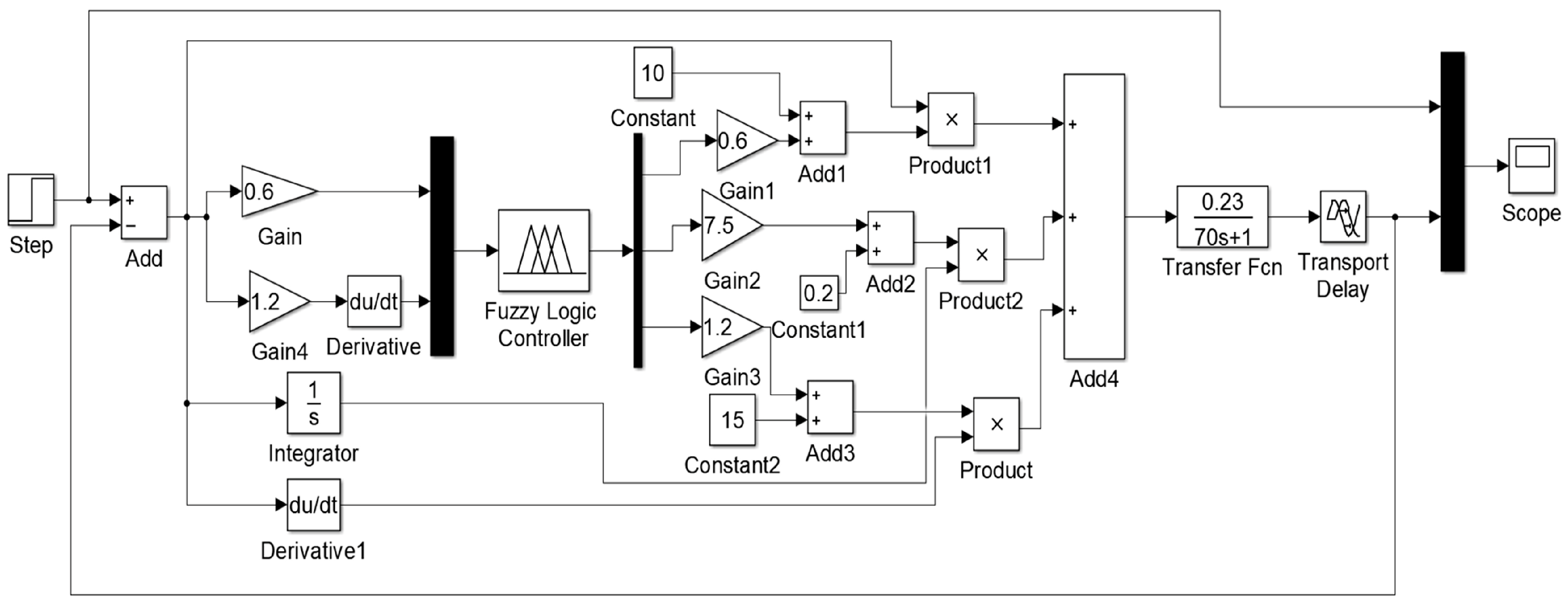
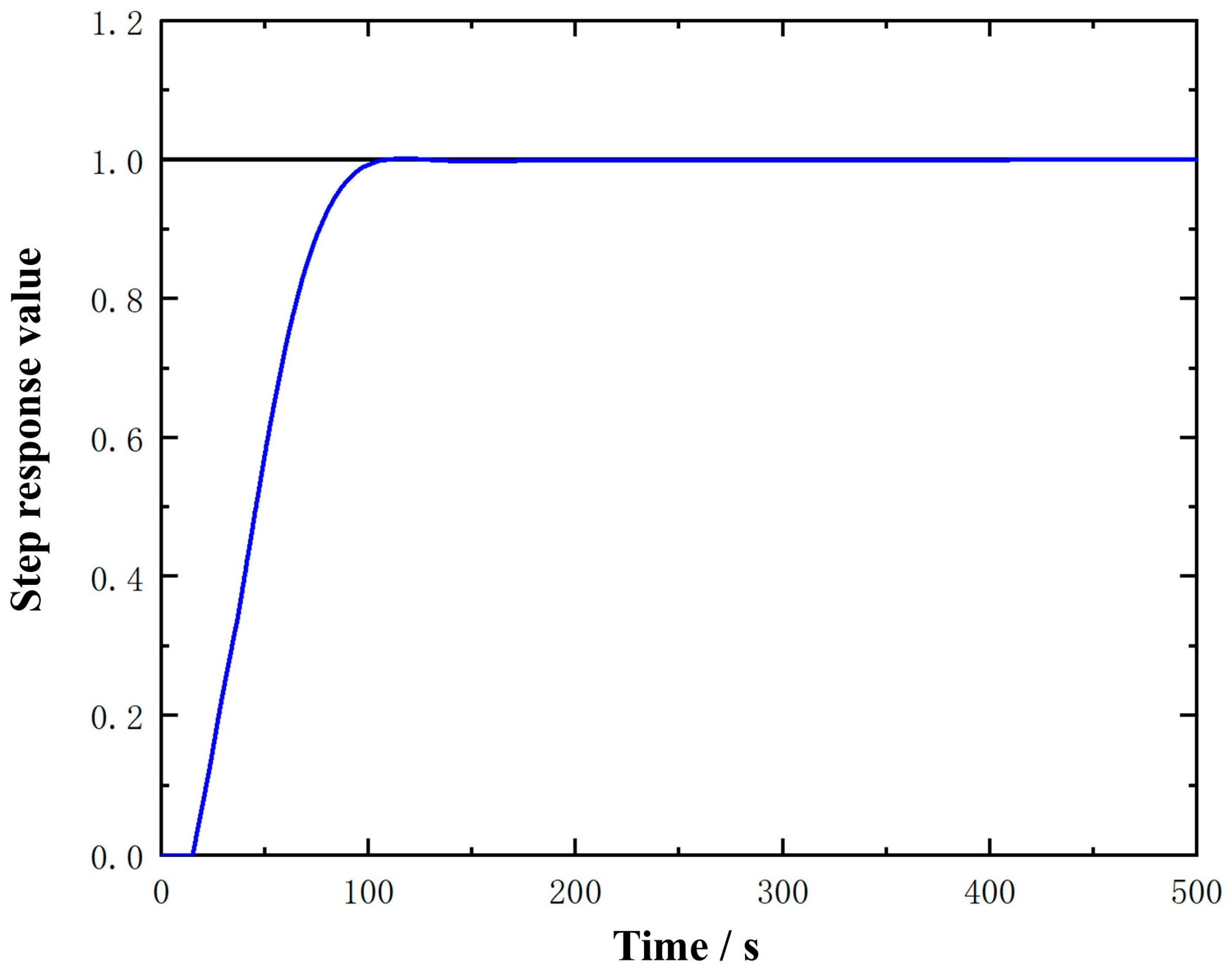
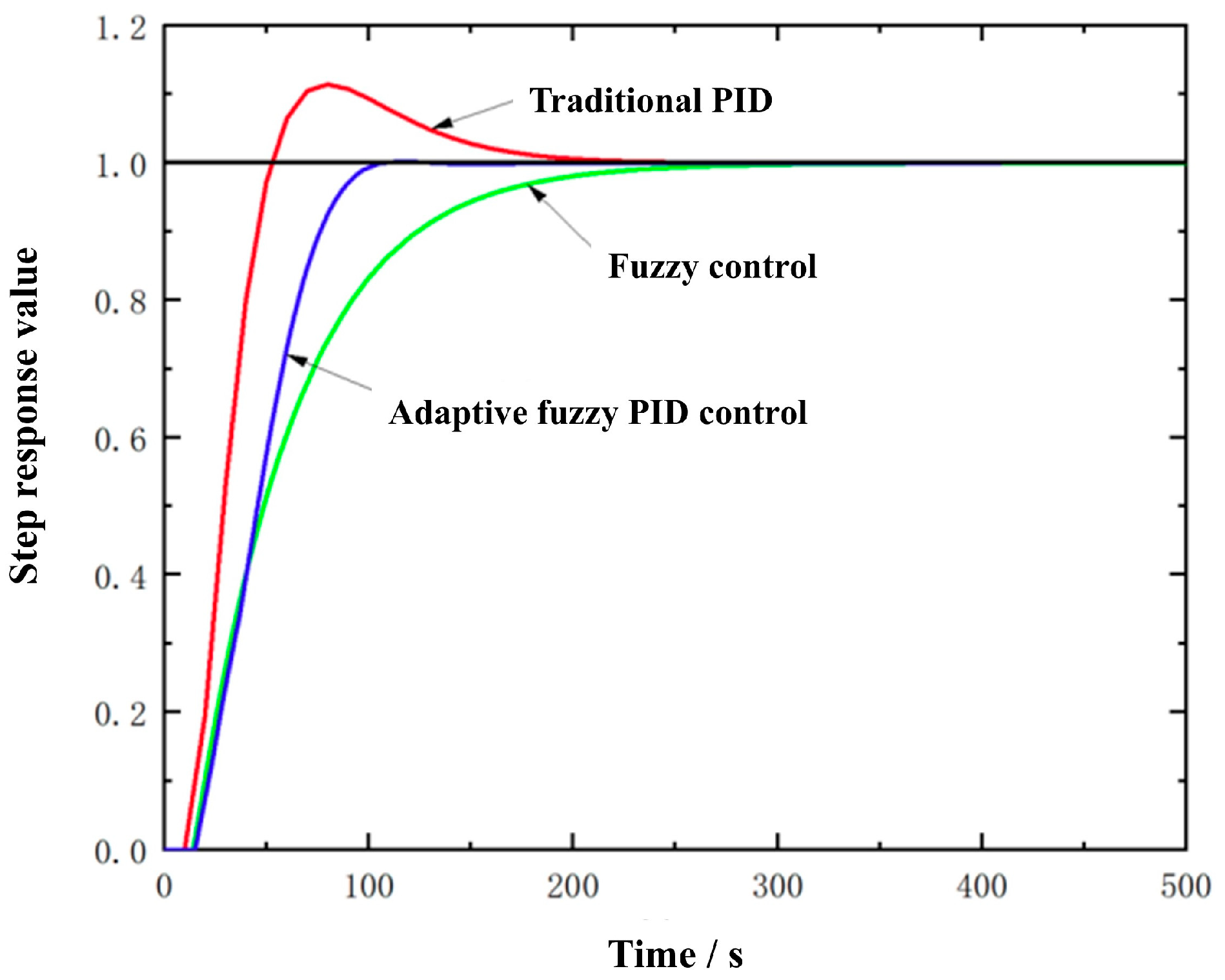
3.1. Analysis of Control Algorithms
3.2. Analysis of Forming Limit Angles
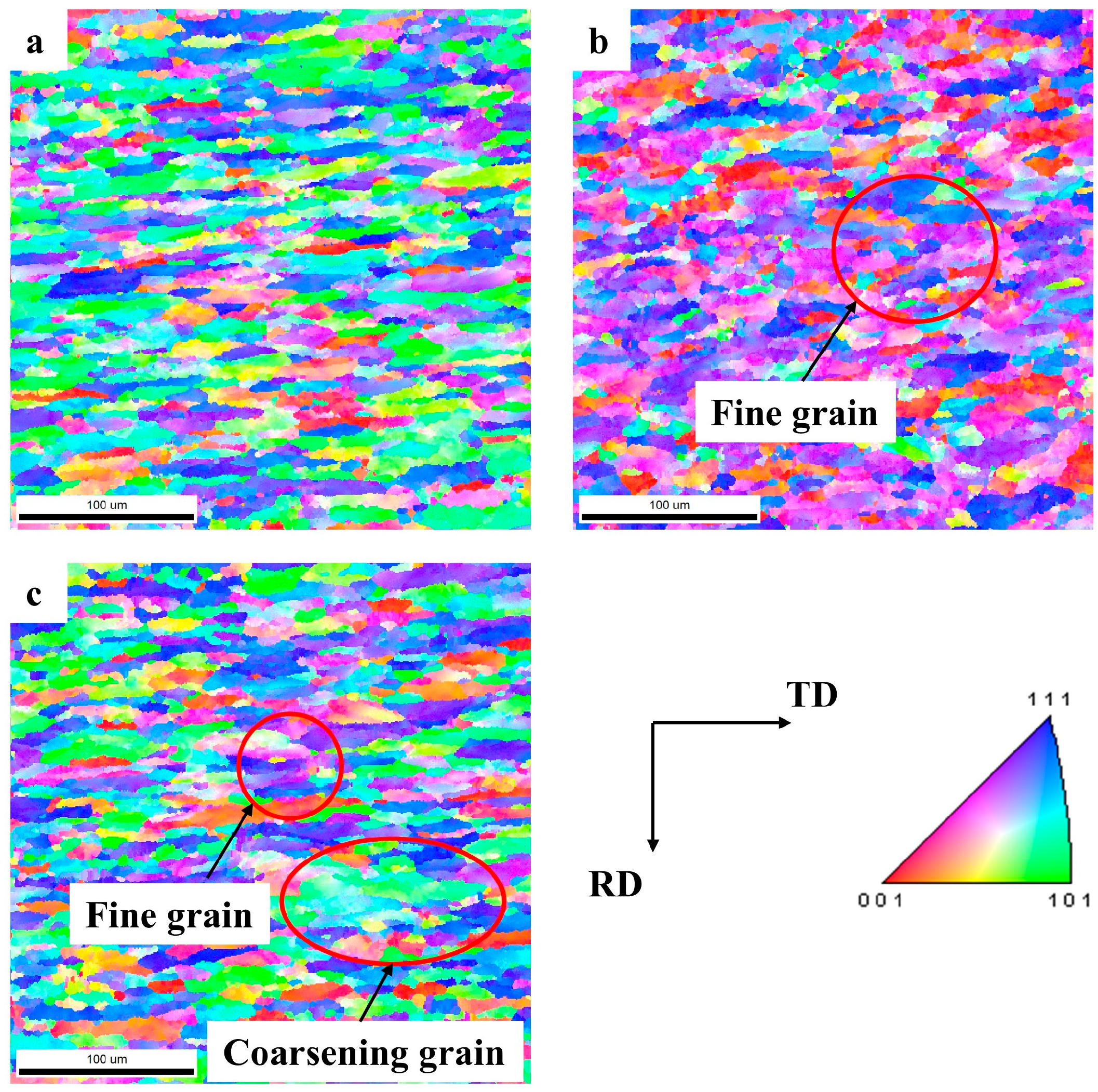
3.3. Analysis of Microstructure
4. Conclusions
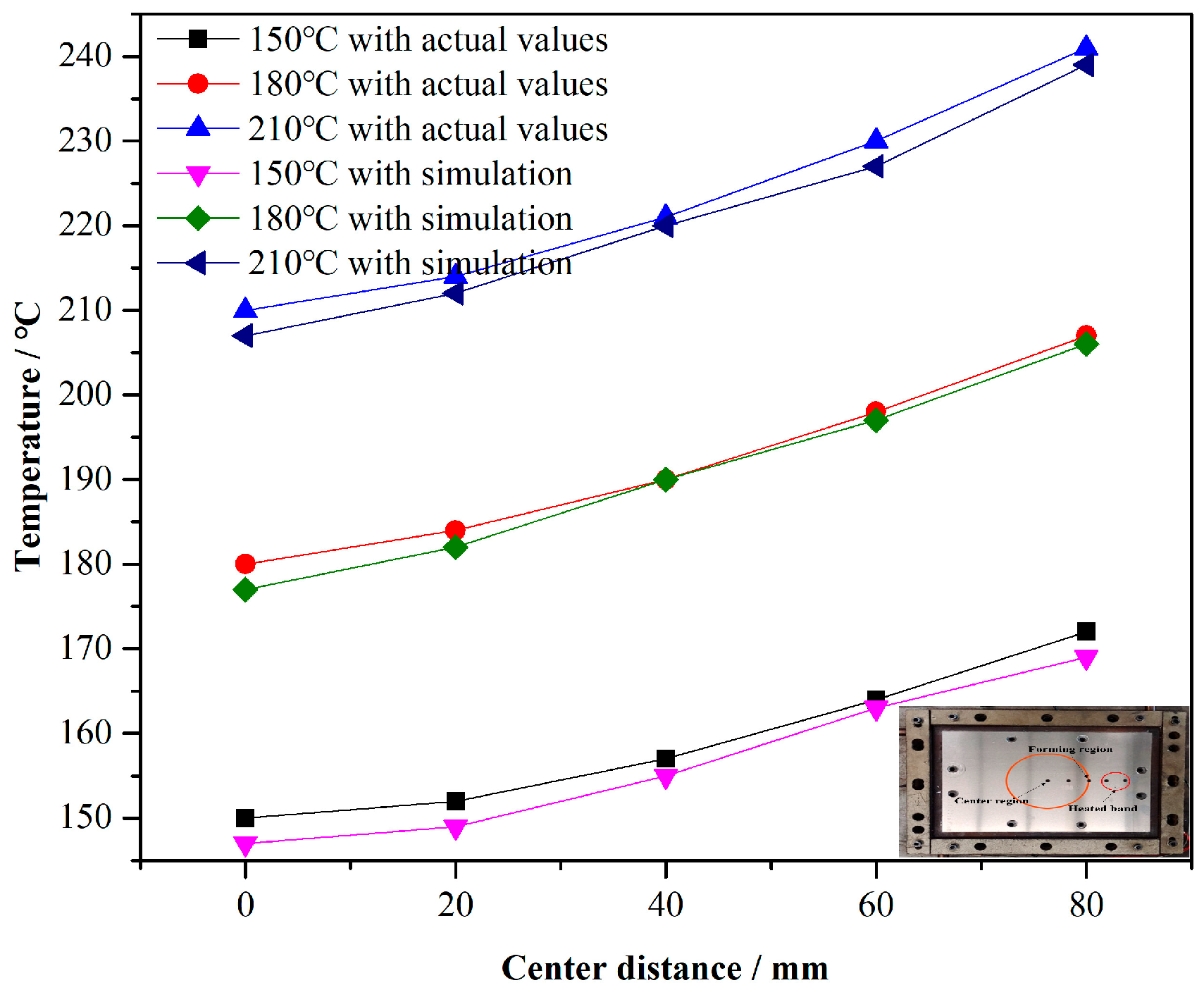
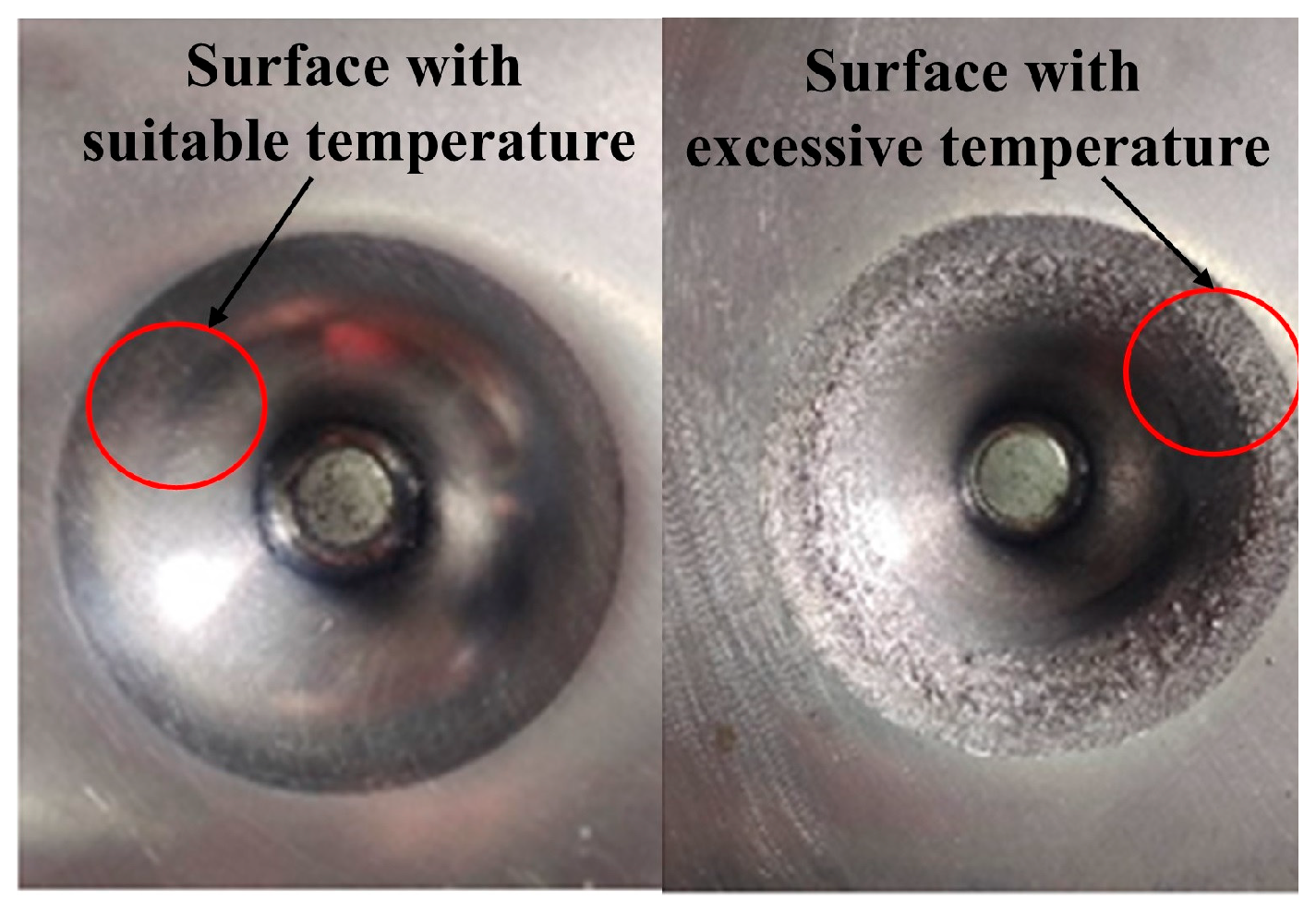
- The material forming region obtains a uniform temperature distribution and better forming performance with temperature control. In contrast, the excessive heating leads to severe material softening and increased wear without temperature control, and then the forming performance is weakened.
- The forming limit angle gradually increases with the increase in the forming temperature in the range of 25–180 °C. When the temperature reaches 210 °C, the forming limit angle decreases to some extent due to excessive softening of the material, which leads to the surface wear and the thickness reduction, and the premature fracture of the part is obtained.
- The effect of the temperature control on the microstructure of the material was studied. The forming region obtains a uniform fine grain distribution at 180 °C with temperature control, and the alternating fine and coarse grains are obtained without temperature control, which leads to the uneven stress distribution and the decrease in the forming performance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, C.X.; Chu, X.R.; Xu, Q.; Chen, J.Q.; Yue, Z.M.; Leotoing, L. Establishment and verification of anisotropic ductile fracture criteria applicable to AA6016-T4 incremental forming. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2025, 316, 110906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignesh, G.; Narayanan, C.S.; Pandivelan, C. Review on incremental sheetmetal forming process: Deformation mechanisms and recent developments. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2025, 18, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczek, L.; Zaba, K.; Trzepiecinski, T.; Wasikowski, M.; Balcerzak, M.; Sitek, R. Influence of Heat Treatment on Properties and Microstructure of EN AW-6082 Aluminium Alloy Drawpieces After Single-Point Incremental Sheet Forming. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Singh, A.; Sidhu, S.S.; Chath, J.S. Surface Integrity of AA6061-T6 Sheets Formed by Single Point Incremental Forming Process. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2025, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Abdelkader, W.; Ben Hmida, R.; Bahloul, R.; Sbayti, M. Parametric study and multi-objective optimization of process design variables in single-point incremental forming of low-carbon steel/CP-titanium bimetallic sheets via a full factorial DoE, GRA and RSM. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. 2025, 47, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhaes, D.C.C.; Montanari, L.; Huitron, S.A.E.; Marrero, J.M.C.; Rubert, J.B.; Evangelhista, S.H.; Kliauga, A.M. Investigation of single point incremental forming parameters and forming limit curves prediction for heterostructured aluminum sheets. Mater. Charact. 2025, 223, 114993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.C.; Zhang, D.W.; Tian, C.; Zhao, S.D. Influence of geometric configurations on friction characteristics during incremental forming process of AA5052 sheet metal. T. Nonferr. Metal. Soc. 2025, 35, 715–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzepieciński, T.; Szpunar, M.; Ostrowski, R.; Ziaja, W.; Motyka, M. Advanced FEM Insights into Pressure-Assisted Warm Single-Point Incremental Forming of Ti-6Al-4V Titanium Alloy Sheet Metal. Metals 2024, 14, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayebi, P.; Nasirin, A.R.; Akbari, H.; Hashemi, R. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Forming Limit Diagrams during Single Point Incremental Forming for Al/Cu Bimetallic Sheets. Metals 2024, 14, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Kumar, S.; Pande, S.; Salunkhe, S.; Ragab, A.E.; Singh, P.K.; Meraz, M.; Davim, J.P. Robot-Assisted Cold and Warm Incremental Sheet Forming of Aluminum Alloy 6061: A Comparative Study. Metals 2023, 13, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahare, H.Y.; Dubey, A.K.; Tiwari, M.K.; Tandon, P. Hammering-Assisted Incremental Forming of Al Alloy 1050: Assessment of Geometrical, Mechanical and Fracture Properties. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2025, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhiraj, V.; Chinnaiyan, S.N. Forming and microstructural behaviors of high strength low alloy 420 steel sheets formed by single point incremental forming process. Mater. Sci. Tech. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leszak, E. Apparatus and Process for Incremental Dieless Forming. U.S. Patent US3342051 A, 19 September 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Allwood, J.M.; Braun, D.; Music, O. The effect of partially cut-out blanks on geometric accuracy in incremental sheet forming. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2010, 210, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gao, Z.; An, Z.; Lin, H.; Sun, P.; Ren, Z.; Qiao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Li, Z. Activation mechanisms of slip systems during hot single point incremental forming of AA2024 sheet. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 2024, 134, 4625–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnus, C.S. Joule heating of the forming zone in incremental sheet metal forming: Part 1: State of the art and thermal process modelling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 2017, 91, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, J.; Seim, P.; Strkle, D.; Thyssen, L.; Kuhlenktter, B. Thermal modeling in electricity assisted incremental sheet forming. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2017, 10, 729–739. [Google Scholar]
- Meier, H.; Magnus, C. Incremental sheet metal forming with direct resistance heating using two moving tools. Key Eng. Mater. 2013, 554, 1362–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möllensiep, D.; Kulessa, P.; Thyssen, L. Regression-based compensation of part inaccuracies in incremental sheet forming at elevated temperatures. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 2020, 109, 1917–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Gao, L.; Hussain, G. Electric hot incremental forming: A novel technique. Int. J. Mach. Tool. Manu. 2008, 48, 1688–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahdani, M.; Mirnia, M.J.; Gorji, H. Experimental investigation of formability and surface finish into resistance single-point incremental forming of Ti–6Al–4V titanium alloy using Taguchi design. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2019, 72, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdos, L.; Argandona, E.S.D.; Ulacia, I. Warm incremental forming of magnesium alloys using hot fluid as heating media. Key Eng. Mater. 2012, 1665, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duflou, J.R.; Callebaut, B.; Verbert, J. Laser assisted incremental forming: Formability and accuracy improvement. CIRP Ann. 2007, 56, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtinen, P.; Väisänen, T.; Salmi, M. The effect of local heating by laser irradiation for aluminum, deep drawing steel and copper sheets in incremental sheet forming. Phys. Procedia 2015, 78, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göttmann, A.; Diettrich, J.; Bergweiler, G. Laser-assisted asymmetric incremental sheet forming of titanium sheet metal parts. Prod. Eng. 2011, 5, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göttmann, A.; Bailly, D.; Bergweiler, G. A novel approach for temperature control in ISF supported by laser and resistance heating. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 2013, 67, 2195–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.J.; Zhao, Z.X.; Lv, Y.T. Effect of process parameters on plastic formability and microstructures of magnesium alloy in single point incremental forming. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2019, 28, 7737–7755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gao, Z.; An, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wu, B.; Zhai, Y. A novel temperature model of regions formed during the preheating stage of belt heating in incremental sheet forming. Trans. FAMENA 2023, 47, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gao, Z.; An, Z.; Lin, H.; Sun, P.; Ren, Z.; Qiao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, Y. Effect Analysis of Process Parameters on Geometric Dimensions during Belt-Heated Incremental Sheet Forming of AA2024 Aluminum Alloy. Coatings 2024, 14, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biao, Y.; Peng, J.H.; Sheng, H.G. Acid-pickling plates and strips speed control system by microwave heating based on self-adaptive fuzzy PID algo-rithm. J. Cent. South. Univ. 2012, 19, 2179–2186. [Google Scholar]
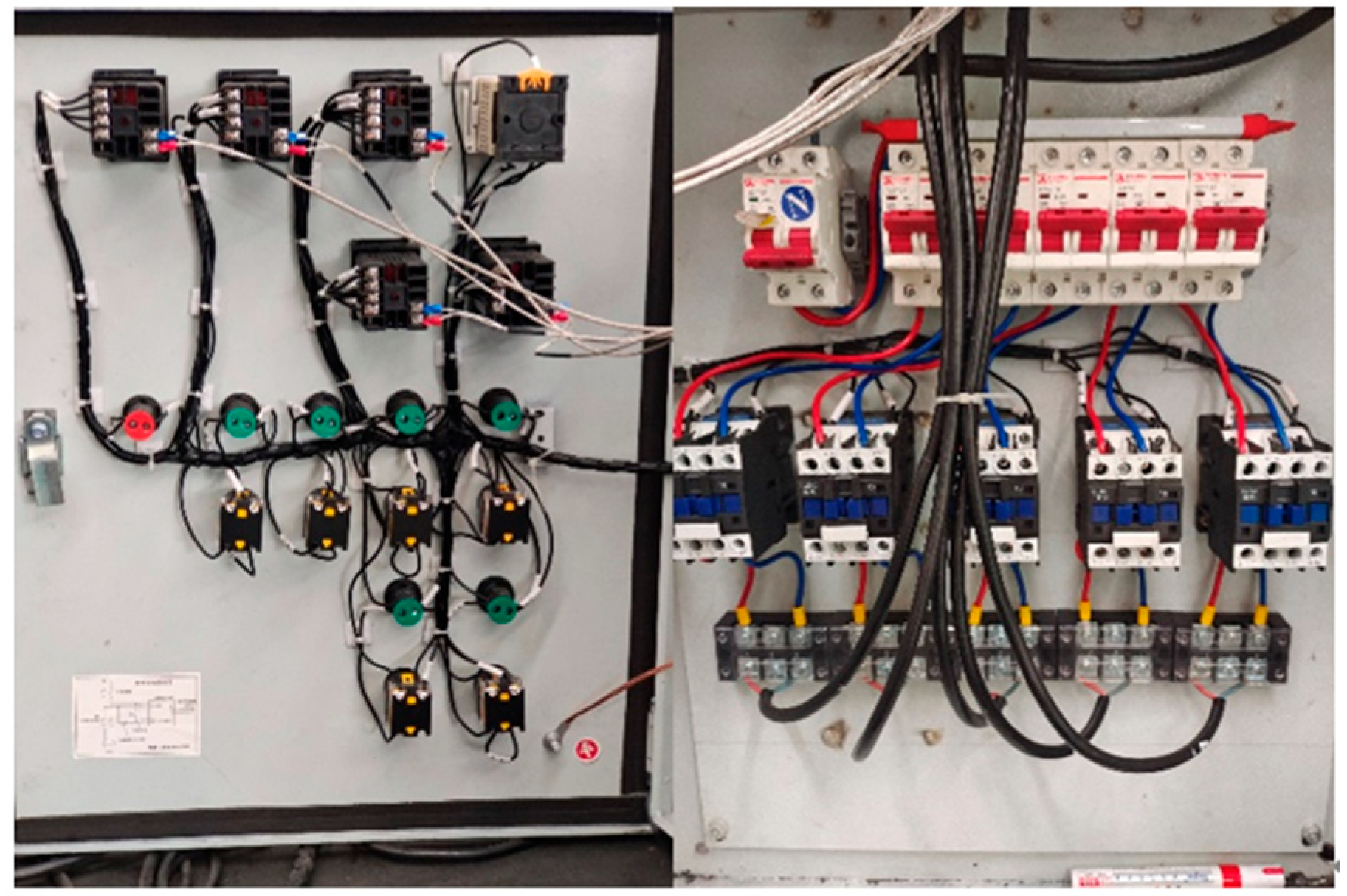
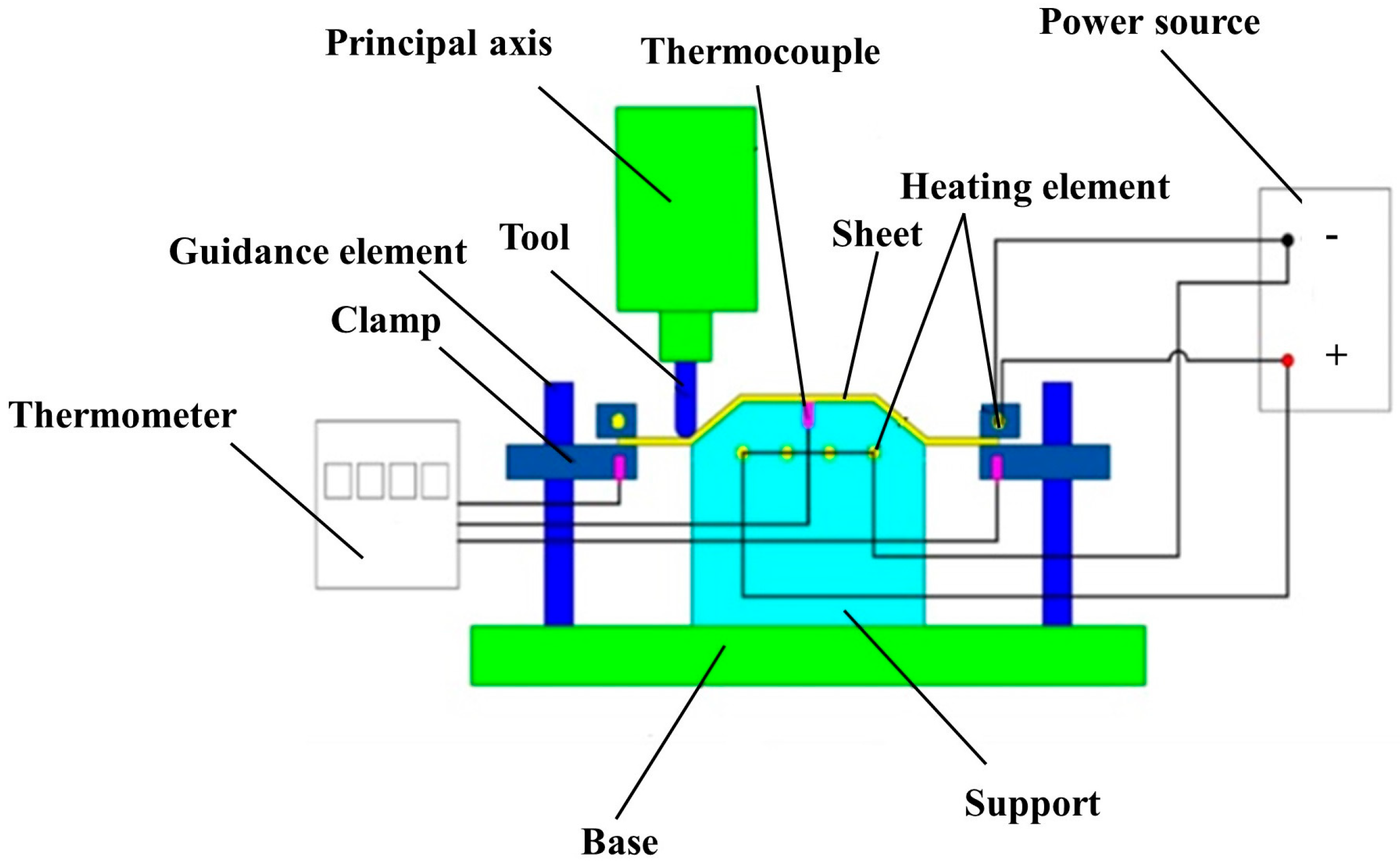
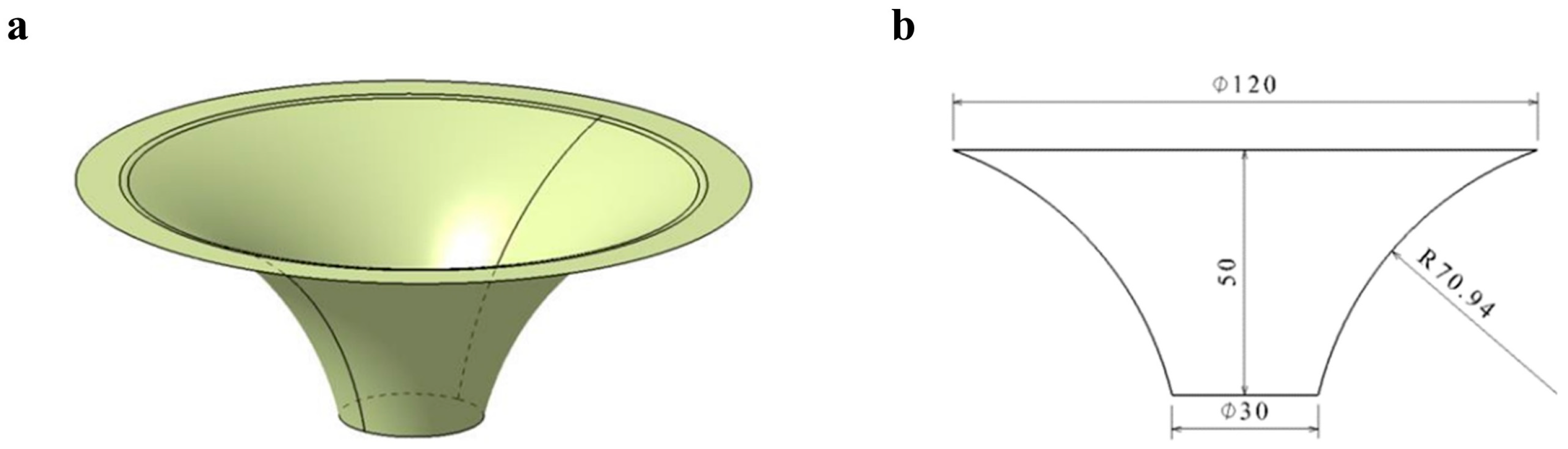
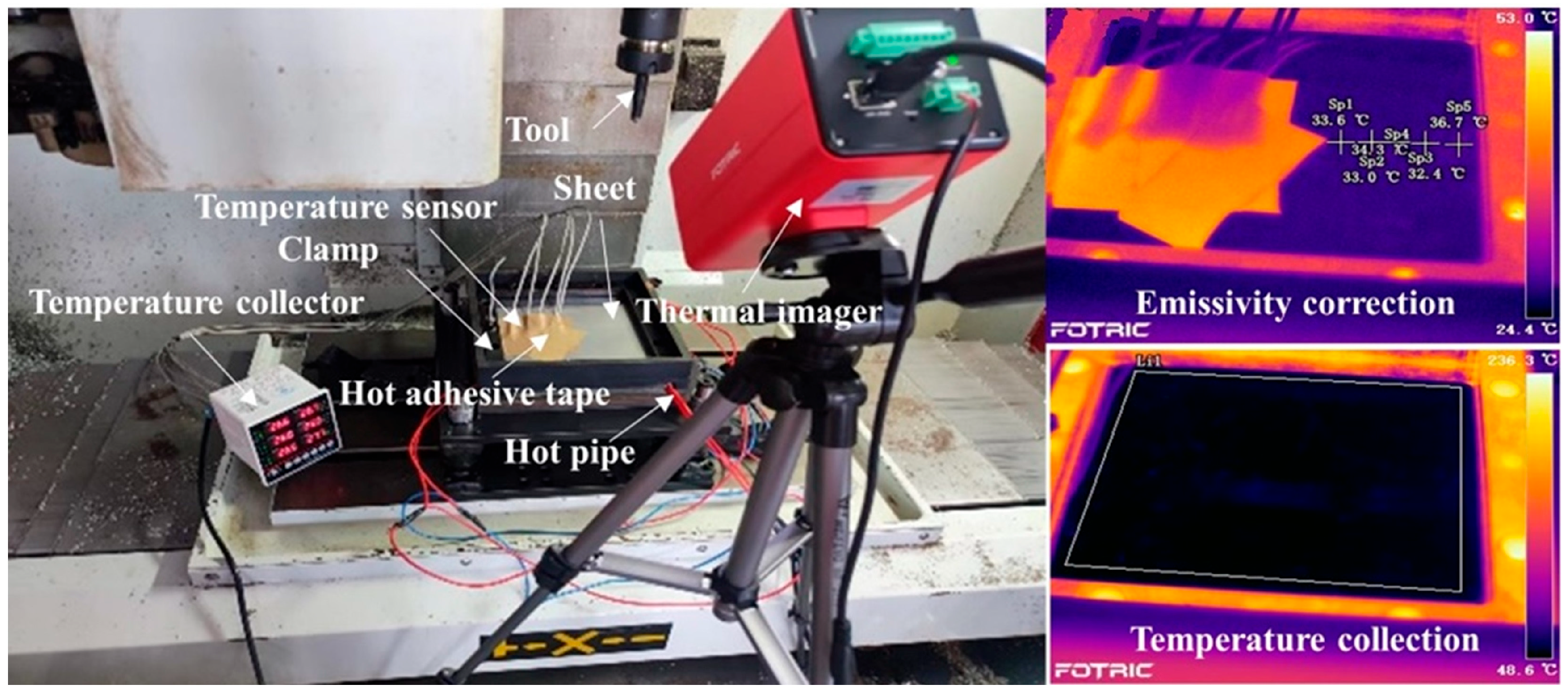

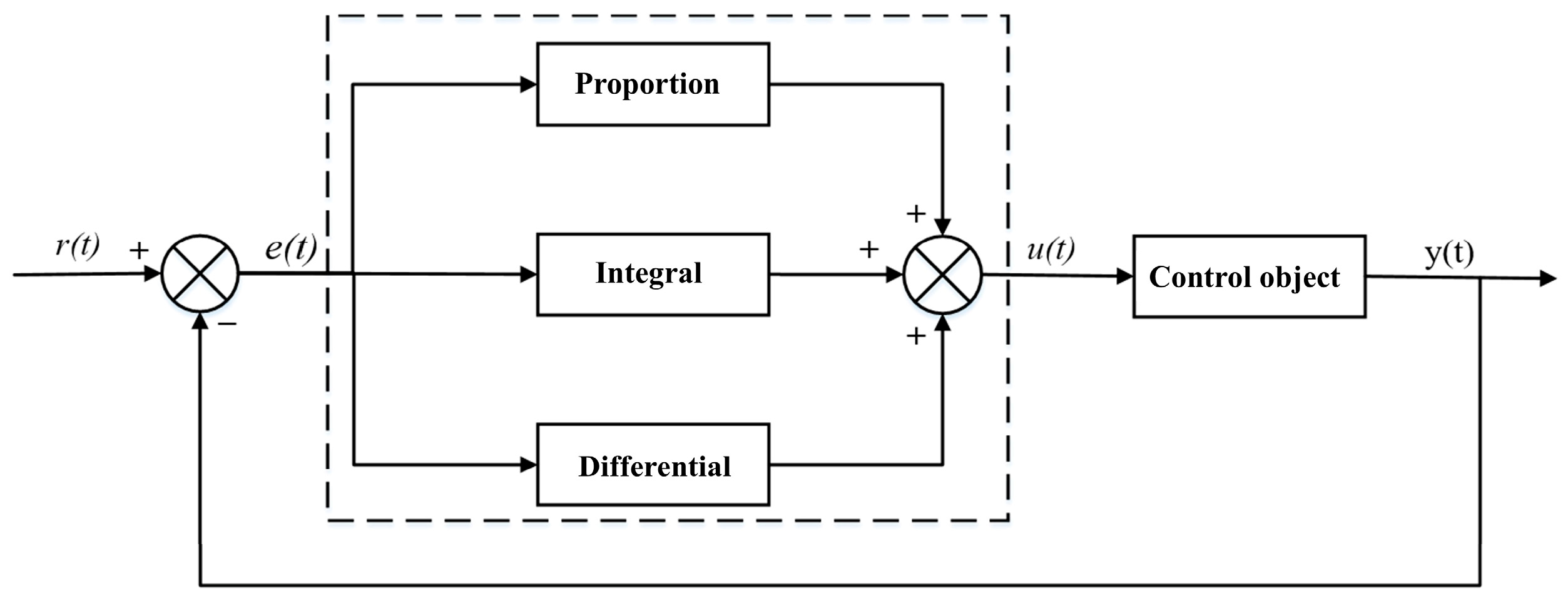



| Al | Si | Fe | Cu | Mn | Mg | Cr | Zn | Ti |
| Balanced | 0.5 | 0.5 | 3.8 | 0.3 | 1.2 | 0.1 | 0.25 | 0.15 |
| No. | Tool Diameter (mm) | Step Depth (mm) | Feed Rate (min/mm) | Temperature (°C) | Temperature Control Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 16 | 0.2 | 1500 | 25 | off |
| 2 | 16 | 0.2 | 1500 | 120 | no |
| 3 | 16 | 0.2 | 1500 | 150 | on |
| 4 | 16 | 0.2 | 1500 | 180 | off |
| 5 | 16 | 0.2 | 1500 | 180 | no |
| 6 | 16 | 0.2 | 1500 | 210 | no |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Gao, Z.; Qian, K.; Liu, L.; Song, J.; Wu, S.; Liu, L.; Zhai, X. Study on Incremental Sheet Forming Performance of AA2024 Aluminum Alloy Based on Adaptive Fuzzy PID Temperature Control. Metals 2025, 15, 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080852
Li Z, Gao Z, Qian K, Liu L, Song J, Wu S, Liu L, Zhai X. Study on Incremental Sheet Forming Performance of AA2024 Aluminum Alloy Based on Adaptive Fuzzy PID Temperature Control. Metals. 2025; 15(8):852. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080852
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhengfang, Zhengyuan Gao, Kaiguo Qian, Lijia Liu, Jiangpeng Song, Shuang Wu, Li Liu, and Xinhao Zhai. 2025. "Study on Incremental Sheet Forming Performance of AA2024 Aluminum Alloy Based on Adaptive Fuzzy PID Temperature Control" Metals 15, no. 8: 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080852
APA StyleLi, Z., Gao, Z., Qian, K., Liu, L., Song, J., Wu, S., Liu, L., & Zhai, X. (2025). Study on Incremental Sheet Forming Performance of AA2024 Aluminum Alloy Based on Adaptive Fuzzy PID Temperature Control. Metals, 15(8), 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080852







